List of ships of the Confederate States Navy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This is a list of ships of the Confederate States Navy (CSN), used by the
This is a list of ships of the Confederate States Navy (CSN), used by the
 The CS Navy ironclad steamer batteries were all designed for national coastal defense.
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: October 28, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: August 5, 1862
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: June 17, 1863
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, ironclad steam sloop, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: April 26, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad gunboat, captured incomplete: February 8, 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, twin screw and double center-wheel steamer, ironclad, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, ironclad, burned incomplete: December 21, 1864
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad, burned: April 25, 1862
*, center-wheel steam sloop, ironclad ram, surrendered: June 3, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad, burned before launching: May 21, 1863
*, twin-screw with center-wheel steamer, ironclad, burned: April 17, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, twin-screw steam sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: March 14, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, accidentally sank: September 27, 1864
*, sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: 18 February 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, wrecked: May 7, 1864
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, scuttled: April 3, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, burned: December 21, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed before launching: June 5, 1862
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: August 5, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, never completed, captured: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: May 11, 1862
*, steam sloop, ironclad, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad gunboat, destroyed before completion: January 1865
The CS Navy ironclad steamer batteries were all designed for national coastal defense.
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: October 28, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: August 5, 1862
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: June 17, 1863
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, ironclad steam sloop, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: April 26, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad gunboat, captured incomplete: February 8, 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, twin screw and double center-wheel steamer, ironclad, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, ironclad, burned incomplete: December 21, 1864
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad, burned: April 25, 1862
*, center-wheel steam sloop, ironclad ram, surrendered: June 3, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad, burned before launching: May 21, 1863
*, twin-screw with center-wheel steamer, ironclad, burned: April 17, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, twin-screw steam sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: March 14, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, accidentally sank: September 27, 1864
*, sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: 18 February 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, wrecked: May 7, 1864
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, scuttled: April 3, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, burned: December 21, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed before launching: June 5, 1862
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: August 5, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, never completed, captured: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: May 11, 1862
*, steam sloop, ironclad, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad gunboat, destroyed before completion: January 1865
 CS Navy wooden floating batteries were towed into firing positions, and as in the case at Charleston Harbor, used for makeshift defense.
*, floating battery
*, floating battery
*, floating battery, scuttled: April 7, 1862
*
CS Navy wooden floating batteries were towed into firing positions, and as in the case at Charleston Harbor, used for makeshift defense.
*, floating battery
*, floating battery
*, floating battery, scuttled: April 7, 1862
*
File:CSSStonewall2.jpg, CSS ''Stonewall'' 1865
File:HMS Scorpion (1863).jpg, HMS ''Scorpion'' 1863
File:HMS Wivern 1865 USNHC NH 52526.jpg, HMS ''Wivern'' 1865
File:Corvette America 1868.jpg, The BAP corvette ''America'' wrecked by the 1868 tsunami at Arica
File:BAP Unión.jpg, BAP ''Unión'' 1880
File:Lisle-Lo último de la Unión.png, The scuttled BAP ''Unión'' 1881
File:Danish Ironclad Danmark (1864).jpg, KMD ''Danmark'' 1864
File:PrinzAdalbertBordeaux.jpg, SMS ''Prinz Adalbert'' 1865


 *, dispatch boat, run aground 1 November 1862; seized and placed in service by the Union
*, side-wheel steamer, burned or captured April 1862
*, tugboat, burned February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, surrendered to U.S. Navy 1865; sold 1866
*, screw steamer, captured by U.S. Navy April 3, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, destroyed incomplete April 1862
*, schooner, burned February 10, 1862
*, steamer, captured: May 5, 1864
* CSS ''Calhoun'', sidewheel gunboat, captured: January 23, 1862
*, sidewheel steamer, destroyed April 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, scuttled: December, 1864
* CSS ''Clifton'', side-wheel gunboat, Texas Marine Department, scuttled March 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 7, 1862
* CSS ''De Soto'', side-wheel steamer, captured: September 30, 1862
*, river steamer, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, steamer, which twice changed hands, managed to survive the Civil War and was presumably decommissioned
*, steamer, tender, destroyed: January 24, 1865
*, steamer, tugboat, captured: February 10, 1862
*, steamer, burned: 1865
*, screw steamer, iron hull, burned: February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, steamer, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
* CSS ''Germantown'' sloop-of-war, sunk as blockship May 10, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged, destroyed: April 23, 1862. Also listed as a Cotton Clad ram (see below) since she had cotton as part of her armor.
*, screw steamer, burned: April 4, 1865
*, steamer, tug
*, side-wheel steamer; Charleston harbor gunboat: sank March 10, 1864
*, cutter, schooner rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, burned: December 21, 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
*, a side-wheel river steamer, burned: January 14, 1863 (See
*, dispatch boat, run aground 1 November 1862; seized and placed in service by the Union
*, side-wheel steamer, burned or captured April 1862
*, tugboat, burned February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, surrendered to U.S. Navy 1865; sold 1866
*, screw steamer, captured by U.S. Navy April 3, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, destroyed incomplete April 1862
*, schooner, burned February 10, 1862
*, steamer, captured: May 5, 1864
* CSS ''Calhoun'', sidewheel gunboat, captured: January 23, 1862
*, sidewheel steamer, destroyed April 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, scuttled: December, 1864
* CSS ''Clifton'', side-wheel gunboat, Texas Marine Department, scuttled March 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 7, 1862
* CSS ''De Soto'', side-wheel steamer, captured: September 30, 1862
*, river steamer, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, steamer, which twice changed hands, managed to survive the Civil War and was presumably decommissioned
*, steamer, tender, destroyed: January 24, 1865
*, steamer, tugboat, captured: February 10, 1862
*, steamer, burned: 1865
*, screw steamer, iron hull, burned: February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, steamer, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
* CSS ''Germantown'' sloop-of-war, sunk as blockship May 10, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged, destroyed: April 23, 1862. Also listed as a Cotton Clad ram (see below) since she had cotton as part of her armor.
*, screw steamer, burned: April 4, 1865
*, steamer, tug
*, side-wheel steamer; Charleston harbor gunboat: sank March 10, 1864
*, cutter, schooner rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, burned: December 21, 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
*, a side-wheel river steamer, burned: January 14, 1863 (See
 *, semi-submersible torpedo boat
*, larger version of ''David'', captured incomplete: February, 1865
*CSS ''Gunnison'', screw steam spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat, captured: February, 1865
*, spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*
* CSS ''St. Patrick'', semi-submersible torpedo boat or submarine
*, screw steamer spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, semi-submersible torpedo boat
*, larger version of ''David'', captured incomplete: February, 1865
*CSS ''Gunnison'', screw steam spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat, captured: February, 1865
*, spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*
* CSS ''St. Patrick'', semi-submersible torpedo boat or submarine
*, screw steamer spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat


 *, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 10, 1864
*, screw steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured
*
* CSS ''Lady Stirling'', side-wheel steamer, captured: October 28, 1864
*
*
*
* CSS ''William G. Hewes'', (later SS ''Ella and Annie''), captured: November 9, 1863
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 10, 1864
*, screw steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured
*
* CSS ''Lady Stirling'', side-wheel steamer, captured: October 28, 1864
*
*
*
* CSS ''William G. Hewes'', (later SS ''Ella and Annie''), captured: November 9, 1863
*
*, side-wheel steamer

 *
* CSS ''City of Vicksburg'', side-wheel steamer transport, damaged when rammed on February 3, 1863 then destroyed: February/March 1863
*
* CSS ''Darlington''
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, captured by its slave pilot
*
* CSS ''City of Vicksburg'', side-wheel steamer transport, damaged when rammed on February 3, 1863 then destroyed: February/March 1863
*
* CSS ''Darlington''
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, captured by its slave pilot
 *, lighthouse tender, schooner rigged
*, tugboat
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned: December 21, 1864
*, receiving ship, burned
*, side-wheel steamer, tugboat, captured: December 12, 1864
*, steam tugboat, sold: March 8, 1863
* CSS ''Satellite'', sidewheel steamer, gunboat/tugboat, destroyed: August, 1863
*, tender, burned: April 4, 1865
* CSS ''St. Philip'', receiving ship, sunk
*, steam tugboat, machinery mounted into CSS ''North Carolina II'' (renamed "Retribution" and "Etta")
*, lighthouse tender, schooner rigged
*, tugboat
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned: December 21, 1864
*, receiving ship, burned
*, side-wheel steamer, tugboat, captured: December 12, 1864
*, steam tugboat, sold: March 8, 1863
* CSS ''Satellite'', sidewheel steamer, gunboat/tugboat, destroyed: August, 1863
*, tender, burned: April 4, 1865
* CSS ''St. Philip'', receiving ship, sunk
*, steam tugboat, machinery mounted into CSS ''North Carolina II'' (renamed "Retribution" and "Etta")
 *, screw steamer
* ''Etiwan'', sloop
* ''Eugenie'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Eugenie Smith'', schooner
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''General Banks'', paddle steamer (later ''Fanny and Jenny'')
* ''Gibraltar'', screw steamer, bark-rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Lady Davis'', steamer
*, paddle-steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, screw steamer (later USS ''Memphis'')
* ''Monticello'', Cuban blockade runner
*, side-wheel steamer
*
* ''Old Dominion'', paddle steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, sloop
*, side-wheel steamer
*''San Quintin'', Cuban blockade runner
*, schooner
* ''Shark'', schooner
*, schooner
*, (ex-''Leopard''), side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Thistle'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Thomas L. Wragg'', side-wheel steamer, brig-rigged (later, privateer ''Rattlesnake'')
*, side-wheel steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
* ''Etiwan'', sloop
* ''Eugenie'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Eugenie Smith'', schooner
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''General Banks'', paddle steamer (later ''Fanny and Jenny'')
* ''Gibraltar'', screw steamer, bark-rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Lady Davis'', steamer
*, paddle-steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, screw steamer (later USS ''Memphis'')
* ''Monticello'', Cuban blockade runner
*, side-wheel steamer
*
* ''Old Dominion'', paddle steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, sloop
*, side-wheel steamer
*''San Quintin'', Cuban blockade runner
*, schooner
* ''Shark'', schooner
*, schooner
*, (ex-''Leopard''), side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Thistle'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Thomas L. Wragg'', side-wheel steamer, brig-rigged (later, privateer ''Rattlesnake'')
*, side-wheel steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
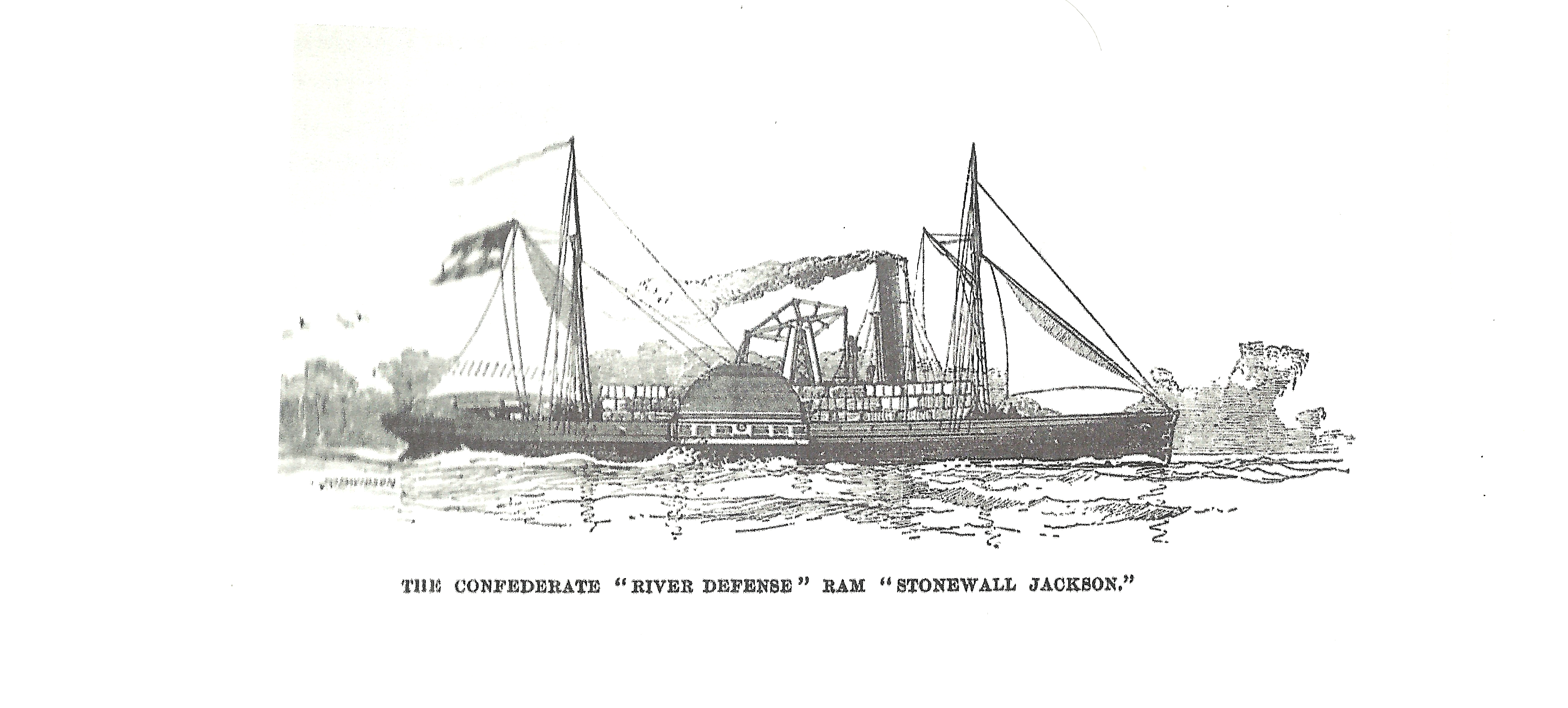





 Used for river defense, CS Army cottonclads were typically more lightly armored and reinforced than a regular ironclad, such as the ''General Sterling Price'', which was converted by placing a 4-inch oak sheath with a 1-inch iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads filled with compressed cotton bales. Many of the cottonclads were outfitted with
Used for river defense, CS Army cottonclads were typically more lightly armored and reinforced than a regular ironclad, such as the ''General Sterling Price'', which was converted by placing a 4-inch oak sheath with a 1-inch iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads filled with compressed cotton bales. Many of the cottonclads were outfitted with
Photos of ships of the Confederate States Navy
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120118132552/http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/sh-us-cs/csa-sh/csa-name.htm , date=2012-01-18
Confederate States of America
The Confederate States of America (CSA), commonly referred to as the Confederate States or the Confederacy was an unrecognized breakaway republic in the Southern United States that existed from February 8, 1861, to May 9, 1865. The Confeder ...
during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
between 1861 and 1865. Included are some types of civilian vessels, such as blockade runners
A blockade runner is a merchant vessel used for evading a naval blockade of a port or strait. It is usually light and fast, using stealth and speed rather than confronting the blockaders in order to break the blockade. Blockade runners usuall ...
, steamboat
A steamboat is a boat that is marine propulsion, propelled primarily by marine steam engine, steam power, typically driving propellers or Paddle steamer, paddlewheels. Steamboats sometimes use the ship prefix, prefix designation SS, S.S. or S/S ...
s, and privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s which contributed to the war efforts by the CSN. Also included are special types of floating batteries
A floating battery is a kind of armed watercraft, often improvised or experimental, which carries heavy armament but has few other qualities as a warship.
History
Use of timber rafts loaded with cannon by Danish defenders of Copenhagen a ...
and harbor defense craft.
CSN Warships
The Secretary of the CS Navy,Stephen Mallory
Stephen Russell Mallory (1812 – November 9, 1873) was a Democratic senator from Florida from 1851 to the secession of his home state and the outbreak of the American Civil War. For much of that period, he was chairman of the Committee on Na ...
, was very aggressive on a limited budget in a land-focused war, and developed a two-pronged warship strategy of building ironclad warships for coastal and national defense, and commerce raiding cruisers, supplemented with exploratory use of special weapons such as torpedo boats and torpedoes.
Batteries
Based upon the successful employment of ironclad warships, particularly batteries, at the Battle of Kinburn, Britain and France decided to focus on armor plated warships, starting with coastalbattery
Battery most often refers to:
* Electric battery, a device that provides electrical power
* Battery (crime), a crime involving unlawful physical contact
Battery may also refer to:
Energy source
*Automotive battery, a device to provide power t ...
designs. Initial ocean going ironclad cruisers, such as the French and the British were only just emerging in 1859 and 1860, and were beyond the budget and timeline necessary for rapid force deployment that the CS Navy needed for immediate coastal defenses in 1861.
Therefore, the Confederate Congress voted $2 million in May 1861 to buy ironclads
An ironclad is a steam-propelled warship protected by iron or steel armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships to explosive or incendiary shells. Th ...
from overseas, and in July and August started work on construction and converting wooden ships locally. On 12 October 1861, the became the first ironclad to enter battle when she fought Union warships on the Mississippi. In February 1862, the even larger joined the Confederate Navy, having been built at Norfolk. The Confederacy built a number of ships designed as versions of the ''Virginia'', of which several saw action. In the failed attack on Charleston
Charleston most commonly refers to:
* Charleston, South Carolina
* Charleston, West Virginia, the state capital
* Charleston (dance)
Charleston may also refer to:
Places Australia
* Charleston, South Australia
Canada
* Charleston, Newfoundlan ...
on April 7, 1863 two small ironclads, and participated in the successful defense of the harbor. For the later attack at Mobile Bay
Mobile Bay ( ) is a shallow inlet of the Gulf of Mexico, lying within the state of Alabama in the United States. Its mouth is formed by the Fort Morgan Peninsula on the eastern side and Dauphin Island, a barrier island on the western side. The ...
, the Union faced the , the Confederacy's most powerful ironclad.
Ironclad steam powered batteries
 The CS Navy ironclad steamer batteries were all designed for national coastal defense.
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: October 28, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: August 5, 1862
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: June 17, 1863
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, ironclad steam sloop, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: April 26, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad gunboat, captured incomplete: February 8, 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, twin screw and double center-wheel steamer, ironclad, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, ironclad, burned incomplete: December 21, 1864
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad, burned: April 25, 1862
*, center-wheel steam sloop, ironclad ram, surrendered: June 3, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad, burned before launching: May 21, 1863
*, twin-screw with center-wheel steamer, ironclad, burned: April 17, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, twin-screw steam sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: March 14, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, accidentally sank: September 27, 1864
*, sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: 18 February 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, wrecked: May 7, 1864
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, scuttled: April 3, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, burned: December 21, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed before launching: June 5, 1862
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: August 5, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, never completed, captured: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: May 11, 1862
*, steam sloop, ironclad, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad gunboat, destroyed before completion: January 1865
The CS Navy ironclad steamer batteries were all designed for national coastal defense.
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: October 28, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: August 5, 1862
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: June 17, 1863
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, ironclad steam sloop, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: February 18, 1865
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: April 26, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad gunboat, captured incomplete: February 8, 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, twin screw and double center-wheel steamer, ironclad, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, sunk: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, ironclad, burned incomplete: December 21, 1864
*, triple-screw steamer, ironclad, burned: April 25, 1862
*, center-wheel steam sloop, ironclad ram, surrendered: June 3, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad, burned before launching: May 21, 1863
*, twin-screw with center-wheel steamer, ironclad, burned: April 17, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, ironclad ram, surrendered: May 10, 1865
*, twin-screw steam sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: March 14, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, accidentally sank: September 27, 1864
*, sloop, ironclad ram, destroyed: 18 February 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, wrecked: May 7, 1864
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, scuttled: April 3, 1865
*, steam sloop, ironclad, burned: December 21, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed before launching: June 5, 1862
*, single screw steamer, ironclad ram, captured: August 5, 1864
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad ram, never completed, captured: April 4, 1865
*, ironclad steam floating battery, scuttled: April 12, 1865
*, screw steamer, ironclad ram, destroyed: May 11, 1862
*, steam sloop, ironclad, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*, twin-screw steamer, ironclad gunboat, destroyed before completion: January 1865
Ironclad floating batteries
CS Navy ironclad floating batteries lacked steam engines for propulsion and were towed into firing positions. *, ironclad floating battery, scuttled: 24 December 1864 *, ironclad floating battery, scuttled: December 21, 1864 *, ironclad floating battery, destroyed: 1865Wooden floating batteries
 CS Navy wooden floating batteries were towed into firing positions, and as in the case at Charleston Harbor, used for makeshift defense.
*, floating battery
*, floating battery
*, floating battery, scuttled: April 7, 1862
*
CS Navy wooden floating batteries were towed into firing positions, and as in the case at Charleston Harbor, used for makeshift defense.
*, floating battery
*, floating battery
*, floating battery, scuttled: April 7, 1862
*Floating Battery of Charleston Harbor
The Floating Battery of Charleston Harbor was an ironclad vessel that was constructed by the Confederacy in early 1861, a few months before the American Civil War ignited. Apart from being a marvel to contemporary Charlestonians, it was a strateg ...
Cruisers
CS Navy cruisers were ocean-going ships designed primarily for the Confederate Navy's strategy of ''guerre de course''. Confederate States Navy cruisers were typically lightly armed, with a couple of large guns or a pivot gun, and often very fast. The Navy planned to add ironclad cruisers to their fleet, successfully procuring one, but too late to be of benefit for the war.Wooden cruisers
*, screw steamer, sloop-of-war, built in Birkenhead, England by John Laird Sons and Company, sunk: June 19, 1864 *, screw steamer, bark-rigged, built in Liverpool, England, seized before delivery: April 5, 1863 * CSS ''America'', racing yacht, scuttled: 1862 *, schooner, captured: June 28, 1863 *, revenue cutter, burned: June 28, 1863 *, screw steamer, burned *, brig, burned: June 12, 1863 *, screw steamer, sloop, captured: October 7, 1864 *, screw steamer, iron, sold: June 1, 1864 *, steamer, destroyed: After leaving port on March 20, 1863 the steamer is destroyed on March 22, 1863 *, bark, burned: June 20, 1863 *, side-wheel steamer, brig rigged, sold and used as privateer ''Rattlesnake'' and sunk, February 28, 1862 *, screw steamer, sloop-of-war, turned over at war's end *, screw steamer, full rigged, iron-framed, turned over to British Government *, screw steamer, sloop, sold: December 19, 1862 *, bark, burned: June 25, 1863 *, twin-screw steamer, sloop, seized: April 9, 1865 by British Government *, bark, seized: December 29, 1863 * CSS ''United States'', frigate, sail, harbor defense use only, scuttledIronclad cruisers
But the CS Navy attempts to procure ironclad cruisers from overseas were frustrated as European nations confiscated ships being built for the Confederacy. Only the ''Stonewall'' was completed and successfully delivered, and she arrived in American waters just in time for the end of the war. *CSS ''North Carolina I'', seized October 1863 and commissioned as *CSS ''Mississippi II'', seized October 1863 and commissioned as *, twin-screw steamer, brig rigged, ironclad, surrendered in Cuba at end of war, returned to US, sold to Japan and renamed * CSS ''Cheops'', sister to ''Stonewall'', built in France and sold to Prussia, October 29, 1865, and named * CSS ''Georgia'' screw corvette 2017 tons ,150 tons BOMPage 77, Clowes, William Laird, ''Four Modern Naval Campaigns'', pub Unit Library, 1902, reprinted Cormarket Press, Sold to Peru after the French government stopped its sale to the Confederacy. Taken into service as BAP ''Unión'' 1864. Scuttled January 1881 to avoid capture. * CSS ''Texas'', screw corvette and sister ship of BAP ''Union''. Sold to Peru after the French government stopped its sale to the Confederacy. Taken into service as BAP ''America''. Lost during the Arica tsunami on 13 August 1868. *''Ironclad Frigate No. 61'', arranged by Captain James H. North, CSN, sold to Denmark, commissioned asGunboats


 *, dispatch boat, run aground 1 November 1862; seized and placed in service by the Union
*, side-wheel steamer, burned or captured April 1862
*, tugboat, burned February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, surrendered to U.S. Navy 1865; sold 1866
*, screw steamer, captured by U.S. Navy April 3, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, destroyed incomplete April 1862
*, schooner, burned February 10, 1862
*, steamer, captured: May 5, 1864
* CSS ''Calhoun'', sidewheel gunboat, captured: January 23, 1862
*, sidewheel steamer, destroyed April 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, scuttled: December, 1864
* CSS ''Clifton'', side-wheel gunboat, Texas Marine Department, scuttled March 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 7, 1862
* CSS ''De Soto'', side-wheel steamer, captured: September 30, 1862
*, river steamer, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, steamer, which twice changed hands, managed to survive the Civil War and was presumably decommissioned
*, steamer, tender, destroyed: January 24, 1865
*, steamer, tugboat, captured: February 10, 1862
*, steamer, burned: 1865
*, screw steamer, iron hull, burned: February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, steamer, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
* CSS ''Germantown'' sloop-of-war, sunk as blockship May 10, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged, destroyed: April 23, 1862. Also listed as a Cotton Clad ram (see below) since she had cotton as part of her armor.
*, screw steamer, burned: April 4, 1865
*, steamer, tug
*, side-wheel steamer; Charleston harbor gunboat: sank March 10, 1864
*, cutter, schooner rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, burned: December 21, 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
*, a side-wheel river steamer, burned: January 14, 1863 (See
*, dispatch boat, run aground 1 November 1862; seized and placed in service by the Union
*, side-wheel steamer, burned or captured April 1862
*, tugboat, burned February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, surrendered to U.S. Navy 1865; sold 1866
*, screw steamer, captured by U.S. Navy April 3, 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, destroyed incomplete April 1862
*, schooner, burned February 10, 1862
*, steamer, captured: May 5, 1864
* CSS ''Calhoun'', sidewheel gunboat, captured: January 23, 1862
*, sidewheel steamer, destroyed April 1862
*, twin-screw steamer, scuttled: December, 1864
* CSS ''Clifton'', side-wheel gunboat, Texas Marine Department, scuttled March 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 7, 1862
* CSS ''De Soto'', side-wheel steamer, captured: September 30, 1862
*, river steamer, destroyed: April 28, 1862
*, steamer, which twice changed hands, managed to survive the Civil War and was presumably decommissioned
*, steamer, tender, destroyed: January 24, 1865
*, steamer, tugboat, captured: February 10, 1862
*, steamer, burned: 1865
*, screw steamer, iron hull, burned: February 10, 1862
*, schooner
*, steamer, tugboat, burned: February 10, 1862
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
* CSS ''Germantown'' sloop-of-war, sunk as blockship May 10, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged, destroyed: April 23, 1862. Also listed as a Cotton Clad ram (see below) since she had cotton as part of her armor.
*, screw steamer, burned: April 4, 1865
*, steamer, tug
*, side-wheel steamer; Charleston harbor gunboat: sank March 10, 1864
*, cutter, schooner rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
*, steamer, burned: December 21, 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
*, a side-wheel river steamer, burned: January 14, 1863 (See Bayou Teche
Bayou Teche (Louisiana French: ''Bayou Têche'') is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 20, 2011 waterway of great cultural significance in south central Louisiana in t ...
and ). Sometimes called an ironclad
An ironclad is a steam engine, steam-propelled warship protected by Wrought iron, iron or steel iron armor, armor plates, constructed from 1859 to the early 1890s. The ironclad was developed as a result of the vulnerability of wooden warships ...
since she had a small amount of railroad iron tacked onto her side.
*, side-wheel river steamer, tug, sunk
*, side-wheel steamer, sunk: May, 1862
*, steamer, tug, dismantled: 1862
*, schooner, scuttled
*, steamer tug, iron, machinery mounted in CSS ''Palmetto''
*, steamer, captured: April, 1862
*, steamer, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, destroyed: June 26, 1862
*, steamer
*, bark
*, side-wheel steamer, sunk: June, 1862
*, screw steamer, sloop rigged, sunk: April 28, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, surrender: 1865
*, cutter
*, sail, burned: January 23, 1863
*, twin-screw gunboat, burned: April 3, 1865
*, steamer, sunk: January 1, 1863
*, steamer
*, steamer, scuttled: Apr, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, CSNA school ship, burned: April 4, 1865
*, screw steamer, sunk: 1865
*, sloop-of-war, burned: 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned: 1863
*, steamer
*, formerly ''St. Nicholas'' until seized and purchased in 1861, side-wheel steamer, burned: April, 1862
*, cutter, schooner rigged
*, burned: April 24, 1862
*, screw steamer, destroyed: April 4, 1865
*
*, side-wheel river steamer
*, steamer, foundered: August 18, 1863
*, formerly ''A.H. Schultz'', until seized and purchased in 1861, side-wheel steamer, used as a flag of truce vessel, sunk: February 17, 1865
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: February 10, 1862
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: August 5, 1864
*, steam tug, sunk
*, side-wheel river steamer, burned
*, burned: 1865
*, side-wheel steamer, sunk: 1863
*, tug, captured: 1862
*
*, screw steamer, tug/tender, iron, burned: April 4, 1865
*
*, side-wheel steamer, burned
*
*, schooner
*, side-wheel steamer, burned: December 19, 1864
*, side-wheel river steamer, wrecked
*, steamer, burned: 1865
Torpedo boats
 *, semi-submersible torpedo boat
*, larger version of ''David'', captured incomplete: February, 1865
*CSS ''Gunnison'', screw steam spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat, captured: February, 1865
*, spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*
* CSS ''St. Patrick'', semi-submersible torpedo boat or submarine
*, screw steamer spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, semi-submersible torpedo boat
*, larger version of ''David'', captured incomplete: February, 1865
*CSS ''Gunnison'', screw steam spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat
*, steam torpedo boat, captured: February, 1865
*, spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
*
* CSS ''St. Patrick'', semi-submersible torpedo boat or submarine
*, screw steamer spar torpedo boat
*, spar torpedo boat
CSN Support ships
Government blockade runners



 *, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 10, 1864
*, screw steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured
*
* CSS ''Lady Stirling'', side-wheel steamer, captured: October 28, 1864
*
*
*
* CSS ''William G. Hewes'', (later SS ''Ella and Annie''), captured: November 9, 1863
*
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured: September 10, 1864
*, screw steamer
*, side-wheel steamer, captured
*
* CSS ''Lady Stirling'', side-wheel steamer, captured: October 28, 1864
*
*
*
* CSS ''William G. Hewes'', (later SS ''Ella and Annie''), captured: November 9, 1863
*
*, side-wheel steamer
Government steamers
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862 * *, screw steamer, burned: February 10, 1862 * *, side-wheel coastal steamer, captured: December, 1864 *, side-wheel river steamer burned: June 28, 1862 *, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862 * * * * * *, stern-wheel river steamer, scuttled: April 7, 1862 * * CSS ''Ida'', side-wheel coastal steamer, captured/burned: December 10, 1864 * *, 1861 *, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862 * *, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862 *, 1861 *, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862 * * *, side-wheel steamer, captured: January, 1862 *, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
Government transports
 *
* CSS ''City of Vicksburg'', side-wheel steamer transport, damaged when rammed on February 3, 1863 then destroyed: February/March 1863
*
* CSS ''Darlington''
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, captured by its slave pilot
*
* CSS ''City of Vicksburg'', side-wheel steamer transport, damaged when rammed on February 3, 1863 then destroyed: February/March 1863
*
* CSS ''Darlington''
*, side-wheel river steamer, captured: April 7, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, captured by its slave pilot Robert Smalls
Robert Smalls (April 5, 1839 – February 23, 1915) was an American politician, publisher, businessman, and maritime pilot. Born into slavery in Beaufort, South Carolina, he freed himself, his crew, and their families during the American Civil W ...
, May 13, 1862
*
*, side-wheel river steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862
Cutters
*, revenue cutter, schooner rigged *, revenue cutter, schooner rigged *, revenue cutter, schooner rigged, dismantled *, revenue cutter, schooner riggedHospital ships
*, stern-wheel river steamer, burned: April 7, 1862Tenders and tugs
 *, lighthouse tender, schooner rigged
*, tugboat
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned: December 21, 1864
*, receiving ship, burned
*, side-wheel steamer, tugboat, captured: December 12, 1864
*, steam tugboat, sold: March 8, 1863
* CSS ''Satellite'', sidewheel steamer, gunboat/tugboat, destroyed: August, 1863
*, tender, burned: April 4, 1865
* CSS ''St. Philip'', receiving ship, sunk
*, steam tugboat, machinery mounted into CSS ''North Carolina II'' (renamed "Retribution" and "Etta")
*, lighthouse tender, schooner rigged
*, tugboat
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned
*, side-wheel steamer tender, burned: December 21, 1864
*, receiving ship, burned
*, side-wheel steamer, tugboat, captured: December 12, 1864
*, steam tugboat, sold: March 8, 1863
* CSS ''Satellite'', sidewheel steamer, gunboat/tugboat, destroyed: August, 1863
*, tender, burned: April 4, 1865
* CSS ''St. Philip'', receiving ship, sunk
*, steam tugboat, machinery mounted into CSS ''North Carolina II'' (renamed "Retribution" and "Etta")
Civilian auxiliary
Privateers
*, privateer steam tug *, privateer cutter, schooner rigged, captured: November 12, 1861 *''Bonita'', 8-gun, 1,110-ton privateer steamer *''Boston'', 5-gun privateer steamer operating out of Mobile burned captured barques ''Lenex'' and ''Texana'' *''Charlotte Clark'', 3-gun, 1,110-ton privateer steamer *''Chesapeake'', 4-gun, 60-ton privateer schooner *, privateer schooner, captured on April 15, 1862, but had itself captured the USA Schooner ''Mary Alice'' on July 25, 1861, the USA Barque ''Glenn'' on July 31 of 1861. *''Dove'', 8-gun, 1,170-ton privateer steamer *''Gallatin'', 150-ton privateer schooner with 2 × 12-pdr *''General N.S. Reneau'', privateer steamer *, privateer schooner *, privateer, which captured the USA Brigandine ''William McGilvery'' on July 25, 1861, the USA Schooner ''Protector'' on July 28, 1861. *, privateer steamer, captured: May 11, 1862 *''Hallie Jackson'', privateer brig captured by USS ''Union'' *, privateer screw steamer *, privateer side-wheel steamer, which captured the Barque ''Ocean Eagle'' on May 16, 1861, the ship ''Milan'' in May, 1861, the Schooner ''Etta'' in May, 1861, the Brigandine ''Panama'' on May 29, 1861, the Schooner ''Mermaid'' on May 24, 1861 and the Schooner ''John Adams'' on May 24, 1861, all within its first month of operation in 1861, and which was burned: 1862 *'' J. M. Chapman'', privateer schooner, captured: March 15, 1863 *, privateer schooner *, privateer brig, ran aground: mid-August, 1861 *''Joseph Landis'', 400-ton privateer steamer *''Josephine'', privateer schooner *, privateer schooner, destroyed: September 14, 1861 *''Lamar'', privateer schooner *, privateer schooner *, privateer screw steamer, which captured the US schooner ''Nathaniel Chase'' on July 25, 1861. *''Mocking Bird'', 8-gun, 1,290-ton privateer steamer operating out of New Orleans *, privateer steamer *''Onward'', 70-ton privateer schooner with 1 × 32-pdr *''Paul Jones'', 2-gun, 160-ton privateer schooner *''Pelican'', 10-gun, 1,479-ton privateer steamer *, privateer, went to sea on July 1, 1861 and sunk on July 28, 1861 by the Union Navy frigate . *''Phenix'', 7-gun, 1,644-ton privateer steamer *, privateer schooner *, privateer schooner, captured: June 3, 1861 *, privateer brig *, privateer side-wheel steamer *''Triton'', 30-ton privateer schooner with 1 × 6-pdr *, privateer steamer *, privateer pilot boat, schooner rigged, which was burned on August 9, 1861, after capturing the US brigandine ''B.T. Martin'' about July 28, 1861 and the schooner ''George G. Baker'' on August 9, 1861, on the day of its demise, whereafter the Union quickly recaptured the ''George G. Baker''.Privateer submersible torpedo boats
*, hand-cranked, sunk: February 17, 1864. Named in honor of its designer, Confederate marine engineerHorace Lawson Hunley
Horace Lawson Hunley (December 29, 1823 – October 15, 1863) was a Confederate States of America, Confederate Marine engineering, marine engineer during the American Civil War. He developed early hand-powered submarines, the most famous of which ...
.
*
*, also known as ''Pioneer II''
*'' Bayou Saint John''
Civilian steamers
*, captured: May 7, 1861 *, captured: May 7, 1861 *, of SavannahCivilian transports
* ''Berwick Bay'', steamer, captured February 3, 1863 *'' O.W. Baker'', steamer, captured February 3, 1863 * ''Moro'', steamer, captured February 3, 1863 *'' Era No. 5'', shallow-draft steamer, captured: February 14, 1863Civilian blockade runners
*, side-wheel steamer *'' Agnes E. Fry'', paddle steamer * ''Alabama'', schooner *, schooner * ''Annie Dees'', steamer, sloop-rigged *, schooner *, side-wheel steamer * ''Bat'', side-wheel steamship, captured: October 10, 1864 *, screw steamer * ''Caroline'', side-wheel steamer (also known as USS ''Arizona'') *, schooner *, side-wheel steamer * , paddle-steamer *, side-wheel steamer * (also known as ''Constance''), side-wheel steamer *, side-wheel steamer *, side-wheel steamer * ''Edith'', steamer (Later CSS ''Chickamauga'') * ''Ella'', side-wheel steamer * ''Ella and Annie'', side-wheel steamer (Captured April 1863) *, screw steamer
* ''Etiwan'', sloop
* ''Eugenie'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Eugenie Smith'', schooner
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''General Banks'', paddle steamer (later ''Fanny and Jenny'')
* ''Gibraltar'', screw steamer, bark-rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Lady Davis'', steamer
*, paddle-steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, screw steamer (later USS ''Memphis'')
* ''Monticello'', Cuban blockade runner
*, side-wheel steamer
*
* ''Old Dominion'', paddle steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, sloop
*, side-wheel steamer
*''San Quintin'', Cuban blockade runner
*, schooner
* ''Shark'', schooner
*, schooner
*, (ex-''Leopard''), side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Thistle'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Thomas L. Wragg'', side-wheel steamer, brig-rigged (later, privateer ''Rattlesnake'')
*, side-wheel steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
* ''Etiwan'', sloop
* ''Eugenie'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Eugenie Smith'', schooner
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''General Banks'', paddle steamer (later ''Fanny and Jenny'')
* ''Gibraltar'', screw steamer, bark-rigged
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Lady Davis'', steamer
*, paddle-steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
*, screw steamer (later USS ''Memphis'')
* ''Monticello'', Cuban blockade runner
*, side-wheel steamer
*
* ''Old Dominion'', paddle steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
*, sloop
*, side-wheel steamer
*''San Quintin'', Cuban blockade runner
*, schooner
* ''Shark'', schooner
*, schooner
*, (ex-''Leopard''), side-wheel steamer
*, side-wheel steamer
* ''Thistle'', side-wheel steamer
* ''Thomas L. Wragg'', side-wheel steamer, brig-rigged (later, privateer ''Rattlesnake'')
*, side-wheel steamer
*, schooner
*, screw steamer
*, steamer
*, schooner
Foreign blockade runners
*, screw steamer *, side-wheel steamer *, screw steamer * ''Denbigh'' side-wheel steamer, schooner rigged * ''Fingal'', steamer *, screw steamer * ''Isabel'' steamer *, schooner *, sloop * ''Lark'', side-wheel steamer *, screw steamer * ''Penquin'', side-wheel steamer *, screw steamer *, screw steamer * ''Prince Albert'', side-wheel steamer *, screw steamer * ''Thistle'', screw steamer *, schooner * ''Victory'', screw steamer *, paddle steamer * ''Wren'', side-wheel steamerCS Army
CSA cotton-clads






 Used for river defense, CS Army cottonclads were typically more lightly armored and reinforced than a regular ironclad, such as the ''General Sterling Price'', which was converted by placing a 4-inch oak sheath with a 1-inch iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads filled with compressed cotton bales. Many of the cottonclads were outfitted with
Used for river defense, CS Army cottonclads were typically more lightly armored and reinforced than a regular ironclad, such as the ''General Sterling Price'', which was converted by placing a 4-inch oak sheath with a 1-inch iron covering on her bow, and by installing double pine bulkheads filled with compressed cotton bales. Many of the cottonclads were outfitted with rams
In engineering, RAMS (reliability, availability, maintainability and safety)River Defense Fleet
The River Defense Fleet was a set of fourteen vessels in Confederate service, intended to assist in the defense of New Orleans in the early days of the American Civil War. All were merchant ships or towboats that were seized by order of the War De ...
cotton-clads:
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
*, stern-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: Apr, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: 1862
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, sunk: June 6, 1862; raised into Union service
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
*, steamer, schooner rigged, cotton-clad ram, destroyed: April 24, 1862
*, steamer, cotton-clad ram, captured: June 6, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, burned: April 24, 1862
*, side-wheel steamer, cotton-clad ram, destroyed: April, 1862
Other CS Army cotton-clads:
*, steamer, cotton-clad, burned: 1863
*, steamer, cotton-clad, operated by Texas Marine Department
*, river steamer, cotton-clad and ironclad ram, exploded: April 14, 1863
*, steamer, cotton-clad, operated by Texas Marine Department
*, river steamer, cotton-clad ram, transferred to CS Navy early 1865, burned: April, 1865
Other CSA Boats
* CSA ''Bayou City'', CS Army gunboat, side-wheel steamer *, CS Army transport, which was captured by the Union on August 10, 1862 while the transport was on theSavannah River
The Savannah River is a major river in the southeastern United States, forming most of the border between the states of South Carolina and Georgia. Two tributaries of the Savannah, the Tugaloo River and the Chattooga River, form the norther ...
in Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
* CSA ''John Simonds'', CS Army support ship, side-wheel steamer, sunk: April 7, 1862
*, CS Army cargo steamer, captured: July 13, 1863
*, CS Army transport, side-wheel steamer, surrendered: May 13, 1862
* CSA ''Neptune'', CS Army tugboat, sank: January 1, 1863
Other
Prizes
*''Alvarado'' - prize bark, captured: by privateer ''Jefferson Davis'', July 21, 1861 *''Enchantress'' - prize schooner, captured: by privateer ''Jefferson Davis'' July 6, 1861Undetermined
*CSS ''Segar'' *CSS ''Smith'' *CSS ''W. R. Miles''See also
*List of ironclads
The list of ironclads includes all steam-propelled warship (supplemented with sails in various cases) and protected by iron or steel armor plates that were built in the early part of the second half of the 19th century, between 1859 and the ea ...
*Blockade runners of the American Civil War
The blockade runners of the American Civil War were seagoing steam ships that were used to get through the Union blockade that extended some along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coastlines and the lower Mississippi River. The Confederate stat ...
*Commerce raiding
Commerce raiding (french: guerre de course, "war of the chase"; german: Handelskrieg, "trade war") is a form of naval warfare used to destroy or disrupt logistics of the enemy on the open sea by attacking its merchant shipping, rather than enga ...
*Confederate privateer
The Confederate privateers were privately owned ships that were authorized by the government of the Confederate States of America to attack the shipping of the United States. Although the appeal was to profit by capturing merchant vessels and seizi ...
*Cotton-clad
Cottonclads were a classification of steam-powered warships where a wooden ship was protected from enemy fire by bales of cotton lining its sides. Cottonclads were prevalent during the American Civil War, particularly in the Confederate States Navy ...
* Letters of marque
* Ransom Bond
* Bibliography of American Civil War naval history
References
Bibliography
*Coski, John M. ''Capital Navy: The Men, Ships and Operations of the James River Squadron'', Campbell, CA: Savas Woodbury Publishers, 1996, * *Gardiner ''Steam, Steel and Shellfire'' *Lambert A., ''Iron Hulls and Armour Plate'' * *Scharf, J. Thomas. ''History of the Confederate States Navy: From its Organization to the Surrender of its Last Vessel.'' New York: Rogers and Sherwood, 1887; repr. The Fairfax Press, 1977. *External links
Photos of ships of the Confederate States Navy
{{Webarchive, url=https://web.archive.org/web/20120118132552/http://www.history.navy.mil/photos/sh-us-cs/csa-sh/csa-name.htm , date=2012-01-18
Confederate States Navy
The Confederate States Navy (CSN) was the Navy, naval branch of the Confederate States Armed Forces, established by an act of the Confederate States Congress on February 21, 1861. It was responsible for Confederate naval operations during the Amer ...
*
*
Confederate Ships
Confederate Ships