Lethbridge, Alberta on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Lethbridge ( ) is a city in the province of
 Lethbridge's economy developed from
Lethbridge's economy developed from
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
, Canada. With a population of 101,482 in its 2019 municipal census, Lethbridge became the fourth Alberta city to surpass 100,000 people. The nearby Canadian Rocky Mountains contribute to the city's warm summers, mild winters, and windy climate. Lethbridge lies southeast of Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
on the Oldman River
The Oldman River is a river in southern Alberta, Canada. It flows roughly west to east from the Rocky Mountains, through the communities of Fort Macleod, Lethbridge, and on to Grassy Lake, where it joins the Bow River to form the South Saskatche ...
.
Lethbridge is the commercial, financial, transportation and industrial centre of southern Alberta. The city's economy developed from drift mining
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above ...
for coal in the late 19th century and agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to ...
in the early 20th century. Half of the workforce is employed in the health, education, retail and hospitality sectors, and the top five employers are government-based. The only university in Alberta south of Calgary is in Lethbridge, and two of the three colleges in southern Alberta have campuses in the city. Cultural venues in the city include performing art theatres, museums and sports centres.
History
Before the 19th century, the Lethbridge area was populated by severalFirst Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
at various times. The Blackfoot
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Bla ...
referred to the area as ''Aksaysim'' ("steep banks"), ''Mek-kio-towaghs'' ("painted rock"), ''Assini-etomochi'' ("where we slaughtered the Cree") and ''Sik-ooh-kotok'' ("coal"). The Sarcee referred to it as ''Chadish-kashi'' ("black/rocks"), the Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
as ''Kuskusukisay-guni'' ("black/rocks"), and the Nakoda (Stoney) as ''Ipubin-saba-akabin'' ("digging coal"). The Kutenai people
The Kutenai ( ), also known as the Ktunaxa ( ; ), Ksanka ( ), Kootenay (in Canada) and Kootenai (in the United States), are an indigenous people of Canada and the United States. Kutenai bands live in southeastern British Columbia, northern ...
referred to it as ''ʔa•kwum''.
After the US Army stopped alcohol trading with the Blackfeet Nation
The Blackfeet Nation ( bla, Aamsskáápipikani, script=Latn, ), officially named the Blackfeet Tribe of the Blackfeet Indian Reservation of Montana, is a federally recognized tribe of Siksikaitsitapi people with an Indian reservation in Monta ...
in Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columbi ...
in 1869, traders John J. Healy and Alfred B. Hamilton started a whiskey trading post at Fort Hamilton, near the future site of Lethbridge. The post's nickname became Fort Whoop-Up
Fort Whoop-Up was the nickname (eventually adopted as the official name) given to a whisky trading post, originally Fort Hamilton, near what is now Lethbridge, Alberta. During the late 19th century, the post served as a centre for trading activ ...
. The whiskey trade led to the Cypress Hills Massacre of many native Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakoda ...
in 1873. The North-West Mounted Police
The North-West Mounted Police (NWMP) was a Canadian para-military police force, established in 1873, to maintain order in the new Canadian North-West Territories (NWT) following the 1870 transfer of Rupert’s Land and North-Western Territory ...
, sent to stop the trade and establish order, arrived at Fort Whoop-Up on October 9, 1874. They managed the post for the next 12 years.
 Lethbridge's economy developed from
Lethbridge's economy developed from drift mines
Drift mining is either the mining of an ore deposit by underground methods, or the working of coal seams accessed by adits driven into the surface outcrop of the coal bed. A drift mine is an underground mine in which the entry or access is above ...
opened by Nicholas Sheran Nicholas Sheran (1841–1882) was an entrepreneur born in New York City. He spent his early years apprenticing as a printer, working on Arctic whalers, and serving in the United States Army.
History
After his service in the American Civil War ...
in 1874 and the North Western Coal and Navigation Company
The North Western Coal and Navigation Company, also known as Alberta Railway and Coal Company or Alberta Railway and Irrigation Company, was a coal mining company formed in London, England in 1882 by Sir Alexander Tilloch Galt, one of Canada's Fat ...
in 1882. North Western's president was William Lethbridge
William Lethbridge (1825–1901) was a lawyer in England. When bookseller W H Smith owner William Henry Smith II decided to become involved in politics in 1864, he enlisted Lethbridge as a managing partner. He sat for a portrait by Frederic ...
, from whom the city derives its name. By the turn of the century, the mines employed about 150 men and produced 300 tonnes of coal each day. In 1896, local collieries were the largest coal producers in the Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. ...
, with production peaking during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. An internment camp
Internment is the imprisonment of people, commonly in large groups, without charges or intent to file charges. The term is especially used for the confinement "of enemy citizens in wartime or of terrorism suspects". Thus, while it can simply ...
was set up at the Exhibition Building in Lethbridge from September 1914 to November 1916. After the war, increasing oil and natural gas production gradually replaced coal production, and the last mine in Lethbridge closed in 1957.
The first rail line in Lethbridge was opened on August 28, 1885, by the Alberta Railway and Coal Company, which bought the North Western Coal and Navigation Company five years later. The rail industry's dependence on coal and the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadi ...
's efforts to settle southern Alberta with immigrants boosted Lethbridge's economy. After the Canadian Pacific Railway (CPR) moved the divisional point In Canada, a divisional point (or division point) is a local operational headquarters for a railway. Divisional points are significant in railway maintenance of way operations. Especially historically, they could be the location of facilities and in ...
of its Crowsnest Line from Fort Macleod to Lethbridge in 1905, the city became the regional centre for Southern Alberta
Southern Alberta is a region located in the Canadian province of Alberta. In 2004, the region's population was approximately 272,017. In the mid-1980s, the CPR moved its rail yards in downtown Lethbridge to nearby Kipp, and Lethbridge ceased being a rail hub.
Between 1907 and 1913, a development boom occurred in Lethbridge, making it the main marketing, distribution and service centre in southern Alberta. Such municipal projects as a water treatment plant, a power plant, a streetcar system, and exhibition buildings—as well as a construction boom and rising real estate prices—transformed the mining town into a significant city. Between World War I and
Environment Canada. Retrieved January 7, 2011. Its high
, Economic Development Lethbridge. 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2016. These factors protect the city from strong northwest and southwest winds and contribute to frequent
Lethbridge Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved December 24, 2006. The average daytime temperature peaks by the end of July/beginning of August, when it reaches . The city's temperature reaches a maximum high of or greater on average once or twice a year. The highest temperature ever recorded in Lethbridge was on August 10, 2018. The lowest temperature ever recorded was on January 7, 1909, December 18, 1924, January 3, 1950, and December 29, 1968.
 Lethbridge is southern Alberta's commercial, distribution, financial and industrial centre (although
Lethbridge is southern Alberta's commercial, distribution, financial and industrial centre (although
Statistics Canada. 2002. 2001 Community Profiles. Released June 27, 2002. Last modified: December 14, 2006. Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 93F0053XIE and the top five employers are government-based. Several national companies are based in Lethbridge. From its founding in 1935, Canadian Freightways based its head office there until moving operations to Calgary in 1948, though its call centre remains in Lethbridge. Taco Time Canada was based in the city from 1978 to 1995 before moving to Calgary. Minute Muffler, which began in 1969, is based in Lethbridge. International
 Lethbridge was designated a Cultural Capital of Canada for the 2004–2005 season. The Southern Alberta Ethnic Association (Multicultural Heritage Centre) promotes multiculturalism and ethnic heritage in the community.
The city is home to venues and organizations promoting the arts. Founded in 1958, the Allied Arts Council of Lethbridge is the largest organization in the city dedicated to preserving and enhancing the local arts. In the spring of 2007, the Allied Arts Council Facilities Steering Committee initiated the Arts Re:Building Together Campaign, a grass roots campaign initiative to raise awareness and support for improving arts facilities in Lethbridge. The campaign identified three arts buildings: the Yates Memorial Centre, the Bowman Arts Centre, and the Southern Alberta Art Gallery as cornerstone facilities in the community requiring care and attention. On July 14, 2007, the Finance Committee of City Council approved four arts capital projects for inclusion in the city's Ten Year Capital Plan. Under the campaign to 2010, the renovation and expansion of the Southern Alberta Art Gallery was completed, a new Community Arts Centre will be built in downtown Lethbridge, the City of Lethbridge has a Public Art Program, and a committee was formed to research the possibility of a new Performing Arts Centre in Lethbridge.
Lethbridge has a
Lethbridge was designated a Cultural Capital of Canada for the 2004–2005 season. The Southern Alberta Ethnic Association (Multicultural Heritage Centre) promotes multiculturalism and ethnic heritage in the community.
The city is home to venues and organizations promoting the arts. Founded in 1958, the Allied Arts Council of Lethbridge is the largest organization in the city dedicated to preserving and enhancing the local arts. In the spring of 2007, the Allied Arts Council Facilities Steering Committee initiated the Arts Re:Building Together Campaign, a grass roots campaign initiative to raise awareness and support for improving arts facilities in Lethbridge. The campaign identified three arts buildings: the Yates Memorial Centre, the Bowman Arts Centre, and the Southern Alberta Art Gallery as cornerstone facilities in the community requiring care and attention. On July 14, 2007, the Finance Committee of City Council approved four arts capital projects for inclusion in the city's Ten Year Capital Plan. Under the campaign to 2010, the renovation and expansion of the Southern Alberta Art Gallery was completed, a new Community Arts Centre will be built in downtown Lethbridge, the City of Lethbridge has a Public Art Program, and a committee was formed to research the possibility of a new Performing Arts Centre in Lethbridge.
Lethbridge has a
 The city, which began as a frontier town, has several historical attractions. The
The city, which began as a frontier town, has several historical attractions. The
 Mass transit in Lethbridge consists of 40 buses (with an average age of 10 years) operating on more than a dozen routes. Traditionally, bus routes in the city started and ended downtown. In the early 21st century, however,
Mass transit in Lethbridge consists of 40 buses (with an average age of 10 years) operating on more than a dozen routes. Traditionally, bus routes in the city started and ended downtown. In the early 21st century, however,
map
. The system was designed to connect the
 The Lethbridge School Division and the separate Holy Spirit Roman Catholic School Division administer grades
The Lethbridge School Division and the separate Holy Spirit Roman Catholic School Division administer grades
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, however, the city experienced an economic slump. Development slowed, drought drove farmers from their farms, and coal mining rapidly declined from its peak. After World War II, irrigation of farmland near Lethbridge led to growth in the city's population and economy. Lethbridge College
Lethbridge College (previously Lethbridge Community College) opened in 1957 as the first publicly funded community college in Canada. Over 4,000 students attend the Lethbridge, Alberta, institution.
Lethbridge College is a member of the Albert ...
(previously Lethbridge Community College) opened in April 1957 and the University of Lethbridge
, mottoeng = ''Let there be light''
, type = Public
, established =
, academic_affiliations = Universities Canada
, endowment = $73 million (2019)
, chancellor = Charles Weasel ...
in 1967.
Geography
The city of Lethbridge is located at 49.7° northlatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
and 112.833° west longitude
Longitude (, ) is a geographic coordinate that specifies the east–west position of a point on the surface of the Earth, or another celestial body. It is an angular measurement, usually expressed in degrees and denoted by the Greek letter l ...
and covers an area of . It is divided by the Oldman River
The Oldman River is a river in southern Alberta, Canada. It flows roughly west to east from the Rocky Mountains, through the communities of Fort Macleod, Lethbridge, and on to Grassy Lake, where it joins the Bow River to form the South Saskatche ...
; its valley has been turned into one of the largest urban park systems in North America at of protected land. Lethbridge is Alberta's third-largest by population after Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
and Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
. It is the third largest in area after Calgary and Edmonton and is near the Canadian Rockies
The Canadian Rockies (french: Rocheuses canadiennes) or Canadian Rocky Mountains, comprising both the Alberta Rockies and the British Columbian Rockies, is the Canadian segment of the North American Rocky Mountains. It is the easternmost part ...
, southeast of Calgary.
Lethbridge is split into three geographical areas: north, south and west. The Oldman River separates West Lethbridge from the other two, while Crowsnest Trail and the Canadian Pacific Railway
The Canadian Pacific Railway (french: Chemin de fer Canadien Pacifique) , also known simply as CPR or Canadian Pacific and formerly as CP Rail (1968–1996), is a Canadian Class I railway incorporated in 1881. The railway is owned by Canadi ...
rail line separate North and South Lethbridge. The newest and largest of the three areas, West Lethbridge
West Lethbridge (or The Westside), is one of three geographical areas in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It is the newest and the fastest growing. It is the home of the University of Lethbridge and is a residential area primarily.
History
West Leth ...
(pop. 40,898) is home to the University of Lethbridge
, mottoeng = ''Let there be light''
, type = Public
, established =
, academic_affiliations = Universities Canada
, endowment = $73 million (2019)
, chancellor = Charles Weasel ...
—which opened at that site in 1971. Although several farms existed on the what is now the Westside, the first housing development was not completed until 1974 and Whoop-Up Drive access opened only in 1975. Much of the city's recent growth has been on the west side, and it has the youngest median age of the three. The north side (pop. 28,172) was originally populated by workers from local coal mines. It has the oldest population of the three areas, is home to multiple industrial parks and includes the former Hamlet of Hardieville, which was annexed by Lethbridge in 1978. South Lethbridge (pop. 32,412) is the commercial heart of the city; it contains the downtown core
The Downtown Core is the historical and downtown centre of the city-state of Singapore and the main commercial area in Singapore excluding reclaimed lands with many integrated resorts such as the Marina Bay Sands, one of the most expensive build ...
, the bulk of retail and hospitality establishments, and the Lethbridge College
Lethbridge College (previously Lethbridge Community College) opened in 1957 as the first publicly funded community college in Canada. Over 4,000 students attend the Lethbridge, Alberta, institution.
Lethbridge College is a member of the Albert ...
.
Climate
Lethbridge has asemi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''BSk BSK is a three-letter abbreviation that may refer to:
Sports
* OFK Beograd, Serbian football club
* FK BSK Borča, Serbian football club
* FK BSK Batajnica, Serbian football club
* FK BSK Banja Luka, Bosnian-Herzegovinian football club
* FK BSK L ...
'') with an average maximum temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied o ...
of and an average minimum temperature of . With precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
averaging , and 264 dry days on average, Lethbridge is the eleventh driest city in Canada. Mean relative humidity hovers between 69 and 78% in the morning throughout the year, but afternoon mean relative humidity is more uneven, ranging from 38% in August to 58% in January. On average, Lethbridge has 116 days with wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few hou ...
speed of or higher, ranking it as the second city in Canada for such weather.Weather WinnersEnvironment Canada. Retrieved January 7, 2011. Its high
elevation
The elevation of a geographic location is its height above or below a fixed reference point, most commonly a reference geoid, a mathematical model of the Earth's sea level as an equipotential gravitational surface (see Geodetic datum § Vert ...
of and close proximity to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
provides Lethbridge with cooler summers than other locations in the Canadian Prairies
The Canadian Prairies (usually referred to as simply the Prairies in Canada) is a region in Western Canada. It includes the Canadian portion of the Great Plains and the Prairie Provinces, namely Alberta, Saskatchewan, and Manitoba. These provin ...
.Lethbridge Trade Area and Commercial Catchment Study, Economic Development Lethbridge. 2016. Retrieved November 28, 2016. These factors protect the city from strong northwest and southwest winds and contribute to frequent
chinook wind
Chinook winds, or simply Chinooks, are two types of prevailing warm, generally westerly winds in western North America: Coastal Chinooks and interior Chinooks. The coastal Chinooks are persistent seasonal, wet, southwesterly winds blowing in from ...
s during the winter. Lethbridge winters have the highest temperatures in the prairies, reducing the severity and duration of winter cold periods and resulting in fewer days with snow
Snow comprises individual ice crystals that grow while suspended in the atmosphere—usually within clouds—and then fall, accumulating on the ground where they undergo further changes.
It consists of frozen crystalline water throughout ...
cover.Community ProfileLethbridge Chamber of Commerce. Retrieved December 24, 2006. The average daytime temperature peaks by the end of July/beginning of August, when it reaches . The city's temperature reaches a maximum high of or greater on average once or twice a year. The highest temperature ever recorded in Lethbridge was on August 10, 2018. The lowest temperature ever recorded was on January 7, 1909, December 18, 1924, January 3, 1950, and December 29, 1968.

Demographics
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted byStatistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultur ...
, the City of Lethbridge had a population of 98,406 living in 40,225 of its 42,862 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of 92,729. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
At the census metropolitan area
The census geographic units of Canada are the census subdivisions defined and used by Canada's federal government statistics bureau Statistics Canada to conduct the country's quinquennial census. These areas exist solely for the purposes of sta ...
(CMA) level in the 2021 census, the Lethbridge CMA had a population of living in of its total private dwellings, a change of from its 2016 population of . With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2021.
The population of the City of Lethbridge according to its 2019 municipal census is 101,482, a change of from its 2018 municipal census population of 99,769. With the 2019 municipal census results, the City of Lethbridge became the fourth city in Alberta to surpass 100,000 people.
In the 2016 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, the City of Lethbridge had a population of 92,729 living in 37,575 of its 39,867 total private dwellings, a change of from its 2011 population of 83,517. With a land area of , it had a population density of in 2016. The same census reported that the metropolitan area of Lethbridge was 117,394 in 2016, up from 105,999 in 2011. Subsequent data from Statistics Canada showed that the 2020 metropolitan population was 128,851, an increase of 1.5% over the previous year.
In 2021, 49.8% of residents were Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, down from 64.6% in 2011. 16.1% of the population were Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, 12.9% were Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
, and 11.3% were Christians of unspecified denomination. All other Christian denominations and Christian-related traditions made up 9.6%, including a large population of Latter Day Saints
The Latter Day Saint movement (also called the LDS movement, LDS restorationist movement, or Smith–Rigdon movement) is the collection of independent church groups that trace their origins to a Christian Restorationist movement founded by Jo ...
adherents(5.8%). 44.3% of the population was nonreligious or secular, up from 32.4% in 2011. 8.1% followed a religion (or spiritual belief) other than Christianity. The largest non-Christian religions were Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
(1.9%), Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
(1.3%), and Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
(1.1%).
According to the 2021 census, 83.9% of residents spoke English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ide ...
as a first language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother tongu ...
. Other common mother tongues were Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
(1.6%), Tagalog (1.4%), Nepali (1.0%), German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
(0.9%), French (0.8%), Chinese Languages
The Sinitic languages (漢語族/汉语族), often synonymous with "Chinese languages", are a group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute the major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is ...
(0.7%), Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic languages, Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C ...
(0.7%) and Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
(0.6%). 1.7% of residents claimed both English and a non-official language as their first language.
Lethbridge was 12.9% visible minorities and 7.1% aboriginal in 2016. Below is a full break down of the demographics. The city is also the home of the largest Bhutanese community in Canada.
Economy
 Lethbridge is southern Alberta's commercial, distribution, financial and industrial centre (although
Lethbridge is southern Alberta's commercial, distribution, financial and industrial centre (although Medicine Hat
Medicine Hat is a city in Southern Alberta, southeast Alberta, Canada. It is located along the South Saskatchewan River. It is approximately east of Lethbridge and southeast of Calgary. This city and the adjacent Town of Redcliff, Alberta, ...
plays a similar role in southeastern Alberta). It has a trading area population of 341,180, including parts of British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, ...
, and provides jobs for up to 86,000 people who commute to and within the city from a radius of .
Lethbridge's economy has traditionally been agriculture-based; however, it has diversified in recent years. Half of the workforce is employed in the health, education, retail and hospitality sectors,Lethbridge Community Profile.Statistics Canada. 2002. 2001 Community Profiles. Released June 27, 2002. Last modified: December 14, 2006. Statistics Canada Catalogue no. 93F0053XIE and the top five employers are government-based. Several national companies are based in Lethbridge. From its founding in 1935, Canadian Freightways based its head office there until moving operations to Calgary in 1948, though its call centre remains in Lethbridge. Taco Time Canada was based in the city from 1978 to 1995 before moving to Calgary. Minute Muffler, which began in 1969, is based in Lethbridge. International
shipping
Freight transport, also referred as ''Freight Forwarding'', is the physical process of transporting Commodity, commodities and merchandise goods and cargo. The term shipping originally referred to transport by sea but in American English, it h ...
company H & R Transport has been based in the city since 1955. Braman Furniture, which has locations in Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
and Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central Ca ...
, was headquartered in Lethbridge from 1991 to 2008.
Lethbridge serves as a hub for commercial activity in the region by providing services and amenities. Many transport
Transport (in British English), or transportation (in American English), is the intentional movement of humans, animals, and goods from one location to another. Modes of transport include air, land (rail and road), water, cable, pipeline, an ...
services, including Red Arrow buses, four provincial highways, rail service
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a pre ...
and an airport
An airport is an aerodrome with extended facilities, mostly for commercial air transport. Airports usually consists of a landing area, which comprises an aerially accessible open space including at least one operationally active surface ...
, are concentrated in or near the city. In 2004, the police services of Lethbridge and Coaldale combined to form the Lethbridge Police Service
The Lethbridge Police Service, formerly known as the Lethbridge Regional Police Service, was established 1905, and serves the city of Lethbridge, a community in southern Alberta of approximately 101,482 in its 2019 municipal census.
History
T ...
. Lethbridge provides municipal water to Coaldale, Coalhurst
Coalhurst (originally named Bridgend) is a town in southern Alberta, Canada. It is located on Highway 3, northwest of Lethbridge. It used to be a coal-mining community.
Around 1930, a large fire broke out in Coalhurst and cost the town ab ...
, Diamond City, Iron Springs, Monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. Life tenure, for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority ...
, Shaughnessy and Turin
Turin ( , Piedmontese language, Piedmontese: ; it, Torino ) is a city and an important business and cultural centre in Northern Italy. It is the capital city of Piedmont and of the Metropolitan City of Turin, and was the first Italian capital ...
.
In 2002, the municipal government organized ''Economic Development Lethbridge'', a body responsible for promoting and developing the city's commercial interests. Two years later, the city joined in a partnership with 24 other local communities to create an economic development alliance called ''SouthGrow'', representing a population of over 140,000. In 2006, Economic Development Lethbridge partnered with SouthGrow Regional Initiative and ''Alberta SouthWest Regional Alliance'' to create the ''Southern Alberta Alternative Energy Partnership''. This partnership promotes business related to alternative energy, including wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to electricity generation, generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable energy, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller Environmental impact of wi ...
, solar power
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic e ...
and biofuel
Biofuel is a fuel that is produced over a short time span from biomass, rather than by the very slow natural processes involved in the formation of fossil fuels, such as oil. According to the United States Energy Information Administration (E ...
, in the region.
Arts and culture
 Lethbridge was designated a Cultural Capital of Canada for the 2004–2005 season. The Southern Alberta Ethnic Association (Multicultural Heritage Centre) promotes multiculturalism and ethnic heritage in the community.
The city is home to venues and organizations promoting the arts. Founded in 1958, the Allied Arts Council of Lethbridge is the largest organization in the city dedicated to preserving and enhancing the local arts. In the spring of 2007, the Allied Arts Council Facilities Steering Committee initiated the Arts Re:Building Together Campaign, a grass roots campaign initiative to raise awareness and support for improving arts facilities in Lethbridge. The campaign identified three arts buildings: the Yates Memorial Centre, the Bowman Arts Centre, and the Southern Alberta Art Gallery as cornerstone facilities in the community requiring care and attention. On July 14, 2007, the Finance Committee of City Council approved four arts capital projects for inclusion in the city's Ten Year Capital Plan. Under the campaign to 2010, the renovation and expansion of the Southern Alberta Art Gallery was completed, a new Community Arts Centre will be built in downtown Lethbridge, the City of Lethbridge has a Public Art Program, and a committee was formed to research the possibility of a new Performing Arts Centre in Lethbridge.
Lethbridge has a
Lethbridge was designated a Cultural Capital of Canada for the 2004–2005 season. The Southern Alberta Ethnic Association (Multicultural Heritage Centre) promotes multiculturalism and ethnic heritage in the community.
The city is home to venues and organizations promoting the arts. Founded in 1958, the Allied Arts Council of Lethbridge is the largest organization in the city dedicated to preserving and enhancing the local arts. In the spring of 2007, the Allied Arts Council Facilities Steering Committee initiated the Arts Re:Building Together Campaign, a grass roots campaign initiative to raise awareness and support for improving arts facilities in Lethbridge. The campaign identified three arts buildings: the Yates Memorial Centre, the Bowman Arts Centre, and the Southern Alberta Art Gallery as cornerstone facilities in the community requiring care and attention. On July 14, 2007, the Finance Committee of City Council approved four arts capital projects for inclusion in the city's Ten Year Capital Plan. Under the campaign to 2010, the renovation and expansion of the Southern Alberta Art Gallery was completed, a new Community Arts Centre will be built in downtown Lethbridge, the City of Lethbridge has a Public Art Program, and a committee was formed to research the possibility of a new Performing Arts Centre in Lethbridge.
Lethbridge has a public library
A public library is a library that is accessible by the general public and is usually funded from public sources, such as taxes. It is operated by librarians and library paraprofessionals, who are also Civil service, civil servants.
There are ...
and three major museum/galleries. The Southern Alberta Art Gallery
The Southern Alberta Art Gallery Maansiksikaitsitapiitsinikssin is a contemporary art gallery located in downtown Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It has three gallery spaces and a gift shop.
History
In 1974, local residents formed the Southern Alber ...
is a contemporary gallery; the community arts centre Casa, administered by the Allied Arts Council; and the University of Lethbridge Art Gallery produces contemporary exhibitions including works from its extensive collection of Canadian, American and European art.
The city is also home to the Lethbridge Symphony, which was founded in 1960 and incorporated as a non-profit in 1961. It has produced several spin-off music groups, including the Southern Alberta Chamber Orchestra, and the still-active Lethbridge Musical Theatre, which produces an annual show. Vox Musica, which traces its roots back to 1968, is a community choir previously based at the University of Lethbridge
, mottoeng = ''Let there be light''
, type = Public
, established =
, academic_affiliations = Universities Canada
, endowment = $73 million (2019)
, chancellor = Charles Weasel ...
. As a fully independent non-profit society, Vox Musica continues to rehearse and perform at Southminster United Church and around the community. Theatrical productions are presented by the University of Lethbridge's drama department and New West Theatre, which performs at the Genevieve E. Yates Memorial Centre
The Genevieve E. Yates Memorial Centre houses two performance theatres in downtown Lethbridge, Alberta. The centre was built starting 15 August 1965 and officially opened 1 May 1966. Deane Yates, a local retailer, donated over $200,000 towards it ...
using its two theatres: the 500-seat proscenium
A proscenium ( grc-gre, προσκήνιον, ) is the metaphorical vertical plane of space in a theatre, usually surrounded on the top and sides by a physical proscenium arch (whether or not truly "arched") and on the bottom by the stage floor ...
Yates Theatre and the 180-seat black box
In science, computing, and engineering, a black box is a system which can be viewed in terms of its inputs and outputs (or transfer characteristics), without any knowledge of its internal workings. Its implementation is "opaque" (black). The te ...
Sterndale Bennett Theatre.
Attractions
 The city, which began as a frontier town, has several historical attractions. The
The city, which began as a frontier town, has several historical attractions. The Lethbridge Viaduct
The Lethbridge Viaduct, commonly known as the High Level Bridge, was constructed between 1907 and 1909 at Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada at a cost of $1,334,525.
Overview
This massive steel trestle over the Oldman River was designed by the Canad ...
, commonly known as the ''High Level Bridge'', is the longest and highest steel trestle bridge in North America. It was completed in 1909 on what was then the city's western edge. Indian Battle Park, in the coulee
Coulee, or coulée ( or ) is a term applied rather loosely to different landforms, all of which refer to a kind of valley or drainage zone. The word ''coulee'' comes from the Canadian French ''coulée'', from French ''couler'' 'to flow'.
The ...
s of the Oldman River
The Oldman River is a river in southern Alberta, Canada. It flows roughly west to east from the Rocky Mountains, through the communities of Fort Macleod, Lethbridge, and on to Grassy Lake, where it joins the Bow River to form the South Saskatche ...
, commemorates the last battle between the Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a Indigenous peoples of the Americas, North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations in Canada ...
and the Blackfoot
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or " Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up the Blackfoot or Bla ...
First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
in 1870.
Originally known as Fort Hamilton, Fort Whoop-Up
Fort Whoop-Up was the nickname (eventually adopted as the official name) given to a whisky trading post, originally Fort Hamilton, near what is now Lethbridge, Alberta. During the late 19th century, the post served as a centre for trading activ ...
was a centre of illegal activities during the late 19th century. It was first built in 1869 by J.J. Healy and A.B. Hamilton as a whiskey post and was destroyed by fire a year later. A second, sturdier structure later replaced the fort.
As the cultural centre of southern Alberta, Lethbridge has notable cultural attractions. Nikka Yuko Japanese Garden
is a garden near Henderson Lake in Lethbridge, Alberta, designed by Dr. Masami Sugimoto and Dr. Tadashi Kubo of Osaka Prefecture University in Japan. The pavilion, shelter, bridges and gates were built in Kyoto, Japan, by five artisans who la ...
in south Lethbridge was opened in 1967 as part of a Canadian centennial celebration attended by Japan's Prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. Th ...
and Princess Takamatsu
, born , was a member of the Japanese Imperial Family. The Princess was married to Prince Takamatsu, the third son of Emperor Taishō and Empress Teimei. She was, therefore, a sister-in-law of Emperor Shōwa and an aunt-in-law of the following e ...
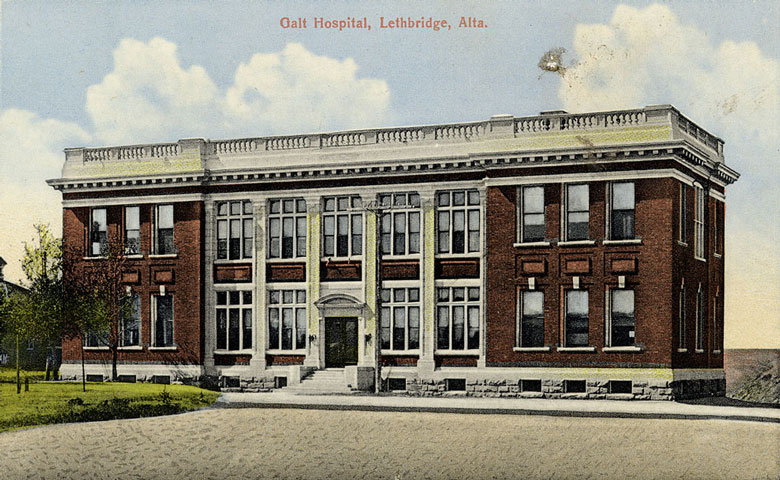
. The Galt Museum & Archives
Galt Museum & Archives is the primary museum in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, and is the largest museum in the province south of Calgary. In 2006, the museum cared for a growing collection of over 20,000 artifacts and 300,000 archival documents a ...
is the largest museum in the Lethbridge area; the building housing the museum served as the city's main hospital during the late 19th century and early 20th centuries. Several other important attractions are based in Lethbridge, including the Lethbridge Military Museum and the Helen Schuler Nature Centre which educates about the river bottom and coulees.
Several structures such as the historic post office are prominent on the skyline of Lethbridge. Less well-known than the High Level Bridge, the post office is one of the most distinctive buildings in Lethbridge. Built in 1912, the four-storey structure is crowned by a functioning clock tower. Other prominent buildings include office towers; the water tower, which was originally built in 1958 and sold to a private developer who converted it into a restaurant; and the Alberta Terminals grain elevators.
From March 2018 to August 2020, Lethbridge was home to ARCHES
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vault ...
, 24-hour supervised drug use site. It was the busiest SCS in North America with 663 visits a day. ''The Star'' called it a "new landmark". The SCS featured injection drug and inhalation drug facilities and it was a subject of disagreement by the nearby business community. The site closed at the end of August 2020 after the province removed grant funding following discovery of misappropriation of public funds.
Sports and recreation
Lethbridge has designated 16 percent of the land within city boundaries as parkland, including theOldman River valley parks system
The Oldman River valley parks system is a continuous collection of eight urban parks in the Oldman River valley of Lethbridge, Alberta, below the prairie level. The parks were created in the 1980s as part of the city's Urban Parks Project. Tod ...
. It has facilities for field sports, numerous baseball diamonds, the Spitz Stadium, the Nicholas Sheran Park
Nicholas Sheran Park is an urban park in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, and is named after one of the city's founders, Nicholas Sheran. The largest park in West Lethbridge, it was conceptualised as a regional park in 1969, and constructed in 1974.
...
(a disc golf course), two skatepark
A skatepark, or skate park, is a purpose-built recreational environment made for skateboarding, BMX, scootering, wheelchairs, and aggressive inline skating. A skatepark may contain half-pipes, handrails, funboxes, vert ramps, stairsets, q ...
s, a BMX track, a climbing wall
A climbing wall is an artificially constructed wall with grips for hands and feet, usually used for indoor climbing, but sometimes located outdoors. Some are brick or wooden constructions, but on most modern walls, the material most often used i ...
, a dozen tennis courts, and seven pools. It is home to five golf courses, including the award-winning Paradise Canyon Golf Resort, and is within of several others.
Built for the 1975 Canada Games, the ENMAX Centre
The ENMAX Centre (formerly Canada Games Sportsplex) is a 5,479-seat multi-purpose arena, in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada.
It features a full-size ice rink, and a walking track. An outdoor sports field, with capacity for 2,000 people, is no longe ...
is Lethbridge's multipurpose arena. The 6,500-seat facility has hosted concerts, three-ring circuses, multicultural events, national curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
championships, basketball events, banquets, skating events and is home to the Lethbridge Hurricanes
The Lethbridge Hurricanes are a Canadian major junior ice hockey team currently members of the Eastern Conference (Central Division) of the Western Hockey League (WHL). The team is based in Lethbridge, Alberta, and play their home games at the ...
, a major Western Hockey League
The Western Hockey League (WHL) is a major junior ice hockey league based in Western Canada and the Northwestern United States. The WHL is one of three leagues that constitutes the Canadian Hockey League (CHL) as the highest level of junior h ...
franchise. The arena has a running track, racquetball and squash courts, and a full-size ice rink. In 1997, the Servus Sports Centre (originally the Lethbridge Soccer Centre) was built directly south of the ENMAX Centre and added two regulation size indoor soccer pitches to the complex. The Lethbridge Kyodokan Judo Club facility is located next to the Community Savings Place, and has been a Judo Canada Regional Training Centre since 2015.
On the city's west side, Phase 1 of the ATB Centre, a recreation complex, opened in 2016 and houses two hockey rinks and the Lethbridge Curling Club. Phase 2 of this project opened in May 2019 and includes a field house with basketball courts and a 300m running track, as well as an aquatics centre with slides and a wave pool.
Several winter sports venues are in or near Lethbridge. The city has six indoor ice arenas with a total ice area of 11,220 square metres (120,800 sq ft) and a total seating capacity of 8,149. Other than the ENMAX Centre, all ice surfaces are available from October to April only. Lethbridge is east of the Castle Mountain ski resort.
In October 2020, the Canadian Junior Football League (CJFL) announced an expansion team would begin play in Lethbridge at the 3,500-seat University of Lethbridge Stadium in 2022. The Lethbridge Vipers will be the seventh team in the Prairie Junior Football Conference and the 19th team in the CJFL.
Government
Eight councillors and amayor
In many countries, a mayor is the highest-ranking official in a municipal government such as that of a city or a town. Worldwide, there is a wide variance in local laws and customs regarding the powers and responsibilities of a mayor as well a ...
make up the Lethbridge City Council The Lethbridge City Council is the legislative governing body that represents the citizens of Lethbridge, Alberta. Eight councillors and the mayor comprise the council. The mayor is the city's chief elected official and the city manager is its chief ...
. City voters elect a new government every four years. The last election was October 18, 2021. Lethbridge does not have a ward system, so the mayor and all councillors are elected at large. The 2009–2011 operating budget of the City of Lethbridge was –278 million, more than half of which came from property tax
A property tax or millage rate is an ad valorem tax on the value of a property.In the OECD classification scheme, tax on property includes "taxes on immovable property or net wealth, taxes on the change of ownership of property through inheri ...
. One Member of Parliament (MP) representing Lethbridge
Lethbridge ( ) is a city in the province of Alberta, Canada. With a population of 101,482 in its 2019 Alberta municipal censuses, 2019 municipal census, Lethbridge became the fourth Alberta city to surpass 100,000 people. The nearby Canadian ...
sits in the House of Commons
The House of Commons is the name for the elected lower house of the bicameral parliaments of the United Kingdom and Canada. In both of these countries, the Commons holds much more legislative power than the nominally upper house of parliament. ...
in Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the core ...
, and two members of Alberta's legislative assembly (MLAs), representing Lethbridge-East
Lethbridge-East is a provincial electoral district in Alberta, Canada, covering the eastern half of the city of Lethbridge. The district is one of 87 in the province mandated to return a single member to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta usi ...
( UCP) and Lethbridge-West
Lethbridge-West is an Alberta provincial electoral district, covering the western half of the city of Lethbridge, including all of West Lethbridge.
Under the Alberta electoral boundary re-distribution of 2004, 13 Street forms most of the divi ...
(NDP
NDP may stand for:
Computing
* Neighbor Discovery Protocol, an Internet protocol
* Nortel Discovery Protocol, a layer two Internet protocol, also called SONMP
* Nondeterministic programming, a type of computer language
Government
* National ...
), sit in the legislative assembly in Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
.
Traditionally, political leanings in Lethbridge have been right-wing
Right-wing politics describes the range of political ideologies that view certain social orders and hierarchies as inevitable, natural, normal, or desirable, typically supporting this position on the basis of natural law, economics, authorit ...
. Federally, from 1917 to 1930, Lethbridge voters switched between various federal parties, but from 1935 to 1957, they voted Social Credit
Social credit is a distributive philosophy of political economy developed by C. H. Douglas. Douglas attributed economic downturns to discrepancies between the cost of goods and the compensation of the workers who made them. To combat what he ...
in each election. Progressive Conservatives held office from 1958 until 1993, when the Reform Party of Canada
The Reform Party of Canada (french: Parti réformiste du Canada) was a right-wing populist and conservative federal political party in Canada that existed under that name from 1987 to 2000. Reform was founded as a Western Canada-based protes ...
was formed. The Reform party and its various subsequent incarnations such as the current Conservative Party of Canada
The Conservative Party of Canada (french: Parti conservateur du Canada), colloquially known as the Tories, is a federal political party in Canada. It was formed in 2003 by the merger of the two main right-leaning parties, the Progressive Con ...
have dominated the polls since. The city's two provincial electoral districts are represented by one government MLA, currently Nathan Neudorf for Lethbridge-East
Lethbridge-East is a provincial electoral district in Alberta, Canada, covering the eastern half of the city of Lethbridge. The district is one of 87 in the province mandated to return a single member to the Legislative Assembly of Alberta usi ...
, and one opposition MLA, currently Shannon Phillips
Shannon Rosella Phillips (born September 4, 1975) is a Canadian politician who was elected in the 2015 and 2019 Alberta general elections to represent the electoral district of Lethbridge-West in the 29th and 30th Alberta Legislatures, respect ...
for Lethbridge-West
Lethbridge-West is an Alberta provincial electoral district, covering the western half of the city of Lethbridge, including all of West Lethbridge.
Under the Alberta electoral boundary re-distribution of 2004, 13 Street forms most of the divi ...
.
Alberta Health Services
Alberta Health Services (AHS) which is headquartered in Edmonton, Alberta is the single health authority for the Canadian province of Alberta and the "largest integrated provincial health care system" in Canada. AHS delivers medical care on beh ...
, the provincial health authority that plans and delivers health services on behalf of the Ministry of Health, administers public health services in Lethbridge. Chinook Health oversees facilities in southwestern Alberta, such as the Chinook Regional Hospital and St. Michael's Health Centre.
Transportation
 Mass transit in Lethbridge consists of 40 buses (with an average age of 10 years) operating on more than a dozen routes. Traditionally, bus routes in the city started and ended downtown. In the early 21st century, however,
Mass transit in Lethbridge consists of 40 buses (with an average age of 10 years) operating on more than a dozen routes. Traditionally, bus routes in the city started and ended downtown. In the early 21st century, however, Lethbridge Transit
Lethbridge Transit manages and operates the municipally-owned public transportation system in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada.
History
Public transit in Lethbridge began in 1912 and consisted of a streetcar system operated by the Lethbridge Municip ...
introduced cross-town and shuttle routes, such as University of Lethbridge
, mottoeng = ''Let there be light''
, type = Public
, established =
, academic_affiliations = Universities Canada
, endowment = $73 million (2019)
, chancellor = Charles Weasel ...
to Lethbridge College, University of Lethbridge to the North Lethbridge terminal, and Lethbridge College to the North Lethbridge terminal. Several routes converge near the Chinook Regional Hospital, although it is not officially a terminal.
The Parks and Recreation department maintains the citywide, pedestrian/cyclist Coal Banks Trail Coal Banks Trail is a 30-kilometre multipurpose recreational path in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It connects all of the city's major urban parks, all three geographical areas, and many smaller parks. While
primarily a community recreation opportu ...
systemmap
. The system was designed to connect the
Oldman River
The Oldman River is a river in southern Alberta, Canada. It flows roughly west to east from the Rocky Mountains, through the communities of Fort Macleod, Lethbridge, and on to Grassy Lake, where it joins the Bow River to form the South Saskatche ...
valley with other areas of the city, including Pavan Park in the north, Henderson Lake in the east, Highways 4 and 5 in the south and a loop in West Lethbridge (including University Drive and McMaster Blvd).
Four provincial highways ( 3, 4, 5, and 25) run through or terminate in Lethbridge. This has led to the creation of major arterial roads, including Mayor Magrath Drive, University Drive and Scenic Drive. This infrastructure and its location on the CANAMEX Corridor
The CANAMEX corridor is a series of improvements to freeways and other transportation infrastructure linking Canada to Mexico through the United States. The corridor was established under the North American Free Trade Agreement.
Currently the corr ...
has helped make Lethbridge and its freight depots a major shipping destination. Lethbridge is north of the United States border via Highways 4 and 5 and south of Calgary
Calgary ( ) is the largest city in the western Canadian province of Alberta and the largest metro area of the three Prairie Provinces. As of 2021, the city proper had a population of 1,306,784 and a metropolitan population of 1,481,806, makin ...
via Highways 2 and 3. Highways 2, 3 and 4 form part of the CANAMEX trade route between Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
, the United States, and Canada.
Lethbridge has a commercial airport, the Lethbridge Airport
Lethbridge Airport , previously Lethbridge County Airport, is located south southeast of Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada. It is 10–15 driving minutes from downtown and has scheduled service to the city of Calgary, Alberta. The airport is classifi ...
, and the CPR
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is an emergency procedure consisting of chest compressions often combined with artificial ventilation in an effort to manually preserve intact brain function until further measures are taken to restore sponta ...
rail yards in Kipp, Alberta (12 km away). The airport provides commercial flights to Calgary, industrial and corporate opportunities, as well as private and charter flights elsewhere. The airport provides customs services for flights arriving from the United States. The rail yards were moved to Kipp, just west of the city, from downtown Lethbridge in 1983. The yards were planned for redevelopment with a mix of multi-family residential, commercial and light industrial land uses. The Park Place Mall
Park Place Mall or Park Place Shopping Centre, is a shopping mall located in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada.
Built in 1988, the + mall covers four city blocks downtown and includes over 120 stores, including three anchor stores, Winners, Shoppers D ...
is now located on the portion of the former rail yards north of 1 Avenue South between Scenic Drive to the west and Stafford Drive to the east.
Education
kindergarten
Kindergarten is a preschool educational approach based on playing, singing, practical activities such as drawing, and social interaction as part of the transition from home to school. Such institutions were originally made in the late 18th cent ...
through 12 locally. The Palliser School Division, which is based in Lethbridge, administers public primary and secondary education in the outlying areas. Lethbridge School Division administers five high schools ( Chinook High School, Immanuel Christian High School, Lethbridge Collegiate Institute
Lethbridge Collegiate Institute (LCI) is a public high school in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada, operated by Lethbridge School District No. 51 that serves grades nine through twelve. LCI was the first school in Lethbridge designated only for seconda ...
, Victoria Park High School, and Winston Churchill High School), four middle schools, and 14 elementary schools in Lethbridge. Immanuel Christian covers grades 6 through 12.
Lethbridge is home to Lethbridge College
Lethbridge College (previously Lethbridge Community College) opened in 1957 as the first publicly funded community college in Canada. Over 4,000 students attend the Lethbridge, Alberta, institution.
Lethbridge College is a member of the Albert ...
, founded in 1957, and the University of Lethbridge
, mottoeng = ''Let there be light''
, type = Public
, established =
, academic_affiliations = Universities Canada
, endowment = $73 million (2019)
, chancellor = Charles Weasel ...
, founded in 1967. Red Crow Community College
Red Crow Community College is a college located on the Kainai Nation reserve in southern Alberta, Canada with a campus in Lethbridge.
Partnerships
Red Crow College is a member of the First Nation & Adult Higher Education Consortium, a non-prof ...
has a campus in the city. During the 2015–2016 school year, the University of Lethbridge and the Lethbridge College had a combined enrolment of 14,820, which represented 20 percent of the city's population.
Media
Lethbridge has two major newspapers: the daily '' Lethbridge Herald'' and the weekly ''Lethbridge Sun Times
''Lethbridge Sun Times'' is a weekly paper in the Lethbridge, Alberta, area, with a circulation of 24,000 in 2007. The paper is part of Alta Newspaper Group, the same company that publishes and distributes the daily ''Lethbridge Herald''.
History ...
''. The university and college each have a student-run, weekly newspaper. There are 11 FM radio stations, including CKXU-FM
CKXU-FM is a Canadian Not-for-profit radio station, broadcasting at 88.3 FM broadcasting, FM, from the University of Lethbridge, in Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada.
History
CKXU began as CKUL in 1972, when a public address system was set up in Secti ...
, a campus radio station located at the University of Lethbridge.
Notable people
See also
*List of communities in Alberta
The province of Alberta, Canada, is divided into ten types of local governments – urban municipalities (including cities, towns, villages and summer villages), specialized municipalities, rural municipalities (including municipal district ...
*List of cities in Alberta
A city is the highest form of all incorporated List of communities in Alberta#Urban municipalities, urban municipality statuses used in the Canadian Province of Alberta. Alberta cities are created when communities with populations of at least 10 ...
*List of people from Lethbridge
This is a list of notable people who are from Lethbridge, Alberta, Canada or have spent a large part or formative part of their career in that city. They are colloquially known as ''Lethbridgians''.
*Ernie Afaganis, CBC sports broadcaster
* Rich ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
* {{Authority control 1890 establishments in the Northwest Territories Cities in Alberta Hudson's Bay Company trading posts Populated places established in 1890