Lakes Valley Conference on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by
 The majority of lakes on Earth are
The majority of lakes on Earth are
 Volcanic lakes are lakes that occupy either local depressions, e.g. craters and
Volcanic lakes are lakes that occupy either local depressions, e.g. craters and
 Glacial lakes are lakes created by the direct action of glaciers and continental ice sheets. A wide variety of glacial processes create enclosed basins. As a result, there are a wide variety of different types of glacial lakes and it is often difficult to define clear-cut distinctions between different types of glacial lakes and lakes influenced by other activities. The general types of glacial lakes that have been recognized are lakes in direct contact with ice, glacially carved rock basins and depressions, morainic and outwash lakes, and glacial drift basins. Glacial lakes are the most numerous lakes in the world. Most lakes in
Glacial lakes are lakes created by the direct action of glaciers and continental ice sheets. A wide variety of glacial processes create enclosed basins. As a result, there are a wide variety of different types of glacial lakes and it is often difficult to define clear-cut distinctions between different types of glacial lakes and lakes influenced by other activities. The general types of glacial lakes that have been recognized are lakes in direct contact with ice, glacially carved rock basins and depressions, morainic and outwash lakes, and glacial drift basins. Glacial lakes are the most numerous lakes in the world. Most lakes in
 The most common type of fluvial lake is a crescent-shaped lake called an ''
The most common type of fluvial lake is a crescent-shaped lake called an ''

 In addition to the mode of origin, lakes have been named and classified according to various other important factors such as thermal stratification, oxygen saturation, seasonal variations in lake volume and water level, salinity of the water mass, relative seasonal permanence, degree of outflow, and so on. The names used by the lay public and in the scientific community for different types of lakes are often informally derived from the morphology of the lakes' physical characteristics or other factors. Also, different cultures and regions of the world have their own popular nomenclature.
In addition to the mode of origin, lakes have been named and classified according to various other important factors such as thermal stratification, oxygen saturation, seasonal variations in lake volume and water level, salinity of the water mass, relative seasonal permanence, degree of outflow, and so on. The names used by the lay public and in the scientific community for different types of lakes are often informally derived from the morphology of the lakes' physical characteristics or other factors. Also, different cultures and regions of the world have their own popular nomenclature.
''Glossary of Biolimnological Terms''
Washington, DC, United States Army Corps of Engineers. * Playa lake is a typically shallow, intermittent lake that covers or occupies a playa either in wet seasons or in especially wet years but subsequently drying up in an arid or semiarid region. * Vlei is a name used in South Africa for a shallow lake which varies considerably in level with the seasons.Theal, G.M., 1877. ''Compendium of South African history and geography, 3rd.'' Institution Press, Lovedale, South Africa.
 Lakes have numerous features in addition to lake type, such as drainage basin (also known as catchment area), inflow and outflow, nutrient content, dissolved oxygen, water pollution, pollutants, pH, and
Lakes have numerous features in addition to lake type, such as drainage basin (also known as catchment area), inflow and outflow, nutrient content, dissolved oxygen, water pollution, pollutants, pH, and  Since the surface water of deep tropical lakes never reaches the temperature of maximum density, there is no process that makes the water mix. The deeper layer becomes oxygen starved and can become saturated with carbon dioxide, or other gases such as sulfur dioxide if there is even a trace of volcano, volcanic activity. Exceptional events, such as earthquakes or landslides, can cause mixing which rapidly brings the deep layers up to the surface and release a vast cloud of gas which lay trapped in solution in the colder water at the bottom of the lake. This is called a limnic eruption. An example is Lake Nyos#The 1986 disaster, the disaster at Lake Nyos in Cameroon. The amount of gas that can be dissolved in water is directly related to pressure. As deep water surfaces, the pressure drops and a vast amount of gas comes out of solution. Under these circumstances carbon dioxide is hazardous because it is heavier than air and displaces it, so it may flow down a river valley to human settlements and cause mass asphyxiation.
The material at the bottom of a lake, or ''lake bed'', may be composed of a wide variety of inorganics, such as silt or sand, and organic material, such as decaying plant or animal matter. The composition of the lake bed has a significant impact on the flora and fauna found within the lake's environs by contributing to the amounts and the types of nutrients available.
A paired (black and white) layer of the varved lake sediments correspond to a year. During winter, when organisms die, carbon is deposited down, resulting to a black layer. At the same year, during summer, only few organic materials are deposited, resulting to a white layer at the lake bed. These are commonly used to track past paleontological events.
Natural lakes provide a Macrocosm and microcosm, microcosm of living and nonliving elements that are relatively independent of their surrounding environments. Therefore, lake organisms can often be studied in isolation from the lake's surroundings.
Since the surface water of deep tropical lakes never reaches the temperature of maximum density, there is no process that makes the water mix. The deeper layer becomes oxygen starved and can become saturated with carbon dioxide, or other gases such as sulfur dioxide if there is even a trace of volcano, volcanic activity. Exceptional events, such as earthquakes or landslides, can cause mixing which rapidly brings the deep layers up to the surface and release a vast cloud of gas which lay trapped in solution in the colder water at the bottom of the lake. This is called a limnic eruption. An example is Lake Nyos#The 1986 disaster, the disaster at Lake Nyos in Cameroon. The amount of gas that can be dissolved in water is directly related to pressure. As deep water surfaces, the pressure drops and a vast amount of gas comes out of solution. Under these circumstances carbon dioxide is hazardous because it is heavier than air and displaces it, so it may flow down a river valley to human settlements and cause mass asphyxiation.
The material at the bottom of a lake, or ''lake bed'', may be composed of a wide variety of inorganics, such as silt or sand, and organic material, such as decaying plant or animal matter. The composition of the lake bed has a significant impact on the flora and fauna found within the lake's environs by contributing to the amounts and the types of nutrients available.
A paired (black and white) layer of the varved lake sediments correspond to a year. During winter, when organisms die, carbon is deposited down, resulting to a black layer. At the same year, during summer, only few organic materials are deposited, resulting to a white layer at the lake bed. These are commonly used to track past paleontological events.
Natural lakes provide a Macrocosm and microcosm, microcosm of living and nonliving elements that are relatively independent of their surrounding environments. Therefore, lake organisms can often be studied in isolation from the lake's surroundings.
 Limnology is the study of inland bodies of water and related ecosystems. Limnology divides lakes into three zones: the ''littoral zone'', a sloped area close to land; the ''photic zone, photic'' or ''open-water zone'', where sunlight is abundant; and the deep-water ''profundal zone, profundal'' or ''benthic zone'', where little sunlight can reach. The depth to which light can penetrate depends on the turbidity of the water, which is determined by the density and size of suspended Particle (ecology), particles. A particle will be in Suspension (chemistry), suspension if its weight is less than the random turbidity forces acting upon it. These particles can be sedimentary or Biotic material, biological in origin (including algae and detritus) and are responsible for the color of the water. Decaying plant matter, for instance, may account for a yellow or brown color, while algae may cause a greenish coloration. In very shallow water bodies, iron oxides make the water reddish brown. Bottom-dwelling detritivorous fish stir the mud in search of food and can be the cause of turbid waters. Piscivorous fish contribute to turbidity by eating plant-eating (planktonivorous) fish, thus increasing the amount of algae (see aquatic trophic cascade).
The light depth or transparency is measured using a ''Secchi disk'', a 20-cm (8 in) disk with alternating white and black Circular sector, quadrants. The depth at which the disk is no longer visible is the ''Secchi depth'', a measure of transparency. The Secchi disk is commonly used to test for eutrophication. For a detailed look at these processes, see lentic ecosystems.
A lake moderates the surrounding region's temperature and climate because water has a very high specific heat capacity (4,186 J·kg−1·K−1). In the daytime a lake can cool the land beside it with local winds, resulting in a sea breeze; in the night it can warm it with a land breeze.
Limnology is the study of inland bodies of water and related ecosystems. Limnology divides lakes into three zones: the ''littoral zone'', a sloped area close to land; the ''photic zone, photic'' or ''open-water zone'', where sunlight is abundant; and the deep-water ''profundal zone, profundal'' or ''benthic zone'', where little sunlight can reach. The depth to which light can penetrate depends on the turbidity of the water, which is determined by the density and size of suspended Particle (ecology), particles. A particle will be in Suspension (chemistry), suspension if its weight is less than the random turbidity forces acting upon it. These particles can be sedimentary or Biotic material, biological in origin (including algae and detritus) and are responsible for the color of the water. Decaying plant matter, for instance, may account for a yellow or brown color, while algae may cause a greenish coloration. In very shallow water bodies, iron oxides make the water reddish brown. Bottom-dwelling detritivorous fish stir the mud in search of food and can be the cause of turbid waters. Piscivorous fish contribute to turbidity by eating plant-eating (planktonivorous) fish, thus increasing the amount of algae (see aquatic trophic cascade).
The light depth or transparency is measured using a ''Secchi disk'', a 20-cm (8 in) disk with alternating white and black Circular sector, quadrants. The depth at which the disk is no longer visible is the ''Secchi depth'', a measure of transparency. The Secchi disk is commonly used to test for eutrophication. For a detailed look at these processes, see lentic ecosystems.
A lake moderates the surrounding region's temperature and climate because water has a very high specific heat capacity (4,186 J·kg−1·K−1). In the daytime a lake can cool the land beside it with local winds, resulting in a sea breeze; in the night it can warm it with a land breeze.
 Lake zones:
* ''Epilittoral'': The zone that is entirely above the lake's normal water level and never submerged by lake water
* ''Littoral'': The zone that encompasses the small area above the normal water level (which is sometimes submerged when the lake's water level increases), reaching to the deepest part of the lake that still allows for submerged Aquatic plant, macrophytic growth
* ''Littoriprofundal'': Transition zone commonly aligned with stratified lakes' metalimnions – too deep for macrophytes but includes photosynthetic algae and bacteria
* ''Profundal'': Sedimentary zone containing no vegetation
Algal community types:
* ''Epipelic'': Algae that grow on sediments
* ''Epilithic'': Algae that grow on rocks
* ''Epipsammic'': Algae that grow on (or within) sand
* ''Epiphytic'': Algae that grow on macrophytes
* ''Epizooic'': Algae that grow on living animals
* ''Metaphyton'': Algae present in the littoral zone, not in a state of suspension nor attached to a substratum (such as a macrophyte)
Lake zones:
* ''Epilittoral'': The zone that is entirely above the lake's normal water level and never submerged by lake water
* ''Littoral'': The zone that encompasses the small area above the normal water level (which is sometimes submerged when the lake's water level increases), reaching to the deepest part of the lake that still allows for submerged Aquatic plant, macrophytic growth
* ''Littoriprofundal'': Transition zone commonly aligned with stratified lakes' metalimnions – too deep for macrophytes but includes photosynthetic algae and bacteria
* ''Profundal'': Sedimentary zone containing no vegetation
Algal community types:
* ''Epipelic'': Algae that grow on sediments
* ''Epilithic'': Algae that grow on rocks
* ''Epipsammic'': Algae that grow on (or within) sand
* ''Epiphytic'': Algae that grow on macrophytes
* ''Epizooic'': Algae that grow on living animals
* ''Metaphyton'': Algae present in the littoral zone, not in a state of suspension nor attached to a substratum (such as a macrophyte)
 The lake may be infilled with deposited sediment and gradually become a wetland such as a swamp or marsh. Large water plants, typically Phragmites, reeds, accelerate this closing process significantly because they partially decompose to form peat soils that fill the shallows. Conversely, peat soils in a marsh can naturally burn and reverse this process to recreate a shallow lake resulting in a dynamic equilibrium between marsh and lake. This is significant since wildfire has been largely suppressed in the developed world over the past century. This has artificially converted many shallow lakes into emergent marshes. Turbid lakes and lakes with many plant-eating fish tend to disappear more slowly. A "disappearing" lake (barely noticeable on a human timescale) typically has extensive plant mats at the water's edge. These become a new habitat for other plants, like Sphagnum, peat moss when conditions are right, and animals, many of which are very rare. Gradually, the lake closes and young peat may form, forming a fen. In lowland river valleys where a river can meander, the presence of peat is explained by the infilling of historical
The lake may be infilled with deposited sediment and gradually become a wetland such as a swamp or marsh. Large water plants, typically Phragmites, reeds, accelerate this closing process significantly because they partially decompose to form peat soils that fill the shallows. Conversely, peat soils in a marsh can naturally burn and reverse this process to recreate a shallow lake resulting in a dynamic equilibrium between marsh and lake. This is significant since wildfire has been largely suppressed in the developed world over the past century. This has artificially converted many shallow lakes into emergent marshes. Turbid lakes and lakes with many plant-eating fish tend to disappear more slowly. A "disappearing" lake (barely noticeable on a human timescale) typically has extensive plant mats at the water's edge. These become a new habitat for other plants, like Sphagnum, peat moss when conditions are right, and animals, many of which are very rare. Gradually, the lake closes and young peat may form, forming a fen. In lowland river valleys where a river can meander, the presence of peat is explained by the infilling of historical
 Only one astronomical body other than Earth is known to harbor large lakes: Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Photographs and spectroscopic analysis by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft show liquid ethane on the surface, which is thought to be mixed with liquid methane. The largest lake on Titan is Kraken Mare which, at an estimated 400,000 km2, is roughly five times the size of Lake Superior (~80,000 km2) and nearly the size of all five Great Lakes of North America combined. The second largest Titanean lake, Ligeia Mare, is almost twice the size of Lake Superior, at an estimated 150,000 km2.
Jupiter's large moon Io (moon), Io is volcanically active, leading to the accumulation of sulfur deposits on the surface. Some photographs taken during the Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' mission appear to show lakes of liquid sulfur in volcanic caldera, though these are more analogous to lakes of lava than of water on Earth.
The planet Mars has only one confirmed lake which is underground and near the south pole. Although the surface of Mars is too cold and has too little atmospheric pressure to permit permanent surface water, geologic evidence appears to confirm that ancient lakes once formed on the surface.
There are dark basaltic plains on the Moon, similar to lunar mare, lunar maria but smaller, which are called ''lacus'' (singular ''lacus'', Latin for "lake") because they were thought by early astronomers to be lakes of water.
Only one astronomical body other than Earth is known to harbor large lakes: Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Photographs and spectroscopic analysis by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft show liquid ethane on the surface, which is thought to be mixed with liquid methane. The largest lake on Titan is Kraken Mare which, at an estimated 400,000 km2, is roughly five times the size of Lake Superior (~80,000 km2) and nearly the size of all five Great Lakes of North America combined. The second largest Titanean lake, Ligeia Mare, is almost twice the size of Lake Superior, at an estimated 150,000 km2.
Jupiter's large moon Io (moon), Io is volcanically active, leading to the accumulation of sulfur deposits on the surface. Some photographs taken during the Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' mission appear to show lakes of liquid sulfur in volcanic caldera, though these are more analogous to lakes of lava than of water on Earth.
The planet Mars has only one confirmed lake which is underground and near the south pole. Although the surface of Mars is too cold and has too little atmospheric pressure to permit permanent surface water, geologic evidence appears to confirm that ancient lakes once formed on the surface.
There are dark basaltic plains on the Moon, similar to lunar mare, lunar maria but smaller, which are called ''lacus'' (singular ''lacus'', Latin for "lake") because they were thought by early astronomers to be lakes of water.
 * The largest lake by surface area is
* The largest lake by surface area is
It is also the world's largest freshwater lake by volume (, but much smaller than the Caspian Sea at ), and the second longest (about from tip to tip). * The world's ancient lake, oldest lake is
It is also the third largest by volume, the second oldest, and the second deepest () in the world, after Lake Baikal. * The world's highest lake, if size is not a criterion, may be the crater lake of Ojos del Salado, at . * The highest large (greater than ) lake in the world is the Lake Puma Yumco, Pumoyong Tso (Pumuoyong Tso), in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, at , above sea level. * The world's highest commercially navigable lake is Lake Titicaca in Peru and Bolivia at . It is also the largest lake in South America. * The world's lowest lake is the
ILEC World Lake Database
LakeNet Global Lake Database
{{Authority control Lakes, Bodies of water Lacustrine landforms
 A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land
Land, also known as dry land, ground, or earth, is the solid terrestrial surface of the planet Earth that is not submerged by the ocean or other bodies of water. It makes up 29% of Earth's surface and includes the continents and various islan ...
, and distinct from any river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
, although, like the much larger oceans, they do form part of the Earth's water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
. Lakes are distinct from lagoon
A lagoon is a shallow body of water separated from a larger body of water by a narrow landform, such as reefs, barrier islands, barrier peninsulas, or isthmuses. Lagoons are commonly divided into ''coastal lagoons'' (or ''barrier lagoons'') a ...
s, which are generally coastal parts of the ocean. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than pond
A pond is an area filled with water, either natural or artificial, that is smaller than a lake. Defining them to be less than in area, less than deep, and with less than 30% emergent vegetation helps in distinguishing their ecology from th ...
s, which also lie on land, though there are no official or scientific definitions. Lakes can be contrasted with river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
s or stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...
s, which usually flow in a channel on land. Most lakes are fed and drained by rivers and streams.
Natural lakes are generally found in mountainous areas, rift zone
A rift zone is a feature of some volcanoes, especially shield volcanoes, in which a set of linear cracks (or rifts) develops in a volcanic edifice, typically forming into two or three well-defined regions along the flanks of the vent. Believed t ...
s, and areas with ongoing glaciation
A glacial period (alternatively glacial or glaciation) is an interval of time (thousands of years) within an ice age that is marked by colder temperatures and glacier advances. Interglacials, on the other hand, are periods of warmer climate betw ...
. Other lakes are found in endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
s or along the courses of mature rivers, where a river channel has widened into a basin. Some parts of the world have many lakes formed by the chaotic drainage patterns left over from the last ice age. All lakes are temporary over long periods of time, as they will slowly fill in with sediments or spill out of the basin containing them.
Many lakes are artificial
Artificiality (the state of being artificial or manmade) is the state of being the product of intentional human manufacture, rather than occurring naturally through processes not involving or requiring human activity.
Connotations
Artificiality ...
and are constructed for industrial or agricultural use, for hydroelectric power
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
generation or domestic water supply, for aesthetic or recreational purposes, or for other activities.
Etymology, meaning, and usage of "lake"
The word ''lake'' comes fromMiddle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old English p ...
('lake, pond, waterway'), from Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain, Anglo ...
('pond, pool, stream'), from Proto-Germanic
Proto-Germanic (abbreviated PGmc; also called Common Germanic) is the reconstructed proto-language of the Germanic branch of the Indo-European languages.
Proto-Germanic eventually developed from pre-Proto-Germanic into three Germanic branc ...
('pond, ditch, slow moving stream'), from the Proto-Indo-European
Proto-Indo-European (PIE) is the reconstructed common ancestor of the Indo-European language family. Its proposed features have been derived by linguistic reconstruction from documented Indo-European languages. No direct record of Proto-Indo-E ...
root ('to leak, drain'). Cognates include Dutch
Dutch commonly refers to:
* Something of, from, or related to the Netherlands
* Dutch people ()
* Dutch language ()
Dutch may also refer to:
Places
* Dutch, West Virginia, a community in the United States
* Pennsylvania Dutch Country
People E ...
('lake, pond, ditch'), Middle Low German
Middle Low German or Middle Saxon (autonym: ''Sassisch'', i.e. " Saxon", Standard High German: ', Modern Dutch: ') is a developmental stage of Low German. It developed from the Old Saxon language in the Middle Ages and has been documented i ...
('water pooled in a riverbed, puddle') as in: :de:Wolfslake, :de:Butterlake, German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
**Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ger ...
('pool, puddle'), and Icelandic ('slow flowing stream'). Also related are the English words ''leak'' and ''leach''.
There is considerable uncertainty about defining the difference between lakes and pond
A pond is an area filled with water, either natural or artificial, that is smaller than a lake. Defining them to be less than in area, less than deep, and with less than 30% emergent vegetation helps in distinguishing their ecology from th ...
s, and neither term has an internationally accepted definition across scientific disciplines or political boundaries. For example, limnologist
Limnology ( ; from Greek λίμνη, ''limne'', "lake" and λόγος, ''logos'', "knowledge") is the study of inland aquatic ecosystems.
The study of limnology includes aspects of the biological, chemical, physical, and geological characteristi ...
s have defined lakes as water bodies that are simply a larger version of a pond, which can have wave action on the shoreline or where wind-induced turbulence plays a major role in mixing the water column. None of these definitions completely excludes ponds and all are difficult to measure. For this reason, simple size-based definitions are increasingly used to separate ponds and lakes. Definitions for ''lake'' range in minimum sizes for a body of water from to . Pioneering animal ecologist Charles Elton Charles Elton may refer to:
*Charles Elton (Born, 1993) Professional Rugby Player for Otago Rugby
* Charles Isaac Elton (1839–1900), English lawyer, politician, writer and antiquarian
* Charles Sutherland Elton (1900–1991), English biologist
...
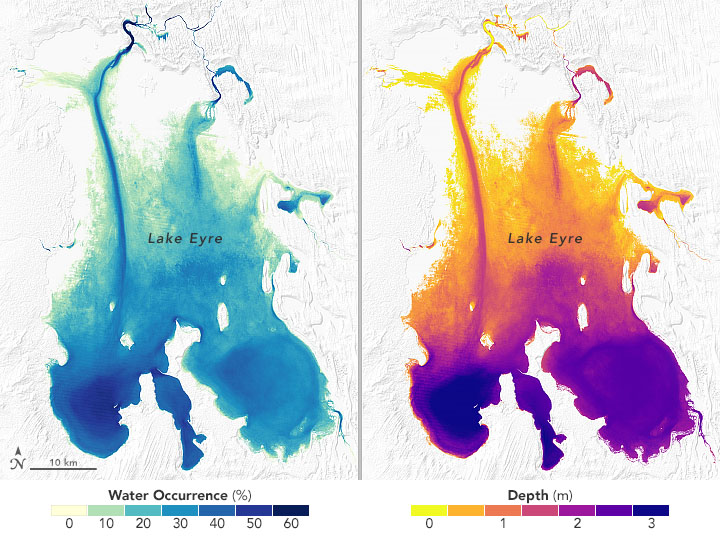
regarded lakes as waterbodies of or more. The term ''lake'' is also used to describe a feature such as Lake Eyre
Lake Eyre ( ), officially known as Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre, is an endorheic lake in east-central Far North South Australia, some north of Adelaide. The shallow lake is the depocentre of the vast endorheic Lake Eyre basin, and contains the ...
, which is a dry basin most of the time but may become filled under seasonal conditions of heavy rainfall. In common usage, many lakes bear names ending with the word ''pond'', and a lesser number of names ending with ''lake'' are, in quasi-technical fact, ponds. One textbook illustrates this point with the following: "In Newfoundland, for example, almost every lake is called a pond, whereas in Wisconsin, almost every pond is called a lake."
One hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
book proposes to define the term "lake" as a body of water with the following five characteristics:
# It partially or totally fills one or several basins connected by strait
A strait is an oceanic landform connecting two seas or two other large areas of water. The surface water generally flows at the same elevation on both sides and through the strait in either direction. Most commonly, it is a narrow ocean channe ...
s;
# It has essentially the same water level in all parts (except for relatively short-lived variations caused by wind, varying ice cover, large inflows, etc.);
# It does not have regular intrusion of seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
;
# A considerable portion of the sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
suspended in the water is captured by the basins (for this to happen they need to have a sufficiently small inflow-to-volume ratio);
# The area measured at the mean water level exceeds an arbitrarily chosen threshold (for instance, one hectare
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100-metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is a ...
).
With the exception of criterion 3, the others have been accepted or elaborated upon by other hydrology publications.
Distribution
 The majority of lakes on Earth are
The majority of lakes on Earth are freshwater
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does include ...
, and most lie in the Northern Hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
at higher latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pol ...
s. Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, with a deranged drainage system, has an estimated 31,752 lakes larger than in surface area. The total number of lakes in Canada is unknown but is estimated to be at least 2 million. Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of B ...
has 187,888 lakes of in area, or larger, of which 56,000 are large ( or larger).
Most lakes have at least one natural outflow in the form of a river
A river is a natural flowing watercourse, usually freshwater, flowing towards an ocean, sea, lake or another river. In some cases, a river flows into the ground and becomes dry at the end of its course without reaching another body of wate ...
or stream
A stream is a continuous body of water, body of surface water Current (stream), flowing within the stream bed, bed and bank (geography), banks of a channel (geography), channel. Depending on its location or certain characteristics, a stream ...
, which maintain a lake's average level by allowing the drainage of excess water. Some lakes do not have a natural outflow and lose water solely by evaporation or underground seepage, or both. These are termed endorheic
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
lakes.
Many lakes are artificial and are constructed for hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
power generation, aesthetic purposes, recreation
Recreation is an activity of leisure, leisure being discretionary time. The "need to do something for recreation" is an essential element of human biology and psychology. Recreational activities are often done for enjoyment, amusement, or pleasur ...
al purposes, industrial use, agricultural
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating Plant, plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of Sedentism, sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of Domestication, domesticated species created food ...
use, or domestic water supply
Water supply is the provision of water by public utilities, commercial organisations, community endeavors or by individuals, usually via a system of pumps and pipes. Public water supply systems are crucial to properly functioning societies. Thes ...
.
The number of lakes on Earth is undetermined because most lakes and ponds are very small and do not appear on maps or satellite imagery
Satellite images (also Earth observation imagery, spaceborne photography, or simply satellite photo) are images of Earth collected by imaging satellites operated by governments and businesses around the world. Satellite imaging companies sell ima ...
. Despite this uncertainty, a large number of studies agree that small ponds are much more abundant than large lakes. For example, one widely cited study estimated that Earth has 304 million lakes and ponds, and that 91% of these are or less in area. Despite the overwhelming abundance of ponds, almost all of Earth's lake water is found in fewer than 100 large lakes; this is because lake volume scales
Scale or scales may refer to:
Mathematics
* Scale (descriptive set theory), an object defined on a set of points
* Scale (ratio), the ratio of a linear dimension of a model to the corresponding dimension of the original
* Scale factor, a number w ...
superlinearly with lake area.
Extraterrestrial lakes exist on the moon Titan, which orbits the planet Saturn
Saturn is the sixth planet from the Sun and the second-largest in the Solar System, after Jupiter. It is a gas giant with an average radius of about nine and a half times that of Earth. It has only one-eighth the average density of Earth; h ...
. The shape of lakes on Titan is very similar to those on Earth. Lakes were formerly present on the surface of Mars, but are now dry lake bed
A dry lake bed, also known as a playa, is a basin or depression that formerly contained a standing surface water body, which disappears when evaporation processes exceeds recharge. If the floor of a dry lake is covered by deposits of alkaline c ...
s.
Types
In 1957, G. Evelyn Hutchinson published a monograph titled ''A Treatise on Limnology'', which is regarded as a landmark discussion and classification of all major lake types, their origin, morphometric characteristics, and distribution. Hutchinson presented in his publication a comprehensive analysis of the origin of lakes and proposed what is a widely accepted classification of lakes according to their origin. This classification recognizes 11 major lake types that are divided into 76 subtypes. The 11 major lake types are: * tectonic lakes * volcanic lakes * glacial lakes * fluvial lakes * solution lakes * landslide lakes * aeolian lakes * shoreline lakes * organic lakes * anthropogenic lakes * meteorite (extraterrestrial impact) lakesTectonic lakes
Tectonic lakes are lakes formed by the deformation and resulting lateral and vertical movements of the Earth's crust. These movements include faulting, tilting, folding, and warping. Some of the largest lakes on Earth arerift lake
A rift lake is a lake formed as a result of subsidence related to movement on faults within a rift zone, an area of extensional tectonics in the continental crust. They are often found within rift valleys and may be very deep. Rift lakes may be ...
s occupying rift valleys, e.g. Central African Rift lakes and Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
. Other well-known tectonic lakes, Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
, the Sea of Aral
The Aral Sea ( ; kk, Арал теңізі, Aral teñızı; uz, Орол денгизи, Orol dengizi; kaa, Арал теңизи, Aral teńizi; russian: Аральское море, Aral'skoye more) was an endorheic lake lying between Kazakh ...
, and other lakes from the Pontocaspian occupy basins that have been separated from the sea by the tectonic uplift of the sea floor above the ocean level.
Often, the tectonic action of crustal extension has created an alternating series of parallel graben
In geology, a graben () is a depressed block of the crust of a planet or moon, bordered by parallel normal faults.
Etymology
''Graben'' is a loan word from German, meaning 'ditch' or 'trench'. The word was first used in the geologic contex ...
s and horsts that form elongate basins alternating with mountain ranges. Not only does this promote the creation of lakes by the disruption of preexisting drainage networks, it also creates within arid regions endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
s that contain salt lakes
A salt lake or saline lake is a landlocked body of water that has a concentration of salt (chemistry), salts (typically sodium chloride) and other dissolved minerals significantly higher than most lakes (often defined as at least three grams of ...
(also called saline lakes). They form where there is no natural outlet, a high evaporation rate and the drainage surface of the water table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
has a higher-than-normal salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
content. Examples of these salt lakes include Great Salt Lake
The Great Salt Lake is the largest saltwater lake in the Western Hemisphere and the eighth-largest terminal lake in the world. It lies in the northern part of the U.S. state of Utah and has a substantial impact upon the local climate, particula ...
and the Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
. Another type of tectonic lake caused by faulting is sag pond
A sag pond is a body of fresh water collected in the lowest parts of a depression (geology), depression formed between two sides of an active geologic fault, strike-slip, transtensional or normal fault zone.
Formation
A sag pond is formed along ...
s.
Volcanic lakes
 Volcanic lakes are lakes that occupy either local depressions, e.g. craters and
Volcanic lakes are lakes that occupy either local depressions, e.g. craters and maar
A maar is a broad, low-relief volcanic crater caused by a phreatomagmatic eruption (an explosion which occurs when groundwater comes into contact with hot lava or magma). A maar characteristically fills with water to form a relatively shallow ...
s, or larger basins, e.g. calderas
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
, created by volcanism
Volcanism, vulcanism or volcanicity is the phenomenon of eruption of molten rock (magma) onto the surface of the Earth or a solid-surface planet or moon, where lava, pyroclastics, and volcanic gases erupt through a break in the surface called ...
. Crater lake
Crater Lake (Klamath language, Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The ...
s are formed in volcanic crater
A volcanic crater is an approximately circular depression in the ground caused by Volcano, volcanic activity. It is typically a bowl-shaped feature containing one or more vents. During Types of volcanic eruptions, volcanic eruptions, molten magm ...
s and calderas, which fill up with precipitation more rapidly than they empty via either evaporation, groundwater discharge, or a combination of both. Sometimes the latter are called caldera lakes, although often no distinction is made. An example is Crater Lake
Crater Lake (Klamath language, Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The ...
in Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
, in the caldera of Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama (''Giiwas'' in the Native American language Klamath language, Klamath) is a complex volcano in the state of Oregon, United States, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountai ...
. The caldera was created in a massive volcanic eruption that led to the subsidence
Subsidence is a general term for downward vertical movement of the Earth's surface, which can be caused by both natural processes and human activities. Subsidence involves little or no horizontal movement, which distinguishes it from slope move ...
of Mount Mazama
Mount Mazama (''Giiwas'' in the Native American language Klamath language, Klamath) is a complex volcano in the state of Oregon, United States, in a segment of the Cascade Volcanoes, Cascade Volcanic Arc and Cascade Range. Most of the mountai ...
around 4860 BCE. Other volcanic lakes are created when either rivers or streams are dammed by lava flow
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or und ...
s or volcanic lahar
A lahar (, from jv, ꦮ꧀ꦭꦲꦂ) is a violent type of mudflow or debris flow composed of a slurry of pyroclastic material, rocky debris and water. The material flows down from a volcano, typically along a river valley.
Lahars are extreme ...
s. The basin which is now Malheur Lake
Malheur Lake is one of the lakes in the Malheur National Wildlife Refuge in Harney County in the U.S. state of Oregon. Located about southeast of Burns, the lake is marsh fed by the Donner und Blitzen River from the south and the Silvies River ...
, Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
was created when a lava flow dammed the Malheur River
The Malheur River (local pronunciation: "MAL-hyure") is a tributary of the Snake River in eastern Oregon in the United States. It drains a Great Basin Desert, high desert area, between the Harney Basin and the Blue Mountains (Oregon), Blue Moun ...
. Among all lake types, volcanic crater lakes most closely approximate a circular shape.
Glacial lakes
 Glacial lakes are lakes created by the direct action of glaciers and continental ice sheets. A wide variety of glacial processes create enclosed basins. As a result, there are a wide variety of different types of glacial lakes and it is often difficult to define clear-cut distinctions between different types of glacial lakes and lakes influenced by other activities. The general types of glacial lakes that have been recognized are lakes in direct contact with ice, glacially carved rock basins and depressions, morainic and outwash lakes, and glacial drift basins. Glacial lakes are the most numerous lakes in the world. Most lakes in
Glacial lakes are lakes created by the direct action of glaciers and continental ice sheets. A wide variety of glacial processes create enclosed basins. As a result, there are a wide variety of different types of glacial lakes and it is often difficult to define clear-cut distinctions between different types of glacial lakes and lakes influenced by other activities. The general types of glacial lakes that have been recognized are lakes in direct contact with ice, glacially carved rock basins and depressions, morainic and outwash lakes, and glacial drift basins. Glacial lakes are the most numerous lakes in the world. Most lakes in northern Europe
The northern region of Europe has several definitions. A restrictive definition may describe Northern Europe as being roughly north of the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, which is about 54th parallel north, 54°N, or may be based on other g ...
and North America have been either influenced or created by the latest, but not last, glaciation, to have covered the region. Glacial lakes include proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around the ...
s, subglacial lake
A subglacial lake is a lake that is found under a glacier, typically beneath an ice cap or ice sheet. Subglacial lakes form at the boundary between ice and the underlying bedrock, where gravitational pressure decreases the pressure melting point ...
s, finger lake
A finger lake, also known as a fjord lake or trough lake, is "a narrow linear body of water occupying a Overdeepening, glacially overdeepened valley and sometimes impounded by a Terminal moraine, morainic dam."Kotlyakov and Komarova (2007), 255. ...
s, and epishelf lakes. Epishelf lakes are highly stratified lakes in which a layer of freshwater, derived from ice and snow melt, is dammed behind an ice shelf
An ice shelf is a large floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic. The b ...
that is attached to the coastline. They are mostly found in Antarctica.
Fluvial lakes
Fluvial (or riverine) lakes are lakes produced by running water. These lakes include plunge pool lakes, fluviatile dams and meander lakes.Oxbow lakes
 The most common type of fluvial lake is a crescent-shaped lake called an ''
The most common type of fluvial lake is a crescent-shaped lake called an ''oxbow lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called '' resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are call ...
'' due to the distinctive curved shape. They can form in river valleys as a result of meandering. The slow-moving river forms a sinuous shape as the outer side of bends are eroded away more rapidly than the inner side. Eventually a horseshoe bend is formed and the river cuts through the narrow neck. This new passage then forms the main passage for the river and the ends of the bend become silted up, thus forming a bow-shaped lake. Their crescent shape gives oxbow lakes a higher perimeter to area ratio than other lake types.
Fluviatile dams
These form where sediment from a tributary blocks the main river.Lateral lakes
These form where sediment from the main river blocks a tributary, usually in the form of alevee
A levee (), dike (American English), dyke (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English), embankment, floodbank, or stop bank is a structure that is usually soil, earthen and that often runs parallel (geometry), parallel to ...
.
Floodplain lakes
Lakes formed by other processes responsible forfloodplain
A floodplain or flood plain or bottomlands is an area of land adjacent to a river which stretches from the banks of its channel to the base of the enclosing valley walls, and which experiences flooding during periods of high discharge.Goudi ...
basin creation. During high floods they are flushed with river water. There are four types: 1. Confluent floodplain lake, 2. Contrafluent-confluent floodplain lake, 3. Contrafluent floodplain lake, 4. Profundal floodplain lake.
Solution lakes
A solution lake is a lake occupying a basin formed by surface dissolution of bedrock. In areas underlain by soluble bedrock, its solution by precipitation and percolating water commonly produce cavities. These cavities frequently collapse to formsinkhole
A sinkhole is a depression or hole in the ground caused by some form of collapse of the surface layer. The term is sometimes used to refer to doline, enclosed depressions that are locally also known as ''vrtače'' and shakeholes, and to openi ...
s that form part of the local karst topography
Karst is a topography formed from the dissolution of soluble rocks such as limestone, dolomite, and gypsum. It is characterized by underground drainage systems with sinkholes and caves. It has also been documented for more weathering-resistant ro ...
. Where groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
lies near the grounds surface, a sinkhole will be filled water as a solution lake. If such a lake consists of a large area of standing water that occupies an extensive closed depression in limestone, it is also called a karst lake
Karst lakes are formed as the result of a collapse of caves, especially in water-soluble rocks such as limestone, gypsum and dolomite. This process is known as karstification. They can cover areas of several 100 square kilometres. Their shallow l ...
. Smaller solution lakes that consist of a body of standing water in a closed depression within a karst region are known as ''karst ponds.''Neuendorf, K.K.E., Mehl Jr., J.P., and Jackson, J.A. (2005). ''Glossary of Geology,'' 5th revised and enlarged ed. Berlin: Springer. Approx. . Limestone caves often contain pools of standing water, which are known as ''underground lake
An underground lake or subterranean lake is a lake underneath the surface of the Earth. Most naturally occurring underground lakes are found in areas of Karst topography, where limestone or other soluble rock has been weathered away, leaving a cav ...
s.'' Classic examples of solution lakes are abundant in the karst regions at the Dalmatian coast
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, stretc ...
of Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
and within large parts of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
.
Landslide lakes
A landslide lake is created by the blockage of ariver valley
A valley is an elongated low area often running between hills or mountains, which will typically contain a river or stream running from one end to the other. Most valleys are formed by erosion of the land surface by rivers or streams over ...
by either mudflow
A mudflow or mud flow is a form of mass wasting involving fast-moving flow of debris that has become liquified by the addition of water. Such flows can move at speeds ranging from 3 meters/minute to 5 meters/second. Mudflows contain a significa ...
s, rockslide
A rockslide is a type of landslide caused by rock failure in which part of the bedding plane of failure passes through compacted rock and material collapses ''en masse'' and not in individual blocks. Note that a rockslide is similar to an avalanc ...
s, or scree
Scree is a collection of broken rock fragments at the base of a cliff or other steep rocky mass that has accumulated through periodic rockfall. Landforms associated with these materials are often called talus deposits. Talus deposits typically ha ...
s. Such lakes are most common in mountainous regions. Although landslide lakes may be large and quite deep, they are typically short-lived. An example of a landslide lake is Quake Lake
Quake Lake (officially Earthquake Lake) is a lake in the
western United States, on the Madison River in southwestern Montana. It was created after an earthquake struck on August 17, 1959, with 28 fatalities. Northwest of West Yellowstone, Qu ...
, which formed as a result of the 1959 Hebgen Lake earthquake.
Most landslide lakes disappear in the first few months after formation, but a landslide dam can burst suddenly at a later stage and threaten the population downstream when the lake water drains out. In 1911, an earthquake triggered a landslide that blocked a deep valley in the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world ...
region of Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, forming the Sarez Lake
Sarez Lake (russian: Сарезское озеро; tg, Сарез кӯл, Sarez Kūl) is a lake in Rushon District of Gorno-Badakhshan province, Tajikistan. Length about , depth few hundred meters, water surface elevation about above sea leve ...
. The Usoi Dam
The Usoi Dam is a natural landslide dam along the Murghab River (Tajikistan), Murghab River in Tajikistan. At high, it is the tallest dam in the world, either natural or man-made. The dam was created on February 18, 1911, when the 7.4-Surface wav ...
at the base of the valley has remained in place for more than 100 years but the terrain below the lake is in danger of a catastrophic flood if the dam were to fail during a future earthquake.
Tal-y-llyn Lake
Tal-y-llyn Lake, ( cy, Llyn Mwyngil), also known as Talyllyn Lake and Llyn Myngul, is a large glacial ribbon lake in Gwynedd, North Wales. It is formed by a post-glacial massive landslip damming up the lake within the glaciated valley. The hamle ...
in north Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
is a landslide lake dating back to the last glaciation in Wales some 20000 years ago.
Aeolian lakes
Aeolian lakes are produced by wind action. These lakes are found mainly inarid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ar ...
environments, although some aeolian lakes are relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
landforms indicative of arid paleoclimates. Aeolian lakes consist of lake basins dammed by wind-blown sand; interdunal lakes that lie between well-oriented sand dunes; and Blowout (geomorphology), deflation basins formed by wind action under previously arid paleoenvironments. Moses Lake in Washington (state), Washington, United States, was originally a shallow natural lake and an example of a lake basin dammed by wind-blown sand.
China's Badain Jaran Desert is a unique landscape of megadunes and elongated interdunal aeolian lakes, particularly concentrated in the southeastern margin of the desert.
Shoreline lakes
Shoreline lakes are generally lakes created by blockage of estuaries or by the uneven accretion of beach ridges by longshore and other currents. They include maritime coastal lakes, ordinarily in drowned estuaries; lakes enclosed by two tombolos or spits connecting an island to the mainland; lakes cut off from larger lakes by a bar; or lakes divided by the meeting of two spits.Organic lakes
Organic lakes are lakes created by the actions of plants and animals. On the whole they are relatively rare in occurrence and quite small in size. In addition, they typically ephemeral features relative to the other types of lakes. The basins in which organic lakes occur are associated with beaver dams, coral lakes, or dams formed by vegetation.Peat lakes
Peat lakes are a form of organic lake. They form where a buildup of partly decomposed plant material in a wet environment leaves the vegetated surface below thewater table
The water table is the upper surface of the zone of saturation. The zone of saturation is where the pores and fractures of the ground are saturated with water. It can also be simply explained as the depth below which the ground is saturated.
T ...
for a sustained period of time. They are often low in nutrients and mildly acidic, with bottom waters low in dissolved oxygen.
Anthropogenic lakes
Anthropogenic lakes are artificially created as a result of human activity. They can be formed by the intentional damming of rivers and streams or the subsequent filling of abandoned excavations by either ground water, precipitation, or a combination of both. The Upper Silesian region of Southern Poland contains an anthropogenic lake district consisting of more than 4,000 water bodies created by human activity. The diverse origins of these lakes include: reservoirs retained by dams, flooded mines, water bodies formed in subsidence basins and hollows, levee ponds, and residual water bodies following river regulation.Meteorite (extraterrestrial impact) lakes
Meteorite lakes, also known as ''crater lakes'' (not to be confused with #Volcanic lakes, volcanic crater lakes), are created by catastrophic Impact event, impacts with the Earth by extraterrestrial objects (either meteorites or asteroids). Examples of meteorite lakes are Lonar Lake in India, Lake El'gygytgyn in northeast Siberia, and the Pingualuit crater lake in Quebec, Canada. As in the cases of El'gygytgyn and Pingualuit, meteorite lakes can contain unique and scientifically valuable sedimentary deposits associated with long records of paleoclimatic changes.Other classification methods
 In addition to the mode of origin, lakes have been named and classified according to various other important factors such as thermal stratification, oxygen saturation, seasonal variations in lake volume and water level, salinity of the water mass, relative seasonal permanence, degree of outflow, and so on. The names used by the lay public and in the scientific community for different types of lakes are often informally derived from the morphology of the lakes' physical characteristics or other factors. Also, different cultures and regions of the world have their own popular nomenclature.
In addition to the mode of origin, lakes have been named and classified according to various other important factors such as thermal stratification, oxygen saturation, seasonal variations in lake volume and water level, salinity of the water mass, relative seasonal permanence, degree of outflow, and so on. The names used by the lay public and in the scientific community for different types of lakes are often informally derived from the morphology of the lakes' physical characteristics or other factors. Also, different cultures and regions of the world have their own popular nomenclature.
By thermal stratification
One important method of lake classification is on the basis of thermal stratification, which has a major influence on the animal and plant life inhabiting a lake, and the fate and distribution of dissolved and suspended material in the lake. For example, the thermal stratification, as well as the degree and frequency of mixing, has a strong control over the distribution of oxygen within the lake. Professor F.-A. Forel,Forel, F.A., 1901. ''Handbuch der Seenkunde. Allgemeine Limnologie.'' J. von Engelhorn, Stuttgart, Germany. also referred to as the "Father of limnology", was the first scientist to classify lakes according to their thermal stratification. His system of classification was later modified and improved upon by G. Evelyn Hutchinson, Hutchinson and Löffler. As the density of water varies with temperature, with a maximum at +4 degrees Celsius, thermal stratification is an important physical characteristic of a lake that controls the fauna and flora, sedimentation, chemistry, and other aspects of individual lakes. First, the colder, denser water typically forms a layer near the bottom, which is called the ''hypolimnion''. Second, normally overlying the hypolimnion is a transition zone known as the ''metalimnion''. Finally, overlying the metalimnion is a surface layer of warmer water with a lower density, called the ''epilimnion''. This typical stratification sequence can vary widely, depending on the specific lake or the time of year, or a combination of both. The classification of lakes by thermal stratification presupposes lakes with sufficient depth to form a hypolimnion; accordingly, very shallow lakes are excluded from this classification system. Based upon their thermal stratification, lakes are classified as either ''holomictic lake, holomictic'', with a uniform temperature and density from top to bottom at a given time of year, or ''meromictic lake, meromictic'', with layers of water of different temperature and density that do not intermix. The deepest layer of water in a meromictic lake does not contain any dissolved oxygen so there are no living aerobic organisms. Consequently, the layers of sediment at the bottom of a meromictic lake remain relatively undisturbed, which allows for the development of lacustrine deposits. In a holomictic lake, the uniformity of temperature and density allows the lake waters to completely mix. Based upon thermal stratification and frequency of turnover, holomictic lakes are divided into amictic lakes, cold monomictic lakes, dimictic lakes, warm monomictic lakes, polymictic lakes, and oligomictic lakes. Lake stratification does not always result from a variation in density because of thermal gradients. Stratification (water), Stratification can also result from a density variation caused by gradients in salinity. In this case, the hypolimnion and epilimnion are separated not by a thermocline but by a ''halocline'', which is sometimes referred to as a ''chemocline''.By seasonal variations in water level and volume
Lakes are informally classified and named according to the seasonal variation in their lake level and volume. Some of the names include: * Ephemeral lake is a short-lived lake or pond. If it fills with water and dries up (disappears) seasonally it is known as an ''intermittent lake''Poehls, D.J. and Smith, G.J. eds. (2009). ''Encyclopedic dictionary of hydrogeology.'' Academic Press. p. 517. They often fill poljes. * Dry lake is a popular name for an ephemeral lake that contains water only intermediately at irregular and infrequent intervals.Last, W.M. and Smol, J.P. (2001). ''Tracking environmental change using lake sediments. Volume 1: basin analysis, coring, and chronological techniques.'' Springer Science & Business Media. * Perennial lake is a lake that has water in its basin throughout the year and is not subject to extreme fluctuations in level.Gangstad, E.O., (1979)''Glossary of Biolimnological Terms''
Washington, DC, United States Army Corps of Engineers. * Playa lake is a typically shallow, intermittent lake that covers or occupies a playa either in wet seasons or in especially wet years but subsequently drying up in an arid or semiarid region. * Vlei is a name used in South Africa for a shallow lake which varies considerably in level with the seasons.Theal, G.M., 1877. ''Compendium of South African history and geography, 3rd.'' Institution Press, Lovedale, South Africa.
By water chemistry
Lakes may be informally classified and named according to the general chemistry of their water mass. Using this classification method, the lake types include: * An ''acid lake'' contains water with a below-neutral pH of less than 6.5. A lake is considered to be highly acidic if its pH drops below 5.5, leading to biological consequences. Such lakes include: acidic ''pit lakes'' occupying abandoned mines and excavations; naturally acidic lakes of Igneous rock, igneous and Metamorphic rock, metamorphic landscapes; Raised bog, peat bogs in northern regions; ''crater lakes'' of active and dormant volcanoes; and lakes acidified by acid rain.Geller, W. et al. (eds.) (2013). ''Acidic Pit Lakes, Environmental Science and Engineering'', Springer-Verlag Berlin HeidelbergRouwet, D. et al. (eds.) (2015). ''Volcanic Lakes, Advances in Volcanology,'' Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg * A ''salt lake'', also known as a ''saline lake'' or ''brine lake'', is an inland body of water situated in an arid or semiarid region, with no outlet to the sea, containing a high concentration of dissolved neutral salts (principally sodium chloride). Examples include the Great Salt Lake in Utah, and the Dead Sea in southwestern Asia. * An ''alkali sink'', also known as an ''alkali flat'' or ''salt flat'', is a shallow saline feature that can be found in low-lying areas of arid regions and in groundwater discharge zones. These features are typically classified as ''dry lakes'', or ''playas'', because they are periodically flooded by rain or flood events and then dry up during drier intervals, leaving accumulations of brines and evaporitic minerals. * A ''Salt pan (geology), salt pan'' is a small shallow natural depression in which water accumulates and evaporates, leaving a salt deposit, or the shallow lake of brackish water that occupies a salt pan. (The term "salt pan" comes from open-pan salt making, a method of extracting salt from brine using large open pans.) * A ''saline pan'' is another name for an ephemeral acid saline lake which precipitates a bottom crust that is subsequently modified during subaerial exposure.Composed of other liquids
* Lava lake is a large volume of molten lava, usually basaltic, contained in a volcanic vent, crater, or broad depression. * Lakes of Titan, Hydrocarbon lakes are bodies of liquid ethane and methane that occupy depressions on the surface of Titan. They were detected by the Cassini–Huygens space probe.Paleolakes
A paleolake (also palaeolake) is a lake that existed in the past when hydrological conditions were different. Quaternary paleolakes can often be identified on the basis ofrelict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
lacustrine landforms, such as relict lake plains and coastal landforms that form recognizable relict shorelines called ''paleoshorelines.'' Paleolakes can also be recognized by characteristic sedimentary deposits that accumulated in them and any fossils that might be contained in these sediments. The paleoshorelines and sedimentary deposits of paleolakes provide evidence for prehistoric hydrological changes during the times that they existed.Goudie, A. (2008). "Arid Climates and Indicators". Gornitz, V. ed., ''Encyclopedia of paleoclimatology and ancient environments''. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 45–51.
There are two types of paleolake:
* A :Former lakes, former lake is a paleolake that no longer exists. Such lakes include prehistoric lakes and those that have permanently dried up, often as the result of either evaporation or human intervention. An example of a former lake is Owens Lake in California, United States. Former lakes are a common feature of the Basin and Range Province, Basin and Range area of southwestern North America.
* A shrunken lake is a paleolake that still exists but has considerably decreased in size over geological time. An example of a shrunken lake is Lake Agassiz, which once covered much of central North America. Two notable remnants of Lake Agassiz are Lake Winnipeg and Lake Winnipegosis.
Paleolakes are of scientific and economic importance. For example, Quaternary paleolakes in semidesert basins are important for two reasons: they played an extremely significant, if transient, role in shaping the floors and piedmont (geography), piedmonts of many basins; and their sediments contain enormous quantities of geologic and paleontologic information concerning past environments. In addition, the organic-rich deposits of pre-Quaternary paleolakes are important either for the thick deposits of oil shale and shale gas contained in them, or as source rocks of petroleum and natural gas. Although of significantly less economic importance, strata deposited along the shore of paleolakes sometimes contain coal seams.Gierlowski-Kordesch, E. and Kelts, K.R. eds. (2000). ''Lake Basins Through Space and Time''. AAPG Studies in Geology 46 (No. 46). The American Association of Petroleum Geologists, Tulsa, OK
Characteristics
 Lakes have numerous features in addition to lake type, such as drainage basin (also known as catchment area), inflow and outflow, nutrient content, dissolved oxygen, water pollution, pollutants, pH, and
Lakes have numerous features in addition to lake type, such as drainage basin (also known as catchment area), inflow and outflow, nutrient content, dissolved oxygen, water pollution, pollutants, pH, and sediment
Sediment is a naturally occurring material that is broken down by processes of weathering and erosion, and is subsequently transported by the action of wind, water, or ice or by the force of gravity acting on the particles. For example, sand an ...
ation.
Changes in the level of a lake are controlled by the difference between the input and output compared to the total volume of the lake. Significant input sources are precipitation onto the lake, runoff carried by streams and channels from the lake's drainage basin, catchment area, groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
channels and aquifers, and artificial sources from outside the catchment area. Output sources are evaporation from the lake, surface and groundwater flows, and any extraction of lake water by humans. As climate conditions and human water requirements vary, these will create fluctuations in the lake level.
Lakes can be also Trophic state index, categorized on the basis of their richness in nutrients, which typically affect plant growth. Nutrient-poor lakes are said to be ''oligotrophic'' and are generally clear, having a low concentration of plant life. ''Mesotrophic lakes'' have good clarity and an average level of nutrients. ''Eutrophic'' lakes are enriched with nutrients, resulting in good plant growth and possible algal blooms. ''eutrophication, Hypertrophic'' lakes are bodies of water that have been excessively enriched with nutrients. These lakes typically have poor clarity and are subject to devastating algal blooms. Lakes typically reach this condition due to human activities, such as heavy use of fertilizers in the lake catchment area. Such lakes are of little use to humans and have a poor ecosystem due to decreased dissolved oxygen.
Due to the unusual relationship between water's temperature and its density, lakes form layers called thermoclines, layers of drastically varying temperature relative to depth. Fresh water is most dense at about 4 degrees Celsius (39.2 °F) at sea level. When the temperature of the water at the surface of a lake reaches the same temperature as deeper water, as it does during the cooler months in temperate climates, the water in the lake can mix, bringing oxygen-starved water up from the depths and bringing oxygen down to decomposing sediments. Deep temperate lakes can maintain a reservoir of cold water year-round, which allows some cities to tap that reservoir for deep lake water cooling.
Limnology
Biological properties
 Lake zones:
* ''Epilittoral'': The zone that is entirely above the lake's normal water level and never submerged by lake water
* ''Littoral'': The zone that encompasses the small area above the normal water level (which is sometimes submerged when the lake's water level increases), reaching to the deepest part of the lake that still allows for submerged Aquatic plant, macrophytic growth
* ''Littoriprofundal'': Transition zone commonly aligned with stratified lakes' metalimnions – too deep for macrophytes but includes photosynthetic algae and bacteria
* ''Profundal'': Sedimentary zone containing no vegetation
Algal community types:
* ''Epipelic'': Algae that grow on sediments
* ''Epilithic'': Algae that grow on rocks
* ''Epipsammic'': Algae that grow on (or within) sand
* ''Epiphytic'': Algae that grow on macrophytes
* ''Epizooic'': Algae that grow on living animals
* ''Metaphyton'': Algae present in the littoral zone, not in a state of suspension nor attached to a substratum (such as a macrophyte)
Lake zones:
* ''Epilittoral'': The zone that is entirely above the lake's normal water level and never submerged by lake water
* ''Littoral'': The zone that encompasses the small area above the normal water level (which is sometimes submerged when the lake's water level increases), reaching to the deepest part of the lake that still allows for submerged Aquatic plant, macrophytic growth
* ''Littoriprofundal'': Transition zone commonly aligned with stratified lakes' metalimnions – too deep for macrophytes but includes photosynthetic algae and bacteria
* ''Profundal'': Sedimentary zone containing no vegetation
Algal community types:
* ''Epipelic'': Algae that grow on sediments
* ''Epilithic'': Algae that grow on rocks
* ''Epipsammic'': Algae that grow on (or within) sand
* ''Epiphytic'': Algae that grow on macrophytes
* ''Epizooic'': Algae that grow on living animals
* ''Metaphyton'': Algae present in the littoral zone, not in a state of suspension nor attached to a substratum (such as a macrophyte)
Circulation
Flora and fauna
Disappearance
 The lake may be infilled with deposited sediment and gradually become a wetland such as a swamp or marsh. Large water plants, typically Phragmites, reeds, accelerate this closing process significantly because they partially decompose to form peat soils that fill the shallows. Conversely, peat soils in a marsh can naturally burn and reverse this process to recreate a shallow lake resulting in a dynamic equilibrium between marsh and lake. This is significant since wildfire has been largely suppressed in the developed world over the past century. This has artificially converted many shallow lakes into emergent marshes. Turbid lakes and lakes with many plant-eating fish tend to disappear more slowly. A "disappearing" lake (barely noticeable on a human timescale) typically has extensive plant mats at the water's edge. These become a new habitat for other plants, like Sphagnum, peat moss when conditions are right, and animals, many of which are very rare. Gradually, the lake closes and young peat may form, forming a fen. In lowland river valleys where a river can meander, the presence of peat is explained by the infilling of historical
The lake may be infilled with deposited sediment and gradually become a wetland such as a swamp or marsh. Large water plants, typically Phragmites, reeds, accelerate this closing process significantly because they partially decompose to form peat soils that fill the shallows. Conversely, peat soils in a marsh can naturally burn and reverse this process to recreate a shallow lake resulting in a dynamic equilibrium between marsh and lake. This is significant since wildfire has been largely suppressed in the developed world over the past century. This has artificially converted many shallow lakes into emergent marshes. Turbid lakes and lakes with many plant-eating fish tend to disappear more slowly. A "disappearing" lake (barely noticeable on a human timescale) typically has extensive plant mats at the water's edge. These become a new habitat for other plants, like Sphagnum, peat moss when conditions are right, and animals, many of which are very rare. Gradually, the lake closes and young peat may form, forming a fen. In lowland river valleys where a river can meander, the presence of peat is explained by the infilling of historical oxbow lake
An oxbow lake is a U-shaped lake or pool that forms when a wide meander of a river is cut off, creating a free-standing body of water. In South Texas, oxbows left by the Rio Grande are called '' resacas''. In Australia, oxbow lakes are call ...
s. In the final stages of Ecological succession, succession, trees can grow in, eventually turning the wetland into a forest.
Some lakes can disappear seasonally. These are called intermittent lakes, ephemeral lakes, or seasonal lakes and can be found in Karst, karstic terrain. A prime example of an intermittent lake is Lake Cerknica in Slovenia or Lag Prau Pulte in Graubünden. Other intermittent lakes are only the result of above-average precipitation in a closed, or endorheic basin
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
, usually filling dry lake beds. This can occur in some of the driest places on earth, like Death Valley. This occurred in the spring of 2005, after unusually heavy rains. The lake did not last into the summer, and was quickly evaporated (see photos to right). A more commonly filled lake of this type is Sevier Lake of west-central Utah.
Sometimes a lake will disappear quickly. On 3 June 2005, in Nizhny Novgorod Oblast, Russia, a lake called Lake Beloye (Nizhny Novgorod Oblast), Lake Beloye vanished in a matter of minutes. News sources reported that government officials theorized that this strange phenomenon may have been caused by a shift in the soil underneath the lake that allowed its water to drain through channels leading to the Oka River.
The presence of ground permafrost is important to the persistence of some lakes. Thawing permafrost may explain the shrinking or disappearance of hundreds of large Arctic lakes across western Siberia. The idea here is that rising air and soil temperatures thaw permafrost, allowing the lakes to drain away into the ground.
Some lakes disappear because of human development factors. The shrinking Aral Sea is described as being "murdered" by the diversion for irrigation of the rivers feeding it.
Extraterrestrial lakes
 Only one astronomical body other than Earth is known to harbor large lakes: Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Photographs and spectroscopic analysis by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft show liquid ethane on the surface, which is thought to be mixed with liquid methane. The largest lake on Titan is Kraken Mare which, at an estimated 400,000 km2, is roughly five times the size of Lake Superior (~80,000 km2) and nearly the size of all five Great Lakes of North America combined. The second largest Titanean lake, Ligeia Mare, is almost twice the size of Lake Superior, at an estimated 150,000 km2.
Jupiter's large moon Io (moon), Io is volcanically active, leading to the accumulation of sulfur deposits on the surface. Some photographs taken during the Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' mission appear to show lakes of liquid sulfur in volcanic caldera, though these are more analogous to lakes of lava than of water on Earth.
The planet Mars has only one confirmed lake which is underground and near the south pole. Although the surface of Mars is too cold and has too little atmospheric pressure to permit permanent surface water, geologic evidence appears to confirm that ancient lakes once formed on the surface.
There are dark basaltic plains on the Moon, similar to lunar mare, lunar maria but smaller, which are called ''lacus'' (singular ''lacus'', Latin for "lake") because they were thought by early astronomers to be lakes of water.
Only one astronomical body other than Earth is known to harbor large lakes: Saturn's largest moon, Titan. Photographs and spectroscopic analysis by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' spacecraft show liquid ethane on the surface, which is thought to be mixed with liquid methane. The largest lake on Titan is Kraken Mare which, at an estimated 400,000 km2, is roughly five times the size of Lake Superior (~80,000 km2) and nearly the size of all five Great Lakes of North America combined. The second largest Titanean lake, Ligeia Mare, is almost twice the size of Lake Superior, at an estimated 150,000 km2.
Jupiter's large moon Io (moon), Io is volcanically active, leading to the accumulation of sulfur deposits on the surface. Some photographs taken during the Galileo spacecraft, ''Galileo'' mission appear to show lakes of liquid sulfur in volcanic caldera, though these are more analogous to lakes of lava than of water on Earth.
The planet Mars has only one confirmed lake which is underground and near the south pole. Although the surface of Mars is too cold and has too little atmospheric pressure to permit permanent surface water, geologic evidence appears to confirm that ancient lakes once formed on the surface.
There are dark basaltic plains on the Moon, similar to lunar mare, lunar maria but smaller, which are called ''lacus'' (singular ''lacus'', Latin for "lake") because they were thought by early astronomers to be lakes of water.
Notable lakes on Earth
 * The largest lake by surface area is
* The largest lake by surface area is Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
, which is despite its name considered as a lake from the point of view of geography. Its surface area is 143,000 sq. mi./371,000 km2.
* The second largest lake by surface area, and the largest freshwater lake by surface area, is Lake Michigan-Huron, which is hydrologically a single lake. Its surface area is 45,300 sq. mi./117,400 km2. For those who consider Lake Michigan-Huron to be separate lakes, and Caspian Sea to be a sea, Lake Superior would be the largest lake at 82,100 km2 (31,700 square miles)
* Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
is the deepest lake in the world, located in Siberia, with a bottom at . Its mean depth is also the greatest in the world ().It is also the world's largest freshwater lake by volume (, but much smaller than the Caspian Sea at ), and the second longest (about from tip to tip). * The world's ancient lake, oldest lake is
Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
, followed by Lake Tanganyika in Tanzania. Lake Maracaibo is considered by some to be the second-oldest lake on Earth, but since it lies at sea level and nowadays is a contiguous body of water with the sea, others consider that it has turned into a small bay.
* The longest lake is Lake Tanganyika, with a length of about (measured along the lake's center line).It is also the third largest by volume, the second oldest, and the second deepest () in the world, after Lake Baikal. * The world's highest lake, if size is not a criterion, may be the crater lake of Ojos del Salado, at . * The highest large (greater than ) lake in the world is the Lake Puma Yumco, Pumoyong Tso (Pumuoyong Tso), in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, at , above sea level. * The world's highest commercially navigable lake is Lake Titicaca in Peru and Bolivia at . It is also the largest lake in South America. * The world's lowest lake is the
Dead Sea
The Dead Sea ( he, יַם הַמֶּלַח, ''Yam hamMelaḥ''; ar, اَلْبَحْرُ الْمَيْتُ, ''Āl-Baḥrū l-Maytū''), also known by other names, is a salt lake bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and the West Bank ...
, bordered by Jordan to the east and Israel and State of Palestine, Palestine to the west, at below sea level. It is also one of the lakes with highest salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quantitie ...
concentration.
* Lake Michigan–Huron has the longest lake coastline in the world: about , excluding the coastline of its many inner islands. Even if it is considered two lakes, Lake Huron alone would still have the longest coastline in the world at .
* The largest island in a lake is Manitoulin Island in Lake Michigan–Huron, Lake Michigan-Huron, with a surface area of . Lake Manitou, on Manitoulin Island, is the largest lake on an island in a lake.
* The largest lake on an island is Nettilling Lake on Baffin Island, with an area of and a maximum length of .
* The largest lake in the world that drains naturally in two directions is Wollaston Lake.
* Lake Toba on the island of Sumatra is in what is probably the largest resurgent caldera on Earth.
* The largest lake completely within the boundaries of a single city is Lake Wanapitei in the city of Greater Sudbury, Sudbury, Ontario, Canada. Before the current city boundaries came into effect in 2001, this status was held by Lake Ramsey, also in Sudbury.
* Lake Enriquillo in Dominican Republic is the only saltwater lake in the world inhabited by crocodiles.
* Lake Bernard, Ontario, Canada, claims to be the largest lake in the world with no islands.
* Lake Saimaa in both South Savonia and South Karelia, Finland, forms the much larger Saimaa basin, which have more shorelines per unit of area than anywhere else in the world, with the total length being nearly .
* The largest lake in one country is Lake Michigan, in the United States. However, it is sometimes considered part of Lake Michigan-Huron, making the record go to Great Bear Lake, Northwest Territories, in Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, the largest lake within one jurisdiction.
* The largest lake on an island in a lake on an island is Crater Lake on Vulcano Island in Lake Taal on the island of Luzon, The Philippines.
* The northernmost named lake on Earth is Upper Dumbell Lake in the Qikiqtaaluk Region of Nunavut, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
at a latitude of 82°28'N. It is southwest of Alert, Nunavut, Alert, the northernmost settlement in the world. There are also several small lakes north of Upper Dumbell Lake, but they are all unnamed and only appear on very detailed maps.
Largest by continent
The largest lakes (surface area) by continent are: * Australia –Lake Eyre
Lake Eyre ( ), officially known as Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre, is an endorheic lake in east-central Far North South Australia, some north of Adelaide. The shallow lake is the depocentre of the vast endorheic Lake Eyre basin, and contains the ...
(salt lake)
* Africa – Lake Victoria, also the third-largest freshwater lake on Earth. It is one of the Great Lakes of Africa.
* Antarctica – Lake Vostok (subglacial)
* Asia – Lake Baikal
Lake Baikal (, russian: Oзеро Байкал, Ozero Baykal ); mn, Байгал нуур, Baigal nuur) is a rift lake in Russia. It is situated in southern Siberia, between the federal subjects of Irkutsk Oblast to the northwest and the Repu ...
(if the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central Asia ...
is considered a lake, it is the largest in Eurasia, but is divided between the two geographic continents)
* Oceania – Lake Eyre
Lake Eyre ( ), officially known as Kati Thanda–Lake Eyre, is an endorheic lake in east-central Far North South Australia, some north of Adelaide. The shallow lake is the depocentre of the vast endorheic Lake Eyre basin, and contains the ...
when filled; the largest permanent (and freshwater) lake in Oceania is Lake Taupo.
* Europe – Lake Ladoga, followed by Lake Onega, both in northwestern Russia.
* North America – Lake Michigan–Huron, which is hydrologically a single lake. However, lakes Lake Huron, Huron and Lake Michigan, Michigan are usually considered separate lakes, in which case Lake Superior would be the largest.
* South America – Lake Titicaca, which is also the highest navigable body of water on Earth at above sea level. The much larger Lake Maracaibo is much older, but perceived by some to no longer be genuinely a lake for multiple reasons.
See also
Notes
References
External links
ILEC World Lake Database
LakeNet Global Lake Database
{{Authority control Lakes, Bodies of water Lacustrine landforms