Java People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Java (; id, Jawa, ; jv, ꦗꦮ; su, ) is one of the Greater Sunda Islands in Indonesia. It is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south and the
Nusa Jawa: Silang Budaya, Bagian 2: Jaringan Asia
'. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama. An Indonesian translation of Lombard, Denys (1990). ''Le carrefour javanais. Essai d'histoire globale (The Javanese Crossroads: Towards a Global History) vol. 2''. Paris: Éditions de l'École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales. p. 12. According to Ma Huan's book (the Yingya Shenlan), the Chinese called Java Chao-Wa, and the island was called She-po in the past. Sulaiman al-Tajir al-Sirafi mentioned two notable islands which separated Arab and
 Java lies between
Java lies between  The area of Java is about . It is about long and up to wide. The island's longest river is the 600 km long
The area of Java is about . It is about long and up to wide. The island's longest river is the 600 km long
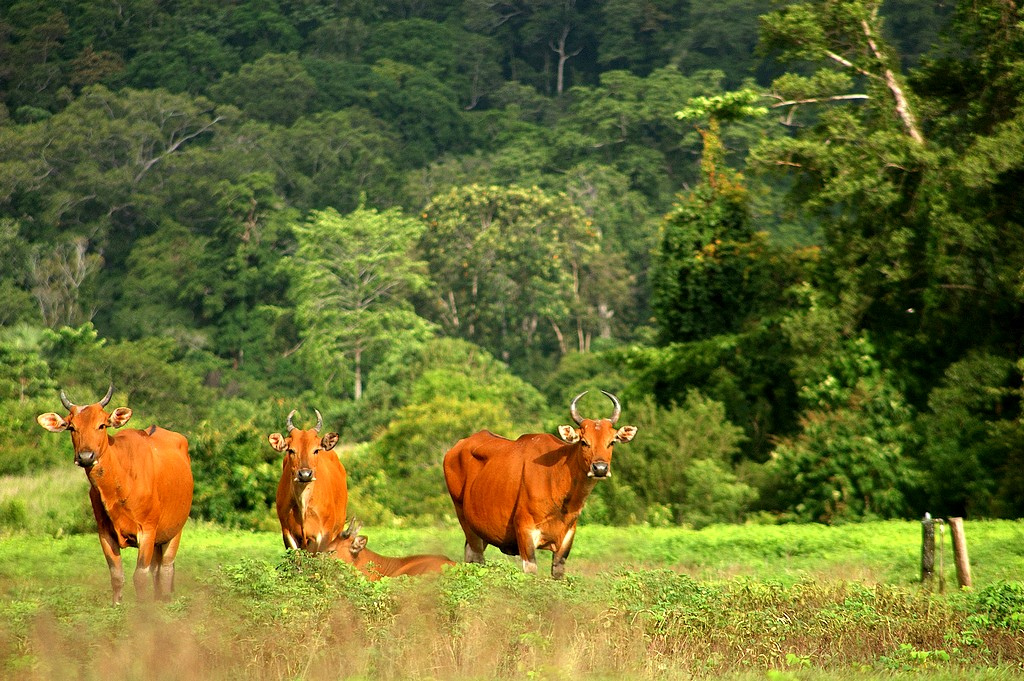 The natural environment of Java is tropical rainforest, with ecosystems ranging from coastal mangrove forest on the north coast, rocky coastal cliffs on the southern coast, and low-lying tropical forest to high altitude rainforest on the slopes of mountainous volcanic regions in the interior. The Javan environment and climate gradually alters from west to east; from wet and humid dense rainforest in western parts, to a dry savanna environment in the east, corresponding to the climate and rainfall in these regions.
The natural environment of Java is tropical rainforest, with ecosystems ranging from coastal mangrove forest on the north coast, rocky coastal cliffs on the southern coast, and low-lying tropical forest to high altitude rainforest on the slopes of mountainous volcanic regions in the interior. The Javan environment and climate gradually alters from west to east; from wet and humid dense rainforest in western parts, to a dry savanna environment in the east, corresponding to the climate and rainfall in these regions. Javan wildlife originally supported a rich biodiversity, where numbers of endemic species of flora and fauna flourished; such as the Javan rhinoceros, Javan banteng,
Javan wildlife originally supported a rich biodiversity, where numbers of endemic species of flora and fauna flourished; such as the Javan rhinoceros, Javan banteng,
 Fossilised remains of ''
Fossilised remains of ''

 The Taruma and
The Taruma and
 Java's contact with the European colonial powers began in 1522 with a treaty between the Sunda kingdom and the Portuguese in Malacca. After its failure, the Portuguese presence was confined to Malacca and to the eastern islands.
In 1596, a four-ship expedition led by Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutch contact with Indonesia. By the end of the 18th century the Dutch had extended their influence over the sultanates of the interior through the Dutch East India Company in Indonesia. Internal conflict prevented the Javanese from forming effective alliances against the Dutch. Remnants of the Mataram survived as the Surakarta (Solo) and Yogyakarta principalities. Javanese kings claimed to rule with divine authority and the Dutch helped them to preserve remnants of a Javanese aristocracy by confirming them as regents or district officials within the colonial administration.
Java's major role during the early part of the colonial period was as a producer of rice. In spice-producing islands like
Java's contact with the European colonial powers began in 1522 with a treaty between the Sunda kingdom and the Portuguese in Malacca. After its failure, the Portuguese presence was confined to Malacca and to the eastern islands.
In 1596, a four-ship expedition led by Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutch contact with Indonesia. By the end of the 18th century the Dutch had extended their influence over the sultanates of the interior through the Dutch East India Company in Indonesia. Internal conflict prevented the Javanese from forming effective alliances against the Dutch. Remnants of the Mataram survived as the Surakarta (Solo) and Yogyakarta principalities. Javanese kings claimed to rule with divine authority and the Dutch helped them to preserve remnants of a Javanese aristocracy by confirming them as regents or district officials within the colonial administration.
Java's major role during the early part of the colonial period was as a producer of rice. In spice-producing islands like 
 In 1815, there may have been five million people in Java. In the second half of the 18th century, population spurts began in districts along the north-central coast of Java, and in the 19th century population grew rapidly across the island. Factors for the great population growth include the impact of Dutch colonial rule including the imposed end to civil war in Java, the increase in the area under rice cultivation, and the introduction of food plants such as cassava and maize that could sustain populations that could not afford rice. Others attribute the growth to the taxation burdens and increased expansion of employment under the Cultivation System to which couples responded by having more children in the hope of increasing their families ability to pay tax and buy goods.
In 1815, there may have been five million people in Java. In the second half of the 18th century, population spurts began in districts along the north-central coast of Java, and in the 19th century population grew rapidly across the island. Factors for the great population growth include the impact of Dutch colonial rule including the imposed end to civil war in Java, the increase in the area under rice cultivation, and the introduction of food plants such as cassava and maize that could sustain populations that could not afford rice. Others attribute the growth to the taxation burdens and increased expansion of employment under the Cultivation System to which couples responded by having more children in the hope of increasing their families ability to pay tax and buy goods.
 Java has been traditionally dominated by an elite class, while the people in the lower classes were often involved in agriculture and fishing. The elite class in Java has evolved over the course of history, as cultural wave after cultural wave immigrated to the island. There is evidence that South Asian emigres were among this elite, as well as Arabian and Persian immigrants during the Islamic eras. More recently, Chinese immigrants have also become part of the economic elite of Java. Although politically the Chinese generally remain sidelined, there are notable exceptions, such as the former governor of Jakarta,
Java has been traditionally dominated by an elite class, while the people in the lower classes were often involved in agriculture and fishing. The elite class in Java has evolved over the course of history, as cultural wave after cultural wave immigrated to the island. There is evidence that South Asian emigres were among this elite, as well as Arabian and Persian immigrants during the Islamic eras. More recently, Chinese immigrants have also become part of the economic elite of Java. Although politically the Chinese generally remain sidelined, there are notable exceptions, such as the former governor of Jakarta,
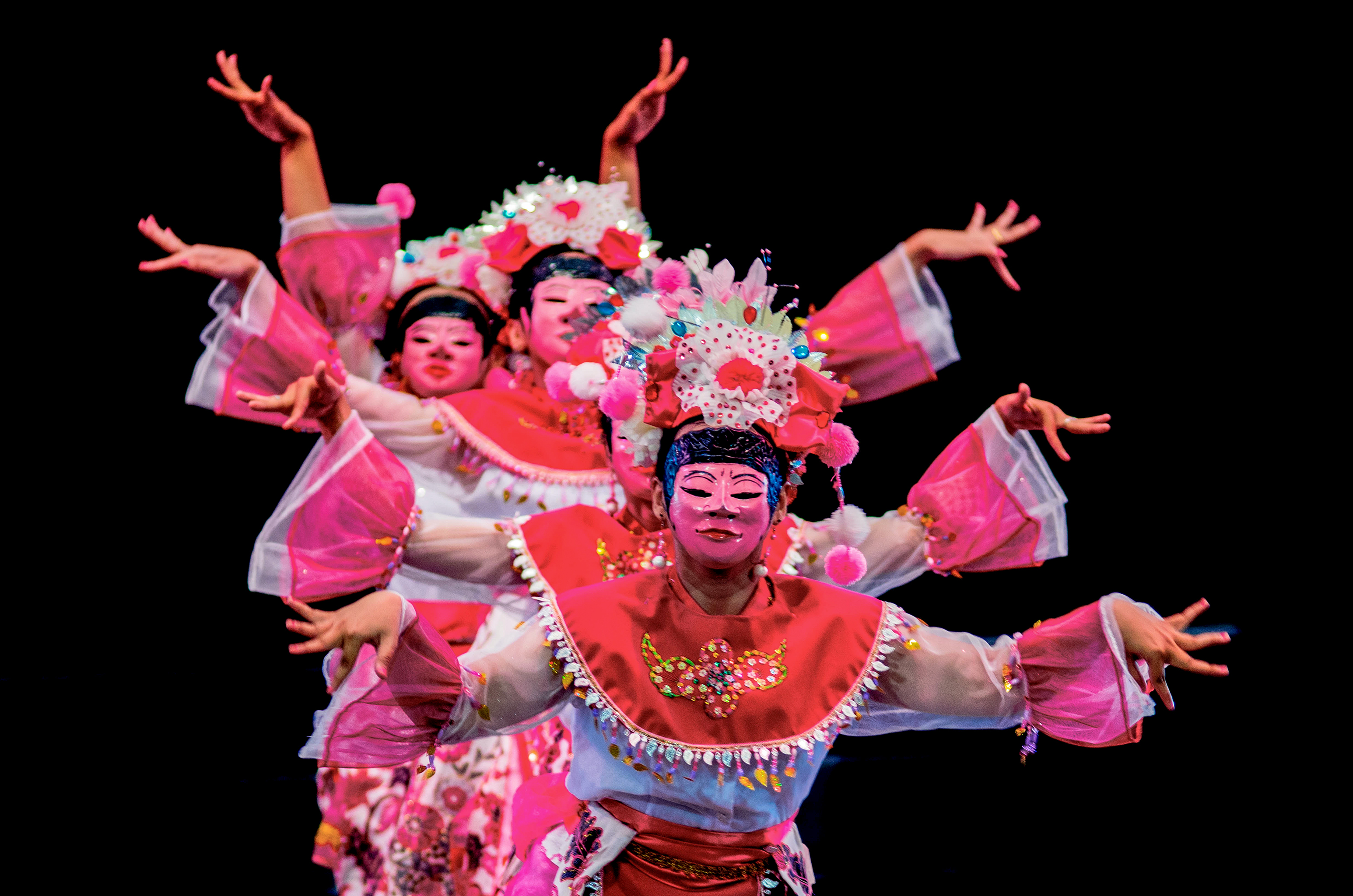 Despite its large population and in contrast to the other larger islands of Indonesia, Java is comparatively homogeneous in ethnic composition. Only two ethnic groups are native to the island—the Javanese and
Despite its large population and in contrast to the other larger islands of Indonesia, Java is comparatively homogeneous in ethnic composition. Only two ethnic groups are native to the island—the Javanese and  The Javanese prose text Tantu Pagelaran (circa 15th century) explained the mythical origin of the island and its volcanic nature.
Four major cultural areas exist on the island: the central part of Java or Yogyakarta is the Javanese people heartland and the north coast of the ''pasisir'' region, the
The Javanese prose text Tantu Pagelaran (circa 15th century) explained the mythical origin of the island and its volcanic nature.
Four major cultural areas exist on the island: the central part of Java or Yogyakarta is the Javanese people heartland and the north coast of the ''pasisir'' region, the  In the southwestern part of Central Java, which is usually named the Banyumasan region, a cultural mingling occurred; bringing together Javanese culture and Sundanese culture to create the Banyumasan culture. In the central Javanese court cities of Yogyakarta and
In the southwestern part of Central Java, which is usually named the Banyumasan region, a cultural mingling occurred; bringing together Javanese culture and Sundanese culture to create the Banyumasan culture. In the central Javanese court cities of Yogyakarta and
 The three major languages spoken on Java are Javanese,
The three major languages spoken on Java are Javanese,
File:Pura Parahyangan Agung Jagatkartta, Candi Siliwangi Shrine.jpg, A Hindu shrine dedicated to King Siliwangi in Pura Parahyangan Agung Jagatkarta, Bogor
File:Candi Mendut 1.jpg, Mendut Vihara, a Buddhist monastery near Mendut temple, Magelang
File:Masjid Agung Yogyakarta.jpg, Kauman Great Mosque, Masjid Gedhe Kauman in Yogyakarta, built in traditional Javanese multi-tiered roof
File:Ganjuran Church, exterior 01.jpg, Ganjuran Church in Bantul, built in traditional Javanese culture, Javanese architecture
Pre-Islamic Javan traditions have encouraged Islam in a mystical direction. There emerged in Java a loosely structured society of religious leadership, revolving around ''kyais'', possessing various degrees of proficiency in pre-Islamic and Islamic Folklore, lore, belief and practice. The kyais are the principal intermediaries between the villages masses and the realm of the supernatural. However, this very looseneess of kyai leadership structure has promoted schism (religion), schism. There were often sharp divisions between orthodox kyais, who merely instructed in Islamic law, with those who taught mysticism and those who sought reformed Islam with modern scientific concepts. As a result, there is a division between ''santri'', who believe that they are more orthodox in their Islamic belief and practice, with ''abangan'', who have mixed pre-Islamic animism, animistic and Hindu-Indian concepts with a superficial acceptance of Islamic belief.
There are also Christians, Christian communities, mostly in the larger cities, though some rural areas of south-central Java are strongly Catholic Church, Roman Catholic. Buddhism, Buddhist communities also exist in the major cities, primarily among the Chinese Indonesian. The Indonesian constitution recognises six official religions.
A wider effect of this division is the number of sects. In the middle of 1956, the Department of Religious Affairs in Yogyakarta reported 63 religious sects in Java other than the official Indonesian religions. Of these, 35 were in
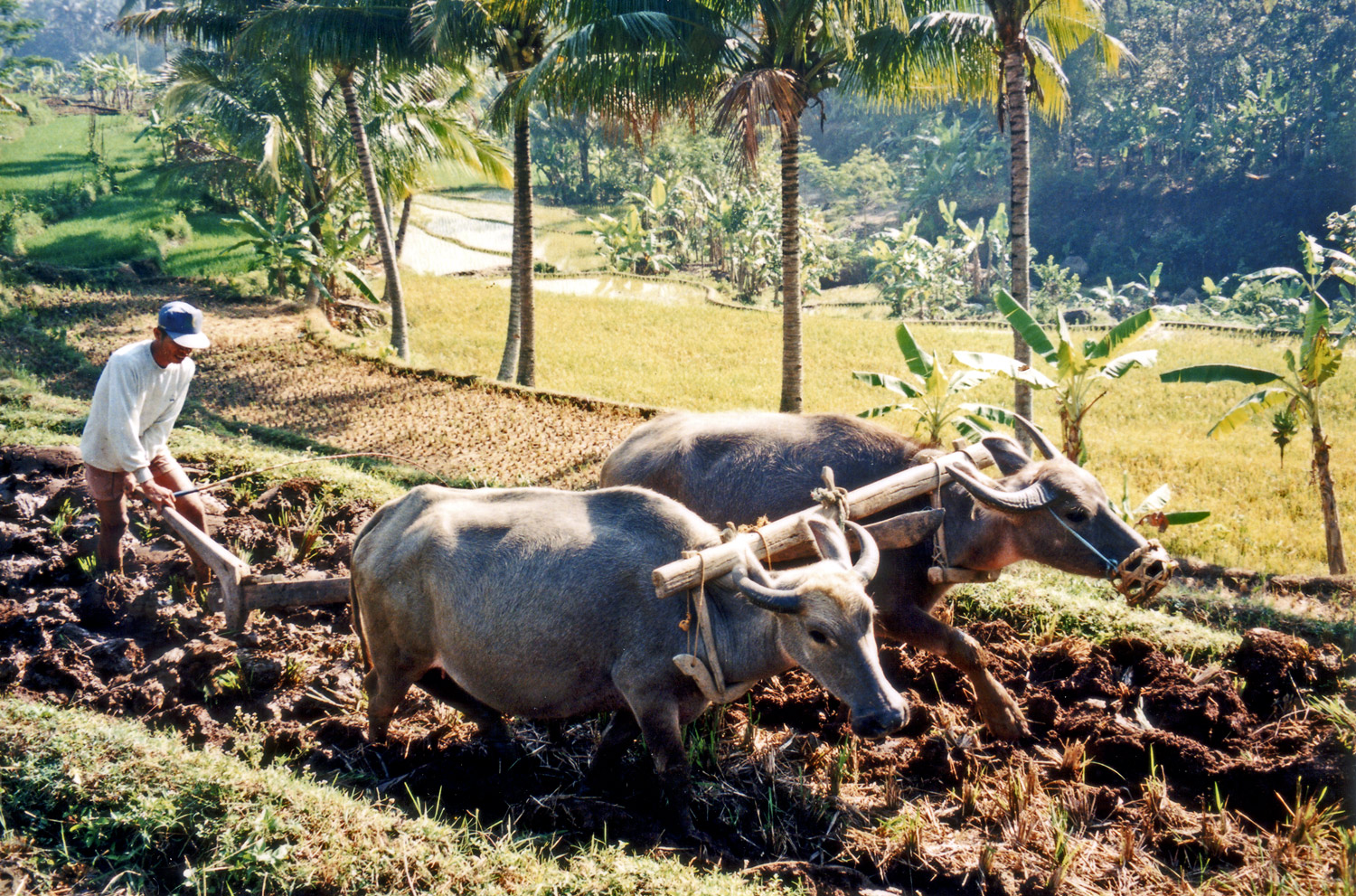 Initially the economy of Java relied heavily on rice agriculture. Ancient kingdoms such as the Tarumanagara, Mataram Kingdom, Mataram, and
Initially the economy of Java relied heavily on rice agriculture. Ancient kingdoms such as the Tarumanagara, Mataram Kingdom, Mataram, and  The VOC set their foothold on Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia in the 17th century and was succeeded by the
The VOC set their foothold on Batavia, Dutch East Indies, Batavia in the 17th century and was succeeded by the  Java has been Indonesia's most developed island since the Dutch East Indies era and continues to be so today in the modern Republic of Indonesia. The road transportation networks that have existed since ancient times were connected and perfected with the construction of Great Post Road, Java Great Post Road by Daendels in the early 19th century. It became the backbone of Java's road infrastructure and laid the base of North Coast Road (Java), Java North Coast Road ( id, Jalan Pantura, abbreviation from "Pantai Utara"). The need to transport commercial produces such as coffee from plantations in the interior of the island to the harbour on the coast spurred the construction of railway networks in Java. Today, industry, business, trade and services flourished in major cities of Java, such as
Java has been Indonesia's most developed island since the Dutch East Indies era and continues to be so today in the modern Republic of Indonesia. The road transportation networks that have existed since ancient times were connected and perfected with the construction of Great Post Road, Java Great Post Road by Daendels in the early 19th century. It became the backbone of Java's road infrastructure and laid the base of North Coast Road (Java), Java North Coast Road ( id, Jalan Pantura, abbreviation from "Pantai Utara"). The need to transport commercial produces such as coffee from plantations in the interior of the island to the harbour on the coast spurred the construction of railway networks in Java. Today, industry, business, trade and services flourished in major cities of Java, such as
Java and The Making of The Nation.
' Humaniora Journal, Gadjah Mada University. {{Authority control Java, Greater Sunda Islands Islands of Indonesia Maritime Southeast Asia
Java Sea
The Java Sea ( id, Laut Jawa, jv, Segara Jawa) is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its nort ...
to the north. With a population of 151.6 million people, Java is the world's most populous island, home to approximately 56% of the Indonesian population.
Indonesia's capital city, Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
, is on Java's northwestern coast. Many of the best known events in Indonesian history took place on Java. It was the centre of powerful Hindu-Buddhist empires, the Islamic sultanates, and the core of the colonial Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
. Java was also the center of the Indonesian struggle for independence during the 1930s and 1940s. Java dominates Indonesia politically, economically and culturally. Four of Indonesia's eight UNESCO world heritage sites are located in Java: Ujung Kulon National Park, Borobudur Temple, Prambanan Temple, and Sangiran Early Man Site
Sangiran is an archaeological excavation site in Java in Indonesia. According to a UNESCO report (1995) "Sangiran is recognized by scientists to be one of the most important sites in the world for studying fossil man, ranking alongside Zhoukou ...
.
Formed by volcanic eruptions due to geologic subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the ...
of the Australian Plate under the Sunda Plate
The Sunda Plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the Equator in the Eastern Hemisphere on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located.
The Sunda Plate was formerly considered a part of the Eurasian Plate, but the GPS measurements have ...
, Java is the 13th largest island in the world and the fifth largest in Indonesia by landmass at about . A chain of volcanic mountains is the east–west spine of the island.
Four main languages are spoken on the island: Javanese, Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
, Madurese, and Betawi. Javanese and Sundanese are the most spoken. The ethnic groups native to the island are the Javanese in the central and eastern parts and Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
in the western parts. The Madurese in the Eastern salient of Java are migrants from Madura Island, while the Betawi in the capital city of Jakarta are hybrids from various ethnic groups in Indonesia. Most residents are bilingual, speaking Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
(the official language of Indonesia) as their first or second language. While the majority of the people of Java are Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, Java's population comprises people of diverse religious beliefs, ethnicities, and cultures.
Java is divided into four administrative provinces: Banten, West Java, Central Java
Central Java ( id, Jawa Tengah) is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakarta in t ...
, and East Java, and two special regions, Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
and Yogyakarta.
Etymology
The origins of the name "Java" are not clear. One possibility is that the island was named after the ''jáwa-wut'' plant, which was said to be common in the island during the time, and that prior to Indianization the island had different names. There are other possible sources: the word ''jaú'' and its variations mean "beyond" or "distant".Raffles, Thomas E.: ''History of Java The History of Java can refer to:
* The history of the island of Java
* ''The History of Java'', an 1817 book on the history of the Java by Stamford Raffles, founder of modern Singapore
* The version history of the Java programming language
* The ...
''. Oxford University Press, 1965, p. 3. And, in Sanskrit ''yava'' means barley, a plant for which the island was famous. "Yavadvipa" is mentioned in India's earliest epic, the Ramayana. Sugriva
''This character is about the vanara, in the Ramayana.''
Sugriva ( sa, सुग्रीव, , ) is a character In the ancient Indian epic Ramayana. He is the younger brother of Vali, whom he succeeded as ruler of the vanara kingdom of Kishk ...
, the chief of Rama's army, dispatched his men to Yavadvipa, the island of Java, in search of Sita. It was hence referred to in India by the Sanskrit name "yāvaka dvīpa" (dvīpa = island). Java is mentioned in the ancient Tamil text '' Manimekalai'' by Chithalai Chathanar which states that Java had a kingdom with a capital called Nagapuram. Another source states that the word "Java" is derived from a Proto-Austronesian root word, meaning "home". The great island of Iabadiu or Jabadiu was mentioned in Ptolemy's '' Geographia'' composed around 150 CE in the Roman Empire. ''Iabadiu'' is said to mean "barley island", to be rich in gold, and have a silver town called Argyra at the west end. The name indicates Java and seems to be derived from the Sanskrit name Java-dvipa (Yavadvipa).The annual news of Songshu and Liangshu (5th century CE) referred to Java as 闍婆 (''She-pó'' or ''She-bó''), He-ling (640–818), then called it She-po again until the Yuan dynasty (1271–1368), where they began mentioning 爪哇 (''Zhao-Wa'' or ''Chao-Wa'').Lombard, Denys (2005)''Nusa Jawa: Silang Budaya, Bagian 2: Jaringan Asia
'. Jakarta: Gramedia Pustaka Utama. An Indonesian translation of Lombard, Denys (1990). ''Le carrefour javanais. Essai d'histoire globale (The Javanese Crossroads: Towards a Global History) vol. 2''. Paris: Éditions de l'École des Hautes Études en Sciences Sociales. p. 12. According to Ma Huan's book (the Yingya Shenlan), the Chinese called Java Chao-Wa, and the island was called She-po in the past. Sulaiman al-Tajir al-Sirafi mentioned two notable islands which separated Arab and
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and ...
: One is 800 farsakh long Al-Rami, which is identified as Sumatra, and the other is Zabaj
Zabag ( Indonesian: ''Sabak''; Chinese: 阇婆 or 闍婆 "''She-bó''"'','' "''Shepo''"; Sanskrit: ''Javaka''; Tamil: சாவகம் "''Savakam''"; Arabic: الزابج "''Zabaj''"; Latin: Jabad) is thought to have been an ancient kingdom loc ...
(Arabic: الزابج, Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
: Sabak), 400 farsakh in length, identified as Java. When John of Marignolli
Giovanni de' Marignolli ( la, Johannes Marignola;. ), variously anglicized as John of Marignolli or John of Florence, was a notable 14th-century Catholic European traveller to medieval China and India.
Life
Early life
Giovanni was born, probab ...
returned from China to Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label=Provençal dialect, Provençal or , ; la, Avenio) is the Prefectures in France, prefecture of the Vaucluse Departments of France, department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur Regions of France, region of So ...
, he stayed at the Kingdom of Saba for a few months, which he said had many elephants and was led by a queen; Saba may be his interpretation of She-bó.' Afanasij Nikitin, a merchant from Tver (in Russia), traveled to India in 1466 and described the land of java, which he call шабайте (shabait/šabajte).
Geography
Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
to the west and Bali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
to the east. Borneo lies to the north, and Christmas Island is to the south. It is the world's 13th largest island. Java is surrounded by the Java Sea
The Java Sea ( id, Laut Jawa, jv, Segara Jawa) is an extensive shallow sea on the Sunda Shelf, between the Indonesian islands of Borneo to the north, Java to the south, Sumatra to the west, and Sulawesi to the east. Karimata Strait to its nort ...
to the north, Sunda Strait
The Sunda Strait ( id, Selat Sunda) is the strait between the Indonesian islands of Java island, Java and Sumatra. It connects the Java Sea with the Indian Ocean.
Etymology
The strait takes its name from the Sunda Kingdom, which ruled the weste ...
to the west, the Indian Ocean to the south and Bali Strait and Madura Strait in the east.
Java is almost entirely of volcanic origin; it contains thirty-eight mountains forming an east–west spine that have at one time or another been active volcanoes. The highest volcano in Java is Mount Semeru, . The most active volcano in Java and also in Indonesia is Mount Merapi, . In total, Java has more than 150 mountains.
Java's mountains and highlands split the interior into a series of relatively isolated regions suitable for wet-rice cultivation; the rice lands of Java are among the richest in the world. Java was the first place where Indonesian coffee
Indonesia was the fourth-largest producer of coffee in the world in 2014.http://www.ico.org/prices/po-production.pdf Coffee cultivation in Indonesia began in the late 1600s and early 1700s, in the early Dutch colonial period, and has played an ...
was grown, starting in 1699. Today, coffea arabica
''Coffea arabica'' (), also known as the Arabic coffee, is a species of flowering plant in the coffee and madder family Rubiaceae. It is believed to be the first species of coffee to have been cultivated and is currently the dominant cultivar, r ...
is grown on the Ijen Plateau by small-holders and larger plantations.
 The area of Java is about . It is about long and up to wide. The island's longest river is the 600 km long
The area of Java is about . It is about long and up to wide. The island's longest river is the 600 km long Solo River
The Solo River (known in Indonesian as Bengawan Solo, with ''Bengawan'' being an Old Javanese word for ''river'', and ''Solo'' derived from the old name for Surakarta) is the longest river in the Indonesian island of Java, it is approximately 600 ...
. The river rises from its source in central Java at the Lawu
The Lawu ( jv, ꦭꦮꦸ), or Mount Lawu ( jv, ꦒꦸꦤꦸꦁꦭꦮꦸ, Gunung Lawu) is a massive compound stratovolcano straddling the border between East Java and Central Java, Indonesia. The north side is deeply eroded and the eastern ...
volcano, then flows north and eastward to its mouth in the Java Sea near the city of Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Indonesia, Indonesian province of East Java and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. L ...
. Other major rivers are Brantas
The Brantas is the longest river in East Java, Indonesia. It has a length of 320 km, and drains an area over 11,000 km2 from the southern slope of Mount Kawi-Kelud-Butak, Mount Wilis, and the northern slopes of Mount Liman-Limas, Mou ...
, Citarum
The Citarum River ( su, Walungan Citarum) is the longest and largest river in West Java, Indonesia. It is the third longest river in Java, after Bengawan Solo and Brantas. It plays an important role in the life of the people of West Java. It has ...
, Cimanuk and Serayu
The Serayu River is a river in Central Java, Indonesia, about 300 km southeast of the capital Jakarta.
Hydrology
The river spanned from northeast to southwest with length around 181 km, and crossring five ''kabupaten'' (regency) in Central ...
.
The average temperature ranges from to ; average humidity is 75%. The northern coastal plains are normally hotter, averaging during the day in the dry season. The south coast is generally cooler than the north, and highland areas inland are even cooler. The wet season begins in November and ends in April. During that rain falls mostly in the afternoons and intermittently during other parts of the year. The wettest months are January and February.
West Java is wetter than East Java, and mountainous regions receive much higher rainfall. The Parahyangan highlands of West Java receive over annually, while the north coast of East Java receives annually.
Natural environment
 The natural environment of Java is tropical rainforest, with ecosystems ranging from coastal mangrove forest on the north coast, rocky coastal cliffs on the southern coast, and low-lying tropical forest to high altitude rainforest on the slopes of mountainous volcanic regions in the interior. The Javan environment and climate gradually alters from west to east; from wet and humid dense rainforest in western parts, to a dry savanna environment in the east, corresponding to the climate and rainfall in these regions.
The natural environment of Java is tropical rainforest, with ecosystems ranging from coastal mangrove forest on the north coast, rocky coastal cliffs on the southern coast, and low-lying tropical forest to high altitude rainforest on the slopes of mountainous volcanic regions in the interior. The Javan environment and climate gradually alters from west to east; from wet and humid dense rainforest in western parts, to a dry savanna environment in the east, corresponding to the climate and rainfall in these regions. Javan wildlife originally supported a rich biodiversity, where numbers of endemic species of flora and fauna flourished; such as the Javan rhinoceros, Javan banteng,
Javan wildlife originally supported a rich biodiversity, where numbers of endemic species of flora and fauna flourished; such as the Javan rhinoceros, Javan banteng, Javan warty pig
The Javan warty pig (''Sus verrucosus''), also called Javan wild pig, is an even-toed ungulate in the family Suidae. It is endemic to the Indonesian islands Java and Bawean, and is considered extinct on Madura. It is listed as Endangered on the ...
, Javan hawk-eagle
The Javan hawk-eagle (''Nisaetus bartelsi'') is a medium-sized, dark brown raptor in the family Accipitridae. It is the national bird of Indonesia, where it is commonly referred to as Garuda, from the bird-like creatures in Hindu and Buddhist myt ...
, Javan peafowl, Javan silvery gibbon, Javan lutung
The East Javan langur (''Trachypithecus auratus''), also known as the ebony lutung, Javan langur or Javan lutung, is an Old World monkey from the Colobinae subfamily. It is most commonly glossy black with a brownish tinge to its legs, sides, and ...
, Java mouse-deer
The Java mouse-deer (''Tragulus javanicus'') is a species of even-toed ungulate in the family Tragulidae. When it reaches maturity it is about the size of a rabbit, making it the smallest living ungulate. It is found in forests in Java and perhap ...
, Javan rusa
The Javan rusa or Sunda sambar (''Rusa timorensis'') is a deer native to Indonesia and East Timor. Introduced populations exist in a wide variety of locations in the Southern Hemisphere.
Taxonomy
Seven subspecies of the Javan rusa are recognis ...
, and Javan leopard. With over 450 bird species and 37 endemic species, Java is a birdwatcher's paradise. There are about 130 freshwater fish species in Java. There are also several endemic amphibian species in Java, including 5 species of tree frogs
A tree frog (or treefrog) is any species of frog that spends a major portion of its lifespan in trees, known as an arboreal state. Several Lineage (evolution), lineages of frogs among the Neobatrachia have given rise to treefrogs, although they a ...
.
Since ancient times, people have opened the rainforest, altered the ecosystem, shaped the landscapes and created rice paddy and terraces to support the growing population. Javan rice terraces have existed for more than a millennium and had supported ancient agricultural kingdoms. The growing human population has put severe pressure on Java's wildlife, as rainforests were diminished and confined to highland slopes or isolated peninsulas. Some of Java's endemic species are now critically endangered, with some already extinct; Java used to have Javan tiger
The Javan tiger was a ''Panthera tigris sondaica'' population native to the Indonesian island of Java until the mid-1970s. It was hunted to extinction, and its natural habitat converted for agricultural land use and infrastructure. It was one of ...
s and Javan elephants, but both have been rendered extinct. Today, several national parks exist in Java that protect the remnants of its fragile wildlife, such as Ujung Kulon
Ujung Kulon National Park is at the westernmost tip of Java (island), Java, in Banten province of Indonesia. It includes the volcanic island group of Krakatoa in Lampung province, and other islands including Panaitan, as well as smaller offshore ...
, Mount Halimun-Salak, Gede Pangrango
Mount Gede Pangrango National Park is a national park in West Java, Indonesia. The park is centred on two volcanoes— Mount Gede and Mount Pangrango—and is 150 km² in area.
It evolved from already existing conservation areas, such as Ci ...
, Baluran, Meru Betiri, Bromo Tengger Semeru and Alas Purwo.
History
 Fossilised remains of ''
Fossilised remains of ''Homo erectus
''Homo erectus'' (; meaning "upright man") is an extinct species of archaic human from the Pleistocene, with its earliest occurrence about 2 million years ago. Several human species, such as '' H. heidelbergensis'' and '' H. antecessor' ...
'', popularly known as the " Java Man", dating back 1.3 million years were found along the banks of the Bengawan Solo River.
The island's exceptional fertility and rainfall allowed the development of wet-field rice cultivation, which required sophisticated levels of cooperation between villages. Out of these village alliances, small kingdoms developed. The chain of volcanic mountains and associated highlands running the length of Java kept its interior regions and peoples separate and relatively isolated. Before the advent of Islamic states and European colonialism, the rivers provided the main means of communication, although Java's many rivers are mostly short. Only the Brantas river and Solo river could provide long-distance communication and this way their valleys supported the centers of major kingdoms. A system of roads, permanent bridges, and toll gates is thought to have been established in Java by at least the mid-17th century. Local powers could disrupt the routes as could the wet season and road use was highly dependent on constant maintenance. Consequently, communication between Java's population was difficult.
The emergence of civilization on the island of Java is often associated with the story of Aji Saka
Aji Saka is a Javanese legend that tells the story of how civilization came to Java, brought by the legendary first king of Java named Aji Saka, and the mythical story of the origin of Javanese script.
Origin
Aji Saka is said to have come from B ...
from 78 AD. Although Aji Saka is said to be the bearer of civilization on Java, the story received several objections and rebuttals from other historical sources. Valmiki's Ramayana, made around 500 BC, records that Java already had a governmental organization long before the story:"Yawadwipa is decorated with seven kingdoms, gold and silver islands, rich in gold mines, and there is Cicira (cold) Mountain that touches the sky with its peak."The Greek geographer Ptolemy called the island as Yabadiou or Sabadiou ( grc, Ιαβαδίου or Σαβαδίου). According to Chinese record '' Míng Shǐ'', the Javanese kingdom was founded in 65 BC, or 143 years before the story of Aji Saka began. The story of Aji Saka is a Neo Javanese story. This story has not yet been found to be relevant in the Old Javanese text. This story tells of events in the Medang Kamulan kingdom in Java in the past. At that time, the king of Medang Kamulan Prabu Dewata Cengkar was replaced by Aji Saka. This story is considered as an allegory of the entry of Indians into Java. Referring to the Liang dynasty information, the Javanese kingdom was divided into two: the pre-Hinduism kingdom and the post-Hindu kingdom, which began in 78 AD.
Hindu–Buddhist kingdoms era

 The Taruma and
The Taruma and Sunda Sunda may refer to:
Europe
* Sunda, Faroe Islands
India
* Sunda (asura), an asura brother of Upasunda
* Sunda (clan), a clan (gotra) of Jats in Haryana and Rajasthan, India
Southeast Asia
* Sundanese (disambiguation)
** Sundanese people ...
kingdoms of western Java appeared in the 4th and 7th centuries respectively, while the Kalingga Kingdom sent embassies to China starting in 640. However, the first major principality was the Mataram Kingdom that was founded in central Java at the beginning of the 8th century. Mataram's religion centered on the Hindu god Shiva, and the kingdom produced some of Java's earliest Hindu temples on the Dieng Plateau. Around the 8th century, the Sailendra dynasty
The Shailendra dynasty (, derived from Sanskrit combined words ''Śaila'' and ''Indra'', meaning "King of the Mountain", also spelled Sailendra, Syailendra or Selendra) was the name of a notable Indianised dynasty that emerged in 8th-century ...
rose in Kedu Plain and become the patron of Mahayana Buddhism. This ancient kingdom built monuments such as the 9th century Borobudur and Prambanan in central Java.
Around the 10th century, the center of power shifted from central to eastern Java. The eastern Javanese kingdoms of Kediri Kediri can refer to:
* Kediri (historical kingdom), a medieval kingdom occupying territory in present-day Indonesia
* Kediri (city), a modern-day city in East Java, Indonesia
** The Kediri meteorite of c. 1940, which fell in East Java, Indonesia ( ...
, Singhasari
Singhasari ( jv, ꦏꦫꦠꦺꦴꦤ꧀ꦱꦶꦔ꧀ꦲꦱꦫꦶ, translit=Karaton Singhasari or , id, Kerajaan Singasari) was a Javanese Hindu kingdom located in east Java between 1222 and 1292. The kingdom succeeded the Kingdom of Kediri as ...
and Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
were mainly dependent on rice agriculture, yet also pursued trade within the Indonesian archipelago, and with China and India. Majapahit was established by Wijaya, and by the end of the reign of Hayam Wuruk (r. 1350–89) it claimed sovereignty over the entire Indonesian archipelago, although control was likely limited to Java, Bali, and Madura. Hayam Wuruk's prime minister, Gajah Mada, led many of the kingdom's territorial conquests. Previous Javanese kingdoms had their power based on agriculture, however, Majapahit took control of ports and shipping lanes and became Java's first commercial empire. With the death of Hayam Wuruk and the coming of Islam to Indonesia, Majapahit went into decline.
Spread of Islam and rise of Islamic sultanates
Islam became the dominant religion in Java at the end of the 16th century. During this era, the Islamic kingdoms of Demak, Cirebon, and Banten were ascendant. TheMataram Sultanate
The Sultanate of Mataram () was the last major independent Javanese kingdom on the island of Java before it was colonised by the Dutch. It was the dominant political force radiating from the interior of Central Java from the late 16th centu ...
became the dominant power of central and eastern Java at the end of the 16th century. The principalities of Surabaya and Cirebon were eventually subjugated such that only Mataram and Banten were left to face the Dutch in the 17th century.
Colonial periods
 Java's contact with the European colonial powers began in 1522 with a treaty between the Sunda kingdom and the Portuguese in Malacca. After its failure, the Portuguese presence was confined to Malacca and to the eastern islands.
In 1596, a four-ship expedition led by Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutch contact with Indonesia. By the end of the 18th century the Dutch had extended their influence over the sultanates of the interior through the Dutch East India Company in Indonesia. Internal conflict prevented the Javanese from forming effective alliances against the Dutch. Remnants of the Mataram survived as the Surakarta (Solo) and Yogyakarta principalities. Javanese kings claimed to rule with divine authority and the Dutch helped them to preserve remnants of a Javanese aristocracy by confirming them as regents or district officials within the colonial administration.
Java's major role during the early part of the colonial period was as a producer of rice. In spice-producing islands like
Java's contact with the European colonial powers began in 1522 with a treaty between the Sunda kingdom and the Portuguese in Malacca. After its failure, the Portuguese presence was confined to Malacca and to the eastern islands.
In 1596, a four-ship expedition led by Cornelis de Houtman was the first Dutch contact with Indonesia. By the end of the 18th century the Dutch had extended their influence over the sultanates of the interior through the Dutch East India Company in Indonesia. Internal conflict prevented the Javanese from forming effective alliances against the Dutch. Remnants of the Mataram survived as the Surakarta (Solo) and Yogyakarta principalities. Javanese kings claimed to rule with divine authority and the Dutch helped them to preserve remnants of a Javanese aristocracy by confirming them as regents or district officials within the colonial administration.
Java's major role during the early part of the colonial period was as a producer of rice. In spice-producing islands like Banda
Banda may refer to:
People
*Banda (surname)
*Banda Prakash (born 1954), Indian politician
*Banda Kanakalingeshwara Rao (1907–1968), Indian actor
*Banda Karthika Reddy (born 1977), Indian politician
*Banda Singh Bahadur (1670–1716), Sikh warr ...
, rice was regularly imported from Java, to supply the deficiency in means of subsistence.
During the Napoleonic wars in Europe, the Netherlands fell to France, as did its colony in the East Indies. During the short-lived Daendels administration, as French proxy rule on Java, the construction of the Great Post Road was commenced in 1808. The road, spanning from Anyer in Western Java to Panarukan in East Java, served as a military supply route and was used in defending Java from British invasion. In 1811, Java was captured by the British, becoming a possession of the British Empire, and Sir Stamford Raffles was appointed as the island's governor. In 1814, Java was returned to the Dutch under the terms of the Treaty of Paris.
 In 1815, there may have been five million people in Java. In the second half of the 18th century, population spurts began in districts along the north-central coast of Java, and in the 19th century population grew rapidly across the island. Factors for the great population growth include the impact of Dutch colonial rule including the imposed end to civil war in Java, the increase in the area under rice cultivation, and the introduction of food plants such as cassava and maize that could sustain populations that could not afford rice. Others attribute the growth to the taxation burdens and increased expansion of employment under the Cultivation System to which couples responded by having more children in the hope of increasing their families ability to pay tax and buy goods.
In 1815, there may have been five million people in Java. In the second half of the 18th century, population spurts began in districts along the north-central coast of Java, and in the 19th century population grew rapidly across the island. Factors for the great population growth include the impact of Dutch colonial rule including the imposed end to civil war in Java, the increase in the area under rice cultivation, and the introduction of food plants such as cassava and maize that could sustain populations that could not afford rice. Others attribute the growth to the taxation burdens and increased expansion of employment under the Cultivation System to which couples responded by having more children in the hope of increasing their families ability to pay tax and buy goods. Cholera
Cholera is an infection of the small intestine by some strains of the bacterium ''Vibrio cholerae''. Symptoms may range from none, to mild, to severe. The classic symptom is large amounts of watery diarrhea that lasts a few days. Vomiting and ...
claimed 100,000 lives in Java in 1820.
The advent of trucks and railways where there had previously only been buffalo and carts, telegraph systems, and more coordinated distribution systems under the colonial government all contributed to famine elimination in Java, and in turn, population growth. There were no significant famines in Java from the 1840s through to the Japanese occupation in the 1940s.Taylor (2003), p. 254. However, other sources claimed the Dutch's Cultivation system is linked to famines and epidemics in the 1840s, firstly in Cirebon and then Central Java
Central Java ( id, Jawa Tengah) is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakarta in t ...
, as cash crops such as indigo and sugar had to be grown instead of rice.
Independence
Indonesian nationalism first took hold in Java in the early 20th century, and the struggle to secure the country's independence following World War II was centered in Java. In 1949, Indonesian independence was recognized.Administration
Java is divided into four provinces and two special regions: * Banten, capital: Serang * West Java, capital:Bandung
Bandung ( su, ᮘᮔ᮪ᮓᮥᮀ, Bandung, ; ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of West Java. It has a population of 2,452,943 within its city limits according to the official estimates as at mid 2021, making it the fourth most ...
*Central Java
Central Java ( id, Jawa Tengah) is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakarta in t ...
, capital: Semarang
Semarang ( jv, ꦏꦸꦛꦯꦼꦩꦫꦁ , Pegon: سماراڠ) is the capital and largest city of Central Java province in Indonesia. It was a major port during the Dutch colonial era, and is still an important regional center and port today. ...
* East Java, capital: Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Indonesia, Indonesian province of East Java and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. L ...
* Special Capital Region of Jakarta
* Special Region of Yogyakarta, capital: Yogyakarta
Demographics
Demographic profile
 Java has been traditionally dominated by an elite class, while the people in the lower classes were often involved in agriculture and fishing. The elite class in Java has evolved over the course of history, as cultural wave after cultural wave immigrated to the island. There is evidence that South Asian emigres were among this elite, as well as Arabian and Persian immigrants during the Islamic eras. More recently, Chinese immigrants have also become part of the economic elite of Java. Although politically the Chinese generally remain sidelined, there are notable exceptions, such as the former governor of Jakarta,
Java has been traditionally dominated by an elite class, while the people in the lower classes were often involved in agriculture and fishing. The elite class in Java has evolved over the course of history, as cultural wave after cultural wave immigrated to the island. There is evidence that South Asian emigres were among this elite, as well as Arabian and Persian immigrants during the Islamic eras. More recently, Chinese immigrants have also become part of the economic elite of Java. Although politically the Chinese generally remain sidelined, there are notable exceptions, such as the former governor of Jakarta, Basuki Tjahaja Purnama
Basuki Tjahaja Purnama (, Pha̍k-fa-sṳ: ''Chûng Van-ho̍k''; born 29 June 1966) is an Indonesian businessman, politician, and former governor of Jakarta. He is also known by his Hakka Chinese nickname Ahok (). He was the second minority gover ...
. Though Java is increasingly becoming more modern and urban, only 75% of the island has electricity. Villages and their rice paddies are still a common sight. Unlike the rest of Java, the population growth in Central Java remains low. Central Java however has a younger population than the national average. The slow population growth can in part be attributed to the choice by many people to leave the more rural Central Java for better opportunities and higher incomes in the bigger cities. Java's population continues to rapidly increase despite many Javanese leaving the island. This is somewhat due to the fact that Java is the business, academic, and cultural hub of Indonesia, which attracts millions of non-Javanese people to its cities. The population growth is most intense in the regions surrounding Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
and Bandung
Bandung ( su, ᮘᮔ᮪ᮓᮥᮀ, Bandung, ; ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of West Java. It has a population of 2,452,943 within its city limits according to the official estimates as at mid 2021, making it the fourth most ...
, which is reflected through the demographic diversity in those areas.
Population development
With a combined population of 151.6 million in the 2020 census (including Madura's 4.0 million), Java is the most populous major island in the world and is home to 56% of Indonesia's population. At nearly 1,200 people per km2 in 2020, it is also one of the most densely populated parts of the world, on a par with Bangladesh. Every region of the island has numerous volcanoes, with the people left to share the remaining flatter land. Because of this, many coasts are heavily populated and cities ring around the valleys surrounding volcanic peaks. The population growth rate more than doubled in economically depressed Central Java in the latest 2010–2020 period vs 2000–2010, indicative of migration or other issues; there were significant volcanic eruptions during the earlier period. Approximately 45% of the population of Indonesia is ethnically Javanese, while Sundanese make a large portion of Java's population as well. The western third of the island (West Java, Banten, and DKI Jakarta) has an even higher population density, of roughly 1,563 per square kilometer and accounts for the lion's share of the population growth of Java. It is home to three metropolitan areas, Greater Jakarta (with outlying areas of Greater Serang and GreaterSukabumi
, nickname = id, Kota Santri en, City of Learners
, image_map = Map of West Java highlighting Sukabumi City.svg
, map_caption = Location within West Java
, mapsize =
, pushpin_map = Ind ...
), Greater Bandung, and Greater Cirebon.
1) Other islands are included in this figure, but are very small in population and area, Nusa Barung 100 km2, Bawean 196 km2, Karimunjawa 78 km2, Kambangan 121 km2, Panaitan 170 km2, Thousand Islands 8.7 km2 – with a combined population of roughly 90,000.
2) Land area of provinces updated in 2010 Census figures, areas by 2020 may be different from past results.
From the 1970s to the fall of the Suharto
Suharto (; ; 8 June 1921 – 27 January 2008) was an Indonesian army officer and politician, who served as the second and the longest serving president of Indonesia. Widely regarded as a military dictator by international observers, Suharto ...
regime in 1998, the Indonesian government ran transmigration programs aimed at resettling the population of Java on other less populated islands of Indonesia. This program has met with mixed results, sometimes causing conflicts between the locals and the recently arrived settlers. Nevertheless, it has caused Java's share of the nation's population to progressively decline.
Jakarta and its outskirts, being the dominant metropolis, is also home to people from all over the nation. East Java is also home to ethnic Balinese, as well as large numbers of Madurans due to their historic poverty.
Ethnicity and culture
 Despite its large population and in contrast to the other larger islands of Indonesia, Java is comparatively homogeneous in ethnic composition. Only two ethnic groups are native to the island—the Javanese and
Despite its large population and in contrast to the other larger islands of Indonesia, Java is comparatively homogeneous in ethnic composition. Only two ethnic groups are native to the island—the Javanese and Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
. A third group is the Madurese, who inhabit the island of Madura off the northeast coast of Java, and have immigrated to East Java in large numbers since the 18th century. The Javanese comprise about two-thirds of the island's population, while the Sundanese and Madurese account for 38% and 10% respectively. The fourth group is the Betawi people that speak a dialect of Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, they are the descendants of the people living around Batavia
Batavia may refer to:
Historical places
* Batavia (region), a land inhabited by the Batavian people during the Roman Empire, today part of the Netherlands
* Batavia, Dutch East Indies, present-day Jakarta, the former capital of the Dutch East In ...
from around the 17th century. Betawis are creole people, mostly descended from various Indonesian archipelago ethnic groups such as Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
, Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
, Javanese, Balinese, Minang, Bugis
The Bugis people (pronounced ), also known as Buginese, are an ethnicity—the most numerous of the three major linguistic and ethnic groups of South Sulawesi (the others being Makassar and Toraja), in the south-western province of Sulawe ...
, Makassar
Makassar (, mak, ᨆᨀᨔᨑ, Mangkasara’, ) is the capital of the Indonesian province of South Sulawesi. It is the largest city in the region of Eastern Indonesia and the country's fifth-largest urban center after Jakarta, Surabaya, Med ...
, Ambonese
The Ambonese, also known as South Moluccans, are an Indonesian ethnic group of mixed Austronesian and Melanesian origin. They are majority Christians followed by Muslims. The Ambonese are from Ambon Island in Maluku, an island group east of Sula ...
, mixed with foreign ethnic groups such as Portuguese, Dutch, Arab, Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of va ...
and Indian brought to or attracted to Batavia to meet labour needs. They have a culture and language distinct from the surrounding Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
and Javanese.
 The Javanese prose text Tantu Pagelaran (circa 15th century) explained the mythical origin of the island and its volcanic nature.
Four major cultural areas exist on the island: the central part of Java or Yogyakarta is the Javanese people heartland and the north coast of the ''pasisir'' region, the
The Javanese prose text Tantu Pagelaran (circa 15th century) explained the mythical origin of the island and its volcanic nature.
Four major cultural areas exist on the island: the central part of Java or Yogyakarta is the Javanese people heartland and the north coast of the ''pasisir'' region, the Sunda Sunda may refer to:
Europe
* Sunda, Faroe Islands
India
* Sunda (asura), an asura brother of Upasunda
* Sunda (clan), a clan (gotra) of Jats in Haryana and Rajasthan, India
Southeast Asia
* Sundanese (disambiguation)
** Sundanese people ...
lands (Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
: , ''Tatar'' ''Sunda'') in the western part of Java and Parahyangan as the heartland, the eastern salient of Java also known as Blambangan. Madura makes up a fifth area having close cultural ties with coastal eastern Java. The ''kejawen of Javanese'' culture is the island's most dominant. Java's remaining aristocracy is based here, and it is the region from where the majority of Indonesia's army, business, and political elite originate. Its language, arts, and etiquette are regarded as the island's most refined and exemplary. The territory from Banyumas
Banyumas ( jv, ꦧꦚꦸꦩꦱ꧀, formerly spelt "Banjoemas") Regency is a regency ( id, kabupaten) in the southwestern part of Central Java province in Indonesia. Its capital is the town of Purwokerto, but that town no longer has a central adm ...
in the west through to Blitar in the east and encompasses Indonesia's most fertile and densely populated agricultural land.''''
 In the southwestern part of Central Java, which is usually named the Banyumasan region, a cultural mingling occurred; bringing together Javanese culture and Sundanese culture to create the Banyumasan culture. In the central Javanese court cities of Yogyakarta and
In the southwestern part of Central Java, which is usually named the Banyumasan region, a cultural mingling occurred; bringing together Javanese culture and Sundanese culture to create the Banyumasan culture. In the central Javanese court cities of Yogyakarta and Surakarta
Surakarta ( jv, ꦯꦸꦫꦏꦂꦠ), known colloquially as Solo ( jv, ꦱꦭ; ), is a city in Central Java, Indonesia. The 44 km2 (16.2 sq mi) city adjoins Karanganyar Regency and Boyolali Regency to the north, Karanganyar Regency and Sukoh ...
, contemporary kings trace their lineages back to the pre-colonial Islamic kingdoms that ruled the region, making those places especially strong repositories of classical Javanese culture. Classic arts of Java include gamelan music and wayang
, also known as ( jv, ꦮꦪꦁ, translit=wayang), is a traditional form of puppet theatre play originating from the Indonesian island of Java. refers to the entire dramatic show. Sometimes the leather puppet itself is referred to as . Perfor ...
puppet shows.
Java was the site of many influential kingdoms in the Southeast Asian region, and as a result, many literary works have been written by Javanese authors. These include ''Ken Arok and Ken Dedes'', the story of the orphan who usurped his king, and married the queen of the ancient Javanese kingdom; and translations of '' Ramayana'' and ''Mahabharata''. Pramoedya Ananta Toer is a famous contemporary Indonesian author, who has written many stories based on his own experiences of having grown up in Java, and takes many elements from Javanese folklore and historical legends.
Languages
Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
and Madurese. Other languages spoken include Betawi (a Malay
Malay may refer to:
Languages
* Malay language or Bahasa Melayu, a major Austronesian language spoken in Indonesia, Malaysia, Brunei and Singapore
** History of the Malay language, the Malay language from the 4th to the 14th century
** Indonesi ...
dialect local to the Jakarta region), Osing language, Osing, Banyumasan, and Tenggerese people, Tenggerese (closely related to Javanese), Baduy language, Baduy and Bantenese language, Bantenese (closely related to Sundanese), Kangean language, Kangeanese (closely related to Madurese), and Balinese language, Balinese. The vast majority of the population also speaks Indonesian
Indonesian is anything of, from, or related to Indonesia, an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It may refer to:
* Indonesians, citizens of Indonesia
** Native Indonesians, diverse groups of local inhabitants of the archipelago
** Indonesian ...
, often as a second language.
Religion
South Asia, Indian influences came first with Shaivism and Buddhism penetrating deeply into society, blending with indigenous tradition and culture. One Conduit (spiritualism), conduit for this were the asceticism, ascetics, called ''resi'', who taught mystical practices. A ''resi'' lived surrounded by students, who took care of their master's daily needs. Resi's authorities were merely ceremonial. At the courts, Brahmin clerics and ''pudjangga'' (sacred literati) legitimised rulers and linked Hinduism, Hindu cosmology to their political needs. Small Hindu enclaves are scattered throughout Java, but there is a large Hindu population along the eastern coast nearestBali
Bali () is a province of Indonesia and the westernmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands. East of Java and west of Lombok, the province includes the island of Bali and a few smaller neighbouring islands, notably Nusa Penida, Nusa Lembongan, and Nu ...
, especially around the town of Banyuwangi.
The coming of Islam, strengthened the status structure of this traditional religious pattern. More than 90 percent of the people of Java are Muslims, on a broad continuum between ''abangan'' (more traditional) and ''santri'' (more modernist). Muslim scholars (''Kyai'') became the new religious elite as Hindu influences receded. Islam recognises no hierarchy of religious leaders nor a formal Clergy, priesthood, but the Dutch East India Company, Dutch colonial government established an elaborate rank order for mosque and other Islamic preaching schools. In Javanese ''pesantren'' (Islamic schools), The ''Kyai'' perpetuated the tradition of the ''resi''. Students around him provided his needs, even peasants around the school.
Central Java
Central Java ( id, Jawa Tengah) is a province of Indonesia, located in the middle of the island of Java. Its administrative capital is Semarang. It is bordered by West Java in the west, the Indian Ocean and the Special Region of Yogyakarta in t ...
, 22 in West Java and six in East Java. These include Javanese beliefs, Kejawen, Javanese beliefs, Sumarah, Subud, etc. Their total membership is difficult to estimate as many of their adherents identify themselves with one of the official religions.Beatty, Andrew, ''Varieties of Javanese Religion: An Anthropological Account'', Cambridge University Press 1999, Sunda Wiwitan is a traditional Sundanese
Sundanese may refer to:
* Sundanese people
* Sundanese language
* Sundanese script
Standard Sundanese script (''Aksara Sunda Baku'', ) is a writing system which is used by the Sundanese people. It is built based on Old Sundanese script (' ...
religion, its adherents still exist in several villages.
Economy
 Initially the economy of Java relied heavily on rice agriculture. Ancient kingdoms such as the Tarumanagara, Mataram Kingdom, Mataram, and
Initially the economy of Java relied heavily on rice agriculture. Ancient kingdoms such as the Tarumanagara, Mataram Kingdom, Mataram, and Majapahit
Majapahit ( jv, ꦩꦗꦥꦲꦶꦠ꧀; ), also known as Wilwatikta ( jv, ꦮꦶꦭ꧀ꦮꦠꦶꦏ꧀ꦠ; ), was a Javanese people, Javanese Hinduism, Hindu-Buddhism, Buddhist thalassocracy, thalassocratic empire in Southeast Asia that was ba ...
were dependent on rice yields and tax. Java was famous for rice surpluses and rice export since ancient times, and rice agriculture contributed to the population growth of the island. Trade with other parts of Asia such as ancient India and China flourished as early as the 4th century, as evidenced by Chinese ceramics found on the island dated to that period. Java also took part in the global trade of Maluku Islands, Maluku spice from ancient times in the Majapahit era, until well into the Dutch East India Company (VOC) era.
Dutch East Indies
The Dutch East Indies, also known as the Netherlands East Indies ( nl, Nederlands(ch)-Indië; ), was a Dutch colony consisting of what is now Indonesia. It was formed from the nationalised trading posts of the Dutch East India Company, which ...
in the 19th century. During these colonial times, the Dutch introduced the cultivation of commercial plants in Java, such as sugarcane, rubber, coffee, tea, and quinine. In the 19th and early 20th century, Javanese coffee gained global popularity. Thus, the name "Java" today has become a synonym for coffee.
 Java has been Indonesia's most developed island since the Dutch East Indies era and continues to be so today in the modern Republic of Indonesia. The road transportation networks that have existed since ancient times were connected and perfected with the construction of Great Post Road, Java Great Post Road by Daendels in the early 19th century. It became the backbone of Java's road infrastructure and laid the base of North Coast Road (Java), Java North Coast Road ( id, Jalan Pantura, abbreviation from "Pantai Utara"). The need to transport commercial produces such as coffee from plantations in the interior of the island to the harbour on the coast spurred the construction of railway networks in Java. Today, industry, business, trade and services flourished in major cities of Java, such as
Java has been Indonesia's most developed island since the Dutch East Indies era and continues to be so today in the modern Republic of Indonesia. The road transportation networks that have existed since ancient times were connected and perfected with the construction of Great Post Road, Java Great Post Road by Daendels in the early 19th century. It became the backbone of Java's road infrastructure and laid the base of North Coast Road (Java), Java North Coast Road ( id, Jalan Pantura, abbreviation from "Pantai Utara"). The need to transport commercial produces such as coffee from plantations in the interior of the island to the harbour on the coast spurred the construction of railway networks in Java. Today, industry, business, trade and services flourished in major cities of Java, such as Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
, Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Indonesia, Indonesian province of East Java and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. L ...
, Semarang
Semarang ( jv, ꦏꦸꦛꦯꦼꦩꦫꦁ , Pegon: سماراڠ) is the capital and largest city of Central Java province in Indonesia. It was a major port during the Dutch colonial era, and is still an important regional center and port today. ...
, and Bandung
Bandung ( su, ᮘᮔ᮪ᮓᮥᮀ, Bandung, ; ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of West Java. It has a population of 2,452,943 within its city limits according to the official estimates as at mid 2021, making it the fourth most ...
; while some traditional Sultanate cities such as Yogyakarta, Surakarta
Surakarta ( jv, ꦯꦸꦫꦏꦂꦠ), known colloquially as Solo ( jv, ꦱꦭ; ), is a city in Central Java, Indonesia. The 44 km2 (16.2 sq mi) city adjoins Karanganyar Regency and Boyolali Regency to the north, Karanganyar Regency and Sukoh ...
, and Cirebon preserved its royal legacy and has become the centre of art, culture and tourism. Industrial estates are also growing in towns on northern coast of Java, especially around Cilegon, Tangerang, Bekasi, Karawang, Gresik and Sidoarjo. The toll road highway networks was built and expanded since the New Order until the present day, connecting major urban centres and surrounding areas, such as in and around Jakarta
Jakarta (; , bew, Jakarte), officially the Special Capital Region of Jakarta ( id, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta) is the capital and largest city of Indonesia. Lying on the northwest coast of Java, the world's most populous island, Jakarta ...
and Bandung
Bandung ( su, ᮘᮔ᮪ᮓᮥᮀ, Bandung, ; ) is the capital city of the Indonesian province of West Java. It has a population of 2,452,943 within its city limits according to the official estimates as at mid 2021, making it the fourth most ...
; also the ones in Cirebon, Semarang
Semarang ( jv, ꦏꦸꦛꦯꦼꦩꦫꦁ , Pegon: سماراڠ) is the capital and largest city of Central Java province in Indonesia. It was a major port during the Dutch colonial era, and is still an important regional center and port today. ...
and Surabaya
Surabaya ( jv, ꦱꦸꦫꦧꦪ or jv, ꦯꦹꦫꦨꦪ; ; ) is the capital city of the Provinces of Indonesia, Indonesian province of East Java and the List of Indonesian cities by population, second-largest city in Indonesia, after Jakarta. L ...
. In addition to these motorways, Java has 16 national highways.
Based on the statistical data by the year of 2021 released by Statistics Indonesia (''Badan Pusat Statistik''), Java alone contributes around 60% of Indonesia's GDP or equivalent to US$686 billion (int$2.0 trillion, PPP).
See also
*History of Indonesia *List of monarchs of Java *Javanese people *Sundanese people * Betawi peopleReferences
Sources
*Further reading
* *Padmo, Soegijanto (2000).Java and The Making of The Nation.
' Humaniora Journal, Gadjah Mada University. {{Authority control Java, Greater Sunda Islands Islands of Indonesia Maritime Southeast Asia