|
Fincastle County
Fincastle County, Virginia, was created by act of the Virginia General Assembly April 8, 1772 from Botetourt County.Pendleton, William C. (1920)''History of Tazewell County and Southwest Virginia: 1748-1920'' pp. 255-57. W. C. Hill Printing Company. As colonial government considered Virginia's western extent to be the Mississippi River, that became Fincastle's western limit. Its eastern boundary was essentially the New River (Wood's River at the time, including what is today the Kanawha River), thus dividing Botetourt County from north to south. The new county encompassed all of present day Kentucky, plus southwestern West Virginia and a slice of Virginia's western "tail". Although no county seat was designated by the act creating the county, the colonial governor ordered it to be placed at the "Lead Mines" of present day Wythe County; the community of Austinville later developed there. The governor of Virginia Colony, John Murray, Earl of Dunmore and Viscount of Fincastle, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Botetourt County, Virginia
Botetourt County ( ) is a US county that lies in the Roanoke Region of the Commonwealth of Virginia. Located in the mountainous portion of the state, the county is bordered by two major ranges, the Blue Ridge Mountains and the Appalachian Mountains. Botetourt County was created in 1770 from part of Augusta County and was named for Norborne Berkeley, known as Lord Botetourt. It originally comprised a vast area, which included the southern portion of present-day West Virginia and all of Kentucky. Portions were set off to form new counties beginning in 1772, until the current borders were established in 1851. Botetourt County is part of the Roanoke Virginia Metropolitan Statistical Area, and the county seat is the town of Fincastle. As of the 2020 census, the county population was 33,596. History First proposed in the House of Burgesses in 1767, Botetourt County was created in 1770 from Augusta County. The county is named for Norborne Berkeley, Baron de Botetourt, more c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dunmore's Proclamation
Dunmore's Proclamation is a historical document signed on November 7, 1775, by John Murray, 4th Earl of Dunmore, royal governor of the British Colony of Virginia. The proclamation declared martial law and promised freedom for slaves of American revolutionaries who left their owners and joined the royal forces, becoming Black Loyalists. Most relevant historians agree that the proclamation was chiefly designed for practical and militaristic reasons rather than moral reasons, such as humanitarianism. Formally proclaimed on November 15, its publication prompted between 800 and 2000 slaves (from both patriot and loyalist owners) to run away and enlist with Dunmore. It also raised a furor among Virginia's slave-owning elites (again of both political persuasions), to whom the possibility of a slave rebellion was a major fear. The proclamation ultimately failed in meeting Dunmore's objectives; he was forced out of the colony in 1776, taking about 300 former slaves with him. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Regions And Territories Of The United States
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colonial Virginia Counties
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to: * Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology) Architecture * American colonial architecture * French Colonial * Spanish Colonial architecture Automobiles * Colonial (1920 automobile), the first American automobile with four-wheel brakes * Colonial (Shaw automobile), a rebranded Shaw sold from 1921 until 1922 * Colonial (1921 automobile), a car from Boston which was sold from 1921 until 1922 Places * The Colonial (Indianapolis, Indiana) * The Colonial (Mansfield, Ohio), a National Register of Historic Places listing in Richland County, Ohio * Ciudad Colonial (Santo Domingo), a historic central neighborhood of Santo Domingo * Colonial Country Club (Memphis), a golf course in Tennessee * Colonial Country Club (Fort Worth), a golf course in Texas ** Fort Worth Invitational or The Colonial, a PGA golf tournament Trains * ''Colonial'' (PRR train), a Pennsylvania Railroad run between Washington, DC and New York C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of West Virginia
The history of West Virginia stems from the 1861 Wheeling Convention, which was an assembly of northwestern Virginian Southern Unionists, who aimed to repeal the Ordinance of Secession that Virginia made during the American Civil War (1861–1865). It became one of two American states that formed during the American Civil War—the other being Nevada in 1864. It was the only state to form from another state during this time, splitting from Virginia. West Virginia was officially admitted as a U.S. state on June 20, 1863. The area that comprises West Virginia was originally part of the British Virginia Colony (1607–1776) and the western part of the U.S. state of Virginia (1776–1863). Western Virginia became sharply divided over the issue of secession from the Union, leading to the separation from Virginia, and formalized by West Virginia's admittance to the Union as a new state in 1863. West Virginia was one of five Civil War border states. During the late 19th and early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
History Of Kentucky
The prehistory and history of Kentucky span thousands of years, and have been influenced by the state's diverse geography and central location. Based on evidence in other regions, it is likely that the human history of Kentucky began sometime before 10,000 BCE. A gradual transition began from a hunter-gatherer economy to agriculture c. 1800 BCE. Around 900 CE, the Mississippian culture took root in western and central Kentucky; the Fort Ancient culture appeared in eastern Kentucky. Although they had many similarities, the Fort Ancient culture lacked the Mississippian's distinctive, ceremonial earthen mounds. The first Europeans to visit Kentucky arrived in the late 17th century was via the Ohio River from the northeast and from the southeast through a natural pass in the Appalachian Mountains. In 1769, frontiersman Daniel Boone while on the first of several hunting expeditions discovered the Cumberland Gap through the lower Appalachians. In a few short years ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commonwealth Of Kentucky
Kentucky ( , ), officially the Commonwealth of Kentucky, is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States and one of the states of the Upper South. It borders Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio to the north; West Virginia and Virginia to the east; Tennessee to the south; and Missouri to the west. Its northern border is defined by the Ohio River. Its capital is Frankfort, and its two largest cities are Louisville and Lexington. Its population was approximately 4.5 million in 2020. Kentucky was admitted into the Union as the 15th state on June 1, 1792, splitting from Virginia in the process. It is known as the "Bluegrass State", a nickname based on Kentucky bluegrass, a species of green grass found in many of its pastures, which has supported the thoroughbred horse industry in the center of the state. Historically, it was known for excellent farming conditions for this reason and the development of large tobacco plantations akin to those in Virginia and North Carolina in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Admission To The Union
Admission may refer to: Arts and media * "Admissions" (''CSI: NY''), an episode of ''CSI: NY'' * ''Admissions'' (film), a 2011 short film starring James Cromwell * ''Admission'' (film), a 2013 comedy film * ''Admission'', a 2019 album by Florida sludge metal band Torche * ''Admission'' (novel), a 2020 novel by Julie Buxbaum Legal proceedings * Admission (law), a statement that may be used in court against the person making it *Acceptance of admissible evidence in court *The process of official inclusion in a state, the opposite of secession Status granted to a person *University and college admission * Admission to the bar, change in status allowing an applicant to become part of a profession Other uses *The process by which patients enter into inpatient care *Admittance, the inverse of impedance See also *Admissibility (other) *List of U.S. states by date of admission to the Union A U.S. state, state of the United States is one of the 50 Federated state, constitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
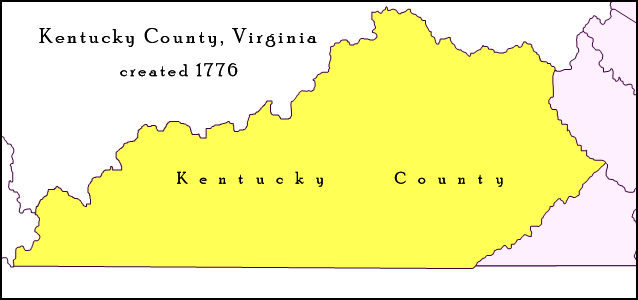
Kentucky County, Virginia
Kentucky County (then alternately spelled Kentucke County) was formed by the Commonwealth of Virginia from the western portion (beyond the Cumberland Mountains) of Fincastle County effective December 31, 1776. The name of the county was taken from a Native American place name that came to be associated with a river in east central Kentucky, and gave the Kentucky River its name. During the three and one-half years of Kentucky County's existence, its seat of government was Harrodstown (then also known as Oldtown, later renamed Harrodsburg). Kentucky County was abolished on June 30, 1780, when it was divided into Fayette, Jefferson, and Lincoln counties. Afterward, these counties and those set off from them later in that decade were designated collectively as the District of Kentucky by the Virginia House of Delegates. The counties of the district frequently petitioned both the Virginia legislature and the Continental Congress seeking statehood. Finally successful, the Commo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |