Janina Appelqvist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ioannina ( el, Ιωάννινα ' ), often called Yannena ( ' ) within Greece, is the capital and largest city of the Ioannina regional unit and of Epirus, an
GOV. results of permanent population 2011
, p. 10571 (p. 97 of pdf), and in Excel format
Table of permanent population 2011
from the sit
Hellenic Statistical AuthorityArchived
24 November 2017. Retrieved 2018-01-09. It lies at an elevation of approximately
''The Muslim Bonaparte: diplomacy and orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece''
Princeton University Press, 1999. . p. 63-66 Ioannina was ceded to Greece in 1913 following the
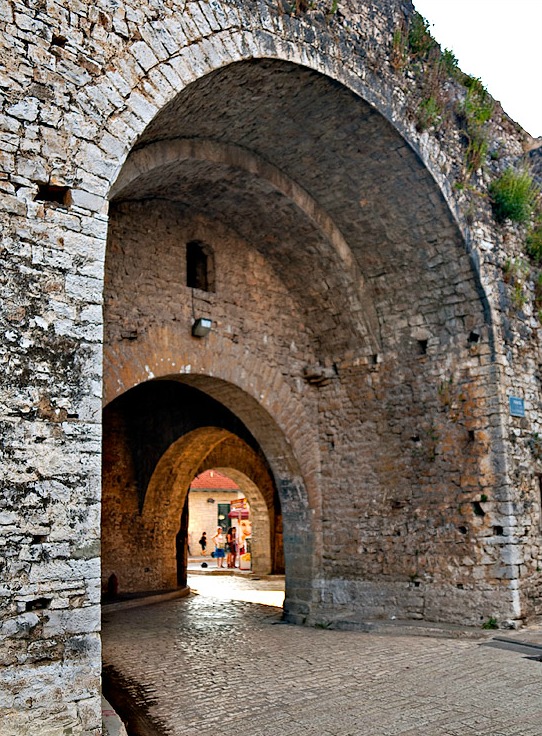 The first indications of human presence in Ioannina basin are dated back to the Paleolithic period (24,000 years ago) as testified by findings in the cavern of Kastritsa. During classical antiquity the basin was inhabited by the Molossians and four of their settlements have been identified there. Despite the extensive destruction suffered in Molossia during the Roman conquest of 167 BC, settlement continued in the basin albeit no longer in an urban pattern.
The exact time of Ioannina's foundation is unknown, but it is commonly identified with an unnamed new, "well-fortified" city, recorded by the historian Procopius as having been built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I for the inhabitants of ancient
The first indications of human presence in Ioannina basin are dated back to the Paleolithic period (24,000 years ago) as testified by findings in the cavern of Kastritsa. During classical antiquity the basin was inhabited by the Molossians and four of their settlements have been identified there. Despite the extensive destruction suffered in Molossia during the Roman conquest of 167 BC, settlement continued in the basin albeit no longer in an urban pattern.
The exact time of Ioannina's foundation is unknown, but it is commonly identified with an unnamed new, "well-fortified" city, recorded by the historian Procopius as having been built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I for the inhabitants of ancient
 Under Michael I, the city was enlarged and fortified anew. The
Under Michael I, the city was enlarged and fortified anew. The
 Under Ottoman rule, Ioannina remained an administrative centre, as the seat of the Sanjak of Ioannina, and experienced a period of relative stability and prosperity. The first Ottoman tax registers for the city dates to 1564, and records 50 Muslim households and 1,250 Christian ones; another register from 15 years later mentions Jews as well.
In 1611 the city suffered a serious setback as a result of a peasant revolt led by Dionysius the Philosopher, the Metropolitan of Larissa. The Greek inhabitants of the city were unaware of the intent of the fighting as previous successes of Dionysius had depended on the element of surprise. Much confusion ensued as Turks and Christians ended up indiscriminately fighting friend and foe alike. The revolt ended in the abolition of all privileges granted to the Christian inhabitants, who were driven away from the castle area and had to settle around it. From then onwards, Turks and Jews were to be established in the castle area. The ''School of the Despots'' at the Church of the Taxiarchs, that had been operating since 1204, was closed. Aslan Pasha also destroyed the monastery of St. John the Baptist within the city walls in 1618 erected in its place the Aslan Pasha Mosque, today housing the Municipal Ethnographic Museum of Ioannina.Γεώργιος Ι. Σουλιώτης ''Γιάννινα (Οδηγός Δημοτικού Μουσείου και Πόλεως'' 1975 The Ottoman reprisals in the wake of the revolt included the confiscation of many '' timars'' previously granted to Christian '' sipahis''; this began a wave of conversions to Islam by the local gentry, who became the so-called ''Tourkoyanniotes'' (Τoυρκογιαννιώτες). The Ottoman traveller Evliya Çelebi, who visited the city in , counted 37 quarters, of which 18 Muslim, 14 Christian, 4 Jewish and 1 Gypsy. He estimated the population at 4,000 hearths.
Under Ottoman rule, Ioannina remained an administrative centre, as the seat of the Sanjak of Ioannina, and experienced a period of relative stability and prosperity. The first Ottoman tax registers for the city dates to 1564, and records 50 Muslim households and 1,250 Christian ones; another register from 15 years later mentions Jews as well.
In 1611 the city suffered a serious setback as a result of a peasant revolt led by Dionysius the Philosopher, the Metropolitan of Larissa. The Greek inhabitants of the city were unaware of the intent of the fighting as previous successes of Dionysius had depended on the element of surprise. Much confusion ensued as Turks and Christians ended up indiscriminately fighting friend and foe alike. The revolt ended in the abolition of all privileges granted to the Christian inhabitants, who were driven away from the castle area and had to settle around it. From then onwards, Turks and Jews were to be established in the castle area. The ''School of the Despots'' at the Church of the Taxiarchs, that had been operating since 1204, was closed. Aslan Pasha also destroyed the monastery of St. John the Baptist within the city walls in 1618 erected in its place the Aslan Pasha Mosque, today housing the Municipal Ethnographic Museum of Ioannina.Γεώργιος Ι. Σουλιώτης ''Γιάννινα (Οδηγός Δημοτικού Μουσείου και Πόλεως'' 1975 The Ottoman reprisals in the wake of the revolt included the confiscation of many '' timars'' previously granted to Christian '' sipahis''; this began a wave of conversions to Islam by the local gentry, who became the so-called ''Tourkoyanniotes'' (Τoυρκογιαννιώτες). The Ottoman traveller Evliya Çelebi, who visited the city in , counted 37 quarters, of which 18 Muslim, 14 Christian, 4 Jewish and 1 Gypsy. He estimated the population at 4,000 hearths.
 Despite the repression and conversions in the 17th century, and the prominence of the Muslim population in the city's affairs, Ioannina retained its Christian majority throughout Ottoman rule, and the Greek language retained a dominant position;
Despite the repression and conversions in the 17th century, and the prominence of the Muslim population in the city's affairs, Ioannina retained its Christian majority throughout Ottoman rule, and the Greek language retained a dominant position; 
 Thus the ''Epiphaniou'' School was founded in 1647 by a Greek merchant of Ioannite origin resident in Venice, Epiphaneios Igoumenos. The ''Gioumeios'' School was founded in 1676 by a benefaction from another wealthy Ioannite Greek from Venice, Emmanuel Goumas. It was renamed ''Balaneios'' by its rector,
Thus the ''Epiphaniou'' School was founded in 1647 by a Greek merchant of Ioannite origin resident in Venice, Epiphaneios Igoumenos. The ''Gioumeios'' School was founded in 1676 by a benefaction from another wealthy Ioannite Greek from Venice, Emmanuel Goumas. It was renamed ''Balaneios'' by its rector,
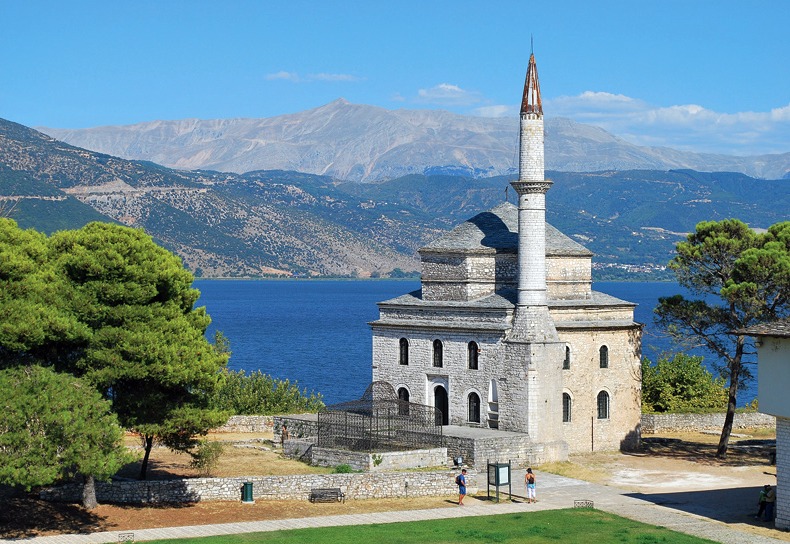 In 1788 the city became the center of the territory ruled by
In 1788 the city became the center of the territory ruled by
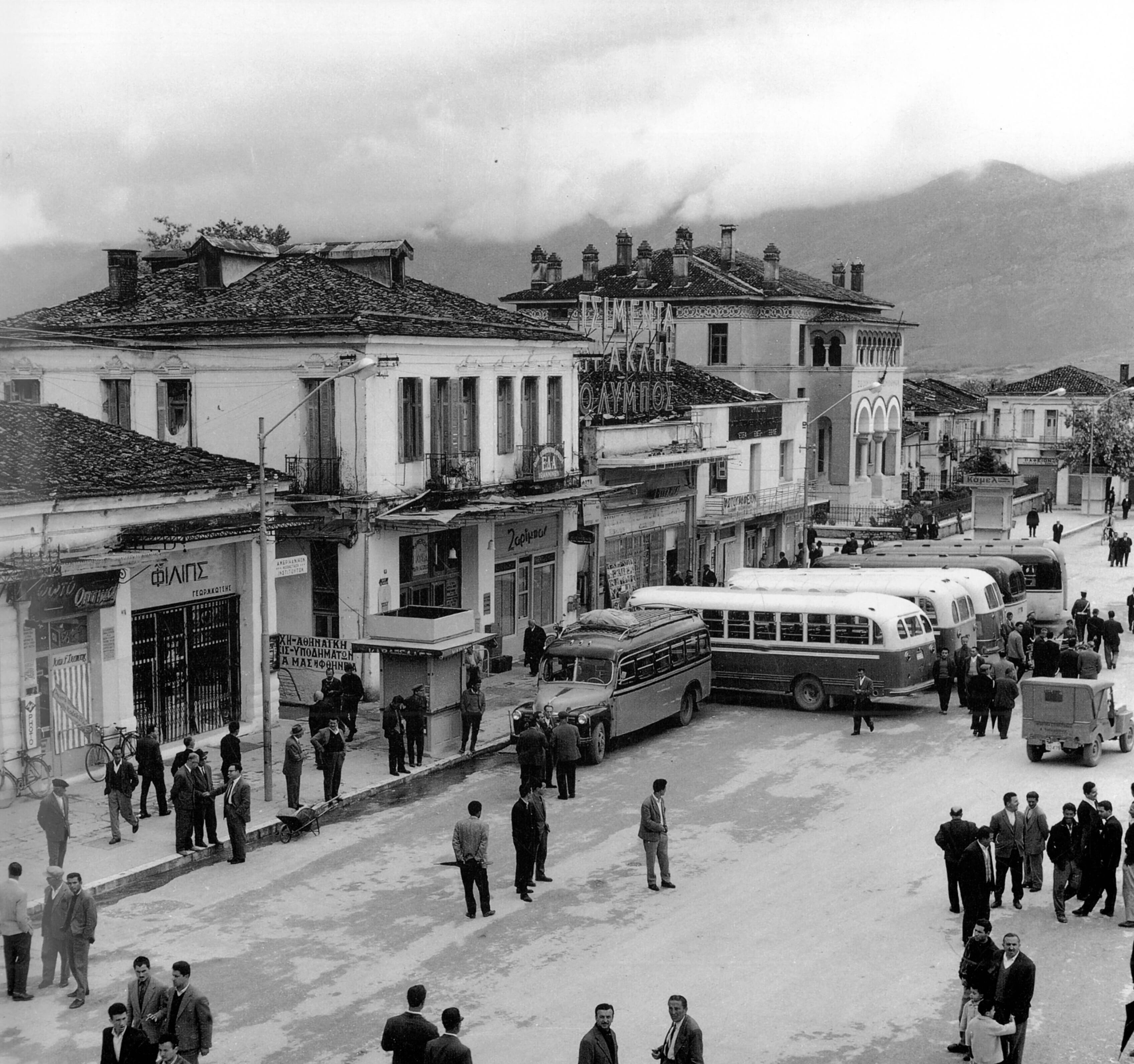
 In 1869, a great part of Ioannina was destroyed by fire. The marketplace was soon reconstructed according to the plans of the German architect Holz, thanks to the personal interest of Ahmet Rashim Pasha, the local governor. Communities of people from Ioannina living abroad were active in financing the construction of most of the city's churches, schools and other elegant buildings of charitable establishments. The first bank of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottoman Bank, opened its first branch in Greece in Ioannina, which shows the power of the city in world trade in the 19th century. As the 19th century came to a close, signs of national agitation emerged among some parts of the city' s population. In 1877 for example, Albanian leaders sent a memorandum to the Ottoman government demanding, among other things, the establishment of Albanian language schools and various Muslim Albanians of the Vilayet formed in Ioannina a committee which aimed at defending Albanian rights. The Greek population of the region authorized a committee to present to European governments their wish for union with Greece; as a result
In 1869, a great part of Ioannina was destroyed by fire. The marketplace was soon reconstructed according to the plans of the German architect Holz, thanks to the personal interest of Ahmet Rashim Pasha, the local governor. Communities of people from Ioannina living abroad were active in financing the construction of most of the city's churches, schools and other elegant buildings of charitable establishments. The first bank of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottoman Bank, opened its first branch in Greece in Ioannina, which shows the power of the city in world trade in the 19th century. As the 19th century came to a close, signs of national agitation emerged among some parts of the city' s population. In 1877 for example, Albanian leaders sent a memorandum to the Ottoman government demanding, among other things, the establishment of Albanian language schools and various Muslim Albanians of the Vilayet formed in Ioannina a committee which aimed at defending Albanian rights. The Greek population of the region authorized a committee to present to European governments their wish for union with Greece; as a result
 According to the local Greek scholar
According to the local Greek scholar  There was a Romaniote Jewish community living in Ioannina before World War II, in addition to a very small number of Sephardi. According to
There was a Romaniote Jewish community living in Ioannina before World War II, in addition to a very small number of Sephardi. According to
Kehila Kedosha Janina Synagogue and Museum retrieved 5 January 2009Raptis, Alekos and Tzallas, Thumios, ''Deportation of Jews of Ioannina'', Kehila Kedosha Janina Synagogue and Museum, 28 July 2005
URL accessed 5 January 2009 The Kehila Kedosha Yashan Synagogue remains locked, only opened for visitors on request. Emigrant Romaniotes return every summer and open the old synagogue. The last time a Bar Mitzvah (the Jewish ritual for celebrating the
 One of the most notable attractions of Ioannina is the inhabited island of Lake Pamvotis which is simply referred to as Island of Ioannina. The island is a short ferry trip from the mainland and can be reached on small motorboats running on varying frequencies depending on the season. The monastery of St Panteleimon, where
One of the most notable attractions of Ioannina is the inhabited island of Lake Pamvotis which is simply referred to as Island of Ioannina. The island is a short ferry trip from the mainland and can be reached on small motorboats running on varying frequencies depending on the season. The monastery of St Panteleimon, where
 At the south-eastern edge of the town on a rocky peninsula of Lake Pamvotis, the castle was the administrative heart of the
At the south-eastern edge of the town on a rocky peninsula of Lake Pamvotis, the castle was the administrative heart of the





 The University of Ioannina ( Greek: Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων, ''Panepistimio Ioanninon'') is a university five kilometres southwest of Ioannina. The university was founded in 1964, as a charter of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and became an independent university in 1970. Today, the university is one of the leading academic institutions in Greece.Top 500 (401 to 500) – The Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2011–201
The University of Ioannina ( Greek: Πανεπιστήμιο Ιωαννίνων, ''Panepistimio Ioanninon'') is a university five kilometres southwest of Ioannina. The university was founded in 1964, as a charter of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki and became an independent university in 1970. Today, the university is one of the leading academic institutions in Greece.Top 500 (401 to 500) – The Times Higher Education World University Rankings 2011–201
/ref>UniversityRankings.ch (SERI) 2015 – University of Ioannin
Retrieved in 3 February 2016. As of 2017, there was a student population of 25,000 enrolled at the university (21,900 at the undergraduate level and 3,200 at the postgraduate level) and 580 faculty members, while teaching is further supplemented by 171 teaching fellows and 132 laboratory staff. The university administrative services are staffed with 420 employees.


 *
*
Air Sea Lines
flew from Lake Pamvotis to
Municipality of Ioannina
Ioannina
– The Greek National Tourism Organization
Ioannina travel guide
"Here Their Stories Will Be Told..." The Valley of the Communities at Yad Vashem, Ioannina
at Yad Vashem website {{Authority control Greek prefectural capitals Greek regional capitals Historic Jewish communities Municipalities of Epirus (region) Populated places in Ioannina (regional unit)
administrative region
Administrative division, administrative unit,Article 3(1). country subdivision, administrative region, subnational entity, constituent state, as well as many similar terms, are generic names for geographical areas into which a particular, ind ...
in north-western Greece. According to the 2011 census, the city population was 65,574, while the municipality had 112,486 inhabitants.GOV. results of permanent population 2011
, p. 10571 (p. 97 of pdf), and in Excel format
Table of permanent population 2011
from the sit
Hellenic Statistical Authority
24 November 2017. Retrieved 2018-01-09.
above sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, on the western shore of Lake Pamvotis (). Ioannina is located northwest of Athens, southwest of Thessaloniki and east of the port of Igoumenitsa in the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
.
The city's foundation has traditionally been ascribed to the Byzantine Emperor Justinian in the 6th century AD, but modern archaeological research has uncovered evidence of Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
settlements. Ioannina flourished in the late Byzantine period (13th–15th centuries). It became part of the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claim ...
following the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
and many wealthy Byzantine families fled there following the sack of Constantinople, with the city experiencing great prosperity and considerable autonomy, despite the political turmoils. Ioannina surrendered to the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
in 1430 and until 1868 it was the administrative center of the Pashalik of Yanina
The Pashalik of Yanina, sometimes referred to as the Pashalik of Ioanina or Pashalik of Janina, was an autonomous pashalik within the Ottoman Empire between 1787 and 1822 covering large areas of Greece, Albania and North Macedonia. The pashali ...
. In the period between the 18th and 19th centuries, the city was a major center of the modern Greek Enlightenment.Fleming Katherine Elizabeth''The Muslim Bonaparte: diplomacy and orientalism in Ali Pasha's Greece''
Princeton University Press, 1999. . p. 63-66 Ioannina was ceded to Greece in 1913 following the
Balkan Wars
The Balkan Wars refers to a series of two conflicts that took place in the Balkan States in 1912 and 1913. In the First Balkan War, the four Balkan States of Greece, Serbia, Montenegro and Bulgaria declared war upon the Ottoman Empire and defe ...
.
The city is also characterized by various green areas and parks, including Molos (Lake Front), Litharitsia Park, Pirsinella Park (Giannotiko Saloni), Suburban Forest. There are two hospitals, the General Hospital of Ioannina "G. Hatzikosta", and the University Hospital of Ioannina. It is also the seat of the University of Ioannina. The city's emblem consists of the portrait of the Byzantine Emperor Justinian crowned by a stylized depiction of the nearby ancient theater of Dodona.
Name
The city's formal name, ''Ioannina'', is probably a corruption of ''Agioannina'' or ''Agioanneia'', 'place of St. John', and is said to be linked to the establishment of a monastery dedicated to Saint John the Baptist, around which the later settlement (in the area of the current Ioannina Castle) grew. According to another theory, the city was named after Ioannina, the daughter of Belisarius, general of the emperor Justinian. There are two forms of the name in Greek, ''Ioannina'' being the formal and historical name, while the colloquial and much more commonly used ''Υannena'' or ''Υannina'' ( el, Γιάννενα, Γιάννινα) represents the vernacular tradition ofDemotic Greek
Demotic Greek or Dimotiki ( el, Δημοτική Γλώσσα, , , ) is the standard spoken language of Greece in modern times and, since the resolution of the Greek language question in 1976, the official language of Greece.
"Demotic Greek" (w ...
. The demotic form also corresponds to those in the neighboring languages (e.g., sq, Janina or , rup, Ianina, Enina or Enãna, mk, Јанина, tr, Yanya).
History
Antiquity and early Middle Ages
 The first indications of human presence in Ioannina basin are dated back to the Paleolithic period (24,000 years ago) as testified by findings in the cavern of Kastritsa. During classical antiquity the basin was inhabited by the Molossians and four of their settlements have been identified there. Despite the extensive destruction suffered in Molossia during the Roman conquest of 167 BC, settlement continued in the basin albeit no longer in an urban pattern.
The exact time of Ioannina's foundation is unknown, but it is commonly identified with an unnamed new, "well-fortified" city, recorded by the historian Procopius as having been built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I for the inhabitants of ancient
The first indications of human presence in Ioannina basin are dated back to the Paleolithic period (24,000 years ago) as testified by findings in the cavern of Kastritsa. During classical antiquity the basin was inhabited by the Molossians and four of their settlements have been identified there. Despite the extensive destruction suffered in Molossia during the Roman conquest of 167 BC, settlement continued in the basin albeit no longer in an urban pattern.
The exact time of Ioannina's foundation is unknown, but it is commonly identified with an unnamed new, "well-fortified" city, recorded by the historian Procopius as having been built by the Byzantine emperor Justinian I for the inhabitants of ancient Euroia Euroea or Euroia ( grc, Εὔροια; also transcribed as Eurœa) was a city in Epirus, in western Greece, during late antiquity. It was abandoned in the early 7th century due to Slavic invasions. During the 4th–8th centuries, it was a bishopric ...
. This view is not supported, however, by any concrete archaeological evidence. Early 21st-century excavations have brought to light fortifications dating to the Hellenistic period, the course of which was largely followed by later reconstruction of the fortress in the Byzantine and Ottoman periods. The identification of the site with one of the ancient cities of Epirus has not yet been possible.
It is not until 879 that the name Ioannina appears for the first time, in the acts of the Fourth Council of Constantinople, which refer to one Zacharias, Bishop of Ioannine, a suffragan
A suffragan bishop is a type of bishop in some Christian denominations.
In the Anglican Communion, a suffragan bishop is a bishop who is subordinate to a metropolitan bishop or diocesan bishop (bishop ordinary) and so is not normally jurisdictiona ...
of Naupaktos. After the Byzantine conquest of Bulgaria, in 1020 Emperor Basil II subordinated the local bishopric to the Archbishopric of Ohrid. The Greek archaeologist K. Tsoures dated the Byzantine city walls and the northeastern citadel of the Ioannina Castle to the 10th century, with additions in the late 11th century, including the south-eastern citadel, traditionally ascribed to the short-lived occupation of the city by the Normans under the leadership of Bohemond of Taranto in 1082. In a chrysobull
A golden bull or chrysobull was a decree issued by Byzantine Emperors and later by monarchs in Europe during the Middle Ages and Renaissance, most notably by the Holy Roman Emperors. The term was originally coined for the golden seal (a ''bull ...
to the Venetians in 1198, the city is listed as part of its own province (''provincia Joanninorum'' or ''Joaninon''). In the treaty of partition
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
of the Byzantine lands after the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, Ioannina was promised to the Venetians, but in the event, it became part of the new state of Epirus, founded by Michael I Komnenos Doukas
Michael I Komnenos Doukas, Latinized as Comnenus Ducas ( el, Μιχαήλ Κομνηνός Δούκας, Mikhaēl Komnēnos Doukas), and in modern sources often recorded as Michael I Angelos, a name he never used, was the founder and first ruler ...
.
Late Middle Ages (1204–1430)
 Under Michael I, the city was enlarged and fortified anew. The
Under Michael I, the city was enlarged and fortified anew. The Metropolitan of Naupaktos
The Metropolis of Nafpaktos and Agios Vlasios ( el, Ιερά Μητρόπολις Ναυπάκτου και Αγίου Βλασίου) is a metropolitan see of the Church of Greece. Its seat is the town of Nafpaktos (Naupaktos or Naupactus, in the ...
, John Apokaukos, reports how the city was but a "small town", until Michael gathered refugees who had fled Constantinople and other parts of the Empire that fell to the crusaders of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
, and settled them there, transforming the city into a fortress and "ark of salvation". Despite frictions with local inhabitants who tried in 1232 to expel the refugees, the latter were eventually successfully settled and Ioannina gained in both population and economic and political importance. In the aftermath of the Battle of Pelagonia
The Battle of Pelagonia or Battle of Kastoriae.g. ; . took place in early summer or autumn 1259, between the Empire of Nicaea and an anti-Nicaean alliance comprising Despotate of Epirus, Sicily and the Principality of Achaea. It was a decisive ev ...
in 1259, much of Epirus was occupied by the Empire of Nicaea
The Empire of Nicaea or the Nicene Empire is the conventional historiographic name for the largest of the three Byzantine Greek''A Short history of Greece from early times to 1964'' by W. A. Heurtley, H. C. Darby, C. W. Crawley, C. M. Woodhouse ...
, and Ioannina was placed under siege. Soon, however, the Epirote ruler Michael II Komnenos Doukas, aided by his younger son John I Doukas, managed to recover their capital of Arta Arta, ARTA, or Artà may refer to:
Places Djibouti
* Arta, Djibouti, a regional capital city in southeastern Djibouti
* Arta Mountains, a mountain range in Djibouti
* Arta Region, Djibouti
Greece
* Arta, Greece, a regional capital city in northwes ...
and relieve Ioannina, evicting the Nicaeans from Epirus. In or , John I Doukas, now ruler of Thessaly, launched a raid against the city and its environs, and a few years later an army from the restored Byzantine Empire unsuccessfully laid siege to the city. Following the assassination in 1318 of the last native ruler, Thomas I Komnenos Doukas
Thomas I Komnenos Doukas ( Latinized as Comnenus Ducas) ( el, Θωμάς Α΄ Κομνηνός Δούκας, translit=Thōmas I Komnēnos Doukas) (c. 1285–1318) ruler of Epirus from c. 1297 until his death in 1318.
Thomas was the son of N ...
, by his nephew Nicholas Orsini
Nicholas Orsini ( gr, Νικόλαος Ορσίνι, ''Nikolaos Orsini'') was count palatine of Cephalonia from 1317 to 1323 and ruler of Epirus from 1318 to 1323.
Nicholas was the son of Count John I Orsini of Cephalonia by Maria, a daughter o ...
, the city refused to accept the latter and turned to the Byzantines for assistance. On this occasion, Emperor Andronikos II Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos II Palaiologos2.jpg
, caption = Miniature from the manuscript of George Pachymeres' ''Historia''
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 11 December 1282 –24 May 1328
, coronation = 8 Novembe ...
elevated the city to a metropolitan bishopric, and in 1319 issued a chrysobull conceding wide-ranging autonomy and various privileges and exemptions on its inhabitants. A Jewish community is also attested in the city in 1319. In the Epirote revolt of 1337–1338 against Byzantine rule, the city remained loyal to Emperor Andronikos III Palaiologos
, image = Andronikos_III_Palaiologos.jpg
, caption = 14th-century miniature. Stuttgart, Württembergische Landesbibliothek.
, succession = Byzantine emperor
, reign = 24 May 1328 – 15 June 1341
, coronation = ...
. Soon afterwards Ioannina fell to the Serb ruler Stephen Dushan
Stephen or Steven is a common English first name. It is particularly significant to Christians, as it belonged to Saint Stephen ( grc-gre, Στέφανος ), an early disciple and deacon who, according to the Book of Acts, was stoned to death; ...
and remained part of the Serbian Empire until 1356, when Dushan's half-brother Simeon Uroš was evicted by Nikephoros II Orsini. The attempt of Nikephoros to restore the Epirote state was short-lived as he was killed in the Battle of Achelous against Albanian
Albanian may refer to:
*Pertaining to Albania in Southeast Europe; in particular:
**Albanians, an ethnic group native to the Balkans
**Albanian language
**Albanian culture
**Demographics of Albania, includes other ethnic groups within the country ...
tribes., but Ioannina was not captured. It thus served as a place of refuge for many Greeks of the region of Vagenetia. In 1366–67 Simeon Uroš, having recovered Epirus and Thessaly, appointed his son-in-law Thomas II Preljubović as the new overlord of Ioannina. Thomas proved a deeply unpopular ruler, but he nonetheless repelled successive attempts by Albanian chieftains including a surprise attack in 1379, whose failure the Ioannites attributed to intervention by their patron saint, Michael.
After Thomas' murder in 1384, the citizens of Ioannina offered their city to Esau de' Buondelmonti, who married Thomas' widow, Maria. Esau recalled those exiled under Thomas and restored the properties confiscated by him. In 1389, Ioannina was besieged by John Bua Spata
Gjin Bua Shpata (sometimes anglicized as ''John Spata'') ( 1358 – 29 October 1399) was an Albanian ruler in Western Greece with the title of Despot. Together with Peter Losha, he led raids into Epirus, Acarnania and Aetolia in 1358. He was re ...
, and only with the aid of an Ottoman army was Esau able to repel the Albanians. Despite the ongoing Ottoman expansion and the conflicts between Turks and Albanians in the vicinity of Ioannina, Esau managed to secure a period of peace for the city, especially following his second marriage to Spata's daughter Irene in . Following Esau's death in 1411, the Ioannites invited the Count palatine of Cephalonia and Zakynthos, Carlo I Tocco, who had already been expanding his domains into Epirus for the last decade, as their new ruler. By 1416 Carlo I Tocco had managed to capture Arta as well, thereby reuniting the core of the old Epirote realm, and received recognition from both the Ottomans and the Byzantine emperor. Ioannina became the summer capital of the Tocco domains, and Carlo I died there in July 1429. His oldest bastard son, Ercole, called on the Ottomans for aid against the legitimate heir, Carlo II Tocco
Carlo II Tocco (died 1448) was the ruler of Epirus from 1429 until his death.
Life
Carlo II was the son of Leonardo II Tocco, the younger brother and co-ruler of Carlo I Tocco, count of Cephalonia and Zante, duke of Leukas, and ruler of Epirus. ...
. In 1430 an Ottoman army, fresh from the capture
Capture may refer to:
*Asteroid capture, a phenomenon in which an asteroid enters a stable orbit around another body
*Capture, a software for lighting design, documentation and visualisation
*"Capture" a song by Simon Townshend
*Capture (band), an ...
of Thessalonica, appeared before Ioannina. The city surrendered after the Ottoman commander, Sinan Pasha, promised to spare the city and respect its autonomy.
Ottoman period (1430–1913)
Center of Greek Enlightenment (17th–18th centuries)
 Despite the repression and conversions in the 17th century, and the prominence of the Muslim population in the city's affairs, Ioannina retained its Christian majority throughout Ottoman rule, and the Greek language retained a dominant position;
Despite the repression and conversions in the 17th century, and the prominence of the Muslim population in the city's affairs, Ioannina retained its Christian majority throughout Ottoman rule, and the Greek language retained a dominant position; Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
was spoken by the Ottoman officials and the garrison, and the Albanian inhabitants used Albanian, but the ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'' and native language of most inhabitants was Greek, including among the ''Tourkoyanniotes'', and was sometimes used by the Ottoman authorities themselves.
The city also soon recovered from the financial effects of the revolt. In the late 17th century Ioannina was a thriving city with respect to population and commercial activity. Evliya Çelebi mentions the presence of 1,900 shops and workshops. The great economic prosperity of the city was followed by remarkable cultural activity. During the 17th and 18th centuries, many important schools were established.Π. Αραβαντινού, ''Βιογραφική Συλλογή Λογίων της Τουρκοκρατίας'', Εκδόσεις Ε.Η.Μ., 1960. Its inhabitants continued their commercial and handicraft activities which allowed them to trade with important European commercial centers, such as Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
and Livorno
Livorno () is a port city on the Ligurian Sea on the western coast of Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the Province of Livorno, having a population of 158,493 residents in December 2017. It is traditionally known in English as Leghorn (pronou ...
, where merchants from Ioannina established commercial and banking houses. The Ioannite diaspora was also culturally active: Nikolaos Glykys (in 1670), Nikolaos Sarros (in 1687) and Dimitrios Theodosiou (in 1755) established private printing presses in Venice, responsible for over 1,600 editions of books for circulation in the Ottoman-ruled Greek lands, and Ioannina was the centre through which these books were channeled into Greece. These were significant historical, theological as well as scientific works, including an algebra book funded by the Zosimades
The Zosimades ( el, Ζωσιμάδες) or Zosimas brothers were 18th-19th century Greek benefactors and merchants.
The Zosimades were six brothers:
*Ioannis Zosimas (1752–1771)
* Anastasios Zosimas (1754–1828)
* Nikolaos Zosimas (1758–1842 ...
brothers, books for use in the schools of Ioannina such as the ''Arithmetica'' of Balanos Vasilopoulos
Balanos Vasilopoulos ( el, Μπαλάνος Βασιλόπουλος; 1694–1760) was a Greek Orthodox cleric, author, mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. He is known for attempting to solve doubling the cube. He was one of the most inf ...
, as well as medical books. At the same time these merchants and entrepreneurs maintained close economic and intellectual relations with their birthplace and founded charity and education establishments. These merchants were to be major national benefactors.
 Thus the ''Epiphaniou'' School was founded in 1647 by a Greek merchant of Ioannite origin resident in Venice, Epiphaneios Igoumenos. The ''Gioumeios'' School was founded in 1676 by a benefaction from another wealthy Ioannite Greek from Venice, Emmanuel Goumas. It was renamed ''Balaneios'' by its rector,
Thus the ''Epiphaniou'' School was founded in 1647 by a Greek merchant of Ioannite origin resident in Venice, Epiphaneios Igoumenos. The ''Gioumeios'' School was founded in 1676 by a benefaction from another wealthy Ioannite Greek from Venice, Emmanuel Goumas. It was renamed ''Balaneios'' by its rector, Balanos Vasilopoulos
Balanos Vasilopoulos ( el, Μπαλάνος Βασιλόπουλος; 1694–1760) was a Greek Orthodox cleric, author, mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. He is known for attempting to solve doubling the cube. He was one of the most inf ...
, in 1725. Here worked several notable personalities of the Greek Enlightenment, such as Bessarion Makris
Bessarion Makris ( el, Βησσαρίων Μακρής, 1635- 1699) was a Greek scholar and theologian.
He was born in Ioannina, northwestern Greece, center of the 17th-18th century Modern Greek Enlightenment. In 1672 Makris became the head of th ...
, the priests Georgios Sougdouris (1685/7–1725) and Anastasios Papavasileiou (1715–?), the monk Methodios Anthrakites, his student Ioannis Vilaras and Kosmas Balanos. The ''Balaneios'' taught philosophy, theology and mathematics. It suffered financially from the dissolution of the Republic of Venice
The Treaty of Campo Formio (today Campoformido) was signed on 17 October 1797 (26 Vendémiaire VI) by Napoleon Bonaparte and Count Philipp von Cobenzl as representatives of the French Republic and the Austrian monarchy, respectively. The treat ...
by the French and finally stopped operation in 1820. The school's library, which hosted several manuscripts and epigrams, was also burned the same year following the capture of Ioannina by the troops the Sultan had sent against Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
. The Maroutses family, also active in Venice, founded the Maroutsaia School
The Maroutsaia School ( el, Μαρουτσαία Σχολή) or Maroutsios was a Greek educational institution that operated in Ioannina from 1742 to 1797. The school reached its peak under Eugenios Voulgaris, one of the main representative of t ...
, which opened in 1742 and its first director Eugenios Voulgaris
Eugenios Voulgaris or Boulgaris ( gr, Εὐγένιος Βούλγαρης; russian: link=yes, Евгений Вулгарский, Евгений Вулгар; 1716–1806) was a Greek Orthodox cleric, author, educator, mathematician, astronome ...
championed the study of the physical sciences (physics and chemistry) as well as philosophy and Greek. The ''Maroutsaia'' also suffered after the fall of Venice and closed in 1797 to be reopened as the Kaplaneios School thanks to a benefaction from an Ioannite living in Russia, Zoes Kaplanes. Its schoolmaster, Athanasios Psalidas
Athanasios Psalidas ( el, Αθανάσιος Ψαλίδας; 1767–1829), was a Greek author, scholar and one of the most renowned figures of the modern Greek Enlightenment.
Life Early years and diaspora
Psalidas was born at 1767 in Ioannina, whe ...
had been a student of Methodios Anthrakites and had also studied in Vienna and in Russia. Psalidas established an important library of thousands of volumes in several languages and laboratories for the study of experimental physics
Experimental physics is the category of disciplines and sub-disciplines in the field of physics that are concerned with the observation of physical phenomena and experiments. Methods vary from discipline to discipline, from simple experiments and ...
and chemistry
Chemistry is the science, scientific study of the properties and behavior of matter. It is a natural science that covers the Chemical element, elements that make up matter to the chemical compound, compounds made of atoms, molecules and ions ...
that aroused the interest and suspicion of Ali Pasha. The ''Kaplaneios'' was burned down along with most of the rest of the city after the entry of the Sultan's armies in 1820. These schools took over the long tradition of the Byzantine era, giving a significant boost to the Greek Enlightenment. "During the 18th century", Neophytos Doukas wrote with some exaggeration, "every author of the Greek world, was either from Ioannina or was a graduate of one of the city's schools."
Ali Pasha's rule (1788–1822)
 In 1788 the city became the center of the territory ruled by
In 1788 the city became the center of the territory ruled by Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
, an area that included the entire northwestern part of Greece, southern parts of Albania, Thessaly as well as parts of Euboea and the Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic regions of Greece, geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmu ...
. The Ottoman-Albanian lord Ali Pasha was one of the most influential personalities of the region in the 18th and 19th centuries. Born in Tepelenë
Tepelenë ( sq-definite, Tepelena) is a city and a municipality in Gjirokastër County, in the south of Albania. The town is located on the left bank of the Vjosa River, about three kilometres downstream from its union with the Drino.
Until the a ...
, he maintained diplomatic relations with the most important European leaders of the time and his court became a point of attraction for many of those restless minds who would become major figures of the Greek Revolution ( Georgios Karaiskakis, Odysseas Androutsos, Markos Botsaris and others). During this time, however, Ali Pasha committed a number of atrocities against the Greek population of Ioannina, culminating in the sewing up of local women in sacks and drowning them in the nearby lake, this period of his rule coincides with the greatest economic and intellectual prosperity of the city. As a couplet has it "''The city was first in arms, money and letters''".
When the French scholar François Pouqueville visited the city during the early years of the 19th century, he counted 3,200 homes (2,000 Christian, 1,000 Muslim, 200 Jewish). The efforts of Ali Pasha to break away from the Sublime Porte alarmed the Ottoman government, and in 1820 (the year before the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
began) he was declared guilty of treason and Ioannina was besieged by Turkish troops. Ali Pasha was assassinated in 1822 in the monastery of St Panteleimon on the island of the lake, where he took refuge while waiting to be pardoned by Sultan Mahmud II.
Last Ottoman century (1822–1913)
The ''Zosimaia
The ''Zosimaia'' School ( el, Ζωσιμαία Σχολή, ''Zosimaía Scholí'') of Ioannina (in Epirus) has been one of the most significant Greek middle-level educational institutions (high schools) during the last period of Ottoman rule in th ...
'' was the first significant educational foundation established after the outbreak of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
(1828). It was financed by a benefaction from the Zosimas brothers and began operating in 1828 and fully probably from 1833. It was a School of Liberal Arts (Greek, Philosophy and Foreign Languages). The mansion of Angeliki Papazoglou became the ''Papazogleios'' school for girls as an endowment following her death; it operated until 1905.
 In 1869, a great part of Ioannina was destroyed by fire. The marketplace was soon reconstructed according to the plans of the German architect Holz, thanks to the personal interest of Ahmet Rashim Pasha, the local governor. Communities of people from Ioannina living abroad were active in financing the construction of most of the city's churches, schools and other elegant buildings of charitable establishments. The first bank of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottoman Bank, opened its first branch in Greece in Ioannina, which shows the power of the city in world trade in the 19th century. As the 19th century came to a close, signs of national agitation emerged among some parts of the city' s population. In 1877 for example, Albanian leaders sent a memorandum to the Ottoman government demanding, among other things, the establishment of Albanian language schools and various Muslim Albanians of the Vilayet formed in Ioannina a committee which aimed at defending Albanian rights. The Greek population of the region authorized a committee to present to European governments their wish for union with Greece; as a result
In 1869, a great part of Ioannina was destroyed by fire. The marketplace was soon reconstructed according to the plans of the German architect Holz, thanks to the personal interest of Ahmet Rashim Pasha, the local governor. Communities of people from Ioannina living abroad were active in financing the construction of most of the city's churches, schools and other elegant buildings of charitable establishments. The first bank of the Ottoman Empire, the Ottoman Bank, opened its first branch in Greece in Ioannina, which shows the power of the city in world trade in the 19th century. As the 19th century came to a close, signs of national agitation emerged among some parts of the city' s population. In 1877 for example, Albanian leaders sent a memorandum to the Ottoman government demanding, among other things, the establishment of Albanian language schools and various Muslim Albanians of the Vilayet formed in Ioannina a committee which aimed at defending Albanian rights. The Greek population of the region authorized a committee to present to European governments their wish for union with Greece; as a result Dimitrios Chasiotis
Dimitrios Chasiotis ( gr, Δημήτρης Χασιώτης; born June 27, 1986) is a Greek former swimmer, who specialized in backstroke events. He represented his nation Greece at the 2008 Summer Olympics, and also swam for Olympiacos in Athen ...
published a memorandum in Paris in 1879.
According to the Ottoman censuses of 1881–1893, the city and its environs (the central '' kaza'' of the Sanjak of Ioannina), had a population comprising 4,759 Muslims, 77,258 Greek Orthodox (including both Greek and Albanian speakers), 3,334 Jews and 207 of foreign nationality. While a number of Turkish-language schools were established at the time, Greek-language education retained its prominent position. Even the city's prominent Muslim families preferred to send their children to well-established Greek institutions, notably the ''Zosimaia''. As a result, the dominance of the Greek language in the city continued: the minutes of the city council were kept in Greek, and the official newspaper, ''Vilayet'', established in 1868, was bilingual in Turkish and Greek.
During the Ottoman period (''turcokracy'') the religious-linguistic minority of "Turco-yanniotes" ( Τουρκογιαννιώτες) existed in Ioannina and neighbouring areas. These were islamized "Yaniotes" (= people from Ioannina), who spoke Greek. There is a limited number of texts written with Greek alphabet in their idiom.
Modern period (since 1913)
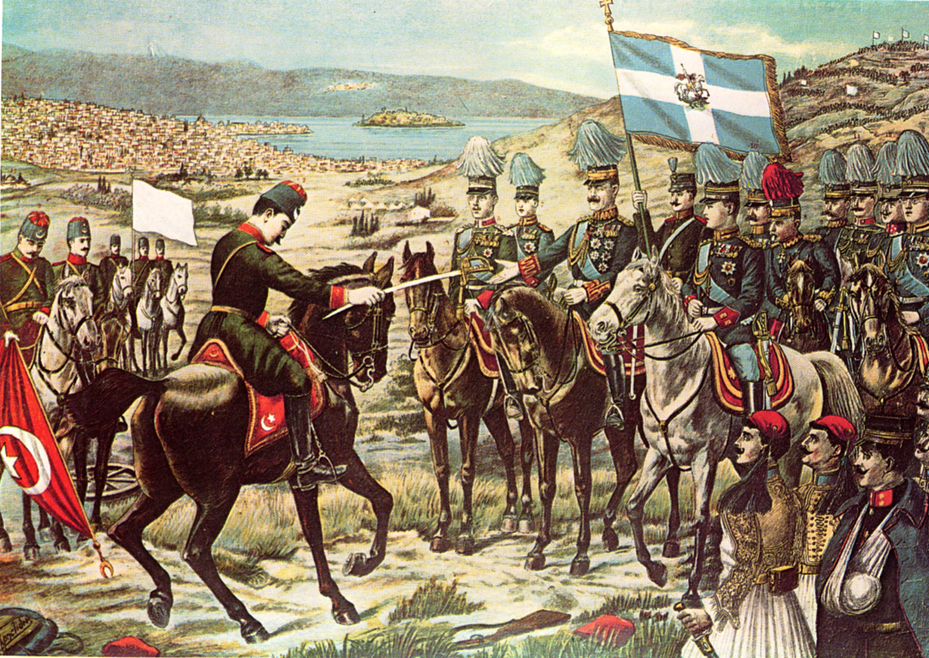
Ioannina was incorporated into the Greek state on 21 February 1913 after theBattle of Bizani
The Battle of Bizani (, ''Máchi tou Bizaníou''; tr, Bizani Muharebesi, italic=no) took place in Epirus on . The battle was fought between Greek and Ottoman forces during the last stages of the First Balkan War, and revolved around the forts ...
in the First Balkan War. The day the city came under the control of the Greek forces, aviator Christos Adamidis
Christos Adamidis ( el, Χρήστος Αδαμίδης, 1885–1949) was a Hellenic Army officer and pioneer of military aviation. He was one of the first Greek officers that received aviation training in France and later participated in air o ...
, a native of the city, landed his Maurice Farman MF.7 biplane in the Town Hall square, to the adulation of an enthusiastic crowd.
Following the Asia Minor Catastrophe (1922) and the Treaty of Lausanne
The Treaty of Lausanne (french: Traité de Lausanne) was a peace treaty negotiated during the Lausanne Conference of 1922–23 and signed in the Palais de Rumine, Lausanne, Switzerland, on 24 July 1923. The treaty officially settled the conflic ...
, the Muslim population was exchanged with Greek refugees from Asia Minor. A small Muslim community of Albanian origin continued to live in Ioannina after the exchange, which in 1940 counted 20 families and had decreased to 8 individuals in 1973. p. 56. "The population exchange between Greece and Turkey which followed removed all those of Turkish origin so that, by 1940, only some twenty Muslim families of Albanian origin were left. In 1973, only eight Muslim remained, living together in an ancient house in the centre of Ioannina. The local authorities, we are told, had refused to allow them to use one of the remaining mosques for worship, their estates remain sequestered and a long battle for what they regard as their rights has so far come to nothing. Although Albanian, they could hope for no sympathy from the present regime in Albania and there was nowhere else for them to go."
In 1940 during World War II the capture of the city became one of the major objectives of the Italian Army. Nevertheless, the Greek defense in Kalpaki pushed back the invading Italians. In April 1941 Ioannina was intensively bombed by the German forces even during the negotiations that led to the capitulation of the Greek army. During the subsequent Axis occupation of Greece, the city's Jewish community was rounded up by the Germans in 1944 and mostly perished in the concentration camps. On 3 October 1943, the German army murdered in reprisal nearly 100 people in the village of Lingiades, 13 kilometres distant from Ioaninna, in what is known as the Lingiades massacre.
The University of Ioannina was founded in 1970; until then, higher education faculties in the city had been part of the Aristotle University of Thessaloniki.
Jewish community
 According to the local Greek scholar
According to the local Greek scholar Panayiotis Aravantinos
Panagiotis Aravantinos ( el, Παναγιώτης Αραβαντινός, 1809 or 1811 – 1870) was a Greek scholar and educator who was born in Parga. He worked primarily in Epirus, which was then under the rule of the Ottoman Empire. As with man ...
, a synagogue destroyed in the 18th century bore an inscription, which dated its foundation in the late 9th century AD. The existing synagogue
A synagogue, ', 'house of assembly', or ', "house of prayer"; Yiddish: ''shul'', Ladino: or ' (from synagogue); or ', "community". sometimes referred to as shul, and interchangeably used with the word temple, is a Jewish house of worshi ...
is located in the old fortified part of the city known as ''"Kastro"'', at 16 Ioustinianou street. Its name means "the Old Synagogue". It was constructed in 1829. Its architecture is typical of the Ottoman era, a large building made of stone. The interior of the synagogue is laid out in the Romaniote way: the Bimah (where the Torah scrolls are read out during service) is on a raised dais on the western wall, the Aron haKodesh (where the Torah scrolls are kept) is on the eastern wall and at the middle there is a wide interior aisle. The names of the Ioanniote Jews who were killed in the Holocaust are engraved in stone on the walls of the synagogue.
Rae Dalven
Rachel Dalven (25 April 1904, Preveza, Janina Vilayet, Ottoman Empire – 27 July 1992, New York City), also known as Rae Dalven, was a Romaniote writer who came to the United States as a child. She is best known for her translations of Cavafy's ...
, 1,950 Jews were living in Ioannina in April 1941. Of these, 1,870 were deported by the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in Na ...
to concentration camps on 25 March 1944, during the final months of German occupation. Almost all of the people deported were murdered on or shortly after 11 April 1944, when the train carrying them reached Auschwitz-Birkenau
Auschwitz concentration camp ( (); also or ) was a complex of over 40 concentration and extermination camps operated by Nazi Germany in occupied Poland (in a portion annexed into Germany in 1939) during World War II and the Holocaust. It con ...
. Only 181 Ioannina Jews are known to have survived the war, including 112 who survived Auschwitz and 69 who fled to join the resistance leader Napoleon Zervas and the National Republican Greek League (EDES). Approximately 164 of these survivors eventually returned to Ioannina.
Today the remaining community has shrunk to about 50 mostly elderly people."The Holocaust in Ioannina"Kehila Kedosha Janina Synagogue and Museum retrieved 5 January 2009Raptis, Alekos and Tzallas, Thumios, ''Deportation of Jews of Ioannina'', Kehila Kedosha Janina Synagogue and Museum, 28 July 2005
URL accessed 5 January 2009 The Kehila Kedosha Yashan Synagogue remains locked, only opened for visitors on request. Emigrant Romaniotes return every summer and open the old synagogue. The last time a Bar Mitzvah (the Jewish ritual for celebrating the
coming of age
Coming of age is a young person's transition from being a child to being an adult. The specific age at which this transition takes place varies between societies, as does the nature of the change. It can be a simple legal convention or can b ...
of a child) was held in the synagogue was in 2000, and was an exceptional event for the community. A monument dedicated to the thousands of Greek Jews who perished during the Holocaust was constructed in the city in a 13th-century Jewish cemetery. In 2003 the memorial was vandalized by unknown anti-Semites. The Jewish cemetery too was repeatedly vandalized in 2009. As a response to the vandalisms, citizens of the city formed an initiative for the protection of the cemetery and organized rallies.
In the municipal election of 2019, independent candidate Moses Elisaf, a 65-year-old doctor was elected mayor of the city, the first Jewish elected mayor in Greece. Elisaf won 50.3 percent of the vote. Elisaf received 17,789 votes, 235 more than his runoff opponent.
Geography
Ioannina lies at an elevation of approximatelyabove sea level
Height above mean sea level is a measure of the vertical distance (height, elevation or altitude) of a location in reference to a historic mean sea level taken as a vertical datum. In geodesy, it is formalized as ''orthometric heights''.
The comb ...
, on the western shore of Lake Pamvotis (). It is located within the Ioannina municipality, and is the capital of Ioannina regional unit and the region of Epirus. Ioannina is located northwest of Athens, southwest of Thessaloniki and east of the port of Igoumenitsa in the Ionian Sea
The Ionian Sea ( el, Ιόνιο Πέλαγος, ''Iónio Pélagos'' ; it, Mar Ionio ; al, Deti Jon ) is an elongated bay of the Mediterranean Sea. It is connected to the Adriatic Sea to the north, and is bounded by Southern Italy, including C ...
.
The municipality Ioannina has an area of 403.322 km2, the municipal unit Ioannina has an area of 47.440 km2, and the community Ioannina (the city proper) has an area of 17.335 km2.
Districts
The present municipality Ioannina was formed at the 2011 local government reform by the merger of the following 6 former municipalities, that became municipal units (constituent communities in brackets): * Ioannina (Ioannina, Exochi, Marmara, Neochoropoulo, Stavraki) * Anatoli (Anatoli, Bafra, Neokaisareia) * Bizani (Ampeleia, Bizani, Asvestochori, Kontsika, Kosmira, Manoliasa, Pedini) * Ioannina Island (Greek: ''Nisos Ioanninon'') * Pamvotida ( Katsikas, Anatoliki, Vasiliki, Dafnoula, Drosochori,Iliokali
Iliokali ( el, Ηλιόκαλη, before 1927: Μορκιούς - ''Morkious'') is a village in the municipal unit of Pamvotida, Ioannina regional unit, Greece. It is situated at the foot of the mountain Driskos, southeast of Lake Ioannina. In 20 ...
, Kastritsa, Koutselio, Krapsi, Longades, Mouzakaioi, Platania, Platanas, Charokopi)
* Perama
Perama ( el, Πέραμα) is a suburb of Piraeus. It is part of Athens urban area and belogs to the Piraeus regional unit. It lies on the southwest edge of the Aegaleo mountains, on the Saronic Gulf coast. It is 8 km northwest of Piraeus, ...
(Perama, Amfithea, Kranoula, Krya, Kryovrysi, Ligkiades, Mazia, Perivleptos, Spothoi)
Climate
Ioannina has a borderline humid subtropical (''Cfa'') and Mediterranean climate (''Csa'') in the Köppen climate classification, and is tempered by its inland location and elevation. Summers are typically hot and moderately dry, while winters are wet and colder than on the coast with frequent frosts and occasional snowfall. Ioannina is the wettest city in Greece. The absolute maximum temperature ever recorded was , while the absolute minimum ever recorded was .Demography
Population of the Municipality of Ioannina. Population censuses, 1981–2011.Landmarks and sights
Isle of Lake Pamvotis
 One of the most notable attractions of Ioannina is the inhabited island of Lake Pamvotis which is simply referred to as Island of Ioannina. The island is a short ferry trip from the mainland and can be reached on small motorboats running on varying frequencies depending on the season. The monastery of St Panteleimon, where
One of the most notable attractions of Ioannina is the inhabited island of Lake Pamvotis which is simply referred to as Island of Ioannina. The island is a short ferry trip from the mainland and can be reached on small motorboats running on varying frequencies depending on the season. The monastery of St Panteleimon, where Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
spent his last days waiting for a pardon from the Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
, is now a museum housing everyday artefacts and relics of his period. There are six monasteries on the island: the monastery of St Nicholas (Ntiliou) or Strategopoulou (11th century), the Monastery of St Nicholas (Spanou) or Philanthropinon (1292), St John the Baptist (1506), Eleousis (1570), St Panteleimon (17th century), and of the Transfiguration of Christ (1851). The monasteries of Strategopoulou and Philanthropinon also functioned as colleges. Alexios Spanos, the monks Proklos and Comnenos, and the Apsarades brothers Theophanis and Nektarios are among those that taught there. The school continued its activities until 1758, when it was superseded by the newer collegial institutions within the city. The island's winding streets are also home to many gift-shops, tavernas, churches and bakeries.
Ioannina Castle
 At the south-eastern edge of the town on a rocky peninsula of Lake Pamvotis, the castle was the administrative heart of the
At the south-eastern edge of the town on a rocky peninsula of Lake Pamvotis, the castle was the administrative heart of the Despotate of Epirus
The Despotate of Epirus ( gkm, Δεσποτᾶτον τῆς Ἠπείρου) was one of the Greek successor states of the Byzantine Empire established in the aftermath of the Fourth Crusade in 1204 by a branch of the Angelos dynasty. It claim ...
, and the Ottoman vilayet. The castle was in constant use until the late Ottoman period and the fortifications underwent several modifications throughout the centuries. The most extensive alterations where conducted during the rule of Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
and were completed in 1815. Several monuments such as the Byzantine baths, the Ottoman baths, the Ottoman library, and the Soufari Sarai
Soufari Sarai ( el, Σουφαρί Σαράι) is a large historical building in the castle of Ioannina, Greece. It was used by the Ottomans as a cavalry school. It is located on the north side of the Castle, near the Turkish Library. It is a large ...
are found within the castle's walls. There are two citadels in the castle. The south-eastern citadel, which bears the name ''Its Kale'' (Ιτς Καλέ, from Turkish '' Iç Kale'', 'inner fortress') is where the Fethiye Mosque
Fethiye () is a city and district of Muğla Province in the Aegean Region of Turkey. It is one of the prominent tourist destinations in the Turkish Riviera. In 2019 its population was 162,686.
History
Fethiye was formerly known as Makri (). ...
, the tomb of Ali Pasha Ali Pasha was the name of numerous Ottoman pashas named Ali. It is most commonly used to refer to Ali Pasha of Ioannina.
People
* Çandarlı Ali Pasha (died 1406), Ottoman grand vizier (1387–1406)
* Hadım Ali Pasha (died 1511), Ottoman grand v ...
, and the Byzantine Museum are located. The north-eastern citadel is dominated by the Aslan Pasha Mosque and also contains a few other monuments dating from the Ottoman period. The old Jewish Synagogue of Ioannina
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
is within the walls of the castle and is one of the oldest and largest buildings of its type surviving in Greece.
The city
Several religious and secular monuments survive from the Ottoman period. In addition to the two mosques surviving within the walls of the castle, two further mosques are preserved outside the walls. The Mosque and Madrassa of Veli Pasha are in the centre of the city, andKaloutsiani Mosque
The Mosque of Kaloutsiani ( tr, Kanlı Çeşme Camii, , mosque of the bloody fountain, rendered in Greek as ) is a historical Ottoman mosque in the town of Ioannina, Epirus, in northwestern Greece. It was built in 1740, and since 2005 it been the ...
can be found in the area of the city with the same name. The now derelict "House of the Archbishop", near the football stadium, is the only old mansion that survived the fire of 1820. Some of the notable landmarks in the city centre also date from the late Ottoman period. The municipal clock tower of Ioannina, designed by local architect Periklis Meliritos, was erected in 1905 to celebrate the Jubilee of sultan Abdul Hamid II
Abdülhamid or Abdul Hamid II ( ota, عبد الحميد ثانی, Abd ül-Hamid-i Sani; tr, II. Abdülhamid; 21 September 1842 10 February 1918) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 31 August 1876 to 27 April 1909, and the last sultan to ...
. The adjacent building houses the VIII Division headquarters. It dates from the late 19th century. Some neoclassical buildings such the post office, the old Zosimaia School, the Papazogleios Weaving School, and the former Commercial School date from the late Ottoman period as do a few arcades in the old commercial centre of the city like Stoa Louli and Stoa Liampei. The churches of the Assumption of the Virgin
The Assumption of Mary is one of the four Catholic_Mariology#Dogmatic_teachings, Marian dogmas of the Catholic Church. Pope Pius XII defined it in 1950 in his apostolic constitution ''Munificentissimus Deus'' as follows:
We proclaim and d ...
at Perivleptos, Saint Nicholas of Kopanon
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
and Saint Marina were rebuilt in the 1850s by funds from Nikolaos Zosimas and his brothers on the foundations of previous churches that perished in the great fire of 1820. The Cathedral of St Athanasius
A cathedral is a church that contains the ''cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denominations ...
was completed in 1933. It was built on the foundations of the previous Orthodox cathedral which was destroyed in the fires of 1820. It is a three-aisled basilica.
Culture



Museums and galleries
Some of the most important museums of the city are within the walls of the castle. The Municipal Ethnographic Museum is hosted in Aslan Pasha Mosque in the north-east citadel. It is divided into three departments, each one representing one of the main communities that inhabited the city: Greek, Ottoman Muslim, and Jewish. The Byzantine Museum is in the south-eastern citadel of the castle. The museum opened in 1995 in order to preserve and present artefacts of the wider region of Epirus covering the period from the 4th to the 19th century. The newest addition to the city's museum, the silversmithing museum, is also in the south-eastern citadel. It is housed in the western bastion of the citadel and outlines the history of the art of silversmithing in Epirus. Outside the walls of the castle, close to the town centre, one will find the Archaeological Museum of Ioannina. It is in the Litharitsia fortress area. It includes archaeological exhibits documenting the human habitation of Epirus from prehistoric times through the late Roman Period, with special emphasis placed on finds from the Dodona sanctuary. TheMunicipal Art Gallery of Ioannina
The Municipal Art Gallery of Ioannina ( el, Δημοτική Πινακοθήκη Ιωαννίνων) is an art museum in Ioannina, Greece that has been open in its current building since 2000. The collection of over 500 items ranges from classical ...
(Dimotiki Pinakothiki) is housed in the Pyrsinella neoclassical building dating from around 1890. The gallery's collection displays major modern works of painters and sculptors, collected through purchases and donations from various collectors and artists. This includes about 500 works, paintings, drawings, prints, pictures and sculptures. The Pavlos Vrellis Greek History Museum is south of the city. It is a wax museum which covers events and personalities from Greek history as well as the history of the region and is the result of the personal work of Pavlos Vrellis.
Education

/ref>UniversityRankings.ch (SERI) 2015 – University of Ioannin
Retrieved in 3 February 2016. As of 2017, there was a student population of 25,000 enrolled at the university (21,900 at the undergraduate level and 3,200 at the postgraduate level) and 580 faculty members, while teaching is further supplemented by 171 teaching fellows and 132 laboratory staff. The university administrative services are staffed with 420 employees.
Local products
* Ioannina is known throughout Greece for its silverwork, with a number of shops selling silver jewelry, bronzeware, and decorative items (serving trays, recreations of shields and swords.) *Hookah
A hookah (Hindustani language, Hindustani: (Nastaleeq), (Devanagari), IPA: ; also see #Names and etymology, other names), shisha, or waterpipe is a single- or multi-stemmed instrument for heating or vaporizing and then smoking either tobacco ...
s (''nargiles'', ναργιλές) are sold to tourists as novelty items and vary in size from small (three inches in height) to quite large ( tall).
Cuisine
* The area is famous for its spring water from Zagori, sold throughout Greece. * The region of Ioannina is well known for the production of feta cheese. * Ioannina is also famous for itsbaklava
Baklava (, or ; ota, باقلوا ) is a layered pastry dessert made of filo pastry, filled with chopped nuts, and sweetened with syrup or honey. It was one of the most popular sweet pastries of Ottoman cuisine.
The pre- Ottoman origin of the ...
.
Media
*Epirus TV1
Epirus TV1 (formerly abbreviated as ''TV1'') is a Greek television channel of Ioannina. It broadcasts in Epirus, in western Central Greece, in Ionian islands, in northwestern Peloponnese, in western Evrytania, in northwestern Ilia and in west par ...
* ''Ipirotikos Agon
Ipirotikos Agon ("Epirot Struggle") (Greek: Ηπειρωτικός Αγών) is one of the oldest newspapers published in Greece. Its headquarters are in Ioannina, Epirus.
History
It was set in 1923 in the region of Epirus and was first publishe ...
'', a locally published newspaper.
* '' Proinos Logos'', a locally published newspaper.
Consulates
The city hosts consulates from the following countries: * Albania * Belgium * NetherlandsIoannina compromise
An informal meeting of the foreign ministers of the states of the European Union took place in Ioannina on 27 March 1994, resulting in the Ioannina compromise.Notable people from Ioannina


Michael Apsaras Michael Apsaras ( el, Μιχαήλ Ἀψαρᾶς) was a 14th-century Greek noble from Ioannina.
Apsaras came from a noble Byzantine family and one of the most influential families in the city of Ioannina. Apsaras received the title of ''protove ...
, 14th century Greek noble.
*Simon Strategopoulos
Simon may refer to:
People
* Simon (given name), including a list of people and fictional characters with the given name Simon
* Simon (surname), including a list of people with the surname Simon
* Eugène Simon, French naturalist and the genus ...
15th-century noble and governor of Ioannina.
* Epifanios Igoumenos (1568–1648), scholar.
* Nikolaos Glykys
Nikolaos ( el, Νικόλαος, ') is a common Greek language, Greek given name which means "Victor of People", a compound of νίκη ''nike (goddess), nikē'' 'victory' and λαός laos' 'people'. The connotation is "people's champion" or "conq ...
(1619–1693), merchant and book publisher.
* Nikolaos Sarros
Nikolaos ( el, Νικόλαος, ') is a common Greek given name which means "Victor of People", a compound of νίκη '' nikē'' 'victory' and λαός laos' 'people'. The connotation is "people's champion" or "conqueror of people". The English ...
(1617–1697), book publisher, owner of one of the first Greek printing-houses in Venice
*Bessarion Makris
Bessarion Makris ( el, Βησσαρίων Μακρής, 1635- 1699) was a Greek scholar and theologian.
He was born in Ioannina, northwestern Greece, center of the 17th-18th century Modern Greek Enlightenment. In 1672 Makris became the head of th ...
(1635–1699), scholar.
* Georgios Sougdouris (1645/7–1725), scholar.
* Methodios Anthrakites (1660–1736), scholar.
* Balanos Vasilopoulos
Balanos Vasilopoulos ( el, Μπαλάνος Βασιλόπουλος; 1694–1760) was a Greek Orthodox cleric, author, mathematician, physicist, and philosopher. He is known for attempting to solve doubling the cube. He was one of the most inf ...
(1694–1760), scholar.
* Dimitrios Theodosiou
Demetrius is the Latinization of names, Latinized form of the Ancient Greek male name, male Greek given names, given name ''Dēmḗtrios'' (), meaning “Demetris” - "devoted to goddess Demeter".
Alternate forms include Demetrios, Dimitrios, ...
(-1782, book publisher.
*Zosimades
The Zosimades ( el, Ζωσιμάδες) or Zosimas brothers were 18th-19th century Greek benefactors and merchants.
The Zosimades were six brothers:
*Ioannis Zosimas (1752–1771)
* Anastasios Zosimas (1754–1828)
* Nikolaos Zosimas (1758–1842 ...
brothers, benefactors, founders of the Zosimaia School.
* Maroutsis family, traders and benefactors.
*Kyra Frosini
Euphrosyne Vasileiou ( el, Ευφροσύνη Βασιλείου; 1773 – 11 January 1800), better known as Kyra Frosini (Κυρά Φροσύνη, "Lady Phrosyne"), was a Greek socialite who was executed for adultery in Ioannina by the Ottoman g ...
(1772–1800), socialite and heroine.
*Lambros Photiadis
Lambros Photiadis ( el, Λάμπρος Φωτιάδης, 1752-1805) was a Greek scholar, director of the Princely Academy of Bucharest and representative of the modern Greek Enlightenment.
Life
Photiadis was born in Ioannina (Epirus), northwester ...
(1752–1805), scholar.
*Zois Kaplanis Zois is a surname and masculine given name which may refer to:
* Antonios Zois (1869–1941), Greek chieftain
* Chris Zois, American psychiatrist and author
* Christos Zois (born 1968), Greek politician
* Karl von Zois (1756–1799), Carniolan amat ...
(1736-1806), merchant, founder of the Kaplaneios School
* Kosmas Balanos (1731–1808), scholar.
*Grigorios Paliouritis Grigorios or Gregorios ( el, Γρηγόριος “watchful; alert; awake”, from ''ἐγρήγορᾰ'' ), and the variant Grigoris (Γρηγόρης), are the Greek forms of the name Gregory. It can refer to:
* Grigoris (catholicos), 4th-centu ...
(1778–1816), scholar.
* Ioannis Vilaras (1771–1823), poet and scholar.
*Athanasios Psalidas
Athanasios Psalidas ( el, Αθανάσιος Ψαλίδας; 1767–1829), was a Greek author, scholar and one of the most renowned figures of the modern Greek Enlightenment.
Life Early years and diaspora
Psalidas was born at 1767 in Ioannina, whe ...
(1767–1829), scholar, of the main contributors of the Modern Greek Enlightenment.
*Georgios Hadjikonstas Georgios (, , ) is a Greek name derived from the word ''georgos'' (, , "farmer" lit. "earth-worker"). The word ''georgos'' (, ) is a compound of ''ge'' (, , "earth", "soil") and ''ergon'' (, , "task", "undertaking", "work").
It is one of the most ...
(1753–1845), benefactor.
*Vasileios Goudas
Vasileios Goudas ( el, Βασίλειος Γούδας; c. 1779 – 1845 ) was a fighter of the Greek War of Independence and an officer of the Greek Army from Epirus.
Biography
Goudas was born in Ioannina or around 1779. He took part in the Gree ...
(1779–1845), fighter of the Greek War of Independence
The Greek War of Independence, also known as the Greek Revolution or the Greek Revolution of 1821, was a successful war of independence by Greek revolutionaries against the Ottoman Empire between 1821 and 1829. The Greeks were later assisted by ...
.
* Athanasios Tsakalov (1790–1851), one of the three founders of Filiki Eteria.
*Michael Christaris
Michael may refer to:
People
* Michael (given name), a given name
* Michael (surname), including a list of people with the surname Michael
Given name "Michael"
* Michael (archangel), ''first'' of God's archangels in the Jewish, Christian and ...
(1773–1851), scholar.
*Elisabeth Kastrisogia
Elizabeth or Elisabeth may refer to:
People
* Elizabeth (given name), a female given name (including people with that name)
* Elizabeth (biblical figure), mother of John the Baptist
Ships
* HMS ''Elizabeth'', several ships
* ''Elisabeth'' (sch ...
(1800–1863), benefactor.
* Georgios Stavros (1787–1869), benefactor, founder of the National Bank of Greece.
*Leonidas Palaskas
Leonidas Palaskas ( el, Λεωνίδας Παλάσκας, 1819 – 14 January 1880) was a distinguished Greek naval officer who served in the French and in the Greek navies, as well as publishing a number of scientific studies.
Life
Leonidas P ...
(1819–1880), Hellenic navy officer.
* Reshid Akif Pasha (1863-1920), Ottoman statesman.
*Georgios Hatzis
Georgios Hatzis ( el, Γεώργιος Χατζής; 1881–1930), also known under the pen name Pelleren, was a Greek author and journalist.
Hatzis was born in Ioannina, northwestern Greece, when the city was still part of the Janina Vilayet ...
(Pelleren) (1881–1930), author and journalist.
*Josef Elijia Josef may refer to
*Josef (given name)
*Josef (surname)
* ''Josef'' (film), a 2011 Croatian war film
*Musik Josef
Musik Josef is a Japanese manufacturer of musical instruments. It was founded by Yukio Nakamura, and is the only company in Japan spe ...
(1901–1931), Jewish Greek poet.
*Patriarch Nicholas V of Alexandria
Nicholas V (1876–1939) served as Greek Patriarch of Alexandria between 1936 and 1939.
He worked very hard on the internal reorganization of the philanthropic institutions of the Church and the harmonious operation of the educational institute ...
(1876–1939)
* Wehib Pasha (1877–1940), Ottoman general.
*Christos Adamidis
Christos Adamidis ( el, Χρήστος Αδαμίδης, 1885–1949) was a Hellenic Army officer and pioneer of military aviation. He was one of the first Greek officers that received aviation training in France and later participated in air o ...
(1885–1949), pioneer aviator and Hellenic Army General.
* Mid’hat Frashëri (1880–1949), politician and writer.
* Mehmet Esat Bülkat (1862–1952), Ottoman general.
*İzzettin Çalışlar
İzzettin Çalışlar (1882 in Yanya ( Ioannina), Janina Vilayet – August 20, 1951 in Istanbul) was an officer of the Ottoman Army and a general of the Turkish Army. He also served as a politician and was a prominent member of the Kemalist
...
(1882–1951), officer of the Ottoman Army.
* Abdülhalik Renda (1881-1957), Chairman of the Turkish National Assembly.
*Markos Avgeris Marcos may refer to:
People with the given name ''Marcos''
*Marcos (given name)
Sports
;Surnamed
* Dayton Marcos, Negro league baseball team from Dayton, Ohio (early twentieth-century)
* Dimitris Markos, Greek footballer
* Nélson Marcos, Portugue ...
(1884–1973), poet.
*Amalia Bakas
Amalia Bakas (born Mazaltov allyMatsa 1897–1979) was a Greek singer and performer in the United States during the 20th century. She was heavily involved in the "Eighth Avenue scene" in New York City and in Greek communities around the United S ...
(1897–1979), singer.
* Dimitrios Hatzis (1913–1981), novelist.
* Dimosthenis Kokkinos (1926–1991), Poet and author.
* Fatma Hikmet İşmen (1918-2006), engineer.
*Pavlos Vrellis
The Pavlos Vrellis Greek History Museum ( el, Μουσείο Ελληνικής Ιστορίας Παύλου Βρέλλη) also known as Pavlos Vrellis Museum of Wax Effigies is a privately owned wax museum in Ioannina regional unit, Greece. It ...
(1922–2010), sculptor.
* Dinos Constantinides (1929–2021), classical music composer.
* Takis Mousafiris (1936–2021), Greek composer and songwriter
*Matsas family, Romaniote Jewish family; most known Minos Matsas
* Hierotheos (Vlachos), theologian.
* Moses Elisaf (b. 1954), elected mayor in June 2019.
*Vana Barba
Vana (or with diacrits, e.g. Váňa) may refer to:
* Vana, Gujarat, a village on Saraushtra peninsula, western India
* Vana State, a former princely state whose seat was in Vana, Gujarat
* Vana, Iran, a village in Mazandaran Province, Iran
* Váň ...
, actress.
* Marios Oikonomou, international football player, played for PAS Giannina, AEK Athens and Italian clubs like Cagliari
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabitant ...
, Bologna, Bari
Bari ( , ; nap, label= Barese, Bare ; lat, Barium) is the capital city of the Metropolitan City of Bari and of the Apulia region, on the Adriatic Sea, southern Italy. It is the second most important economic centre of mainland Southern Italy a ...
, SPAL.
* Georgios Dasios
Georgios Dasios ( el, Γεώργιος Ντάσιος; born 12 May 1983) is a Greek former professional footballer who played as a right-back.
Career
Born in Ioannina, Dasios has spent his entire career playing for local side PAS Giannina and ...
played for PAS Giannina and became the Director of the club.
* Stefanos Ntouskos
Stefanos Ntouskos ( el, Στέφανος Ντούσκος; born 29 March 1997) is a Greek competitive rower. He won a gold medal in the Rowing at the 2020 Summer Olympics – Men's single sculls, men's single sculls, at the 2020 Summer Olympics. ...
(b 1997), gold medal in the Men's single sculls, at the 2020 Summer Olympics
The , officially the and also known as , was an international multi-sport event held from 23 July to 8 August 2021 in Tokyo, Japan, with some preliminary events that began on 21 July.
Tokyo was selected as the host city during the ...
.
* Amanda Tenfjord (b 1997), singer and songwriter, Greek representative at Eurovision 2022
The Eurovision Song Contest 2022 was the 66th edition of the Eurovision Song Contest. It took place in Turin, Italy, following the country's victory at the with the song "" by Måneskin. Organised by the European Broadcasting Union (EBU) and h ...
Sports
Ioannina is home to a major sports team called PAS Giannina. It's an inspiration for many of old as well as new supporters of the whole region of Epirus, even outside Ioannina. Rowing is also very popular in Ioannina; the lake hosted several international events and serves as the venue for part of the annual Greek Rowing Championships.Transport
* Ioannina is served by Ioannina National Airport. * The Egnatia Odos highway, part of the E90, passes by Ioannina. It links the west coast port of Igoumenitsa with the borders.Air Sea Lines
flew from Lake Pamvotis to
Corfu
Corfu (, ) or Kerkyra ( el, Κέρκυρα, Kérkyra, , ; ; la, Corcyra.) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea, of the Ionian Islands, and, including its small satellite islands, forms the margin of the northwestern frontier of Greece. The isl ...
with seaplanes. Air Sea Lines has suspended flights from Corfu to Ioannina since 2007.
* Long-distance buses ( KTEL) travel daily to Athens (6–6.5 hours) and Thessaloniki (3 hours).
In popular culture
*"Yanina" figures prominently in theAlexandre Dumas
Alexandre Dumas (, ; ; born Dumas Davy de la Pailleterie (), 24 July 1802 – 5 December 1870), also known as Alexandre Dumas père (where '' '' is French for 'father', to distinguish him from his son Alexandre Dumas fils), was a French writer ...
' novel "The Count of Monte Cristo".
International relations
Twin towns – sister cities
Ioannina istwinned
Twinning (making a twin of) may refer to:
* In biology and agriculture, producing two offspring (i.e., twins) at a time, or having a tendency to do so;
* Twin towns and sister cities, towns and cities involved in town twinning
* Twinning inst ...
with:
* Požarevac, Serbia
* Ayia Napa, Cyprus
* Limassol, Cyprus
* Himara, Albania
* Kiryat Ono, Israel
* Nizhyn, Ukraine
* Schwerte, Germany
See also
* Epirus *Maroutsaia School
The Maroutsaia School ( el, Μαρουτσαία Σχολή) or Maroutsios was a Greek educational institution that operated in Ioannina from 1742 to 1797. The school reached its peak under Eugenios Voulgaris, one of the main representative of t ...
* Uprising in Yanina
The uprising in Epirus of 1611, also known as uprising of Dionysios Skylosophos, was an anti-Ottoman Empire, Ottoman rebellion by Albanians, Albanian peasants, organized by the former Greek Orthodox bishop Dionysios Skylosophos, Dionysios. The pe ...
* Zagori, region and municipality near Ioannina
Citations
General sources
* * * * * * *External links
Official
Municipality of Ioannina
Travel
Ioannina
– The Greek National Tourism Organization
Ioannina travel guide
Historical
"Here Their Stories Will Be Told..." The Valley of the Communities at Yad Vashem, Ioannina
at Yad Vashem website {{Authority control Greek prefectural capitals Greek regional capitals Historic Jewish communities Municipalities of Epirus (region) Populated places in Ioannina (regional unit)