|
LC80
The educational computer LC80 was a single-board computer manufactured in the German Democratic Republic (GDR) and intended for teaching purposes. It was the first computer that retail customers could buy in the GDR. History and development The development of the LC 80 started in 1983. At the Leipzig Trade Fair in the spring of 1984 it was presented to the public. Early in 1985 the LC80 was on the market, making it the first computer available to retail customers in the GDR. The computers Z 9001 and HC 900 that had been shown at the same spring fair, could not be manufactured in sufficient quantity and were thus available only to educational institutions. The production probably ended around 1986/87. Technical details The LC80 was programmed by entering hexadecimal machine codes via a built-in 25-key calculator keyboard (16 hexadecimal keys, 7 function keys, NMI, Reset). Programs could be saved and loaded via cassette tape or EPROM. Beside the CPU the board contai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
LC80
The educational computer LC80 was a single-board computer manufactured in the German Democratic Republic (GDR) and intended for teaching purposes. It was the first computer that retail customers could buy in the GDR. History and development The development of the LC 80 started in 1983. At the Leipzig Trade Fair in the spring of 1984 it was presented to the public. Early in 1985 the LC80 was on the market, making it the first computer available to retail customers in the GDR. The computers Z 9001 and HC 900 that had been shown at the same spring fair, could not be manufactured in sufficient quantity and were thus available only to educational institutions. The production probably ended around 1986/87. Technical details The LC80 was programmed by entering hexadecimal machine codes via a built-in 25-key calculator keyboard (16 hexadecimal keys, 7 function keys, NMI, Reset). Programs could be saved and loaded via cassette tape or EPROM. Beside the CPU the board contain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt
VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was an important manufacturer of active electronic components in East Germany. It should not be confused with the more well-known VEB Kombinat Robotron Dresden which used integrated circuits from Kombinat Mikroelektronik in its computers. Their products often carried the trademark RFT, but this was used on most electronic products from East Germany from otherwise unrelated companies. History The Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt was formed in 1978 when the ''VVB Bauelemente und Vakuumtechnik'' was split into ''VEB Kombinat Elektronische Bauelemente Teltow'' for passive electronic components and ''VEB Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt'' for active electronic components. However, the history of many of the individual plants reaches back further, in some cases to before the Second World War. In 1971 the first integrated circuits had been manufactured — the D100C (TTL) by Halbleiterwerk Frankfurt (Oder) and the U101D (PMOS logic) by Funkwerk Er ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robotron Z1013
The MRB Z1013 (german: Mikrorechnerbausatz, links=no, lit=microcomputer kit) was an East German single-board computer produced by VEB Robotron Riesa which was primarily intended for private use and educational institutions. It was powered by a U880 processor (a Z80 clone) and sold together with a membrane (flat foil) keyboard. Initially, the kit was equipped with 16-KByte DRAM, which was later replaced by a 64-KByte version. The kits first became available for sale in 1985 and were distributed in a unique way at the time. To purchase it, buyers had to send a postcard to the Robotron shop in Erfurt and wait six to twelve months and then to pick the kits up in person. The package contained the assembled and tested motherboard, a membrane keyboard, various small parts and detailed technical documentation. This basic kit was shipped without a power supply or casing for the PCB. Most users tended to program the kit using the BASIC interpreter, which was loadable from compact casset ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microprocessor Development Board
A microprocessor development board is a printed circuit board containing a microprocessor and the minimal support logic needed for an electronic engineer or any person that wants to become acquainted with the microprocessor on the board and to learn to program it. It also served users of the microprocessor as a method to prototype applications in products. Unlike a general-purpose system such as a home computer, usually a development board contains little or no hardware dedicated to a user interface. It will have some provision to accept and run a user-supplied program, such as downloading a program through a serial port to flash memory, or some form of programmable memory in a socket in earlier systems. History The reason for the existence of a development board was solely to provide a system for learning to use a new microprocessor, not for entertainment. So everything superfluous was left out to keep costs down. Even an enclosure was not supplied, nor a power supply. This is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
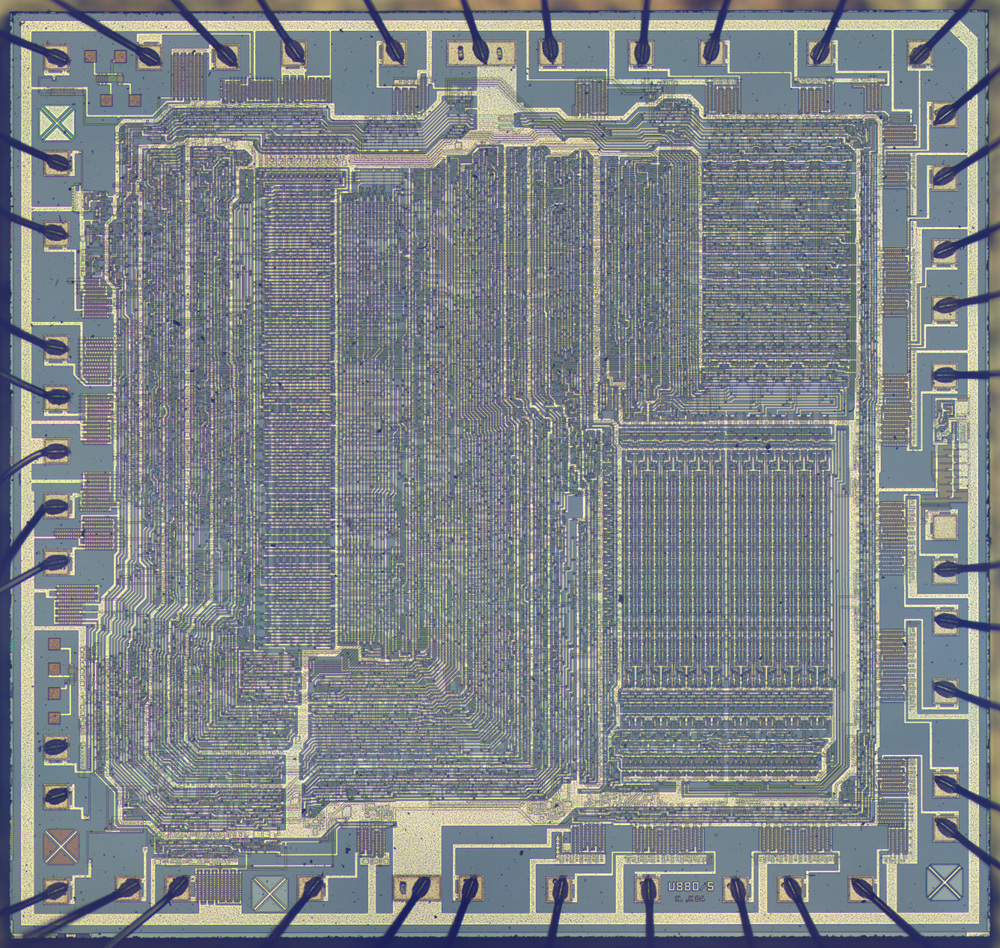
U880
The U880 is an 8-bit microprocessor that was manufactured by VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" Erfurt (abbreviated as MME; part of Kombinat Mikroelektronik Erfurt) in the German Democratic Republic. Production of the U880 started in 1980 at VEB Funkwerk Erfurt (abbreviated as FWE; the plant was renamed to VEB Mikroelektronik "Karl Marx" in 1983). The U880 is an unlicensed clone of the Zilog Z80 microprocessor, also supporting illegal opcodes and bugs, except for very minor differences like not setting the CY flag for the command (when L goes zero). Processor variants The U880 was manufactured in NMOS technology and encased in a plastic DIL40 package with a pin spacing of 2.5 mm (export versions had the Western pin spacing of 2.54 mm; Russian variants also came in a ceramic package). The military version of the U880 has an additional "MEK 4" marking. Image:Robotron UA880D MME 1.jpg, UA880D (1986) Image:Robotron UB880D MME S1 1.jpg, UB880D S1 hobbyist version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MK14
The MK14 (Microcomputer Kit 14) was a computer kit sold by Science of Cambridge of the United Kingdom, first introduced in 1977 for £39.95. The price was very low for a complete computer system at the time, and Science of Cambridge eventually sold over fifteen thousand kits. History In 1977, Ian Williamson approached Clive Sinclair and Chris Curry with a computer design based around the National Semiconductor SC/MP processor. Sinclair and Curry both liked the idea and saw the potential of making a low cost microprocessor system available to the hobbyist market. Initially it was planned to market a kit based on the Williamson design. However, after National Semiconductor had been contacted regarding a bulk purchase of the SC/MP processor Sinclair and Curry decided to use the chip manufacturer's own design. This design used all National Semiconductor chips and the company allowed the use of its designs, the SC/MP Introkit and Keyboard Kit, for free. The National Semiconductor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TK-80
The TK-80 (μCOM Training Kit TK-80) was an 8080-based single-board computer kit developed by Nippon Electric Company (NEC) in 1976. It was originally developed for engineers who considered using the '' μCOM-80 family'' in their product. It was successful among hobbyists in late 1970s in Japan, due to its reasonable price and an expensive computer terminal not being required. History NEC started as a telecommunications equipment vendor, and their business was heavily dependent on Nippon Telegraph and Telephone Public Corporation (NTT). To increase private demand and exports, NEC began developing new industries such as computers and semiconductors in the 1950s. Although those businesses were not profitable enough, NEC continued investing profits from successful telecommunication business. In the 1970s, the Semiconductor Division developed several microprocessors including Intel compatible processors, and in 1976 got a second-source agreement with Intel to produce the 8080 micro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acorn System 1
The Acorn System 1, initially called the Acorn Microcomputer (Micro-Computer), was an early 8-bit microcomputer for hobbyists, based on the MOS 6502 CPU, and produced by British company Acorn Computers from 1979. The main parts of the system were designed by then-Cambridge-undergraduate student Sophie Wilson, with a cassette interface designed by Steve Furber.http://www.stairwaytohell.com/articles/SG-SophieWilson.html Sophie Wilson - 2007 Interview with Stuart Goodwin It was Acorn's first product, and was based on an automated cow feeder. It was a small machine built on two Eurocard-standard circuit boards and it could be purchased ready-built or in kit form. *one card (shown right) with the I/O part of the computer: a LED seven segment display, a 25-key keypad ( hex+function keys), and a cassette CUTS interface (the circuitry to the left of the keypad) *the second card (the computer board - see below), which included the CPU, RAM/ROM memory, and support chips *the two boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zilog Z80
The Z80 is an 8-bit microprocessor introduced by Zilog as the startup company's first product. The Z80 was conceived by Federico Faggin in late 1974 and developed by him and his 11 employees starting in early 1975. The first working samples were delivered in March 1976, and it was officially introduced on the market in July 1976. With the revenue from the Z80, the company built its own chip factories and grew to over a thousand employees over the following two years. The Zilog Z80 is a software-compatible extension and enhancement of the Intel 8080 and, like it, was mainly aimed at embedded systems. Although used in that role, the Z80 also became one of the most widely used CPUs in desktop computers and home computers from the 1970s to the mid-1980s. It was also common in military applications, musical equipment such as synthesizers (like the Roland Jupiter-8), and coin-operated arcade games of the late 1970s and early 1980s, including '' Pac-Man''. Zilog licensed the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
MEK6800D2
The MEK6800D2 was a Microprocessor development board, development board for the Motorola 6800 microprocessor, produced by Motorola in 1976. It featured a keyboard with hexadecimal keys and an LED display, but also featured an RS-232 asynchronous serial interface for a Teleprinter, Teletype or other terminal. Data and programs could be loaded from and saved to an audio cassette tape. There was an on-board Machine code monitor, monitor program called ''JBUG (analogous to an operating system on a modern computer)'' fitted in a 1K byte ROM, and the maximum RAM capacity on board was 512 bytes, but this could be expanded via the Motorola ''EXORciser'' computer bus interface. The hardware consisted of two circuit boards. The keyboard-display module contained a 16 key (hexadecimal) data entry section, and eight function keys labeled M, E, R, G, V, N, L, and Pl along with a 6 hex digit LED display. The keyboard-display board connected to the microcomputer module by a 50-conductor ribbon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.Potash USGS 2008 Minerals Yearbook The name derives from ''pot ash'', plant ashes or soaked in water in a pot, the primary means of manufacturing potash before the . The word '''' is derived from ''potash''. Potash is produced worldwide in amounts exceeding 90 million |
Morse Code
Morse code is a method used in telecommunication to encode text characters as standardized sequences of two different signal durations, called ''dots'' and ''dashes'', or ''dits'' and ''dahs''. Morse code is named after Samuel Morse, one of the inventors of the telegraph. International Morse code encodes the 26 basic Latin letters through , one accented Latin letter (), the Arabic numerals, and a small set of punctuation and procedural signals ( prosigns). There is no distinction between upper and lower case letters. Each Morse code symbol is formed by a sequence of ''dits'' and ''dahs''. The ''dit'' duration is the basic unit of time measurement in Morse code transmission. The duration of a ''dah'' is three times the duration of a ''dit''. Each ''dit'' or ''dah'' within an encoded character is followed by a period of signal absence, called a ''space'', equal to the ''dit'' duration. The letters of a word are separated by a space of duration equal to three ''dits'', ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |