Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a
state in the
Southeastern region of the
United States and one of the states of the
Upper South. It borders
Illinois,
Indiana, and
Ohio to the north;
West Virginia and
Virginia to the east;
Tennessee to the south; and
Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
. Its capital is
Frankfort, and its two largest cities are
Louisville and
Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020.
Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792,
splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on
Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina in the central and western parts of the state with the use of enslaved labor during the Antebellum South and Civil War period. Kentucky ranks 5th nationally in goat farming, 8th in
beef cattle production, and 14th in corn production.
Kentucky has also been a long-standing major center of the
tobacco industry. Today, Kentucky's economy has expanded to importance in non-agricuIturaI sectors, including auto manufacturing, energy fuel production, and medical facilities.
The state ranks 4th among US states in the number of automobiles and trucks assembled.
The state is home to the world's longest
cave system in
Mammoth Cave National Park
Mammoth Cave National Park is an American national park in west-central Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper Sout ...
, as well as the greatest length of navigable waterways and streams in the
contiguous United States
The contiguous United States (officially the conterminous United States) consists of the 48 adjoining U.S. states and the Federal District of the United States of America. The term excludes the only two non-contiguous states, Alaska and Hawaii ...
, and the two largest man-made lakes east of the
Mississippi River. Kentucky is also known for its
culture, which includes
horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
,
bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
,
moonshine
Moonshine is high-proof liquor that is usually produced illegally. The name was derived from a tradition of creating the alcohol during the nighttime, thereby avoiding detection. In the first decades of the 21st century, commercial dist ...
,
coal,
"My Old Kentucky Home" historic state park,
automobile manufacturing,
tobacco,
bluegrass music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music
The term American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as ''traditional music'', ''traditional folk music'', ''contemporary folk music'', ''vernacular music,'' or ...
,
college basketball,
Louisville Slugger baseball bats,
Kentucky Fried Chicken
KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) is an American fast food restaurant chain headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, that specializes in fried chicken. It is the world's second-largest restaurant chain (as measured by sales) after McDonald's, with 2 ...
, and the
Kentucky colonel.
Etymology
In 1776 the counties of
Virginia beyond the
Appalachian Mountains became known to European Americans as
Kentucky County
Kentucky County (then alternately spelled Kentucke County) was formed by the Commonwealth of Virginia from the western portion (beyond the Cumberland Mountains) of Fincastle County effective December 31, 1776. The name of the county was taken ...
,
named for the
Kentucky River. The precise etymology of the name is uncertain.
One theory sees the word based on an
Iroquoian name meaning "(on) the meadow" or "(on) the prairie"
[Mithun, Marianne. 1999. ''Languages of Native North America''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pg. 312]
(cf.
Mohawk ''kenhtà:ke'',
Seneca ''gëdá'geh'' (
phonemic ), "at the field").
Another theory suggests a derivation from the term ''Kenta Aki'', which could have come from an
Algonquian language, in particular from
Shawnee. Folk etymology translates this as "Land of Our Fathers". The closest approximation in another Algonquian language,
Ojibwe, translates as "Land of Our In-Laws", thus making a fairer English translation "The Land of Those Who Became Our Fathers". In any case, the word ''aki'' means "land" in most Algonquian languages.
A third theory states that the name Kentucky may be a corruption of the word ''Catawba'', in reference to the
Catawba people who inhabited Kentucky.
History
Native American settlement
It is not known exactly when the first humans arrived in what is now Kentucky. Based on the evidence in other regions, humans were likely living in Kentucky prior to 10,000 BCE, but "archaeological evidence of their occupation has yet to be documented".
Around 1800 BCE, a gradual transition began from a hunter-gatherer economy to agriculturalism. Around 900 CE, a
Mississippian culture
The Mississippian culture was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American civilization that flourished in what is now the Midwestern United States, Midwestern, Eastern United States, Eastern, and Southeastern United States from appr ...
took root in western and central Kentucky; by contrast, a
Fort Ancient culture appeared in eastern Kentucky. While the two had many similarities, the distinctive ceremonial earthwork mounds constructed in the former's centers were not part of the culture of the latter.
In about the 10th century, the Kentucky native people's variety of corn became highly productive, supplanting the
Eastern Agricultural Complex, and replaced it with a maize-based agriculture in the
Mississippian era. French explorers in the 17th century documented numerous tribes living in Kentucky until the
Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
in the 1670s; however, by the time that European colonial explorers and settlers began entering Kentucky in greater numbers in the mid-18th century, there were no major Native American settlements in the region.
As of the 16th century, the area known as Kentucky was home to tribes from five different culture groupsIroquoian, Sioux, Algonquian, Muskogean and Yuchi. Around the Bluestone River was the Siouan
Tutelo. North of the Tennessee River was the
Yuchi and south of it was the
Cherokee. Much of the interior of the state was controlled by the Algonquian
Cisca; the confluence region of the Mississippi and Ohio was home to the
Chickasaw. During a period known as the
Beaver Wars
The Beaver Wars ( moh, Tsianì kayonkwere), also known as the Iroquois Wars or the French and Iroquois Wars (french: Guerres franco-iroquoises) were a series of conflicts fought intermittently during the 17th century in North America throughout t ...
, 1640–1680, another Algonquian tribe called the Maumee, or
Mascouten
The Mascouten (also ''Mascoutin'', ''Mathkoutench'', ''Muscoden,'' or ''Musketoon'') were a tribe of Algonquian-speaking Native Americans located in the Midwest. They are believed to have dwelt on both sides of the Mississippi River, adjacent to ...
was chased out of southern Michigan. The vast majority of them moved to Kentucky, pushing the Kispoko east and war broke out with the Tutelo that pushed them deeper into Appalachia, where they merged with the
Saponi and Moneton. The Maumee were closely related to the Miami of Indiana. Later, the Kispoko merged with the Shawnee (who broke off from the Powhatan on the east coast) and the Thawikila of Ohio to form the larger
Shawnee nation which inhabited the Ohio River Valley into the 19th century.
The Cherokee from the south and Shawnee from the northeast also sent parties into the area regularly for hunting.
European settlement
In 1774 James Harrod founded the first permanent European settlement in Kentucky at the site of present-day Harrodsburg.
County of Kentucky and statehood
On December 31, 1776, by an act of the
Virginia General Assembly, the portion of
Fincastle County west of the Appalachians extending to the Mississippi River, previously known as Kentucky (or Kentucke) territory, was split off into its own county of
Kentucky. Harrod's Town (Oldtown as it was known at the time) was named the county seat. The county was subdivided into
Jefferson,
Lincoln and
Fayette Counties in 1780, but continued to be administered as the District of Kentucky even as new counties were split off.
On several occasions the region's residents petitioned the General Assembly and the
Confederation Congress for separation from Virginia and
statehood
A state is a centralized political organization that imposes and enforces rules over a population within a territory. There is no undisputed definition of a state. One widely used definition comes from the German sociologist Max Weber: a "sta ...
. Ten constitutional conventions were held in
Danville between 1784 and 1792.
One petition, which had Virginia's assent, came before the Confederation Congress in early July 1788. Unfortunately, its consideration came up a day after word of
New Hampshire's all-important ninth
ratification of the proposed
Constitution, thus establishing it as the new framework of governance for the United States. In light of this development, Congress thought that it would be "unadvisable" to admit Kentucky into the Union, as it could do so "under the Articles of Confederation" only, but not "under the Constitution", and so declined to take action.
On December 18, 1789, Virginia again gave its consent to Kentucky statehood. The
United States Congress gave its approval on February 4, 1791. (This occurred two weeks before Congress approved
Vermont's petition for statehood.) Kentucky officially became the fifteenth state in the Union on June 1, 1792.
Isaac Shelby, a military veteran from Virginia, was elected its first Governor.
Native Americans and European colonists
A 1790 U.S. government report states that 1,500Kentucky settlers had been killed by Native Americans since the end of the
Revolutionary War. As more settlers entered the area, warfare broke out with the Native Americans over their traditional hunting grounds. Historian Susan Sleeper-Smith documents the role of Kentucky settlers in displacing Native American communities living in the northern Ohio River Valley during the late 18th century.
19th century

Central Kentucky, the bluegrass region, as well as Western Kentucky, were the areas of the state with the most
slave owners.
Planters cultivated
tobacco and hemp (see
Hemp in Kentucky) on plantations with the use of enslaved labor, and were noted for their quality
livestock. During the 19th century, Kentucky slaveholders began to sell unneeded slaves to the
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
, with Louisville becoming a major slave market and departure
port for slaves being transported downriver.
Kentucky was one of the
border states during the
American Civil War, and it remained neutral within the
Union. Despite this, representatives from 68 of 110 counties met at
Russellville calling themselves the "Convention of the People of Kentucky" and passed an
Ordinance of Secession
An Ordinance of Secession was the name given to multiple resolutions drafted and ratified in 1860 and 1861, at or near the beginning of the Civil War, by which each seceding Southern state or territory formally declared secession from the United ...
on November 20, 1861. They established a
Confederate government of Kentucky with its capital in
Bowling Green. The Confederate shadow government was never popularly elected statewide, though 116 delegates were sent representing 68 Kentucky counties which at the time made up a little over half the territory of the Commonwealth to the Russellville Convention in 1861, and were occupied and governed by the Confederacy at some point in the duration of the war, and Kentucky had full representation within the Confederate Government. Although Confederate forces briefly controlled Frankfort, they were expelled by Union forces before a Confederate government could be installed in the state capital. After the expulsion of Confederate forces after the Battle of Perryville, this government operated in-exile. Though it existed throughout the war, Kentucky's provisional government only had governing authority in areas of Kentucky under direct Confederate control and had very little effect on the events in the Commonwealth or in the war once they were driven out of the state.
Kentucky remained officially "neutral" throughout the war due to the
Southern Unionists sympathies of a majority of the Commonwealth's citizens who were split between the struggle of Kentucky's sister Southern States fully in the
Confederate States of America and a continued loyalty to the Unionist cause that was also prevalent in other areas of the South such as in East Tennessee, West Virginia, Western North Carolina, and others. Despite this, some 21st-century Kentuckians observe
Confederate Memorial Day on
Confederate leader
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
' birthday, June 3, and participate in Confederate battle re-enactments. Both Davis and U.S. president
Abraham Lincoln were born in Kentucky.
John C. Breckinridge, the 14th and youngest-ever Vice President was born in Lexington, Kentucky at Cabell's Dale Farm. Breckenridge was expelled from the U. S. Senate for his support of the Confederacy.
On January 30, 1900, Governor
William Goebel, flanked by two bodyguards, was mortally wounded by an
assassin while walking to the State Capitol in downtown Frankfort. Goebel was contesting the
Kentucky gubernatorial election of 1899, which
William S. Taylor was initially believed to have won. For several months,
J. C. W. Beckham
John Crepps Wickliffe Beckham (August 5, 1869 – January 9, 1940) was an American attorney serving as the List of governors of Kentucky, 35th Governor of Kentucky and a United States Senate, United States Senator from Kentucky. He was the s ...
, Goebel's running mate, and Taylor fought over who was the legal governor until the
Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. federal court cases, and over state court cases that involve a point o ...
ruled in May in favor of Beckham. After fleeing to
Indiana, Taylor was indicted as a co-conspirator in Goebel's
assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
. Goebel is the only governor of a U.S. state to have been assassinated while in office.
20th century
The
Black Patch Tobacco Wars, a vigilante action, occurred in Western Kentucky in the early 20th century. As a result of the
tobacco industry monopoly, tobacco farmers in the area were forced to sell their crops at prices that were too low. Many local farmers and activists united in a refusal to sell their crops to the major tobacco companies.
An Association meeting occurred in downtown
Guthrie, where a vigilante wing of "Night Riders", formed. The riders terrorized farmers who sold their tobacco at the low prices demanded by the tobacco corporations. They burned several tobacco warehouses throughout the area, stretching as far west as
Hopkinsville to
Princeton. In the later period of their operation, they were known to physically assault farmers who broke the boycott. Governor
Augustus E. Willson declared
martial law and deployed the
Kentucky National Guard
The Kentucky National Guard comprises the:
*Kentucky Army National Guard
*Kentucky Air National Guard
See also
* Kentucky Active Militia, the state defense force of Kentucky which replaced the Kentucky National Guard during World War I and World ...
to end the wars.
On October 15, 1959, a
B-52 carrying two
nuclear weapons collided in midair with a KC-135 tanker near
Hardinsburg, Kentucky. One of the nuclear bombs was damaged by fire but both weapons were recovered.
Geography
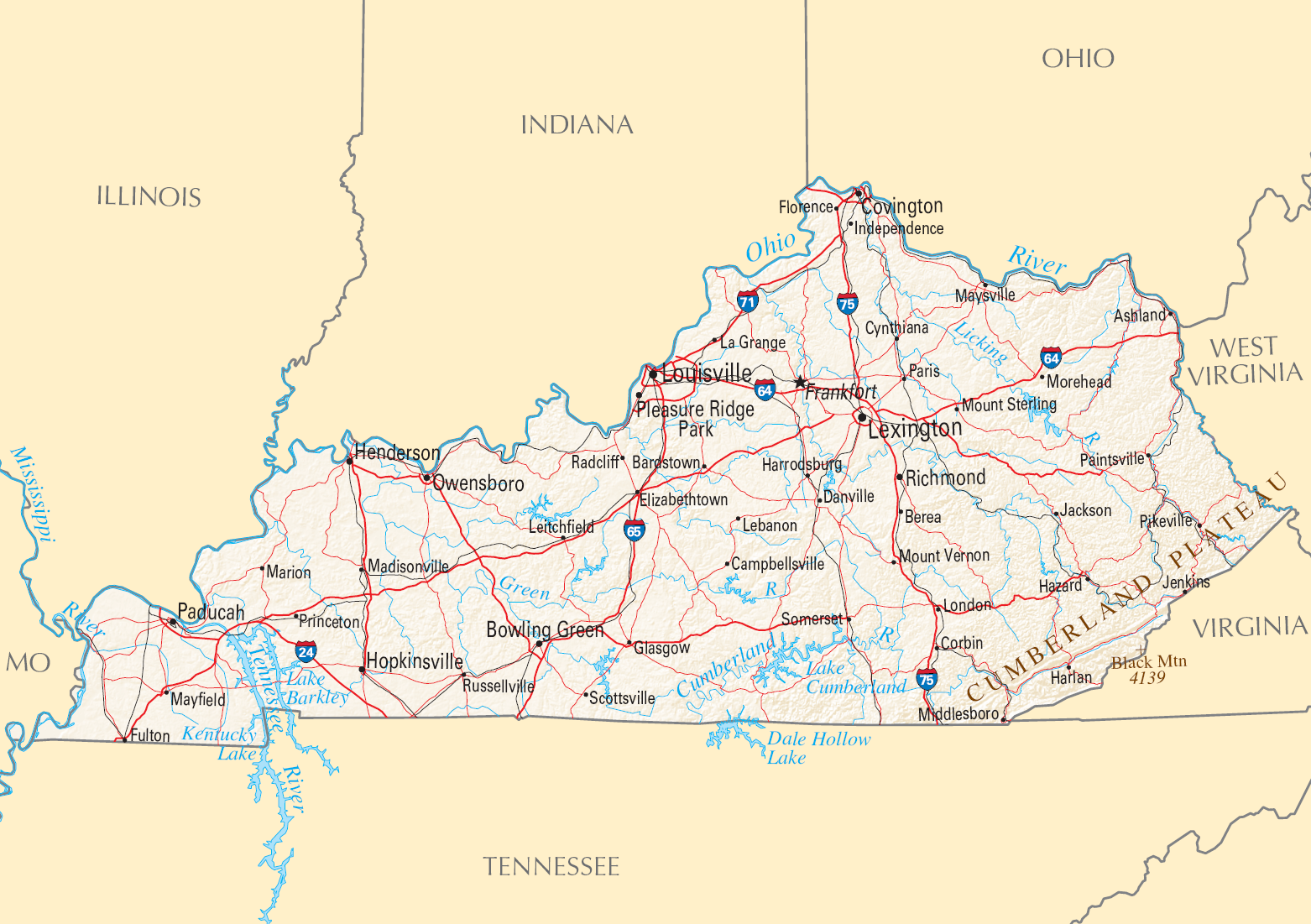
Kentucky is situated in the
Upland South. A significant portion of eastern Kentucky is part of
Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
.
Kentucky borders seven states, from the
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
and the
Southeast.
West Virginia lies to the northeast,
Virginia to the east,
Tennessee to the south,
Missouri to the west,
Illinois to the northwest, and
Indiana and
Ohio to the north. Only Missouri and Tennessee, both of which border eight states, touch more.
Kentucky's northern border is formed by the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
and its western border by the
Mississippi River; however, the official border is based on the courses of the rivers as they existed when Kentucky became a state in 1792. For instance, northbound travelers on
U.S. 41 from Henderson, after crossing the Ohio River, will be in Kentucky for about .
Ellis Park, a thoroughbred racetrack, is located in this small piece of Kentucky. Waterworks Road is part of the only land border between Indiana and Kentucky.
Kentucky has a non-contiguous part known as
Kentucky Bend, at the far west corner of the state. It exists as an
exclave
An enclave is a territory (or a small territory apart of a larger one) that is entirely surrounded by the territory of one other state or entity. Enclaves may also exist within territorial waters. ''Enclave'' is sometimes used improperly to deno ...
surrounded completely by
Missouri and
Tennessee, and is included in the boundaries of
Fulton County. Road access to this small part of Kentucky on the Mississippi River (populated by 18 people ) requires a trip through Tennessee.
The epicenter of the
1811–12 New Madrid earthquakes was near this area, causing the Mississippi River to flow backwards in some places. Though the series of quakes changed the area geologically and affected the small number of inhabitants of the area at the time, the Kentucky Bend is the result of a surveying error, not the New Madrid earthquake.
Regions

Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the
Cumberland Plateau
The Cumberland Plateau is the southern part of the Appalachian Plateau in the Appalachian Mountains of the United States. It includes much of eastern Kentucky and Tennessee, and portions of northern Alabama and northwest Georgia. The terms "Alle ...
in the east, which contains much of the historic coal mines; the north-central
Bluegrass region, where the major cities and the capital are located; the south-central and western
Pennyroyal Plateau (also known as the Pennyrile or Mississippi Plateau); the
Western Coal Fields; and the far-west
Jackson Purchase.
The Bluegrass region is commonly divided into two regions, the Inner Bluegrass encircling around
Lexington, and the Outer Bluegrass that contains most of the northern portion of the state, above the
Knobs. Much of the outer Bluegrass is in the
Eden Shale Hills Eden Shale Hills of the Eden Shale soil type is a broad area of short, steep hills roughly separating the Inner Bluegrass region and Outer Bluegrass region of Kentucky. They occur generally from around Oldham County in the West to Fleming County
...
area, made up of short, steep, and very narrow hills.
Climate
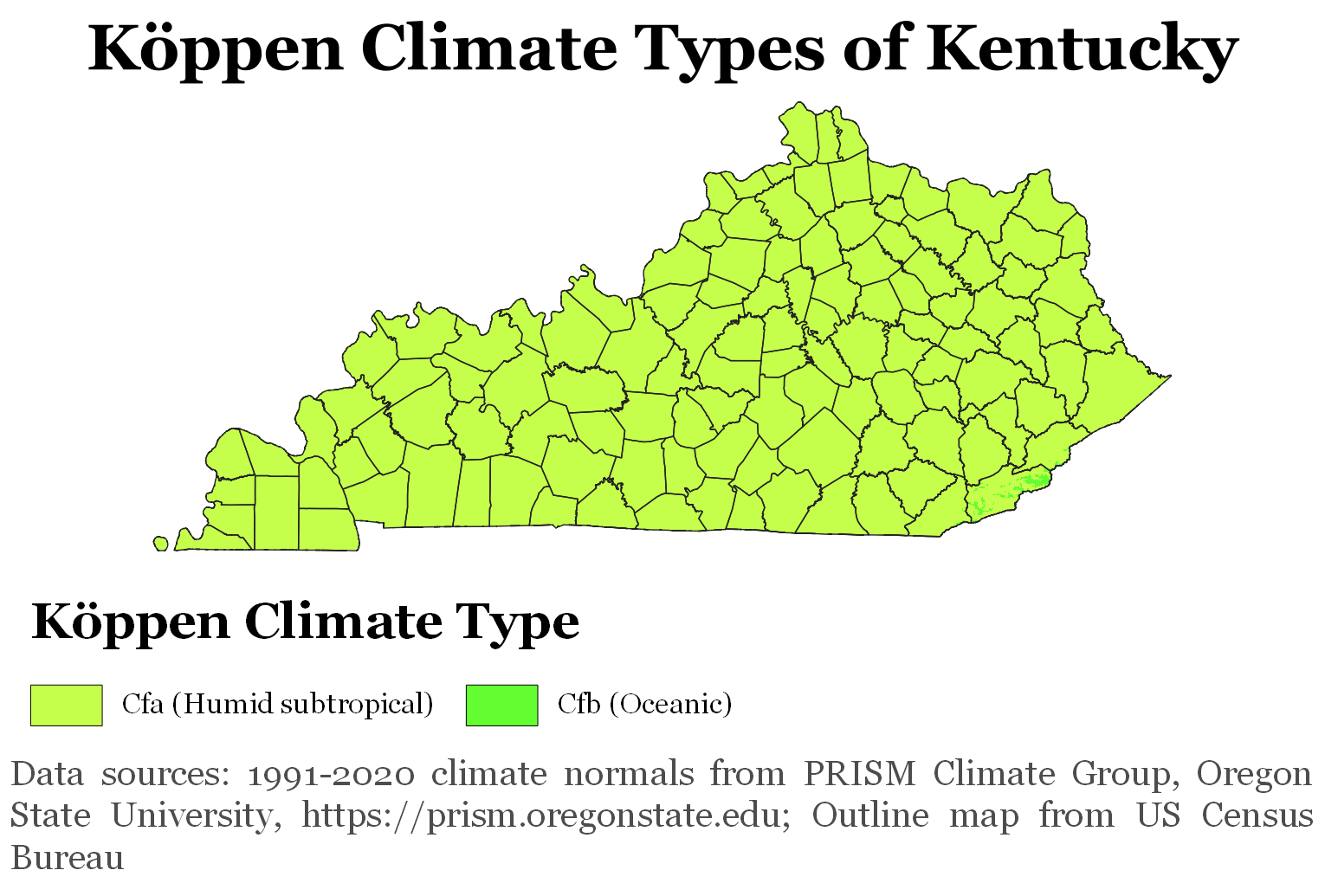
Located within the southeastern interior portion of North America, Kentucky has a climate that is best described as a
humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(Köppen: ''Cfa''), only small higher areas of the southeast of the state has an
oceanic climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate, is the humid temperate climate sub-type in Köppen classification ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool summers and mild winters ( ...
(''Cfb'') influenced by the
Appalachians. Temperatures in Kentucky usually range from daytime summer highs of to the winter low of . The average precipitation is a year. Kentucky has four distinct seasons, with substantial variations in the severity of summer and winter. The highest recorded temperature was at
Greensburg on July 28, 1930, while the lowest recorded temperature was at
Shelbyville on
January 19, 1994. The state rarely experiences the extreme cold of far northern states, nor the high heat of the states in the
Deep South
The Deep South or the Lower South is a cultural and geographic subregion in the Southern United States. The term was first used to describe the states most dependent on plantations and slavery prior to the American Civil War. Following the war ...
. Temperatures seldom drop below 0 degrees or rise above 100 degrees. Rain and snowfall totals about 45 inches per year.
The climate varies markedly within the state. The northern parts tend to be about five degrees cooler than those in the western parts of the state.
Somerset in the south-central part receives ten more inches of rain per year than, for instance,
Covington Covington may refer to:
People
* Covington (surname)
Places United Kingdom
* Covington, Cambridgeshire
* Covington, South Lanarkshire
United States
* Covington, Georgia
* Covington, Indiana
* Covington, Kentucky, the largest American cit ...
to the north. Average temperatures for the entire Commonwealth range from the low 30s in January to the high 70s in mid-July. The annual average temperature varies from : of in the far north as an average annual temperature and of in the extreme southwest.
In general, Kentucky has relatively hot,
humid
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depen ...
, rainy summers, and moderately cold and rainy winters. Mean maximum temperatures in July vary from ; the mean minimum July temperatures are . In January the mean maximum temperatures range from ; the mean minimum temperatures range from . Temperature means vary with northern and far-eastern mountain regions averaging five degrees cooler year-round, compared to the relatively warmer areas of the southern and western regions of the state. Precipitation also varies north to south with the north averaging of , and the south averaging of . Days per year below the freezing point vary from about sixty days in the southwest to more than a hundred days in the far-north and far-east.
Natural disasters
Lakes and rivers

Kentucky has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than Alaska.
Kentucky is the only U.S. state to have a continuous border of rivers running along three of its sidesthe
Mississippi River to the west, the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
to the north, and the
Big Sandy River and
Tug Fork to the east.
Its major internal rivers include the
Kentucky River,
Tennessee River,
Cumberland River
The Cumberland River is a major waterway of the Southern United States. The U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed June 8, 2011 river drains almost of southern Kentucky and ...
,
Green River and
Licking River.
Though it has only three major natural lakes,
Kentucky is home to many
artificial lakes. Kentucky has both the largest artificial lake east of the Mississippi in water volume (
Lake Cumberland) and surface area (
Kentucky Lake). Kentucky Lake's of shoreline, of water surface, and of flood storage are the most of any lake in the
TVA system.
Kentucky's of streams provides one of the most expansive and complex stream systems in the nation.
Natural environment and conservation

Kentucky has an expansive park system, which includes one national park, two National Recreation Areas, two National Historic Parks, two
national forests
A state forest or national forest is a forest that is administered or protected by some agency of a sovereign state, sovereign or federated state, or territory (country subdivision), territory.
Background
The precise application of the terms va ...
, two National Wildlife Refuges, 45
state park
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the sub-national level within those nations which use "state" as a political subdivision. State parks are typically established by a state to preserve a location on account of its natural ...
s, of state forest, and 82
wildlife management areas.
Kentucky has been part of two of the most successful wildlife reintroduction projects in United States history. In the winter of 1997, the
Kentucky Department of Fish and Wildlife Resources began to re-stock
elk in the state's eastern counties, which had been extinct from the area for over 150 years. , the herd had reached the project goal of 10,000 animals, making it the largest herd east of the
Mississippi River.
The state also stocked
wild turkeys in the 1950s. There were reported to be fewer than 900 at one point. Once nearly extinct here, wild turkeys thrive throughout today's Kentucky. Hunters officially reported a record 29,006 birds taken during the 23-day season in spring 2009.
In 1991 the Land Between the Lakes partnered with the U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service for the Red Wolf Recovery Program, a captive breeding program.
Natural attractions


*
Cumberland Gap, chief passageway through the
Appalachian Mountains in early American history.
*
Cumberland Falls, the only place in the Western Hemisphere where a "
moonbow" may be regularly seen, due to the spray of the falls.
*
Mammoth Cave National Park
Mammoth Cave National Park is an American national park in west-central Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper Sout ...
, featuring the world's longest known cave system.
*
Red River Gorge Geological Area, part of the
Daniel Boone National Forest.
*
Land Between the Lakes, a
National Recreation Area managed by the
United States Forest Service.
*
Big South Fork National River and Recreation Area near
Whitley City.
*
Black Mountain
Black Mountain may refer to:
Places Australia
* Black Mountain (Australian Capital Territory), a mountain in Canberra
* Black Mountain, New South Wales, a village in Armidale Regional Council, New South Wales
* Black Mountain, Queensland, a loca ...
, state's highest point.
Runs along the south ridge of Pine Mountain in Letcher County, Kentucky. The highest point located in Harlan County.
*
Bad Branch Falls State Nature Preserve, state nature preserve on southern slope of Pine Mountain in
Letcher County. Includes one of the largest concentrations of rare and endangered species in the state, as well as a waterfall and a Kentucky Wild River.
*
Jefferson Memorial Forest, located in the southern fringes of
Louisville in the
Knobs region, the largest municipally run forest in the United States.
*
Lake Cumberland, of shoreline located in South Central Kentucky.
*
Natural Bridge, located in
Slade, Kentucky
Slade is an unincorporated community in Powell County, Kentucky, United States. Their post office closed in 2004.
Landmarks
The community is home to the Natural Bridge State Resort Park.
Slade is a popular location for accommodations for cli ...
Powell County.
*
Breaks Interstate Park, located in southeastern
Pike County, Kentucky and Southwestern
Virginia. The Breaks is commonly known as the "Grand Canyon of the South".
Administrative divisions
Counties
Kentucky is subdivided into 120
counties, the largest being
Pike County at , and the most populous being
Jefferson County (which
coincides with the
Louisville Metro governmental area) with 741,096 residents .
County government, under the
Kentucky Constitution of 1891, is vested in the
County Judge/Executive, (formerly called the County Judge) who serves as the
executive head of the county, and a
legislature called a
Fiscal Court. Despite the unusual name, the Fiscal Court no longer has
judicial functions.
Consolidated city-county governments
Kentucky's two most populous counties, Jefferson and Fayette, have their
governments consolidated with the governments of their largest cities. ''Louisville-Jefferson County Government'' (
Louisville Metro) and ''Lexington-Fayette Urban County Government'' (
Lexington Metro) are unique in that their city councils and county Fiscal Court structures have been merged into a single entity with a single
chief executive, the
Metro Mayor and Urban County Mayor, respectively. Although the counties still exist as subdivisions of the state, in reference the names Louisville and Lexington are used to refer to the entire area coextensive with the former cities and counties.
Major cities
The
Metro Louisville
Louisville ( , , ) is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Kentucky and the 28th most-populous city in the United States. Louisville is the historical seat and, since 2003, the nominal seat of Jefferson County, on the Indiana border.
...
government area has a 2018 population of 1,298,990. Under
United States Census Bureau methodology, the population of Louisville was 623,867. The latter figure is the population of the so-called
"balance"the parts of Jefferson County that were either unincorporated or within the City of Louisville before the formation of the merged government in 2003. In 2018 the
Louisville Combined Statistical Area (CSA) had a population of 1,569,112; including 1,209,191 in Kentucky, which means more than 25% of the state's population now lives in the Louisville CSA. Since 2000, over one-third of the state's population growth has occurred in the Louisville CSA. In addition, the top 28 wealthiest places in Kentucky are in Jefferson County and seven of the 15 wealthiest counties in the state are located in the Louisville CSA.
The second-largest city is Lexington with a 2018 census population of 323,780, its metro had a population of 516,697, and its
CSA
CSA may refer to:
Arts and media
* Canadian Screen Awards, annual awards given by the Academy of Canadian Cinema & Television
* Commission on Superhuman Activities, a fictional American government agency in Marvel Comics
* Crime Syndicate of Amer ...
, which includes the
Frankfort and
Richmond statistical areas, having a population of 746,310. The
Northern Kentucky area, which comprises the seven Kentucky counties in the
Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky metropolitan area, had a population of 447,457 in 2018. The metropolitan areas of Louisville, Lexington, and Northern Kentucky have a combined population of 2,402,958 , which is 54% of the state's total population on only about 19% of the state's land. This area is often referred to as the Golden triangle as it contains a majority of the state's wealth, population, population growth, and economic growth, it is also where most of the state's largest cities by population are located. It is referred to as the Golden triangle as the metro areas of Lexington, Louisville, and Northern Kentucky/Cincinnati outline a triangle shape. Interstates I-71, I-75, and I-64 form the triangle shape. Additionally, all counties in Kentucky that are part of an MSA or CSA have a total population of 2,970,694, which is 67% of the state's population.
Bowling Green had a population of 67,067, making it the third most populous city in the state. The
Bowling Green metropolitan area had an estimated population of 174,835; and the
combined statistical area it shares with
Glasgow has an estimated population of 228,743.
The two other fast-growing urban areas in Kentucky are the
Bowling Green area and the "Tri-Cities Region" of southeastern Kentucky, comprising
Somerset,
London and
Corbin.
Although only one town in the "Tri-Cities" (Somerset) currently has more than 12,000 people, the area has been experiencing heightened population and job growth since the 1990s. Growth has been especially rapid in Laurel County, which outgrew areas such as Scott and Jessamine counties around Lexington or Shelby and Nelson Counties around Louisville. London significantly grew in population in the 2000s, from 5,692 in 2000 to 7,993 in 2010. London also landed a
Wal-Mart distribution center in 1997, bringing thousands of jobs to the community.
In northeast Kentucky, the greater
Ashland area is an important transportation, manufacturing, and medical center.
Iron and
petroleum production, as well as the transport of coal by rail and
barge, have been historical pillars of the region's economy. Due to a decline in the area's industrial base, Ashland has seen a sizable reduction in its population since 1990; however, the population of the area has since stabilized with the medical service industry taking a greater role in the local economy. The Ashland area, including the counties of
Boyd and
Greenup, is part of the
Huntington-Ashland, WV-KY-OH, Metropolitan Statistical Area (MSA). As of the 2000 census, the MSA had a population of 288,649. More than 21,000 of those people () reside within the city limits of Ashland.
The largest county in Kentucky by area is
Pike, which contains
Pikeville and suburb
Coal Run Village
Coal Run Village (sometimes simply Coal Run) is a list of Kentucky cities, home rule-class city in Pike County, Kentucky, Pike County, Kentucky, in the United States. Bordered to the north, south, and east by Pikeville, Kentucky, Pikeville, the po ...
. The county and surrounding area is the most populated region in the state that is not part of a
Micropolitan Statistical Area or a
Metropolitan Statistical Area containing nearly 200,000 people in five counties:
Floyd County,
Martin County,
Letcher County, and neighboring
Mingo County, West Virginia. Pike County contains slightly more than 68,000 people.
Only three U.S. states have capitals with smaller populations than Kentucky's
Frankfort (pop. 25,527):
Augusta, Maine
Augusta is the capital of the U.S. state of Maine and the county seat of Kennebec County.
The city's population was 18,899 at the 2020 census, making it the tenth-most populous city in Maine, and third-least populous state capital in the Un ...
(pop. 18,560),
Pierre, South Dakota (pop. 13,876), and
Montpelier, Vermont (pop. 8,035).
Demographics

The
United States Census Bureau determined that the population of Kentucky was 4,505,836 in 2020, increasing since the
2010 United States census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
.

As of July 1, 2016, Kentucky had an estimated population of 4,436,974, which is an increase of 12,363 from the prior year and an increase of 97,607, or 2.2%, since the year 2010. This includes a
natural increase since the last census of 73,541 people (that is 346,968 births minus 273,427 deaths) and an increase due to net migration of 26,135 people into the state.
Immigration from outside the United States resulted in a net increase of 40,051 people, and migration within the country produced a net decrease of 13,916 people. , Kentucky's population included about 149,016 foreign-born persons (3.4%). In 2016 the population density of the state was 110 people per square mile (42.5/km
2).
Kentucky's population has grown during every decade since records have been kept. But during most decades of the 20th century there was also net out-migration from Kentucky. Since 1900, rural Kentucky counties have had a net loss of more than a million people to migration, while urban areas have experienced a slight net gain.
Kentucky's
center of population
In demographics, the center of population (or population center) of a region is a geographical point that describes a centerpoint of the region's population. There are several ways of defining such a "center point", leading to different geogr ...
is in
Washington County, in the city of
Willisburg.
Race and ancestry
According to U.S. Census Bureau official statistics, the largest ancestry in 2013 was
American totalling 20.2%. In 1980, before the status of ethnic American was an available option on the official census, the largest claimed ancestries in the commonwealth were
English (49.6%),
Irish (26.3%), and
German (24.2%). In the state's most urban counties of
Jefferson,
Oldham,
Fayette,
Boone,
Kenton Kenton may refer to:
Places Canada
*Kenton, Manitoba
South Africa
*Kenton-on-Sea
United Kingdom
*Kenton, Devon
*Kenton, London
**Kenton station, Kenton Road, Kenton, London
*Kenton, Newcastle upon Tyne, Tyne and Wear
*Kenton, Suffolk
**Kenton ra ...
, and
Campbell, German is the largest reported ancestry. Americans of
Scots-Irish and
English stock are present throughout the entire state. Many residents claim Irish ancestry because of known "Scots-Irish" among their ancestors, who immigrated from Ireland, where their ancestors had moved for a period from Scotland during the plantation period.
As of the 1980s, the only counties in the United States where over half of the population cited "
English" as their only ancestry group were in the hills of eastern Kentucky (virtually every county in this region had a majority of residents identifying as exclusively English in ancestry).
[James Paul Allen and Eugene James Turner, ''We the People: An Atlas of America's Ethnic Diversity'' (Macmillan, 1988), 41.]
The
Ridgetop Shawnee organized in the early 21st century as a non-profit to gain structure for their community and increase awareness of Native Americans in Kentucky. In the 2000 census, some 20,000 people in the state identified as Native American (0.49%). In June 2011, Jerry "2 Feather" Thornton, a
Cherokee, led a team in the Voyage of Native American Awareness 2011 canoe journey, to begin on the Green River in
Rochester, Kentucky and travel through to the Ohio River at
Henderson.
African Americans, who were mostly enslaved at the time, made up 25% of Kentucky's population before the
Civil War; they were held and worked primarily in the central
Bluegrass region, an area of hemp and tobacco cultivation, as well as raising blooded livestock. The number of African Americans living in Kentucky declined during the 20th century. Many migrated during the early part of the century to the industrial North and Midwest during the
Great Migration for jobs and the chance to leave the segregated, oppressive societies. Today, less than 9% of the state's total population is African-American.
The state's African-American population is highly urbanized and 52% of them live in the Louisville metropolitan area; 44.2% of them reside in
Jefferson County. The county's population is 20% African American. Other areas with high concentrations, besides Christian and Fulton counties and the Bluegrass region, are the cities of
Paducah and
Lexington. Some mining communities in far Southeastern Kentucky have populations that are between five and 10 percent African-American.
Language
In 2000 96.1% of all residents five years old and older spoke only
English at home, a decrease from 97.5% in 1990.
Speech patterns in the state generally reflect the first settlers' Virginia and Kentucky backgrounds. South Midland features are best preserved in the mountains, with
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
in most other areas of Kentucky, but some common to Midland and Southern are widespread.
After a vowel, the /r/ may be weak or missing. For instance, ''Coop'' has the vowel of ''put'', but the root rhymes with ''boot''. In southern Kentucky, earthworms are called ''redworms'', a burlap bag is known as a ''tow sack'' or the ''Southern grass sack'', and green beans are called ''snap beans''. In Kentucky English, a young man may ''carry'', not escort, his girlfriend to a party.
is the second-most-spoken language in Kentucky, after English.
Religion

, the
Association of Religion Data Archives (ARDA)
reported the following groupings of Kentucky's 4,339,367 residents:
* 48% not affiliated with any religious group, 2,101,653 persons
* 42%
Protestant Christian, 1,819,860 adherents
** 33%
Evangelical Protestant, 1,448,947 adherents (23% within the
Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wor ...
, 1,004,407 adherents)
** 7.1%
Mainline Protestant
The mainline Protestant churches (also called mainstream Protestant and sometimes oldline Protestant) are a group of Protestant denominations in the United States that contrast in history and practice with evangelical, fundamentalist, and charis ...
, 305,955 adherents (4.4% in the
United Methodist Church, 189,596 adherents)
** 1.5%
Black Protestant, 64,958 adherents
* 8.3%
Catholic Church, 359,783 adherents
* 0.74%
Latter-day Saints, 31,991 adherents
* 0.60% other religions, 26,080 adherents (0.26%
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, 0.16%
Judaism, 0.06%
Buddhism, 0.01%
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, other
Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, etc.)
Kentucky is home to several seminaries.
Southern Baptist Theological Seminary
The Southern Baptist Theological Seminary (SBTS) is a Baptist theological institute in Louisville, Kentucky. It is affiliated with the Southern Baptist Convention. The seminary was founded in 1859 in Greenville, South Carolina, where it was at ...
in
Louisville is the principal seminary for the
Southern Baptist Convention
The Southern Baptist Convention (SBC) is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is the world's largest Baptist denomination, and the largest Protestant and second-largest Christian denomination in the United States. The wor ...
. Louisville is also the home of the
Louisville Presbyterian Theological Seminary, an institution of the
Presbyterian Church (USA)
The Presbyterian Church (USA), abbreviated PC(USA), is a mainline Protestant denomination in the United States. It is the largest Presbyterian denomination in the US, and known for its liberal stance on doctrine and its ordaining of women and ...
. Lexington has one seminary,
Lexington Theological Seminary
Lexington Theological Seminary is a private Christian seminary in Lexington, Kentucky. Although it is related to the Christian Church (Disciples of Christ), it is intentionally ecumenical with almost 50 percent of its enrollment coming from o ...
(affiliated with the
Disciples of Christ
The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination in the United States and Canada. The denomination started with the Restoration Movement during the Second Great Awakening, first existing during the 19th ...
). The Baptist Seminary of Kentucky is located on the campus of
Georgetown College in Georgetown.
Asbury Theological Seminary, a multi-denominational seminary in the
Methodist tradition, is located in nearby
Wilmore.
In addition to seminaries, there are several colleges affiliated with denominations:
* In Louisville,
Bellarmine University
Bellarmine University (BU; ) is a private Catholic university in Louisville, Kentucky. It opened on October 3, 1950, as Bellarmine College, established by Archbishop John A. Floersh of the Archdiocese of Louisville and named after Saint Rober ...
and
Spalding University are affiliated with the
Roman Catholic Church.
* In
Lexington,
Transylvania University is affiliated with the
Disciples of Christ
The Christian Church (Disciples of Christ) is a mainline Protestant Christian denomination in the United States and Canada. The denomination started with the Restoration Movement during the Second Great Awakening, first existing during the 19th ...
.
* In
Owensboro,
Kentucky Wesleyan College
Kentucky Wesleyan College (KWC) is a private Methodist college in Owensboro, Kentucky. The college is known for its liberal arts programs. Fall 2018 enrollment was 830 students.
History
Kentucky Wesleyan College was founded in 1858 by the Ken ...
is associated with the
United Methodist Church, and
Brescia University is associated with the Roman Catholic Church.
* In Pikeville, the
University of Pikeville is affiliated with the
Presbyterian Church (USA)
The Presbyterian Church (USA), abbreviated PC(USA), is a mainline Protestant denomination in the United States. It is the largest Presbyterian denomination in the US, and known for its liberal stance on doctrine and its ordaining of women and ...
.
* In Wilmore,
Asbury University (a separate institution from the seminary) is associated with the
Christian College Consortium.
* The
Baptist denomination is associated with several colleges:
**
University of the Cumberlands, in
Williamsburg
Williamsburg may refer to:
Places
*Colonial Williamsburg, a living-history museum and private foundation in Virginia
*Williamsburg, Brooklyn, neighborhood in New York City
*Williamsburg, former name of Kernville (former town), California
*Williams ...
**
Campbellsville University, in
Campbellsville
Campbellsville is a city in central Kentucky founded in 1817 by Andrew Campbell. It is known for Campbellsville University, Taylor Regional Hospital health care system, its historic downtown, and the proximity to Green River Lake State Park. C ...
**
Georgetown College, in
Georgetown
**
Clear Creek Baptist Bible College
Clear Creek Baptist Bible College (CCBBC) is a Private college, private Baptist Bible college in Pineville, Kentucky. It is affiliated with the Kentucky Baptist Convention (Southern Baptist Convention). CCBBC provides a Bible-based education focu ...
, in
Pineville, Kentucky
Pineville () is a home rule-class city in Bell County, Kentucky, United States. It is the seat of its county. The population was 1,732 as of the 2010 census. It is located on a small strip of land between the Cumberland River and Pine Mountain ...
*
Grayson
Grayson may refer to:
Places Canada
* Grayson, Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Grayson No. 184, Saskatchewan
United States
* Grayson, California
* Grayson, Georgia
** Grayson High School
* Grayson, Kentucky
* Grayson, Louisiana
* Gra ...
in
Carter County is home to
Kentucky Christian University which is affiliated with the Christian Churches and Churches of Christ.
*The
Abbey of Our Lady of Gethsemani is located in
Bardstown, Kentucky. Author
Thomas Merton
Thomas Merton (January 31, 1915 – December 10, 1968) was an American Trappist monk, writer, theologian, mystic, poet, social activist and scholar of comparative religion. On May 26, 1949, he was ordained to the Catholic priesthood and giv ...
, known as a social activist, worked to reconcile Christianity with other major religions, had converted to Catholicism as a young man, and became a Trappist monk; he lived and worked here from 1941 until his death in 1968.
Louisville is home to the
Cathedral of the Assumption, the third-oldest Catholic cathedral in continuous use in the United States. The city also holds the headquarters of the
Presbyterian Church (USA)
The Presbyterian Church (USA), abbreviated PC(USA), is a mainline Protestant denomination in the United States. It is the largest Presbyterian denomination in the US, and known for its liberal stance on doctrine and its ordaining of women and ...
and their printing press. Reflecting late 19th, 20th and 21st-century immigration from different countries, Louisville also has
Jewish,
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, and
Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
communities.
In 1996 the Center for Interfaith Relations established the Festival of Faiths, the first and oldest annual interfaith festival to be held in the United States.
The Christian creationist apologetics group,
Answers in Genesis, along with its
Creation Museum, is headquartered in
Petersburg, Kentucky.
Economy


Early in its history, Kentucky gained recognition for its excellent farming conditions. It was the site of the first commercial
winery in the United States (started in present-day
Jessamine County
Jessamine County () is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. As of the 2020 census, the population was 52,991. Its county seat is Nicholasville. The county was founded in December 1798. Jessamine County is part of the Lexington-Fayet ...
in 1799) and due to the high calcium content of the soil in the Bluegrass region quickly became a major horse breeding (and later racing) area. Today Kentucky ranks 5th nationally in goat farming, 8th in
beef cattle production, and 14th in corn production.
Kentucky has also been a long-standing major center of the tobacco industryboth as a center of business and tobacco farming.
Today Kentucky's economy has expanded to importance in non-agricultural terms as well, especially in auto manufacturing, energy fuel production, and medical facilities.
Kentucky ranks 4th among U.S. states in the number of automobiles and trucks assembled.
The
Chevrolet Corvette,
Cadillac XLR (2004–2009),
Ford Escape,
Ford Super Duty trucks,
Ford Expedition,
Lincoln Navigator,
Toyota Camry,
,
,
Toyota Venza,
and
Lexus ES 350 are assembled in Kentucky.
Kentucky has historically been a major coal producer, but the coal industry has been in decline since the 1980s, and the number of people employed in the coal industry there dropped by more than half between 2011 and 2015.
, 24% of electricity produced in the U.S. depended on either enriched uranium rods coming from the
Paducah Gaseous Diffusion Plant (the only domestic site of low-grade uranium enrichment), or from the 107,336 tons of coal extracted from the state's two coal fields (which combined produce 4% percent of the electricity in the United States).
Kentucky produces 95% of the world's supply of
bourbon whiskey
Bourbon () is a type of barrel-aged American whiskey made primarily from corn. The name derives from the French Bourbon dynasty, although the precise source of inspiration is uncertain; contenders include Bourbon County in Kentucky and Bourbo ...
, and the number of barrels of bourbon being aged in Kentucky (more than 5.7million) exceeds the state's population.
[Associated Press]
Bourbon, Tennessee Whiskey Sales Up in US; Exports Top $1B
(February 3, 2015). Bourbon has been a growing marketwith production of Kentucky bourbon rising 170 percent between 1999 and 2015.
In 2019 the state had more than fifty distilleries for bourbon production.
Kentucky exports reached a record $22.1billion in 2012, with products and services going to 199 countries.
According to the Kentucky Cabinet for Economic Development, the primary state agency in Kentucky responsible for creating new jobs and new investment in the state, new business investment in Kentucky in 2012 totaled nearly $2.7billion, with the creation of more than 14,000 new jobs. One such investment was L'Oréal in Northern Kentucky, which added 200 jobs on top of the 280 already in existing facilities in Florence and Walton.
Fort Knox
Fort Knox is a United States Army installation in Kentucky, south of Louisville and north of Elizabethtown. It is adjacent to the United States Bullion Depository, which is used to house a large portion of the United States' official gold res ...
, a
United States Army post best known as the site of the
United States Bullion Depository
The United States Bullion Depository, often known as Fort Knox, is a fortified vault building located next to the United States Army post of Fort Knox, Kentucky. It is operated by the United States Department of the Treasury. The vault is used ...
, which is used to house a large portion of the United States official
gold reserves, is located in Kentucky between Louisville and
Elizabethtown. In May 2010, the
Army Human Resource Center of Excellence, the largest office building in the state at nearly opened at Fort Knox. The complex employs nearly 4,300 soldiers and civilians.
Kentucky contains two of the twenty
U.S. Federal Penitentiaries:
USP Big Sandy (in the east in
Martin County near
Inez
Inez is a feminine given name. It is the English spelling of the Spanish and Portuguese name Inés/Inês/Inez, the forms of the given name " Agnes". The name is pronounced as , , or .
Agnes is a woman's given name, which derives from the Greek w ...
) and
USP McCreary (in the south in
McCreary County
McCreary County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. Its county seat is Whitley City. The county is named for James B. McCreary, a Confederate war soldier and two-time Governor of Kentucky (1875–1879, 1911–1915). During his se ...
in the
Daniel Boone National Forest).
The total gross state product for 2020 was $212.539billion. Its per capita income was $25,888 in 2017. An organization called the
Institute for Truth in Accounting
Truth in Accounting (TIA), formerly known as the Institute for Truth in Accounting, is an American think tank that promotes fiscal transparency and accountability. Its stated goal is "to educate and empower citizens with understandable, reliable, ...
estimated that the state government's debts exceeded its available assets by $26,300 per taxpayer , ranking the state as having the 5th highest such debt burden in the nation.
As of December 2021, the state's unemployment rate is 3.9%. In 2014 Kentucky was found to be the most affordable U.S. state in which to live.
Taxation
Tax is collected by the
Kentucky Department of Revenue.
There are six
income tax brackets, ranging from 2% to 6% of personal income. The sales tax rate in Kentucky is 6%.
Kentucky has a broadly based classified
property tax system. All classes of property, unless exempted by the Constitution, are taxed by the state, although at widely varying rates. Many of these classes are exempted from taxation by local government. Of the classes that are subject to local taxation, three have special rates set by the
General Assembly, one by the
Kentucky Supreme Court and the remaining classes are subject to the full local rate, which includes the tax rate set by the local taxing bodies plus all voted levies. Real property is assessed on 100% of the fair market value and property taxes are due by December 31. Once the primary source of state and local government revenue, property taxes now account for only about 6% of the Kentucky's annual General Fund revenues.
Until January 1, 2006, Kentucky imposed a tax on intangible personal property held by a taxpayer on January1 of each year. The Kentucky intangible tax was repealed under House Bill 272. Intangible property consisted of any property or investment that represents evidence of value or the right to value. Some types of intangible property included: bonds, notes, retail
repurchase agreements, accounts receivable, trusts, enforceable contracts sale of real estate (land contracts), money in hand, money in
safe deposit boxes, annuities, interests in estates, loans to stockholders, and commercial paper.
Government-promoted slogans
In December 2002, the Kentucky governor
Paul Patton unveiled the state slogan "It's that friendly",
in hope of drawing more people into the state based on the idea of
southern hospitality. This campaign was neither a failure nor a success. Though it was meant to embrace southern values, many Kentuckians rejected the slogan as cheesy and generic.
It was quickly seen that the slogan did not encourage tourism as much as initially hoped for. So government decided to create a different slogan to embrace Kentucky as a whole while also encouraging more people to visit the Bluegrass.
In 2004, then Governor
Ernie Fletcher launched a comprehensive
branding campaign with the hope of making the state's $12–14million advertising budget more effective. The resulting "Unbridled Spirit" brand was the result of a $500,000 contract with New West, a Kentucky-based public relations advertising and marketing firm, to develop a viable brand and tag line. The Fletcher administration aggressively marketed the brand in both the public and private sectors. Since that time, the "Welcome to Kentucky" signs at border areas have an "Unbridled Spirit" symbol on them.
Tourism
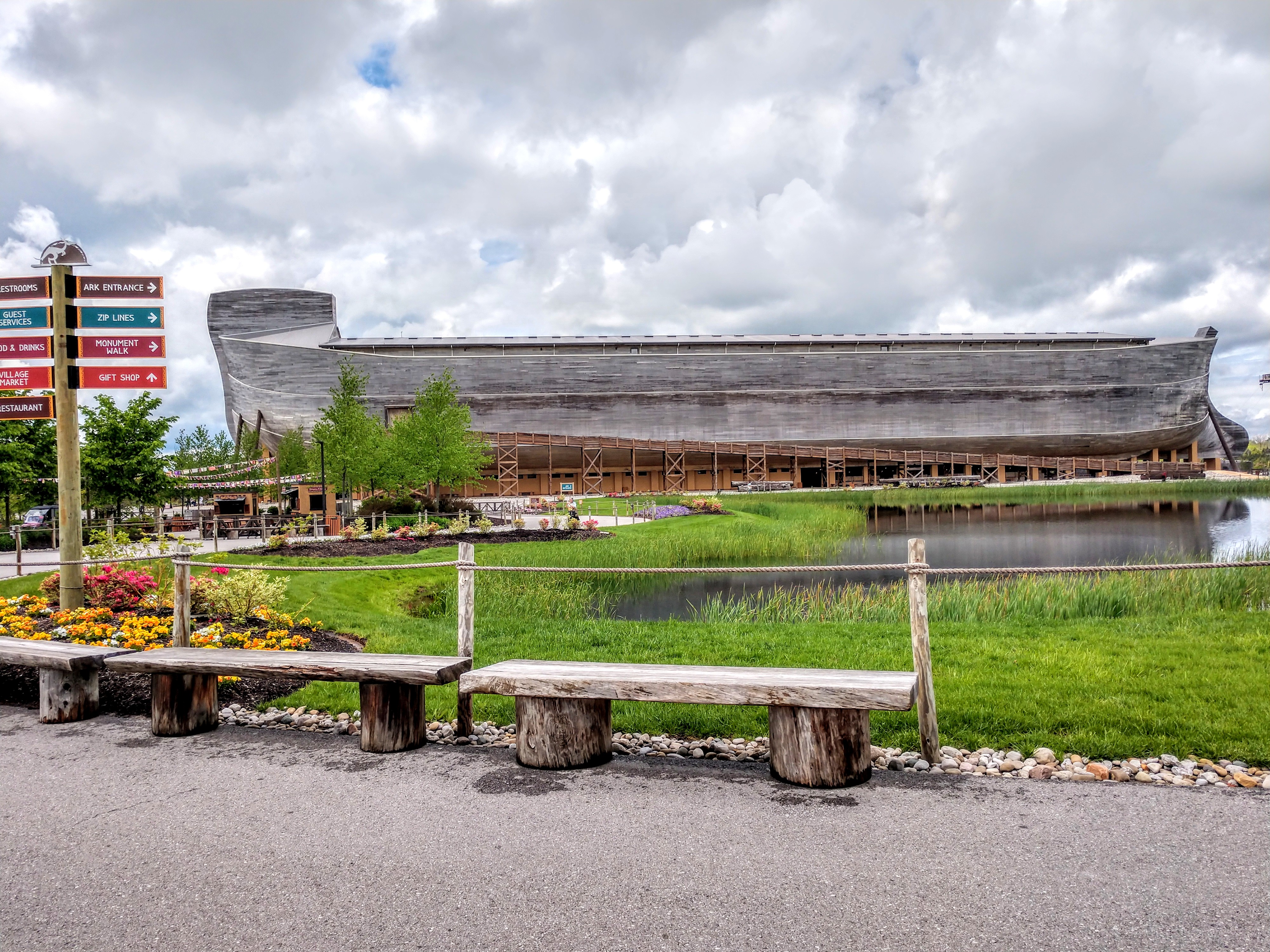

Tourism has become an increasingly important part of the Kentucky economy. In 2019 tourism grew to $7.6billion in economic impact. Key attractions include
horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
with events like
the Kentucky Derby
The Kentucky Derby is a horse race held annually in Louisville, Kentucky, United States, almost always on the first Saturday in May, capping the two-week-long Kentucky Derby Festival. The competition is a Grade I stakes race for three-year ...
and the
Keeneland Fall and Spring Meets,
bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
distillery tours, including along the
Kentucky Bourbon Trail
The Kentucky Bourbon Trail (sometimes informally shortened to "the Bourbon Trail") is the name of a program sponsored by the Kentucky Distillers' Association (KDA) to promote the Bourbon whiskey industry in Kentucky. The KDA has registered the ...
and Louisville Urban Bourbon Trail, and natural attractions such as the state's many lakes and parks to include
Mammoth Cave,
Lake Cumberland and
Red River Gorge.
The state also has several religious destinations such as the
Creation Museum and
Ark Encounter of
Answers in Genesis.
Horse industry
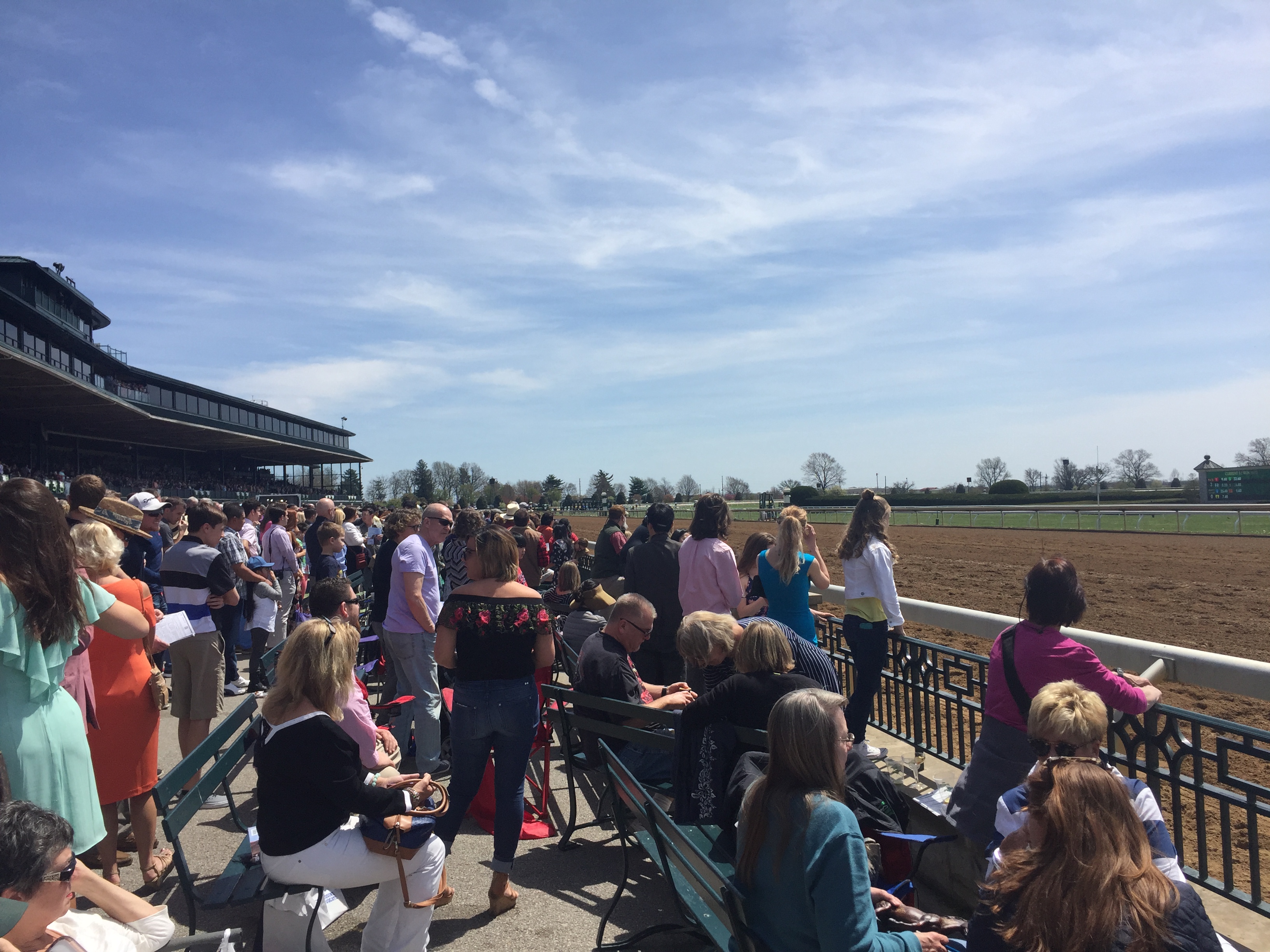

Horse Racing has long been associated with Kentucky.
Churchill Downs
Churchill Downs is a horse racing complex located on Central Avenue in south Louisville, Kentucky, United States, famed for hosting the annual Kentucky Derby. It officially opened in 1875 and was named for Samuel Churchill, whose family was ...
, the home of the Derby, is a large venue with a capacity exceeding 165,000. The track hosts multiple events throughout the year and is a significant draw to the city of Louisville.
Keeneland Race Course, in Lexington, hosts two major meets, the Spring and Fall running. Beyond hosting races Keeneland also hosts a significant horse auction drawing buyers from around the world. In 2019 $360million was spent on the September Yearling sale. The
Kentucky Horse Park in
Georgetown hosts multiple events throughout the year, including international equestrian competitions and also offers horseback riding from April to October.
Education


Kentucky maintains eight public four-year universities. There are two general tiers: major research institutions (the
University of Kentucky and the
University of Louisville) and regional universities, which encompass the remaining six schools. The regional schools have specific target counties that many of their programs are targeted towards (such as Forestry at
Eastern Kentucky University or Cave Management at
Western Kentucky University), however, most of their curriculum varies little from any other public university.
The University of Kentucky (UK) and the University of Louisville (UofL) have the highest academic rankings and admissions standards although the regional schools aren't without their national recognized departmentsexamples being Western Kentucky University's nationally ranked Journalism Department or
Morehead State University offering one of the nation's only Space Science degrees. UK is the flagship and land grant of the system and has agriculture extension services in every county. The two research schools split duties related to the medical field, UK handles all medical outreach programs in the eastern half of the state while UofL does all medical outreach in the state's western half.
The state's sixteen public two-year colleges have been governed by the
Kentucky Community and Technical College System since the passage of the Postsecondary Education Improvement Act of 1997, commonly referred to as House Bill 1. Before the passage of House Bill 1, most of these colleges were under the control of the
University of Kentucky.
Transylvania University, a liberal arts university located in Lexington, was founded in 1780 as the oldest university west of the
Allegheny Mountains.
Berea College, located at the extreme southern edge of the Bluegrass below the Cumberland Plateau, was the first coeducational college in the
South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
to admit both black and white students, doing so from its very establishment in 1855. This policy was successfully challenged in the
United States Supreme Court in the case of ''
Berea College v. Kentucky'' in 1908. This decision effectively segregated Berea until the landmark ''
Brown v. Board of Education'' in 1954.
There are 173 school districts and 1,233 public schools in Kentucky. For the 2010 to 2011 school year, there were approximately 647,827 students enrolled in public school.
Kentucky has been the site of much educational reform over the past two decades. In 1989 the
Kentucky Supreme Court ruled the state's education system was unconstitutional. The response of the
General Assembly was passage of the
Kentucky Education Reform Act (KERA) the following year. Years later, Kentucky has shown progress, but most agree that further reform is needed.
The
West Virginia teachers' strike in 2018 inspired
teachers in other states, including Kentucky, to take similar action.
Transportation

Roads
Kentucky is served by six major
Interstate highways
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
(
I-24
Interstate 24 (I-24) is an Interstate Highway in the Midwestern and Southeastern United States. It runs diagonally from I-57, south of Marion, Illinois, to Chattanooga, Tennessee, at I-75. It travels through Illinois, Kentucky, Tennessee, ...
,
I-64,
I-65,
I-69,
I-71, and
I-75), seven
parkways, and six bypasses and spurs (
I-165,
I-169,
I-264,
I-265,
I-275, and
I-471
Interstate 471 (I-471) is a Interstate Highway, linking I-71 in Downtown Cincinnati, Ohio, to I-275 in Highland Heights, Kentucky. South of I-275, the expressway continues south to U.S. Route 27 (US 27) as unsigned Kentucky Route&nbs ...
). The parkways were originally
toll roads, but on November 22, 2006, Governor
Ernie Fletcher ended the toll charges on the
William H. Natcher Parkway
The William H. Natcher Green River Parkway was the designation for a freeway that ran from Bowling Green to Owensboro in the US commonwealth of Kentucky. The Natcher Parkway was one of nine highways that were a part of Kentucky's parkway syste ...
and the
Audubon Parkway
The Audubon Parkway is a four-lane controlled-access freeway (formerly a toll road) connecting the cities of Henderson and Owensboro, Kentucky. Named for John James Audubon, an early American naturalist, the Audubon's western terminus is at US&n ...
, the last two parkways in Kentucky to charge tolls for access. The related
toll booths have been demolished.
Ending the tolls some seven months ahead of schedule was generally agreed to have been a positive economic development for transportation in Kentucky. In June 2007, a law went into effect raising the speed limit on rural portions of Kentucky Interstates and parkways from .
Road tunnels include the interstate
Cumberland Gap Tunnel and the rural
Nada Tunnel.
Rails
 Amtrak
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides service to
Ashland,
South Portsmouth,
Maysville and
Fulton. The ''
Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**''Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**''Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, the ...
'' (trains 50 and 51) is the line that offers Amtrak service to Ashland, South Shore, Maysville and South Portsmouth. The ''
City of New Orleans'' (trains 58 and 59) serve Fulton. The
Northern Kentucky area is served by the ''Cardinal'' at
Cincinnati Union Terminal. The terminal is just across the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
in
Cincinnati.
Norfolk Southern Railway
The Norfolk Southern Railway is a Class I freight railroad in the United States formed in 1982 with the merger of Norfolk and Western Railway and Southern Railway. With headquarters in Atlanta, the company operates 19,420 route miles (31 ...
passes through the Central and Southern parts of the Commonwealth, via its Cincinnati, New Orleans, and Texas Pacific (CNO&TP) subsidiary. The line originates in
Cincinnati and terminates 338 miles south in
Chattanooga, Tennessee.
, there were approximately of railways in Kentucky, with about 65% of those being operated by
CSX Transportation
CSX Transportation , known colloquially as simply CSX, is a Class I freight railroad operating in the Eastern United States and the Canadian provinces of Ontario and Quebec. The railroad operates approximately 21,000 route miles () of track. ...
.
Coal was by far the most common cargo, accounting for 76% of cargo loaded and 61% of cargo delivered.
Bardstown
Bardstown is a home rule-class city in Nelson County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 11,700 in the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Nelson County.
Bardstown is named for the pioneering Bard brothers. David Bard obtained a l ...
features a
tourist attraction known as ''My Old Kentucky Dinner Train''. Run along a stretch of rail purchased from
CSX in 1987, guests are served a four-course meal as they make a two-and-a-half-hour round-trip between Bardstown and Limestone Springs. The
Kentucky Railway Museum is located in nearby
New Haven.
Other areas in Kentucky are reclaiming old railways in
rail trail
A rail trail is a shared-use path on railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed, but may also share the right of way with active railways, light rail, or streetcar ...
projects. One such project is Louisville's
Big Four Bridge
The Big Four Bridge is a six-span former railroad truss bridge that crosses the Ohio River, connecting Louisville, Kentucky, and Jeffersonville, Indiana. It was completed in 1895, updated in 1929, taken out of rail service in 1968, and converte ...
. When the bridge's Indiana approach ramps opened in 2014, completing the pedestrian connection across the Ohio River, the Big Four Bridge
rail trail
A rail trail is a shared-use path on railway right of way. Rail trails are typically constructed after a railway has been abandoned and the track has been removed, but may also share the right of way with active railways, light rail, or streetcar ...
became the second-longest pedestrian-only bridge in the world. The longest pedestrian-only bridge is also found in Kentuckythe
Newport Southbank Bridge, popularly known as the "Purple People Bridge", connecting
Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
to
Cincinnati, Ohio.
Air
Kentucky's primary airports include
Louisville International Airport (Standiford Field (SDF)) of
Louisville,
Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport (CVG) of
Cincinnati/
Covington Covington may refer to:
People
* Covington (surname)
Places United Kingdom
* Covington, Cambridgeshire
* Covington, South Lanarkshire
United States
* Covington, Georgia
* Covington, Indiana
* Covington, Kentucky, the largest American cit ...
, and
Blue Grass Airport (LEX) in
Lexington. Louisville International Airport is home to
UPS's
Worldport, its international air-sorting hub. Cincinnati/Northern Kentucky International Airport is the largest airport in the state, and is a focus city for passenger airline
Delta Air Lines and headquarters of its
Delta Private Jets. The airport is one of
DHL Aviation
DHL Aviation is a division of DHL (owned by Deutsche Post) responsible for providing air transport capacity. It is not a single airline but a group of airlines that are either owned, co-owned or chartered by DHL Express.
Overview
DHL currently ...
's three super-hubs, serving destinations throughout the Americas, Europe, Africa, and Asia, making it the 7th busiest airport in the U.S. and 36th in the world based on passenger and cargo operations. CVG is also a focus city for
Frontier Airlines
Frontier Airlines is a major ultra-low-cost U.S. airline headquartered in Denver, Colorado. It operates flights to over 100 destinations throughout the United States and 31 international destinations, and employs more than 3,000 staff. The ca ...
and is the largest O&D airport and base for
Allegiant Air, along with home to a maintenance for
American Airlines subsidiary
PSA Airlines and
Delta Air Lines subsidiary
Endeavor Air. There are also a number of regional airports scattered across the state.
On August 27, 2006, Blue Grass Airport was the site of a crash that killed 47 passengers and 2crew members aboard a
Bombardier CRJ designated
Comair Flight 191, or Delta Air Lines Flight 5191, sometimes mistakenly identified by the press as Comair Flight 5191. The lone survivor was the flight's
first officer, James Polehinke, who doctors determined to be brain damaged and unable to recall the crash at all.
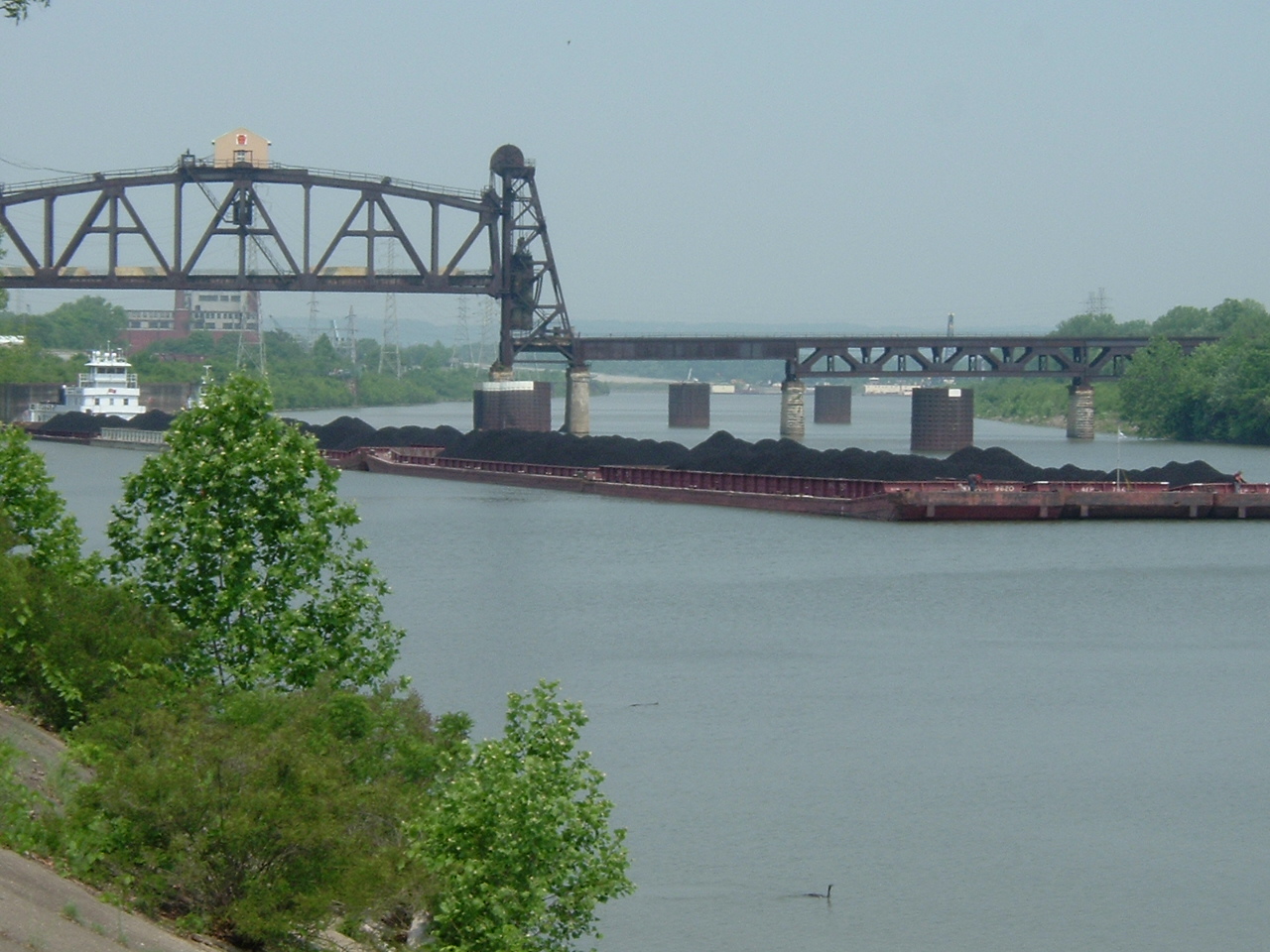

Water
As the state is bounded by two of the largest rivers in North America, water transportation has historically played a major role in Kentucky's economy. Louisville was a major port for steamships in the nineteenth century. Today, most barge traffic on Kentucky waterways consists of coal that is shipped from both the Eastern and Western Coalfields, about half of which is used locally to power many power plants located directly off the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
, with the rest being exported to other countries, most notably Japan.
Many of the largest ports in the United States are located in or adjacent to Kentucky, including:
*
Huntington-Tristate (includes
Ashland, Kentucky), largest
inland port and 7th largest overall
* Cincinnati-Northern Kentucky, 5th largest inland port and 43rd overall
* Louisville-Southern Indiana, 7th largest inland port and 55th overall
As a state, Kentucky ranks 10th overall in port tonnage.
The only natural obstacle along the entire length of the Ohio River is the
Falls of the Ohio, located just west of
Downtown Louisville.
Law and government
Kentucky is one of four
U.S. states to officially use the term ''
commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
.'' The term was used for Kentucky as it had also been used by Virginia, from which Kentucky was created. The term has no particular significance in its meaning and was chosen to emphasize the distinction from the status of royal colonies as a place governed for the general welfare of the populace. Kentucky was originally styled as the "State of Kentucky" in the act admitting it to the union since that is how it was referred to in Kentucky's first constitution.
The commonwealth term was used in citizen petitions submitted between 1786 and 1792 for the creation of the state. It was also used in the title of a history of the state that was published in 1834 and was used in various places within that book in references to Virginia and Kentucky. The other three states officially called "commonwealths" are
Massachusetts,
Pennsylvania, and
Virginia.
Puerto Rico and the
Northern Mariana Islands are also formally commonwealths.
Kentucky is one of only five states that elect their state officials in odd-numbered years (the others being
Louisiana,
Mississippi,
New Jersey, and
Virginia). Kentucky holds elections for these offices every four years in the years preceding Presidential election years. Thus, Kentucky held gubernatorial elections in 2011, 2015 and 2019.
Executive branch

The executive branch is headed by the
governor, who serves as both
head of state and
head of government. The
lieutenant governor
A lieutenant governor, lieutenant-governor, or vice governor is a high officer of state, whose precise role and rank vary by jurisdiction. Often a lieutenant governor is the deputy, or lieutenant, to or ranked under a governor — a "second-in-comm ...
may or may not have executive authority depending on whether the person is a member of the Governor's
cabinet. Under the current
Kentucky Constitution, the lieutenant governor assumes the duties of the governor only if the governor is incapacitated. (Before 1992 the lieutenant governor assumed power any time the governor was out of the state.) The governor and lieutenant governor usually run on a single ticket (also per a 1992 constitutional amendment) and are elected to four-year terms. The current governor is
Andy Beshear, and the lieutenant governor is
Jacqueline Coleman. Both are
Democrats.
The executive branch is organized into the following "cabinets", each headed by a secretary who is also a member of the governor's cabinet:
*
General Government Cabinet
*
Transportation Cabinet
*
Cabinet for Economic Development
*
Finance and Administration Cabinet
*
Tourism, Arts, and Heritage Cabinet
*
Education and Workforce Development Cabinet
*
Cabinet for Health and Family Services
*
Justice and Public Safety Cabinet
*
Personnel Cabinet
*
Labor Cabinet
*
Energy and Environment Cabinet
*
Public Protection Cabinet
The cabinet system was introduced in 1972 by Governor
Wendell Ford to consolidate hundreds of government entities that reported directly to the governor's office.
Other elected constitutional offices include the
Secretary of State,
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general.
In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have exec ...
, Auditor of Public Accounts,
State Treasurer
In the state governments of the United States, 48 of the 50 states have the executive position of treasurer. New York abolished the position in 1926; duties were transferred to New York State Comptroller. Texas abolished the position of Texas ...
and Commissioner of Agriculture. Currently, Republican
Michael G. Adams serves as the Secretary of State. The commonwealth's chief prosecutor, law enforcement officer, and law officer is the Attorney General, currently Republican
Daniel Cameron. The Auditor of Public Accounts is Republican
Mike Harmon. Republican
Allison Ball is the current Treasurer. Republican
Ryan Quarles is the current Commissioner of Agriculture.
Legislative branch

Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a
bicameral
Bicameralism is a type of legislature, one divided into two separate assemblies, chambers, or houses, known as a bicameral legislature. Bicameralism is distinguished from unicameralism, in which all members deliberate and vote as a single grou ...
body known as the
Kentucky General Assembly.
The
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
is considered the
upper house. It has 38 members and is led by the
President of the Senate
President of the Senate is a title often given to the presiding officer of a senate. It corresponds to the speaker in some other assemblies.
The senate president often ranks high in a jurisdiction's succession for its top executive office: for e ...
, currently
Robert Stivers
Bertram Robert Stivers II (born December 24, 1961), is a Republican member of the Kentucky Senate representing the 25th Senate District since 1997. He served as the Republican Majority Leader of the Kentucky State Senate through 2012, and becam ...
(
R).
The
House of Representatives has 100 members, and is led by the Speaker of the House, currently
David Osborne of the Republican Party.
In November 2016, Republicans won control of the House for the first time since 1922, and currently have supermajorities in both the House and Senate.
Judicial branch
The judicial branch of Kentucky is called the Kentucky Court of Justice and comprises courts of
limited jurisdiction Limited jurisdiction, or special jurisdiction, is the court's jurisdiction only on certain types of cases such as bankruptcy, and family matters.
Courts of limited jurisdiction, as opposed to general jurisdiction, derive power from an issuing autho ...
called District Courts; courts of general jurisdiction called
Circuit Courts; specialty courts such as Drug Court and Family Court; an intermediate appellate court, the
Kentucky Court of Appeals; and a court of last resort, the
Kentucky Supreme Court.
The Kentucky Court of Justice is headed by the
Chief Justice of the Commonwealth. The chief justice is appointed by, and is an elected member of, the Supreme Court of Kentucky. The current chief justice is
John D. Minton Jr.
John D. Minton Jr. (born March 19, 1952 in Fort Lauderdale, Florida) is an American lawyer who served as the chief justice of the Kentucky Supreme Court from 2008 to 2023.
Unlike federal judges, who are usually appointed, justices serving on Kentucky state courts are chosen by the state's populace in non-partisan elections.
Federal representation

Kentucky's two
U.S. Senators are
Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell
Addison Mitchell McConnell III (born February 20, 1942) is an American politician and retired attorney serving as the senior United States senator from Kentucky and the Senate minority leader since 2021. Currently in his seventh term, McConne ...
and
Rand Paul
Randal Howard Paul (born January 7, 1963) is an American physician and politician serving as the junior U.S. senator from Kentucky since 2011. A member of the Republican Party, he is a son of former three-time presidential candidate and 12 ...
, both Republicans. The state is divided into six
Congressional Districts, represented by Republicans
James Comer (
1st
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and rec ...
),
Brett Guthrie (
2nd
A second is the base unit of time in the International System of Units (SI).
Second, Seconds or 2nd may also refer to:
Mathematics
* 2 (number), as an ordinal (also written as ''2nd'' or ''2d'')
* Second of arc, an angular measurement unit ...
),
Thomas Massie (
4th
Fourth or the fourth may refer to:
* the ordinal form of the number 4
* ''Fourth'' (album), by Soft Machine, 1971
* Fourth (angle), an ancient astronomical subdivision
* Fourth (music), a musical interval
* ''The Fourth'' (1972 film), a Sovie ...
),
Hal Rogers
Harold Dallas Rogers (born December 31, 1937) is an American lawyer and politician serving his 21st term as the U.S. representative for , having served since 1981. He is a member of the Republican Party. Upon Don Young's death in 2022, Rogers b ...
(
5th
Fifth is the ordinal form of the number five.
Fifth or The Fifth may refer to:
* Fifth Amendment to the United States Constitution, as in the expression "pleading the Fifth"
* Fifth column, a political term
* Fifth disease, a contagious rash tha ...
) and
Andy Barr (
6th
6 (six) is the natural number following 5 and preceding 7. It is a composite number and the smallest perfect number.
In mathematics
Six is the smallest positive integer which is neither a square number nor a prime number; it is the second small ...
) and Democrat
John Yarmuth (
3rd
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* Second#Sexagesimal divisions of calendar time and day, 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (d ...
).
In the federal judiciary, Kentucky is served by two
United States district courts: the
Eastern District of Kentucky, with its primary seat in Lexington, and the
Western District of Kentucky, with its primary seat in Louisville. Appeals are heard in the
Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit
The United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit (in case citations, 6th Cir.) is a federal court with appellate jurisdiction over the district courts in the following districts:
* Eastern District of Kentucky
* Western District of ...
, based in
Cincinnati, Ohio.
Law

Kentucky's body of laws, known as the
Kentucky Revised Statutes (KRS), were enacted in 1942 to better organize and clarify the whole of Kentucky law. The statutes are enforced by local
police,
sheriffs and deputy sheriffs, and
constable
A constable is a person holding a particular office, most commonly in criminal law enforcement. The office of constable can vary significantly in different jurisdictions. A constable is commonly the rank of an officer within the police. Other peop ...
s and deputy constables. Unless they have completed a
police academy elsewhere, these officers are required to complete Police Officer Professional Standards (POPS) training at the Kentucky Department of Criminal Justice Training Center on the campus of
Eastern Kentucky University in
Richmond. Additionally, in 1948, the
Kentucky General Assembly established the
Kentucky State Police
The Kentucky State Police (KSP) is a department of the Kentucky Justice and Public Safety Cabinet, and the official State Police force of the Commonwealth of Kentucky, responsible for statewide law enforcement. The department was founded in 194 ...
, making it the 38th state to create a force whose jurisdiction extends throughout the given state.
Kentucky is one of the
32 states in the United States that sanctions the
death penalty
Capital punishment, also known as the death penalty, is the state-sanctioned practice of deliberately killing a person as a punishment for an actual or supposed crime, usually following an authorized, rule-governed process to conclude that t ...
for certain murders defined as heinous. Those convicted of capital crimes after March 31, 1998, are always executed by
lethal injection
Lethal injection is the practice of injecting one or more drugs into a person (typically a barbiturate, paralytic, and potassium solution) for the express purpose of causing rapid death. The main application for this procedure is capital puni ...
; those convicted on or before this date may opt for the
electric chair. Only
three people have been executed in Kentucky since the
U.S. Supreme Court re-instituted the practice in 1976. The most notable execution in Kentucky was that of
Rainey Bethea on August 14, 1936. Bethea was publicly hanged in
Owensboro for the
rape and murder of Lischia Edwards. Irregularities with the execution led to this becoming the last public execution in the United States.
Kentucky has been on the front lines of the debate over displaying the
Ten Commandments on public property. In the 2005 case of ''
McCreary County v. ACLU of Kentucky'', the
U.S. Supreme Court upheld the decision of the
Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals that a display of the
Ten Commandments in the
Whitley City courthouse of
McCreary County
McCreary County is a county located in the U.S. state of Kentucky. Its county seat is Whitley City. The county is named for James B. McCreary, a Confederate war soldier and two-time Governor of Kentucky (1875–1879, 1911–1915). During his se ...
was unconstitutional. Later that year, Judge
Richard Fred Suhrheinrich
Richard Fred Suhrheinrich (born August 15, 1936) is a Senior United States circuit judge of the United States Court of Appeals for the Sixth Circuit serving in Lansing, Michigan He had been a United States district judge of the United States Dis ...
, writing for the
Sixth Circuit Court of Appeals in the case of ''
ACLU
The American Civil Liberties Union (ACLU) is a nonprofit organization founded in 1920 "to defend and preserve the individual rights and liberties guaranteed to every person in this country by the Constitution and laws of the United States". T ...
of Kentucky v.
Mercer County'', wrote that a display including the
Mayflower Compact
The Mayflower Compact, originally titled Agreement Between the Settlers of New Plymouth, was the first governing document of Plymouth Colony. It was written by the men aboard the ''Mayflower,'' consisting of separatist Puritans, adventurers, an ...
, the
Declaration of Independence, the
Ten Commandments, the
Magna Carta
(Medieval Latin for "Great Charter of Freedoms"), commonly called (also ''Magna Charta''; "Great Charter"), is a royal charter of rights agreed to by King John of England at Runnymede, near Windsor, on 15 June 1215. First drafted by the ...
, ''
The Star-Spangled Banner'', and the
national motto could be erected in the
Mercer County courthouse.
Kentucky has also been known to have unusually high political candidacy age laws, especially compared to surrounding states. The origin of this is unknown, but it has been suggested it has to do with the commonwealth tradition.
A 2008 study found that Kentucky's Supreme Court to be the least influential high court in the nation with its decisions rarely being followed by other states.
Politics

Since the late 1990s, Kentucky has supported
Republican candidates for most federal political offices, and, more recently, for state-level office as well. The state leaned toward the
Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
from 1860 (when the Whig Party dissolved) to the 1990s, and was considered a swing state at the presidential level for most of the latter half of the 20th century.
The southeastern region of the state aligned with the
Union during the war and has consistently supported Republican candidates. The central and western portions of the state were heavily Democratic in the years leading to the Civil War and in the decades following the war. Kentucky was part of the Democratic
Solid South in the second half of the nineteenth century and through the majority of the twentieth century.
Mirroring a broader national reversal of party composition, the Kentucky Democratic Party of the twenty-first century primarily consists of liberal whites, African Americans, and other minorities. Although most of the state's voters have reliably elected Republican candidates for federal office since the late 1990s, Democrats held an advantage in party registration until 2022. On July 15, 2022, the
Kentucky Secretary of State
The secretary of state of Kentucky is one of the constitutional officers of the U.S. state of Kentucky. It is now an elected office, but was an appointed office prior to 1891. The current secretary of state is Republican Michael Adams, who was e ...
's office announced that for the first time in its history, the commonwealth had more registered
Republicans
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
than registered Democrats, with 45.19% of the state's voters registered as Republicans, 45.12% registered as Democrats, and 9.69% registered with
another political party or as independents.
From 1964 through 2004, Kentucky voted for the eventual winner of the election for President of the United States; however, in the
2008 election
This electoral calendar 2008 lists the national/federal direct elections held in 2008 in the de jure and de facto sovereign states and their dependent territories. Referendums are included, even though they are not elections. By-elections are no ...
the state lost its
bellwether status. Republican
John McCain
John Sidney McCain III (August 29, 1936 – August 25, 2018) was an American politician and United States Navy officer who served as a United States senator from Arizona from 1987 until his death in 2018. He previously served two terms ...
won Kentucky, but he lost the national popular and electoral vote to Democrat
Barack Obama (McCain carried Kentucky 57% to 41%). 116 of Kentucky's 120 counties supported former
Massachusetts Governor
Mitt Romney
Willard Mitt Romney (born March 12, 1947) is an American politician, businessman, and lawyer serving as the junior United States senator from Utah since January 2019, succeeding Orrin Hatch. He served as the 70th governor of Massachusetts f ...
in the 2012 election while he lost to Barack Obama nationwide.
Voters in the Commonwealth have supported the previous three Democratic candidates elected to the White House in the late 20th century, all from Southern states:
Lyndon B. Johnson (
Texas) in 1964,
Jimmy Carter (
Georgia) in 1976, and
Bill Clinton (
Arkansas) in 1992 and 1996. In the twenty-first century presidential elections, the state has become a Republican stronghold, supporting that party's presidential candidates by double-digit margins from 2000 through 2020. At the same time, voters have continued to elect Democratic candidates to state and local offices in many jurisdictions.
Elliott County, Kentucky is notable for having held the longest streak of any county in the United States voting Democratic. Founded in 1869, Elliott County supported the Democratic nominee in every presidential election from
1872
Events
January–March
* January 12 – Yohannes IV is crowned Emperor of Ethiopia in Axum, the first ruler crowned in that city in over 500 years.
* February 2 – The government of the United Kingdom buys a number of forts on ...
(the first in which it participated) until
2012
File:2012 Events Collage V3.png, From left, clockwise: The passenger cruise ship Costa Concordia lies capsized after the Costa Concordia disaster; Damage to Casino Pier in Seaside Heights, New Jersey as a result of Hurricane Sandy; People gather ...
. In
2016
File:2016 Events Collage.png, From top left, clockwise: Bombed-out buildings in Ankara following the 2016 Turkish coup d'état attempt; the impeachment trial of Brazilian President Dilma Rousseff; Damaged houses during the 2016 Nagorno-Karabakh ...
,
Donald Trump became the first Republican to ever carry the county, and he did so in a 44-point landslide, highlighting the modern Republican Party's dominance among rural whites and many ancestrally Democratic, socially-conservative voters.
Kentucky is one of the most
anti-abortion
Anti-abortion movements, also self-styled as pro-life or abolitionist movements, are involved in the abortion debate advocating against the practice of abortion and its legality. Many anti-abortion movements began as countermovements in respons ...
states in the United States. A 2014 poll conducted by
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
found that 57% of Kentucky's population thought that
abortion should be illegal in all/most cases, while only 36% thought that abortion should be legal in all/most cases.
In a 2020 study, Kentucky was ranked as the 8th hardest state for citizens to vote in.
Culture

Kentucky
culture is generally considered to be firmly
Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
; it is unique in that it is also influenced by the
Midwest
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four Census Bureau Region, census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of ...
and
Southern Appalachia, blending with the native upper Southern culture in certain areas of the state. The state is known for
bourbon Bourbon may refer to:
Food and drink
* Bourbon whiskey, an American whiskey made using a corn-based mash
* Bourbon barrel aged beer, a type of beer aged in bourbon barrels
* Bourbon biscuit, a chocolate sandwich biscuit
* A beer produced by ...
and
whiskey distilling,
tobacco,
horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic p ...
, and
college basketball. Kentucky is more similar to the
Upland South in terms of ancestry that is predominantly American.
Nevertheless, during the 19th century, Kentucky did receive a substantial number of German immigrants, who settled mostly in the Midwest and parts of the Upper South, along the Ohio River primarily in Louisville, Covington and Newport. Only Maryland, Delaware and West Virginia have higher German ancestry percentages than Kentucky among Census-defined Southern states, although Kentucky's percentage is closer to Arkansas and Virginia's than the previously named state's percentages.
Scottish Americans,
English Americans and
Scotch-Irish American
Scotch-Irish (or Scots-Irish) Americans are American descendants of Ulster Protestants who emigrated from Ulster in northern Ireland to America during the 18th and 19th centuries, whose ancestors had originally migrated to Ireland mainly from t ...
s have heavily influenced Kentucky culture, and are present in every part of the state. As of the 1980s the only counties in the United States where more than half the population cited "English" as their only ancestry group were all in the hills of eastern Kentucky (and made up virtually every county in this region).
Kentucky was a
slave state, and black people once comprised over one-quarter of its population; however, it lacked the
cotton plantation system though it did support significant and large scale tobacco plantation systems in the western and central parts of the state more similar to the plantations developed in Virginia and North Carolina than those in the Deep South, and never had the same high percentage of African Americans as most other slave states. While less than 8% of the total population is black, Kentucky has a relatively significant rural African American population in the Central and Western areas of the state.
Kentucky adopted the
Jim Crow
The Jim Crow laws were state and local laws enforcing racial segregation in the Southern United States. Other areas of the United States were affected by formal and informal policies of segregation as well, but many states outside the Sout ...
system of
racial segregation in most public spheres after the Civil War. Louisville's 1914 ordinance for residential racial segregation was
struck down by the US Supreme Court in 1917. However, in 1908 Kentucky enacted the
Day Law, "An Act to Prohibit White and Colored Persons from Attending the Same School", which
Berea College unsuccessfully challenged at the US Supreme Court in 1908; in 1948,
Lyman T. Johnson
Lyman Tefft Johnson (June 12, 1906 – October 3, 1997) was an American educator and influential role model for racial desegregation in Kentucky. He is best known as the plaintiff whose successful legal challenge opened the University of Kentucky ...
filed suit for admission to the
University of Kentucky; as a result in the summer of 1949, nearly thirty African American students entered UK graduate and professional programs. Kentucky integrated its schools after the 1954 ''
Brown v. Board of Education'' verdict, later adopting the first state civil rights act in the South in 1966.

Kentucky celebrates
Confederate Memorial Day as a state holiday on June 3, on the anniversary of Jefferson Davis's birthday. The biggest day in American horse racing, the
Kentucky Derby
The Kentucky Derby is a horse race held annually in Louisville, Kentucky, United States, almost always on the first Saturday in May, capping the two-week-long Kentucky Derby Festival. The competition is a Grade I stakes race for three-year ...
, is preceded by the two-week
Derby Festival in Louisville. The Derby Festival features many events, including Thunder Over Louisville, the Pegasus Parade, the Great Steamboat Race, Fest-a-Ville, the Chow Wagon, BalloonFest, BourbonVille, and many others leading up to the big race.
Louisville also plays host to the
Kentucky State Fair and the
Kentucky Shakespeare Festival.
Bowling Green, the state's third-largest city and home to the
only assembly plant in the world that manufactures the
Chevrolet Corvette, opened the
National Corvette Museum in 1994. The fourth-largest city,
Owensboro, gives credence to its nickname of "Barbecue Capital of the World" by hosting the annual
International Bar-B-Q Festival.
Old Louisville
Old Louisville is a historic district and neighborhood in central Louisville, Kentucky, United States. It is the third largest such district in the United States, and the largest preservation district featuring almost entirely Victorian architect ...
, the largest
historic preservation district in the United States featuring
Victorian architecture and the third largest overall, hosts the
St. James Court Art Show
The St. James Court Art Show, colloquially called the St. James Art Fair, or just St. James, is a popular free public outdoor annual arts and crafts show held since 1957 in the Old Louisville neighborhood of Louisville, Kentucky, in the St. James ...
, the largest outdoor art show in the United States. The neighborhood was also home to the
Southern Exposition (1883–1887), which featured the first public display of
Thomas Edison's
light bulb
An electric light, lamp, or light bulb is an electrical component that produces light. It is the most common form of artificial lighting. Lamps usually have a base made of ceramic, metal, glass, or plastic, which secures the lamp in the soc ...
, and was the setting of
Alice Hegan Rice's novel, ''
Mrs. Wiggs of the Cabbage Patch
''Mrs. Wiggs of the Cabbage Patch'' is a 1901 novel by American author Alice Hegan Rice, about a southern family humorously coping with poverty. It was highly popular on its release,Lowell Hayes Harrison, ''A New History of Kentucky'' (1997), p. ...
''.
Fairview, was the birthplace of
Jefferson Davis
Jefferson F. Davis (June 3, 1808December 6, 1889) was an American politician who served as the president of the Confederate States from 1861 to 1865. He represented Mississippi in the United States Senate and the House of Representatives as a ...
, who would become President of the
Confederate States of America and had the
Jefferson Davis Memorial, a 351-foot concrete obelisk, built in 1917.
Hodgenville, the birthplace of
Abraham Lincoln, hosts the annual Lincoln Days Celebration, and also hosted the kick-off for the National Abraham Lincoln Bicentennial Celebration in February 2008.
Bardstown
Bardstown is a home rule-class city in Nelson County, Kentucky, United States. The population was 11,700 in the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Nelson County.
Bardstown is named for the pioneering Bard brothers. David Bard obtained a l ...
celebrates its heritage as a major bourbon-producing region with the
Kentucky Bourbon Festival.
Glasgow mimics
Glasgow, Scotland by hosting the
Glasgow Highland Games The Glasgow Highland Games are a regional highland games and Scotland, Scottish heritage celebration held annually in and near Glasgow, Kentucky. The main festival grounds are located at Barren River Lake State Resort Park, about from Glasgow, whil ...
, its own version of the
Highland Games, and
Sturgis hosts "Little Sturgis", a mini version of
Sturgis, South Dakota's annual
Sturgis Motorcycle Rally.
Winchester
Winchester is a City status in the United Kingdom, cathedral city in Hampshire, England. The city lies at the heart of the wider City of Winchester, a local government Districts of England, district, at the western end of the South Downs Nation ...
celebrates an original Kentucky creation,
Beer Cheese, with its
Beer Cheese Festival held annually in June. Beer Cheese was developed in
Clark County at some point in the 1940s along the Kentucky River.
The residents of tiny
Benton Benton may refer to:
Places
Canada
*Benton, a local service district south of Woodstock, New Brunswick
*Benton, Newfoundland and Labrador
United Kingdom
* Benton, Devon, near Bratton Fleming
* Benton, Tyne and Wear
United States
*Benton, Alabam ...
pay tribute to their favorite tuber, the
sweet potato
The sweet potato or sweetpotato (''Ipomoea batatas'') is a dicotyledonous plant that belongs to the Convolvulus, bindweed or morning glory family (biology), family, Convolvulaceae. Its large, starchy, sweet-tasting tuberous roots are used as a r ...
, by hosting
Tater Day
Benton is a home rule-class city in Marshall County, Kentucky, United States. The current mayor of this city is Rita Dotson. The population was 4,756 at the 2020 census. It is the county seat of Marshall County.
History
Benton was founded in 1 ...
. Residents of
Clarkson in
Grayson County celebrate their city's ties to the honey industry by celebrating the Clarkson Honeyfest. The Clarkson Honeyfest is held the last Thursday, Friday and Saturday in September, and is the "Official State Honey Festival of Kentucky".
Music
Renfro Valley, Kentucky is home to Renfro Valley Entertainment Center and the Kentucky Music Hall of Fame and is known as "Kentucky's Country Music Capital", a designation given it by the Kentucky State Legislature in the late 1980s. The Renfro Valley Barn Dance was where Renfro Valley's musical heritage began, in 1939, and influential country music luminaries like
Red Foley,
Homer & Jethro,
Lily May Ledford
Lily May Ledford (March 17, 1917 – July 14, 1985) was an American clawhammer banjo and fiddle player. After gaining regional radio fame in the late 1930s as head of the Coon Creek Girls, one of the first all-female string bands to appear ...
&the Original
Coon Creek Girls, Martha Carson and many others have performed as regular members of the shows there over the years. The
Renfro Valley Gatherin' is today America's second-oldest continually broadcast radio program of any kind. It is broadcast on local radio station
WRVK and a syndicated network of nearly 200 other stations across the United States and Canada every week.

Contemporary Christian music
Contemporary Christian music, also known as CCM, Christian pop, and occasionally inspirational music is a genre of modern popular music, and an aspect of Christian media, which is lyrically focused on matters related to the Christian faith and s ...
star
Steven Curtis Chapman is a
Paducah native, and
Rock and Roll Hall of Fame
The Rock and Roll Hall of Fame (RRHOF), sometimes simply referred to as the Rock Hall, is a museum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and othe ...
rs
The Everly Brothers are closely connected with
Muhlenberg County, where older brother Don was born.
Merle Travis
Merle Robert Travis (November 29, 1917 – October 20, 1983) was an American country and western singer, songwriter, and guitarist born in Rosewood, Kentucky, United States. His songs' lyrics often discussed both the lives and the economic expl ...
, Country &Western artist known for both his signature "
Travis picking
Fingerstyle guitar is the technique of playing the guitar or bass guitar by plucking the strings directly with the fingertips, fingernails, or picks attached to fingers, as opposed to flatpicking (plucking individual notes with a single ple ...
" guitar playing style, as well as his hit song "
Sixteen Tons", was also born in
Muhlenberg County. Kentucky was also home to
Mildred and
Patty Hill, the
Louisville sisters credited with composing the tune to the ditty
Happy Birthday to You in 1893;
Loretta Lynn (
Johnson County),
Brian Littrell and
Kevin Richardson of the
Backstreet Boys, and
Billy Ray Cyrus (
Flatwoods).
However, its depth lies in its signature sound
Bluegrass music
Bluegrass music is a genre of American roots music
The term American folk music encompasses numerous music genres, variously known as ''traditional music'', ''traditional folk music'', ''contemporary folk music'', ''vernacular music,'' or ...
.
Bill Monroe, "The Father of Bluegrass", was born in the small
Ohio County town of
Rosine, while
Ricky Skaggs,
Keith Whitley
Jackie Keith Whitley (July 1, 1954 – May 9, 1989) was an American country music singer and songwriter. During his career, Whitley released only two albums but charted 12 singles on the ''Billboard'' country charts, and 7 more after his death.
...
,
David "Stringbean" Akeman,
Louis Marshall "Grandpa" Jones, Sonny and
Bobby Osborne, and
Sam Bush (who has been compared to Monroe) all hail from Kentucky. The Bluegrass Music Hall of Fame & Museum is located in
Owensboro, while the annual
Festival of the Bluegrass is held in
Lexington.
Kentucky is also home to famed
jazz musician and pioneer,
Lionel Hampton
Lionel Leo Hampton (April 20, 1908 – August 31, 2002) was an American jazz vibraphonist, pianist, percussionist, and bandleader. Hampton worked with jazz musicians from Teddy Wilson, Benny Goodman, and Buddy Rich, to Charlie Parker, Charles M ...
.
Blues
Blues is a music genre and musical form which originated in the Deep South of the United States around the 1860s. Blues incorporated spirituals, work songs, field hollers, shouts, chants, and rhymed simple narrative ballads from the Afr ...
legend
W. C. Handy and
R&B singer
Wilson Pickett also spent considerable time in Kentucky. The R&B group
Midnight Star and Hip-Hop group
Nappy Roots
Nappy Roots is an American alternative Southern rap group. The group met in Bowling Green, Kentucky in 1995 while attending Western Kentucky University. They are best known for their hit singles " Po' Folks", "Awnaw", " Roun' The Globe" and "Go ...
were both formed in Kentucky, as were country acts
The Kentucky Headhunters,
Montgomery Gentry and
Halfway to Hazard,
The Judds, as well as
Dove Award
A Dove Award is an accolade by the Gospel Music Association (GMA) of the United States to recognize outstanding achievement in the Christian music industry. The awards are presented annually. Formerly held in Nashville, Tennessee, the Dove Awards ...
-winning Christian groups
Audio Adrenaline (rock) and
Bride (metal). Heavy Rock band
Black Stone Cherry hails from rural Edmonton. Rock band
My Morning Jacket with lead singer and guitarist
Jim James originated out of Louisville, as well as bands
Wax Fang,
White Reaper,
Tantric. Rock bands
Cage the Elephant,
Sleeper Agent
A sleeper agent, also called sleeper cell, is a spy who is placed in a target country or organization not to undertake an immediate mission but to act as a potential asset if activated. Even if unactivated, the "sleeper agent" is still an asset ...
, and
Morning Teleportation are also from Bowling Green. The bluegrass groups Driftwood and Kentucky Rain, along with
Nick Lachey of the pop band
98 Degrees are also from Kentucky.
King Crimson guitarist
Adrian Belew is from
Covington Covington may refer to:
People
* Covington (surname)
Places United Kingdom
* Covington, Cambridgeshire
* Covington, South Lanarkshire
United States
* Covington, Georgia
* Covington, Indiana
* Covington, Kentucky, the largest American cit ...
.
Post rock band
Slint also hails from Louisville. Noted singer and actress
Rosemary Clooney
Rosemary Clooney (May 23, 1928 – June 29, 2002) was an American singer and actress. She came to prominence in the early 1950s with the song "Come On-a My House", which was followed by other pop numbers such as " Botch-a-Me", " Mambo Italiano", ...
was a native of
Maysville, her legacy being celebrated at the annual music festival bearing her name. Noted songwriter and actor
Will Oldham is from Louisville. More recently in the limelight are country artists
Chris Stapleton
Christopher Alvin Stapleton (born April 15, 1978) is an American singer-songwriter, guitarist, and record producer. He was born in Lexington, Kentucky, and grew up in Staffordsville, Kentucky. In 2001, Stapleton moved to Nashville, Tennessee, to ...
,
Sturgill Simpson
John Sturgill Simpson (born June 8, 1978) is an American country music singer-songwriter and actor. As of February 2022, he has released seven albums as a solo artist. His first two albums, '' High Top Mountain'' and '' Metamodern Sounds in Cou ...
,
Tyler Childers, and
Chris Knight Christopher or Chris Knight may refer to:
Film and television
* Christopher Knight (actor) (born 1957), American actor
*Christopher Knight (filmmaker), blogger and filmmaker
* Chris Knight (''Neighbours''), fictional character in the soap opera '' ...
.
In eastern Kentucky,
old-time music carries on the tradition of ancient ballads and reels developed in historical Appalachia.
Literature
Kentucky has played a major role in Southern and American literature, producing works that often celebrate the working class, rural life, nature, and explore issues of class, extractive economy, and family. Major works from the state include ''
Uncle Tom's Cabin'' (1852) by
Harriet Beecher Stowe
Harriet Elisabeth Beecher Stowe (; June 14, 1811 – July 1, 1896) was an American author and abolitionist. She came from the religious Beecher family and became best known for her novel ''Uncle Tom's Cabin'' (1852), which depicts the harsh ...
, widely seen as one of the impetuses for the American Civil War; ''The Little Shepherd of Kingdom Come'' (1908) by
John Fox Jr.
John Fox Jr. (December 16, 1862 – July 8, 1919) was an American journalist, novelist, and short story writer.
Biography
Born in Stony Point, Kentucky, to John William Fox Sr. and Minerva Worth Carr, Fox studied English at Harvard University ...
, which was the first novel to sell a million copies in the United States; ''
All the King's Men'' by
Robert Penn Warren (1946), rated as the 36th best
English-language novel of the 20th century; ''The Dollmaker'' (1954) by
Harriette Arnow
Harriette Simpson Arnow (July 7, 1908 – March 22, 1986) was an American novelist and historian, who lived in Kentucky and Michigan. Arnow has been called an expert on the people of the Southern Appalachian Mountains, but she herself loved citie ...
; ''
Night Comes to the Cumberlands
''Night Comes to the Cumberlands'' (1963) is a book by Harry Caudill that brought attention to poverty in Appalachia and is credited with making the Appalachian area a focus of the United States government's "war on poverty". In ''Poverty in th ...
'' (1962) by
Harry Caudill
Harry Monroe Caudill (May 3, 1922 – November 29, 1990) was an American author, historian, lawyer, legislator, and environmentalist from Letcher County, in the coalfields of southeastern Kentucky.
Biography
Caudill served in World War II ...
, which contributed to initiating the U.S. Government's
War on poverty, and others.
Author
Thomas Merton
Thomas Merton (January 31, 1915 – December 10, 1968) was an American Trappist monk, writer, theologian, mystic, poet, social activist and scholar of comparative religion. On May 26, 1949, he was ordained to the Catholic priesthood and giv ...
lived most of his life and wrote most of his booksincluding ''
The Seven Storey Mountain
''The Seven Storey Mountain'' is the 1948 autobiography of Thomas Merton, an American Trappist monk and priest who was a noted author in the 1940s, 1950s and 1960s. Merton finished the book in 1946 at the age of 31, five years after entering Get ...
'' (1948), ranked on ''
National Review'' list of the 100 best non-fiction books of the centuryduring his time as a monk at the
Abbey of Our Lady of Gethsemani near Bardstown, Kentucky. Author
Hunter S. Thompson
Hunter Stockton Thompson (July 18, 1937 – February 20, 2005) was an American journalist and author who founded the gonzo journalism movement. He rose to prominence with the publication of '' Hell's Angels'' (1967), a book for which he s ...
is also a native of the state. Since the later part of the 20th century, several writers from Kentucky have published widely read and critically acclaimed books, including:
Wendell Berry (
fl.
''Floruit'' (; abbreviated fl. or occasionally flor.; from Latin for "they flourished") denotes a date or period during which a person was known to have been alive or active. In English, the unabbreviated word may also be used as a noun indicatin ...
1960–),
Silas House (fl. 2001–),
Barbara Kingsolver
Barbara Kingsolver (born April 8, 1955) is an American novelist, essayist and poet. She was raised in rural Kentucky and lived briefly in the Congo in her early childhood. Kingsolver earned degrees in biology at DePauw University and the Univers ...
(fl. 1988–), poet
Maurice Manning (fl. 2001–), and
Bobbie Ann Mason (fl. 1988–).
Well-known playwrights from Kentucky include
Marsha Norman
Marsha Norman (born September 21, 1947) is an American playwright, screenwriter, and novelist. She received the 1983 Pulitzer Prize for Drama for her play '' 'night, Mother''. She wrote the book and lyrics for such Broadway musicals as ''The Se ...
(works include ''
'night, Mother
''night, Mother'' is a play by American playwright Marsha Norman. The play won the 1983 Pulitzer Prize for Drama and was nominated for the Tony Award for Best Play.
The play is about a daughter, Jessie, and her mother, Thelma. It begins with Je ...
'', 1983) and
Naomi Wallace (works include ''
One Flea Spare'', 1995).

Cuisine
Kentucky's cuisine is generally similar to and is a part of traditional southern cooking, although in some areas of the state it can blend elements of both the South and Midwest, mixing Midwestern with the native Southern cuisine of the area. One original Kentucky dish is called the
Hot Brown, a dish normally layered in this order: toasted bread, turkey, bacon, tomatoes and topped with
mornay sauce. It was developed at the
Brown Hotel in
Louisville. The
Pendennis Club in Louisville is the birthplace of the
Old Fashioned
Old-fashioned may refer to:
* Old fashioned (cocktail), a whiskey cocktail
** Old Fashioned glass, a type of drinking glass named after the cocktail
* ''Old Fashioned'' (film), a 2015 film by Rik Swartzwelder
* "Old-fashioned" (short story) a 19 ...
cocktail. Also, Western Kentucky is known for its own regional style of Southern barbecue. Central Kentucky is the birthplace of
Beer Cheese.
Harland Sanders, a
Kentucky colonel, originated
Kentucky Fried Chicken
KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) is an American fast food restaurant chain headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, that specializes in fried chicken. It is the world's second-largest restaurant chain (as measured by sales) after McDonald's, with 2 ...
at his service station in
North Corbin, though the first franchised
KFC
KFC (Kentucky Fried Chicken) is an American fast food restaurant chain headquartered in Louisville, Kentucky, that specializes in fried chicken. It is the world's second-largest restaurant chain (as measured by sales) after McDonald's, with 2 ...
was located in
South Salt Lake, Utah.
Sports

Kentucky is the home of several sports teams such as
Minor League Baseball's Triple-A
Louisville Bats
The Louisville Bats are a Minor League Baseball team of the International League (IL) and the Triple-A (baseball), Triple-A affiliate of the Cincinnati Reds. They are located in Louisville, Kentucky, and are named in dual reference to the bat, win ...
and High-A
Bowling Green Hot Rods. It is also home to the independent
Atlantic League of Professional Baseball
The Atlantic League of Professional Baseball (ALPB) is a professional independent baseball league based in the United States. It is an official MLB Partner League based in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern United States. The Atlantic League's ...
's
Lexington Legends and the
Frontier League's
Florence Y'alls. The
Lexington Horsemen and
Louisville Fire of the now-defunct
af2 had been interested in making a move up to the "major league"
Arena Football League, but nothing has come of those plans.
The
northern part of the state lies across the
Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
from Cincinnati, which is home to the
National Football League's
Cincinnati Bengals
The Cincinnati Bengals are a professional American football team based in Cincinnati. The Bengals compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's American Football Conference (AFC) AFC North, North division. The c ...
,
Major League Baseball's
Cincinnati Reds
The Cincinnati Reds are an American professional baseball team based in Cincinnati. They compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) National League Central, Central division and were a charter member of ...
. It is not uncommon for fans to park in the city of
Newport
Newport most commonly refers to:
*Newport, Wales
*Newport, Rhode Island, US
Newport or New Port may also refer to:
Places Asia
*Newport City, Metro Manila, a Philippine district in Pasay
Europe
Ireland
*Newport, County Mayo, a town on the ...
and use the
Newport Southbank Pedestrian Bridge, locally known as the "Purple People Bridge", to walk to these games in Cincinnati. Also,
Georgetown College in
Georgetown was the location for the Bengals' summer training camp, until it was announced in 2012 that the Bengals would no longer use the facilities.
As in many states, especially those without major league professional sports teams, college athletics are prominent. This is especially true of the state's three
DivisionI Football Bowl Subdivision (FBS) programs, including the
Kentucky Wildcats, the
Western Kentucky Hilltoppers, and the
Louisville Cardinals. The
Wildcats,
Hilltoppers, and
Cardinals are among the most tradition-rich college men's basketball teams in the United States, combining for 11 National Championships and 24 NCAA Final Fours; all three are high on the lists of total all-time wins, wins per season, and average wins per season.
The Kentucky Wildcats are particularly notable, leading all DivisionI programs in all-time wins, win percentage, NCAA tournament appearances, and being second only to
UCLA in NCAA championships. Louisville Cardinals football, Louisville has also stepped onto the football scene in recent years, including winning the 2007 Orange Bowl as well as the 2013 Sugar Bowl, and also producing 2016 NCAA Division I FBS football season, 2016 Heisman Trophy winner Lamar Jackson. WKU Hilltoppers football, Western Kentucky, the 2002 NCAA Division I Football Championship, national champion in DivisionI-AA football (now Football Championship Subdivision (FCS)), completed its transition to DivisionI FBS football in 2009.
The
Kentucky Derby
The Kentucky Derby is a horse race held annually in Louisville, Kentucky, United States, almost always on the first Saturday in May, capping the two-week-long Kentucky Derby Festival. The competition is a Grade I stakes race for three-year ...
is a horse race held annually in Louisville on the first Saturday in May. The Valhalla Golf Club in Louisville has hosted several editions of the PGA Championship, Senior PGA Championship and Ryder Cup since the 1990s.
The NASCAR Cup Series held a race at the Kentucky Speedway in Sparta, Kentucky from 2011 to 2020. The NASCAR Nationwide Series and the Camping World Truck Series also raced there through 2020. The IndyCar Series previously raced there as well.
Ohio Valley Wrestling in Louisville was the primary location for training and rehab for WWE professional wrestlers from 2000 until 2008, when WWE moved its contracted talent to Florida Championship Wrestling. OVW later became the primary developmental territory for Total Nonstop Action Wrestling (TNA) from 2011 to 2013.
In 2014 Louisville City FC, a professional soccer team in the league then known as USL Pro and now as the United Soccer League, was announced. The team made its debut in 2015, playing home games at Louisville Slugger Field. In its first season, Louisville City was the official reserve side for Orlando City SC, who made its debut in Major League Soccer at the same time. That arrangement ended in 2016 when Orlando City established a Orlando City B, directly controlled reserve side in the USL.
Kentucky colonel
The distinction of being named a Kentucky colonel is the highest title of honor bestowed by the Commonwealth of Kentucky. Commissions for Kentucky colonels are given by the Governor of Kentucky, Governor and the
Secretary of State to individuals in recognition of noteworthy accomplishments and outstanding service to a community, state or the nation. The sitting Governor of Kentucky, governor of the Commonwealth of Kentucky bestows the honor of a colonel's commission (document), commission, by issuance of letters patent. Kentucky colonels are commissioned for life and act officially as the state's goodwill ambassadors.
See also
* Index of Kentucky-related articles
* Outline of Kentucky
Notes
References
Bibliography
Politics
Miller, Penny M. ''Kentucky Politics & Government: Do We Stand United?'' (1994)* Jewell, Malcolm E. and Everett W. Cunningham, ''Kentucky Politics'' (1968).
History
Surveys and reference
* Bodley, Temple and Samuel M. Wilson. ''History of Kentucky'' 4 vols. (1928).
* Harry M. Caudill, Caudill, Harry M., ''Night Comes to the Cumberlands'' (1963).
* Channing, Steven. ''Kentucky: A Bicentennial History'' (1977).
* Clark, Thomas Dionysius. ''A History of Kentucky'' (many editions, 1937–1992).
* Collins, Lewis. ''History of Kentucky'' (1880).
*
* Lowell H. Harrison, Harrison, Lowell H. and James C. Klotter. ''A New History of Kentucky'' (1997).
* Kleber, John E. et al. ''The Kentucky Encyclopedia'' (1992), standard reference history.
* James C. Klotter, Klotter, James C. ''Our Kentucky: A Study of the Bluegrass State'' (2000), high school text
* Lucas, Marion Brunson and Wright, George C. ''A History of Blacks in Kentucky'' 2 vols. (1992).
World-Wide Web Resources – Notable Kentucky African Americans* Share, Allen J. ''Cities in the Commonwealth: Two Centuries of Urban Life in Kentucky'' (1982).
* Wallis, Frederick A. and Hambleton Tapp. ''A Sesqui-Centennial History of Kentucky'' 4 vols. (1945).
* Ward, William S., ''A Literary History of Kentucky'' (1988) ().
WPA, ''Kentucky: A Guide to the Bluegrass State '' (1939) classic guide.
*
Specialized scholarly studies
Bakeless, John. ''Daniel Boone, Master of the Wilderness'' (1989)* Blakey, George T. ''Hard Times and New Deal in Kentucky, 1929–1939'' (1986)
* Coulter, E. Merton. ''The Civil War and Readjustment in Kentucky'' (1926)
* Davis, Alice. "Heroes: Kentucky's Artists from Statehood to the New Millennium" (2004)
* Ellis, William E. ''The Kentucky River'' (2000).
* Faragher, John Mack. ''Daniel Boone'' (1993)
Fenton, John H. ''Politics in the Border States: A Study of the Patterns of Political Organization, and Political Change, Common to the Border States: Maryland, West Virginia, Kentucky, and Missouri'' (1957)* Harlow, Luke E. ''Religion, Race, and the Making of Confederate Kentucky, 1830–1880.'' New York: Cambridge University Press, 2014.
* Ireland, Robert M. ''The County in Kentucky History'' (1976)
*
* Kelly, Andrew, Ed. "Kentucky by Design: The Decorative Arts and American Culture". Lexington, University Press of Kentucky, 2015.
* James C. Klotter, Klotter, James C. ''Kentucky: Portrait in Paradox, 1900–1950'' (1992)
* Pearce, John Ed. ''Divide and Dissent: Kentucky Politics, 1930–1963'' (1987)
* Remini, Robert V. ''Henry Clay: Statesman for the Union'' (1991).
Sonne, Niels Henry. ''Liberal Kentucky, 1780–1828'' (1939)* Tapp, Hambleton and James C. Klotter. ''Kentucky Decades of Discord, 1865–1900'' (1977)
Townsend, William H. ''Lincoln and the Bluegrass: Slavery and Civil War in Kentucky'' (1955)Waldrep, Christopher ''Night Riders: Defending Community in the Black Patch, 1890–1915'' (1993)tobacco wars
External links
*
*
Kentucky Department of TourismGPS Specific Map of Kentucky Destinations (map)USGS real-time, geographic, and other scientific resources of KentuckyEnergy & Environmental Data for KentuckyKentucky State Facts from USDAKentucky: Unbridled SpiritKentucky Virtual Library*
Kentucky State Databases– Annotated list of searchable databases produced by Kentucky state agencies and compiled by the Government Documents Roundtable of the American Library Association.
*
{{coord, 37, -86, dim:300000_region:US-KY_type:adm1st, name=Commonwealth of Kentucky, display=title
Kentucky,
1792 establishments in the United States
Southern United States
States and territories established in 1792
States of the United States
U.S. states with multiple time zones
Contiguous United States
 Central Kentucky, the bluegrass region, as well as Western Kentucky, were the areas of the state with the most slave owners. Planters cultivated tobacco and hemp (see Hemp in Kentucky) on plantations with the use of enslaved labor, and were noted for their quality livestock. During the 19th century, Kentucky slaveholders began to sell unneeded slaves to the
Central Kentucky, the bluegrass region, as well as Western Kentucky, were the areas of the state with the most slave owners. Planters cultivated tobacco and hemp (see Hemp in Kentucky) on plantations with the use of enslaved labor, and were noted for their quality livestock. During the 19th century, Kentucky slaveholders began to sell unneeded slaves to the  Kentucky is situated in the Upland South. A significant portion of eastern Kentucky is part of
Kentucky is situated in the Upland South. A significant portion of eastern Kentucky is part of  Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the
Kentucky can be divided into five primary regions: the  Located within the southeastern interior portion of North America, Kentucky has a climate that is best described as a
Located within the southeastern interior portion of North America, Kentucky has a climate that is best described as a  Kentucky has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than Alaska.
Kentucky is the only U.S. state to have a continuous border of rivers running along three of its sidesthe Mississippi River to the west, the
Kentucky has more navigable miles of water than any other state in the union, other than Alaska.
Kentucky is the only U.S. state to have a continuous border of rivers running along three of its sidesthe Mississippi River to the west, the  Kentucky has an expansive park system, which includes one national park, two National Recreation Areas, two National Historic Parks, two
Kentucky has an expansive park system, which includes one national park, two National Recreation Areas, two National Historic Parks, two  * Cumberland Gap, chief passageway through the Appalachian Mountains in early American history.
* Cumberland Falls, the only place in the Western Hemisphere where a " moonbow" may be regularly seen, due to the spray of the falls.
*
* Cumberland Gap, chief passageway through the Appalachian Mountains in early American history.
* Cumberland Falls, the only place in the Western Hemisphere where a " moonbow" may be regularly seen, due to the spray of the falls.
*  The United States Census Bureau determined that the population of Kentucky was 4,505,836 in 2020, increasing since the
The United States Census Bureau determined that the population of Kentucky was 4,505,836 in 2020, increasing since the  Early in its history, Kentucky gained recognition for its excellent farming conditions. It was the site of the first commercial winery in the United States (started in present-day
Early in its history, Kentucky gained recognition for its excellent farming conditions. It was the site of the first commercial winery in the United States (started in present-day  Tourism has become an increasingly important part of the Kentucky economy. In 2019 tourism grew to $7.6billion in economic impact. Key attractions include
Tourism has become an increasingly important part of the Kentucky economy. In 2019 tourism grew to $7.6billion in economic impact. Key attractions include  Horse Racing has long been associated with Kentucky.
Horse Racing has long been associated with Kentucky. 
 Kentucky maintains eight public four-year universities. There are two general tiers: major research institutions (the University of Kentucky and the University of Louisville) and regional universities, which encompass the remaining six schools. The regional schools have specific target counties that many of their programs are targeted towards (such as Forestry at Eastern Kentucky University or Cave Management at Western Kentucky University), however, most of their curriculum varies little from any other public university.
The University of Kentucky (UK) and the University of Louisville (UofL) have the highest academic rankings and admissions standards although the regional schools aren't without their national recognized departmentsexamples being Western Kentucky University's nationally ranked Journalism Department or Morehead State University offering one of the nation's only Space Science degrees. UK is the flagship and land grant of the system and has agriculture extension services in every county. The two research schools split duties related to the medical field, UK handles all medical outreach programs in the eastern half of the state while UofL does all medical outreach in the state's western half.
The state's sixteen public two-year colleges have been governed by the Kentucky Community and Technical College System since the passage of the Postsecondary Education Improvement Act of 1997, commonly referred to as House Bill 1. Before the passage of House Bill 1, most of these colleges were under the control of the University of Kentucky.
Transylvania University, a liberal arts university located in Lexington, was founded in 1780 as the oldest university west of the Allegheny Mountains.
Berea College, located at the extreme southern edge of the Bluegrass below the Cumberland Plateau, was the first coeducational college in the
Kentucky maintains eight public four-year universities. There are two general tiers: major research institutions (the University of Kentucky and the University of Louisville) and regional universities, which encompass the remaining six schools. The regional schools have specific target counties that many of their programs are targeted towards (such as Forestry at Eastern Kentucky University or Cave Management at Western Kentucky University), however, most of their curriculum varies little from any other public university.
The University of Kentucky (UK) and the University of Louisville (UofL) have the highest academic rankings and admissions standards although the regional schools aren't without their national recognized departmentsexamples being Western Kentucky University's nationally ranked Journalism Department or Morehead State University offering one of the nation's only Space Science degrees. UK is the flagship and land grant of the system and has agriculture extension services in every county. The two research schools split duties related to the medical field, UK handles all medical outreach programs in the eastern half of the state while UofL does all medical outreach in the state's western half.
The state's sixteen public two-year colleges have been governed by the Kentucky Community and Technical College System since the passage of the Postsecondary Education Improvement Act of 1997, commonly referred to as House Bill 1. Before the passage of House Bill 1, most of these colleges were under the control of the University of Kentucky.
Transylvania University, a liberal arts university located in Lexington, was founded in 1780 as the oldest university west of the Allegheny Mountains.
Berea College, located at the extreme southern edge of the Bluegrass below the Cumberland Plateau, was the first coeducational college in the 
 Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides service to Ashland, South Portsmouth, Maysville and Fulton. The ''
Amtrak, the national passenger rail system, provides service to Ashland, South Portsmouth, Maysville and Fulton. The ''
 The executive branch is headed by the governor, who serves as both head of state and head of government. The
The executive branch is headed by the governor, who serves as both head of state and head of government. The  Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a
Kentucky's legislative branch consists of a  Kentucky's body of laws, known as the Kentucky Revised Statutes (KRS), were enacted in 1942 to better organize and clarify the whole of Kentucky law. The statutes are enforced by local police, sheriffs and deputy sheriffs, and
Kentucky's body of laws, known as the Kentucky Revised Statutes (KRS), were enacted in 1942 to better organize and clarify the whole of Kentucky law. The statutes are enforced by local police, sheriffs and deputy sheriffs, and  Kentucky culture is generally considered to be firmly
Kentucky culture is generally considered to be firmly  Kentucky celebrates Confederate Memorial Day as a state holiday on June 3, on the anniversary of Jefferson Davis's birthday. The biggest day in American horse racing, the
Kentucky celebrates Confederate Memorial Day as a state holiday on June 3, on the anniversary of Jefferson Davis's birthday. The biggest day in American horse racing, the 

 Kentucky is the home of several sports teams such as Minor League Baseball's Triple-A
Kentucky is the home of several sports teams such as Minor League Baseball's Triple-A