Komatiite on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Komatiite () is a type of
Komatiite () is a type of

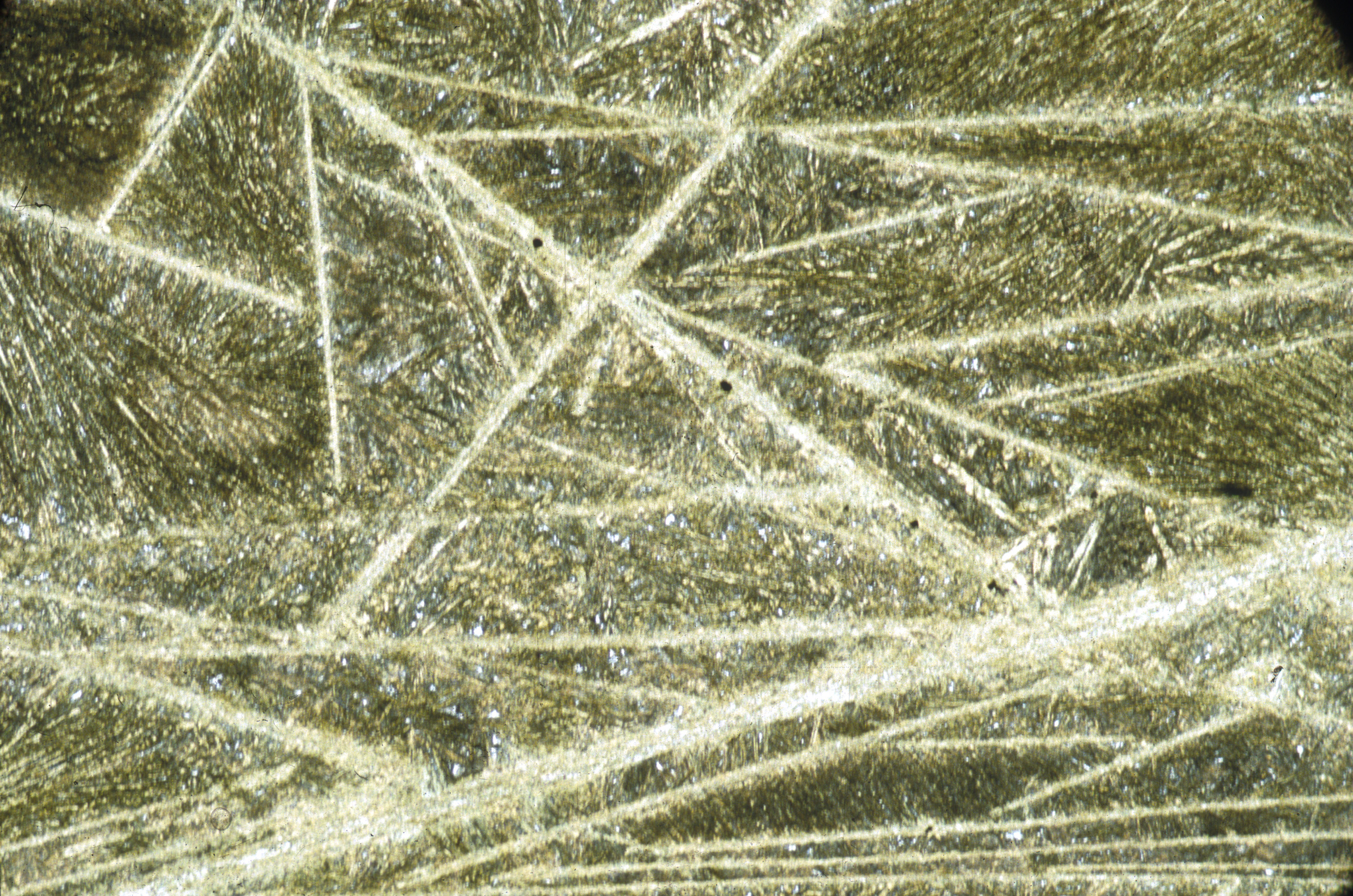 A common and distinctive texture is known as ''spinifex texture'' and consists of long acicular phenocrysts of olivine (or
A common and distinctive texture is known as ''spinifex texture'' and consists of long acicular phenocrysts of olivine (or 

PDF
accessed 7-25-2005 * Vernon R.H., 2004, ''A Practical Guide to Rock Microstructure'', (pp. 43–69, 150–152) Cambridge University Press. * Arndt, N.T., and Nisbet, E.G. (1982), ''Komatiites''. Unwin Hyman, . Hardcover. * Arndt, N.T., and Lesher, C.M. (2005), Komatiites, in Selley, RC, Cocks, L.R.M., Plimer, I.R. (Editors), ''Encyclopedia of Geology'' 3, Elsevier, New York, pp. 260–267 * Faure, F., Arndt, N.T. Libourel, G. (2006), Formation of spinifex texture in komatiite: An experimental study. J. Petrol 47, 1591–1610. * Arndt, N.T., Lesher, C.M. and Barnes, S.J. (2008), ''Komatiite'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 488 pp., .
accessed 7-25-2005
Komatiites and astrobiology
(with text in French) retrieved 2009-05-17 {{Volcanoes Ultramafic rocks Volcanology Igneous petrology Metamorphic rocks Volcanic rocks Subvolcanic rocks
 Komatiite () is a type of
Komatiite () is a type of ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
mantle-derived volcanic rock
Volcanic rock (often shortened to volcanics in scientific contexts) is a rock formed from lava erupted from a volcano. In other words, it differs from other igneous rock by being of volcanic origin. Like all rock types, the concept of volcanic r ...
defined as having crystallised from a lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
of at least 18 wt% MgO. Komatiites have low silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic tab ...
, potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin ''kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmosphe ...
and aluminium
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. I ...
, and high to extremely high magnesium
Magnesium is a chemical element with the symbol Mg and atomic number 12. It is a shiny gray metal having a low density, low melting point and high chemical reactivity. Like the other alkaline earth metals (group 2 of the periodic ta ...
content. Komatiite was named for its type locality along the Komati River
The Komati River, also known as the Inkomati River or Incomati River (in Mozambique, from Portuguese Rio Incomati), is a river in South Africa, Eswatini and Mozambique. Originating in north-western Eswatini, it is joined by the Crocodile R ...
in South Africa, and frequently displays spinifex texture composed of large dendritic plates of olivine
The mineral olivine () is a magnesium iron silicate with the chemical formula . It is a type of nesosilicate or orthosilicate. The primary component of the Earth's upper mantle, it is a common mineral in Earth's subsurface, but weathers quickl ...
and pyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
.
Komatiites are rare rocks; almost all komatiites were formed during the Archaean Eon (4.0–2.5 billion years ago), with few younger (Proterozoic
The Proterozoic () is a geological eon spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8million years ago. It is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". It is also the longest eon of the Earth's geologic time scale, and it is subdivided ...
or Phanerozoic
The Phanerozoic Eon is the current geologic eon in the geologic time scale, and the one during which abundant animal and plant life has existed. It covers 538.8 million years to the present, and it began with the Cambrian Period, when anima ...
) examples known. This restriction in age is thought to be due to cooling of the mantle, which may have been hotter during the Archaean. The early Earth had much higher heat production, due to the residual heat from planetary accretion
In astrophysics, accretion is the accumulation of particles into a massive object by gravitationally attracting more matter, typically gaseous matter, in an accretion disk. Most astronomical objects, such as galaxies, stars, and planets, are form ...
, as well as the greater abundance of radioactive
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
isotopes, particularly shorter lived ones like uranium 235
Uranium-235 (235U or U-235) is an isotope of uranium making up about 0.72% of natural uranium. Unlike the predominant isotope uranium-238, it is fissile, i.e., it can sustain a nuclear chain reaction. It is the only fissile isotope that exists ...
which produce more decay heat
Decay heat is the heat released as a result of radioactive decay. This heat is produced as an effect of radiation on materials: the energy of the alpha, beta or gamma radiation is converted into the thermal movement of atoms.
Decay heat occurs na ...
. Lower temperature mantle melts such as basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
and picrite
Picrite basalt or picrobasalt is a variety of high-magnesium olivine basalt that is very rich in the mineral olivine. It is dark with yellow-green olivine phenocrysts (20-50%) and black to dark brown pyroxene, mostly augite.
The olivine-rich p ...
have essentially replaced komatiites as an eruptive lava on the Earth's surface.
Geographically, komatiites are predominantly restricted in distribution to the Archaean shield
A shield is a piece of personal armour held in the hand, which may or may not be strapped to the wrist or forearm. Shields are used to intercept specific attacks, whether from close-ranged weaponry or projectiles such as arrows, by means of a ...
areas, and occur with other ultramafic
Ultramafic rocks (also referred to as ultrabasic rocks, although the terms are not wholly equivalent) are igneous and meta-igneous rocks with a very low silica content (less than 45%), generally >18% MgO, high FeO, low potassium, and are composed ...
and high-magnesian mafic
A mafic mineral or rock is a silicate mineral or igneous rock rich in magnesium and iron. Most mafic minerals are dark in color, and common rock-forming mafic minerals include olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, and biotite. Common mafic rocks include ...
volcanic rocks in Archaean greenstone belt
Greenstone belts are zones of variably metamorphosed mafic to ultramafic volcanic sequences with associated sedimentary rocks that occur within Archaean and Proterozoic cratons between granite and gneiss bodies.
The name comes from the green ...
s. The youngest komatiites are from the island of Gorgona on the Caribbean oceanic plateau
An oceanic or submarine plateau is a large, relatively flat elevation that is higher than the surrounding relief with one or more relatively steep sides.
There are 184 oceanic plateaus in the world, covering an area of or about 5.11% of the ...
off the Pacific coast of Colombia, and a rare example of Proterozoic komatiite is found in the Winnipegosis komatiite belt
The Winnipegosis komatiite belt is a long and wide greenstone belt located in the Lake Winnipegosis area of central Manitoba, Canada. It has no surface exposure and was identified based on geophysical signatures and drilling during mineral e ...
in Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, Canada.
Petrology

Magmas
Magma () is the molten or semi-molten natural material from which all igneous rocks are formed. Magma is found beneath the surface of the Earth, and evidence of magmatism has also been discovered on other terrestrial planets and some natural sa ...
of komatiitic compositions have a very high melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
, with calculated eruption temperatures up to, and possibly in excess of 1600 °C. Basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
ic lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or un ...
s normally have eruption temperatures of about 1100 to 1250 °C. The higher melting temperatures required to produce komatiite have been attributed to the presumed higher geothermal gradient
Geothermal gradient is the rate of temperature change with respect to increasing depth in Earth's interior. As a general rule, the crust temperature rises with depth due to the heat flow from the much hotter mantle; away from tectonic plate bo ...
s in the Archaean Earth.
Komatiitic lava was extremely fluid when it erupted (possessing the viscosity
The viscosity of a fluid is a measure of its resistance to deformation at a given rate. For liquids, it corresponds to the informal concept of "thickness": for example, syrup has a higher viscosity than water.
Viscosity quantifies the inte ...
close to that of water but with the density of rock). Compared to the basaltic lava of the Hawaiian plume basalts at ~1200 °C, which flows the way treacle
Treacle () is any uncrystallised syrup made during the refining of sugar.Oxford Dictionary The most common forms of treacle are golden syrup, a pale variety, and a darker variety known as black treacle, similar to molasses. Black treacle has ...
or honey does, the komatiitic lava would have flowed swiftly across the surface, leaving extremely thin lava flows (down to 10 mm thick). The major komatiitic sequences preserved in Archaean rocks are thus considered to be lava tubes
A lava tube, or pyroduct, is a natural conduit formed by flowing lava from a volcanic vent that moves beneath the hardened surface of a lava flow. If lava in the tube empties, it will leave a cave.
Formation
A lava tube is a type of lava ca ...
, ponds of lava etc., where the komatiitic lava accumulated.
Komatiite chemistry is different from that of basaltic and other common mantle-produced magmas, because of differences in degrees of partial melting
Partial melting occurs when only a portion of a solid is melted. For mixed substances, such as a rock containing several different minerals or a mineral that displays solid solution, this melt can be different from the bulk composition of the soli ...
. Komatiites are considered to have been formed by high degrees of partial melting, usually greater than 50%, and hence have high MgO with low K2O and other incompatible element In petrology and geochemistry, an incompatible element is one that is unsuitable in size and/or charge to the cation sites of the minerals of which it is included. It is defined by the partition coefficient between rock-forming minerals and melt b ...
s.
There are two geochemical classes of komatiite; aluminium undepleted komatiite (AUDK) (also known as Group I komatiites) and aluminium depleted komatiite (ADK) (also known as Group II komatiites), defined by their Al2O3/TiO2 ratios. These two classes of komatiite are often assumed to represent a real petrological
Petrology () is the branch of geology that studies rocks and the conditions under which they form. Petrology has three subdivisions: igneous, metamorphic, and sedimentary petrology. Igneous and metamorphic petrology are commonly taught together ...
source difference between the two types related to depth of melt generation. Al-depleted komatiites have been modeled by melting experiments as being produced by high degrees of partial melting at high pressure where garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
in the source is not melted, whereas Al-undepleted komatiites are produced by high degrees of partial melts at lesser depth. However, recent studies of fluid inclusions in chrome spinels from the cumulate zones of komatiite flows have shown that a single komatiite flow can be derived from the mixing of parental magmas with a range of Al2O3/TiO2 ratios, calling into question this interpretation of the formations of the different komatiite groups. Komatiites probably form in extremely hot mantle plumes or in Archaean subduction zones.
Boninite
Boninite is an extrusive rock high in both magnesium and silica, thought to be usually formed in fore-arc environments, typically during the early stages of subduction. The rock is named for its occurrence in the Izu-Bonin arc south of Japan. ...
magmatism is similar to komatiite magmatism but is produced by fluid-fluxed melting above a subduction zone. Boninites with 10–18% MgO tend to have higher large-ion lithophile elements (LILE: Ba, Rb, Sr) than komatiites.
Mineralogy
The pristine volcanic mineralogy of komatiites is composed of forsteritic olivine (Fo90 and upwards), calcic and often chromianpyroxene
The pyroxenes (commonly abbreviated to ''Px'') are a group of important rock-forming inosilicate minerals found in many igneous and metamorphic rocks. Pyroxenes have the general formula , where X represents calcium (Ca), sodium (Na), iron (Fe II) ...
, anorthite (An85 and upwards) and chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can s ...
.
A considerable population of komatiite examples show a cumulate texture and morphology
Morphology, from the Greek and meaning "study of shape", may refer to:
Disciplines
* Morphology (archaeology), study of the shapes or forms of artifacts
* Morphology (astronomy), study of the shape of astronomical objects such as nebulae, galaxies ...
. The usual cumulate mineralogy
Mineralogy is a subject of geology specializing in the scientific study of the chemistry, crystal structure, and physical (including optical) properties of minerals and mineralized artifacts. Specific studies within mineralogy include the proces ...
is highly magnesium rich forsterite
Forsterite (Mg2SiO4; commonly abbreviated as Fo; also known as white olivine) is the magnesium-rich end-member of the olivine solid solution series. It is isomorphous with the iron-rich end-member, fayalite. Forsterite crystallizes in the orthor ...
olivine, though chromian pyroxene cumulates are also possible (though rarer).
Volcanic rocks rich in magnesium may be produced by accumulation of olivine phenocrysts
300px, feldspathic phenocrysts. This granite, from the Switzerland">Swiss side of the Mont Blanc massif, has large white plagioclase phenocrysts, triclinic minerals that give trapezoid shapes when cut through). 1 euro coins, 1 euro coin (diameter ...
in basalt melts of normal chemistry: an example is picrite
Picrite basalt or picrobasalt is a variety of high-magnesium olivine basalt that is very rich in the mineral olivine. It is dark with yellow-green olivine phenocrysts (20-50%) and black to dark brown pyroxene, mostly augite.
The olivine-rich p ...
. Part of the evidence that komatiites are not magnesium-rich simply because of cumulate olivine is textural: some contain spinifex texture
Texture may refer to:
Science and technology
* Surface texture, the texture means smoothness, roughness, or bumpiness of the surface of an object
* Texture (roads), road surface characteristics with waves shorter than road roughness
* Texture ...
, a texture attributable to rapid crystallization
Crystallization is the process by which solid forms, where the atoms or molecules are highly organized into a structure known as a crystal. Some ways by which crystals form are precipitating from a solution, freezing, or more rarely deposi ...
of the olivine in a thermal gradient in the upper part of a lava flow. "Spinifex" texture is named after the common name for the Australian grass '' Triodia'', which grows in clumps with similar shapes.
Another line of evidence is that the MgO content of olivines formed in komatiites is toward the nearly pure MgO forsterite composition, which can only be achieved in bulk by crystallisation of olivine from a highly magnesian melt.
The rarely preserved flow top breccia
Breccia () is a rock composed of large angular broken fragments of minerals or rocks cemented together by a fine-grained matrix.
The word has its origins in the Italian language, in which it means "rubble". A breccia may have a variety of di ...
and pillow margin zones in some komatiite flows are essentially volcanic glass, quenched
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as ph ...
in contact with overlying water or air. Because they are rapidly cooled, they represent the liquid composition of the komatiites, and thus record an anhydrous
A substance is anhydrous if it contains no water. Many processes in chemistry can be impeded by the presence of water; therefore, it is important that water-free reagents and techniques are used. In practice, however, it is very difficult to achie ...
MgO content of up to 32% MgO. Some of the highest magnesian komatiites with clear textural preservation are those of the Barberton belt
The Barberton Greenstone Belt is situated on the eastern edge of Kaapvaal Craton in South Africa. It is known for its gold mineralisation and for its komatiites, an unusual type of ultramafic volcanic rock named after the Komati River that flows t ...
in South Africa, where liquids with up to 34% MgO can be inferred using bulk rock and olivine compositions.
The mineralogy of a komatiite varies systematically through the typical stratigraphic section of a komatiite flow and reflects magmatic processes which komatiites are susceptible to during their eruption and cooling. The typical mineralogical variation is from a flow base composed of olivine cumulate, to a spinifex textured zone composed of bladed olivine and ideally a pyroxene spinifex zone and olivine-rich chill zone on the upper eruptive rind of the flow unit.
Primary (magmatic) mineral species also encountered in komatiites include olivine, the pyroxenes augite, pigeonite
Pigeonite is a mineral in the clinopyroxene subgroup of the pyroxene group. It has a general formula of . The calcium cation fraction can vary from 5% to 25%, with iron and magnesium making up the rest of the cations.
Pigeonite crystallizes in th ...
and bronzite
Bronzite is a member of the pyroxene group of minerals, belonging with enstatite and hypersthene to the orthorhombic series of the group. Rather than a distinct species, it is really a ferriferous variety of enstatite, which owing to partial alt ...
, plagioclase
Plagioclase is a series of tectosilicate (framework silicate) minerals within the feldspar group. Rather than referring to a particular mineral with a specific chemical composition, plagioclase is a continuous solid solution series, more prope ...
, chromite
Chromite is a crystalline mineral composed primarily of iron(II) oxide and chromium(III) oxide compounds. It can be represented by the chemical formula of FeCr2O4. It is an oxide mineral belonging to the spinel group. The element magnesium can s ...
, ilmenite
Ilmenite is a titanium-iron oxide mineral with the idealized formula . It is a weakly magnetic black or steel-gray solid. Ilmenite is the most important ore of titanium and the main source of titanium dioxide, which is used in paints, printing ...
and rarely pargasitic amphibole
Amphibole () is a group of inosilicate minerals, forming prism or needlelike crystals, composed of double chain tetrahedra, linked at the vertices and generally containing ions of iron and/or magnesium in their structures. Its IMA symbol is A ...
. Secondary (metamorphic) minerals include serpentine, chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ...
, amphibole, sodic plagioclase, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
, iron oxides and rarely phlogopite
Phlogopite is a yellow, greenish, or reddish-brown member of the mica family of phyllosilicates. It is also known as magnesium mica.
Phlogopite is the magnesium endmember of the biotite solid solution series, with the chemical formula KMg3AlSi3O ...
, baddeleyite
Baddeleyite is a rare zirconium oxide mineral (ZrO2 or zirconia), occurring in a variety of monoclinic prismatic crystal forms. It is transparent to translucent, has high indices of refraction, and ranges from colorless to yellow, green, and dar ...
, and pyrope
The mineral pyrope is a member of the garnet group. Pyrope is the only member of the garnet family to always display red colouration in natural samples, and it is from this characteristic that it gets its name: from the Greek for ''fire'' and ''e ...
or hydrogrossular garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives.
All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different s ...
.
Metamorphism
All known komatiites have beenmetamorphosed
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causin ...
, therefore should technically be termed 'metakomatiite' though the prefix meta is inevitably assumed. Many komatiites are highly altered and serpentinized or carbonated
Carbonation is the chemical reaction of carbon dioxide to give carbonates, bicarbonates, and carbonic acid. In chemistry, the term is sometimes used in place of carboxylation, which refers to the formation of carboxylic acids.
In inorganic ch ...
from metamorphism and metasomatism
Metasomatism (from the Greek μετά ''metá'' "change" and σῶμα ''sôma'' "body") is the chemical alteration of a rock by hydrothermal and other fluids. It is the replacement of one rock by another of different mineralogical and chemical com ...
. This results in significant changes to the mineralogy and the texture.
Hydration vs. carbonation
The metamorphic mineralogy of ultramafic rocks, particularly komatiites, is only partially controlled by composition. The character of the connate fluids which are present during low temperature metamorphism whether prograde or retrograde control the metamorphic assemblage of a metakomatiite (''hereafter the prefix meta- is assumed''). The factor controlling the mineral assemblage is thepartial pressure
In a mixture of gases, each constituent gas has a partial pressure which is the notional pressure of that constituent gas as if it alone occupied the entire volume of the original mixture at the same temperature. The total pressure of an ideal gas ...
of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide (chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is transpar ...
within the metamorphic fluid, called the XCO2. If XCO2 is above 0.5, the metamorphic reactions favor formation of talc
Talc, or talcum, is a Clay minerals, clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thi ...
, magnesite
Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula (magnesium carbonate). Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.
Occurrence
Magnesite occurs as veins in and an alteration product of ultramafic ro ...
(magnesium carbonate), and tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and fe ...
amphibole. These are classed as talc-carbonation reactions. Below XCO2 of 0.5, metamorphic reactions in the presence of water favor production of serpentinite
Serpentinite is a rock composed predominantly of one or more serpentine group minerals, the name originating from the similarity of the texture of the rock to that of the skin of a snake. Serpentinite has been called ''serpentine'' or ''ser ...
.
There are thus two main classes of metamorphic komatiite; carbonated and hydrated. Carbonated komatiites and peridotites form a series of rocks dominated by the minerals chlorite, talc, magnesite or dolomite Dolomite may refer to:
*Dolomite (mineral), a carbonate mineral
*Dolomite (rock), also known as dolostone, a sedimentary carbonate rock
*Dolomite, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
*Dolomite, California, United States, an unincor ...
and tremolite. Hydrated metamorphic rock assemblages are dominated by the minerals chlorite, serpentine-antigorite
Antigorite is a lamellated, monoclinic mineral in the phylosilicate serpentine subgroup with the ideal chemical formula of (Mg,Fe2+)3Si2O5(OH)4. It is the high-pressure polymorph of serpentine and is commonly found in metamorphosed serpentinite ...
and brucite
Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Mg( OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal vein mineral in metamorphosed limestones and chlorite schists; and ...
. Traces of talc, tremolite and dolomite may be present, as it is very rare that no carbon dioxide is present in metamorphic fluids. At higher metamorphic grades, anthophyllite
Anthophyllite is an orthorhombic amphibole mineral: ☐Mg2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 (☐ is for a vacancy, a point defect in the crystal structure), magnesium iron inosilicate hydroxide. Anthophyllite is polymorphic with cummingtonite. Some forms of antho ...
, enstatite
Enstatite is a mineral; the magnesium endmember of the pyroxene silicate mineral series enstatite (MgSiO3) – ferrosilite (FeSiO3). The magnesium rich members of the solid solution series are common rock-forming minerals found in igneous and m ...
, olivine and diopside
Diopside is a monoclinic pyroxene mineral with composition . It forms complete solid solution series with hedenbergite () and augite, and partial solid solutions with orthopyroxene and pigeonite. It forms variably colored, but typically dull ...
dominate as the rock mass dehydrates.
Mineralogic variations in komatiite flow facies
Komatiite tends to fractionate from high-magnesium compositions in the flow bases where olivine cumulates dominate, to lower magnesium compositions higher up in the flow. Thus, the current metamorphic mineralogy of a komatiite will reflect the chemistry, which in turn represents an inference as to its volcanologicalfacies
In geology, a facies ( , ; same pronunciation and spelling in the plural) is a body of rock with specified characteristics, which can be any observable attribute of rocks (such as their overall appearance, composition, or condition of formatio ...
and stratigraphic position.
Typical metamorphic mineralogy is tremolite
Tremolite is a member of the amphibole group of silicate minerals with composition: Ca2(Mg5.0-4.5Fe2+0.0-0.5)Si8O22(OH)2. Tremolite forms by metamorphism of sediments rich in dolomite and quartz. Tremolite forms a series with actinolite and fe ...
-chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ...
, or talc
Talc, or talcum, is a Clay minerals, clay mineral, composed of hydrated magnesium silicate with the chemical formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. Talc in powdered form, often combined with corn starch, is used as baby powder. This mineral is used as a thi ...
-chlorite mineralogy in the upper spinifex zones. The more magnesian-rich olivine-rich flow base facies tend to be free from tremolite and chlorite mineralogy and are dominated by either serpentine-brucite
Brucite is the mineral form of magnesium hydroxide, with the chemical formula Mg( OH)2. It is a common alteration product of periclase in marble; a low-temperature hydrothermal vein mineral in metamorphosed limestones and chlorite schists; and ...
+/- anthophyllite
Anthophyllite is an orthorhombic amphibole mineral: ☐Mg2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 (☐ is for a vacancy, a point defect in the crystal structure), magnesium iron inosilicate hydroxide. Anthophyllite is polymorphic with cummingtonite. Some forms of antho ...
if hydrated, or talc-magnesite
Magnesite is a mineral with the chemical formula (magnesium carbonate). Iron, manganese, cobalt, and nickel may occur as admixtures, but only in small amounts.
Occurrence
Magnesite occurs as veins in and an alteration product of ultramafic ro ...
if carbonated. The upper flow facies tend to be dominated by talc, chlorite, tremolite, and other magnesian amphiboles (anthophyllite
Anthophyllite is an orthorhombic amphibole mineral: ☐Mg2Mg5Si8O22(OH)2 (☐ is for a vacancy, a point defect in the crystal structure), magnesium iron inosilicate hydroxide. Anthophyllite is polymorphic with cummingtonite. Some forms of antho ...
, cummingtonite
Cummingtonite ( ) is a metamorphic amphibole with the chemical composition , magnesium iron silicate hydroxide.
Monoclinic cummingtonite is compositionally similar and polymorphic with orthorhombic anthophyllite, which is a much more common ...
, gedrite
Gedrite is a crystal belonging to the orthorhombic ferromagnesian subgroup of the amphibole supergroup of the double chain inosilicate minerals with the ideal chemical formula .
Gedrite is the magnesium (Mg) rich endmember of a solid solution ser ...
, etc.).
For example, the typical flow facies (see below) may have the following mineralogy;
Geochemistry
Komatiite can be classified according to the following geochemical criteria; * SiO2; typically 40–45% * MgO greater than 18% * Low K2O (<0.5%) * Low CaO and Na2O (<2% combined) * Low Ba, Cs, Rb (incompatible element In petrology and geochemistry, an incompatible element is one that is unsuitable in size and/or charge to the cation sites of the minerals of which it is included. It is defined by the partition coefficient between rock-forming minerals and melt b ...
) enrichment; ΣLILE <1,000 ppm
* High Ni (>400 ppm), Cr (>800 ppm), Co (>150 ppm)
The above geochemical classification must be the essentially unaltered magma chemistry and not the result of crystal accumulation (as in peridotite
Peridotite ( ) is a dense, coarse-grained igneous rock consisting mostly of the silicate minerals olivine and pyroxene. Peridotite is ultramafic, as the rock contains less than 45% silica. It is high in magnesium (Mg2+), reflecting the high prop ...
). Through a typical komatiite flow sequence the chemistry of the rock will change according to the internal fractionation which occurs during eruption. This tends to lower MgO, Cr, Ni, and increase Al, K2O, Na, CaO and SiO2 toward the top of the flow.
Rocks rich in MgO, K2O, Ba, Cs, and Rb may be lamprophyre
Lamprophyres () are uncommon, small-volume ultrapotassic igneous rocks primarily occurring as dikes, lopoliths, laccoliths, stocks, and small intrusions. They are alkaline silica-undersaturated mafic or ultramafic rocks with high magnesium oxid ...
s, kimberlite
Kimberlite is an igneous rock and a rare variant of peridotite. It is most commonly known to be the main host matrix for diamonds. It is named after the town of Kimberley in South Africa, where the discovery of an diamond called the Star of ...
s or other rare ultramafic, potassic or ultrapotassic rocks.
Morphology and occurrence
Komatiites often showpillow lava
Pillow lavas are lavas that contain characteristic pillow-shaped structures that are attributed to the extrusion of the lava underwater, or ''subaqueous extrusion''. Pillow lavas in volcanic rock are characterized by thick sequences of disconti ...
structure, autobrecciated upper margins consistent with underwater eruption forming a rigid upper skin to the lava flows. Proximal volcanic facies are thinner and interleaved with sulfidic sediments, black shales, chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
s and tholeiitic basalts
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90% of a ...
. Komatiites were produced from a relatively wet mantle. Evidence of this is from their association with felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
s, occurrences of komatiitic tuff
Tuff is a type of rock made of volcanic ash ejected from a vent during a volcanic eruption. Following ejection and deposition, the ash is lithified into a solid rock. Rock that contains greater than 75% ash is considered tuff, while rock cont ...
s, niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
anomalies and by S- and H2O-borne rich mineralizations.
Textural features
 A common and distinctive texture is known as ''spinifex texture'' and consists of long acicular phenocrysts of olivine (or
A common and distinctive texture is known as ''spinifex texture'' and consists of long acicular phenocrysts of olivine (or pseudomorph
In mineralogy, a pseudomorph is a mineral or mineral compound that appears in an atypical form (crystal system), resulting from a substitution process in which the appearance and dimensions remain constant, but the original mineral is replaced b ...
s of alteration minerals after olivine) or pyroxene which give the rock a bladed appearance especially on a weathered surface. Spinifex texture is the result of rapid crystallization of highly magnesian liquid in the thermal gradient at the margin of the flow or sill.
''Harrisite texture'', first described from intrusive rock
Intrusive rock is formed when magma penetrates existing rock, crystallizes, and solidifies underground to form ''Igneous intrusion, intrusions'', such as batholiths, dike (geology), dikes, Sill (geology), sills, laccoliths, and volcanic necks.I ...
s (not komatiites) at Harris Bay
Harris may refer to:
Places Canada
* Harris, Ontario
* Northland Pyrite Mine (also known as Harris Mine)
* Harris, Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Harris No. 316, Saskatchewan
Scotland
* Harris, Outer Hebrides (sometimes called the Isle of ...
on the island of Rùm
Rùm (), a Scottish Gaelic name often anglicised to Rum (), is one of the Small Isles of the Inner Hebrides, in the district of Lochaber, Scotland. For much of the 20th century the name became Rhum, a spelling invented by the former owner, Sir ...
in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to the ...
, is formed by nucleation of crystals on the floor of a magma chamber
A magma chamber is a large pool of liquid rock beneath the surface of the Earth. The molten rock, or magma, in such a chamber is less dense than the surrounding country rock, which produces buoyant forces on the magma that tend to drive it upw ...
. Harrisites are known to form megacrystal aggregates of pyroxene and olivine up to 1 metre in length. Harrisite texture is found in some very thick lava flows of komatiite, for example in the Norseman-Wiluna Greenstone Belt of Western Australia, in which crystallization of cumulate
Cumulate rocks are igneous rocks formed by the accumulation of crystals from a magma either by settling or floating. Cumulate rocks are named according to their texture; cumulate texture is diagnostic of the conditions of formation of this group o ...
s has occurred.


Volcanology
Komatiitevolcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
morphology is interpreted to have the general form and structure of a shield volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more v ...
, typical of most large basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanite, aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the planetary surface, surface of a terrestrial ...
edifices, as the magmatic event which forms komatiites erupts less magnesian materials.
However, the initial flux of the most magnesian magmas is interpreted to form a channelised flow facie, which is envisioned as a fissure vent releasing highly fluid komatiitic lava onto the surface. This then flows outwards from the vent fissure, concentrating into topographical lows, and forming channel environments composed of high MgO olivine adcumulate flanked by a 'sheeted flow facies' aprons of lower MgO olivine and pyroxene thin-flow spinifex sheets.
The typical komatiite lava flow has six stratigraphically related elements;
* A1 – pillowed and variolitic chilled flow top, often grading and transitional with sediment
* A2 – Zone of quickly chilled, feathery acicular olivine-clinopyroxene-glass representing a chilled margin A chilled margin is a shallow intrusive or volcanic rock texture characterised by a glassy or fine-grained zone along the margin where the magma or lava has contacted air, water, or particularly much cooler rock. This is caused by rapid crystalli ...
on the top of the flow unit
* A3 – Olivine spinifex sequence composed of sheaf and book-like olivine spinifex, representing a downward-growing crystal accumulation on the flow top
* B1 – Olivine mesocumulate to orthocumulate, representing a harrisite grown in flowing liquid melt
* B2 – Olivine adcumulate composed of >93% interlocking equant olivine crystals
* B3 – Lower chill margin composed of olivine adcumulate to mesocumulate, with finer grain size.
Individual flow units may not be entirely preserved, as subsequent flow units may thermally erode the A zone spinifex flows. In the distal thin flow facies, B zones are poorly developed to absent, as not enough through-flowing liquid existed to grow the adcumulate.
The channel and sheeted flows are then covered by high-magnesian basalts and tholeiitic basalts as the volcanic event evolves to less magnesian compositions. The subsequent magmatism, being higher silica melts, tends to form a more typical shield volcano architecture.
Intrusive komatiites
Komatiite magma is extremely dense and unlikely to reach the surface, being more likely to pool lower within the crust. Modern (post-2004) interpretations of some of the larger olivine adcumulate bodies in theYilgarn craton
The Yilgarn Craton is a large craton that constitutes the bulk of the Western Australian land mass. It is bounded by a mixture of sedimentary basins and Proterozoic fold and thrust belts. Zircon grains in the Jack Hills, Narryer Terrane have b ...
have revealed that the majority of komatiite olivine adcumulate occurrences are likely to be subvolcanic A subvolcanic rock, also known as a hypabyssal rock, is an intrusive igneous rock that is emplaced at depths less than within the crust, and has intermediate grain size and often porphyritic texture between that of volcanic rocks and plutonic r ...
to intrusive in nature.
This is recognised at the Mt Keith nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
deposit where wall-rock intrusive textures and xenolith
A xenolith ("foreign rock") is a rock fragment (country rock) that becomes enveloped in a larger rock during the latter's development and solidification. In geology, the term ''xenolith'' is almost exclusively used to describe inclusions in igne ...
s of felsic
In geology, felsic is a modifier describing igneous rocks that are relatively rich in elements that form feldspar and quartz.Marshak, Stephen, 2009, ''Essentials of Geology,'' W. W. Norton & Company, 3rd ed. It is contrasted with mafic rocks, whi ...
country rocks have been recognised within the low-strain contacts. Rosengren, N. M., Beresford, S. W., Grguric, B. A., & Cas, R.A.F. 2005. An intrusive origin for the komatiitic dunite-hosted Mount Keith disseminated nickel sulfide deposit, Western Australia. Economic Geology, 100(1), 149–156. https://doi.org/10.2113/100.1.0149 The previous interpretations of these large komatiite bodies was that they were "super channels" or reactivated channels, which grew to over 500 m in stratigraphic thickness during prolonged volcanism.
These intrusions are considered to be ''channelised sills'', formed by injection of komatiitic magma into the stratigraphy, and inflation of the magma chamber. Economic nickel-mineralised olivine adcumulate bodies may represent a form of sill-like conduit, where magma pools in a staging chamber before erupting onto the surface.
Economic importance
The economic importance of komatiite was first widely recognised in the early 1960s with the discovery of massive nickel sulfide mineralisation atKambalda, Western Australia
Kambalda is a small mining town about from the mining city of Kalgoorlie in Western Australia, within the Goldfields. It is split into two townsites apart, Kambalda East and Kambalda West; and is located on the western edge of a giant salt la ...
. Komatiite-hosted nickel-copper sulfide mineralisation today accounts for about 14% of the world's nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
production, mostly from Australia, Canada and South Africa.
Komatiites are associated with nickel and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
deposits in Australia, Canada, South Africa and most recently in the Guiana shield
The Guiana Shield (french: Plateau des Guyanes, Bouclier guyanais; nl, Hoogland van Guyana, Guianaschild; pt, Planalto das Guianas, Escudo das Guianas; es, Escudo guayanés) is one of the three cratons of the South American Plate. It is a ...
of South America.
See also
* * * * * * *References
Bibliography
* Hess, P. C. (1989), ''Origins of Igneous Rocks'', President and Fellows of Harvard College (pp. 276–285), . * Hill R.E.T, Barnes S.J., Gole M.J. and Dowling S.E. (1990), ''Physical volcanology of komatiites; A field guide to the komatiites of the Norseman-Wiluna Greenstone Belt, Eastern Goldfields Province, Yilgarn Block, Western Australia.'', Geological Society of Australia. * Blatt, Harvey and Robert Tracy (1996), ''Petrology'', 2nd ed., Freeman (pp. 196–7), . * S. A. Svetov, A. I. Svetova, and H. Huhma, 1999, ''Geochemistry of the Komatiite–Tholeiite Rock Association in the Vedlozero–Segozero Archean Greenstone Belt, Central Karelia'', Geochemistry International, Vol. 39, Suppl. 1, 2001, pp. S24–S38accessed 7-25-2005 * Vernon R.H., 2004, ''A Practical Guide to Rock Microstructure'', (pp. 43–69, 150–152) Cambridge University Press. * Arndt, N.T., and Nisbet, E.G. (1982), ''Komatiites''. Unwin Hyman, . Hardcover. * Arndt, N.T., and Lesher, C.M. (2005), Komatiites, in Selley, RC, Cocks, L.R.M., Plimer, I.R. (Editors), ''Encyclopedia of Geology'' 3, Elsevier, New York, pp. 260–267 * Faure, F., Arndt, N.T. Libourel, G. (2006), Formation of spinifex texture in komatiite: An experimental study. J. Petrol 47, 1591–1610. * Arndt, N.T., Lesher, C.M. and Barnes, S.J. (2008), ''Komatiite'', Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, 488 pp., .
External links
accessed 7-25-2005
Komatiites and astrobiology
(with text in French) retrieved 2009-05-17 {{Volcanoes Ultramafic rocks Volcanology Igneous petrology Metamorphic rocks Volcanic rocks Subvolcanic rocks