Kiribati Dollars $1 And $2 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Kiribati (), officially the Republic of Kiribati ( gil, ibaberikiKiribati),Kiribati
''The World Factbook''.
Europa (web portal). Retrieved 29 January 2016. is an
''The World Factbook''.
Europa (web portal). Retrieved 29 January 2016. is an
island country
An island country, island state or an island nation is a country whose primary territory consists of one or more islands or parts of islands. Approximately 25% of all independent countries are island countries. Island countries are historically ...
in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
in the central Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. The permanent population is over 119,000 (2020), more than half of whom live on Tarawa
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
''
''
32 atolls and one remote raised coral island,
Banaba
BanabaThe correct spelling and etymology in Gilbertese should be ''Bwanaba'' but the Constitution of Kiribati writes Banaba. Because of the spelling in English or French, the name was very often written Paanapa or Paanopa, as it was in 1901 Ac ...
. There is a total land area of dispersed over of ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wo ...
.
Their spread straddles the equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can als ...
and the 180th meridian
The 180th meridian or antimeridian is the meridian (geography), meridian 180° both east and west of the prime meridian in a Geographic coordinate system, geographical coordinate system. The longitude at this line can be given as either east ...
, although the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
goes around Kiribati and swings far to the east, almost reaching the 150° W meridian. This brings Kiribati's easternmost islands, the southern Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
south of Hawaii, into the same day as the Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
and places them in the most advanced time zone on Earth: UTC+14
UTC+14:00 is an identifier for a time offset from UTC of +14:00. This is the earliest time zone on Earth, meaning that areas in this zone are the first to see a new day, and therefore the first to celebrate a New Year. It is also referred to as t ...
. Kiribati is the only country in the world to be situated in all four cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
hemispheres.
Kiribati gained its independence from the United Kingdom, becoming a sovereign state
A sovereign state or sovereign country, is a polity, political entity represented by one central government that has supreme legitimate authority over territory. International law defines sovereign states as having a permanent population, defin ...
in 1979. The capital, South Tarawa
South Tarawa ( gil, Tarawa Teinainano) is the capital and hub of the Republic of Kiribati and home to more than half of Kiribati's population. The South Tarawa population centre consists of all the small islets from Betio in the west to Bonriki ...
, now the most populated area, consists of a number of islets, connected by a series of causeway
A causeway is a track, road or railway on the upper point of an embankment across "a low, or wet place, or piece of water". It can be constructed of earth, masonry, wood, or concrete. One of the earliest known wooden causeways is the Sweet Tra ...
s. These comprise about half the area of Tarawa atoll
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
''
 The name ''Kiribati'' was adopted in 1979 at independence. It is the
The name ''Kiribati'' was adopted in 1979 at independence. It is the

 In 1886, an Anglo-German agreement partitioned the "unclaimed" central Pacific, leaving
In 1886, an Anglo-German agreement partitioned the "unclaimed" central Pacific, leaving
''
phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
; however, those mines are no longer viable with fisheries
Fishery can mean either the enterprise of raising or harvesting fish and other aquatic life; or more commonly, the site where such enterprise takes place ( a.k.a. fishing ground). Commercial fisheries include wild fisheries and fish farms, both ...
and export of copra
Copra (from ) is the dried, white flesh of the coconut from which coconut oil is extracted. Traditionally, the coconuts are sun-dried, especially for export, before the oil, also known as copra oil, is pressed out. The oil extracted from copr ...
driving much of the economy. Kiribati is one of the least developed countries in the world and is highly dependent on international aid for its economy.
Kiribati is a member of the Pacific Community
The Pacific Community (PC), formerly the South Pacific Commission (SPC), is an international development organisation governed by 27 members, including 22 Pacific island countries and territories. The organisation's headquarters are in Nouméa ...
(SPC), Commonwealth of Nations
The Commonwealth of Nations, simply referred to as the Commonwealth, is a political association of 56 member states, the vast majority of which are former territories of the British Empire. The chief institutions of the organisation are the Co ...
, the IMF, the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, the OACPS and became a full member of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and international security, security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be ...
in 1999 As an island nation, the islands are very vulnerable to climate change and addressing climate change has been a central part of its international policy, as a member of the Alliance of Small Island States
Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small island countries. AOSIS was established in 1990, ahead of the Second World Climate Conference. The main purpose of the alliance is to con ...
.
Etymology and pronunciation
The name is pronounced ; ''Kiribass'' as ''-ti'' in theGilbertese language
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages.
The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the i ...
represents an '' s'' sound and its people, the I-Kiribati, as ''e-Kiribassi''
 The name ''Kiribati'' was adopted in 1979 at independence. It is the
The name ''Kiribati'' was adopted in 1979 at independence. It is the Gilbertese
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages.
The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the i ...
rendition of ''Gilberts'', the plural of the English name of the nation's main archipelago, the ''Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
''. It was named ''îles Gilbert'' (French for ''Gilbert Islands'') in about 1820 by Russian admiral Adam von Krusenstern and French captain Louis Duperrey, after the British captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
Thomas Gilbert. Gilbert and captain John Marshall
John Marshall (September 24, 1755July 6, 1835) was an American politician and lawyer who served as the fourth Chief Justice of the United States from 1801 until his death in 1835. He remains the longest-serving chief justice and fourth-longes ...
sighted some of the islands in 1788, while crossing the "outer passage" route from Port Jackson
Port Jackson, consisting of the waters of Sydney Harbour, Middle Harbour, North Harbour and the Lane Cove and Parramatta Rivers, is the ria or natural harbour of Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. The harbour is an inlet of the Tasman Sea (p ...
to Canton. Both von Krusenstern's and Duperrey's maps, published in 1824, were written in French. In French, the Northern Islands were until then called ''îles Mulgrave'' and Byron Island was not part of them.
In English, the archipelago, particularly the southern part, was often referred to as the Kingsmills in the 19th century, although the name Gilbert Islands was used increasingly, including in the Western Pacific Order in Council
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
*Western, New York, a town in the US
*Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that id ...
of 1877 and in the Pacific Order of 1893.
The name Gilbert, already in the name of the British protectorate since 1892, was incorporated into the name of the entire Gilbert and Ellice Islands Colony
The Gilbert and Ellice Islands (GEIC as a colony) in the Pacific Ocean were part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. They were a protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a colony until 1 January 1976. The history of the colony w ...
(GEIC) from 1916 and was retained after the Ellice Islands became the separate nation of Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northeast ...
in 1976. The spelling of ''Gilberts'' in the Gilbertese language
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages.
The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the i ...
as ''Kiribati'' may be found in books in Gilbertese prepared by missionaries, but with the meaning of Gilbertese (demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
and language) (see e.g., Hawaiian Board of Missionaries, 1895). The first mention as a dictionary entry of the word ''Kiribati'' as the native name of the country was written down in 1952 by in his comprehensive ''Dictionnaire gilbertin-français''.
It is often suggested that the indigenous name for the Gilbert Islands proper is ''Tungaru'' (see e.g., , 1952–1953, or Arthur Grimble
Sir Arthur Francis Grimble, (Hong Kong, 11 June 1888 – London, 13 December 1956) was a British Colonial Service administrator and writer.
Biography
Grimble was educated at Chigwell School and Magdalene College, Cambridge. He then went ...
, 1989). However, the rendition Kiribati for Gilberts was chosen as the official name of the new independent nation by the Chief Minister, Sir Ieremia Tabai
Ieremia Tienang Tabai (modern spelling: Tabwai; born 16 December 1949) is an I-Kiribati politician who served as the first Beretitenti President of the Republic of Kiribati, after being the youngest ever Chief minister of the Commonwealth of Na ...
and his Cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
, on such grounds that it was modern, and to comprehend the inclusion of outer islands (e.g., the Phoenix Group and Line Islands), which were not considered part of the Tungaru (or Gilberts) chain.
History

Early history
The area now called Kiribati, mainly the 16Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
, has been inhabited by Austronesian peoples
The Austronesian peoples, sometimes referred to as Austronesian-speaking peoples, are a large group of peoples in Taiwan, Maritime Southeast Asia, Micronesia, coastal New Guinea, Island Melanesia, Polynesia, and Madagascar that speak Austro ...
speaking the same Oceanic language
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ...
, from North to South, including the southernmost Nui, since sometime between 3000 BCMacdonald, Barrie (2001) ''Cinderellas of the Empire: towards a history of Kiribati and Tuvalu'', Institute of Pacific Studies, University of the South Pacific
The University of the South Pacific (USP) is a public university, public research university with locations spread throughout a dozen countries in Oceania. Established in 1968, the university is organised as an intergovernmental organisation and ...
, Suva, Fiji, , p. 1 and AD 1300. The area was not completely isolated; later, voyagers from Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono an ...
, Tonga
Tonga (, ; ), officially the Kingdom of Tonga ( to, Puleʻanga Fakatuʻi ʻo Tonga), is a Polynesian country and archipelago. The country has 171 islands – of which 45 are inhabited. Its total surface area is about , scattered over in ...
, and Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
introduced some Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
n and Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n cultural aspects, respectively. Intermarriage and intense navigation between the islands tended to blur cultural differences and resulted in a significant degree of cultural homogenization Local oral historians chiefly in the form of lore keepers suggest that the area was first inhabited by a group of seafaring people from Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
, who were described as being dark-skinned frizzy-haired and short in stature. These indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
were then visited by early Austronesian seafarers from the west, a place called ''Matang'', orally described as being tall and fair-skinned. Eventually, both groups intermittently clashed and intermingled until they slowly became a uniform population.
Around 1300 A.D, there was a mass exodus from Samoa
Samoa, officially the Independent State of Samoa; sm, Sāmoa, and until 1997 known as Western Samoa, is a Polynesian island country consisting of two main islands (Savai'i and Upolu); two smaller, inhabited islands (Manono Island, Manono an ...
at the same time that cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
was forcefully abolished there, leading to the addition of Polynesian ancestry into the mix of most Gilbertese people. These Samoans would later bring strong features of Polynesian languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family.
There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austron ...
and culture, creating clans based on their own Samoan traditions and slowly intertwining with the indigenous clans and powers already dominant in Kiribati. Around the 15th century, starkly contrasting systems of governance arose between the Northern Islands, primarily under chiefly rule (''uea''), and the Central and Southern Islands, primarily under the rule of their council of elders (''unimwaane''). Tabiteuea
Tabiteuea (formerly Drummond's Island) is an atoll in the Gilbert Islands, Kiribati, farther south of Tarawa. This atoll is the bigger and the most populated of the Gilbert Islands but Tarawa. The atoll consists of one main island, in the nor ...
could be an exception as the sole island that is known as maintaining a traditional egalitarian
Egalitarianism (), or equalitarianism, is a school of thought within political philosophy that builds from the concept of social equality, prioritizing it for all people. Egalitarian doctrines are generally characterized by the idea that all hum ...
society. The name Tabiteuea stems from the root phrase Tabu-te-Uea meaning "chiefs are forbidden". Civil war soon became a factor, with acquisition of land being the main form of conquest. Clans and chiefs began fighting over resources, fuelled by hatred and reignited blood feuds, which may have started months, years, or even decades before.
The turmoil lasted well into the European visitation and colonial era, which led to certain islands decimating their foes with the help of guns and cannon-equipped ships that some Europeans were coerced into using by the more cunning and persuasive among the I-Kiribati leaders. The typical military arms of the I-Kiribati at this time were shark-tooth-embedded wooden spears, knives and swords, and garbs of armour fashioned from dense coconut fibre. They chiefly used these instead of the gunpowder and weapons of steel available at the time, because of the strong sentimental value of the equipment handed down through generations. Ranged weapons, such as bows, slings and javelins, were seldom used; hand-to-hand combat
Hand-to-hand combat (sometimes abbreviated as HTH or H2H) is a physical confrontation between two or more persons at short range (grappling distance or within the physical reach of a handheld weapon) that does not involve the use of weapons.Huns ...
was a prominent skill still practised today, though seldom mentioned because of various taboos associated with it, secrecy being the primary one. Abemama
Abemama (Apamama) is an atoll, one of the Gilberts group in Kiribati, and is located southeast of Tarawa and just north of the Equator. Abemama has an area of and a population of 3,299 . The islets surround a deep lagoon. The eastern part of ...
's High Chief Tembinok'
Tembinok', or Tem Binoka, (reigned 1878 – 10 November 1891) was the ''Uea'' (High Chief) of Abemama, Aranuka and Kuria, in the Gilbert Islands, during the late 19th century.
Biography
Tembinok'′s grandfather, Temkarotu (d. 1860), was ...
was the last of the dozens of expansionist Chiefs of Gilbert Islands of this period, despite Abemama historically conforming to the traditional Southern Island's governance of their respective "''unimwaane''". He was immortalised in Robert Louis Stevenson
Robert Louis Stevenson (born Robert Lewis Balfour Stevenson; 13 November 1850 – 3 December 1894) was a Scottish novelist, essayist, poet and travel writer. He is best known for works such as ''Treasure Island'', ''Strange Case of Dr Jekyll a ...
's book ''In the South Seas'', which delved into the High Chief's character and method of rule during Stevenson's stay in Abemama. The 90th anniversary of his arrival in the Gilbert Islands was chosen to celebrate the independence of Kiribati on 12 July 1979.
Colonial era
Chance visits by European ships occurred in the 17th and 18th centuries, while those ships attempted circumnavigations of the world, or sought sailing routes from the south to north Pacific Ocean. A passing trade, whaling the On-The-Line grounds, and labour ships associated withblackbirding
Blackbirding involves the coercion of people through deception or kidnapping to work as slaves or poorly paid labourers in countries distant from their native land. The term has been most commonly applied to the large-scale taking of people in ...
of Kanakas
Kanakas were workers (a mix of voluntary and involuntary) from various Pacific Islands employed in British colonies, such as British Columbia (Canada), Fiji, Solomon Islands, Vanuatu, Papua New Guinea and Queensland (Australia) in the 19t ...
workers, visited the islands in large numbers during the 19th century, with social, economic, political, religious and cultural consequences. More than 9,000 workers were sent abroad from 1845 to 1895, most of them not returning.
The passing trade gave rise to European, Chinese, Samoan and other residents from the 1830s: they included beachcombers
''The Beachcombers'' is a Canadian comedy-drama television series that ran on CBC Television from October 1, 1972, to December 12, 1990. With over 350 episodes, it is one of the longest-running dramatic series ever made for English-language Canad ...
, castaways, traders and missionaries.
Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
in the German sphere of influence, while Ocean Island and the future GEIC wound up in the British sphere of influence. In 1892, local Gilbertese authorities (an ''uea'', a chief from the Northern Gilbert Group, and ''atun te boti'' or head of clan) on each of the Gilbert Islands agreed to Captain E.H.M. Davis commanding HMS ''Royalist'' of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
declaring them part of a British protectorate, along with the nearby Ellice Islands
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northea ...
. They were administered by a resident commissioner
Resident commissioner was or is an official title of several different types of commissioners, who were or are representatives of any level of government. Historically, they were appointed by the British Crown in overseas protectorates (such ...
based first on Makin Islands (1893–95), then in Betio
Betio is the largest township of Kiribati's capital city, South Tarawa, and the country's main port. The settlement is located on a separate islet at the extreme southwest of the atoll.
Betio Post Office opened on 5 April 1957 and closed in 1964. ...
, Tarawa
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
''
''
Ocean Island (1908–1942), protectorate who was under the  The islands became the
The islands became the  In 1902, the Pacific Cable Board laid the first trans-Pacific telegraph cable from
In 1902, the Pacific Cable Board laid the first trans-Pacific telegraph cable from  After the
After the
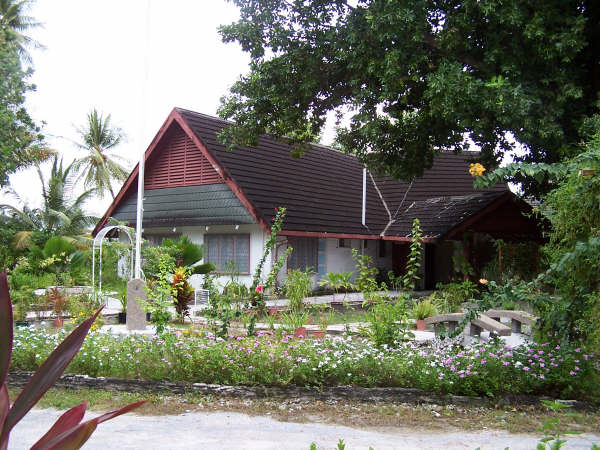 The Gilbert Islands gained independence as the Republic of Kiribati on 12 July 1979. Then, in September, the United States relinquished all claims to the sparsely inhabited
The Gilbert Islands gained independence as the Republic of Kiribati on 12 July 1979. Then, in September, the United States relinquished all claims to the sparsely inhabited
 The
The
 Law enforcement in Kiribati is carried out by the Kiribati Police Service which is responsible for all law enforcement and paramilitary duties for the island nation. There are police posts located on all of the islands. The police have one patrol boat, the Pacific-class patrol boat RKS Teanoai II (301), RKS ''Teanoai II''. Kiribati has no military and relies on both Australia and New Zealand for its defence.
The main prison in Kiribati is located in
Law enforcement in Kiribati is carried out by the Kiribati Police Service which is responsible for all law enforcement and paramilitary duties for the island nation. There are police posts located on all of the islands. The police have one patrol boat, the Pacific-class patrol boat RKS Teanoai II (301), RKS ''Teanoai II''. Kiribati has no military and relies on both Australia and New Zealand for its defence.
The main prison in Kiribati is located in

 There are 21 inhabited islands in Kiribati. Kiribati can be geographically divided into three archipelagoes or groups of islands, which have no administrative functions. They are:
*
There are 21 inhabited islands in Kiribati. Kiribati can be geographically divided into three archipelagoes or groups of islands, which have no administrative functions. They are:
*

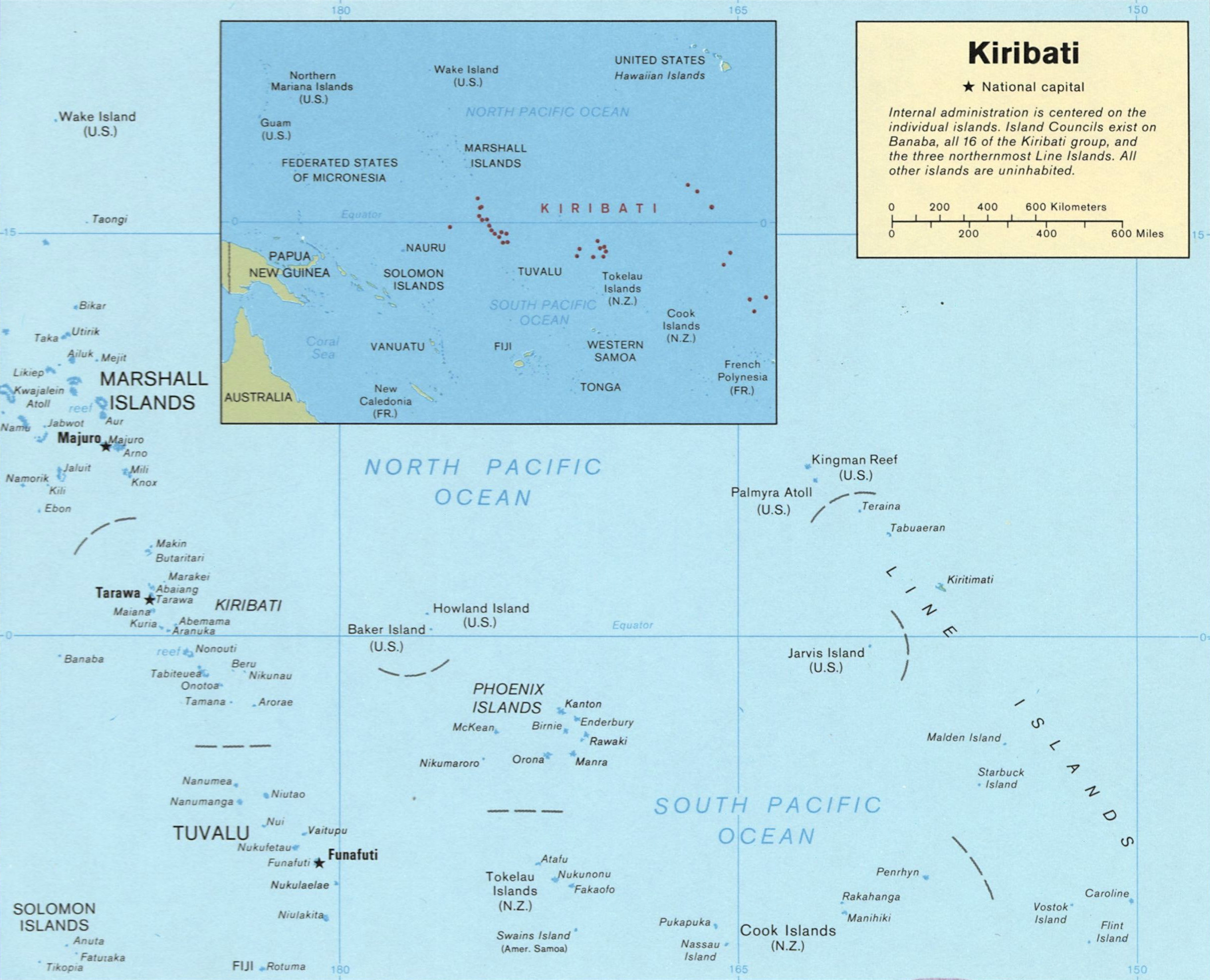
 Kiribati consists of List of islands of Kiribati, 32 atolls and one solitary island (Banaba), extending into the eastern and western hemispheres, as well as the northern and southern hemispheres. Its extensive exclusive economic zone covers three, non-contiguous, traditional geographic subregions: Banaba (
Kiribati consists of List of islands of Kiribati, 32 atolls and one solitary island (Banaba), extending into the eastern and western hemispheres, as well as the northern and southern hemispheres. Its extensive exclusive economic zone covers three, non-contiguous, traditional geographic subregions: Banaba (
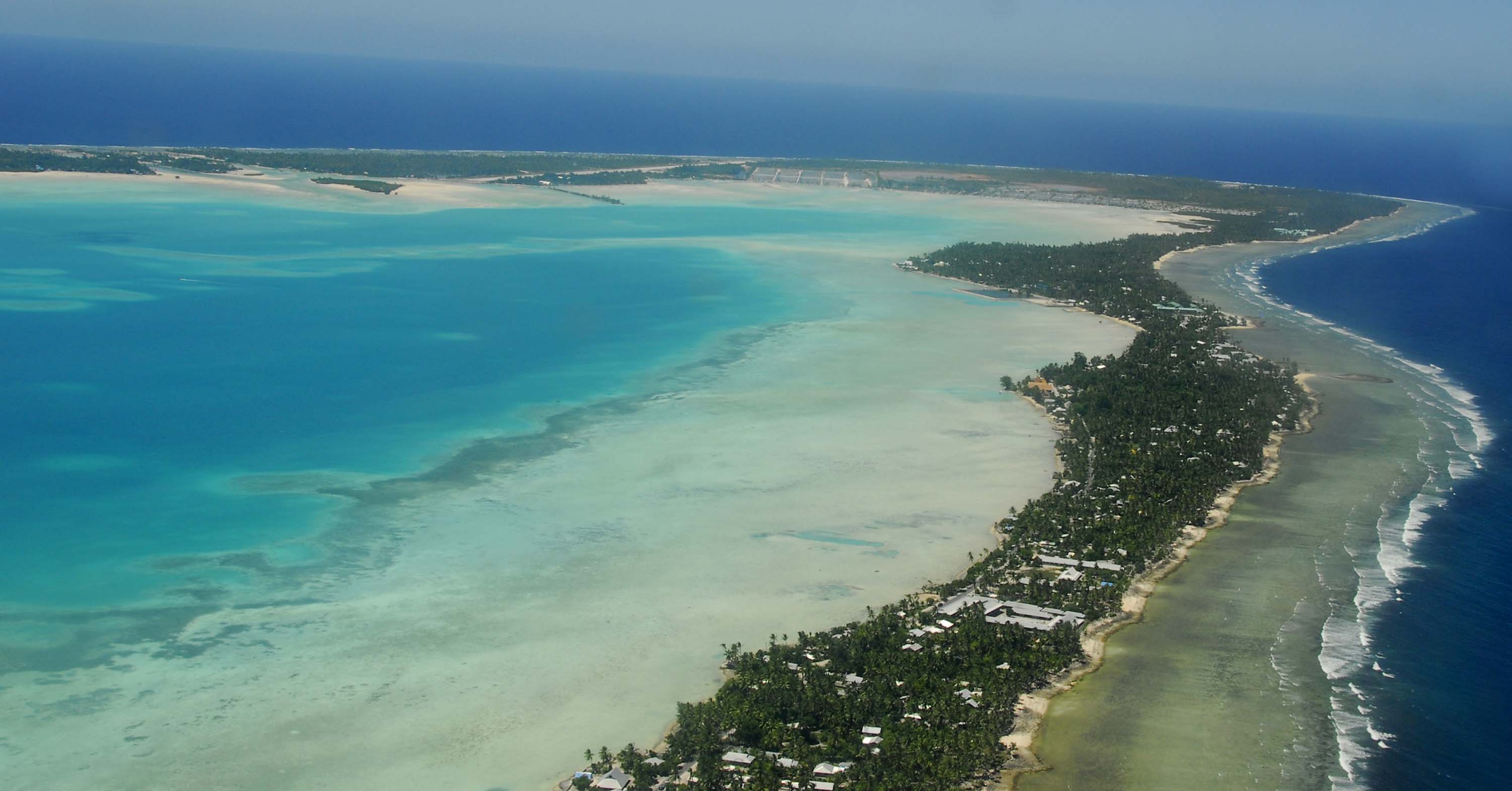
 The atolls and reef islands can respond to changes in sea-level. Paul Kench at the University of Auckland in New Zealand and Arthur Webb at the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission in Fiji released a study in 2010 on the dynamic response of atolls and reef islands in the central Pacific. Kiribati was mentioned in the study, and Webb and Kench found that the three major urbanised islands in Kiribati—Betio, Bairiki and Nanikai—increased by 30% (36 hectares), 16.3% (5.8 hectares) and 12.5% (0.8 hectares), respectively.
The study by Paul Kench and Arthur Webb recognises that the islands are extremely vulnerable to sea level rise, and concluded that: "This study did not measure vertical growth of the island surface nor does it suggest there is any change in the height of the islands. Since land height has not changed the vulnerability of the greater part of the land area of each island to submergence due to sea level rise is also unchanged and these low-lying atolls remain immediately and extremely vulnerable to inundation or sea water flooding."
The Climate Change in the Pacific Report of 2011 describes Kiribati as having a low risk of cyclones; however in March 2015 Kiribati experienced flooding and destruction of seawalls and coastal infrastructure as the result of Cyclone Pam, a Category 5 cyclone that devastated Vanuatu. Kiribati remains exposed to the risk that cyclones can strip the low-lying islands of their vegetation and soil.
Gradual sea-level rise also allows for coral polyp (zoology), polyp activity to raise the atolls with the sea level. However, if the increase in sea level occurs at a rate faster than coral growth, or if polyp activity is damaged by ocean acidification, then the resilience of the atolls and reef islands is less certain. Also, coral bleaching has occurred on more than 60% of the coral reefs in the Maldives.
The Kiribati Adaptation Program (KAP), started in 2003, is a US$5.5 million initiative that was originally enacted by the national government of Kiribati with the support of the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the
The atolls and reef islands can respond to changes in sea-level. Paul Kench at the University of Auckland in New Zealand and Arthur Webb at the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission in Fiji released a study in 2010 on the dynamic response of atolls and reef islands in the central Pacific. Kiribati was mentioned in the study, and Webb and Kench found that the three major urbanised islands in Kiribati—Betio, Bairiki and Nanikai—increased by 30% (36 hectares), 16.3% (5.8 hectares) and 12.5% (0.8 hectares), respectively.
The study by Paul Kench and Arthur Webb recognises that the islands are extremely vulnerable to sea level rise, and concluded that: "This study did not measure vertical growth of the island surface nor does it suggest there is any change in the height of the islands. Since land height has not changed the vulnerability of the greater part of the land area of each island to submergence due to sea level rise is also unchanged and these low-lying atolls remain immediately and extremely vulnerable to inundation or sea water flooding."
The Climate Change in the Pacific Report of 2011 describes Kiribati as having a low risk of cyclones; however in March 2015 Kiribati experienced flooding and destruction of seawalls and coastal infrastructure as the result of Cyclone Pam, a Category 5 cyclone that devastated Vanuatu. Kiribati remains exposed to the risk that cyclones can strip the low-lying islands of their vegetation and soil.
Gradual sea-level rise also allows for coral polyp (zoology), polyp activity to raise the atolls with the sea level. However, if the increase in sea level occurs at a rate faster than coral growth, or if polyp activity is damaged by ocean acidification, then the resilience of the atolls and reef islands is less certain. Also, coral bleaching has occurred on more than 60% of the coral reefs in the Maldives.
The Kiribati Adaptation Program (KAP), started in 2003, is a US$5.5 million initiative that was originally enacted by the national government of Kiribati with the support of the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the
 Kiribati has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification, Af). From April to October, there are predominant northeastern winds and stable temperatures close to . From November to April, western gales bring rain.
Kiribati wet season (''te Auu-Meang'') also recognized as the Tropical cyclone (TC) (''te Angibuaka'') season starts from November to April every year. Kiribati therefore typically experiences more extreme weather events associated with Tropical disturbances (TD) or Tropical cyclones during te Auu-Meang. But Tropical cyclones rarely develop or pass along the equator where Kiribati is located. However, based on past events, Kiribati has been impacted from distant Tropical cyclone (TC) and the impacts were observed while the systems are in their development stages (Tropical Low/disturbance) or even before they reach Tropical cyclone category.
The fair season starts when ''Ten Rimwimata'' (Antares) appears in the sky after sunset, from May to November, when more gentle winds and currents and less rain. Then towards December, when ''Nei Auti'' (Pleiades) replaces Antares, the season of sudden westerly winds and more heavy rain discourages any far travel from island to island.
Kiribati does not experience cyclones but effects may occasionally be experienced during cyclone seasons affecting nearby Pacific Island countries such as Fiji.
Precipitation varies significantly between islands. For example, the annual average is 3,000 mm (120 in) in the north and 500 mm (20 in) in the south of the Gilbert Islands. Most of these islands are in the dry belt of the equatorial oceanic climatic zone and experience prolonged droughts.
Kiribati has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification, Af). From April to October, there are predominant northeastern winds and stable temperatures close to . From November to April, western gales bring rain.
Kiribati wet season (''te Auu-Meang'') also recognized as the Tropical cyclone (TC) (''te Angibuaka'') season starts from November to April every year. Kiribati therefore typically experiences more extreme weather events associated with Tropical disturbances (TD) or Tropical cyclones during te Auu-Meang. But Tropical cyclones rarely develop or pass along the equator where Kiribati is located. However, based on past events, Kiribati has been impacted from distant Tropical cyclone (TC) and the impacts were observed while the systems are in their development stages (Tropical Low/disturbance) or even before they reach Tropical cyclone category.
The fair season starts when ''Ten Rimwimata'' (Antares) appears in the sky after sunset, from May to November, when more gentle winds and currents and less rain. Then towards December, when ''Nei Auti'' (Pleiades) replaces Antares, the season of sudden westerly winds and more heavy rain discourages any far travel from island to island.
Kiribati does not experience cyclones but effects may occasionally be experienced during cyclone seasons affecting nearby Pacific Island countries such as Fiji.
Precipitation varies significantly between islands. For example, the annual average is 3,000 mm (120 in) in the north and 500 mm (20 in) in the south of the Gilbert Islands. Most of these islands are in the dry belt of the equatorial oceanic climatic zone and experience prolonged droughts.
 Kiribati contains three ecosystems: Central Polynesian tropical moist forests, Eastern Micronesia tropical moist forests, and Western Polynesian tropical moist forests.
Because of the relatively young geological age of the islands and atolls and high level of soil salination, the flora of Kiribati is somewhat unhealthy. The Gilbert Islands contain about 83 indigenous and 306 introduced plants, whereas the corresponding numbers for Line and Phoenix Islands are 67 and 283. None of these species are Endemism, endemic, and about half of the indigenous ones have a limited distribution and became endangered or nearly extinct due to human activities such as phosphate mining.
Coconut, Pandanus tectorius, pandanus palms and breadfruit trees are the most common ''wild'' plants,Kiribati
Kiribati contains three ecosystems: Central Polynesian tropical moist forests, Eastern Micronesia tropical moist forests, and Western Polynesian tropical moist forests.
Because of the relatively young geological age of the islands and atolls and high level of soil salination, the flora of Kiribati is somewhat unhealthy. The Gilbert Islands contain about 83 indigenous and 306 introduced plants, whereas the corresponding numbers for Line and Phoenix Islands are 67 and 283. None of these species are Endemism, endemic, and about half of the indigenous ones have a limited distribution and became endangered or nearly extinct due to human activities such as phosphate mining.
Coconut, Pandanus tectorius, pandanus palms and breadfruit trees are the most common ''wild'' plants,Kiribati
''Encyclopædia Britannica'' whereas the five most cultivated crops but the traditional ''Babai'', ''Cyrtosperma merkusii'', are imported Chinese cabbage, pumpkin, tomato, watermelon and cucumber. Over eighty per cent of the population participates in either farming or fishing. Seaweed farming is an important part of the economy , with two major species ''Eucheuma alcarezii'' and ''Eucheuma spinosium'' introduced to the local lagoons from the Philippines in 1977. It competes with collection of the black-lipped pearl oyster (''Pinctada margaritifera'') and shellfish, which are dominated by the strombid gastropod (''Strombus luhuanus'') and Anadara cockles (''Anadara uropigimelana''), whereas the stocks of the giant clam (''Tridacna gigas'') have been largely exhausted. Kiribati has a few land mammals, none being indigenous or endemic. They include the Polynesian rat (''Rattus exulans''), dogs, cats and pigs. Among the 75 bird species, the Bokikokiko (''Acrocephalus aequinoctialis'') is endemic to

 Kiribati has few natural resources. Commercially viable
Kiribati has few natural resources. Commercially viable
 Kiribati has had two domestic airlines: Air Kiribati and Coral Sun Airways. Both airlines are based in Tarawa's Bonriki International Airport and serve destinations across the Gilbert Islands and Line Islands only:
Kiribati has had two domestic airlines: Air Kiribati and Coral Sun Airways. Both airlines are based in Tarawa's Bonriki International Airport and serve destinations across the Gilbert Islands and Line Islands only:
 The November 2020 census showed a population of 119,940. About 90% lived in the
The November 2020 census showed a population of 119,940. About 90% lived in the
Western Pacific High Commission
The British Western Pacific Territories (BWPT) was the name of a colonial entity, created in 1877, for the administration, under a single representative of the British Crown, styled High Commissioner for the Western Pacific, of a series of Paci ...
based in Fiji. Banaba
BanabaThe correct spelling and etymology in Gilbertese should be ''Bwanaba'' but the Constitution of Kiribati writes Banaba. Because of the spelling in English or French, the name was very often written Paanapa or Paanopa, as it was in 1901 Ac ...
, known to Europeans as Ocean Island, was added to the protectorate in 1900, because of the phosphate rock
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxi ...
of its soil (discovered in 1900). This discovery and the mining ended the contracting of Kanakas workers to farm plantations in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, established_ ...
, German Samoa
German Samoa (german: Deutsch-Samoa) was a German protectorate from 1900 to 1920, consisting of the islands of Upolu, Savai'i, Apolima and Manono, now wholly within the independent state of Samoa, formerly ''Western Samoa''. Samoa was the last ...
or Central America, with all the needed workers being used in Ocean Island extraction.
The conduct of William Telfer Campbell
William Telfer Campbell (1863 - 1929), born in India, was the second Resident Commissioner of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands protectorate, from 1895 to 1909.
Campbell had started his career in the Royal Irish Constabulary. He was twice the ...
, the second resident commissioner of the Gilberts and Ellice Islands of 1896 to 1908, was criticised as to his legislative, judicial and administrative management (including allegations of forced labour exacted from islanders) and became the subject of the 1909 report by Arthur Mahaffy. In 1913, an anonymous correspondent to ''The New Age
''The New Age'' was a British weekly magazine (1894–1938), inspired by Fabian socialism, and credited as a major influence on literature and the arts during its heyday from 1907 to 1922, when it was edited by Alfred Richard Orage. It published ...
'' newspaper described the maladministration of W. Telfer Campbell and questioned the partiality of Arthur Mahaffy, because he was a former colonial official in the Gilberts. The anonymous correspondent also criticised the operations of the Pacific Phosphate Company
John T. Arundel (1 September 1841 – 30 November 1919) was an English entrepreneur who was instrumental in the development of the mining of phosphate rock on the Pacific islands of Nauru and Banaba (Ocean Island). Williams & Macdonald (1985) ...
on Ocean Island.
 The islands became the
The islands became the crown colony
A Crown colony or royal colony was a colony administered by The Crown within the British Empire. There was usually a Governor, appointed by the British monarch on the advice of the UK Government, with or without the assistance of a local Counci ...
of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands
The Gilbert and Ellice Islands (GEIC as a colony) in the Pacific Ocean were part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. They were a protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a colony until 1 January 1976. The history of the colony w ...
in 1916. The Northern Line Islands, including Christmas Island (Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
), were added to the colony in 1919, and the Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic ...
were added in 1937 with the purpose of a Phoenix Islands Settlement Scheme
The Phoenix Islands Settlement Scheme was begun in 1938 in the western Pacific ocean and was the last attempt at human colonisation within the British Empire.
History
Conceived by Henry E. "Harry" Maude, lands commissioner of the Gilbert and El ...
. On 12 July 1940, Pan Am
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United States ...
Airways' '' American Clipper'' landed at Canton Island
Canton Island (also known as Kanton or Abariringa), previously known as Mary Island, Mary Balcout's Island or Swallow Island, is the largest, northernmost, and , the sole inhabited island of the Phoenix Islands, in the Republic of Kiribati. It i ...
for the first time during a flight from Honolulu
Honolulu (; ) is the capital and largest city of the U.S. state of Hawaii, which is in the Pacific Ocean. It is an unincorporated county seat of the consolidated City and County of Honolulu, situated along the southeast coast of the island ...
to Auckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
.
Sir Arthur Grimble
Sir Arthur Francis Grimble, (Hong Kong, 11 June 1888 – London, 13 December 1956) was a British Colonial Service administrator and writer.
Biography
Grimble was educated at Chigwell School and Magdalene College, Cambridge. He then went ...
was a cadet administrative officer based at Tarawa (1913–1919) and became Resident Commissioner of the Gilbert and Ellice Islands colony in 1926.
 In 1902, the Pacific Cable Board laid the first trans-Pacific telegraph cable from
In 1902, the Pacific Cable Board laid the first trans-Pacific telegraph cable from Bamfield
Bamfield is a community that is surrounded by Crown Land, First Nation Lands belonging to the Huu-ay-aht Nations, and portions of the Pacific Rim National Park, located on Barkley Sound, Vancouver Island in British Columbia. The community, with ...
, British Columbia to Fanning Island
Tabuaeran, also known as Fanning Island, is an atoll that is part of the Line Islands of the central Pacific Ocean and part of Kiribati. The land area is , and the population in 2015 was 2,315. The maximum elevation is about 3 m (10 f ...
(Tabuaeran) in the Line Islands, and from Fiji to Fanning Island, thus completing the All Red Line
The All Red Line was a system of electrical telegraphs that linked much of the British Empire. It was inaugurated on 31 October 1902. The informal name derives from the common practice of colouring the territory of the British Empire red or ...
, a series of telegraph lines circumnavigating the globe completely within the British Empire. The location of Fanning Island, one of the closest formations to Hawaii, led to its annexation by the British Empire in 1888. Nearby candidates including Palmyra Island
Palmyra Atoll (), also referred to as Palmyra Island, is one of the Northern Line Islands (southeast of Kingman Reef and north of Kiribati). It is located almost due south of the Hawaiian Islands, roughly one-third of the way between Hawaii an ...
were not favoured due to the lack of adequate landing sites.
The United States eventually incorporated the Northern Line Islands into its territories, and did the same with the Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic ...
, which lie between Gilberts and the Line Islands, including Howland, Jarvis, and Baker
A baker is a tradesperson who bakes and sometimes sells breads and other products made of flour by using an oven or other concentrated heat source. The place where a baker works is called a bakery.
History
Ancient history
Since grains ha ...
islands, thus causing a territorial dispute. That was eventually resolved and they finally became part of Kiribati under the Treaty of Tarawa
On September 20, 1979, representatives of the newly independent Republic of Kiribati and of the United States met in Tarawa to sign a treaty of friendship between the two nations, known as the Treaty of Tarawa. More formally, the treaty is entit ...
.
 After the
After the attack on Pearl Harbor
The attack on Pearl HarborAlso known as the Battle of Pearl Harbor was a surprise military strike by the Imperial Japanese Navy Air Service upon the United States against the naval base at Pearl Harbor in Honolulu, Territory of Hawaii, j ...
, during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Butaritari
Butaritari is an atoll in the Pacific Ocean island nation of Kiribati. The atoll is roughly four-sided. The south and southeast portion of the atoll comprises a nearly continuous islet. The atoll reef is continuous but almost without islets al ...
and Tarawa, and others of the Northern Gilbert group, were occupied by Japan from 1941 to 1943. Betio
Betio is the largest township of Kiribati's capital city, South Tarawa, and the country's main port. The settlement is located on a separate islet at the extreme southwest of the atoll.
Betio Post Office opened on 5 April 1957 and closed in 1964. ...
became an airfield and supply base. The expulsion of the Japanese military in late 1943 involved one of the bloodiest battles in US Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through combi ...
history. Marines landed in November 1943 and the Battle of Tarawa
The Battle of Tarawa was fought on 20–23 November 1943 between the United States and Japan at the Tarawa Atoll in the Gilbert Islands, and was part of Operation Galvanic, the U.S. invasion of the Gilberts. Nearly 6,400 Japanese, Koreans, an ...
ensued. Ocean Island, the headquarters of the colony, was bombed, evacuated and occupied by Japan in 1942 and only freed in 1945, after the massacre of all but one of the Gilbertese on the island by the Japanese forces. Funafuti
Funafuti is the capital of the island nation of Tuvalu. It has a population of 6,320 people (2017 census), and so it has more people than the rest of Tuvalu combined, with approximately 60% of the population. It consists of a narrow sweep of la ...
hosted then the provisional headquarters of the colony from 1942 to 1946, when Tarawa returned to host the headquarters, replacing Ocean Island.
At the end of 1945, most of the remaining inhabitants of Banaba, repatriated from Kosrae
Kosrae ( ), formerly known as Kusaie or Strong's Island, is an island in the Federated States of Micronesia. The State of Kosrae is one of the four states of the Federated States of Micronesia, and includes the main island of Kosrae and a few near ...
, Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
and Tarawa, were relocated to Rabi Island
Rabi (pronounced ) is a volcano, volcanic island in northern Fiji. It is an outlier to Taveuni (5 kilometers west), in the Vanua Levu Group. It covers an area of 66.3 square kilometers, reaching a maximum altitude of 463 meters and has a shoreli ...
, a land of Fiji that the British government had acquired in 1942 for this purpose.
On 1 January 1953, the British Western Pacific High Commissioner of the colony was transferred from Fiji to the new capital of Honiara
Honiara () is the capital and largest city of Solomon Islands, situated on the northwestern coast of Guadalcanal. , it had a population of 92,344 people. The city is served by Honiara International Airport and the seaport of Point Cruz, and lie ...
, to the British Solomon Islands
The British Solomon Islands Protectorate was first declared over the southern Solomons in 1893, when Captain Gibson, R.N., of , declared the southern islands a British protectorate. Other islands were subsequently declared to form part o ...
, with the Gilberts' Resident Commissioner still headquartered in Tarawa.
Further military operations in the colony occurred in the late 1950s and early 1960s when Christmas Island
Christmas Island, officially the Territory of Christmas Island, is an Australian external territory comprising the island of the same name. It is located in the Indian Ocean, around south of Java and Sumatra and around north-west of the ...
was used by the United States and United Kingdom for nuclear weapons testing
Nuclear weapons tests are experiments carried out to determine nuclear weapons' effectiveness, Nuclear weapon yield, yield, and explosive capability. Testing nuclear weapons offers practical information about how the weapons function, how detona ...
including hydrogen bombs
A thermonuclear weapon, fusion weapon or hydrogen bomb (H bomb) is a second-generation nuclear weapon design. Its greater sophistication affords it vastly greater destructive power than first-generation nuclear bombs, a more compact size, a lowe ...
.
Institutions of internal self-rule were established on Tarawa from about 1967. The Ellice Islands asked for separation from the rest of the colony in 1974 and granted their own internal self-rule institutions. The separation entered into force on 1 January 1976. In 1978, the Ellice Islands became the independent nation of Tuvalu
Tuvalu ( or ; formerly known as the Ellice Islands) is an island country and microstate in the Polynesian subregion of Oceania in the Pacific Ocean. Its islands are situated about midway between Hawaii and Australia. They lie east-northeast ...
.Ridgell, Reilly (1995) ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia''. 3rd Edition. Honolulu: Bess Press. . p. 95.
Independence
 The Gilbert Islands gained independence as the Republic of Kiribati on 12 July 1979. Then, in September, the United States relinquished all claims to the sparsely inhabited
The Gilbert Islands gained independence as the Republic of Kiribati on 12 July 1979. Then, in September, the United States relinquished all claims to the sparsely inhabited Phoenix
Phoenix most often refers to:
* Phoenix (mythology), a legendary bird from ancient Greek folklore
* Phoenix, Arizona, a city in the United States
Phoenix may also refer to:
Mythology
Greek mythological figures
* Phoenix (son of Amyntor), a ...
and Line Islands, in a 1979 treaty of friendship with Kiribati ( ratified in 1983). Although the indigenous Gilbertese
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages.
The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the i ...
name for the Gilbert Islands proper is "Tungaru", the new state chose the name "Kiribati", the Gilbertese spelling of "Gilberts", because it was more modern and as an equivalent of the former colony to acknowledge the inclusion of Banaba, the Line Islands, and the Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic ...
. The last two archipelagoes were never initially occupied by Gilbertese until the British authorities, and later the Republic Government, resettled Gilbertese there under resettlement schemes. In 1982, the first elections since independence were held. A no confidence vote provoked the 1983 new election. In the post-independence era, overcrowding
Overcrowding or crowding is the condition where more people are located within a given space than is considered tolerable from a safety and health perspective. Safety and health perspectives depend on current environments and on local cultural n ...
has been an issue, at least in British and aid organisations' eyes. In 1988, an announcement was made that 4,700 residents of the main island group would be resettled onto less-populated islands. In September 1994, Teburoro Tito
Teburoro Tito (''modern'' spelling Tiito, pronounced Seetoh) (born 25 August 1953) is an I-Kiribati politician who served as the President and foreign minister of Kiribati from 1 October 1994 to 28 March 2003. He was elected for the first time in ...
from the opposition was elected president.
In 1995, Kiribati unilaterally moved the international date line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
far to the east to encompass the Line Islands group, so that the nation would no longer be divided by the date line. The move, which fulfilled one of President Tito's campaign promises, was intended to allow businesses across the expansive nation to keep the same business week. This also enabled Kiribati to become the first country to see the dawn of the third millennium
In contemporary history, the third millennium of the anno Domini or Common Era in the Gregorian calendar is the current millennium spanning the years 2001 to 3000 (21st to 30th centuries). Ongoing futures studies seek to understand what is li ...
, an event of significance for tourism. Tito was re-elected in 1998. In 1999, Kiribati became a full member of the United Nations, 20 years after independence. In 2002, Kiribati passed a controversial law that enabled the government to shut down newspaper publishers. The legislation followed the launching of Kiribati's first successful non-government-run newspaper. President Tito was re-elected in 2003 but was removed from office in March 2003 by a no-confidence vote and replaced by a Council of State. Anote Tong
Anote Tong (; born 11 June 1952 in Tabuaeran, Line Islands) is an I-Kiribati politician for the Pillars of Truth party and environmental activist with half Chinese heritage, who served as President of Kiribati, from 2003 to 2016. He won the elect ...
of the opposition party Boutokaan Te Koaua
Pillars of Truth ( gil, Boutokaan te Koaua; BK or BTK) was a political party in Kiribati, until 2020 when it merged with the Kiribati First Party to create the Boutokaan Kiribati Moa Party.
The party was created through a split in the Natio ...
was elected to succeed Tito in July 2003. He was re-elected in 2007 and in 2011.
In June 2008, Kiribati officials asked Australia and New Zealand to accept Kiribati citizens as permanent refugees. Kiribati is expected to be the first country to lose all its land territory to climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
. In June 2008, the Kiribati President Anote Tong said that the country had reached "the point of no return." He added, "To plan for the day when you no longer have a country is indeed painful but I think we have to do that."
In January 2012, Anote Tong was re-elected for a third and last successive term. In early 2012, the government of Kiribati purchased the 2,200-hectare Natoavatu Estate on the second largest island of Fiji, Vanua Levu
Vanua Levu (pronounced ), formerly known as Sandalwood Island, is the second largest island of Fiji. Located to the north of the larger Viti Levu, the island has an area of and a population of 135,961 .
Geology
Fiji lies in a tectonically ...
. At the time it was widely reported that the government planned to evacuate the entire population of Kiribati to Fiji. In April 2013, President Tong began urging citizens to evacuate the islands and migrate elsewhere. In May 2014, the Office of the President confirmed the purchase of some 5,460 acres of land on Vanua Levu at a cost of 9.3 million Australian dollars.
In March 2016, Taneti Maamau
Taneti Maamau (modern spelling: Taaneti Mwamwau, born 16 September 1960) is an I-Kiribati politician who has served as the 5th President of Kiribati since 11 March 2016.
Political career
A member of Tobwaan Kiribati Party, he began his career ...
was elected Elected may refer to:
* "Elected" (song), by Alice Cooper, 1973
* ''Elected'' (EP), by Ayreon, 2008
*The Elected, an American indie rock band
See also
*Election
An election is a formal group decision-making process by which a populatio ...
as the new President of Kiribati. He was the fifth president since the country became independent in 1979. In June 2020, President Maamau won re-election
The incumbent is the current holder of an office or position, usually in relation to an election. In an election for president, the incumbent is the person holding or acting in the office of president before the election, whether seeking re-ele ...
for second four-year term. President Maamau was considered pro-China and he supported closer ties with Beijing. The 2022 Kiribati constitutional crisis started with the suspension of all 5 major Justices of the judiciary of Kiribati
The Judiciary of Kiribati is the branch of the Government of Kiribati which interprets and applies the laws of the country. In addition to the Constitution of Kiribati and the corpus of laws, the laws of Kiribati include customary law, which the c ...
.
Politics
 The
The Constitution of Kiribati
The Constitution of Kiribati is the supreme law of Kiribati, which was implemented in 1979. The constitution was subsequently amended in the years 1995, 2016, and 2018. The constitution established the principles of the Bill of Rights and the pro ...
, promulgated 12 July 1979, provides for free and open elections in a parliamentary
A parliamentary system, or parliamentarian democracy, is a system of democracy, democratic government, governance of a sovereign state, state (or subordinate entity) where the Executive (government), executive derives its democratic legitimacy ...
democratic republic.
The executive branch consists of a president
President most commonly refers to:
*President (corporate title)
*President (education), a leader of a college or university
*President (government title)
President may also refer to:
Automobiles
* Nissan President, a 1966–2010 Japanese ful ...
(''te Beretitenti''), a vice-president
A vice president, also director in British English, is an officer in government or business who is below the president (chief executive officer) in rank. It can also refer to executive vice presidents, signifying that the vice president is on t ...
and a cabinet
Cabinet or The Cabinet may refer to:
Furniture
* Cabinetry, a box-shaped piece of furniture with doors and/or drawers
* Display cabinet, a piece of furniture with one or more transparent glass sheets or transparent polycarbonate sheets
* Filing ...
. The president, who is also chief of the cabinet, is directly elected by the citizens, after the legislature nominates three or four persons from among its members to be candidates in the ensuing presidential election. The president is limited to serving three four-year terms, and remains a member of the assembly. The cabinet is composed of the president, vice-president, and 13 ministers (appointed by the president) who are also ministers of parliament.
The legislative branch is the unicameral ''Maneaba ni Maungatabu
The House of Assembly (, ) is the Legislature of Kiribati. Since 2016, it has 45 members, 44 elected for a four-year term in 23 single-seat and multi-seat constituencies and 1 non-elected delegate from the Banaban community on Rabi Island in Fi ...
'' (House of Assembly). Its members are elected, including by constitutional mandate, a nominated representative of the Banaban people in Rabi Island
Rabi (pronounced ) is a volcano, volcanic island in northern Fiji. It is an outlier to Taveuni (5 kilometers west), in the Vanua Levu Group. It covers an area of 66.3 square kilometers, reaching a maximum altitude of 463 meters and has a shoreli ...
, Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
(Banaba, former Ocean Island), in addition to, until 2016, the attorney general, who served as an ''ex officio'' member from 1979 to 2016. Legislators serve for a four-year term.
The constitutional provisions governing administration of justice are similar to those in other former British possessions in that the judiciary is free from governmental interference. The judicial branch is made up of the High Court (in Betio) and the Court of Appeal. The president appoints the presiding judges.
Local government is through island councils with elected members. Local affairs are handled in a manner similar to town meetings in colonial America. Island councils make their own estimates of revenue and expenditure and generally are free from central government controls. There are a total of 21 inhabited islands in Kiribati. Each inhabited island has its own council. Since independence, Kiribati is no longer divided into districts (see Subdivisions of Kiribati
In Kiribati, there are no longer official administrative divisions but it is possible to divide Kiribati geographically into one isolated island and three archipelagos or island groups:
* Banaba – isolated island
* Gilbert Islands
* Line Islan ...
).
Kiribati has formal political parties but their organisation is quite informal. Ad hoc opposition groups tend to coalesce around specific issues. There is universal suffrage at age 18. Today the only recognisable parties are the Boutokaan Kiribati Moa Party
The Boutokaan Kiribati Moa Party (BKM) is a political party in Kiribati from the merger of the Kiribati First Party and Boutokaan te Koaua in 2020.
History
The party was established in May 2020, after the merger of the Pillars of Truth with ...
, former ''Boutokaan te Koaua'', and Tobwaan Kiribati Party
The Tobwaan Kiribati Party ( en, Embracing Kiribati Party; TKP) is a political party in Kiribati.
History
The party was established in January 2016 as a merger of the Maurin Kiribati Party and the United Coalition Party. The two parties had won ...
.
Foreign relations
Kiribati maintains close relations with its Pacific neighbours, Australia, New Zealand, Japan and Fiji. The first three of these provide the bulk of the country's foreign aid.Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
and Japan also have specified-period licences to fish in Kiribati's waters. There are three resident diplomatic missions headquartered in South Tarawa
South Tarawa ( gil, Tarawa Teinainano) is the capital and hub of the Republic of Kiribati and home to more than half of Kiribati's population. The South Tarawa population centre consists of all the small islets from Betio in the west to Bonriki ...
: the Embassies of the Republic of China
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the northeast ...
(Taiwan) until 2019, replaced by People's Republic of China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
in 2020 and the High Commissions of Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
. A US Embassy
The United States has the second most diplomatic missions of any country in the world after Mainland China, including 166 of the 193 member countries of the United Nations, as well as observer state Vatican City and non-member countries Kosovo a ...
will open in 2023.
In November 1999, Kiribati agreed to allow Japan's National Space Development Agency
The , or NASDA, was a Japanese national space agency established on October 1, 1969 under the National Space Development Agency Law only for peaceful purposes. Based on the Space Development Program enacted by the Minister of Education, Culture, ...
to lease land on Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
(formerly Christmas Island) for 20 years, on which to build a spaceport
A spaceport or cosmodrome is a site for launching or receiving spacecraft, by analogy to a seaport for ships or an airport for aircraft. The word ''spaceport'', and even more so ''cosmodrome'', has traditionally been used for sites capable ...
. The agreement stipulated that Japan was to pay US$840,000 per year and would also pay for any damage to roads and the environment. A Japanese-built downrange tracking station
A ground station, Earth station, or Earth terminal is a terrestrial radio station designed for extraplanetary telecommunication with spacecraft (constituting part of the ground segment of the spacecraft system), or reception of radio waves fro ...
operates on Kiritimati and an abandoned airfield on the island was designated as the landing strip for a proposed reusable unmanned space shuttle called HOPE-X
HOPE (H-II Orbiting Plane) was a Japanese experimental spaceplane project designed by a partnership between NASDA and NAL (both now part of JAXA), started in the 1980s. It was positioned for most of its lifetime as one of the main Japanese contri ...
. HOPE-X, however, was eventually cancelled by Japan in 2003.
As one of the world's most vulnerable nations to the effects of global warming
The effects of climate change impact the physical environment, ecosystems and human societies. The environmental effects of climate change are broad and far-reaching. They affect the Effects of climate change on the water cycle, water cycle, ...
, Kiribati has been an active participant in international diplomatic efforts relating to climate change, most importantly the UNFCCC
The United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) established an international environmental treaty to combat "dangerous human interference with the climate system", in part by stabilizing greenhouse gas concentrations in the ...
conferences of the parties (COP). Kiribati is a member of the Alliance of Small Island States
Alliance of Small Island States (AOSIS) is an intergovernmental organization of low-lying coastal and small island countries. AOSIS was established in 1990, ahead of the Second World Climate Conference. The main purpose of the alliance is to con ...
(AOSIS), an intergovernmental organisation of low-lying coastal and small island countries.
Established in 1990, the main purpose of the alliance is to consolidate the voices of Small Island Developing States
Small Island Developing States (SIDS) are a group of developing countries that are small island countries which tend to share similar sustainable development challenges. These include small but growing populations, limited resources, remoteness, ...
(SIDS) to address global warming. AOSIS has been very active from its inception, putting forward the first draft text in the Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
negotiations as early as 1994.
In 2009, President Tong attended the Climate Vulnerable Forum
The Climate Vulnerable Forum (CVF) is a global partnership of countries that are disproportionately affected by the consequences of climate change. The forum addresses the negative effects of climate change as a result of heightened socioeconomic ...
(Climate Vulnerable Forum, V11) in the Maldives, with 10 other countries that are Climate change vulnerability, vulnerable to climate change, and signed the Bandos Island declaration on 10 November 2009, pledging to show moral leadership and commence greening their economies by voluntarily committing to achieving carbon neutrality.
In November 2010, Kiribati hosted the Tarawa Climate Change Conference (TCCC) to support the president of Kiribati's initiative to hold a consultative forum between vulnerable states and their partners. The conference strove to create an enabling environment for multi-party negotiations under the auspices of the UNFCCC. The conference was a successor event to the Climate Vulnerable Forum. The ultimate objective of TCCC was to reduce the number and intensity of fault lines between parties to the COP process, explore elements of agreement between the parties and thereby to support Kiribati's and other parties' contribution to COP16 held in Cancun, Mexico, from 29 November to 10 December 2010.
In 2013, President Tong spoke of climate-change induced sea level rise as "inevitable". "For our people to survive, then they will have to migrate. Either we can wait for the time when we have to move people en masse or we can prepare them—beginning from now ..." In New York in 2014, per ''The New Yorker'', President Tong told ''The New York Times'' that "according to the projections, within this century, the water will be higher than the highest point in our lands". In 2014, President Tong finalised the purchase of a stretch of land on Vanua Levu
Vanua Levu (pronounced ), formerly known as Sandalwood Island, is the second largest island of Fiji. Located to the north of the larger Viti Levu, the island has an area of and a population of 135,961 .
Geology
Fiji lies in a tectonically ...
, one of the larger Fiji islands, 2,000 km away. A move described by Tong as an "absolute necessity" should the nation be completely submerged under water.
In 2013, attention was drawn to a claim of a Kiribati man of being a Environmental migrant#Asia and the Pacific, "climate change refugee" under the Convention relating to the Status of Refugees (1951). However, this claim was determined by the New Zealand High Court to be untenable. The New Zealand Court of Appeal also rejected the claim in a Teitiota v Chief Executive Ministry of Business, Innovation and Employment, 2014 decision.
On further appeal, the New Zealand Supreme Court confirmed the earlier adverse rulings against the application for refugee status, but rejected the proposition "that environmental degradation resulting from climate change or other natural disasters could never create a pathway into the Refugee Convention or protected person jurisdiction". In 2017, Kiribati signed the UN treaty on the Prohibition of Nuclear Weapons.
On 20 September 2019, the government of Kiribati restored its diplomatic relationship with the People's Republic of China and simultaneously stopped its diplomatic relationship with Taiwan. China offered a 737 aircraft and ferries to Kiribati for the decision, according to Taiwan's foreign minister, Joseph Wu.
Peace Corps
From 1973 though 2008, a total of almost 500 Peace Corps, US Peace Corps volunteers were based on the Islands, as many as 45 in a given year. Activities included assisting in the planning, design and construction of wells, libraries, and other infrastructure, and agricultural, environmental, and community health education. In 2006, volunteer placement was significantly scaled down due to the reduction of consistent air transportation to the outer islands; it was later ended because the associated ability to provide medical care to volunteers could not be assured. In July 2022, US Vice President Harris announced plans to build a new embassy in Kiribati and Tonga and reestablish the Peace Corps presence in the region.Law enforcement and military
 Law enforcement in Kiribati is carried out by the Kiribati Police Service which is responsible for all law enforcement and paramilitary duties for the island nation. There are police posts located on all of the islands. The police have one patrol boat, the Pacific-class patrol boat RKS Teanoai II (301), RKS ''Teanoai II''. Kiribati has no military and relies on both Australia and New Zealand for its defence.
The main prison in Kiribati is located in
Law enforcement in Kiribati is carried out by the Kiribati Police Service which is responsible for all law enforcement and paramilitary duties for the island nation. There are police posts located on all of the islands. The police have one patrol boat, the Pacific-class patrol boat RKS Teanoai II (301), RKS ''Teanoai II''. Kiribati has no military and relies on both Australia and New Zealand for its defence.
The main prison in Kiribati is located in Betio
Betio is the largest township of Kiribati's capital city, South Tarawa, and the country's main port. The settlement is located on a separate islet at the extreme southwest of the atoll.
Betio Post Office opened on 5 April 1957 and closed in 1964. ...
, named the Walter Betio Prison. There is also a prison in London, Kiribati, London on Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
.
Male LGBT rights in Kiribati, homosexuality is illegal in Kiribati, with a penalty up to 14 years in prison, according to a historical British law, but this law is not enforced. Kiribati has not yet followed the lead of the United Kingdom, following its Wolfenden report, to decriminalise acts of male homosexuality, beginning with provisions in the UK's Sexual Offences Act 1957. Female homosexuality is legal, but lesbians may face violence and discrimination. However, employment discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation is prohibited.
Administrative divisions
 There are 21 inhabited islands in Kiribati. Kiribati can be geographically divided into three archipelagoes or groups of islands, which have no administrative functions. They are:
*
There are 21 inhabited islands in Kiribati. Kiribati can be geographically divided into three archipelagoes or groups of islands, which have no administrative functions. They are:
* Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
* Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic ...
, in one of the List of largest protected areas in the world, largest marine protected areas on Earth (was the largest from 2008 to 2010)
* Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
The original districts before independence were:
* Banaba
BanabaThe correct spelling and etymology in Gilbertese should be ''Bwanaba'' but the Constitution of Kiribati writes Banaba. Because of the spelling in English or French, the name was very often written Paanapa or Paanopa, as it was in 1901 Ac ...
(Ocean Island)
* Tarawa Atoll
* Northern Gilbert Islands
* Central Gilbert Island
* South Gilbert Islands, Southern Gilbert Islands
* Line Islands
The Line Islands, Teraina Islands or Equatorial Islands (in Gilbertese, ''Aono Raina'') are a chain of 11 atolls (with partly or fully enclosed lagoons) and coral islands (with a surrounding reef) in the central Pacific Ocean, south of the Hawa ...
Four of the former districts (including Tarawa) lie in the Gilbert Islands, where most of the country's population lives. Five of the Line Islands are uninhabited (Malden Island, Starbuck Island, Millenium Island, Vostok Island and Flint Island). The Phoenix Islands are uninhabited except for Kanton Island, Kanton, and have no representation. Banaba itself is sparsely inhabited now. There is also a non-elected representative of the Banabans on Rabi Island
Rabi (pronounced ) is a volcano, volcanic island in northern Fiji. It is an outlier to Taveuni (5 kilometers west), in the Vanua Levu Group. It covers an area of 66.3 square kilometers, reaching a maximum altitude of 463 meters and has a shoreli ...
in Fiji.
Each of the 21 inhabited islands has its own local council that takes care of daily affairs. There is one council for each inhabited island, with two exceptions: Tarawa Atoll has three councils: Betio
Betio is the largest township of Kiribati's capital city, South Tarawa, and the country's main port. The settlement is located on a separate islet at the extreme southwest of the atoll.
Betio Post Office opened on 5 April 1957 and closed in 1964. ...
Town Council, (TUC) for the rest of South Tarawa
South Tarawa ( gil, Tarawa Teinainano) is the capital and hub of the Republic of Kiribati and home to more than half of Kiribati's population. The South Tarawa population centre consists of all the small islets from Betio in the west to Bonriki ...
) and Eutan Tarawa Council (ETC) (for North Tarawa); and Tabiteuea
Tabiteuea (formerly Drummond's Island) is an atoll in the Gilbert Islands, Kiribati, farther south of Tarawa. This atoll is the bigger and the most populated of the Gilbert Islands but Tarawa. The atoll consists of one main island, in the nor ...
has two councils.
Geography


 Kiribati consists of List of islands of Kiribati, 32 atolls and one solitary island (Banaba), extending into the eastern and western hemispheres, as well as the northern and southern hemispheres. Its extensive exclusive economic zone covers three, non-contiguous, traditional geographic subregions: Banaba (
Kiribati consists of List of islands of Kiribati, 32 atolls and one solitary island (Banaba), extending into the eastern and western hemispheres, as well as the northern and southern hemispheres. Its extensive exclusive economic zone covers three, non-contiguous, traditional geographic subregions: Banaba (Melanesia
Melanesia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It extends from Indonesia's New Guinea in the west to Fiji in the east, and includes the Arafura Sea.
The region includes the four independent countries of Fiji, Va ...
n-Micronesian area), the Gilbert Islands (Micronesia) and the Line Islands, Line and Phoenix Islands (Polynesia
Polynesia () "many" and νῆσος () "island"), to, Polinisia; mi, Porinihia; haw, Polenekia; fj, Polinisia; sm, Polenisia; rar, Porinetia; ty, Pōrīnetia; tvl, Polenisia; tkl, Polenihia (, ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of ...
). The groups of islands are:
* Banaba: an isolated island between Nauru
Nauru ( or ; na, Naoero), officially the Republic of Nauru ( na, Repubrikin Naoero) and formerly known as Pleasant Island, is an island country and microstate in Oceania, in the Central Pacific. Its nearest neighbour is Banaba Island in Ki ...
and the Gilbert Islands
* Gilbert Islands: 16 atolls located some north of Fiji
Fiji ( , ,; fj, Viti, ; Fiji Hindi: फ़िजी, ''Fijī''), officially the Republic of Fiji, is an island country in Melanesia, part of Oceania in the South Pacific Ocean. It lies about north-northeast of New Zealand. Fiji consists ...
* Phoenix Islands: 8 atolls and coral islands located some southeast of the Gilberts
* Line Islands: 8 atolls and one reef, located about east of the Gilberts
Banaba (or Ocean Island) is a Raised coral atoll, raised-coral island. It was once a rich source of phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
s, but was exhausted in mining before independence. The rest of the land in Kiribati consists of the sand and reef rock islets of atolls or coral islands, which rise only one or two metres above sea level.
The soil is thin and calcareous. It has a low water-holding capacity and low organic matter and nutrient content—except for calcium, sodium, and magnesium. Banaba is one of the least suitable places for agriculture in the world.
Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
(previously Christmas Island) in the Line Islands is the world's largest atoll. Based on a 1995 realignment of the International Date Line
The International Date Line (IDL) is an internationally accepted demarcation on the surface of Earth, running between the South and North Poles and serving as the boundary between one calendar day and the next. It passes through the Pacific O ...
, the Line Islands were the first area to enter into a new year, including year 2000. For that reason, Caroline Island was renamed Millennium Island in 1997. The majority of Kiribati, including the capital, is not first, for example New Zealand (UTC+13 in January) has an earlier new year.
Environmental issues
According to the Pacific Regional Environment Programme (previously South Pacific Regional Environment Programme), two small uninhabited Kiribati islets, Tebua Tarawa and Abanuea, disappeared underwater in 1999. The United Nations Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change predicts that sea levels will rise by about 50 cm (20 in) by 2100 due to global warming and a further rise would be inevitable. It is thus likely that within a century the nation's arable land will become subject to increased soil salination and will be largely submerged. The exposure of Kiribati to changes in sea levels is exacerbated by the Pacific decadal oscillation, which is a climate switch phenomenon that results in changes from periods of La Niña to periods of El Niño. This has an effect on sea levels. For example, in 2000, there was a switch from periods of downward pressure of El Niño on sea levels to an upward pressure of La Niña on sea levels, which upward pressure causes more frequent and higher high tide levels. The Perigean spring tide (often called a king tide) can result in seawater flooding low-lying areas of the islands of Kiribati.
 The atolls and reef islands can respond to changes in sea-level. Paul Kench at the University of Auckland in New Zealand and Arthur Webb at the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission in Fiji released a study in 2010 on the dynamic response of atolls and reef islands in the central Pacific. Kiribati was mentioned in the study, and Webb and Kench found that the three major urbanised islands in Kiribati—Betio, Bairiki and Nanikai—increased by 30% (36 hectares), 16.3% (5.8 hectares) and 12.5% (0.8 hectares), respectively.
The study by Paul Kench and Arthur Webb recognises that the islands are extremely vulnerable to sea level rise, and concluded that: "This study did not measure vertical growth of the island surface nor does it suggest there is any change in the height of the islands. Since land height has not changed the vulnerability of the greater part of the land area of each island to submergence due to sea level rise is also unchanged and these low-lying atolls remain immediately and extremely vulnerable to inundation or sea water flooding."
The Climate Change in the Pacific Report of 2011 describes Kiribati as having a low risk of cyclones; however in March 2015 Kiribati experienced flooding and destruction of seawalls and coastal infrastructure as the result of Cyclone Pam, a Category 5 cyclone that devastated Vanuatu. Kiribati remains exposed to the risk that cyclones can strip the low-lying islands of their vegetation and soil.
Gradual sea-level rise also allows for coral polyp (zoology), polyp activity to raise the atolls with the sea level. However, if the increase in sea level occurs at a rate faster than coral growth, or if polyp activity is damaged by ocean acidification, then the resilience of the atolls and reef islands is less certain. Also, coral bleaching has occurred on more than 60% of the coral reefs in the Maldives.
The Kiribati Adaptation Program (KAP), started in 2003, is a US$5.5 million initiative that was originally enacted by the national government of Kiribati with the support of the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the
The atolls and reef islands can respond to changes in sea-level. Paul Kench at the University of Auckland in New Zealand and Arthur Webb at the South Pacific Applied Geoscience Commission in Fiji released a study in 2010 on the dynamic response of atolls and reef islands in the central Pacific. Kiribati was mentioned in the study, and Webb and Kench found that the three major urbanised islands in Kiribati—Betio, Bairiki and Nanikai—increased by 30% (36 hectares), 16.3% (5.8 hectares) and 12.5% (0.8 hectares), respectively.
The study by Paul Kench and Arthur Webb recognises that the islands are extremely vulnerable to sea level rise, and concluded that: "This study did not measure vertical growth of the island surface nor does it suggest there is any change in the height of the islands. Since land height has not changed the vulnerability of the greater part of the land area of each island to submergence due to sea level rise is also unchanged and these low-lying atolls remain immediately and extremely vulnerable to inundation or sea water flooding."
The Climate Change in the Pacific Report of 2011 describes Kiribati as having a low risk of cyclones; however in March 2015 Kiribati experienced flooding and destruction of seawalls and coastal infrastructure as the result of Cyclone Pam, a Category 5 cyclone that devastated Vanuatu. Kiribati remains exposed to the risk that cyclones can strip the low-lying islands of their vegetation and soil.
Gradual sea-level rise also allows for coral polyp (zoology), polyp activity to raise the atolls with the sea level. However, if the increase in sea level occurs at a rate faster than coral growth, or if polyp activity is damaged by ocean acidification, then the resilience of the atolls and reef islands is less certain. Also, coral bleaching has occurred on more than 60% of the coral reefs in the Maldives.
The Kiribati Adaptation Program (KAP), started in 2003, is a US$5.5 million initiative that was originally enacted by the national government of Kiribati with the support of the Global Environment Facility (GEF), the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
, the United Nations Development Program, and the Japanese government. Australia later joined the coalition, donating US$1.5 million to the effort. The program aims to take place over six years, supporting measures that reduce Kiribati's vulnerability to the effects of climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
and sea level rise by raising awareness of climate change, assessing and protecting available water resources, and managing inundation.
At the start of the Adaptation Program, representatives from each of the inhabited atolls identified key climatic changes that had taken place over the past 20–40 years and proposed coping mechanisms to deal with these changes under four categories of urgency of need. The program is now focusing on the country's most vulnerable sectors in the most highly populated areas.
Initiatives include improving water supply management in and around Tarawa; coastal management protection measures such as mangrove re-plantation and protection of public infrastructure; strengthening laws to reduce coastal erosion; and population settlement planning to reduce personal risks.
Climate
 Kiribati has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification, Af). From April to October, there are predominant northeastern winds and stable temperatures close to . From November to April, western gales bring rain.
Kiribati wet season (''te Auu-Meang'') also recognized as the Tropical cyclone (TC) (''te Angibuaka'') season starts from November to April every year. Kiribati therefore typically experiences more extreme weather events associated with Tropical disturbances (TD) or Tropical cyclones during te Auu-Meang. But Tropical cyclones rarely develop or pass along the equator where Kiribati is located. However, based on past events, Kiribati has been impacted from distant Tropical cyclone (TC) and the impacts were observed while the systems are in their development stages (Tropical Low/disturbance) or even before they reach Tropical cyclone category.
The fair season starts when ''Ten Rimwimata'' (Antares) appears in the sky after sunset, from May to November, when more gentle winds and currents and less rain. Then towards December, when ''Nei Auti'' (Pleiades) replaces Antares, the season of sudden westerly winds and more heavy rain discourages any far travel from island to island.
Kiribati does not experience cyclones but effects may occasionally be experienced during cyclone seasons affecting nearby Pacific Island countries such as Fiji.
Precipitation varies significantly between islands. For example, the annual average is 3,000 mm (120 in) in the north and 500 mm (20 in) in the south of the Gilbert Islands. Most of these islands are in the dry belt of the equatorial oceanic climatic zone and experience prolonged droughts.
Kiribati has a tropical rainforest climate (Köppen climate classification, Af). From April to October, there are predominant northeastern winds and stable temperatures close to . From November to April, western gales bring rain.
Kiribati wet season (''te Auu-Meang'') also recognized as the Tropical cyclone (TC) (''te Angibuaka'') season starts from November to April every year. Kiribati therefore typically experiences more extreme weather events associated with Tropical disturbances (TD) or Tropical cyclones during te Auu-Meang. But Tropical cyclones rarely develop or pass along the equator where Kiribati is located. However, based on past events, Kiribati has been impacted from distant Tropical cyclone (TC) and the impacts were observed while the systems are in their development stages (Tropical Low/disturbance) or even before they reach Tropical cyclone category.
The fair season starts when ''Ten Rimwimata'' (Antares) appears in the sky after sunset, from May to November, when more gentle winds and currents and less rain. Then towards December, when ''Nei Auti'' (Pleiades) replaces Antares, the season of sudden westerly winds and more heavy rain discourages any far travel from island to island.
Kiribati does not experience cyclones but effects may occasionally be experienced during cyclone seasons affecting nearby Pacific Island countries such as Fiji.
Precipitation varies significantly between islands. For example, the annual average is 3,000 mm (120 in) in the north and 500 mm (20 in) in the south of the Gilbert Islands. Most of these islands are in the dry belt of the equatorial oceanic climatic zone and experience prolonged droughts.
Ecology
 Kiribati contains three ecosystems: Central Polynesian tropical moist forests, Eastern Micronesia tropical moist forests, and Western Polynesian tropical moist forests.
Because of the relatively young geological age of the islands and atolls and high level of soil salination, the flora of Kiribati is somewhat unhealthy. The Gilbert Islands contain about 83 indigenous and 306 introduced plants, whereas the corresponding numbers for Line and Phoenix Islands are 67 and 283. None of these species are Endemism, endemic, and about half of the indigenous ones have a limited distribution and became endangered or nearly extinct due to human activities such as phosphate mining.
Coconut, Pandanus tectorius, pandanus palms and breadfruit trees are the most common ''wild'' plants,Kiribati
Kiribati contains three ecosystems: Central Polynesian tropical moist forests, Eastern Micronesia tropical moist forests, and Western Polynesian tropical moist forests.
Because of the relatively young geological age of the islands and atolls and high level of soil salination, the flora of Kiribati is somewhat unhealthy. The Gilbert Islands contain about 83 indigenous and 306 introduced plants, whereas the corresponding numbers for Line and Phoenix Islands are 67 and 283. None of these species are Endemism, endemic, and about half of the indigenous ones have a limited distribution and became endangered or nearly extinct due to human activities such as phosphate mining.
Coconut, Pandanus tectorius, pandanus palms and breadfruit trees are the most common ''wild'' plants,Kiribati''Encyclopædia Britannica'' whereas the five most cultivated crops but the traditional ''Babai'', ''Cyrtosperma merkusii'', are imported Chinese cabbage, pumpkin, tomato, watermelon and cucumber. Over eighty per cent of the population participates in either farming or fishing. Seaweed farming is an important part of the economy , with two major species ''Eucheuma alcarezii'' and ''Eucheuma spinosium'' introduced to the local lagoons from the Philippines in 1977. It competes with collection of the black-lipped pearl oyster (''Pinctada margaritifera'') and shellfish, which are dominated by the strombid gastropod (''Strombus luhuanus'') and Anadara cockles (''Anadara uropigimelana''), whereas the stocks of the giant clam (''Tridacna gigas'') have been largely exhausted. Kiribati has a few land mammals, none being indigenous or endemic. They include the Polynesian rat (''Rattus exulans''), dogs, cats and pigs. Among the 75 bird species, the Bokikokiko (''Acrocephalus aequinoctialis'') is endemic to
Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
.
There are 600–800 species of inshore and pelagic finfish, some 200 species of corals and about 1000 species of shellfish. Fishing mostly targets the family Scombridae, particularly the skipjack tuna and yellowfin tuna as well as flying fish (''Cypselurus'' spp.).
Dogs were already accompanying the first inhabitants but were re-introduced by European settlers: they have continued to grow in numbers and are roaming in traditional packs, particularly around South Tarawa.
Economy

phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
deposits on Banaba
BanabaThe correct spelling and etymology in Gilbertese should be ''Bwanaba'' but the Constitution of Kiribati writes Banaba. Because of the spelling in English or French, the name was very often written Paanapa or Paanopa, as it was in 1901 Ac ...
were exhausted at the time of independence. Copra and fish now represent the bulk of production and exports. Kiribati has the lowest GDP out of any sovereign state in Oceania
Oceania (, , ) is a region, geographical region that includes Australasia, Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia. Spanning the Eastern Hemisphere, Eastern and Western Hemisphere, Western hemispheres, Oceania is estimated to have a land area of ...
, and is considered one of the Least developed country, least developed countries in the world.
In one form or another, Kiribati gets a large portion of its income from abroad. Examples include fishing licences, development assistance, workers' remittances, especially the seafarers issued from Marine Training Centre, and a few tourists. Given Kiribati's limited domestic production ability, it must import nearly all of its essential foodstuffs and manufactured items; it depends on these external sources of income for financing.
The economy of Kiribati benefits from international development assistance programs. The multilateral donors providing development assistance in 2009 were the European Union (A$9 million), the United Nations Development Programme (A$3.7 million), UNICEF, and the World Health Organization (A$100,000). The bilateral donors providing development assistance in 2009 were Australia (A$11 million), Japan (A$2 million), New Zealand (A$6.6 million), Taiwan
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is a country in East Asia, at the junction of the East and South China Seas in the northwestern Pacific Ocean, with the People's Republic of China (PRC) to the northwest, Japan to the nort ...
(A$10.6 million), and other donors providing A$16.2 million, including technical assistance grants from the Asian Development Bank.
The major donors in 2010/2011 were Australia (A$15 million), Taiwan (A$11 million); New Zealand (A$6 million), the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Interna ...
(A$4 million) and the Asian Development Bank.
In 1956, Gilbert and Ellice Islands
The Gilbert and Ellice Islands (GEIC as a colony) in the Pacific Ocean were part of the British Empire from 1892 to 1976. They were a protectorate from 1892 to 12 January 1916, and then a colony until 1 January 1976. The history of the colony w ...
established a sovereign wealth fund to act as a store of wealth for the country's earnings from phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
mining.
In 2008, the Revenue Equalization Reserve Fund was valued at US$400 million. The RERF assets declined from A$637 million (420% of GDP) in 2007 to A$570.5 million (350% of GDP) in 2009 as the result of the Financial crisis of 2007–08, global financial crisis and exposure to failed Icelandic banks. In addition, draw-downs were made by the government of Kiribati to finance budgetary shortfalls during this period.
In May 2011, the IMF country report assessment of the economy of Kiribati is that "After two years of contraction, the economy recovered in the second half of 2010 and inflation pressure dissipated. It is estimated to have grown by 1.75% for the year. Despite a weather-related drop in copra production, private sector activity appears to have picked up, especially in retail. Tourist arrivals rebounded by 20% compared to 2009, although from a very low base.
Despite the rise in world food and fuel prices, inflation has bounced from 2008 crisis-highs into negative territory, reflecting the strong appreciation of the Australian dollar, which is used as the domestic currency, and a decline in the world price of rice. Credit growth in the overall economy declined in 2009 as economic activity stalled. But it started to pick up in the second half of 2010 as the recovery gained traction".
A major Australian bank, Australia and New Zealand Banking Group, ANZ, maintains a presence on Kiribati with a number of branches and Automated teller machine, ATM units.
Ornamental fish
Kiribati is a major exporter of hand-caught ornamental fish. There are eight licensed operators based onKiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
(Christmas Island). At the end of 2005, the number of pet fish exported was 110,000. All operators have a land-based facility but fish are kept in containers on the reef until the day before the shipment. This is to reduce the running cost and the mortality of pet fish to be exported. The flame angelfish (''Centropyge loriculus'') is the major species exported.
Transport
 Kiribati has had two domestic airlines: Air Kiribati and Coral Sun Airways. Both airlines are based in Tarawa's Bonriki International Airport and serve destinations across the Gilbert Islands and Line Islands only:
Kiribati has had two domestic airlines: Air Kiribati and Coral Sun Airways. Both airlines are based in Tarawa's Bonriki International Airport and serve destinations across the Gilbert Islands and Line Islands only: Banaba
BanabaThe correct spelling and etymology in Gilbertese should be ''Bwanaba'' but the Constitution of Kiribati writes Banaba. Because of the spelling in English or French, the name was very often written Paanapa or Paanopa, as it was in 1901 Ac ...
and the Phoenix Islands
The Phoenix Islands, or Rawaki, are a group of eight atolls and two submerged coral reefs that lie east of the Gilbert Islands and west of the Line Islands in the central Pacific Ocean, north of Samoa. They are part of the Kiribati, Republic ...
are not served by the domestic carriers.
Cassidy International Airport on Kiritimati
Kiritimati (also known as Christmas Island) is a Pacific Ocean atoll in the northern Line Islands. It is part of the Republic of Kiribati. The name is derived from the English word "Christmas" written in Gilbertese according to its phonology, ...
has an international service provided by Fiji Airways: Nadi International Airport, Nadi to Cassidy Airport and then to Daniel K. Inouye International Airport, Honolulu.
Communications and media
The islands’ remote location in the Central Pacific at approximately the International Date Line and spanning hundreds of miles north and south of the equator has meant that communications between them has always been challenging and conducted primarily by radio and print media. Television Kiribati, TV Kiribati Ltd, was owned by the government operated between 2004 and mid-2012, but could not reach all of the Islands. Radio Kiribati, based on Tarawa and operated by the government's Broadcasting and Publications Authority (BPA) on 1440 kHz AM is the only form of mass media that reaches all the major islands. Transmission hours are limited and local content in Gilbertese is supplemented by English summaries and BBC News. The BPA and a private broadcaster also operate FM stations accessible on Tarawa. Inter-island communications for many years relied on a centralized shortwave radio network operated by Telecom Services Kiribati, Ltd (TSKL) based in each Island's Council Headquarters. Numerous issues including low availability, maintenance, privacy, and only one per island led TSKL to adopt satellite-based telephones. However, the system is more expensive and still only located at Council Headquarters. Print weeklies in Gilbertese include the ''Te Uekara'' published by the government, ''Te Mauri'' published by the Kiribati Protestant Church, and the ''Kiribati Independent'', published fromAuckland
Auckland (pronounced ) ( mi, Tāmaki Makaurau) is a large metropolitan city in the North Island of New Zealand. The List of New Zealand urban areas by population, most populous urban area in the country and the List of cities in Oceania by po ...
as well as the ''Kiribati Newstar'', published in English.
In December 2019, SpaceX launched the Kacific Broadband Satellites, Kacific1 broadband satellite that provides 100Mbit/s mobile and broadband service to 25 countries throughout to the Asia-Pacific region including Kiribati. Three of the satellite's 56 spot beams provide overlapping coverage of the Gilbert Islands and Tuvalu; however, the more eastern regions of the country, the Phoenix and Line Islands, are outside of the satellite's coverage.
The Southern Cross NEXT cable system, which entered service in July 2022, connects the US to Australia and provides service to Kiribati (Tarawa) through the Kiritimati Branch with one fiber pair. The network, which is an upgrade to the existing Southern Cross Cable, also connects to Samoa, Fiji, and New Zealand.
In June 2021, the World Bank-backed procurement for the East Micronesian Cable system was cancelled due to security concerns. The undersea fiberoptic system, which would have originated in Guam, was "designed to improve the communications in the island nations of Nauru, Kiribati and Federated States of Micronesia (FSM)."
Demographics
Gilbert Islands
The Gilbert Islands ( gil, Tungaru;Reilly Ridgell. ''Pacific Nations and Territories: The Islands of Micronesia, Melanesia, and Polynesia.'' 3rd. Ed. Honolulu: Bess Press, 1995. p. 95. formerly Kingsmill or King's-Mill IslandsVery often, this n ...
, with 52.9% of them on South Tarawa, including Betio
Betio is the largest township of Kiribati's capital city, South Tarawa, and the country's main port. The settlement is located on a separate islet at the extreme southwest of the atoll.
Betio Post Office opened on 5 April 1957 and closed in 1964. ...
, the biggest township.
Until recently, people lived mostly in villages with populations between 50 and 3,000 on the outer islands. Most houses are made of materials obtained from coconut and pandanus trees. Frequent droughts and infertile soil hinder reliable large-scale agriculture, so the islanders have largely turned to the sea for livelihood and subsistence. Most are outrigger sailors and fishermen. Copra plantations serve as a second source of employment. In recent years, large numbers of citizens have moved to the more urban island capital of Tarawa, where Betio is the largest town and South Tarawa reunites larger towns like Bikenibeu or Teaoraereke. Increasing urbanisation has raised the population of South Tarawa to 63,017.
Ethnicity
The native people of Kiribati are called I-Kiribati. Ethnically, the I-Kiribati are Oceanic languages, Oceanians and Micronesians, a sub-ethnicity of Austronesian peoples, Austronesians. Recent archaeological evidence indicates that Austronesians originally settled the islands thousands of years ago . Around the 14th century, Fijians, Samoans, and Tongans invaded the islands, thus diversifying the ethnic range and introducing Polynesian languages, Polynesian linguistic traits. Intermarriage among all ancestral groups, however, has led to a population reasonably homogeneous in appearance and traditions.Languages
The people of Kiribati speakGilbertese
Gilbertese or taetae ni Kiribati, also Kiribati (sometimes ''Kiribatese''), is an Austronesian language spoken mainly in Kiribati. It belongs to the Micronesian branch of the Oceanic languages.
The word ''Kiribati'', the current name of the i ...
, an Oceanic language
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages ...
. English is the other official language, but is not used very often outside the island capital of Tarawa
Tarawa is an atoll and the capital of the Republic of Kiribati,Kiribati
''
''
 Primary education is free and compulsory for the first 9 years, beginning at age 6. Mission schools are slowly being absorbed into the government primary school system. Higher education is expanding; students may seek technical, teacher or marine training, or study in other countries.
Primary education is free and compulsory for the first 9 years, beginning at age 6. Mission schools are slowly being absorbed into the government primary school system. Higher education is expanding; students may seek technical, teacher or marine training, or study in other countries. The uniqueness of Kiribati when compared with other forms of Pacific island dance is its emphasis on the outstretched arms of the dancer and the sudden birdlike movement of the head. The Great frigatebird, Frigate bird (''Fregata minor'') on the Kiribati flag refers to this bird-like style of Kiribati dancing. Most dances are in the standing or sitting position with movement limited and staggered. Smiling whilst dancing is generally considered vulgar within the context of Kiribati dancing. This is due to its origin of not being solely as a form of entertainment but as a form of storytelling and a display of the skill, beauty and endurance of the dancer.
The uniqueness of Kiribati when compared with other forms of Pacific island dance is its emphasis on the outstretched arms of the dancer and the sudden birdlike movement of the head. The Great frigatebird, Frigate bird (''Fregata minor'') on the Kiribati flag refers to this bird-like style of Kiribati dancing. Most dances are in the standing or sitting position with movement limited and staggered. Smiling whilst dancing is generally considered vulgar within the context of Kiribati dancing. This is due to its origin of not being solely as a form of entertainment but as a form of storytelling and a display of the skill, beauty and endurance of the dancer.
 Kiribati has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1998 and the Summer Olympics since 2004. It sent three competitors to its first Olympics, two sprinters and a weightlifter. Kiribati won its first ever Commonwealth Games medal at the 2014 Commonwealth Games when weightlifter David Katoatau won Gold in the 105 kg Group.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport. Kiribati Islands Football Federation (KIFF) is an associate member of the Oceania Football Confederation, but not of world-governing body FIFA. Instead, they are member of ConIFA. Kiribati national football team, Kiribati National team has played ten matches, all of which it has lost, and all at the Football at the Pacific Games, Pacific Games from 1979 to 2011. The Kiribati football stadium is Bairiki National Stadium, which has a capacity of 2,500.
The is home to a number of local sporting teams.
Kiribati has competed at the Commonwealth Games since 1998 and the Summer Olympics since 2004. It sent three competitors to its first Olympics, two sprinters and a weightlifter. Kiribati won its first ever Commonwealth Games medal at the 2014 Commonwealth Games when weightlifter David Katoatau won Gold in the 105 kg Group.
Association football, Football is the most popular sport. Kiribati Islands Football Federation (KIFF) is an associate member of the Oceania Football Confederation, but not of world-governing body FIFA. Instead, they are member of ConIFA. Kiribati national football team, Kiribati National team has played ten matches, all of which it has lost, and all at the Football at the Pacific Games, Pacific Games from 1979 to 2011. The Kiribati football stadium is Bairiki National Stadium, which has a capacity of 2,500.
The is home to a number of local sporting teams.