Korotkoff sounds on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking
Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking
Audio recordings of Korotkoff sounds
Slide seven of twenty-two, Cardiff University/Prfysgol Caerdydd. {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Audible medical signs Blood pressure
 Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking
Korotkoff sounds are the sounds that medical personnel listen for when they are taking blood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
using a non-invasive
A medical procedure is defined as ''non-invasive'' when no break in the skin is created and there is no contact with the mucosa, or skin break, or internal body cavity beyond a natural or artificial body orifice. For example, deep palpation and p ...
procedure. They are named after Nikolai Korotkov, a Russian physician who discovered them in 1905, when he was working at the Imperial Medical Academy in St. Petersburg, the Russian Empire.
Description
The sounds heard during the measurement ofblood pressure
Blood pressure (BP) is the pressure of circulating blood against the walls of blood vessels. Most of this pressure results from the heart pumping blood through the circulatory system. When used without qualification, the term "blood pressure ...
are not the same as the heart sounds
Heart sounds are the noises generated by the beating heart and the resultant flow of blood through it. Specifically, the sounds reflect the turbulence created when the heart valves snap shut. In cardiac auscultation, an examiner may use a stet ...
heard during chest auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (he ...
that are due to vibrations inside the ventricles associated with the snapping shut of the valves
A valve is a device or natural object that regulates, directs or controls the flow of a fluid (gases, liquids, fluidized solids, or slurries) by opening, closing, or partially obstructing various passageways. Valves are technically fitting ...
. If a stethoscope
The stethoscope is a medical device for auscultation, or listening to internal sounds of an animal or human body. It typically has a small disc-shaped resonator that is placed against the skin, and one or two tubes connected to two earpieces. ...
is placed over the brachial artery
The brachial artery is the major blood vessel of the (upper) arm. It is the continuation of the axillary artery beyond the lower margin of teres major muscle. It continues down the ventral surface of the arm until it reaches the cubital foss ...
in the antecubital fossa
The cubital fossa, chelidon, or elbow pit, is the triangular area on the anterior side of the upper limb between the arm and forearm of a human or other hominid animals. It lies anteriorly to the elbow (Latin ) when in standard anatomical positio ...
in a normal person (without arterial disease), no sound should be audible. As the heart
The heart is a muscular Organ (biology), organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as ca ...
beats, these pulses are transmitted smoothly via laminar (non-turbulent) blood flow throughout the arteries, and no sound is produced. Similarly, if the cuff of a sphygmomanometer
A sphygmomanometer ( ), a blood pressure monitor, or blood pressure gauge, is a device used to measure blood pressure, composed of an inflatable cuff to collapse and then release the artery under the cuff in a controlled manner, and a mercury ...
is placed around a patient's upper arm and inflated to a pressure above the patient's systolic blood pressure, there will be no sound audible. This is because the pressure in the cuff is high enough such that it completely occludes the blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
flow
Flow may refer to:
Science and technology
* Fluid flow, the motion of a gas or liquid
* Flow (geomorphology), a type of mass wasting or slope movement in geomorphology
* Flow (mathematics), a group action of the real numbers on a set
* Flow (psyc ...
. This is similar to a flexible tube or pipe with fluid in it that is being pinched shut.
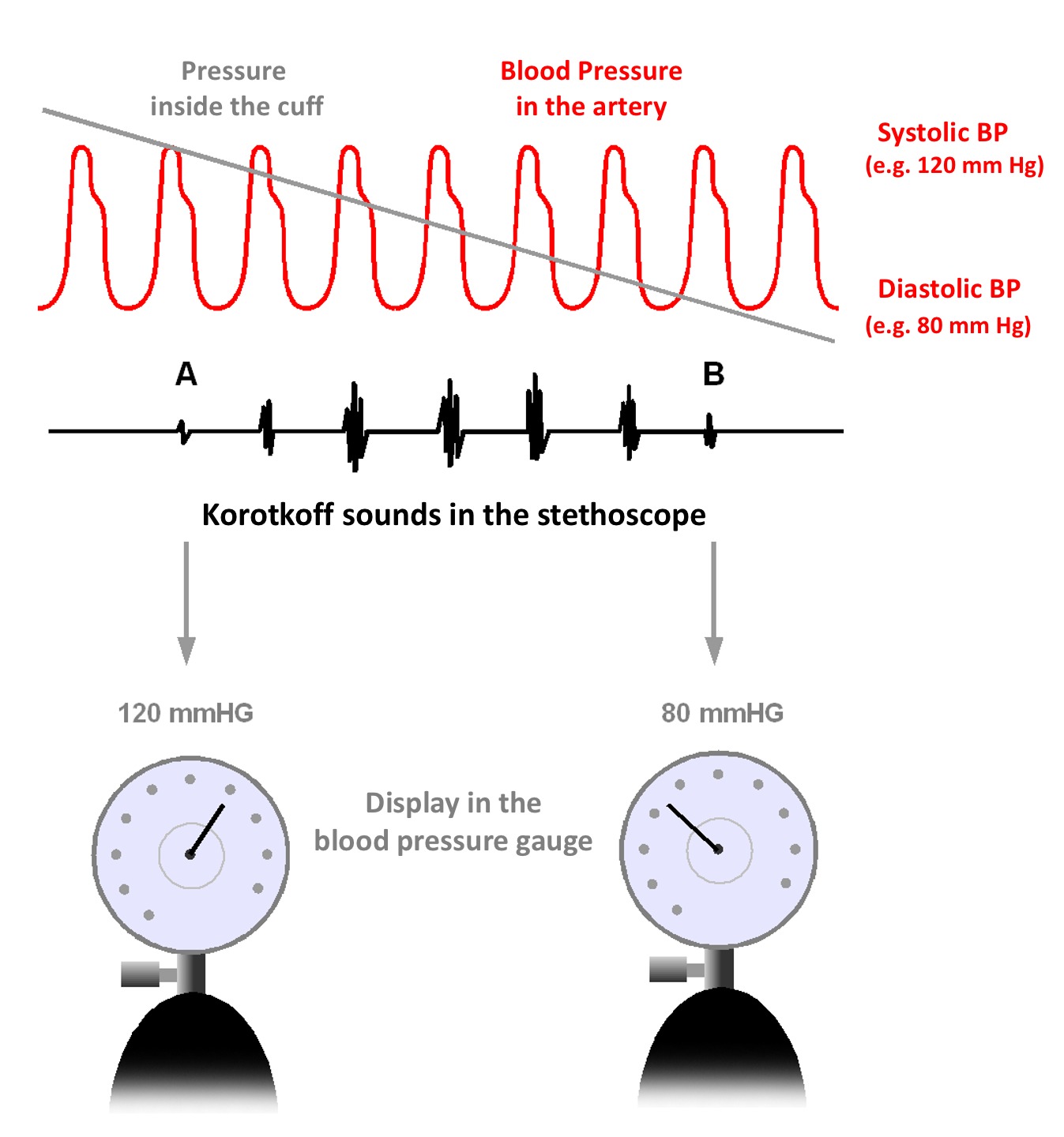
If the pressure is dropped to a level equal to that of the patient's systolic blood pressure, the first Korotkoff sound will be heard. As the pressure in the cuff is the same as the pressure produced by the heart, some blood will be able to pass through the upper arm when the pressure in the artery rises during systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ...
. This blood
Blood is a body fluid in the circulatory system of humans and other vertebrates that delivers necessary substances such as nutrients and oxygen to the cells, and transports metabolic waste products away from those same cells. Blood in the cir ...
flows in spurts as the pressure in the artery rises above the pressure in the cuff and then drops back down beyond the cuffed region, resulting in turbulence
In fluid dynamics, turbulence or turbulent flow is fluid motion characterized by chaotic changes in pressure and flow velocity. It is in contrast to a laminar flow, which occurs when a fluid flows in parallel layers, with no disruption between ...
that produces an audible sound.
As the pressure in the cuff is allowed to fall further, thumping sounds continue to be heard as long as the pressure in the cuff is between the systolic and diastolic pressures, as the arterial pressure keeps on rising above and dropping back below the pressure in the cuff.
Eventually, as the pressure in the cuff drops further, the sounds change in quality, then become muted, and finally disappear altogether. This occurs because, as the pressure in the cuff drops below the diastolic blood pressure, the cuff no longer provides any restriction to blood flow allowing the blood flow to become smooth again with no turbulence and thus produce no further audible sound.
The five Korotkoff sounds
There are five Korotkoff sounds: # Phase I: The first appearance of faint, repetitive, clear tapping sounds which gradually increase in intensity for at least two consecutive beats is the systolic blood pressure. # Phase II: A brief period may follow during which the sounds soften and acquire a swishing quality. # Phase III: The return of sharper sounds, which become crisper to regain, or even exceed, the intensity of Phase I sounds. # Phase IV: The distinct abrupt muffling of sounds, which become soft and blowing in quality. # Phase V: The point at which all sounds finally disappear completely is the diastolic pressure. The second and third Korotkoff sounds have no knownclinical significance In medicine and psychology, clinical significance is the practical importance of a treatment effect—whether it has a real genuine, palpable, noticeable effect on daily life.
Types of significance Statistical significance
Statistical significance ...
.
In some patients, sounds may disappear altogether for a short time between Phase II and III, which is referred to as auscultatory gap.
Systolic and diastolic blood pressure
Traditionally, the systolic blood pressure is taken to be the pressure at which the first Korotkoff sound is first heard and the diastolic blood pressure is the pressure at which the fourth Korotkoff sound is just barely audible. However, there has recently been a move towards the use of the fifth Korotkoff sound (i.e. silence) as the diastolic blood pressure, as this has been felt to be more reproducible. Forpaediatrics
Pediatrics ( also spelled ''paediatrics'' or ''pædiatrics'') is the branch of medicine that involves the medical care of infants, children, adolescents, and young adults. In the United Kingdom, paediatrics covers many of their youth until the ...
, there has been controversy regarding whether to use auscultation
Auscultation (based on the Latin verb ''auscultare'' "to listen") is listening to the internal sounds of the body, usually using a stethoscope. Auscultation is performed for the purposes of examining the circulatory and respiratory systems (he ...
of the fourth or fifth Korotkoff sound as an indicator of diastolic pressure. Current clinical practice guidelines recommend using the fifth Korotkoff sound (but if this is undetectable, using the fourth).
The time average of the first Korotkoff sound represents a reliable pressure marker of systole
Systole ( ) is the part of the cardiac cycle during which some chambers of the heart contract after refilling with blood. The term originates, via New Latin, from Ancient Greek (''sustolē''), from (''sustéllein'' 'to contract'; from ...
of the heart. The time average of the fourth Korotkoff sound represents a reliable pressure marker of diastole
Diastole ( ) is the relaxed phase of the cardiac cycle when the chambers of the heart are re-filling with blood. The contrasting phase is systole when the heart chambers are contracting. Atrial diastole is the relaxing of the atria, and ventricu ...
of the heart.
See also
* Auscultatory gap * Pulse pressureReferences
External links
Audio recordings of Korotkoff sounds
Slide seven of twenty-two, Cardiff University/Prfysgol Caerdydd. {{Use dmy dates, date=April 2017 Audible medical signs Blood pressure