Lab colour space on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

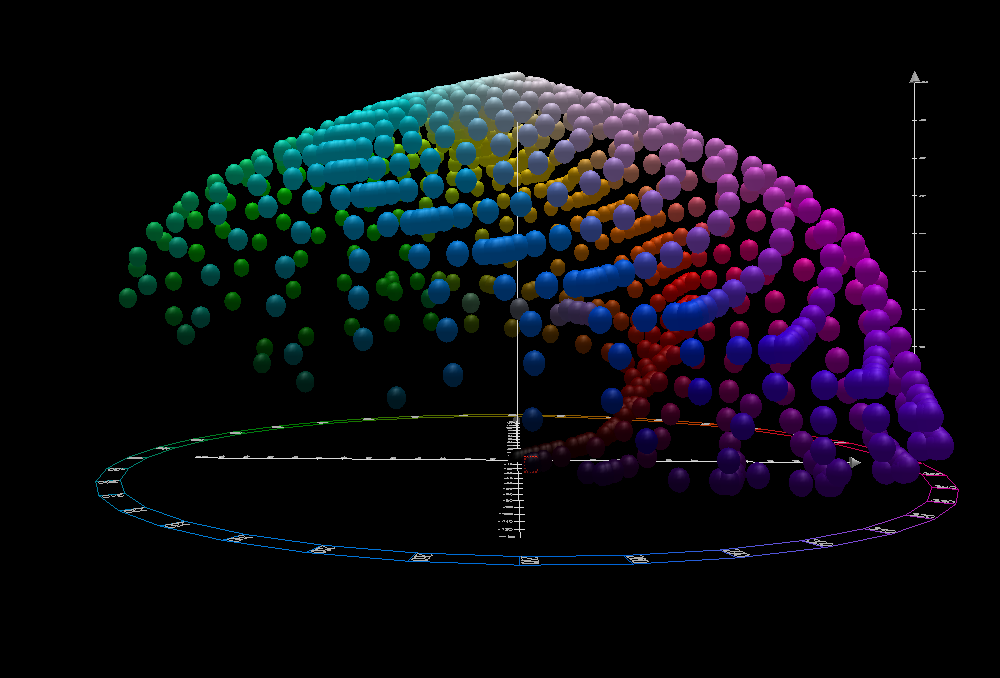
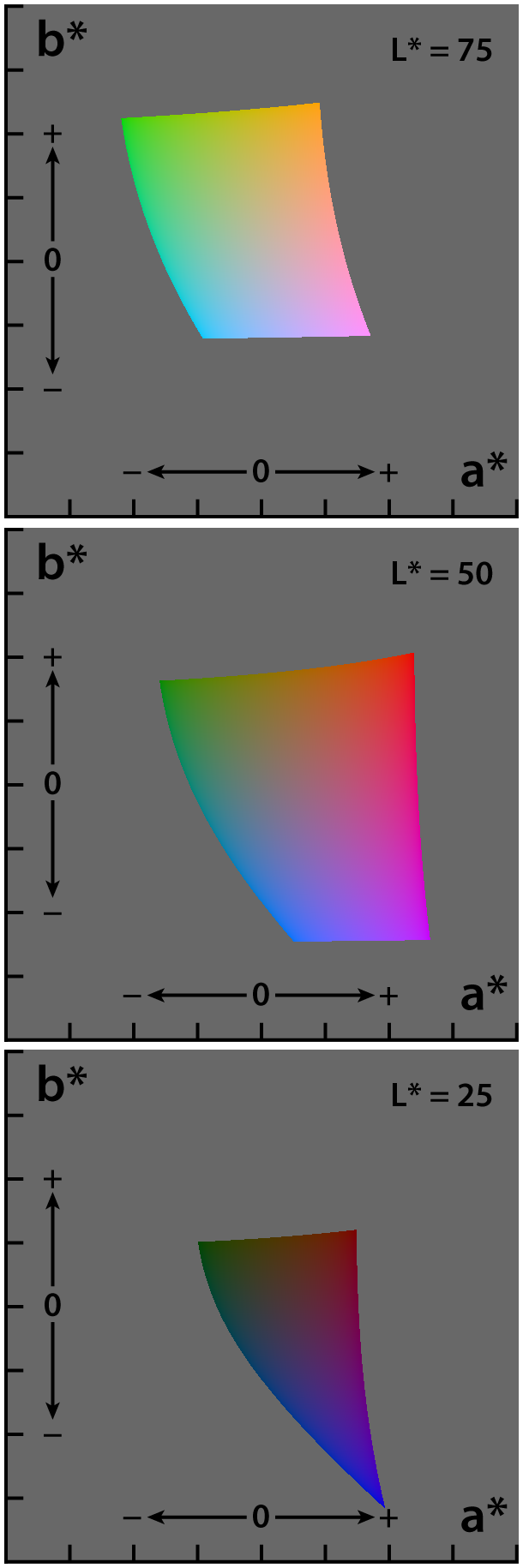 The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'', is a
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'', is a
Specification ICC.1:2004-10 (Profile version 4.2.0.0)
Image technology color management — Architecture, profile format and data structure,'' (2006). While the intention behind CIELAB was to create a space that was more perceptually uniform than CIEXYZ using only a simple formula, CIELAB is known to lack perceptual uniformity, particularly in the area of blue hues. The asterisks (*) after ''L*'', ''a*,'' and ''b*'' are pronounced ''star'' and are part of the full name to distinguish ''L''*''a''*''b''* from Hunter's ''Lab'', described below. Since the ''L*a*b*'' model has three axes, it requires a three-dimensional space to be represented completely. Also, because each axis is non-linear, it is not possible to create a two-dimensional chromaticity diagram. Additionally, the visual representations shown in the plots of the full CIELAB gamut on this page are an approximation, as it is impossible for a monitor to display the full gamut of LAB colors.
TIFF: Revision 6.0
'' Adobe Developers Association, 1992 * CIELAB (any white point) is available in
Demonstrative color conversion applet
CIE Colorimetry 15-3
CIE Technical Report Colorimetry 15 third edition (2004). An authoritative reference.
Whitepaper on understanding colors
by X-rite. {{Color space Color space 1976 introductions


 The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'', is a
The CIELAB color space, also referred to as ''L*a*b*'', is a color space
A color space is a specific organization of colors. In combination with color profiling supported by various physical devices, it supports reproducible representations of colorwhether such representation entails an analog or a digital represe ...
defined by the International Commission on Illumination
The International Commission on Illumination (usually abbreviated CIE for its French name Commission internationale de l'éclairage) is the international authority on light, illumination, colour, and colour spaces. It was established in 1913 a ...
(abbreviated CIE) in 1976. It expresses color as three values: ''L*'' for perceptual lightness and ''a*'' and ''b*'' for the four unique colors of human vision: red, green, blue and yellow. CIELAB was intended as a perceptually uniform space, where a given numerical change corresponds to a similar perceived change in color. While the LAB space is not truly perceptually uniform, it nevertheless is useful in industry for detecting small differences in color.
Like the CIEXYZ
In 1931, the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) published the CIE 1931 color spaces which define the relationship between the visible spectrum and human color vision. The CIE color spaces are mathematical models that comprise a "stan ...
space it derives from, CIELAB color space is a device-independent, "standard observer" model. The colors it defines are not relative to any particular device such as a computer monitor or a printer, but instead relate to the CIE standard observer which is an averaging of the results of color matching experiments under laboratory conditions.
Coordinates
The CIELAB space is three-dimensional and covers the entiregamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. cam ...
(range) of human color perception. It is based on the opponent model of human vision, where red and green form an opponent pair and blue and yellow form an opponent pair. This makes CIELAB a Hering opponent color space. The nature of the transformations also characterizes it as a chromatic value color space. The lightness value, ''L*'' (pronounced "L star"), defines black at 0 and white at 100. The ''a*'' axis is relative to the green–red opponent colors, with negative values toward green and positive values toward red. The ''b*'' axis represents the blue–yellow opponents, with negative numbers toward blue and positive toward yellow.
The lightness value, ''L*'' in CIELAB is calculated using the cube root of the relative luminance
Relative luminance Y follows the Luminance, photometric definition of luminance L including spectral weighting for human vision, but while luminance L is a measure of light in units such as cd/m^2, relative luminance Y values are normalized as ...
with an offset near black. This results in an ''effective'' power curve with an exponent of approximately 0.43 which represents the human eye's response to light under daylight (photopic
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under well-lit conditions (luminance levels from 10 to 108 cd/m2). In humans and many other animals, photopic vision allows color perception, mediated by cone cells, and a significantly higher vis ...
) conditions.
The ''a*'' and ''b*'' axes are unbounded and depending on the reference white they can easily exceed ±150 to cover the human gamut. Nevertheless, software implementations often clamp these values for practical reasons. For instance, if integer math is being used it is common to clamp ''a*'' and ''b*'' in the range of −128 to 127.
CIELAB is calculated relative to a reference white, for which the CIE recommends the use of CIE Standard illuminant
A standard illuminant is a theoretical source of visible light with a spectral power distribution that is published. Standard illuminants provide a basis for comparing images or colors recorded under different lighting.
CIE illuminants
The Inte ...
D65. D65 is used in the vast majority of industries and applications, with the notable exception being the printing industry which uses D50. The International Color Consortium
The International Color Consortium (ICC) was formed in 1993 by eight vendors in order to create an open, vendor-neutral color management system which would function transparently across all operating systems and software packages.
Overview
Th ...
largely supports the printing industry and uses D50 with either CIEXYZ or CIELAB in the Profile Connection Space, for v2 and v4 ICC profiles.International Color Consortium, Specification ICC.1:2004-10 (Profile version 4.2.0.0)
Image technology color management — Architecture, profile format and data structure,'' (2006). While the intention behind CIELAB was to create a space that was more perceptually uniform than CIEXYZ using only a simple formula, CIELAB is known to lack perceptual uniformity, particularly in the area of blue hues. The asterisks (*) after ''L*'', ''a*,'' and ''b*'' are pronounced ''star'' and are part of the full name to distinguish ''L''*''a''*''b''* from Hunter's ''Lab'', described below. Since the ''L*a*b*'' model has three axes, it requires a three-dimensional space to be represented completely. Also, because each axis is non-linear, it is not possible to create a two-dimensional chromaticity diagram. Additionally, the visual representations shown in the plots of the full CIELAB gamut on this page are an approximation, as it is impossible for a monitor to display the full gamut of LAB colors.
Perceptual differences
The nonlinear relations for ''L*'', ''a*'' and ''b*'' are intended to mimic the nonlinear response of the visual system. Furthermore, uniform changes of components in the ''L*a*b*'' color space aim to correspond to uniform changes in perceived color, so the relative perceptual differences between any two colors in ''L*a*b*'' can be approximated by treating each color as a point in a three-dimensional space (with three components: ''L*'', ''a*'', ''b*'') and taking theEuclidean distance
In mathematics, the Euclidean distance between two points in Euclidean space is the length of the line segment between them. It can be calculated from the Cartesian coordinates of the points using the Pythagorean theorem, and therefore is o ...
between them.
RGB and CMYK conversions
In order to convert RGB orCMYK
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
values to or from ''L*a*b*'', the RGB or CMYK data must be linearized relative to light. The reference illuminant of the RGB or CMYK data must be known, as well as the RGB primary coordinates or the CMYK printer's reference data in the form of a color lookup table (CLUT).
In color managed systems, ICC profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes o ...
s contains these needed data, which are then used to perform the conversions.
Range of coordinates
As mentioned previously, the ''L''* coordinate nominally ranges from 0 to 100. The range of ''a''* and ''b''* coordinates is technically unbounded, though it is commonly clamped to the range of −128 to 127 for use with integer code values, though this results in potentially clipping some colors depending on the size of the source color space. The gamut's large size and inefficient utilization of the coordinate space means the best practice is to use floating-point values for all three coordinates.Advantages
Unlike the RGB andCMYK
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
color models, CIELAB is designed to approximate human vision. The ''L*'' component closely matches human perception of lightness, though it does not take the Helmholtz–Kohlrausch effect
The Helmholtz–Kohlrausch effect (named after Hermann von Helmholtz and V. A. Kohlrausch) is a perceptual phenomenon wherein the intense saturation of spectral hue is perceived as part of the color's luminance. This brightness increase by sat ...
into account. CIELAB is less uniform in the color axes, but is useful for predicting small differences in color.
The CIELAB coordinate space represents the entire gamut
In color reproduction and colorimetry, a gamut, or color gamut , is a convex set containing the colors that can be accurately represented, i.e. reproduced by an output device (e.g. printer or display) or measured by an input device (e.g. cam ...
of human photopic (daylight) vision and far exceeds the gamut for sRGB or CMYK. In an integer implementation such as TIFF, ICC or Photoshop, the large coordinate space results in substantial data inefficiency due to unused code values. Only about 35% of the available coordinate code values are inside the CIELAB gamut with an integer format.
Using CIELAB in an 8-bit per channel integer format typically results in significant quantization errors. Even 16-bit per channel can result in clipping, as the full gamut extends past the bounding coordinate space. Ideally, CIELAB should be used with floating-point data to minimize obvious quantization errors.
CIE standards and documents are copyrighted by the CIE and must be purchased; however, the formulas for CIELAB are available on the CIE website.
Converting between CIELAB and CIE XYZ coordinates
From CIE XYZ to CIELAB
: where ''t'' is or : : , , and describe the color stimulus considered and , , describe a specified white achromatic reference illuminant. for the CIE 1931 (2°) standard colorimetric observer and assuming normalization where the reference white has , the values are: For Standard Illuminant D65: : For illuminant D50, which is used in the printing industry: : The division of the domain of the function into two parts was done to prevent an infinite slope at . The function was assumed to be linear below some and was assumed to match the part of the function at in both value and slope. In other words: : The intercept was chosen so that would be 0 for : . The above two equations can be solved for and : : where .From CIELAB to CIEXYZ
The reverse transformation is most easily expressed using the inverse of the function ''f'' above: : where : and where .Cylindrical model
The "CIELCh" or "CIEHLC" space is a color space based on CIELAB, which uses thepolar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are
*the point's distance from a reference ...
''C''* ( chroma, colorfulness of the color) and ''h''° (hue angle, angle of the hue in the CIELAB color wheel) instead of the Cartesian coordinates
In geometry, a Cartesian coordinate system (, ) in a plane is a coordinate system that specifies each point uniquely by a pair of real numbers called ''coordinates'', which are the signed distances to the point from two fixed perpendicular o ...
''a''* and ''b''*. The CIELAB lightness L* remains unchanged.
The conversion of ''a''* and ''b''* to ''C''* and ''h''° is performed as follows:
:
Conversely, given the polar coordinates
In mathematics, the polar coordinate system specifies a given point (mathematics), point in a plane (mathematics), plane by using a distance and an angle as its two coordinate system, coordinates. These are
*the point's distance from a reference ...
, conversion to Cartesian coordinates is achieved with:
:
The LCh (or HLC) color space is not the same as the HSV, HSL or HSB color models, although their values can also be interpreted as a base color, saturation and lightness of a color. The HSL values are a polar coordinate transformation of what is technically defined RGB cube color space. LCh is still perceptually uniform.
Further, ''H'' and ''h'' are not identical, because HSL space uses as primary colors the three additive primary colors red, green and blue (''H'' = 0, 120, 240°). Instead, the LCh system uses the four colors red, yellow, green and blue (''h'' = 0, 90, 180, 270°). Regardless the angle ''h'', ''C'' = 0 means the achromatic colors (non saturated), that is, the gray axis.
The simplified spellings LCh, LCh(ab), LCH, LCH(ab) and HLC are common, but the letter presents a different order. HCL color space (Hue-Chroma-Luminance) on the other hand is a commonly used alternative name for the L*C*h(uv) color space, also known as the ''cylindrical representation'' or ''polar CIELUV''. This name is commonly used by information visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating Graphics, graphic or visual Representation (arts), representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and i ...
practitioners who want to present data without the bias implicit in using varying saturation. The name Lch(ab) is sometimes used to differentiate from L*C*h(uv).
Other related color spaces
A related color space, the CIE 1976 ''L''*''u''*''v''* color space (a.k.a. CIELUV), preserves the same ''L*'' as ''L*a*b*'' but has a different representation of the chromaticity components. CIELAB and CIELUV can also be expressed in cylindrical form (CIELCh ab and CIELChuv, respectively), with the chromaticity components replaced by correlates of chroma and hue. Since the work on CIELAB and CIELUV, the CIE has been incorporating an increasing number of color appearance phenomena into their models and difference equations to better predict human color perception. Thesecolor appearance model
A color appearance model (CAM) is a mathematical model that seeks to describe the perceptual aspects of human color vision, i.e. viewing conditions under which the appearance of a color does not tally with the corresponding physical measurement ...
s, of which CIELAB is a simple example, culminated with CIECAM02
In colorimetry, CIECAM02 is the color appearance model published in 2002 by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) Technical Committee 8-01 (''Color Appearance Modelling for Color Management Systems'') and the successor of Color appe ...
.
Oklab is built on the same spatial structure and achieves greater perceptual uniformity.
Usage
Some systems and software applications that support CIELAB include: * CIELAB is used by Datacolorspectrophotometers
Spectrophotometry is a branch of electromagnetic spectroscopy concerned with the quantitative measurement of the reflection or transmission properties of a material as a function of wavelength. Spectrophotometry uses photometers, known as sp ...
, including the related color difference calculations.
* CIELAB is used by the PantoneLive library.
* CIELAB is used extensively by X-Rite as a color space with their hardware and software color measuring systems.
* CIELAB D50 is available in Adobe Photoshop
Adobe Photoshop is a raster graphics editor developed and published by Adobe Inc., Adobe for Microsoft Windows, Windows and macOS. It was created in 1987 by Thomas Knoll, Thomas and John Knoll. It is the most used tool for professional digital ...
, where it is called "Lab mode".
* CIELAB is available in Affinity Photo
Affinity Photo is a raster graphics editor developed by Serif Ltd. for iPadOS, macOS, and Windows, alongside Affinity Designer and Affinity Publisher. Development of Affinity Photo started in 2009 as a raster graphics editor for macOS. Its fir ...
by changing the document's Colour Format to "Lab (16 bit)". The white point, which defaults to D50, can be changed by ICC profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes o ...
.
* CIELAB D50 is available in ICC profile
In color management, an ICC profile is a set of data that characterizes a color input or output device, or a color space, according to standards promulgated by the International Color Consortium (ICC). Profiles describe the color attributes o ...
s as a profile connection space named "Lab color space".
* CIELAB (any white point) is a supported color space in TIFF
Tag Image File Format or Tagged Image File Format, commonly known by the abbreviations TIFF or TIF, is an image file format for storing raster graphics images, popular among graphic artists, the publishing industry, and photographers. TIFF is w ...
image files.TIFF: Revision 6.0
'' Adobe Developers Association, 1992 * CIELAB (any white point) is available in
PDF
Portable document format (PDF), standardized as ISO 32000, is a file format developed by Adobe Inc., Adobe in 1992 to present documents, including text formatting and images, in a manner independent of application software, computer hardware, ...
documents, where it is called the "Lab color space".
* CIELAB is an option in Digital Color Meter on macOS
macOS, previously OS X and originally Mac OS X, is a Unix, Unix-based operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc., Apple since 2001. It is the current operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. With ...
described as "L*a*b*".
* CIELAB is available in the RawTherapee photo editor, where it is called the "Lab color space".
* CIELAB is used by GIMP
Gimp or GIMP may refer to:
Clothing
* Bondage suit, also called a gimp suit, a type of suit used in BDSM
* Bondage mask, also called a gimp mask, often worn in conjunction with a gimp suit
Embroidery and crafts
* Gimp (thread), an ornamental tr ...
for the hue-chroma adjustment filter, fuzzy-select and paint-bucket. There is also a LCh(ab) color picker.
* Web browser support for CIELAB was introduced as part of CSS Color Module Level 4, and is supported in all major browsers.
Hunter Lab
See also
*Color theory
Color theory, or more specifically traditional color theory, is a historical body of knowledge describing the behavior of colors, namely in color mixing, color contrast effects, color harmony, color schemes and color symbolism. Modern color th ...
* Opponent process
The opponent process is a color theory that states that the human visual system interprets information about color by processing signals from photoreceptor cells in an antagonistic manner. The opponent-process theory suggests that there are thre ...
* HSL and HSV
HSL and HSV are the two most common cylindrical coordinate system, cylindrical-coordinate representations of points in an RGB color model. The two representations rearrange the geometry of RGB in an attempt to be more intuitive and color vision, ...
* RGB color model
The RGB color model is an additive color, additive color model in which the red, green, and blue primary colors of light are added together in various ways to reproduce a broad array of colors. The name of the model comes from the initials ...
* CMYK color model
The CMYK color model (also known as process color, or four color) is a subtractive color model, based on the CMY color model, used in color printing, and is also used to describe the printing process itself. The abbreviation ''CMYK'' refers ...
* CIELUV
* CIECAM02
In colorimetry, CIECAM02 is the color appearance model published in 2002 by the International Commission on Illumination (CIE) Technical Committee 8-01 (''Color Appearance Modelling for Color Management Systems'') and the successor of Color appe ...
* HCL color space
* Oklab color space
Notes
References
External links
Demonstrative color conversion applet
CIE Colorimetry 15-3
CIE Technical Report Colorimetry 15 third edition (2004). An authoritative reference.
Whitepaper on understanding colors
by X-rite. {{Color space Color space 1976 introductions