Licata on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''
 Licata served as an Allied landing point during the 1943 Operation HUSKY
Licata served as an Allied landing point during the 1943 Operation HUSKY  Licata has however maintained its artistic importance, and tourism has begun to flourish again in recent times. Nevertheless, the economy is heavily reliant on the fishing industry.
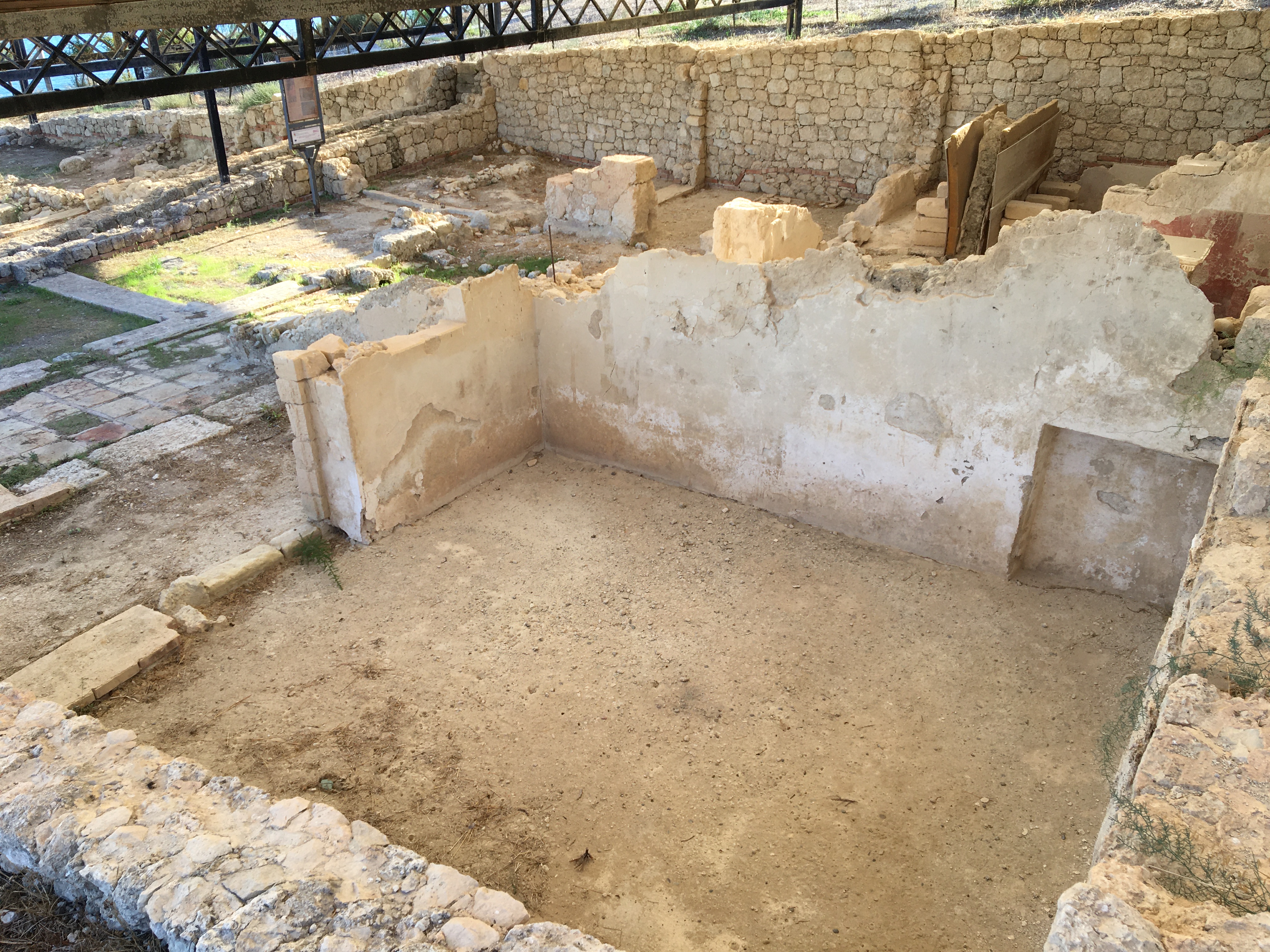
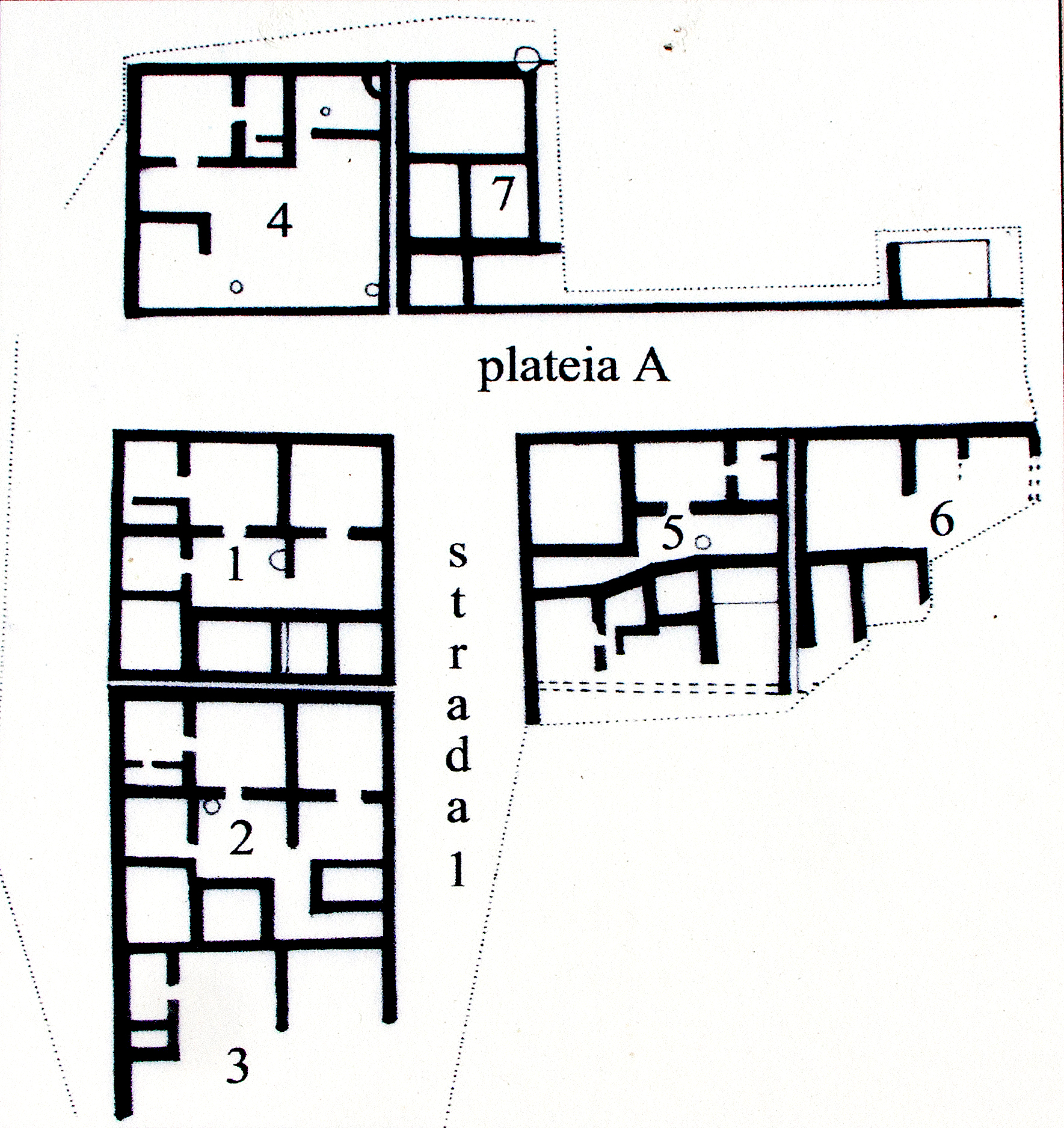
The Museo Civico displays many archaeological finds, notably material from burial grounds dating from prehistoric times to the 3rd century BC.
Licata has however maintained its artistic importance, and tourism has begun to flourish again in recent times. Nevertheless, the economy is heavily reliant on the fishing industry.
The Museo Civico displays many archaeological finds, notably material from burial grounds dating from prehistoric times to the 3rd century BC.
on-line
Richard Stillwell, ed. ''Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites'', 1976:
"Phintias (Licata) Sicily"
Licata official website
Licata Today website
* {{authority control Coastal towns in Sicily Ancient cities in Sicily Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Italy Colonies of Magna Graecia Archaeological sites in the province of Agrigento Populated places established in the 3rd century BC 3rd-century BC establishments in Italy


 Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''
Licata (, ; grc, Φιντίας, whence la, Phintias or ''Plintis''), formerly also Alicata (), is a city and ''comune
The (; plural: ) is a local administrative division of Italy, roughly equivalent to a township or municipality. It is the third-level administrative division of Italy, after regions ('' regioni'') and provinces (''province''). The can also ...
'' located on the south coast of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, at the mouth of the Salso River
The Salso ( Sicilian: ''Salsu''), also known as the Imera Meridionale (Greek: ; Latin Himera), is a river of Sicily. It rises in the Madonie Mountains (Latin: Nebrodes Mons; Sicilian: Munti Madunìi) and, traversing the provinces of Enna and Calt ...
(the ancient ''Himera''), about midway between Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of ...
and Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Cal ...
. It is a major seaport
A port is a maritime facility comprising one or more wharves or loading areas, where ships load and discharge cargo and passengers. Although usually situated on a sea coast or estuary, ports can also be found far inland, such as Ham ...
developed at the turn of the twentieth century, shipping sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, the refining of which has made Licata the largest European exporting centre, and asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
, and at times shipping cheese
Cheese is a dairy product produced in wide ranges of flavors, textures, and forms by coagulation of the milk protein casein. It comprises proteins and fat from milk, usually the milk of cows, buffalo, goats, or sheep. During production, ...
.
West of the port city there is a series of pocket beaches separated by wave-cut headlands as high as . (Amore 2002).
History
Ancient
The settlement was frequented by the Phoenicians who traded there between the 12th and 8th centuries BC. At the end of the 7th century BC the Geloi (inhabitants of ancient Gela) built a fortified station to guard the mouth of theSalso
The Salso ( Sicilian: ''Salsu''), also known as the Imera Meridionale (Greek: ; Latin Himera), is a river of Sicily. It rises in the Madonie Mountains (Latin: Nebrodes Mons; Sicilian: Munti Madunìi) and, traversing the provinces of Enna and Ca ...
(''Himera'') river. In the first half of 6th century BC Phalaris
Phalaris ( el, Φάλαρις) was the tyrant of Akragas (now Agrigento) in Sicily, from approximately 570 to 554 BC.
History
Phalaris was renowned for his excessive cruelty. Among his alleged atrocities is cannibalism: he was said to have e ...
, tyrant of Agrigento
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of ...
, built a fortified outpost.
The first settlement was probably founded by colonists from Gela.
At the Battle of the Himera River (311 BC)
The Battle of the Himera River was fought in 311 BC between Carthage and Syracuse near the mouth of the Himera river (the modern Salso river). Hamilcar, grandson of Hanno the Great, led the Carthaginians, while the Syracusans were led by Agathocl ...
near the town, Agothocles was beaten by the Carthaginians and the town fell into their hands.
The city itself was re-founded on the right bank of the Salso in 282 BC, by Phintias, tyrant of Agrigentum
Agrigento (; scn, Girgenti or ; grc, Ἀκράγας, translit=Akrágas; la, Agrigentum or ; ar, كركنت, Kirkant, or ''Jirjant'') is a city on the southern coast of Sicily, Italy and capital of the province of Agrigento. It was one of ...
, who named it for himself (Phintias), after razing the city of Gela
Gela (Sicilian and ; grc, Γέλα) is a city and (municipality) in the Autonomous Region of Sicily, Italy; in terms of area and population, it is the largest municipality on the southern coast of Sicily. Gela is part of the Province of Cal ...
and resettling its population here. As late as the 1st century BC, inscriptions and coins show that the inhabitants retained the name ''Geloi''.
Phintias was laid out on a great scale, with walls, temples and an agora
The agora (; grc, ἀγορά, romanized: ', meaning "market" in Modern Greek) was a central public space in ancient Greek city-states. It is the best representation of a city-state's response to accommodate the social and political order of t ...
. The setting took advantage of a small natural harbour, about across, in a bay on the coast that is now infilled. The site was protected by the headland now named Monte San Michele. Phintias, however, never rose to the importance of Gela.
At nearby Cape Ecnomus, in 256 BC the Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
won the Battle of Cape Ecnomus
The Battle of Cape Ecnomus or Eknomos ( grc, Ἔκνομος) was a naval battle, fought off southern Sicily, in 256 BC, between the fleets of Carthage and the Roman Republic, during the First Punic War (264–241 BC). It was the largest bat ...
in the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of three wars fought between Rome and Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years, in the longest continuous conflict and grea ...
and freed the city from the Carthaginians. In 249 BC it afforded shelter to a Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a letter ...
fleet which was, however, attacked by the Carthaginians
The Punic people, or western Phoenicians, were a Semitic people in the Western Mediterranean who migrated from Tyre, Phoenicia to North Africa during the Early Iron Age. In modern scholarship, the term ''Punic'' – the Latin equivalent of the ...
and many of the ships sunk. Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the estab ...
also alludes to it as a seaport, carrying on a considerable export trade in corn.
Under the Romans Phintias became a large commercial emporium. But in Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
's time it seems to have fallen into the same state of decay with the other cities on the south coast of Sicily, as he does not mention it among the few exceptions. Pliny
Pliny may refer to:
People
* Pliny the Elder (23–79 CE), ancient Roman nobleman, scientist, historian, and author of ''Naturalis Historia'' (''Pliny's Natural History'')
* Pliny the Younger (died 113), ancient Roman statesman, orator, w ...
, notices the Phintienses (or Phthinthienses as the name is written in some manuscripts) among the stipendiary towns of Sicily; and its name is found also in Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
; but it is strange that both these writers reckon it among the inland towns of Sicily, though its maritime position is clearly attested both by Diodorus and Cicero. The ''Antonine Itinerary
The Antonine Itinerary ( la, Itinerarium Antonini Augusti, "The Itinerary of the Emperor Antoninus") is a famous ''itinerarium'', a register of the stations and distances along various roads. Seemingly based on official documents, possibly ...
'' also gives a place called Plintis, doubtless a corruption of Phintias, which it places on the road from Agrigentum along the coast towards Syracuse, at the distance of from the former city. This distance agrees tolerably well with that from Agrigento to Licata, though somewhat less.
Middle and Modern Ages
The historical centre of the town, near the coastal castle of Lympiados, dates from the period ofByzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
domination. In 827 the Arabs conquered Licata, and their rule lasted for more than two centuries, ending when the town was captured by the Normans
The Normans (Norman language, Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norsemen, Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Fran ...
on July 25, 1086. During the Norman-Hohenstaufen age the town flourished and was awarded the title of ''Cittè Demaniale'' ("Crown's City").
In 1270 Licata (then having some 7,000 inhabitants) rebelled against Angevine rule as part of the uprising known as the Sicilian Vespers
The Sicilian Vespers ( it, Vespri siciliani; scn, Vespiri siciliani) was a successful rebellion on the island of Sicily that broke out at Easter 1282 against the rule of the French-born king Charles I of Anjou, who had ruled the Kingdom of S ...
. Thereafter the town came under the control of the House of Trastámara
The House of Trastámara (Spanish, Aragonese and Catalan: Casa de Trastámara) was a royal dynasty which first ruled in the Crown of Castile and then expanded to the Crown of Aragon in the late middle ages to the early modern period.
They were a ...
, who in 1447 granted it the title of ''fidelissima'' ("Most Faithful"). In 1553, after the city was sacked by Dragut
Dragut ( tr, Turgut Reis) (1485 – 23 June 1565), known as "The Drawn Sword of Islam", was a Muslim Ottoman naval commander, governor, and noble, of Turkish or Greek descent. Under his command, the Ottoman Empire's maritime power was extended ...
's corsairs, it was decided to rebuild the walls, together with a large tower which was erected on the summit of Sant'Angelo hill.
Licata began to flourish once more in the 16th century, thanks in part to the presence of a community of Maltese immigrants, and this period of prosperity continued well into the 17th century, when the first settlements appeared outside the wall, housing the growing Maltese community, and numerous buildings were constructed or rebuilt in the Baroque style. The port also enjoyed a period of prosperity, largely resulting from the export of grain.
Contemporary era
In 1820 Licata rose against theBourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by Bras ...
rulers of the Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and a ...
, led by patriot Matteo Vecchio Verderame. During the Expedition of the Thousand
The Expedition of the Thousand ( it, Spedizione dei Mille) was an event of the Italian Risorgimento that took place in 1860. A corps of volunteers led by Giuseppe Garibaldi sailed from Quarto, near Genoa (now Quarto dei Mille) and landed in Ma ...
under Giuseppe Garibaldi
Giuseppe Maria Garibaldi ( , ;In his native Ligurian language, he is known as ''Gioxeppe Gaibado''. In his particular Niçard dialect of Ligurian, he was known as ''Jousé'' or ''Josep''. 4 July 1807 – 2 June 1882) was an Italian general, patr ...
, the town contributed with a whole corps, and housed for a night Garibaldi's son Menotti and his general Nino Bixio
Gerolamo "Nino" Bixio (, ; 2 October 1821 – 16 December 1873) was an Italian general, patriot and politician, one of the most prominent figures in the Italian unification.
Life and career
He was born Gerolamo Bixio in Genoa. While still a boy ...
.
The 1870s saw the construction of two bridges connecting to the sulphur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
mines inland, and five refineries (including the then largest in Europe) were built. This brought a considerable economic expansion, leading to the creation of several elegant residences in Licata.
Allied invasion of Sicily
The Allied invasion of Sicily, also known as Operation Husky, was a major campaign of World War II in which the Allied forces invaded the island of Sicily in July 1943 and took it from the Axis powers ( Fascist Italy and Nazi Germany). It bega ...
of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. War damage and the decline in competitiveness in the sulphur industry caused economic decline, forcing many people to emigrate to northern Italy or abroad. As a town occupied by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
, it served as a model for John Hersey
John Richard Hersey (June 17, 1914 – March 24, 1993) was an American writer and journalist. He is considered one of the earliest practitioners of the so-called New Journalism, in which storytelling techniques of fiction are adapted to n ...
's novel ''A Bell for Adano''.
Geography
The municipality borders withButera
Butera ( Sicilian: ''Vutera'') is an Italian town and a ''comune'' in the province of Caltanissetta, in the southern part of the island of Sicily. It is bounded by the ''comuni'' of Gela, Licata, Mazzarino, Ravanusa and Riesi. It has a populatio ...
( CL), Camastra, Campobello di Licata, Naro
Naro ( scn, Naru ) is a ''comune'' in the province of Agrigento, on the island of Sicily, Italy. It is bounded by the comuni of Agrigento, Caltanissetta, Camastra, Campobello di Licata, Canicattì, Castrofilippo, Delia, Italy, Delia, Favara, Ag ...
, Palma di Montechiaro
Palma di Montechiaro ( scn, Parma di Muntichiaru) is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Agrigento, Sicily, southern Italy. Many Greek archaeological findings have been found near the town.
Formerly known as Palma, in 1863, Montechiaro ...
and Ravanusa. It counts the hamlets (''frazioni
A ''frazione'' (plural: ) is a type of subdivision of a ''comune'' (municipality) in Italy, often a small village or hamlet outside the main town. Most ''frazioni'' were created during the Fascist Italy (1922–1943), Fascist era (1922–1943) as ...
'') of Mollarella and Torre di Gaffe.
Main sights
* Archaeological remains of the ancient Greek city, including 7 ''domus'' near the centre of the city at Monte Sant'Angelo. The 17th centuryCastel Sant'Angelo
The Mausoleum of Hadrian, usually known as Castel Sant'Angelo (; English: ''Castle of the Holy Angel''), is a towering cylindrical building in Parco Adriano, Rome, Italy. It was initially commissioned by the Roman Emperor Hadrian as a mausol ...
is located nearby.
* The necropolis of Monte Petrulla
* The ''Grangela'', and hydraulic work of Pre-Hellenistic times
* ''Frourion'' of Falaride, a Greek fortress
* The lighthouse, which is the third tallest in Italy
* Church of ''Santa Maria La Nova'', built in the 15th century but renovated in later years. It houses the Black Christ's Chapel.
* the ''Carmine'' (13th century), including a church and a convent, rebuilt in the 18th century under design by Giovanni Biagio Amico.
* ''Palazzo di Città'', a noteworthy example of Sicilian Liberty style
Liberty style ( it, Stile Liberty) was the Italian variant of Art Nouveau, which flourished between about 1890 and 1914. It was also sometimes known as ''stile floreale'', ''arte nuova'', or ''stile moderno''. It took its name from Arthur Lasenby ...
, designed by Ernesto Basile
Ernesto Basile (31 January 1857 – 26 August 1932, in Palermo) was an Italian architect and an exponent of modernisme and Liberty style, the Italian variant of Art Nouveau. His style was known for its eclectic fusion of ancient, medieval and ...
.
Sister cities
*Cestas
Cestas (; oc-gsc, Cestàs) is a commune in the Gironde department in Nouvelle-Aquitaine in southwestern France.
Population
Economy
Cestas Solar Park was the biggest solar park in Europe when Neoen opened it in December 2015.
See also
*Co ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
* Reinheim
Reinheim is a town in the Darmstadt-Dieburg district, in Hesse, Germany. It is situated southeast of Darmstadt.
International relations
Twin towns - Sister cities
Reinheim is twinned with:
* Licata, Italy (since 29.6.2001)
* Cestas, France ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
See also
* A.S.D. Licata 1931 *Licata Airfield
Licata Airfield is an abandoned World War II military airfield in Italy, located in the vicinity of Licata, Sicily. It was a temporary fighter airfield constructed in the immediate aftermath of Operation Husky by U.S. Army Engineers using pierc ...
Notes
References
* * C. Amore ''et al.'', "Historical evolution of the Salso River mouth, with respoect to the Licata harbour system" in Eurocoast/EUCC, ''Littoral 2002''on-line
Richard Stillwell, ed. ''Princeton Encyclopedia of Classical Sites'', 1976:
"Phintias (Licata) Sicily"
External links
Licata official website
Licata Today website
* {{authority control Coastal towns in Sicily Ancient cities in Sicily Ancient Greek archaeological sites in Italy Colonies of Magna Graecia Archaeological sites in the province of Agrigento Populated places established in the 3rd century BC 3rd-century BC establishments in Italy