Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 VEB
VEB

 VEB
VEB Kombinat
Combine (russian: Комбинат) is a term for industrial business groups, conglomerates or trusts in the former socialist countries. Examples include VEB Kombinat Robotron, an electronics manufacturer, and IFA, a manufacturer of vehicles ...
Mikroelektronik Erfurt was an important manufacturer of active electronic components in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
. It should not be confused with the more well-known VEB Kombinat Robotron Dresden which used integrated circuits from Kombinat Mikroelektronik in its computers.
Their products often carried the trademark
A trademark (also written trade mark or trade-mark) is a type of intellectual property consisting of a recognizable sign, design, or expression that identifies products or services from a particular source and distinguishes them from others ...
RFT, but this was used on most electronic products from East Germany from otherwise unrelated companies.
History
The Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was formed in 1978 when the ''VVB Bauelemente und Vakuumtechnik'' was split into ''VEB Kombinat Elektronische BauelementeTeltow
Teltow [] is a town in the Potsdam-Mittelmark district, in Brandenburg, Germany.
Geography
Teltow is part of the agglomeration of Berlin. The distance to the Berlin city centre is , while the distance to Potsdam is .
The Teltow Canal links the ...
'' for passive electronic components and ''VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt'' for active electronic components. However, the history of many of the individual plants reaches back further, in some cases to before the Second World War. In 1971 the first integrated circuits had been manufactured — the D100C (TTL
TTL may refer to:
Photography
* Through-the-lens metering, a camera feature
* Zenit TTL, an SLR film camera named for its TTL metering capability
Technology
* Time to live, a computer data lifespan-limiting mechanism
* Transistor–transistor lo ...
) by Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder)
VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) (abbreviated HFO or HWF) was the largest manufacturer of semiconductor devices in the German Democratic Republic. In 1989, HFO produced 110 million integrated circuits (70% of all integrated circuits produced ...
and the U101D (PMOS logic
PMOS or pMOS logic (from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor) is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS lo ...
) by Funkwerk Erfurt. To put this into perspective, the first TTL circuits went into production in the US 10 years and at Siemens in West Germany 5 years before East Germany. The first microprocessor, the U808D, followed in 1978, 6 years after the Intel 8008
The Intel 8008 ("''eight-thousand-eight''" or "''eighty-oh-eight''") is an early byte-oriented microprocessor designed by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC), implemented and manufactured by Intel, and introduced in April 1972. It is an 8-bit CP ...
that the U808 was cloned from. Further milestones were the U880 (Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were ...
clone) in 1980 and the first 16-bit microprocessor U8000 (Zilog Z8000
The Z8000 ("''zee-'' or ''zed-eight-thousand''") is a 16-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog in early 1979. The architecture was designed by Bernard Peuto while the logic and physical implementation was done by Masatoshi Shima, assisted by a ...
clone) in 1984. The ruling Socialist Unity Party of Germany
The Socialist Unity Party of Germany (german: Sozialistische Einheitspartei Deutschlands, ; SED, ), often known in English as the East German Communist Party, was the founding and ruling party of the German Democratic Republic (GDR; East German ...
had identified the development of the microelectronics sector as a primary goal. Huge sums were spent in order to catch up to the West — between 1986 and 1990 about 7% of the country-wide industry investment. However, this effort was hampered by several factors: the general inefficiency of the planned economy, insufficient cooperation with other Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance (, ; English abbreviation COMECON, CMEA, CEMA, or CAME) was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of s ...
countries, and western CoCom
The Cocom or Cocomes were a Maya family or dynasty who controlled the Yucatán Peninsula in the late Postclassic period. Their capital was at Mayapan. The dynasty was founded by Hunac Ceel
Hunac Ceel Cauich (fl. late 12th and early 13th centu ...
export restrictions that prevented the importation of semiconductor manufacturing equipment. Nonetheless, the development program achieved samples of a 1Mbit dRAM chip (U61000
U61000 was the first 1- Mbit DRAM microchip produced in the German Democratic Republic by Zentrum Mikroelektronik Dresden in September 1988 based on CMOS technology.http://www.bild.bundesarchiv.de/archives/barchpic/search/_1228628738/?search ie ...
) in 1988 and a 32-bit processor (U80701
The U80701 is a 32-bit microprocessor developed from 1986-1990 in the German Democratic Republic. It was manufactured by VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt (MME) in NMOS technology and is encased in a ceramic quad flat package (CQFP-68 pac ...
) in 1989. Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt achieved a feature size of 3 µm on 4-inch wafers in 1984 (plant ESO I), 2.5 µm in 1988 (plant ESO II), and 1.5 µm on 5-inch wafers in 1990 (plant ESO III). In 1989, Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) produced 110 million integrated circuits and Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt produced 35 million.
After 1990
Following theGerman reunification
German reunification (german: link=no, Deutsche Wiedervereinigung) was the process of re-establishing Germany as a united and fully sovereign state, which took place between 2 May 1989 and 15 March 1991. The day of 3 October 1990 when the Ge ...
, Kombinat Mikroelektronik was dissolved and operated for a time as a holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
under the name ''PTC-electronic AG'' which was 100% owned by the Treuhandanstalt
The (" Trust agency"), colloquially referred to as , was an agency established by the government of the German Democratic Republic to reprivatise/privatise East German enterprises, Volkseigene Betriebe (VEBs), prior to German reunification. C ...
. Most products from Kombinat Mikroelektronik could not be sold on the world market and many plants were liquidated by the Treuhandanstalt in 1991.
The ''Thesys Gesellschaft für Mikroelektronik mbH'' and the '' X-FAB Gesellschaft zur Fertigung von Wafern mbH'' were created in 1992 from parts of VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
(which had operated under the name ERMIC GmbH from 1990 until 1992). In 1999 both companies were combined as ''X-FAB Semiconductor Foundries GmbH''. In 2007, X-FAB took over another former part of Kombinat Mikroelektronik: the foundry
A foundry is a factory that produces metal castings. Metals are cast into shapes by melting them into a liquid, pouring the metal into a mold, and removing the mold material after the metal has solidified as it cools. The most common metals pr ...
of the former VEB ZFTM Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
. ZFTM Dresden had become ''Zentrum Mikroelektronik Dresden GmbH'' (ZMD) in 1993. After several ownership changes and the sale of the foundry to X-FAB, ZMD was renamed to ZMDI
Zentrum Mikroelektronik Dresden (ZMD) was regarded as the heart of East Germany's microelectronics research in the 1980s as well as its most advanced integrated circuit manufacturer. Together with TU Dresden and VEB Spurenmetalle Freiberg, ZMD f ...
and the remaining fab-less design house was ultimately sold to Integrated Device Technology
Integrated Device Technology, Inc., is an American corporation headquartered in San Jose, California, that designs, manufactures, and markets low-power, high-performance mixed-signal semiconductor solutions for the advanced communications, com ...
in 2015. Not far from Dresden in Freiberg
Freiberg is a university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called ''Große Kreisstadt'' (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsen district.
Its historic town centre has been placed under heritage c ...
, the wafer production of VEB Spurenmetalle continued through Siltronic
Siltronic AG is a manufacturer of wafers made of hyperpure silicon, the basis for modern micro- and nanotechnology. The Munich-based company is one of the world's leading manufacturers of wafers for the semiconductor industry.
History
The compa ...
and Freiberger Compound Materials GmbH. Together with TU Dresden
TU Dresden (for german: Technische Universität Dresden, abbreviated as TUD and often wrongly translated as "Dresden University of Technology") is a public research university, the largest institute of higher education in the city of Dresden, th ...
, VEB ZFTM and VEB Spurenmetalle formed the foundation for Silicon Saxony
Silicon Saxony is a registered industry association of nearly 300 companies in the microelectronics and related sectors in Saxony, Germany, with around 40,000 employees. Many, but not all, of those firms are situated in the north of Dresden.
Wit ...
, a cluster of microelectronics companies that came to include new fabs by Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
(later Infineon Technologies
Infineon Technologies AG is a German semiconductor manufacturer founded in 1999, when the semiconductor operations of the former parent company Siemens AG were spun off. Infineon has about 50,280 employees and is one of the ten largest semicon ...
) and AMD
Advanced Micro Devices, Inc. (AMD) is an American multinational semiconductor company based in Santa Clara, California, that develops computer processors and related technologies for business and consumer markets. While it initially manufactur ...
(later GlobalFoundries
GlobalFoundries Inc. (GF or GloFo) is a multinational semiconductor contract manufacturing and design company incorporated in the Cayman Islands and headquartered in Malta, New York. Created by the divestiture of the manufacturing arm of AMD, ...
).
The Frankfurt (Oder) region did not fare as well. VEB Halbleiterwerk was succeeded, in turn, by Halbleiterwerk GmbH, System Microelectronic Innovation GmbH (SMI), Silicon Microelectronic Integration GmbH (SiMI), Megaxess GmbH Deutschland, and Microtechnology Services Frankfurt (Oder) GmbH (MSF), each with less employees than its predecessor. The website of MSF disappeared around 2009. Construction on a new semiconductor plant, Communicant Semiconductor Technologies, had started already but this endeavour collapsed in 2003. Only IHP, the research institute that had supported VEB Halbleiterwerk, remained after that.
At VEB Werk für Fernsehelektronik Berlin, the production of electronic tubes and optoelectronics was shut down step by step until only the relatively modern manufacturing of colour CRTs remained. In 1993 the CRT manufacturing was taken over by Samsung SDI
Samsung SDI Co., Ltd. () is a battery and electronic materials manufacturer headquartered in Yongin, Gyeonggi-do, South Korea. Samsung SDI operates its business with Energy Solutions and Electronic Materials segment. The Energy Solution segment ma ...
. In 2005, when LCD screens largely replaced CRTs, the plant was shut down entirely.
VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Liebknecht" Stahnsdorf became Leistungselektronik Stahnsdorf AG (LES AG) which was liquidated by the Treuhandanstalt in 1992. The semiconductor manufacturing was sold to Indian investors and continued under the name Lesag HBB. When the investors withdrew in the middle of the 1990s, the number of employees had fallen from 3000 in 1989 to 79. In 1996, several former employees founded SeCoS Halbleitertechnologie GmbH to continue semicondutor manufacturing in Stahnsdort. By 2001, the patents and rights of SeCoS were transferred to SeCoS Corporation in Taiwan. Only the small group developing silicon pressure sensors survived in Stahnsdorf and was acquired by Endress+Hauser
Endress+Hauser (Endress and Hauser) is a Switzerland, Swiss-based globally operating process and laboratory instrumentation and automation supplier. The family company achieved net sales of approximately 2.9 billion euros in 2021 with a total work ...
.
In Neuhaus am Rennweg
Neuhaus am Rennweg is a town in the district of Sonneberg, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated in the Thuringian Forest, 17 km north of Sonneberg, and 22 km southwest of Saalfeld. The former municipalities Lichte and Piesau
Piesau ...
, the SMD packaging of VEB Mikroelektronik "Anna Seghers" became part of Zetex Semiconductors
Zetex Semiconductors plc is a UK-based manufacturer of discrete semiconductor devices such as diodes and transistors.
Corporate history
Originally a subsidiary of Ferranti Semiconductor, Zetex took its name from Ferranti's ZTX series of bip ...
which was in turn acquired by Diodes Incorporated
Diodes Incorporated is a global manufacturer and supplier of application specific standard products within the discrete, logic, analog, and mixed-signal semiconductor markets. Diodes serves the consumer electronics, computing, communications, in ...
.
Divisions
The ''Kombinat'' consisted of a number of plants across East Germany (listed with their production profile in 1989): * VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
" Erfurt
Erfurt () is the capital and largest city in the Central German state of Thuringia. It is located in the wide valley of the Gera river (progression: ), in the southern part of the Thuringian Basin, north of the Thuringian Forest. It sits i ...
(MME), before 1983 Funkwerk Erfurt (FWE) — ''Kombinat'' headquarters; NMOS and CMOS digital integrated circuits
* VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder)
VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) (abbreviated HFO or HWF) was the largest manufacturer of semiconductor devices in the German Democratic Republic. In 1989, HFO produced 110 million integrated circuits (70% of all integrated circuits produced ...
(HFO) — bipolar analogue and digital integrated circuits, mixed-signal integrated circuit
A mixed-signal integrated circuit is any integrated circuit that has both analog circuits and digital circuits on a single semiconductor die.CMOS integrated circuits, low-power
bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipola ...
s
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Anna Seghers
Anna Seghers (; born ''Anna Reiling,'' 19 November 1900 – 1 June 1983), is the pseudonym of a German writer notable for exploring and depicting the moral experience of the Second World War. Born into a Jewish family and married to a Hungarian ...
" Neuhaus am Rennweg
Neuhaus am Rennweg is a town in the district of Sonneberg, in Thuringia, Germany. It is situated in the Thuringian Forest, 17 km north of Sonneberg, and 22 km southwest of Saalfeld. The former municipalities Lichte and Piesau
Piesau ...
, before 1981 Röhrenwerk Neuhaus am Rennweg (RWN) — bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipola ...
s
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Liebknecht
Karl Paul August Friedrich Liebknecht (; 13 August 1871 – 15 January 1919) was a German socialist and anti-militarist. A member of the Social Democratic Party of Germany (SPD) beginning in 1900, he was one of its deputies in the Reichstag fro ...
" Stahnsdorf (MLS), before 1981 Gleichrichterwerk Stahnsdorf (GWS) — power semiconductor device
A power semiconductor device is a semiconductor device used as a switch or rectifier in power electronics (for example in a switch-mode power supply). Such a device is also called a power device or, when used in an integrated circuit, a power IC ...
s (silicon rectifier diodes, bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipola ...
s), pressure sensors
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Robert Harnau" Großräschen
Großräschen ( Sorbian: ''Rań'') is a town in Lower Lusatia, in Germany. Administratively, it is part of the district of Oberspreewald-Lausitz, in the state of Brandenburg.
Geographical position
Großräschen is south of the ''Niederlausitzer ...
, former Gleichrichterwerk Großräschen — selenium rectifier
A selenium rectifier is a type of metal rectifier, invented in 1933. They were used in power supplies for electronic equipment and in high-current battery-charger applications until they were superseded by silicon diode rectifiers in the late 1960 ...
s and silicon rectifier diodes
* VEB Werk für Fernsehelektronik Berlin (WF) — CRTs, LED
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
s, LCDs, optoelectronics
Optoelectronics (or optronics) is the study and application of electronic devices and systems that find, detect and control light, usually considered a sub-field of photonics. In this context, ''light'' often includes invisible forms of radiat ...
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck
Friedrich Wilhelm Reinhold Pieck (; 3 January 1876 – 7 September 1960) was a German communist politician who served as the chairman of the Socialist Unity Party from 1946 to 1950 and as president of the German Democratic Republic from 1949 to ...
" Mühlhausen (MPM), before 1982 Röhrenwerk Mühlhausen — low-power diodes (including Zener diode
A Zener diode is a special type of diode designed to reliably allow current to flow "backwards" (inverted polarity) when a certain set reverse voltage, known as the ''Zener voltage'', is reached.
Zener diodes are manufactured with a great var ...
s); also KC85
The KC 85 ('KC' meaning "Kleincomputer", or "small computer") were models of microcomputers built in East Germany, first in 1984 by VEB Robotron (the KC 85/1) and later by VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" Mühlhausen (KC 85/2, KC 85/3 and K ...
series home computers, pocket calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized ...
s
* VEB Röhrenwerk Rudolstadt
Rudolstadt is a town in the German federal state Thuringia, with the Thuringian Forest to the southwest, and to Jena and Weimar to the north.
The former capital of Schwarzburg-Rudolstadt, the town is built along the River Saale inside a wide v ...
, before 1961 Phönix Röntgenröhrenwerk Rudolstadt — X-ray tube
An X-ray tube is a vacuum tube that converts electrical input power into X-rays. The availability of this controllable source of X-rays created the field of radiography, the imaging of partly opaque objects with penetrating radiation. In contrast ...
s
* VEB Applikationszentrum Elektronik Berlin (AEB) — import of electronic components, documentation, application support
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Friedrich Engels
Friedrich Engels ( ,"Engels"
'' Ilmenau, before 1983 Elektroglas Ilmenau —
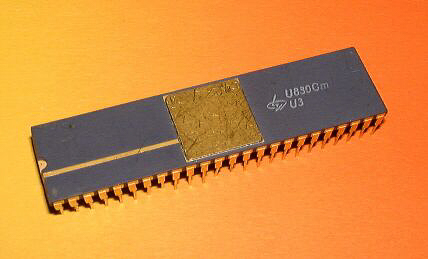 The U830, U8032, U8047, and U320C20 were manufactured by ZFTM Dresden while all other processors came from Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt.
* U808 — 8-bit microprocessor, clone of the
The U830, U8032, U8047, and U320C20 were manufactured by ZFTM Dresden while all other processors came from Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt.
* U808 — 8-bit microprocessor, clone of the
MHG SY625-05 1.jpg, Rectifier diode SY625/0,5 (VEB Mikroelektronik "Robert Harnau" Großräschen, 1990)
GD241 Transistor.jpg, Germanium power transistor GD241 (VEB Mikroelektronik "Anna Seghers" Neuhaus am Rennweg, 1983)
MLS Leistungstransistoren.jpg, Silicon power transistors (VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Liebknecht" Stahnsdorf, 1987 - 1989)
WF Optokoppler.jpg,
TV-spiel.jpg, Video game console BSS 01 ('' Bildschirmspiel 01''; VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder), 1980)
LC80 innen.jpg, Microcomputer learning kit
'' Ilmenau, before 1983 Elektroglas Ilmenau —
semiconductor package
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
s
* VEB Mikroelektronik Secura-Werke Berlin — components for CRTs; also photocopiers
* VEB Mikroelektronik "Bruno Baum" Zehdenick
Zehdenick is a town in the Oberhavel district, in Brandenburg, Germany. It is situated on the river Havel, southeast of Fürstenberg/Havel, and north of Berlin (centre). Since 31 July 2013, the city has the additional appellation "Havelstadt".
...
, before 1977 Isolierwerk Zehdenick — punched parts, insulating materials
* VEB Spurenmetalle Freiberg
Freiberg is a university and former mining town in Saxony, Germany. It is a so-called ''Große Kreisstadt'' (large county town) and the administrative centre of Mittelsachsen district.
Its historic town centre has been placed under heritage c ...
— silicon and gallium arsenide wafers
A wafer is a crisp, often sweet, very thin, flat, light and dry biscuit, often used to decorate ice cream, and also used as a garnish on some sweet dishes. Wafers can also be made into cookies with cream flavoring sandwiched between them. They ...
* VEB Glaskolbenwerk Weißwasser
Weißwasser ( hsb, Běła Woda) is a town in Upper Lusatia in eastern Saxony, Germany.
Weißwasser is the third largest town in the Görlitz district after Görlitz and Zittau. The town's landmark is its water tower. The town is part of the re ...
— glass envelopes for CRTs
Two plants from Kombinat Mikroelektronik were moved to VEB Kombinat "Carl Zeiss
Carl Zeiss (; 11 September 1816 – 3 December 1888) was a German scientific instrument maker, optician and businessman. In 1846 he founded his workshop, which is still in business as Carl Zeiss AG. Zeiss gathered a group of gifted practica ...
" Jena
Jena () is a German city and the second largest city in Thuringia. Together with the nearby cities of Erfurt and Weimar, it forms the central metropolitan area of Thuringia with approximately 500,000 inhabitants, while the city itself has a po ...
in 1986:
* VEB Zentrum für Forschung und Technologie Mikroelektronik Dresden (ZFTM) — development and pilot production of integrated circuits
* VEB Hochvakuum Dresden — equipment for physical vapor deposition
Physical vapor deposition (PVD), sometimes called physical vapor transport (PVT), describes a variety of vacuum deposition methods which can be used to produce thin films and coatings on substrates including metals, ceramics, glass, and polym ...
The East German clock and watch industry formed part of the Kombinat Mikroelektronik as the ''Leitbereich Uhren'' (Clock Directorate) with a number of plants:
* VEB Uhrenwerke Ruhla
is a town situated in the forest of Thuringia in the district of Wartburgkreis in Germany, immediately next to the Rennsteig. Thal and Kittelsthal are parts of the town.
History
Within the German Empire (1871-1918), part of Ruhla belonged to ...
— also CMOS integrated circuits, primarily for watches and clocks
* VEB Uhrenwerk Glashütte
Glashütte [] is a town in Saxony, Germany, known as the birthplace of the German watchmaking industry and has a population of about 7,000. Historically, it was first mentioned in a document circa 1445. In January 2008, the former municipality Re ...
* VEB Uhrenwerk Weimar
Weimar is a city in the state of Thuringia, Germany. It is located in Central Germany between Erfurt in the west and Jena in the east, approximately southwest of Leipzig, north of Nuremberg and west of Dresden. Together with the neighbouri ...
* VEB Plastverarbeitung Eisenach
Eisenach () is a town in Thuringia, Germany with 42,000 inhabitants, located west of Erfurt, southeast of Kassel and northeast of Frankfurt. It is the main urban centre of western Thuringia and bordering northeastern Hessian regions, situat ...
* VEB Feinwerktechnik Dresden
Dresden (, ; Upper Saxon: ''Dräsdn''; wen, label=Upper Sorbian, Drježdźany) is the capital city of the German state of Saxony and its second most populous city, after Leipzig. It is the 12th most populous city of Germany, the fourth larg ...
Products
Microprocessors
 The U830, U8032, U8047, and U320C20 were manufactured by ZFTM Dresden while all other processors came from Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt.
* U808 — 8-bit microprocessor, clone of the
The U830, U8032, U8047, and U320C20 were manufactured by ZFTM Dresden while all other processors came from Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt.
* U808 — 8-bit microprocessor, clone of the Intel 8008
The Intel 8008 ("''eight-thousand-eight''" or "''eighty-oh-eight''") is an early byte-oriented microprocessor designed by Computer Terminal Corporation (CTC), implemented and manufactured by Intel, and introduced in April 1972. It is an 8-bit CP ...
* U830 — asynchronous 8-bit processor slice for PDP-11 compatible computers
* U8032 — 16-bit arithmetic coprocessor slice
* U880
The U880 is an 8-bit microprocessor that was manufactured by VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt (abbreviated as MME; part of Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt) in the German Democratic Republic. Production of the U880 started in 1980 at VEB ...
— 8-bit microprocessor, clone of the Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were ...
* U881 through U886 — 8-bit microcontrollers, clones of the Zilog Z8
The Zilog Z8 is a microcontroller architecture, originally introduced in 1979, which today also includes the Z8 Encore!, eZ8 Encore!, eZ8 Encore! XP, and eZ8 Encore! MC families.
Signifying features of the architecture are up to 4,096 fast ...
* U8000
The Z8000 ("''zee-'' or ''zed-eight-thousand''") is a 16-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog in early 1979. The architecture was designed by Bernard Peuto while the logic and physical implementation was done by Masatoshi Shima, assisted by a ...
— 16-bit microprocessors, clones of the Zilog Z8000
The Z8000 ("''zee-'' or ''zed-eight-thousand''") is a 16-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog in early 1979. The architecture was designed by Bernard Peuto while the logic and physical implementation was done by Masatoshi Shima, assisted by a ...
* U8047 — 4-bit microcontroller
* U84C00 — 8-bit microprocessor, CMOS version of the Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were ...
, pilot production only
* U80601
The U80601 was a 16-bit microprocessor made in 1989-1990 by Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt in the former German Democratic Republic of East Germany. It was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a PLCC or ceramic (CLCC) package (first ...
— 16-bit microprocessor, clone of the Intel 80286
The Intel 80286 (also marketed as the iAPX 286 and often called Intel 286) is a 16-bit microprocessor that was introduced on February 1, 1982. It was the first 8086-based CPU with separate, non- multiplexed address and data buses and also the ...
, pilot production only
* U80701
The U80701 is a 32-bit microprocessor developed from 1986-1990 in the German Democratic Republic. It was manufactured by VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt (MME) in NMOS technology and is encased in a ceramic quad flat package (CQFP-68 pac ...
— 32-bit microprocessor, clone of the MicroVAX 78032
The MicroVAX 78032 (otherwise known as the DC333) is a microprocessor developed and fabricated by Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC) that implements a subset of the VAX instruction set architecture (ISA). The 78032 is used exclusively in DEC's ...
, pilot production only
* U320C20 — 16-bit digital signal processor, CMOS version of the Texas Instruments TMS32020, pilot production only
Other components
Optocoupler
An opto-isolator (also called an optocoupler, photocoupler, or optical isolator) is an electronic component that transfers electrical signals between two isolated circuits by using light. Opto-isolators prevent high voltages from affecting the ...
s (VEB Werk für Fernsehelektronik Berlin)
MME IC.jpg, PMOS logic
PMOS or pMOS logic (from p-channel metal–oxide–semiconductor) is a family of digital circuits based on p-channel, enhancement mode metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors (MOSFETs). In the late 1960s and early 1970s, PMOS lo ...
IC U108D (VEB Funkwerk Erfurt, 1982); all other IC from VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) 1985 - 1989
FWE U552C 1.jpg, EPROM
An EPROM (rarely EROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power s ...
U552C (256x8 bit, VEB Funkwerk Erfurt, 1983)
CarlZeissJena U61000C 1.jpg, dRAM U61000CC12 (1Mx1 bit, VEB ZFTM Dresden - marked as "Carl Zeiss Jena", 1989)
UWR V4001D S1.jpg, 4000-series integrated circuit (VEB Uhrenwerke Ruhla, 1987)
Consumer goods
LC80
The educational computer LC80 was a single-board computer manufactured in the German Democratic Republic (GDR) and intended for teaching purposes. It was the first computer that retail customers could buy in the GDR.
History and development ...
('' Lerncomputer 80''; VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt, 1984)
Schachcomputer-CM.jpg, Chess computer CM ('' Chess Master''; VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt, 1984)
Taschenrechner Calculator VEB Mikroelektronik SR1con.jpg, Pocket calculator SR1 ('' Schulrechner 1''; VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" Mühlhausen, 1984)
KC85-2-1.jpg, Home computer KC85/2 ('' Kleincomputer 85/2''; VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" Mühlhausen, 1984)
Semiconductor designation
The type designations for both discrete semiconductor devices and integrated circuits were specified in state standard TGL 38015. The designations for discrete semiconductors are similar to thePro Electron Pro Electron or EECA is the European type designation and registration system for active components (such as semiconductors, liquid crystal displays, sensor devices, electronic tubes and cathode ray tubes).
Pro Electron was set up in 1966 in Bru ...
specification and are discussed there.
The type designation for integrated circuits initially (in 1971) consisted of one letter for the basic type and temperature range, a three-digit type number, and one letter for the package type. Over time this proved inflexible and the plants started adding letters for further temperature ranges, speed classes, etc. (e.g. a second letter after the basic type to indicate the speed class of a processor, as in UD8820M). In order to curb these somewhat uncoordinated extensions and also out of a desire to keep the type numbers in common with international equivalents, the standard was revised in 1986 (the revision came into force in April 1987). Almost arbitrary type numbers were allowed now , including additional letters in the type number if the international equivalent had them (e.g. U74HCT02DK). The temperature range was added as a separate letter at the end. A 2-digit number could follow the temperature letter in order to indicate the maximum clock frequency of a microprocessor (in MHz, e.g U880DC08) or the access time of a memory circuit (in units of nanoseconds or tens of nanoseconds, e.g. U60998CC12). Existing type designations were kept even if they did not fully conform to the new standard (e.g. V4028D). Integrated circuits that did not meet the official specifications, were sold as ''hobbyist versions''. More often than not, these were the only versions available to hobbyists. Before 1987 the hobbyist versions were assigned separate basic type letters while keeping the type number (e.g. an A109D that did not meet its specifications would become an R109D). From 1987 onwards, ''S1'' was appended to the unchanged type designation for hobbyist versions (e.g. U6516D S1).
New package type letters were added in 1987 while the previously defined letters remained unchanged.
In the early years all integrated circuit packages were manufactured with a spacing of 2.5 mm between pins just like in the Soviet Union and unlike the 2.54 mm (1/10") spacing used in the West. Over time more and more circuits with 16 or more pins were produced with a 2.54 mm spacing. Where a certain circuit was available with either of the two spacings, TGL 38015 required that the version with a 2.54 mm spacing be marked with the letter "Z" (for german: Zoll) on the package.
The temperature range letter was introduced only in 1987 and therefore not many integrated circuits were labelled with it.
Beside the type designation the manufacturing date was printed on integrated circuits. From 1978 onwards the IEC 60062 letter and digit code
The RKM code, also referred to as "letter and numeral code for resistance and capacitance values and tolerances", "letter and digit code for resistance and capacitance values and tolerances", or informally as "R notation" is a notation to specif ...
was used for manufacturing date (the respective state standard TGL 31667 does not mention IEC 60062 but the encoding is identical).
Following the dissolution of Kombinat Mikroelektronik in 1990, the plants in Frankfurt (Oder) and Erfurt kept using the East German integrated circuit designation until 1992 while ZMD in Dresden applied a slightly modified version until about 2005 (albeit with the date code in a 4-digit year/month format since 1991).
The East German integrated circuit designation was also used by ''Componentes Electrónicos "Ernesto Che Guevara"'' in Pinar del Río
Pinar del Río is the capital city of Pinar del Río Province, Cuba. With a population of 139,336 (2004) in a municipality of 190,332, it is the 10th-largest city in Cuba. Inhabitants of the area are called ''Pinareños''.
History
Pinar del R� ...
in the late 1980s (e.g. A210).
See also
* Electronics industry in East Germany *VEB Robotron
VEB Kombinat Robotron (or simply Robotron) was the biggest East German electronics manufacturer. It was based in Dresden and employed 68,000 people (1989). It produced personal computers, SM EVM minicomputers, the ESER mainframe computers, se ...
External links
References
{{reflist, refs= {{cite web , title=VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt , url=http://www.robotrontechnik.de/index.htm?/html/standorte/kme.htm , publisher=robotron technik .de , language=de , date=2016-11-29 , accessdate=2017-11-01 {{cite web , title=VEB SECURA-Werke Berlin , url=http://www.robotrontechnik.de/index.htm?/html/standorte/secura.htm , publisher=robotron technik .de , language=de , date=2016-11-29 , accessdate=2017-11-03 {{cite book , title=In 35 Jahren von der Empfängerröhre zum Kleincomputer , first=Claus-Dieter , last=Schröter , publisher=VEB Mikroelektronik "Wilhelm Pieck" Mühlhausen , language=de , date=1987 {{cite web , title=Isolierstoffe für den Weltmarkt , url=http://www.maz-online.de/Lokales/Oberhavel/Gransee/Isolierstoffe-fuer-den-Weltmarkt , publisher=Märkische Allgemeine , first=Cindy , last=Lüderitz , language=de , date=2016-02-02 , accessdate=2017-11-03 {{cite web , title=VEB Elektroglas Ilmenau (DDR), (- 1983) , url=http://zs.thulb.uni-jena.de/receive/jportal_jpinst_00015604 , publisher=Thüringer Universitäts- und Landesbibliothek Jena , accessdate=2017-11-02 {{cite web , title=VEB Phönix Röntgenröhrenwerk Rudolstadt , url=http://www.oldtimeradio.de/firma-117.php , language=de , publisher=Old Time Radio , date=2015-02-08 , accessdate=2017-11-02 {{cite news , title=Ehrennamen "Karl Marx" für Erfurter Betrieb , url=https://www.nd-archiv.de/ausgabe/1983-10-06 , newspaper=Neues Deutschland , language=de , date=1983-10-06 , accessdate=2017-11-03 {{cite web , title=Die Halbleiterindustrie in der DDR , url=http://www.all-electronics.de/die-halbleiterindustrie-in-der-ddr/ , language=de , publisher=Hüthig GmbH , first=Jörg , last=Berkner , date=2016-04-12 , accessdate=2017-11-07 {{cite web , title=Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt , url=http://www.erfurt-web.de/KombinatMikroelektronik , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20070927235324/http://www.erfurt-web.de/KombinatMikroelektronik , archive-date=2007-09-27 , language=de , accessdate=2017-11-14 {{cite web , title=IDT Completes Acquisition of ZMDI , publisher=IDT , url=https://www.idt.com/about/press-room/idt-completes-acquisition-zmdi , date=2015-12-07 , accessdate=2017-11-14 {{cite web , title=Mikroelektronik "Karl Liebknecht" Stahnsdorf (MLS) , url=http://imt-museum.de/de/das-museum/ausstellung/elektronik-fi/gleichrichter-stahnsdorf , language=de , publisher=Industriemuseum Region Teltow e. V. , accessdate=2022-07-28 {{cite web , title=Die Geschichte der Geräte-und Regler-Werke Teltow , url=http://imt-museum.de/de/das-museum/ausstellung/automatisierung-fi/geraete-und-regler-werke-teltow , language=de , publisher=Industriemuseum Region Teltow e. V. , accessdate=2022-07-28 {{cite web , title=Endress+Hauser Stahnsdorf , url=https://www.endress.com/en/Endress-Hauser-group/endresshauser-at-a-glance/group-structure/worldwide-network/stahnsdorf , publisher=Endress+Hauser Management AG , accessdate=2017-11-30 {{cite web , title=Sites , url=https://www.siltronic.com/en/our-company/sites.html , publisher=Siltronic AG , accessdate=2017-11-20 {{cite web , title=Company history , url=http://www.freiberger.com/en/company/company-history.html , publisher=Freiberger Compound Materials GmbH , accessdate=2017-11-20 {{cite web , first=Gabriele , last=Valerius , title=Gleiche Chancen ungleich genutzt? Erwerbsbiographische Mobilitätspfade im ostdeutschen Transformationsprozeß zwischen 1990 und 1996. Studie zum beruflichen Verbleib einer ausgewählten Ingenieurgruppe des VEB Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) , publisher=Frankfurter Institut für Transformationsstudien an der Europa Universität Viadrina , work=Arbeitsberichte - Discussion Papers , volume=98,2 , place=Frankfurt (Oder) , date=1998 , issn=1431-0708 , url=https://www.europa-uni.de/de/forschung/institut/institut_fit/publikationen/discussion_papers/1998/98-02-Valerius.pdf , language=de , accessdate=2022-11-30 , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20161104010253/https://www.europa-uni.de/de/forschung/institut/institut_fit/publikationen/discussion_papers/1998/98-02-Valerius.pdf , archive-date=2016-11-04 {{cite web , archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20020118154948/http://www.megaxess.de/ , archive-date = 2002-01-18 , url = http://www.megaxess.de , title = About Us , publisher = Megaxess GmbH Deutschland , accessdate = 2017-11-27 , url-status = dead {{cite web , archive-url = https://web.archive.org/web/20090611051342/http://www.msfg.de/ , archive-date = 2009-06-11 , url = http://www.msfg.de , title = Welcome , publisher = MSF Microtechnology Services Frankfurt (Oder) GmbH , accessdate = 2017-11-29 , url-status = dead {{cite web , title=Das Oberspreewerk Berlin — Die Umbenennung in Werk für Fernsehelektronik - WF , url=http://www.hts-homepage.de/DDR/OSW.html#WF , first=Hans-Thomas , last=Schmidt , language=de , accessdate=2017-11-30 {{cite web , title=Mikroelektronik 'Anna Seghers', Neuhaus a.R, VEB, RFT; (Ostd.) - vorm. Röhrenwerk , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/dsp_hersteller_detail.cfm?Company_Id=1734 , publisher=Radiomuseum , language=de , accessdate=2017-11-30 {{cite web , title=Company Profile , url=https://www.diodes.com/about/corporate-info/company-profile/ , publisher=Diodes Incorporated , date=2017 , accessdate=2017-11-30 {{cite book , title=TGL 38015: Halbleiterbauelemente; Diskrete Halbleiterbauelemente und integrierte Halbleiterschaltkreise; Bildung der Typbezeichnung und Gestaltung der Typkennzeichnung , trans-title=TGL 38015: Semiconductor Devices; Discrete Semiconductor Devices and Integrated Semiconductor Circuits; Formation of Type Designation and Marking , publisher=Verlag für Standardisierung , place=Leipzig , language=de , date=May 1986 , url=https://www.bbr-server.de/bauarchivddr/archiv/tglarchiv/tgl30001bis40000/tgl38001bis38500/tgl-38015-mai-1986.pdf , accessdate=2017-12-02 {{cite book , title=TGL 31667: Bauelemente der Elektronik; Kennzeichnung; Herstellungsdatum , trans-title=TGL 31667: Electronic Components; Designation; Date of Manufacture , publisher=Verlag für Standardisierung , place=Leipzig , language=de , date=October 1979 , url=https://www.bbr-server.de/bauarchivddr/archiv/tglarchiv/tgl30001bis40000/tgl31501bis32000/tgl-31667-okt-1979.pdf , accessdate=2018-01-09 {{cite web , title=B589N , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_b589n.html , accessdate=2017-12-20 {{cite web , title=A210K , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_a210k.html , accessdate=2017-12-20 {{cite web , title=U131G , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_u131g.html , accessdate=2017-12-20 {{cite web , title=B3370 , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_b3370.html , accessdate=2017-12-20 {{cite web , title=IA338D , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_ia338d.html , accessdate=2021-05-14 {{cite web , title=DK708G , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_dk708g.html , accessdate=2021-05-14 {{cite web , title=UL224D , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_ul224d.html , accessdate=2021-05-14 {{cite web , title=DS8283D , publisher=Radiomuseum.org , url=https://www.radiomuseum.org/tubes/tube_ds8283d.html , accessdate=2021-05-14 {{cite web , title=SRAM Part Codes , publisher=ZMD , url=http://www.zmd.de/pdf/SRAM_PART_ID.pdf , archive-url=https://web.archive.org/web/20051218201445/http://www.zmd.de/pdf/SRAM_PART_ID.pdf , archive-date=2005-12-18 , accessdate=2018-01-10 {{cite journal , title=Bericht von der Leipziger Frühjahrsmesse 1971 - Bauelemente , trans-title=Report from the Leipzig Spring Fair 1971 - Components , language=de , pages=309–311 , journal=Radio Fernsehen Elektronik , issn=0033-7900 , publisher=VEB Verlag Technik , place=Berlin , year=1971 , volume=20 , issue=10 {{cite journal , first=W.E. , last=Schlegel , title=Leipziger Frühjahrsmesse 1986 - Bauelemente , trans-title=Leipzig Spring Fair 1986 - Components , language=de , pages=346 , journal=Radio Fernsehen Elektronik , issn=0033-7900 , publisher=VEB Verlag Technik , place=Berlin , year=1986 , volume=35 , issue=6 {{cite journal , first=Frank , last=Meinecke , title=16-bit Mikroprozessor U 8000 , trans-title=16-bit microprocessor U 8000 , language=de , pages=687–691 , journal=Radio Fernsehen Elektronik , issn=0033-7900 , publisher=VEB Verlag Technik , place=Berlin , year=1985 , volume=34 , issue=11 {{cite magazine , first1=R. , last1=Galle , first2=K. , last2=Benning , title=Amateurschaltkreise des VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik , trans-title=Hobbyist integrated circuits from VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik , language=de , pages=77–78 , journal= Funkamateur , issn=0016-2833 , publisher=Militärverlag der DDR , place=Berlin , year=1984 , volume=33 , issue=2 {{cite book , first=Gareth , last=Dale , title=Between State Capitalism and Globalisation , chapter=Microelectronics: between internationalisation and autarky , pages=185–191 , publisher=Peter Lang AG , place=Bern , year=2004 , isbn=3-03910-181-1 {{cite web , first=Peter , last=Salomon , title=Halbleiter aus Frankfurt – Eine Rezension , pages=4 , url=http://www.ps-blnkd.de/Rezension%20HFO-Buch.pdf , language=de , accessdate=2020-03-16 {{cite web , first=Peter , last=Könnicke , title=Standhaft am Werktor , language=de , url=https://www.pnn.de/potsdam-mittelmark/standhaft-am-werkstor/22290388.html , publisher=Potsdamer Neueste Nachrichten , date=2005-03-03 , accessdate=2021-09-07 {{cite web , title=About SeCoS , url=http://www.secosgmbh.com/about_us.php , publisher=SeCoS Corporation , place=Taipei , accessdate=2021-09-07 Home computer hardware companies Volkseigene Betriebe Defunct companies of Germany Science and technology in East Germany Electronics companies of Germany Semiconductor companies of Germany