KDE Software Compilation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The KDE Software Compilation (KDE SC) was an umbrella term for the
/ref> These included DCOP (Desktop COmmunication Protocol), KIO (an application I/O library),
 As of August 2014, KDE no longer provides synchronized releases of the entire software compilation; instead the software is split into three parts:
*
As of August 2014, KDE no longer provides synchronized releases of the entire software compilation; instead the software is split into three parts:
*
KDE-Artwork
Additional icons, styles, etc. * KDE-Admin * KDE-SDK * KDE-Bindings
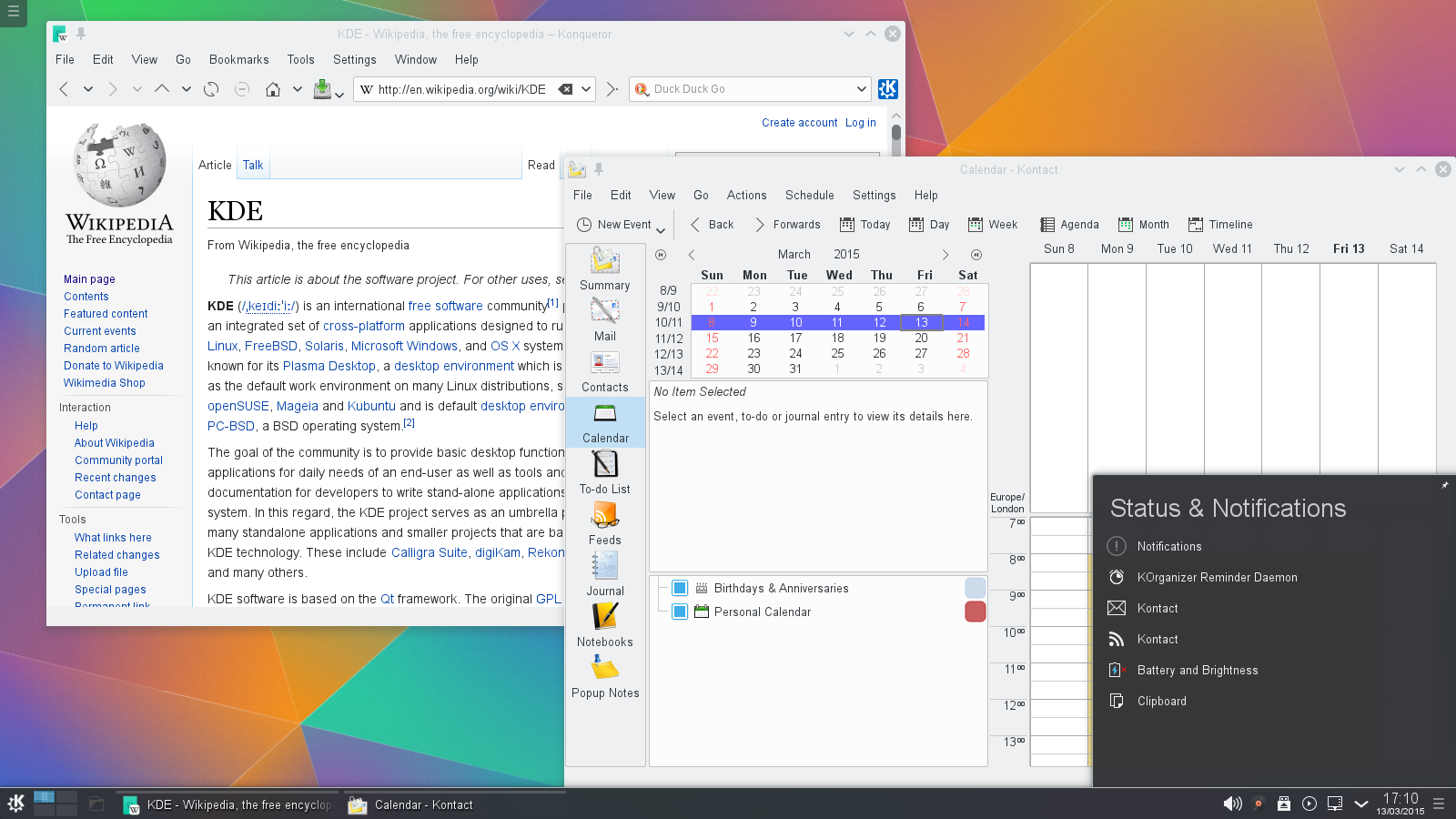 Major applications by KDE Software Compilation include:
*
Major applications by KDE Software Compilation include:
*
The KDE websiteKDE.News
news announcements
KDE community forums
the official forum board
Planet KDE
blog aggregate
KDE wikisKDE LocalizationKDE-Apps
KDE and Qt software repository
KDE-LookKDE-Files
{{FLOSS 1998 software Free desktop environments KDE software Unix windowing system-related software Utilities for Linux Utilities for macOS Utilities for Windows
desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphica ...
plus a range of included applications produced by KDE
KDE is an international free software community that develops free and open-source software. As a central development hub, it provides tools and resources that allow collaborative work on this kind of software. Well-known products include the ...
. From its 1.0 release in July 1998 until the release of version 4.4 in February 2010, the Software Compilation was simply known as KDE, which stood for K Desktop Environment until the rebrand. The then called KDE SC was used from 4.4 onward until the final release 4.14 in July 2014. It consisted of the KDE Plasma 4
KDE Plasma 4 was the fourth generation of the KDE workspace environments. It consisted of three workspaces, each targeting a certain platform: ''Plasma Desktop'' for traditional desktop PCs and notebooks, ''Plasma Netbook'' for netbooks, and ''Pl ...
desktop and those KDE applications, whose development teams chose to follow the Software Compilation's release schedule. After that, the KDE SC was split into three separate product entities: KDE Plasma, KDE Frameworks
KDE Frameworks is a collection of libraries and software frameworks readily available to any Qt-based software stacks or applications on multiple operating systems. Featuring frequently needed functionality solutions like hardware integration, fi ...
and KDE Applications
The KDE Gear (also known as the KDE Applications Bundle or KDE Applications) is a set of applications and supporting libraries that are developed by the KDE community, primarily used on Linux-based operating systems but mostly multiplatform, and ...
, each with their own independent release schedules.
History
Origins
KDE was founded in 1996 byMatthias Ettrich
Matthias Ettrich (born 14 June 1972) is a German computer scientist and founder of the KDE and LyX projects.
Early life
Ettrich was born in Bietigheim-Bissingen, Baden-Württemberg, and went to school in Beilstein while living with his paren ...
, who was then a student at the University of Tübingen
The University of Tübingen, officially the Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen (german: Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen; la, Universitas Eberhardina Carolina), is a public research university located in the city of Tübingen, Baden-Wü ...
. At the time, he was troubled by certain aspects of the Unix
Unix (; trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems that derive from the original AT&T Unix, whose development started in 1969 at the Bell Labs research center by Ken Thompson, Dennis Ritchie, and ot ...
desktop. Among his qualms was that none of the applications
Application may refer to:
Mathematics and computing
* Application software, computer software designed to help the user to perform specific tasks
** Application layer, an abstraction layer that specifies protocols and interface methods used in a c ...
looked, felt, or worked alike. He proposed the formation of not only a set of applications, but, rather, a desktop environment
In computing, a desktop environment (DE) is an implementation of the desktop metaphor made of a bundle of programs running on top of a computer operating system that share a common graphical user interface (GUI), sometimes described as a graphica ...
, in which users could expect things to look, feel and work consistently. He also wanted to make this desktop easy to use; one of his complaints with desktop applications of the time was that his girlfriend could not use them. His initial Usenet
Usenet () is a worldwide distributed discussion system available on computers. It was developed from the general-purpose Unix-to-Unix Copy (UUCP) dial-up network architecture. Tom Truscott and Jim Ellis conceived the idea in 1979, and it was ...
post spurred a lot of interest, and the KDE project was born.
Ettrich chose to use Trolltech's Qt framework
Qt (pronounced "cute") is cross-platform software for creating graphical user interfaces as well as cross-platform applications that run on various software and hardware platforms such as Linux, Windows, macOS, Android or embedded systems wit ...
for the KDE project. Other programmers quickly started developing KDE/Qt applications, and by early 1997, a few applications were being released.
First series
On 12 July 1998, '' K Desktop Environment 1.0'' was released. In November 1998, the Qt toolkit was dual-licensed under the free/open source
Open source is source code that is made freely available for possible modification and redistribution. Products include permission to use the source code, design documents, or content of the product. The open-source model is a decentralized sof ...
Q Public License
The Q Public License (QPL) is a non-copyleft license, created by Trolltech for its free edition of the Qt. It was used until Qt 3.0, as Trolltech toolkit version 4.0 was released under GPL version 2.
It fails the Debian Free Software Guidelin ...
(QPL) and a proprietary license for proprietary software developers. Debate continued about compatibility with the GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the Four Freedoms (Free software), four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was th ...
(GPL), so in September 2000, Trolltech made the Unix version of the Qt libraries available under the GPL, in addition to the QPL. Trolltech continued to require licenses for developing proprietary software
Proprietary software is software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and int ...
with Qt. The core libraries of KDE are collectively licensed under the GNU LGPL
The GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL) is a free-software license published by the Free Software Foundation (FSF). The license allows developers and companies to use and integrate a software component released under the LGPL into their own ...
, but the only way for proprietary software to make use of them was to be developed under the terms of the Qt proprietary license.
Second series
Beginning 23 October 2000, the second series of releases, ''K Desktop Environment 2
K Desktop Environment 2 was the second series of releases of the K Desktop Environment. There were three major releases in this series.
Major updates
K Desktop Environment 2 introduced significant technological improvements compared to its pre ...
'', introduced significant technological improvements.KDE 2.0 Release Announcement/ref> These included DCOP (Desktop COmmunication Protocol), KIO (an application I/O library),
KParts
KDE Frameworks is a collection of libraries and software frameworks readily available to any Qt-based software stacks or applications on multiple operating systems. Featuring frequently needed functionality solutions like hardware integration, fi ...
(a component object model, which allows an application to embed another within itself), and KHTML
KHTML is a browser engine developed by the KDE project. It is the default engine of the Konqueror browser, but it has not been actively worked on since 2016. Moreover, KHTML will be discontinued for KDE Frameworks 6.
Built on the KParts fra ...
(an HTML
The HyperText Markup Language or HTML is the standard markup language for documents designed to be displayed in a web browser. It can be assisted by technologies such as Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) and scripting languages such as JavaScri ...
rendering and drawing engine).
Third series
The third series was much larger than previous series, consisting of six major releases starting on 3 April 2002. The API changes between ''K Desktop Environment 2'' and ''K Desktop Environment 3'' were comparatively minor, meaning that the KDE 3 can be seen as largely a continuation of the ''K Desktop Environment 2'' series. All releases of ''K Desktop Environment 3'' were built upon Qt 3, which was only released under the GPL for Linux and Unix-like operating systems, includingMac OS X
macOS (; previously OS X and originally Mac OS X) is a Unix operating system developed and marketed by Apple Inc. since 2001. It is the primary operating system for Apple's Mac (computer), Mac computers. Within the market of ...
. It is marked stable running on Mac OS X since 2008. Unlike KDE SC 4, however, it requires an X11 server to operate. In 2002, members of the KDE on Cygwin project began porting the GPL licensed Qt/X11 code base to Windows.
Fourth series
KDE Software Compilation 4
KDE Software Compilation 4 (KDE SC 4) was the only series of the so-called KDE Software Compilation (short: KDE SC), first released in January 2008 and the last release being 4.14.3 released in November 2014. It was the follow-up to K Desktop En ...
, first released on 11 January 2008, is based on Qt 4, which is also released under the GPL for Windows and Mac OS X. Therefore, KDE SC 4 applications can be compiled and run natively on these operating systems as well. KDE Software Compilation 4 on Mac OS X is currently considered beta, while on Windows it is not in the final state, so applications can be unsuitable for day to day use.
KDE SC 4 includes many new technologies and technical changes. The centerpiece is a redesigned desktop and panels collectively called Plasma, which replaces Kicker
Kicker or The Kicker may refer to:
Sports
* Placekicker, a position in American and Canadian football
* ''Kicker'' (sports magazine), in Germany
* Kicker, the German colloquial term for an association football player
* Kicker, the word used i ...
, KDesktop
KDesktop is the component of the K Desktop Environment 3 and earlier, which provides a virtual background window to draw icons or other graphics on. In conjunction with Kicker and SuperKaramba, it constitutes the graphical shell.
In KDE Software ...
, and SuperKaramba
SuperKaramba is a tool, a so-called widget engine, that allows the creation of functionality enhancement modules (desktop widgets) on the KDE desktop. The desktop widgets are usually embedded directly into the background and do not disturb the ...
by integrating their functionality into one piece of technology; Plasma is intended to be more configurable for those wanting to update the decades-old desktop metaphor
In computing, the desktop metaphor is an interface metaphor which is a set of unifying concepts used by graphical user interfaces to help users interact more easily with the computer. The desktop metaphor treats the computer monitor as if it is t ...
. There are a number of new frameworks, including Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phon ...
(a new multimedia interface making KDE independent of any one specific media backend) Solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount o ...
(an API for network and portable devices), and Decibel
The decibel (symbol: dB) is a relative unit of measurement equal to one tenth of a bel (B). It expresses the ratio of two values of a power or root-power quantity on a logarithmic scale. Two signals whose levels differ by one decibel have a po ...
(a new communication framework to integrate all communication protocols into the desktop). Also featured is a metadata and search framework, incorporating Strigi as a full-text file indexing service, and NEPOMUK
Nepomuk (; german: Pomuk) is a town in Plzeň-South District in the Plzeň Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 3,700 inhabitants. It is known as the birthplace of Saint John of Nepomuk, who was born here around 1340 and whose statue can b ...
with KDE integration.
Starting with Qt 4.5, Qt was also made available under the LGPL version 2.1, a major step for KDE adoption in corporate and proprietary environments, as the LGPL permits proprietary applications to link to libraries licensed under the LGPL.
Post-fourth series
 As of August 2014, KDE no longer provides synchronized releases of the entire software compilation; instead the software is split into three parts:
*
As of August 2014, KDE no longer provides synchronized releases of the entire software compilation; instead the software is split into three parts:
* KDE Frameworks 5
KDE Frameworks is a collection of libraries and software frameworks readily available to any Qt-based software stacks or applications on multiple operating systems. Featuring frequently needed functionality solutions like hardware integration, fi ...
, a collection of libraries and software frameworks (5.0 released on July 7, 2014, and new major releases are made monthly)
* KDE Plasma 5
KDE Plasma 5 is the fifth and current generation of the graphical workspaces environment created by KDE primarily for Linux systems. KDE Plasma 5 is the successor of KDE Plasma 4 and was first released on 15 July 2014.
It includes a new default ...
, a desktop environment (5.0 released on July 15, 2014, and new major releases are made every three months)
* KDE Applications
The KDE Gear (also known as the KDE Applications Bundle or KDE Applications) is a set of applications and supporting libraries that are developed by the KDE community, primarily used on Linux-based operating systems but mostly multiplatform, and ...
, a bundle of applications and supporting libraries (14.12 was the first version incorporating Frameworks 5 based applications, and introduced date-based version numbers).
Major changes include a move from Qt 4 to Qt 5, support for the next-generation display server protocol Wayland, support for the next-generation rendering API
This is a glossary of terms relating to computer graphics
Computer graphics deals with generating images with the aid of computers. Today, computer graphics is a core technology in digital photography, film, video games, cell phone and comp ...
Vulkan
Vulkan is a low- overhead, cross-platform API, open standard for 3D graphics and computing. Vulkan targets high-performance real-time 3D graphics applications, such as video games and interactive media. Vulkan is intended to offer higher perfor ...
and modularization of the KDE core libraries.
Initial releases of Frameworks 5 and Plasma 5 were made available in July 2014.
Development
Source code
KDE SC releases are made to the KDE FTP server in the form ofsource code
In computing, source code, or simply code, is any collection of code, with or without comments, written using a human-readable programming language, usually as plain text. The source code of a program is specially designed to facilitate the wo ...
with configure scripts, which are compiled by operating system vendors and integrated with the rest of their systems before distribution. Most vendors use only stable and tested versions of KDE SC, providing it in the form of easily installable, pre-compiled packages. The source code of every stable and development version of KDE SC is stored in the KDE source code repository, using Git
Git () is a distributed version control system: tracking changes in any set of files, usually used for coordinating work among programmers collaboratively developing source code during software development. Its goals include speed, data in ...
. KDE Platform
KDE Platform 4 was a collection of libraries and software frameworks by KDE that served as technological foundation for KDE Software Compilation 4 distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). KDE Platform 4 was the successor to ...
is licensed under the LGPL, BSD license, MIT license
The MIT License is a permissive free software license originating at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) in the late 1980s. As a permissive license, it puts only very limited restriction on reuse and has, therefore, high license comp ...
, or X11 license. Applications also allow GPL. Documentation also allow FDL. CMake
In software development, CMake is cross-platform free and open-source software for build automation, testing, packaging and installation of software by using a compiler-independent method. CMake is not a build system itself; it generates an ...
modules must be licensed under the BSD licence.
Major releases
Major releases are releases that begin a series (version number X.0). These releases are allowed to breakbinary compatibility
Binary-code compatibility (binary compatible or object-code-compatible) is a property of a computer system, meaning that it can run the same executable code, typically machine code for a general-purpose computer CPU, that another computer syste ...
with the predecessor, or to put it differently, all following releases (X.1, X.2, ...) will guarantee binary portability (API
An application programming interface (API) is a way for two or more computer programs to communicate with each other. It is a type of software interface, offering a service to other pieces of software. A document or standard that describes how ...
& ABI). This means, for instance, that software that was developed for KDE 3.0 will work on all (future) KDE 3 releases; however, an application developed for KDE 2 is not guaranteed to be able to make use of the KDE 3 libraries. KDE major version numbers follow the Qt release cycle, meaning that KDE SC 4 is based on Qt 4, while KDE 3 was based on Qt 3.
Qt 5.0 was released 19 December 2012, Qt 5.2 12 December 2013. And for example KDE Frameworks 5.21.0 requires Qt >= 5.4, and no longer supports Qt 5.3 (cf. Qt version history).
Standard releases
There are two main types of standard releases: Feature releases and bugfix releases. Feature releases have two version numbers, for example 3.5 and contain new features. As soon as a feature release is ready and announced, work on the next feature release starts. A feature release needs several months to be finished and many bugs that are fixed during this time arebackport
Backporting is the action of taking parts from a newer version of a software system or software component and porting them to an older version of the same software. It forms part of the maintenance step in a software development process, and it is ...
ed to the stable branch, meaning that these fixes are incorporated into the last stable release by bugfix releases. During the KDE SC 4 series, KDE SC had a feature release roughly every six months. Since the split, KDE Plasma releases a new feature version roughly every 3–4 months.
Bugfix releases have three version numbers, e.g. KDE 1.1.1, and focus on fixing bugs, minor glitches, and making small usability improvements. Bugfix releases in general do not allow new features, although some releases include small enhancements. A shortened release schedule is used. Starting with the KDE SC 4 series, KDE SC has a maintenance release roughly every month, except during the month of a feature release, while with Plasma 5, bugfix releases tend to happen even shorter like 2–3 weeks.
Release cycle
The KDE team releases new versions on a regular basis.Lines of Code
* KDE 1.0 hadLoC
LOC, L.O.C., Loc, LoC, or locs may refer to:
Places
* Lóc, a village in Sângeorgiu de Pădure, Mureș County, Romania
* Lócs, a village in Vas county, Hungary
* Line of Contact, meeting place of Western and Eastern Allied forces at the e ...
.
* KDE 4.3 had LoC.
Implementation
Most KDE software uses Qt which runs on most Unix andUnix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-li ...
systems (including Mac OS X), Android and Microsoft Windows.
CMake
In software development, CMake is cross-platform free and open-source software for build automation, testing, packaging and installation of software by using a compiler-independent method. CMake is not a build system itself; it generates an ...
serves as the build tool. This allows KDE to support a wider range of platforms, including Windows.
GNU gettext
In computing, gettext is an internationalization and localization (i18n and l10n) system commonly used for writing multilingual programs on Unix-like computer operating systems. One of the main benefits of gettext is that it separates programmi ...
is used for translation. Doxygen
Doxygen ( ) is a documentation generator and static analysis tool for software source trees. When used as a documentation generator, Doxygen extracts information from specially-formatted comments within the code. When used for analysis, Doxyge ...
is used to generate api documentation.
Overview
* KDE Software Compilation: KDE Software Compilation (KDE SC) is the coordinated releases of new software versions, gathering elements from the previous components to build an integrated core of software. The KDE SC is not a product as a single entity. *Calligra Suite
Calligra Suite is a graphic art and office suite by KDE. It is available for desktop PCs, tablet computers, and smartphones. It contains applications for word processing, spreadsheets, presentation, databases, vector graphics, and digital paintin ...
: Integrated office suite.
* KDEWebdev: Web development tools.
* KDE-Extragear: Extragear is a collection of applications associated with KDE. Those applications are not part the official software compilation, but they are still part of the project.
* KDE-Playground: This package contains pre-release and unstable software. It is a place for applications to mature.
Packages
The Software Compilation consists of the following packages: * KDE-Libs: A collection oflibraries
A library is a collection of materials, books or media that are accessible for use and not just for display purposes. A library provides physical (hard copies) or digital access (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location or a vir ...
that provides frameworks
A framework is a generic term commonly referring to an essential supporting structure which other things are built on top of.
Framework may refer to:
Computing
* Application framework, used to implement the structure of an application for an op ...
and functionality for developers.
* KDE-Base: The base set of files, libraries and programs needed by the Software Compilation. KDE-Base is divided into three parts:
** Applications: Containing the applications that form the KDE desktop, like Konqueror, Dolphin, KWrite, and Konsole.
** Runtime: Applications required by KDE apps to function properly at runtime.
** Workspace: Provides the graphical environments.
* KDE-Plasma-Addons: Additional Plasma widgets.
* KDE-Network
* KDE-Pim
* KDE-Graphics
* KDE-Multimedia
* Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phon ...
* KDE-Accessibility: Accessibility applications.
* KDE-Utilities
* KDE-Edu
* KDE-Games
* KDE-Toys
KDE-Artwork
Additional icons, styles, etc. * KDE-Admin * KDE-SDK * KDE-Bindings
Base technologies
*KHTML
KHTML is a browser engine developed by the KDE project. It is the default engine of the Konqueror browser, but it has not been actively worked on since 2016. Moreover, KHTML will be discontinued for KDE Frameworks 6.
Built on the KParts fra ...
– HTML rendering engine, forked into WebKit
WebKit is a browser engine developed by Apple and primarily used in its Safari web browser, as well as on the iOS and iPadOS version of any web browser. WebKit is also used by the BlackBerry Browser, PlayStation consoles beginning from the PS ...
in 2004
* KJS - JavaScript engine
A JavaScript engine is a software component that executes JavaScript code. The first JavaScript engines were mere interpreters, but all relevant modern engines use just-in-time compilation for improved performance.
JavaScript engines are typica ...
* KIO – Extensible network-transparent file access
* Kiosk
Historically, a kiosk () was a small garden pavilion open on some or all sides common in Iran, Persia, the Indian subcontinent, and in the Ottoman Empire from the 13th century onward. Today, several examples of this type of kiosk still exist ...
– Allows disabling features within KDE to create a more controlled environment
* KParts
KDE Frameworks is a collection of libraries and software frameworks readily available to any Qt-based software stacks or applications on multiple operating systems. Featuring frequently needed functionality solutions like hardware integration, fi ...
– Lightweight in-process graphical component framework
* KWin
KWin is a window manager for the X Window System and a Wayland compositor. It is released as a part of KDE Plasma 5, for which it is the default window manager. KWin can also be used on its own or with other desktop environments.
KWin can be c ...
– Window manager
A window manager is system software that controls the placement and appearance of windows within a windowing system in a graphical user interface. Most window managers are designed to help provide a desktop environment. They work in conjunction ...
* XMLGUI – Allows defining UI elements, such as menus and toolbars via XML
Extensible Markup Language (XML) is a markup language and file format for storing, transmitting, and reconstructing arbitrary data. It defines a set of rules for encoding documents in a format that is both human-readable and machine-readable ...
files
* Phonon
In physics, a phonon is a collective excitation in a periodic, Elasticity (physics), elastic arrangement of atoms or molecules in condensed matter physics, condensed matter, specifically in solids and some liquids. A type of quasiparticle, a phon ...
– Multimedia framework
A multimedia framework is a software framework that handles media on a computer and through a network. A good multimedia framework offers an intuitive API and a modular architecture to easily add support for new audio, video and container formats ...
* Plasma – Desktop and panel widget engine
A software widget is a relatively simple and easy-to-use software application or component made for one or more different software platforms.
A desk accessory or applet is an example of a simple, stand-alone user interface, in contrast with a ...
* Solid
Solid is one of the State of matter#Four fundamental states, four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and Plasma (physics), plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount o ...
– Device integration framework
* Sonnet – Spell checker
* ThreadWeaver
ThreadWeaver is a system library initially developed for KDE Software Compilation 4 and later refactored for KDE Frameworks 5.
ThreadWeaver allows developers to easily take advantage of multi-core processors and multithreading. In ThreadWeaver th ...
– Library to use multiprocessor
Multiprocessing is the use of two or more central processing units (CPUs) within a single computer system. The term also refers to the ability of a system to support more than one processor or the ability to allocate tasks between them. There ar ...
systems more effectively
Applications
 Major applications by KDE Software Compilation include:
*
Major applications by KDE Software Compilation include:
* Ark
Ark or ARK may refer to:
Biblical narratives and religion Hebrew word ''teva''
* Noah's Ark, a massive vessel said to have been built to save the world's animals from a flood
* Ark of bulrushes, the boat of the infant Moses
Hebrew ''aron''
* ...
– Archiving tool
* Dragon Player
Dragon Player is a simple media player (application software), media player for the KDE desktop environment. It is the renamed continuation of a video player for KDE 3 called Codeine, which was originally created and developed by Max Howell, and ...
– Media player.
* Dolphin
A dolphin is an aquatic mammal within the infraorder Cetacea. Dolphin species belong to the families Delphinidae (the oceanic dolphins), Platanistidae (the Indian river dolphins), Iniidae (the New World river dolphins), Pontoporiidae (the ...
– File manager
A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders. The most common operations performed on files or groups of files include creating, opening (e.g. viewing, playing, editing or pr ...
* Falkon
Falkon (formerly QupZilla) is a free and open-source web browser developed by KDE. It is built on the QtWebEngine, which is a wrapper for the Chromium browser core.
Both KaOS and openMandriva Lx use Falkon as their default browser.
Featu ...
- Web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
* Gwenview
Gwenview is an image viewer for Unix-like systems (including Linux) and is released as part of the KDE Applications bundle. The current maintainer is Aurélien Gâteau. The word "Gwen" means "white" in the Breton language and is commonly used as ...
– Image viewer
An image viewer or image browser is a computer program that can display stored graphical images; it can often handle various graphics file formats. Such software usually renders the image according to properties of the display such as color depth, ...
* Kate Kate name may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Kate (given name), a list of people and fictional characters with the given name or nickname
* Gyula Káté (born 1982), Hungarian amateur boxer
* Lauren Kate (born 1981), American autho ...
/ KWrite – Text editor
A text editor is a type of computer program that edits plain text. Such programs are sometimes known as "notepad" software (e.g. Windows Notepad). Text editors are provided with operating systems and software development packages, and can be us ...
* Konsole
Konsole is a free and open-source terminal emulator graphical application which is part of KDE Applications and ships with the KDE desktop environment. Konsole was originally written by Lars Doelle. It ls licensed under the GPL-2.0-or-later and ...
– Terminal emulator
A terminal emulator, or terminal application, is a computer program that emulates a video terminal within some other display architecture. Though typically synonymous with a shell or text terminal, the term ''terminal'' covers all remote termin ...
* Kontact
Kontact is a personal information manager and groupware software suite developed by KDE. It supports calendars, contacts, notes, to-do lists, news, and email. It offers a number of inter-changeable graphical UIs (KMail, KAddressBook, Akregator ...
– Personal information manager
A personal information manager (often referred to as a PIM tool or, more simply, a PIM) is a type of application software that functions as a personal organizer. The acronym PIM is now, more commonly, used in reference to personal information manag ...
featuring an e-mail client
An email client, email reader or, more formally, message user agent (MUA) or mail user agent is a computer program used to access and manage a user's email.
A web application which provides message management, composition, and reception functio ...
, a news client
A newsreader is an application program that reads articles on Usenet distributed throughout newsgroups. Newsreaders act as clients which connect to a news server, via the Network News Transfer Protocol (NNTP), to download articles and post new ar ...
, a feed aggregator
Feed or The Feed may refer to:
Animal foodstuffs
* Animal feed, food given to domestic animals in the course of animal husbandry
** Fodder, foodstuffs manufactured for animal consumption
** Forage, foodstuffs that animals gather themselves, s ...
, to-do lists, etc.
* Konqueror
Konqueror is a free and open-source web browser and file manager that provides web access and file-viewer functionality for file systems (such as local files, files on a remote FTP server and files in a disk image). It forms a core part of t ...
– Web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used on ...
and file manager
A file manager or file browser is a computer program that provides a user interface to manage files and folders. The most common operations performed on files or groups of files include creating, opening (e.g. viewing, playing, editing or pr ...
* Kopete
Kopete is a multi-protocol, free software instant messaging client released as part of the KDE Software Compilation. Although it can run in numerous environments, it was designed for and integrates with the KDE Plasma Workspaces. Kopete was star ...
– Instant messaging client
* KRDC – a remote desktop
In computing, the term remote desktop refers to a software- or operating system feature that allows a personal computer's desktop environment to be run remotely off of one system (usually a PC, but the concept applies equally to a server or a ...
client
Client(s) or The Client may refer to:
* Client (business)
* Client (computing), hardware or software that accesses a remote service on another computer
* Customer or client, a recipient of goods or services in return for monetary or other valuabl ...
. Both the Virtual Network Computing
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop-sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. It transmits the keyboard and mouse input from one computer to another, relaying the g ...
(VNC) and Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) protocols are supported, so Unix-like
A Unix-like (sometimes referred to as UN*X or *nix) operating system is one that behaves in a manner similar to a Unix system, although not necessarily conforming to or being certified to any version of the Single UNIX Specification. A Unix-li ...
and Windows
Windows is a group of several proprietary graphical operating system families developed and marketed by Microsoft. Each family caters to a certain sector of the computing industry. For example, Windows NT for consumers, Windows Server for serv ...
PC can be accessed using this software. As part of the GSoC, project developers helped make Libvncserver compile on Windows platforms, allowing for a port to Windows.
Licensing
In November 1998, the Qt framework was dual-licensed under thefree and open-source
Free and open-source software (FOSS) is a term used to refer to groups of software consisting of both free software and open-source software where anyone is freely licensed to use, copy, study, and change the software in any way, and the source ...
Q Public License
The Q Public License (QPL) is a non-copyleft license, created by Trolltech for its free edition of the Qt. It was used until Qt 3.0, as Trolltech toolkit version 4.0 was released under GPL version 2.
It fails the Debian Free Software Guidelin ...
(QPL) and a commercial license for proprietary software
Proprietary software is software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and int ...
developers. The same year, the KDE Free Qt foundation was created which guarantees that Qt would fall under a variant of the very liberal BSD license
BSD licenses are a family of permissive free software licenses, imposing minimal restrictions on the use and distribution of covered software. This is in contrast to copyleft licenses, which have share-alike requirements. The original BSD lic ...
should Trolltech cease to exist or no free version of Qt be released during 12 months.
Debate continued about compatibility with the GNU General Public License (GPL), hence in September 2000 Trolltech made the Unix version of the Qt libraries available under the GPL in addition to the QPL which eliminated the concerns of the Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)#501(c)(3), 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed ...
. Trolltech continued to require licenses for developing proprietary software
Proprietary software is software that is deemed within the free and open-source software to be non-free because its creator, publisher, or other rightsholder or rightsholder partner exercises a legal monopoly afforded by modern copyright and int ...
with Qt. The core libraries of KDE are collectively licensed under the GNU LGPL but the only way for proprietary software to make use of them was to be developed under the terms of the Qt proprietary license.
Starting with Qt 4.5, Qt was also made available under the LGPL version 2.1, now allowing proprietary applications to legally use the open source Qt version.
See also
*KDE Platform
KDE Platform 4 was a collection of libraries and software frameworks by KDE that served as technological foundation for KDE Software Compilation 4 distributed under the GNU Lesser General Public License (LGPL). KDE Platform 4 was the successor to ...
* Comparison of X Window System desktop environments
References
External links
The KDE website
news announcements
KDE community forums
the official forum board
Planet KDE
blog aggregate
KDE wikis
KDE and Qt software repository
KDE-Look
{{FLOSS 1998 software Free desktop environments KDE software Unix windowing system-related software Utilities for Linux Utilities for macOS Utilities for Windows