Lung fibrosis on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Pulmonary fibrosis is a condition in which the lungs become scarred over time. Symptoms include shortness of breath, a dry cough, feeling tired, weight loss, and nail clubbing. Complications may include pulmonary hypertension, respiratory failure, pneumothorax, and lung cancer.
Causes include environmental pollution, certain medications, connective tissue diseases, infections, and interstitial lung diseases. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF), an interstitial lung disease of unknown cause, is most common. Diagnosis may be based on symptoms,
Date last updated: 9 February 2010 * Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, most often resulting from inhaling dust contaminated with bacterial, fungal, or animal products * Cigarette smoking can increase the risk or make the illness worse * Some typical connective tissue diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, SLE and scleroderma * Other diseases that involve connective tissue, such as sarcoidosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis * Infections, including COVID-19 * Certain medications, e.g. amiodarone, bleomycin ( pingyangmycin), busulfan,
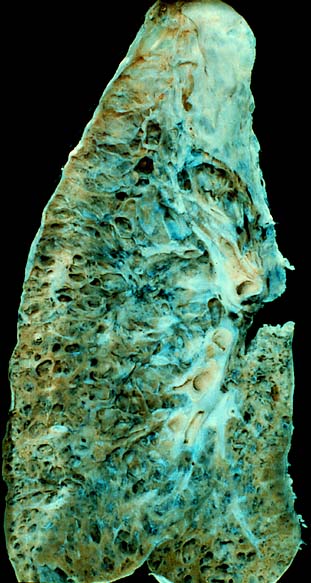
 The diagnosis can be confirmed by lung biopsy. A videoscopic assisted thoracoscopic wedge biopsy (VATS) under general anesthesia may be necessary to obtain enough tissue to make an accurate diagnosis. This kind of biopsy involves placement of several tubes through the chest wall, one of which is used to cut off a piece of lung to send for evaluation. The removed tissue is examined histopathologically by microscopy to confirm the presence and pattern of fibrosis as well as presence of other features that may indicate a specific cause e.g. specific types of mineral dust or possible response to therapy e.g. a pattern of so-called non-specific interstitial fibrosis.
Misdiagnosis is common because, while overall pulmonary fibrosis is not rare, each individual type of pulmonary fibrosis is uncommon and the evaluation of patients with these diseases is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Terminology has been standardized but difficulties still exist in their application. Even experts may disagree with the classification of some cases.
On
The diagnosis can be confirmed by lung biopsy. A videoscopic assisted thoracoscopic wedge biopsy (VATS) under general anesthesia may be necessary to obtain enough tissue to make an accurate diagnosis. This kind of biopsy involves placement of several tubes through the chest wall, one of which is used to cut off a piece of lung to send for evaluation. The removed tissue is examined histopathologically by microscopy to confirm the presence and pattern of fibrosis as well as presence of other features that may indicate a specific cause e.g. specific types of mineral dust or possible response to therapy e.g. a pattern of so-called non-specific interstitial fibrosis.
Misdiagnosis is common because, while overall pulmonary fibrosis is not rare, each individual type of pulmonary fibrosis is uncommon and the evaluation of patients with these diseases is complex and requires a multidisciplinary approach. Terminology has been standardized but difficulties still exist in their application. Even experts may disagree with the classification of some cases.
On
medical imaging
Medical imaging is the technique and process of imaging the interior of a body for clinical analysis and medical intervention, as well as visual representation of the function of some organs or tissues (physiology). Medical imaging seeks to rev ...
, lung biopsy, and lung function tests.
There is no cure and there are limited treatment options available. Treatment is directed towards efforts to improve symptoms and may include oxygen therapy
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactica ...
and pulmonary rehabilitation. Certain medications may be used to try to slow the worsening of scarring. Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
may occasionally be an option. At least 5 million people are affected globally. Life expectancy is generally less than five years.
Signs and symptoms
Symptoms of pulmonary fibrosis are mainly: * Shortness of breath, particularly with exertion * Chronic dry, hacking coughing * Fatigue and weakness * Chest discomfort including chest pain * Loss of appetite and rapid weight loss Pulmonary fibrosis is suggested by a history of progressive shortness of breath ( dyspnea) with exertion. Sometimes fine inspiratory crackles can be heard at the lung bases on auscultation. Achest X-ray
A chest radiograph, called a chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film, is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in med ...
may or may not be abnormal, but high-resolution CT will frequently demonstrate abnormalities.
Cause
Pulmonary fibrosis may be a secondary effect of other diseases. Most of these are classified as interstitial lung diseases. Examples include autoimmune disorders, viral infections and bacterial infection like tuberculosis which may cause fibrotic changes in both lung's upper or lower lobes and other microscopic injuries to the lung. However, pulmonary fibrosis can also appear without any known cause. In this case, it is termed "idiopathic". Most idiopathic cases are diagnosed as '' idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis''. This is a diagnosis of exclusion of a characteristic set of histologic/pathologic features known as usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP). In either case, there is a growing body of evidence which points to a genetic predisposition in a subset of patients. For example, a mutation in surfactant protein C (SP-C) has been found to exist in some families with a history of pulmonary fibrosis.Autosomal dominant
In genetics, dominance is the phenomenon of one variant (allele) of a gene on a chromosome masking or overriding the effect of a different variant of the same gene on the other copy of the chromosome. The first variant is termed dominant and t ...
mutations in the '' TERC'' or '' TERT'' genes, which encode telomerase, have been identified in about 15 percent of pulmonary fibrosis patients.
Diseases and conditions that may cause pulmonary fibrosis as a secondary effect include:
* Inhalation of environmental and occupational pollutants, such as metals in asbestosis, silicosis
Silicosis is a form of occupational lung disease caused by inhalation of crystalline silica dust. It is marked by inflammation and scarring in the form of nodular lesions in the upper lobes of the lungs. It is a type of pneumoconiosis. Silicos ...
and exposure to certain gases. Coal miners, ship workers and sand blaster
Sandblasting, sometimes known as abrasive blasting, is the operation of forcibly propelling a stream of abrasive material against a surface under high pressure to smooth a rough surface, roughen a smooth surface, shape a surface or remove su ...
s among others are at higher risk.MedlinePlus > Pulmonary FibrosisDate last updated: 9 February 2010 * Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, most often resulting from inhaling dust contaminated with bacterial, fungal, or animal products * Cigarette smoking can increase the risk or make the illness worse * Some typical connective tissue diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis, ankylosing spondylitis, SLE and scleroderma * Other diseases that involve connective tissue, such as sarcoidosis and granulomatosis with polyangiitis * Infections, including COVID-19 * Certain medications, e.g. amiodarone, bleomycin ( pingyangmycin), busulfan,
methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, apomorphine, and nitrofurantoin
* Radiation therapy to the chest
Pathogenesis
Pulmonary fibrosis involves gradual exchange of normal lungparenchyma
Parenchyma () is the bulk of functional substance in an animal organ or structure such as a tumour. In zoology it is the name for the tissue that fills the interior of flatworms.
Etymology
The term ''parenchyma'' is New Latin from the word π ...
with fibrotic tissue. The replacement of normal lung with scar tissue causes irreversible decrease in oxygen diffusion capacity, and the resulting stiffness or decreased compliance makes pulmonary fibrosis a restrictive lung disease.
Pulmonary fibrosis is perpetuated by aberrant wound healing, rather than chronic inflammation.
It is the main cause of restrictive lung disease that is intrinsic to the lung parenchyma. In contrast, quadriplegia and kyphosis are examples of causes of restrictive lung disease that do not necessarily involve pulmonary fibrosis.
Diagnosis
spirometry
Spirometry (meaning ''the measuring of breath'') is the most common of the pulmonary function tests (PFTs). It measures lung function, specifically the amount (volume) and/or speed (flow) of air that can be inhaled and exhaled. Spirometry is he ...
, as a restrictive lung disease, both the FEV1 (forced expiratory volume in 1 second) and FVC (forced vital capacity) are reduced so the FEV1/FVC ratio
The FEV1/FVC ratio, also called Tiffeneau-Pinelli index, is a calculated ratio used in the diagnosis of obstructive and restrictive lung disease. It represents the proportion of a person's vital capacity that they are able to expire in the first ...
is normal or even increased in contrast to obstructive lung disease where this ratio is reduced. The values for residual volume and total lung capacity are generally decreased in restrictive lung disease.
Treatment
Pulmonary fibrosis creates scar tissue. The scarring is permanent once it has developed. Slowing the progression and prevention depends on the underlying cause: * Treatment options for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis are very limited. Though research trials are ongoing, there is no evidence that any medications can significantly help this condition. Lung transplantation is the only therapeutic option available in severe cases. Since some types of lung fibrosis can respond to corticosteroids (such as prednisone) and/or other medications that suppress the body's immune system, these types of drugs are sometimes prescribed in an attempt to slow the processes that lead to fibrosis. :The immune system is felt to play a central role in the development of many forms of pulmonary fibrosis. The goal of treatment with immune suppressive agents such as corticosteroids is to decrease lung inflammation and subsequent scarring. Responses to treatment are variable. Those whose conditions improve with immune suppressive treatment probably do not have idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis has no significant treatment or cure. * Two pharmacological agents intended to prevent scarring in mild idiopathic fibrosis are pirfenidone, which reduced reductions in the 1-year rate of decline inFVC FVC may refer to:
* Fair Vote Canada, an electoral reform advocacy group in Canada
* Ferraz de Vasconcelos (CPTM), a railway station in Brazil
* Financial vehicle corporation in the European Union
* Fingerprint Verification Competition
* FIRST V ...
. Pirfenidone also reduced the decline in distances on the 6-minute walk test, but had no effect on respiratory symptoms. The second agent is nintedanib, which acts as antifibrotic, mediated through the inhibition of a variety of tyrosine kinase receptors (including platelet-derived growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and vascular endothelial growth factor). A randomized clinical trial showed it reduced lung-function decline and acute exacerbations.
* Anti-inflammatory agents have only limited success in reducing the fibrotic process. Some of the other types of fibrosis, such as non-specific interstitial pneumonia, may respond to immunosuppressive therapy such as corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are a class of steroid hormones that are produced in the adrenal cortex of vertebrates, as well as the synthetic analogues of these hormones. Two main classes of corticosteroids, glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids, are involve ...
. However, only a minority of patients respond to corticosteroids alone, so additional immunosuppressants, such as cyclophosphamide
Cyclophosphamide (CP), also known as cytophosphane among other names, is a medication used as chemotherapy and to suppress the immune system. As chemotherapy it is used to treat lymphoma, multiple myeloma, leukemia, ovarian cancer, breast cancer ...
, azathioprine, methotrexate
Methotrexate (MTX), formerly known as amethopterin, is a chemotherapy agent and immune-system suppressant. It is used to treat cancer, autoimmune diseases, and ectopic pregnancies. Types of cancers it is used for include breast cancer, leuke ...
, penicillamine, and cyclosporine may be used. Colchicine has also been used with limited success. There are ongoing trials with newer drugs such as IFN-γ and mycophenolate mofetil.
* Hypersensitivity pneumonitis, a less severe form of pulmonary fibrosis, is prevented from becoming aggravated by avoiding contact with the causative material.
* Oxygen supplementation
Oxygen therapy, also known as supplemental oxygen, is the use of oxygen as medical treatment. Acute indications for therapy include hypoxemia (low blood oxygen levels), carbon monoxide toxicity and cluster headache. It may also be prophylactica ...
improves the quality of life and exercise capacity. Lung transplantation
Lung transplantation, or pulmonary transplantation, is a surgical procedure in which one or both lungs are replaced by lungs from a donor. Donor lungs can be retrieved from a living or deceased donor. A living donor can only donate one lung lobe. ...
may be considered for some patients.
Prognosis

Hypoxia
Hypoxia means a lower than normal level of oxygen, and may refer to:
Reduced or insufficient oxygen
* Hypoxia (environmental), abnormally low oxygen content of the specific environment
* Hypoxia (medical), abnormally low level of oxygen in the tis ...
caused by pulmonary fibrosis can lead to pulmonary hypertension, which, in turn, can lead to heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
of the right ventricle. Hypoxia can be prevented with oxygen supplementation.
Pulmonary fibrosis may also result in an increased risk for pulmonary emboli
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blockage of an artery in the lungs by a substance that has moved from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream (embolism). Symptoms of a PE may include shortness of breath, chest pain particularly upon breathing ...
, which can be prevented by anticoagulant
Anticoagulants, commonly known as blood thinners, are chemical substances that prevent or reduce coagulation of blood, prolonging the clotting time. Some of them occur naturally in blood-eating animals such as leeches and mosquitoes, where the ...
s.
Epidemiology
Five million people worldwide are affected by pulmonary fibrosis. The rates below are per 100,000 persons, and the ranges reflect narrow and broad inclusion criteria, respectively. These data do not reflect any increased rates due to the COVID-19 pandemic; pulmonary fibrosis is a known symptom of COVID-19 and is estimated (as of July 2020) to occur in roughly 1/3rd of patients hospitalized for COVID-19. Based on these rates, pulmonary fibrosis prevalence in the United States could range from more than 29,000 to almost 132,000, based on the population in 2000 that was 18 years or older. The actual numbers may be significantly higher due to misdiagnosis. Typically, patients are in their forties and fifties when diagnosed while the incidence of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis increases dramatically after the age of fifty. However, loss of pulmonary function is commonly ascribed to old age, heart disease or to more common lung diseases.References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Pulmonary Fibrosis Lung disorders Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate