Loire wine on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Loire Valley wine region includes the
French wine
French wine is produced all throughout France, in quantities between 50 and 60 million hectolitres per year, or 7–8 billion bottles. France is one of the largest wine producers in the world, along with Italian, Spanish, and America ...
regions
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
situated along the river Loire
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône ...
from the Muscadet
Muscadet ( , , ) is a French wine, French white wine. It is made at the western end of the Loire Valley (wine), Loire Valley, near the city of Nantes in the Pays de la Loire region. It is made from the Melon de Bourgogne grape, often referred t ...
region near the city of Nantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabita ...
on the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe an ...
coast to the region
In geography, regions, otherwise referred to as zones, lands or territories, are areas that are broadly divided by physical characteristics (physical geography), human impact characteristics (human geography), and the interaction of humanity and t ...
of Sancerre
Sancerre () is a medieval hilltop town (ville) and commune in the Cher department, France overlooking the river Loire. It is noted for its wine.
History
Located in the area of Gaul settled by the powerful Celtic (Gaule Celtique) tribe, the Bitu ...
and Pouilly-Fumé
Pouilly-Fumé is an ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) for the dry sauvignon blanc white wine produced around Pouilly-sur-Loire, in the Nièvre département. Another white wine produced in the same area but with a different grape vari ...
just southeast of the city of Orléans
Orléans (;"Orleans"
(US) and France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. In between are the regions of (US) and France France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
Anjou wine
Anjou wine is produced in the Loire Valley wine region of France near the city of Angers. The wines of region are often grouped together with the wines of nearby Saumur as "Anjou-Saumur". Along with the wines produced further east in Touraine, Anj ...
, Saumur
Saumur () is a commune in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France.
The town is located between the Loire and Thouet rivers, and is surrounded by the vineyards of Saumur itself, Chinon, Bourgueil, Coteaux du Layon, etc.. Saumur statio ...
, Bourgueil
Bourgueil () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France.
Population
Bourgueil wine
Bourgueil is an ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) for wine in the Loire Valley region, and produces primarily red wine from th ...
, Chinon
Chinon () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department, Centre-Val de Loire, France.
The traditional province around Chinon, Touraine, became a favorite resort of French kings and their nobles beginning in the late 15th and early 16th centuri ...
, and Vouvray
Vouvray (, , ) is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. It is around 9 km east of the centre of Tours.
It is best known for its production of white wine, rated among the best in France.
Population
Education
Schoo ...
. The Loire Valley itself follows the river through the Loire
The Loire (, also ; ; oc, Léger, ; la, Liger) is the longest river in France and the 171st longest in the world. With a length of , it drains , more than a fifth of France's land, while its average discharge is only half that of the Rhône ...
department to the river's origins in the Cévennes
, etymology=
, photo=Point Sublime-Gorges du Tarn-Frankreich.jpg
, photo_caption=The Gorges du Tarn
, country= France
, subdivision2=
, subdivision2_type=Départements
, parent= Massif Central
, area_km2=
, length_km=
, length_orient ...
but the majority of the wine production takes place in the regions noted above. The area includes 87 appellation
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
s under the ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée
An appellation is a legally defined and protected geographical indication primarily used to identify where the grapes for a wine were grown, although other types of food often have appellations as well. Restrictions other than geographical boun ...
'' (AOC), ''Vin Délimité de Qualité Superieure
Vin or VIN may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* Vîn TV, a Kurdish language satellite television channel founded in 2007
* ''Vos Iz Neias?'', an American Jewish online news site
* Coastal radio station VIN Geraldton (callsign), a statio ...
'' (VDQS) and ''Vin de pays
''Vin de pays'' (, "country wine") was a French wine classification that was above the ''vin de table'' classification, but below the ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) classification and below the former ''vin délimité de qualité s ...
'' systems. While the majority of production is white wine from the Chenin blanc, Sauvignon blanc
is a green-skinned grape variety that originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French words ''sauvage'' ("wild") and ''blanc'' ("white") due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in ...
and Melon de Bourgogne
Melon de Bourgogne or Melon is a variety of white grape grown primarily in the Loire Valley region of France. It is also grown in North America. It is best known through its use in the white wine Muscadet.
In the U.S., Federal law prevents ...
grapes, there are red wines made (especially around the Chinon
Chinon () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department, Centre-Val de Loire, France.
The traditional province around Chinon, Touraine, became a favorite resort of French kings and their nobles beginning in the late 15th and early 16th centuri ...
region) from Cabernet franc
Cabernet Franc is one of the major black grape varieties worldwide. It is principally grown for blending with Cabernet Sauvignon and Merlot in the Bordeaux style, but can also be vinified alone, as in the Loire's Chinon. In addition to being us ...
. In addition to still wines, rosé
A rosé () is a type of wine that incorporates some of the color from the grape skins, but not enough to qualify it as a red wine. It may be the oldest known type of wine, as it is the most straightforward to make with the skin contact method. ...
, sparkling and dessert wine
Dessert wines, sometimes called pudding wines in the United Kingdom, are sweet wines typically served with dessert.
There is no simple definition of a dessert wine. In the UK, a dessert wine is considered to be any sweet wine drunk with a meal ...
s are also produced. With ''Crémant
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne regi ...
'' production throughout the Loire, it is the second largest sparkling wine producer in France after Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 196-198 Dorling Kindersley 2005 Among these different wine styles, Loire wines tend to exhibit characteristic fruitiness with fresh, crisp flavors-especially in their youth.C. Fallis, editor ''The Encyclopedic Atlas of Wine'' pg 168-176 Global Book Publishing 2006 The Loire Valley has a long history of winemaking
Winemaking or vinification is the production of wine, starting with the selection of the fruit, its fermentation into alcohol, and the bottling of the finished liquid. The history of wine-making stretches over millennia. The science of wine and ...
dating back to the 1st century. In the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, the wines of the Loire Valley were the most esteemed wines in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
and France, even more prized than those from Bordeaux
Bordeaux ( , ; Gascon oc, Bordèu ; eu, Bordele; it, Bordò; es, Burdeos) is a port city on the river Garonne in the Gironde department, Southwestern France. It is the capital of the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region, as well as the prefectur ...
.J. Robinson (ed) ''"The Oxford Companion to Wine"'' Third Edition pg 408-410 Oxford University Press 2006
History
Archaeological
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
evidence suggest that the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
planted the first vineyards in the Loire Valley during their settlement of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
in the 1st century AD. By the 5th century, the flourishing viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for ''vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of ''Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ran ...
of the area was noted in a publication by the poet Sidonius Apollinaris
Gaius Sollius Modestus Apollinaris Sidonius, better known as Sidonius Apollinaris (5 November of an unknown year, 430 – 481/490 AD), was a poet, diplomat, and bishop. Sidonius is "the single most important surviving author from 5th-century Gaul ...
. In his work the ''History of the Franks'', Bishop Gregory of Tours
Gregory of Tours (30 November 538 – 17 November 594 AD) was a Gallo-Roman historian and Bishop of Tours, which made him a leading prelate of the area that had been previously referred to as Gaul by the Romans. He was born Georgius Florenti ...
wrote of the frequent plundering
Looting is the act of stealing, or the taking of goods by force, typically in the midst of a military, political, or other social crisis, such as war, natural disasters (where law and civil enforcement are temporarily ineffective), or rioting. ...
by the Breton
Breton most often refers to:
*anything associated with Brittany, and generally
** Breton people
** Breton language, a Southwestern Brittonic Celtic language of the Indo-European language family, spoken in Brittany
** Breton (horse), a breed
**Ga ...
s of the area's wine stocks. By the 11th century the wines of Sancerre had a reputation across Europe for their high quality. In the High Middle Ages, the wines of the Loire Valley were the most esteemed wines in England and France, even more prized than those from Bordeaux.
Climate and geography
The Loire river has a significant effect on themesoclimate
In viticulture, there are several levels of regional climates that are used to describe the ''terroir'' or immutable characteristics of an area. These levels can be as broad as a macroclimate which includes entire wine regions or as small as a mic ...
of the region, adding the necessary extra few degree
Degree may refer to:
As a unit of measurement
* Degree (angle), a unit of angle measurement
** Degree of geographical latitude
** Degree of geographical longitude
* Degree symbol (°), a notation used in science, engineering, and mathematics
...
s of temperature that allows grapes to grow when the areas to the north and south of the Loire Valley have shown to be unfavorable to viticulture. In addition to finding vineyards along the Loire, several of the river's tributaries
A tributary, or affluent, is a stream or river that flows into a larger stream or main stem (or parent) river or a lake. A tributary does not flow directly into a sea or ocean. Tributaries and the main stem river drain the surrounding drainage b ...
are also well planted-including the rivers Allier
Allier ( , , ; oc, Alèir) is a department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region that borders Cher to the west, Nièvre to the north, Saône-et-Loire and Loire to the east, Puy-de-Dôme to the south, and Creuse to the south-west. Named afte ...
, Cher
Cher (; born Cherilyn Sarkisian; May 20, 1946) is an American singer, actress and television personality. Often referred to by the media as the Honorific nicknames in popular music, "Goddess of Pop", she has been described as embodying female ...
, Indre
Indre (; oc, Endre) is a landlocked department in central France named after the river Indre. The inhabitants of the department are known as the ''Indriens'' (masculine; ) and ''Indriennes'' (feminine; ). Indre is part of the current administ ...
, Loir
The Loir () is a long river in western France. It is a left tributary of the Sarthe. Its source is in the Eure-et-Loir department, north of Illiers-Combray. It joins the river Sarthe in Briollay, north of the city of Angers.
It is indirectly a ...
, Sèvre Nantaise
The Sèvre Nantaise () is a river in the Pays de la Loire regions in western France. It is a left-bank tributary of the Loire. Its total length is . Its source is in the Deux-Sèvres department, near Secondigny. It flows from south to north thro ...
and Vienne
Vienne (; Poitevin-Saintongeais: ''Viéne'') is a landlocked department in the French region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine. It takes its name from the river Vienne. It had a population of 438,435 in 2019. The area has a
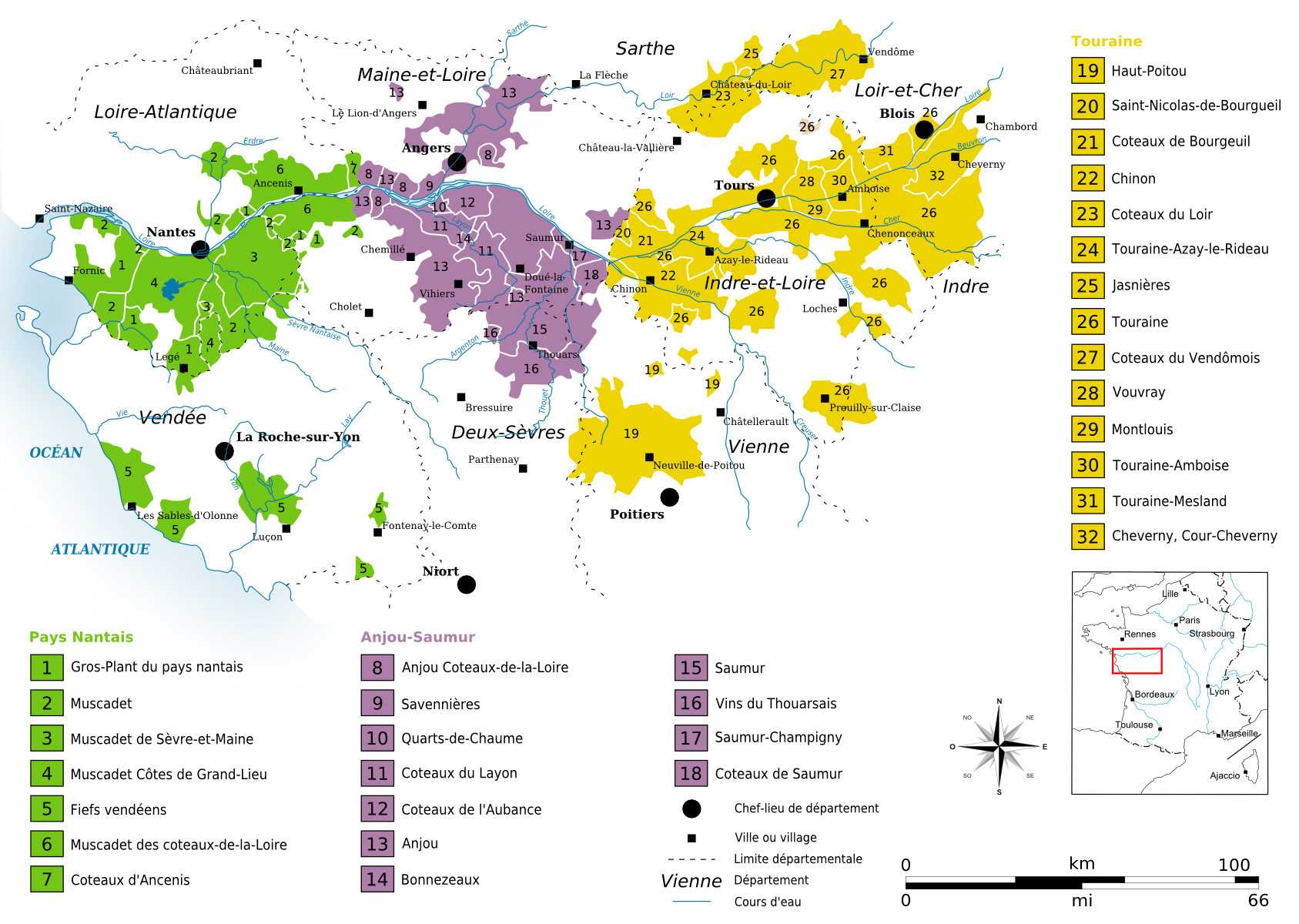
 The Loire Valley is often divided into three sections. The Upper Loire includes the Sauvignon blanc dominated areas of
The Loire Valley is often divided into three sections. The Upper Loire includes the Sauvignon blanc dominated areas of
Official Site of Loire Valley winesLoire Valley vintage chartsThe wines of the Loire
- The official website of France (in English) {{Portal bar, Wine, France Wine regions of France
continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
that is influenced heavily by the Loire and the Atlantic Ocean at the western edge of the region. The climate can be very cool with spring time frost
Frost is a thin layer of ice on a solid surface, which forms from water vapor in an above-freezing atmosphere coming in contact with a solid surface whose temperature is below freezing, and resulting in a phase change from water vapor (a gas) ...
being a potential hazard for the vines. During the harvest
Harvesting is the process of gathering a ripe crop from the fields. Reaping is the cutting of grain or pulse for harvest, typically using a scythe, sickle, or reaper. On smaller farms with minimal mechanization, harvesting is the most labor-i ...
months rain can cause the grapes to be harvested under ripe but can also aid in the development of ''Botrytis cinerea
''Botrytis cinerea'' is a necrotrophic fungus that affects many plant species, although its most notable hosts may be wine grapes. In viticulture, it is commonly known as "botrytis bunch rot"; in horticulture, it is usually called "grey mould" or ...
'' for the region's dessert wines.
Temperature, rainfall and average sunshine time in Angers
Angers (, , ) is a city in western France, about southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the Maine-et-Loire department and was the capital of the province of Anjou until the French Revolution. The inhabitants of both the city and the prov ...
(Anjou Anjou may refer to:
Geography and titles France
* County of Anjou, a historical county in France and predecessor of the Duchy of Anjou
**Count of Anjou, title of nobility
*Duchy of Anjou, a historical duchy and later a province of France
**Duk ...
):
Viticulture and winemaking
With over planted under vine, the Loire Valley is about two-thirds the size of theBordeaux wine
Bordeaux wine ( oc, vin de Bordèu, french: vin de Bordeaux) is produced in the Bordeaux region of southwest France, around the city of Bordeaux, on the Garonne River. To the north of the city the Dordogne River joins the Garonne forming the ...
region.K. MacNeil ''The Wine Bible'' pg 259-272 Workman Publishing 2001 Due to its location and marginal climate, the overall quality of a vintage
Vintage, in winemaking, is the process of picking grapes and creating the finished product—wine (see Harvest (wine)). A vintage wine is one made from grapes that were all, or primarily, grown and harvested in a single specified year. In certa ...
has a dramatic effect on the quality of the region's wines—more so than with other French wine regions. The most common hazard is that the cool climate will prevent the grapes from ripening
Ripening is a process in fruits that causes them to become more palatable. In general, fruit becomes sweeter, less green, and softer as it ripens. Even though the acidity of fruit increases as it ripens, the higher acidity level does not make the ...
fully and developing the sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
s needed to balance the naturally high acidity
In computer science, ACID ( atomicity, consistency, isolation, durability) is a set of properties of database transactions intended to guarantee data validity despite errors, power failures, and other mishaps. In the context of databases, a sequ ...
of the grapes. During these cool vintages the Sauvignon blanc based wines are lighter in color, less fruity and have more pronounced mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ( ...
notes. The Cabernet franc based wines are also lighter in color with more vegetal or "weed
A weed is a plant considered undesirable in a particular situation, "a plant in the wrong place", or a plant growing where it is not wanted.Harlan, J. R., & deWet, J. M. (1965). Some thoughts about weeds. ''Economic botany'', ''19''(1), 16-24. ...
"-like aromas. In riper vintages, a Loire Cabernet franc will develop aromas of raspberries
The raspberry is the edible fruit of a multitude of plant species in the genus ''Rubus'' of the rose family, most of which are in the subgenus '' Idaeobatus''. The name also applies to these plants themselves. Raspberries are perennial with w ...
and lead pencil shavings.
The Loire Valley has a high density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematical ...
of vine plantings with an average of 1,600-2,000 vines per acre (4,000-5,000 per hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is a ...
). Some Sancerre vineyards have as many as 10,000 plants per hectare. With more vines competing for the same limited resources in the soil, the density is designed to compensate for the excessive yields that some of the grape varieties, like Chenin blanc, are prone to have. In recent times, pruning
Pruning is a horticultural, arboricultural, and silvicultural practice involving the selective removal of certain parts of a plant, such as branches, buds, or roots.
The practice entails the ''targeted'' removal of diseased, damaged, dead, ...
and canopy management
In viticulture, the canopy of a grapevine includes the parts of the vine visible aboveground - the trunk, cordon, stems, leaves, flowers, and fruit. The canopy plays a key role in light energy capture via photosynthesis, water use as regulated b ...
have started to limit yields more effectively.
Winemaking in the Loire is characterised by a general avoidance of barrel ageing
A barrel or cask is a hollow cylindrical container with a bulging center, longer than it is wide. They are traditionally made of wooden staves and bound by wooden or metal hoops. The word vat is often used for large containers for liquids, ...
and malolactic fermentation
Malolactic conversion (also known as malolactic fermentation or MLF) is a process in winemaking in which tart-tasting malic acid, naturally present in grape must, is converted to softer-tasting lactic acid. Malolactic fermentation is most often p ...
. However some winemakers have begun experimenting with both. Chaptalization
Chaptalization is the process of adding sugar to unfermented grape must in order to increase the alcohol content after fermentation. The technique is named after its developer, the French chemist Jean-Antoine-Claude Chaptal. This process is not in ...
is permitted here and can help wine makers compensate for the under ripeness of the grapes in some years. For red wines there has been more emphasis on extending the maceration time of skin contact in order to bring out more color and tannin
Tannins (or tannoids) are a class of astringent, polyphenolic biomolecules that bind to and precipitate proteins and various other organic compounds including amino acids and alkaloids.
The term ''tannin'' (from Anglo-Norman ''tanner'', ...
s into the wine. Temperature control is also an important consideration with the cold autumn weather sometimes requiring that the must
Must (from the Latin ''vinum mustum'', "young wine") is freshly crushed fruit juice (usually grape juice) that contains the skins, seeds, and stems of the fruit. The solid portion of the must is called pomace and typically makes up 7–23% of t ...
be heated in order to complete fermentation
Fermentation is a metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes. In biochemistry, it is narrowly defined as the extraction of energy from carbohydrates in the absence of oxygen. In food ...
fully.
Wine regions

 The Loire Valley is often divided into three sections. The Upper Loire includes the Sauvignon blanc dominated areas of
The Loire Valley is often divided into three sections. The Upper Loire includes the Sauvignon blanc dominated areas of Sancerre
Sancerre () is a medieval hilltop town (ville) and commune in the Cher department, France overlooking the river Loire. It is noted for its wine.
History
Located in the area of Gaul settled by the powerful Celtic (Gaule Celtique) tribe, the Bitu ...
and Pouilly-Fumé. The Middle Loire is dominated by more Chenin blanc and Cabernet franc wines found in the regions around Touraine
Touraine (; ) is one of the traditional provinces of France. Its capital was Tours. During the political reorganization of French territory in 1790, Touraine was divided between the departments of Indre-et-Loire, :Loir-et-Cher, Indre and Vie ...
, Saumur
Saumur () is a commune in the Maine-et-Loire department in western France.
The town is located between the Loire and Thouet rivers, and is surrounded by the vineyards of Saumur itself, Chinon, Bourgueil, Coteaux du Layon, etc.. Saumur statio ...
, Chinon
Chinon () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department, Centre-Val de Loire, France.
The traditional province around Chinon, Touraine, became a favorite resort of French kings and their nobles beginning in the late 15th and early 16th centuri ...
and Vouvray
Vouvray (, , ) is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France. It is around 9 km east of the centre of Tours.
It is best known for its production of white wine, rated among the best in France.
Population
Education
Schoo ...
. The Lower Loire that leads to the mouth of the river's entrance to the Atlantic goes through the Muscadet region which is dominated by wines of the Melon de Bourgogne grape.J. Robinson ''Jancis Robinson's Wine Course'' Third Edition pg 180-184 Abbeville Press 2003 Spread out across the Loire Valley are 87 appellations under the AOC, VDQS and Vin de Pays systems. There are two generic designations that can be used across the whole of the Loire Valley. The ''Crémant de Loire'' which refers to any sparkling wine made according to the traditional method
The traditional method is the process used in the Champagne region of France to produce Champagne. It is also the method used in various French regions to produce sparkling wines (not called “Champagne”), in Spain to produce Cava, in Portu ...
of Champagne
Champagne (, ) is a sparkling wine originated and produced in the Champagne wine region of France under the rules of the appellation, that demand specific vineyard practices, sourcing of grapes exclusively from designated places within it, spe ...
. The ''Vin de Pays du Jardin de la France'' refers to any varietal
A varietal wine is a wine made primarily from a single named grape variety, and which typically displays the name of that variety on the wine label.The American Heritage Dictionary of the English Language, Fourth Edition, 2000.winepros.com.au. ...
ly labeled wine, such as Chardonnay
Chardonnay (, , ) is a green-skinned grape variety used in the production of white wine. The variety originated in the Burgundy wine region of eastern French wine, France, but is now grown wherever wine is produced, from English wine, Englan ...
, that is produced in the region outside of an AOC designation.
Sancerre & Pouilly-Fumé
Sauvignon blanc
is a green-skinned grape variety that originates from the Bordeaux region of France. The grape most likely gets its name from the French words ''sauvage'' ("wild") and ''blanc'' ("white") due to its early origins as an indigenous grape in ...
and Pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
are the principal grapes of this region that is centered around the appellation of Sancerre and Pouilly-Fumé. The two towns of Sancerre and Pouilly-sur-Loire (where Pouilly-Fumé is made) sit on opposite sides of the Loire river with Sancerre being about to the northwest of Pouilly. The ''Fumé'' is said to come from the ''silex'' flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and start fir ...
interspersed with the limestone in the area that can give a smoky gunflint note to the wine. Another possibility for the name is the early morning fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
created by the Loire river that can blanket the vineyards. Wines labeled with just Pouilly or Pouilly-sur-Loire
Pouilly-sur-Loire (, literally ''Pouilly on Loire'') is a commune in the Nièvre department in central France.
Pouilly-sur-Loire is a town noted for the white wine known as Pouilly-Fumé
Pouilly-Fumé is an ''appellation d'origine contrôl� ...
are often made from the Chasselas
Chasselas or Chasselas blanc is a wine grape variety grown mainly in Switzerland, France, Germany, Portugal, Hungary, Romania, New Zealand, Croatia and Chile. Chasselas is mostly winemaking, vinified to be a full, Dry (wine), dry and fruit ...
grape.H. Johnson & J. Robinson ''The World Atlas of Wine'' pg 122 Mitchell Beazley Publishing 2005
Unlike many areas of France, the Sancerre region is heavily mechanized with the use of mechanical harvesting
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of ...
rather than hand pickers. One of the best known producers in the region is Didier Dageneau who, until his death in 2008, was an influential voice in the area advocating the reduction of yields and the use of organic viticulture.
Pouilly-Fumé only produces white wines while Sancerre produces red, white and rosé wines. The white Sauvignon blanc based wines from this region has characteristic gooseberry
Gooseberry ( or (American and northern British) or (southern British)) is a common name for many species of ''Ribes'' (which also includes currants), as well as a large number of plants of similar appearance. The berries of those in the genu ...
and grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' × ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink.
Grapefruit is ...
flavors with the Pouilly-Fumé version typically being more full bodied and rich in texture. The red Pinot noir wines are very light in both body and color that are not very similar to other French expression of the grape like those in Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The c ...
. Smaller appellations in the region include-
*Menetou-Salon
Menetou-Salon is a commune in the Cher department in the Centre-Val de Loire region of France. Inhabitants of the area are known as ''Monestrosaloniens''.
Geography
The commune is located 16 kilometres North of Bourges on the RD11.
Direction ...
- White, red and rosé
* Quincy - White wine
* Reuilly - White, red and rosé
The region was under the influence of the Duchy of Burgundy
The Duchy of Burgundy (; la, Ducatus Burgundiae; french: Duché de Bourgogne, ) emerged in the 9th century as one of the successors of the ancient Kingdom of the Burgundians, which after its conquest in 532 had formed a constituent part of the ...
for most of its history which partly the reason why plantings were once heavily dominated by the Pinot noir grape. The Phylloxera epidemic
The Great French Wine Blight was a severe blight of the mid-19th century that destroyed many of the vineyards in France and laid waste to the wine industry. It was caused by an aphid that originated in North America and was carried across the Atl ...
of the 19th century altered that dynamic when many of the Pinot noir vineyards were wiped out by the louse
Louse ( : lice) is the common name for any member of the clade Phthiraptera, which contains nearly 5,000 species of wingless parasitic insects. Phthiraptera has variously been recognized as an order, infraorder, or a parvorder, as a result o ...
. In their place, plantings of the easier to cultivate Sauvignon blanc vine began to increase. While there are still isolated batches of Pinot noir in the region, Sauvignon blanc is now the most heavily planted.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 211 Dorling Kindersley 2005
Anjou-Saumur
The Anjou region of the Middle Loire is situated around the town ofAngers
Angers (, , ) is a city in western France, about southwest of Paris. It is the prefecture of the Maine-et-Loire department and was the capital of the province of Anjou until the French Revolution. The inhabitants of both the city and the prov ...
and is known primarily for the rosé wines based on the Grolleau and Cabernet franc, including the ''Rosé d'Anjou'' and the ''Cabernet d'Anjou''. White wine made from the Chenin blanc is known as ''Anjou Blanc'' while ''Anjou Rouge'' is often made from Gamay
Gamay is a purple-colored grape variety used to make red wines, most notably grown in Beaujolais and in the Loire Valley around Tours. Its full name is Gamay Noir à Jus Blanc. It is a very old cultivar, mentioned as long ago as the 15th centu ...
. Some of the higher quality wines are often labeled with the AOC designation ''Anjou-Villages''. The Chenin blanc grape has been planted in the region since at least 845 AD when it was planted at the Abbey of Glanfeuil. Throughout the years it was known in the region under a variety of synonyms
A synonym is a word, morpheme, or phrase that means exactly or nearly the same as another word, morpheme, or phrase in a given language. For example, in the English language, the words ''begin'', ''start'', ''commence'', and ''initiate'' are all ...
including ''Pineau de la Loire'' and ''Franc-blanc''.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 202 Dorling Kindersley 2005
The area around Saumur is the third largest sparkling wine appellation in France after the Champagne region and the Crémant d'Alsace AOC
Sparkling wine is a wine with significant levels of carbon dioxide in it, making it fizzy. While the phrase commonly refers to champagne, European Union countries legally reserve that term for products exclusively produced in the Champagne reg ...
with more than 12 million bottles of Saumur Mousseux produced each year. Unlike Champagne which is made with Chardonnay, Pinot noir and Pinot Meunier, Saumur sparkling wine is based on the Chenin blanc grape. The area around Saumur-Champigny produces red wine based on the Cabernet franc grape that is similar in profile to the wines produced in St-Nicolas-de-Bourgueil.
Vouvray and Touraine
The region around Vouvray,Montlouis-sur-Loire
Montlouis-sur-Loire (, literally ''Montlouis on Loire'') is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France.
It was mentioned in the 6th century as ''vicus montis Laudiacensis'' by Gregory of Tours.
Population
Events
Since 1987, ...
and Touraine has some of the most diverse plantings of all the Loire region and makes a wide variety of white, red and rosé wines. For white wines the main grape is Chenin blanc but Sauvignon blanc and (to a smaller extent) Chardonnay is also planted. For red wines the main grape is Cabernet franc with some smaller plantings of Cabernet Sauvignon
Cabernet Sauvignon () is one of the world's most widely recognized red wine grape varieties. It is grown in nearly every major wine producing country among a diverse spectrum of climates from Australia and British Columbia, Canada to Lebanon' ...
, Gamay and Malbec
Malbec () is a purple grape variety used in making red wine. The grapes tend to have an inky dark color and robust tannins, and are known as one of the six grapes allowed in the blend of red Bordeaux wine. In France, plantations of Malbec are n ...
. The rosé wines are made from an assortment of Gamay, Pineau d'aunis, Pinot gris
Pinot Gris, Pinot Grigio (, ) or Grauburgunder is a white wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. Thought to be a mutant clone of the Pinot Noir variety, it normally has a grayish-blue fruit, accounting for its name, but the gra ...
and Pinot noir
Pinot Noir () is a red-wine grape variety of the species ''Vitis vinifera''. The name may also refer to wines created predominantly from pinot noir grapes. The name is derived from the French language, French words for ''pine'' and ''black.' ...
. The villages of Vouvray and Montlouis are the largest appellations in the region and make only white wines from Chenin blanc. The wines can vary in sweetness
Sweetness is a Taste#Basic tastes, basic taste most commonly Perception, perceived when eating foods rich in sugars. Sweet tastes are generally regarded as pleasure, pleasurable. In addition to sugars like sucrose, many other chemical compounds ...
from bone dry (often appearing as ''sec'' on the wine label
Wine labels are important sources of information for consumers since they tell the type and origin of the wine. The label is often the only resource a buyer has for evaluating the wine before purchasing it. Certain information is ordinarily incl ...
) to very sweet ''moelleux'' wines that are often infected by noble rot
Noble rot (french: pourriture noble; german: Edelfäule; it, Muffa nobile; hu, Aszúsodás) is the beneficial form of a grey fungus, ''Botrytis cinerea'', affecting wine grapes. Infestation by ''Botrytis'' requires moist conditions. If the we ...
.
For years the Touraine region would compete with the Beaujolais
Beaujolais ( , ) is a French ''Appellation d'Origine Contrôlée'' (AOC) wine generally made of the Gamay grape, which has a thin skin and is low in tannins. Like most AOC wines they are not labeled varietally. Whites from the region, which mak ...
region for the release of an early bottling of Gamay that would rival the Beaujolais nouveau
Beaujolais nouveau ( , ) is a red wine made from Gamay grapes produced in the Beaujolais region of France. It is a ''vin de primeur'', Fermentation (wine), fermented for just a few weeks before being released for sale on the third Thursday of N ...
. While the competition is not so much of a focal point now, there are still some producers who release early bottlings of the wine around the same time as Beaujolais. The soil around the Touraine area is a variety of limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
with excellent drainage that is known as tuffeau
Tuffeau stone — in French, simply ''tuffeau'' or ''tufeau'' — is a local limestone of the Loire Valley of France. It is characterized as a chalky or sandy, fine-grained limestone, white to yellowish-cream in appearance, and micaceous (cont ...
which is the same material used to build many of the famous Loire Valley Château
A château (; plural: châteaux) is a manor house or residence of the lord of the manor, or a fine country house of nobility or gentry, with or without fortifications, originally, and still most frequently, in French-speaking regions.
Nowaday ...
x.
Chinon
The area around Chinon,Bourgueil
Bourgueil () is a commune in the Indre-et-Loire department in central France.
Population
Bourgueil wine
Bourgueil is an ''appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) for wine in the Loire Valley region, and produces primarily red wine from th ...
and Saint-Nicolas-de-Bourgueil produces the majority of the Loire Valley's red wine based on the Cabernet franc grape—known in this areas as ''Breton''. The wines of the Chinon area are the softest and rich expression of the grape while the Bourgueil area produces more tannic and firm wines. The St-Nicolas-de-Bourgueil area produces the lightest colored wines. In the 19th century, the wines of the Chinon area were compared favorably by critics to the wines of Château Margaux
Château Margaux (), archaically La Mothe de Margaux, is a wine estate of Bordeaux wine, and was one of four wines to achieve ''Premier cru'' (first growth) status in the Bordeaux Classification of 1855. The estate's best wines are very expens ...
and even today is considered some of the best expression of the Cabernet franc grape. The wines from this region can achieve a nice purple color with notes of raspberry fruit and graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
. Unlike Cabernet franc from warmer climates, Chinon are typically served slightly cooler than most red wine.H. Johnson & J. Robinson, ''The World Atlas of Wine'', pg 120. Mitchell Beazley Publishing, 2005.
Muscadet
The Muscadet region is located at the westernmost edge of the Loire Valley near the city ofNantes
Nantes (, , ; Gallo: or ; ) is a city in Loire-Atlantique on the Loire, from the Atlantic coast. The city is the sixth largest in France, with a population of 314,138 in Nantes proper and a metropolitan area of nearly 1 million inhabita ...
. In the 17th century, Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
wine merchants laid the foundation for the Muscadet style by encouraging the villagers of Nantes to plant the early ripening Melon de Bourgogne
Melon de Bourgogne or Melon is a variety of white grape grown primarily in the Loire Valley region of France. It is also grown in North America. It is best known through its use in the white wine Muscadet.
In the U.S., Federal law prevents ...
grape to use in the production of their ''brandewijn''—distilled
Distillation, or classical distillation, is the process of separating the components or substances from a liquid mixture by using selective boiling and condensation, usually inside an apparatus known as a still. Dry distillation is the heating ...
wine with brandy
Brandy is a liquor produced by distilling wine. Brandy generally contains 35–60% alcohol by volume (70–120 US proof) and is typically consumed as an after-dinner digestif. Some brandies are aged in wooden casks. Others are coloured with ...
added to it. Following the devastation in 1709 of winter frost to many of the vineyards in the Loire-Atlantique
Loire-Atlantique (; br, Liger-Atlantel; before 1957: ''Loire-Inférieure'', br, Liger-Izelañ, link=no) is a department in Pays de la Loire on the west coast of France, named after the river Loire and the Atlantic Ocean. It had a population o ...
, King Louis XIV
, house = Bourbon
, father = Louis XIII
, mother = Anne of Austria
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France
, death_date =
, death_place = Palace of Vers ...
ordered that the frost resistant Melon de Bourgogne grape be given preferential treatment in the replanting of the area. Despite the inference of "Muskiness" in its name, Muscadet is a neutral flavor wine and the Melon de Bourgogne grape has no relation to the Muscat
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is s ...
family of grapes.T. Stevenson ''"The Sotheby's Wine Encyclopedia"'' pg 200 Dorling Kindersley 2005 The area's four appellation all produces white wine made from the Melon de Bourgogne grape. The appellations are-
*Muscadet-Sèvre et Maine
*Muscadet-Côtes de Grand Lieu
*Muscadet-Coteaux de la Loire
*Muscadet- A generic appellation covering the whole of the Loire-Atlantique department.
The wines of the Muscadet-Sèvre et Maine and Muscadet-Côtes de Grand Lieu appellation are often bottled ''sur lie
Lees are deposits of dead yeast or residual yeast and other particles that precipitate, or are carried by the action of " fining", to the bottom of a vat of wine after fermentation and aging. The same while brewing beer at a brewery is known as ...
'' straight from the tank that they are fermented in without any racking or filtering
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component tha ...
. This create wines that can be very cloudy and require decanting to remove sediments but also produces wines that can be fuller bodied and show extra dimensions of freshness.
The white wines of the Coteaux du Layon
Coteaux du Layon is an ''Appellation d'origine contrôlée'' (AOC) for sweet white wine in the Loire Valley wine region of France. Coteaux du Layon is situated in the Anjou district of the region, along the river Layon, which is a tributary of the ...
, Montlouis-sur-Loire, Savennières, and Vouvray are based on Chenin blanc and are known for their high acidity when young and ability to develop and age well. The villages of Sancerre and Pouilly-sur-Loire
Pouilly-sur-Loire (, literally ''Pouilly on Loire'') is a commune in the Nièvre department in central France.
Pouilly-sur-Loire is a town noted for the white wine known as Pouilly-Fumé
Pouilly-Fumé is an ''appellation d'origine contrôl� ...
are known for their crisp and herbaceous Sauvignon blancs. Some producers in the area are experimenting with oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
aging their Sauvignon blanc to give them more rounder and softer appeal. The villages of Bourgueil, Chinon and Saumur are known for their Cabernet franc based wines that range from light and fruity in Saumur to rich and velvety in Chinon. The Muscadet wines from the Pays de la Loire
Pays de la Loire (; ; br, Broioù al Liger) is one of the 18 regions of France, in the west of the mainland. It was created in the 1950s to serve as a zone of influence for its capital, Nantes, one of a handful of "balancing metropolises" ().
...
are made from the Melon de Bourgogne grape and are known for their citrus and mineral notes.
In addition to the main production grapes, several local grapes are also used to make wine in smaller quantities. These include the Tressallier grape of Saint-Pourçain-sur-Sioule
Saint-Pourçain-sur-Sioule (, literally ''Saint-Pourçain on Sioule''; Auvergnat: ''Sant Porçanh de Siula'') is a commune in the Allier department in Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes in central France. It is named after Saint Pourçain, a 6th century ...
, the Romorantin
Romorantin is a traditional French variety of white wine grape, that is a sibling of Chardonnay. Once quite widely grown in the Loire, it has now only seen in the Cour-Cheverny AOC. It produces intense, minerally wines somewhat reminiscent of ...
of Cheverny
Cheverny () is a commune in the French department of Loir-et-Cher, administrative region of Centre-Val de Loire.
It lies in the Loire Valley, about southeast of Blois.
Population
Sights
The commune is the site of the Château de Cheverny.
...
, the Menu pineau and Groslot
Grolleau or Grolleau noir is a red French wine grape variety that is grown primarily in the Loire Valley of France. The name is derived from the French word ''grolle'', meaning "crow" and is said to reflect the deep black berries of the Grollea ...
of Touraine and the Gros Plant
Folle blanche, also known as Picpoule, Gros Plant, and Enrageat blanc, is a wine grape variety from southwest France. It was the traditional grape variety in Cognac and Armagnac production until the 20th century. Folle blanche is an offspring o ...
of Nantes. There is also some plantings of Cabernet Sauvignon, Chardonnay, Gamay, Malbec, Pineau d'aunis, and Pinot gris, Pinot noir.
A characteristic of many Loire wines (both red and white) is the high acidity which highlights the fresh, crisp flavors of their youth only to go through a "dumb phase" between 2 and 5 years of age when the wines flavors are drastically toned down. Many of the better made examples come out of this period with their full palate of flavors and can continue to age well into 20 years. Some of the Sauvignon blanc based wines like Sancerre buck this trend and instead stay more low key till their third year when they mature and develop their full assortment of flavors before they eventually fade around their 7-10th year. However the best made examples in top vintages can often live much longer. Some classic examples of Vouvray can even reach the levels of longevity commonly associated with Port
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
.H. Johnson & J. Robinson ''The World Atlas of Wine'' pg 121 Mitchell Beazley Publishing 2005
Wineries
Historically the wineries of the Loire Valley have been small, family owned operations that do a lot of estate bottling. The mid-1990s saw an increase in the number ofnégociant
A winemaker or vintner is a person engaged in winemaking. They are generally employed by wineries or wine companies, where their work includes:
*Cooperating with viticulturists
*Monitoring the maturity of grapes to ensure their quality and to dete ...
and co-operative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
to where now about half of Sancerre and almost 80% of Muscadet is bottled by a négociant or co-op.
References
External links
Official Site of Loire Valley wines
- The official website of France (in English) {{Portal bar, Wine, France Wine regions of France