J. E. B. Stuart on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart (February 6, 1833May 12, 1864) was a
 Stuart was born at
Stuart was born at
 Also in 1855, Stuart met Flora Cooke, the daughter of the commander of the 2nd U.S. Dragoon Regiment,
Also in 1855, Stuart met Flora Cooke, the daughter of the commander of the 2nd U.S. Dragoon Regiment,
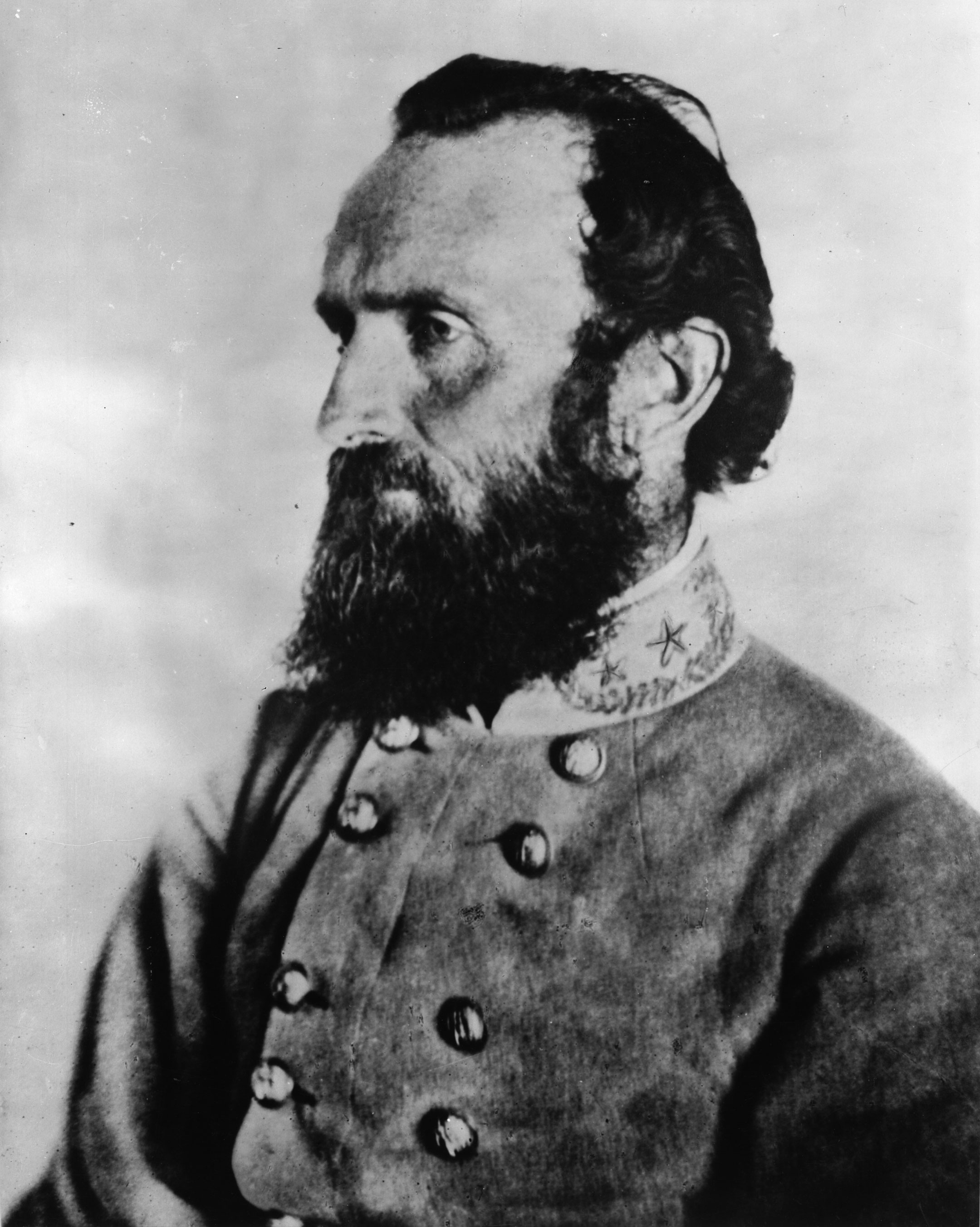 After early service in the
After early service in the
 Early in the Northern Virginia Campaign, Stuart was promoted to
Early in the Northern Virginia Campaign, Stuart was promoted to
 In the December 1862
In the December 1862 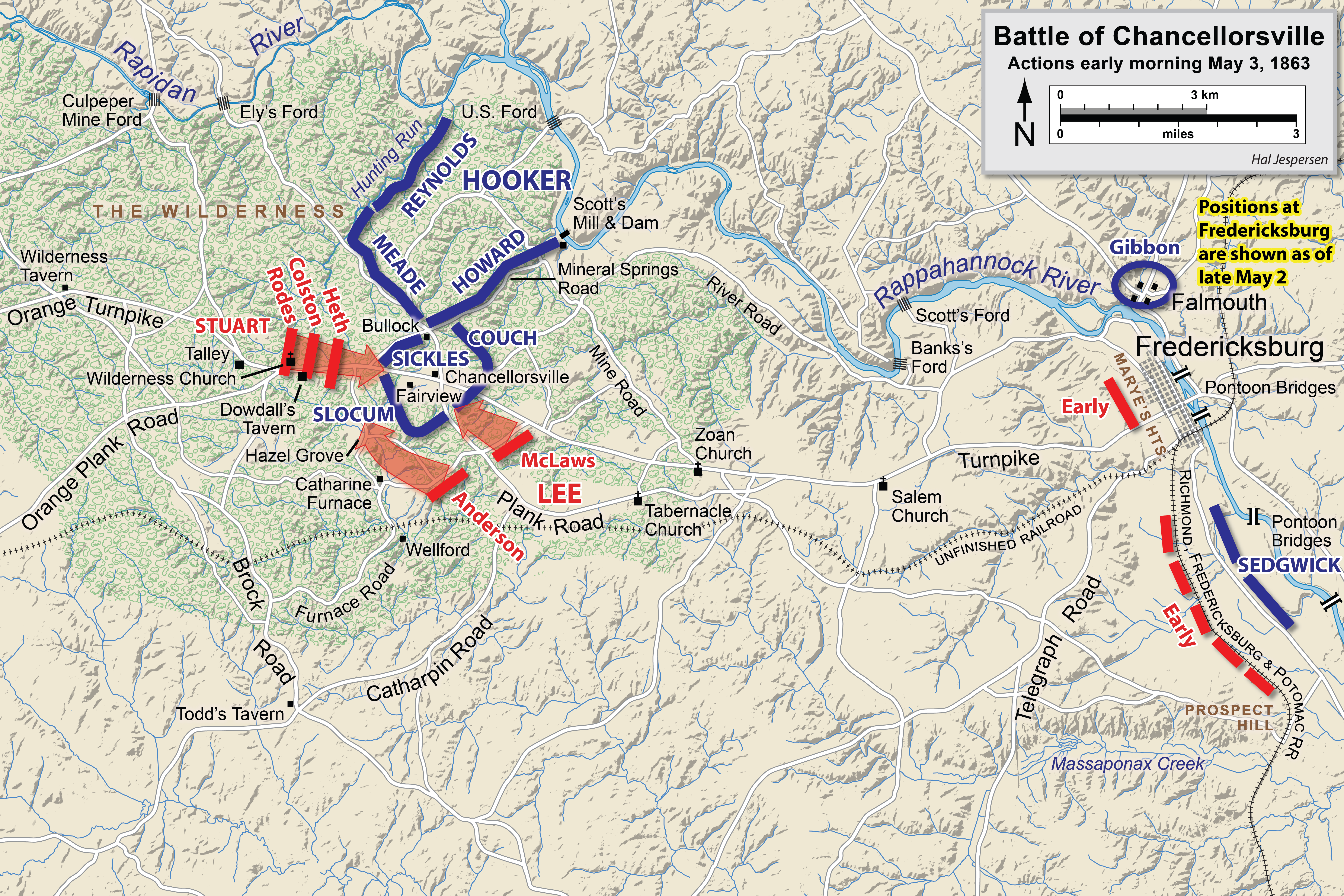 At the
At the
 Lee was not able to attend the review, however, so it was repeated in his presence on June 8, although the repeated performance was limited to a simple parade without battle simulations. Despite the lower level of activity, some of the cavalrymen and the newspaper reporters at the scene complained that all Stuart was doing was feeding his ego and exhausting the horses. Lee ordered Stuart to cross the Rappahannock the next day and raid Union forward positions, screening the Confederate Army from observation or interference as it moved north. Anticipating this imminent offensive action, Stuart ordered his tired troopers back into bivouac around Brandy Station.
Army of the Potomac commander Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker interpreted Stuart's presence around Culpeper to be indicative of preparations for a raid on his army's supply lines. In reaction, he ordered his cavalry commander, Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton, to take a combined arms force of 8,000 cavalrymen and 3,000 infantry on a "spoiling raid" to "disperse and destroy" the 9,500 Confederates. Pleasonton's force crossed the Rappahannock in two columns on June 9, 1863, the first crossing at Beverly's Ford (Brig. Gen. John Buford's division) catching Stuart by surprise, waking him and his staff to the sound of gunfire. The second crossing, at Kelly's Ford, surprised Stuart again, and the Confederates found themselves assaulted from front and rear in a spirited melee of mounted combat. A series of confusing charges and countercharges swept back and forth across Fleetwood Hill, which had been Stuart's headquarters the previous night. After ten hours of fighting, Pleasonton ordered his men to withdraw across the Rappahannock.
Although Stuart claimed a victory because the Confederates held the field, Brandy Station is considered a tactical draw, and both sides came up short. Pleasonton was not able to disable Stuart's force at the start of an important campaign and he withdrew before finding the location of Lee's infantry nearby. However, the fact that the Southern cavalry had not detected the movement of two large columns of Union cavalry, and that they fell victim to a surprise attack, was an embarrassment that prompted serious criticism from fellow generals and the Southern press. The fight also revealed the increased competency of the Union cavalry, and foreshadowed the decline of the formerly invincible Southern mounted arm.
Lee was not able to attend the review, however, so it was repeated in his presence on June 8, although the repeated performance was limited to a simple parade without battle simulations. Despite the lower level of activity, some of the cavalrymen and the newspaper reporters at the scene complained that all Stuart was doing was feeding his ego and exhausting the horses. Lee ordered Stuart to cross the Rappahannock the next day and raid Union forward positions, screening the Confederate Army from observation or interference as it moved north. Anticipating this imminent offensive action, Stuart ordered his tired troopers back into bivouac around Brandy Station.
Army of the Potomac commander Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker interpreted Stuart's presence around Culpeper to be indicative of preparations for a raid on his army's supply lines. In reaction, he ordered his cavalry commander, Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton, to take a combined arms force of 8,000 cavalrymen and 3,000 infantry on a "spoiling raid" to "disperse and destroy" the 9,500 Confederates. Pleasonton's force crossed the Rappahannock in two columns on June 9, 1863, the first crossing at Beverly's Ford (Brig. Gen. John Buford's division) catching Stuart by surprise, waking him and his staff to the sound of gunfire. The second crossing, at Kelly's Ford, surprised Stuart again, and the Confederates found themselves assaulted from front and rear in a spirited melee of mounted combat. A series of confusing charges and countercharges swept back and forth across Fleetwood Hill, which had been Stuart's headquarters the previous night. After ten hours of fighting, Pleasonton ordered his men to withdraw across the Rappahannock.
Although Stuart claimed a victory because the Confederates held the field, Brandy Station is considered a tactical draw, and both sides came up short. Pleasonton was not able to disable Stuart's force at the start of an important campaign and he withdrew before finding the location of Lee's infantry nearby. However, the fact that the Southern cavalry had not detected the movement of two large columns of Union cavalry, and that they fell victim to a surprise attack, was an embarrassment that prompted serious criticism from fellow generals and the Southern press. The fight also revealed the increased competency of the Union cavalry, and foreshadowed the decline of the formerly invincible Southern mounted arm.
 Following a series of small cavalry battles in June as Lee's army began marching north through the Shenandoah Valley, Stuart may have had in mind the glory of circumnavigating the enemy army once again, desiring to erase the stain on his reputation of the surprise at Brandy Station. General Lee gave orders to Stuart on June 22 on how he was to participate in the march north. The exact nature of those orders has been argued by the participants and historians ever since, but the essence was that Stuart was instructed to guard the mountain passes with part of his force while the Army of Northern Virginia was still south of the Potomac, and that he was to cross the river with the remainder of the army and screen the right flank of Ewell's Second Corps. Instead of taking a direct route north near the Blue Ridge Mountains, however, Stuart chose to reach Ewell's flank by taking his three best brigades (those of Brig. Gen.
Following a series of small cavalry battles in June as Lee's army began marching north through the Shenandoah Valley, Stuart may have had in mind the glory of circumnavigating the enemy army once again, desiring to erase the stain on his reputation of the surprise at Brandy Station. General Lee gave orders to Stuart on June 22 on how he was to participate in the march north. The exact nature of those orders has been argued by the participants and historians ever since, but the essence was that Stuart was instructed to guard the mountain passes with part of his force while the Army of Northern Virginia was still south of the Potomac, and that he was to cross the river with the remainder of the army and screen the right flank of Ewell's Second Corps. Instead of taking a direct route north near the Blue Ridge Mountains, however, Stuart chose to reach Ewell's flank by taking his three best brigades (those of Brig. Gen.

 He suffered great pain as an ambulance took him to Richmond to await his wife's arrival at the home of Dr. Charles Brewer, his brother-in-law. As he was being driven from the field in an ambulance wagon, Stuart noticed disorganized ranks of retreating men and called out to them his last words on the battlefield: "Go back, go back, and do your duty, as I have done mine, and our country will be safe. Go back, go back! I had rather die than be whipped."McClellan, Henry B. I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press.
Stuart ordered his sword and spurs be given to his son. As his aide Major McClellan left his side, Confederate President Jefferson Davis came in, took General Stuart's hand, and asked, "General, how do you feel?" Stuart answered "Easy, but willing to die, if God and my country think I have fulfilled my destiny and done my duty." His last whispered words were: "I am resigned; God's will be done." He died at 7:38 p.m. on May 12, the following day, before Flora Stuart reached his side. He was 31 years old. Stuart was buried in Richmond's Hollywood Cemetery. Upon learning of Stuart's death, General Lee is reported to have said that he could hardly keep from weeping at the mere mention of Stuart's name and that Stuart had never given him a bad piece of information. John Huff, the private who had fatally wounded Stuart, was killed in action just a few weeks later at the
He suffered great pain as an ambulance took him to Richmond to await his wife's arrival at the home of Dr. Charles Brewer, his brother-in-law. As he was being driven from the field in an ambulance wagon, Stuart noticed disorganized ranks of retreating men and called out to them his last words on the battlefield: "Go back, go back, and do your duty, as I have done mine, and our country will be safe. Go back, go back! I had rather die than be whipped."McClellan, Henry B. I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press.
Stuart ordered his sword and spurs be given to his son. As his aide Major McClellan left his side, Confederate President Jefferson Davis came in, took General Stuart's hand, and asked, "General, how do you feel?" Stuart answered "Easy, but willing to die, if God and my country think I have fulfilled my destiny and done my duty." His last whispered words were: "I am resigned; God's will be done." He died at 7:38 p.m. on May 12, the following day, before Flora Stuart reached his side. He was 31 years old. Stuart was buried in Richmond's Hollywood Cemetery. Upon learning of Stuart's death, General Lee is reported to have said that he could hardly keep from weeping at the mere mention of Stuart's name and that Stuart had never given him a bad piece of information. John Huff, the private who had fatally wounded Stuart, was killed in action just a few weeks later at the
 Like his intimate friend,
Like his intimate friend, 
United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cla ...
officer from Virginia who became a Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
general during the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
. He was known to his friends as "Jeb,” from the initials of his given names. Stuart was a cavalry
Historically, cavalry (from the French word ''cavalerie'', itself derived from "cheval" meaning "horse") are soldiers or warriors who fight mounted on horseback. Cavalry were the most mobile of the combat arms, operating as light cavalry ...
commander known for his mastery of reconnaissance and the use of cavalry in support of offensive operations. While he cultivated a cavalier image (red-lined gray cape, the yellow waist sash of a regular cavalry officer, hat cocked to the side with an ostrich plume, red flower in his lapel, often sporting cologne), his serious work made him the trusted eyes and ears of Robert E. Lee
Robert Edward Lee (January 19, 1807 – October 12, 1870) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, towards the end of which he was appointed the overall commander of the Confederate States Army. He led the Army of Nort ...
's army and inspired Southern morale.
Stuart graduated from West Point in 1854, and served in Texas and Kansas with the U.S. Army. Stuart was a veteran of the frontier conflicts with Native Americans and the violence of Bleeding Kansas, and he participated in the capture of John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800–1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763–1842), Ir ...
at Harpers Ferry. He resigned his commission when his home state of Virginia seceded, to serve in the Confederate Army, first under Stonewall Jackson
Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson (January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, considered one of the best-known Confederate commanders, after Robert E. Lee. He played a prominent role in nearl ...
in the Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge- ...
, but then in increasingly important cavalry commands of the Army of Northern Virginia, playing a role in all of that army's campaigns until his death.
He established a reputation as an audacious cavalry commander and on two occasions (during the Peninsula Campaign and the Maryland Campaign) circumnavigated the Union
Union commonly refers to:
* Trade union, an organization of workers
* Union (set theory), in mathematics, a fundamental operation on sets
Union may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
Music
* Union (band), an American rock group
** ''Un ...
Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
, bringing fame to himself and embarrassment to the North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
. At the Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville, April 30 – May 6, 1863, was a major battle of the American Civil War (1861–1865), and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville campaign.
Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because h ...
, he distinguished himself as a temporary commander of the wounded Stonewall Jackson's infantry corps.
Stuart's most famous campaign, the Gettysburg Campaign, was flawed when his long separation from Lee's army left Lee unaware of Union troop movements so that Lee was surprised and almost trapped at the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
. Stuart received criticism from the Southern press as well as the proponents of the Lost Cause movement after the war. During the 1864 Overland Campaign, Union Maj. Gen. Philip Sheridan
General of the Army Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close as ...
's cavalry launched an offensive to defeat Stuart, who was mortally wounded at the Battle of Yellow Tavern.
Early life and background
 Stuart was born at
Stuart was born at Laurel Hill Farm
Laurel Hill Farm is a private park and historic home located in Ararat, Virginia. The birthplace of James Ewell Brown "Jeb" Stuart, seventy-five acres of the owned by the Stuart Family was saved in 1992 by the J. E. B. Stuart Birthplace Preserv ...
, a plantation in Patrick County
Patrick County is a county located on the central southern border of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,608. Its county seat is Stuart. It is located within both the rolling hills and valleys of the Pi ...
, Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, near the border with North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. He was the eighth of eleven children and the youngest of the five sons to survive past early age. His father, Archibald Stuart
Archibald Stuart (December 2, 1795 – September 20, 1855) was a nineteenth-century politician and lawyer from Virginia. He was the first cousin of Alexander Hugh Holmes Stuart and the father of Confederate General James Ewell Brown "Jeb" S ...
, was a War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
veteran, slaveholder, attorney, and Democratic politician who represented Patrick County in both houses of the Virginia General Assembly
The Virginia General Assembly is the legislative body of the Commonwealth of Virginia, the oldest continuous law-making body in the Western Hemisphere, the first elected legislative assembly in the New World, and was established on July 30, 161 ...
, and also served one term in the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the Lower house, lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the United States Senate, Senate being ...
. His mother Elizabeth Letcher Pannill Stuart ran the family farm, and was known as a strict religious woman with a good sense for business.
He was of Scottish
Scottish usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
*Scottish Gaelic, a Celtic Goidelic language of the Indo-European language family native to Scotland
*Scottish English
*Scottish national identity, the Scottish ide ...
descent (including some Scots-Irish). His great-grandfather, Major Alexander Stuart, commanded a regiment at the Battle of Guilford Court House
The Battle of Guilford Court House was on March 15, 1781, during the American Revolutionary War, at a site that is now in Greensboro, the seat of Guilford County, North Carolina. A 2,100-man British force under the command of Lieutenant General ...
during the Revolutionary War.Thomas, p. 5. His father Archibald was a cousin of attorney Alexander Hugh Holmes Stuart.
Education
Stuart was educated at home by his mother and tutors until the age of twelve, when he left Laurel Hill to be educated by various teachers in Wytheville, Virginia, and at the home of his aunt Anne (Archibald's sister) and her husband Judge James Ewell Brown (Stuart's namesake) at Danville. He enteredEmory and Henry College
Emory & Henry College (E&H or Emory) is a private liberal arts college in Emory, Virginia. The campus comprises of Washington County, which is part of the Appalachian highlands of Southwest Virginia. Founded in 1836, Emory & Henry College is ...
when he was fifteen, and attended from 1848 to 1850.
During the summer of 1848, Stuart attempted to enlist in the U.S. Army, but was rejected as underaged. He obtained an appointment in 1850 to the United States Military Academy
The United States Military Academy (USMA), also known metonymically as West Point or simply as Army, is a United States service academy in West Point, New York. It was originally established as a fort, since it sits on strategic high groun ...
at West Point, New York
West Point is the oldest continuously occupied military post in the United States. Located on the Hudson River in New York, West Point was identified by General George Washington as the most important strategic position in America during the Ame ...
, from Representative
Representative may refer to:
Politics
*Representative democracy, type of democracy in which elected officials represent a group of people
*House of Representatives, legislative body in various countries or sub-national entities
*Legislator, someon ...
Thomas Hamlet Averett, the man who had defeated his father in the 1848 election. Stuart was a popular student and was happy at the Academy. Although he was not handsome in his teen years, his classmates called him by the nickname "Beauty", which they described as his "personal comeliness in inverse ratio to the term employed." He quickly grew a beard after graduation and a fellow officer remarked that he was "the only man he ever saw that beard improved."
Robert E. Lee was appointed superintendent of the academy in 1852, and Stuart became a friend of the family, seeing them socially on frequent occasions. Lee's nephew, Fitzhugh Lee, also arrived at the academy in 1852. In Stuart's final year, in addition to achieving the cadet rank of second captain of the corps, he was one of eight cadets designated as honorary "cavalry officers" for his skills in horsemanship. Stuart graduated 13th in his class of 46 in 1854. He ranked tenth in his class in cavalry tactics
For much of history, humans have used some form of cavalry for war and, as a result, cavalry tactics have evolved over time. Tactically, the main advantages of cavalry over infantry troops were greater mobility, a larger impact, and a higher pos ...
. Although he enjoyed the civil engineering curriculum at the academy and did well in mathematics, his poor drawing skills hampered his engineering studies, and he finished 29th in that discipline.
United States Army
Stuart was commissioned abrevet
Brevet may refer to:
Military
* Brevet (military), higher rank that rewards merit or gallantry, but without higher pay
* Brevet d'état-major, a military distinction in France and Belgium awarded to officers passing military staff college
* Aircre ...
second lieutenant
Second lieutenant is a junior commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces, comparable to NATO OF-1 rank.
Australia
The rank of second lieutenant existed in the military forces of the Australian colonies and Australian Army until ...
and assigned to the U.S. Regiment of Mounted Riflemen
The 3rd Cavalry Regiment, formerly 3rd Armored Cavalry Regiment ("Brave Rifles") is a regiment of the United States Army currently stationed at Fort Hood, Texas.
The regiment has a history in the United States Army that dates back to 19 May 1 ...
in Texas. After an arduous journey, he reached Fort Davis on January 28, 1855, and was a leader for three months on scouting missions over the San Antonio
("Cradle of Freedom")
, image_map =
, mapsize = 220px
, map_caption = Interactive map of San Antonio
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = United States
, subdivision_type1= U.S. state, State
, subdivision_name1 = Texas
, s ...
to El Paso
El Paso (; "the pass") is a city in and the seat of El Paso County in the western corner of the U.S. state of Texas. The 2020 population of the city from the U.S. Census Bureau was 678,815, making it the 23rd-largest city in the U.S., the s ...
Road. He was soon transferred to the newly formed 1st Cavalry Regiment (1855) at Fort Leavenworth
Fort Leavenworth () is a United States Army installation located in Leavenworth County, Kansas, in the city of Leavenworth, Kansas, Leavenworth. Built in 1827, it is the second oldest active United States Army post west of Washington, D.C., an ...
, Kansas Territory
The Territory of Kansas was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from May 30, 1854, until January 29, 1861, when the eastern portion of the territory was admitted to the United States, Union as the Slave and ...
, where he became regimental quartermaster and commissary officer under the command of Col.
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Edwin V. Sumner
Edwin Vose Sumner (January 30, 1797March 21, 1863) was a career United States Army officer who became a Union Army general and the oldest field commander of any Army Corps on either side during the American Civil War. His nicknames "Bull" or "Bul ...
. He was promoted to first lieutenant
First lieutenant is a commissioned officer military rank in many armed forces; in some forces, it is an appointment.
The rank of lieutenant has different meanings in different military formations, but in most forces it is sub-divided into a s ...
in 1855.
Marriage
 Also in 1855, Stuart met Flora Cooke, the daughter of the commander of the 2nd U.S. Dragoon Regiment,
Also in 1855, Stuart met Flora Cooke, the daughter of the commander of the 2nd U.S. Dragoon Regiment, Lieutenant Colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
Philip St. George Cooke. Burke Davis described Flora as "an accomplished horsewoman, and though not pretty, an effective charmer," to whom "Stuart succumbed with hardly a struggle." They became engaged in September, less than two months after meeting. Stuart humorously wrote of his rapid courtship in Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, "'' Veni, Vidi, Victus sum''" (I came, I saw, I was conquered). Although a gala wedding had been planned for Fort Riley, Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, the death of Stuart's father on September 20 caused a change of plans and the marriage on November 14 was small and limited to family witnesses. Their first child, a girl, was born in 1856 but died the same day. On November 14, 1857, Flora gave birth to another daughter, whom the parents named Flora after her mother. The family relocated in early 1858 to Fort Riley, where they remained for three years. The couple owned two slaves until 1859, one inherited from his father's estate, the other purchased.
Bleeding Kansas
Stuart's leadership capabilities were soon recognized. He was a veteran of the frontier conflicts with Native Americans and the antebellum violence of Bleeding Kansas. He was wounded on July 29, 1857, while fighting at Solomon River,Kansas
Kansas () is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its capital is Topeka, and its largest city is Wichita. Kansas is a landlocked state bordered by Nebraska to the north; Missouri to the east; Oklahoma to the south; and Colorado to the ...
, against the Cheyenne
The Cheyenne ( ) are an Indigenous people of the Great Plains. Their Cheyenne language belongs to the Algonquian language family. Today, the Cheyenne people are split into two federally recognized nations: the Southern Cheyenne, who are enroll ...
. Col. Sumner ordered a charge with drawn sabers against a wave of Native American arrows. Scattering the under-armed warriors, Stuart and three other lieutenants chased one down, whom Stuart wounded in the thigh with his pistol. The Cheyenne turned and fired at Stuart with an old-fashioned pistol, striking him in the chest with a bullet, which did little more damage than to pierce the skin. Stuart returned in September to Fort Leavenworth and was reunited with his wife.
John Brown
In 1859, Stuart developed a new piece of cavalry equipment, for which he receivedpatent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A p ...
number 25,684 on October 4—a saber hook, or an "improved method of attaching sabers to belts." The U.S. government paid Stuart $5,000 for a "right to use" license and Stuart contracted with Knorr, Nece and Co. of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Sinc ...
to manufacture his hook. While in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, to discuss government contracts, and in conjunction with his application for an appointment into the quartermaster department, Stuart heard about John Brown John Brown most often refers to:
*John Brown (abolitionist) (1800–1859), American who led an anti-slavery raid in Harpers Ferry, Virginia in 1859
John Brown or Johnny Brown may also refer to:
Academia
* John Brown (educator) (1763–1842), Ir ...
's raid on the U.S. Arsenal at Harpers Ferry. Stuart volunteered to be aide-de-camp to Col. Robert E. Lee and accompanied Lee with a company of U.S. Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the Marines, maritime land force military branch, service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary warfare, exped ...
from the Marine Barracks, 8th & I, Washington, DC. and four companies of Maryland militia. While delivering Lee's written surrender ultimatum to the leader of the group, who had been calling himself Isaac Smith, Stuart recognized "Old Osawatomie Brown" from his days in Kansas.
Resignation
Stuart was promoted tocaptain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
on April 22, 1861, but resigned from the U.S. Army on May 3, 1861, to join the Confederate States Army
The Confederate States Army, also called the Confederate Army or the Southern Army, was the military land force of the Confederate States of America (commonly referred to as the Confederacy) during the American Civil War (1861–1865), fighting ...
, following the secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
of Virginia. On June 26, 1860, Flora gave birth to a son, Philip St. George Cooke Stuart, but his father changed the name to James Ewell Brown Stuart, Jr. ("Jimmie"), in late 1861 out of disgust with his father-in-law. Upon learning that his father-in-law, Col. Cooke, would remain in the U.S. Army during the coming war, Stuart wrote to his brother-in-law (future Confederate Brig. Gen. John Rogers Cooke
John Rogers Cooke (June 9, 1833 – April 10, 1891) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War. He was the son of Union general Philip St. George Cooke and the brother-in-law of Confederate cavalry leader Jeb Stuart.
Early and fami ...
), "He will regret it but once, and that will be continuously."
Confederate Army
Early service
Stuart was commissioned as alieutenant colonel
Lieutenant colonel ( , ) is a rank of commissioned officers in the armies, most marine forces and some air forces of the world, above a major and below a colonel. Several police forces in the United States use the rank of lieutenant colone ...
of Virginia Infantry in the Confederate Army on May 10, 1861. Maj. Gen.
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
Robert E. Lee, now commanding the armed forces of Virginia, ordered him to report to Colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge of ...
Thomas J. Jackson
Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson (January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, considered one of the best-known Confederate commanders, after Robert E. Lee. He played a prominent role in near ...
at Harper's Ferry. Jackson chose to ignore Stuart's infantry designation and assigned him on July 4 to command all the cavalry companies of the Army of the Shenandoah, organized as the 1st Virginia Cavalry Regiment. He was promoted to colonel on July 16.
 After early service in the
After early service in the Shenandoah Valley
The Shenandoah Valley () is a geographic valley and cultural region of western Virginia and the Eastern Panhandle of West Virginia. The valley is bounded to the east by the Blue Ridge Mountains, to the west by the eastern front of the Ridge- ...
, Stuart led his regiment in the First Battle of Bull Run (where Jackson got his nickname, "Stonewall"), and participated in the pursuit of the retreating Federals. He then commanded the Army's outposts along the upper Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augus ...
until given command of the cavalry brigade for the army then known as the Army of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
(later named the Army of Northern Virginia). He was promoted to brigadier general
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed ...
on September 24, 1861.
Peninsula
In 1862, the UnionArmy of the Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confedera ...
began its Peninsula Campaign against Richmond, Virginia
(Thus do we reach the stars)
, image_map =
, mapsize = 250 px
, map_caption = Location within Virginia
, pushpin_map = Virginia#USA
, pushpin_label = Richmond
, pushpin_m ...
, and Stuart's cavalry brigade assisted Gen. Joseph E. Johnston's army as it withdrew up the Virginia Peninsula
The Virginia Peninsula is a peninsula in southeast Virginia, USA, bounded by the York River, James River, Hampton Roads and Chesapeake Bay. It is sometimes known as the ''Lower Peninsula'' to distinguish it from two other peninsulas to the ...
in the face of superior numbers. Stuart fought at the Battle of Williamsburg
The Battle of Williamsburg, also known as the Battle of Fort Magruder, took place on May 5, 1862, in York County, James City County, and Williamsburg, Virginia, as part of the Peninsula Campaign of the American Civil War. It was the first pitc ...
, but in general the terrain and weather on the Peninsula did not lend themselves to cavalry operations.
However, when Gen. Robert E. Lee became commander of the Army of Northern Virginia, he requested that Stuart perform reconnaissance to determine whether the right flank of the Union army was vulnerable. Stuart set out with 1,200 troopers on the morning of June 12 and, having determined that the flank was indeed vulnerable, took his men on a complete circumnavigation of the Union army, returning after 150 miles on June 15 with 165 captured Union soldiers, 260 horses and mules, and various quartermaster and ordnance supplies. His men met no serious opposition from the more decentralized Union cavalry, coincidentally commanded by his father-in-law, Col. Cooke, and their total casualties amounted to one man killed. The maneuver was a public relations sensation and Stuart was greeted with flower petals thrown in his path at Richmond. He had become as famous as Stonewall Jackson in the eyes of the Confederacy.
Northern Virginia
 Early in the Northern Virginia Campaign, Stuart was promoted to
Early in the Northern Virginia Campaign, Stuart was promoted to major general
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of a ...
on July 25, 1862, and his command was upgraded to the Cavalry Division.Wert, pp. 125–29; Davis, pp. 167–72. He was nearly captured and lost his signature plumed hat and cloak to pursuing Federals during a raid in August, but in a retaliatory raid at Catlett's Station the following day, managed to overrun Union army commander Maj. Gen. John Pope's headquarters, and not only captured Pope's full uniform, but also intercepted orders that provided Lee with valuable intelligence concerning reinforcements for Pope's army.
At the Second Battle of Bull Run
The Second Battle of Bull Run or Battle of Second Manassas was fought August 28–30, 1862, in Prince William County, Virginia, as part of the American Civil War. It was the culmination of the Northern Virginia Campaign waged by Confederate ...
(Second Manassas), Stuart's cavalry followed the massive assault by Longstreet's infantry against Pope's army, protecting its flank with artillery batteries. Stuart ordered Brig. Gen. Beverly Robertson
Beverly Holcombe Robertson (June 5, 1827 – December 12, 1910) was a cavalry officer in the United States Army on the Western frontier and a Confederate States Army general during the American Civil War.
Early life
Robertson was born on a ...
's brigade to pursue the Federals and in a sharp fight against Brig. Gen. John Buford's brigade, Col. Thomas T. Munford
Thomas Taylor Munford (March 29, 1831 – February 27, 1918) was an American farmer, iron, steel and mining company executive and Confederate colonel and acting brigadier general during the American Civil War.
Biography
Munford was born in R ...
's 2nd Virginia Cavalry
The 2nd Virginia Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment raised in Virginia for service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It fought mostly with the Army of Northern Virginia.
The unit was organized by Colonel Jubal E ...
was overwhelmed until Stuart sent in two more regiments as reinforcements. Buford's men, many of whom were new to combat, retreated across Lewis's Ford and Stuart's troopers captured over 300 of them. Stuart's men harassed the retreating Union columns until the campaign ended at the Battle of Chantilly.
Maryland
During the Maryland Campaign of September 1862, Stuart's cavalry screened the army's movement north. He bears some responsibility for Robert E. Lee's lack of knowledge of the position and celerity of the pursuing Army of the Potomac under George B. McClellan. For a five-day period, Stuart rested his men and entertained local civilians at a gala ball atUrbana, Maryland
Urbana ( ) is a suburban census-designated place located in Frederick County, Maryland, United States. It lies at the I-270/ MD 80 interchange, approximately southeast of Frederick and about northwest of Washington, D.C. Urbana started to develo ...
. His reports make no reference to intelligence gathering by his scouts or patrols. As the Union Army drew near to Lee's divided army, Stuart's men skirmished at various points on the approach to Frederick and Stuart was not able to keep his brigades concentrated enough to resist the oncoming tide. He misjudged the Union routes of advance, ignorant of the Union force threatening Turner's Gap, and required assistance from the infantry of Maj. Gen. D.H. Hill
Lieutenant-General Daniel Harvey Hill (July 12, 1821 – September 24, 1889), commonly known as D. H. Hill, was a senior officer of the Confederate States Army who commanded infantry in the eastern and western theaters of the American Civil War ...
to defend the South Mountain South Mountain or South Mountains may refer to:
Canada
* South Mountain, a village in North Dundas, Ontario
* South Mountain (Nova Scotia), a mountain range
* South Mountain (band), a Canadian country music group
United States
Landforms
* Sou ...
passes in the Battle of South Mountain. His horse artillery bombarded the flank of the Union army as it opened its attack in the Battle of Antietam
The Battle of Antietam (), or Battle of Sharpsburg particularly in the Southern United States, was a battle of the American Civil War fought on September 17, 1862, between Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia and Union G ...
. By mid-afternoon, Stonewall Jackson ordered Stuart to command a turning movement with his cavalry against the Union right flank and rear, which if successful would be followed up by an infantry attack from the West Woods. Stuart began probing the Union lines with more artillery barrages, which were answered with "murderous" counterbattery fire and the cavalry movement intended by Jackson was never launched.
Three weeks after Lee's army had withdrawn back to Virginia, on October 10–12, 1862, Stuart performed another of his audacious circumnavigations of the Army of the Potomac, his Chambersburg Raid—126 miles in under 60 hours, from Darkesville, West Virginia to as far north as Mercersburg, Pennsylvania and Chambersburg
Chambersburg is a borough in and the county seat of Franklin County, in the South Central region of Pennsylvania, United States. It is in the Cumberland Valley, which is part of the Great Appalachian Valley, and north of Maryland and the Mas ...
and around to the east through Emmitsburg, Maryland
Emmitsburg is a town in Frederick County, Maryland, United States, south of the Mason-Dixon line separating Maryland from Pennsylvania. Founded in 1785, Emmitsburg is the home of Mount St. Mary's University. The town has two Catholic pilgrima ...
and south through Hyattstown, Maryland
Hyattstown is an unincorporated community in Montgomery County, Maryland, United States.
Established in 1798 by founder Jesse Hyatt, Hyattstown is located on Maryland Route 355 in upper Montgomery County. In this full-service town, there was ...
and White's Ford
White's Ford was an important ford over the Potomac River during the American Civil War. It was used in many major actions, including the crossing into Maryland of the Confederate army prior to the Maryland Campaign and Confederate Major Genera ...
to Leesburg, Virginia—once again embarrassing his Union opponents and seizing horses and supplies, but at the expense of exhausted men and animals, without gaining much military advantage. Jubal Early referred to it as "the greatest horse stealing expedition" that only "annoyed" the enemy. Stuart gave his friend Jackson a fine, new officer's tunic, trimmed with gold lace, commissioned from a Richmond tailor, which he thought would give Jackson more of the appearance of a proper general (something to which Jackson was notoriously indifferent).
McClellan pushed his army slowly south, urged by President Lincoln to pursue Lee, crossing the Potomac starting on October 26. As Lee began moving to counter this, Stuart screened Longstreet's Corps and skirmished numerous times in early November against Union cavalry and infantry around Mountville, Aldie, and Upperville. On November 6, Stuart received sad news by telegram that his daughter Flora had died just before her fifth birthday of typhoid fever
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
on November 3.
Fredericksburg and Chancellorsville
 In the December 1862
In the December 1862 Battle of Fredericksburg
The Battle of Fredericksburg was fought December 11–15, 1862, in and around Fredericksburg, Virginia, in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. The combat, between the Union Army of the Potomac commanded by Maj. Gen. Ambrose Burnsi ...
, Stuart and his cavalry—most notably his horse artillery under Major John Pelham—protected Stonewall Jackson's flank at Hamilton's Crossing. General Lee commended his cavalry, which "effectually guarded our right, annoying the enemy and embarrassing his movements by hanging on his flank, and attacking when the opportunity occurred." Stuart reported to Flora the next day that he had been shot through his fur collar but was unhurt.
After Christmas, Lee ordered Stuart to conduct a raid north of the Rappahannock River to "penetrate the enemy's rear, ascertain if possible his position & movements, & inflict upon him such damage as circumstances will permit." With 1,800 troopers and a horse artillery battery assigned to the operation, Stuart's raid reached as far north as four miles south of Fairfax Court House, seizing 250 prisoners, horses, mules, and supplies. Tapping telegraph lines, his signalmen intercepted messages between Union commanders, and Stuart sent a personal telegram to Union Quartermaster General Montgomery C. Meigs
Montgomery Cunningham Meigs (; May 3, 1816 – January 2, 1892) was a career United States Army officer and civil engineer, who served as Quartermaster General of the U.S. Army during and after the American Civil War. Meigs strongly opposed sece ...
, "General Meigs will in the future please furnish better mules; those you have furnished recently are very inferior."
On March 17, 1863, Stuart's cavalry clashed with a Union raiding party at Kelly's Ford. The minor victory was marred by the death of Major Pelham, which caused Stuart profound grief, as he thought of him as close as a younger brother. He wrote to a Confederate Congressman, "The noble, the chivalric, the gallant Pelham is no more. ... Let the tears of agony we have shed, and the gloom of mourning throughout my command bear witness." Flora was pregnant at the time and Stuart told her that if it were a boy, he wanted him to be named John Pelham Stuart. (Virginia Pelham Stuart was born October 9.)
 At the
At the Battle of Chancellorsville
The Battle of Chancellorsville, April 30 – May 6, 1863, was a major battle of the American Civil War (1861–1865), and the principal engagement of the Chancellorsville campaign.
Chancellorsville is known as Lee's "perfect battle" because h ...
, Stuart accompanied Stonewall Jackson on his famous flanking march of May 2, 1863, and started to pursue the retreating soldiers of the Union XI Corps 11 Corps, 11th Corps, Eleventh Corps, or XI Corps may refer to:
* 11th Army Corps (France)
* XI Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* XI Corps (German Empire), a unit of the Imperial German Army
* XI ...
when he received word that both Jackson and his senior division commander, Maj. Gen. A.P. Hill
Ambrose Powell Hill Jr. (November 9, 1825April 2, 1865) was a Confederate general who was killed in the American Civil War. He is usually referred to as A. P. Hill to differentiate him from another, unrelated Confederate general, Daniel Harvey Hi ...
, had been wounded. Hill, bypassing the next most senior infantry general in the corps, Brig. Gen. Robert E. Rodes
Robert Emmett (or Emmet) Rodes (March 29, 1829 – September 19, 1864) was a Confederate general in the American Civil War, and the first of Robert E. Lee's divisional commanders not trained at West Point. His division led Stonewall Jackson's ...
, sent a message ordering Stuart to take command of the Second Corps. Although the delays associated with this change of command effectively ended the flanking attack the night of May 2, Stuart performed creditably as an infantry corps commander the following day, launching a strong and well-coordinated attack against the Union right flank at Chancellorsville. When Union troops abandoned Hazel Grove, Stuart had the presence of mind to quickly occupy it and bombard the Union positions with artillery. Stuart relinquished his infantry command on May 6 when Hill returned to duty. Stephen W. Sears
Stephen Ward Sears (born July 27, 1932) is an American historian specializing in the American Civil War.
Early life and education
Sears is a graduate of Oberlin College.
Career
As an author, he has concentrated on the military history of the A ...
wrote:
Stonewall Jackson died on May 10 and Stuart was once again devastated by the loss of a close friend, telling his staff that the death was a "national calamity." Jackson's wife, Mary Anna, wrote to Stuart on August 1, thanking him for a note of sympathy: "I need not assure you of which you already know, that your friendship & admiration were cordially reciprocated by him. I have frequently heard him speak of Gen'l Stuart as one of his warm personal friends, & also express admiration for your Soldierly qualities."
Brandy Station
Returning to the cavalry for the Gettysburg Campaign, Stuart endured the two low points in his career, starting with the Battle of Brandy Station, the largest predominantly cavalry engagement of the war. By June 5, two of Lee's infantry corps were camped in and around Culpeper. Six miles northeast, holding the line of the Rappahannock River, Stuart bivouacked his cavalry troopers, mostly near Brandy Station, screening the Confederate Army against surprise by the enemy. Stuart requested a full field review of his troops by Gen. Lee. This grand review on June 5 included nearly 9,000 mounted troopers and four batteries of horse artillery, charging in simulated battle at Inlet Station, about two miles (three km) southwest of Brandy Station. Lee was not able to attend the review, however, so it was repeated in his presence on June 8, although the repeated performance was limited to a simple parade without battle simulations. Despite the lower level of activity, some of the cavalrymen and the newspaper reporters at the scene complained that all Stuart was doing was feeding his ego and exhausting the horses. Lee ordered Stuart to cross the Rappahannock the next day and raid Union forward positions, screening the Confederate Army from observation or interference as it moved north. Anticipating this imminent offensive action, Stuart ordered his tired troopers back into bivouac around Brandy Station.
Army of the Potomac commander Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker interpreted Stuart's presence around Culpeper to be indicative of preparations for a raid on his army's supply lines. In reaction, he ordered his cavalry commander, Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton, to take a combined arms force of 8,000 cavalrymen and 3,000 infantry on a "spoiling raid" to "disperse and destroy" the 9,500 Confederates. Pleasonton's force crossed the Rappahannock in two columns on June 9, 1863, the first crossing at Beverly's Ford (Brig. Gen. John Buford's division) catching Stuart by surprise, waking him and his staff to the sound of gunfire. The second crossing, at Kelly's Ford, surprised Stuart again, and the Confederates found themselves assaulted from front and rear in a spirited melee of mounted combat. A series of confusing charges and countercharges swept back and forth across Fleetwood Hill, which had been Stuart's headquarters the previous night. After ten hours of fighting, Pleasonton ordered his men to withdraw across the Rappahannock.
Although Stuart claimed a victory because the Confederates held the field, Brandy Station is considered a tactical draw, and both sides came up short. Pleasonton was not able to disable Stuart's force at the start of an important campaign and he withdrew before finding the location of Lee's infantry nearby. However, the fact that the Southern cavalry had not detected the movement of two large columns of Union cavalry, and that they fell victim to a surprise attack, was an embarrassment that prompted serious criticism from fellow generals and the Southern press. The fight also revealed the increased competency of the Union cavalry, and foreshadowed the decline of the formerly invincible Southern mounted arm.
Lee was not able to attend the review, however, so it was repeated in his presence on June 8, although the repeated performance was limited to a simple parade without battle simulations. Despite the lower level of activity, some of the cavalrymen and the newspaper reporters at the scene complained that all Stuart was doing was feeding his ego and exhausting the horses. Lee ordered Stuart to cross the Rappahannock the next day and raid Union forward positions, screening the Confederate Army from observation or interference as it moved north. Anticipating this imminent offensive action, Stuart ordered his tired troopers back into bivouac around Brandy Station.
Army of the Potomac commander Maj. Gen. Joseph Hooker interpreted Stuart's presence around Culpeper to be indicative of preparations for a raid on his army's supply lines. In reaction, he ordered his cavalry commander, Maj. Gen. Alfred Pleasonton, to take a combined arms force of 8,000 cavalrymen and 3,000 infantry on a "spoiling raid" to "disperse and destroy" the 9,500 Confederates. Pleasonton's force crossed the Rappahannock in two columns on June 9, 1863, the first crossing at Beverly's Ford (Brig. Gen. John Buford's division) catching Stuart by surprise, waking him and his staff to the sound of gunfire. The second crossing, at Kelly's Ford, surprised Stuart again, and the Confederates found themselves assaulted from front and rear in a spirited melee of mounted combat. A series of confusing charges and countercharges swept back and forth across Fleetwood Hill, which had been Stuart's headquarters the previous night. After ten hours of fighting, Pleasonton ordered his men to withdraw across the Rappahannock.
Although Stuart claimed a victory because the Confederates held the field, Brandy Station is considered a tactical draw, and both sides came up short. Pleasonton was not able to disable Stuart's force at the start of an important campaign and he withdrew before finding the location of Lee's infantry nearby. However, the fact that the Southern cavalry had not detected the movement of two large columns of Union cavalry, and that they fell victim to a surprise attack, was an embarrassment that prompted serious criticism from fellow generals and the Southern press. The fight also revealed the increased competency of the Union cavalry, and foreshadowed the decline of the formerly invincible Southern mounted arm.
Stuart's ride in the Gettysburg Campaign
 Following a series of small cavalry battles in June as Lee's army began marching north through the Shenandoah Valley, Stuart may have had in mind the glory of circumnavigating the enemy army once again, desiring to erase the stain on his reputation of the surprise at Brandy Station. General Lee gave orders to Stuart on June 22 on how he was to participate in the march north. The exact nature of those orders has been argued by the participants and historians ever since, but the essence was that Stuart was instructed to guard the mountain passes with part of his force while the Army of Northern Virginia was still south of the Potomac, and that he was to cross the river with the remainder of the army and screen the right flank of Ewell's Second Corps. Instead of taking a direct route north near the Blue Ridge Mountains, however, Stuart chose to reach Ewell's flank by taking his three best brigades (those of Brig. Gen.
Following a series of small cavalry battles in June as Lee's army began marching north through the Shenandoah Valley, Stuart may have had in mind the glory of circumnavigating the enemy army once again, desiring to erase the stain on his reputation of the surprise at Brandy Station. General Lee gave orders to Stuart on June 22 on how he was to participate in the march north. The exact nature of those orders has been argued by the participants and historians ever since, but the essence was that Stuart was instructed to guard the mountain passes with part of his force while the Army of Northern Virginia was still south of the Potomac, and that he was to cross the river with the remainder of the army and screen the right flank of Ewell's Second Corps. Instead of taking a direct route north near the Blue Ridge Mountains, however, Stuart chose to reach Ewell's flank by taking his three best brigades (those of Brig. Gen. Wade Hampton Wade Hampton may refer to the following people:
People
*Wade Hampton I (1752–1835), American soldier in Revolutionary War and War of 1812 and U.S. congressman
*Wade Hampton II (1791–1858), American plantation owner and soldier in War of 1812
*W ...
, Brig. Gen. Fitzhugh Lee, and Col. John R. Chambliss
John Randolph Chambliss Jr. (January 23, 1833 – August 16, 1864) was a career military officer, serving in the United States Army and then, during the American Civil War, in the Confederate States Army. A brigadier general of cavalry, Chambliss w ...
, the latter replacing the wounded Brig. Gen. W.H.F. "Rooney" Lee) between the Union army and Washington, moving north through Rockville to Westminster
Westminster is an area of Central London, part of the wider City of Westminster.
The area, which extends from the River Thames to Oxford Street, has many visitor attractions and historic landmarks, including the Palace of Westminster, Bu ...
and on into Pennsylvania, hoping to capture supplies along the way and cause havoc near the enemy capital. Stuart and his three brigades departed Salem Depot at 1 a.m. on June 25.
Unfortunately for Stuart's plan, the Union army's movement was underway and his proposed route was blocked by columns of Federal infantry, forcing him to veer farther to the east than either he or General Lee had anticipated. This prevented Stuart from linking up with Ewell as ordered and deprived Lee of the use of his prime cavalry force, the "eyes and ears" of the army, while advancing into unfamiliar enemy territory.
Stuart's command crossed the Potomac River at 3 a.m. on June 28. At Rockville they captured a wagon train of 140 brand-new, fully loaded wagons and mule teams. This wagon train would prove to be a logistical hindrance to Stuart's advance, but he interpreted Lee's orders as placing importance on gathering supplies. The proximity of the Confederate raiders provoked some consternation in the national capital and two Union cavalry brigades and an artillery battery were sent to pursue the Confederates. Stuart supposedly said that were it not for his fatigued horses "he would have marched down the 7th Street Road ndtook Abe & Cabinet prisoners."
In Westminster on June 29, his men clashed briefly with and overwhelmed two companies of Union cavalry, chasing them a long distance on the Baltimore road, which Stuart claimed caused a "great panic" in the city of Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
. The head of Stuart's column encountered Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick's cavalry as it passed through Hanover
Hanover (; german: Hannover ; nds, Hannober) is the capital and largest city of the German state of Lower Saxony. Its 535,932 (2021) inhabitants make it the 13th-largest city in Germany as well as the fourth-largest city in Northern Germany ...
and scattered it on June 30; the Battle of Hanover
The Battle of Hanover took place on June 30, 1863, in Hanover in southwestern York County, Pennsylvania, as part of the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War.
Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart's Confederate cavalry, which was riding north to get ...
ended after Kilpatrick's men regrouped and drove the Confederates out of town. Stuart's brigades had been better positioned to guard their captured wagon train than to take advantage of the encounter with Kilpatrick. After a 20-mile trek in the dark, his exhausted men reached Dover
Dover () is a town and major ferry port in Kent, South East England. It faces France across the Strait of Dover, the narrowest part of the English Channel at from Cap Gris Nez in France. It lies south-east of Canterbury and east of Maidstone ...
on the morning of July 1, as the Battle of Gettysburg
The Battle of Gettysburg () was fought July 1–3, 1863, in and around the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, by Union and Confederate forces during the American Civil War. In the battle, Union Major General George Meade's Army of the Po ...
was commencing without them.
Stuart headed next for Carlisle
Carlisle ( , ; from xcb, Caer Luel) is a city that lies within the Northern England, Northern English county of Cumbria, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, Scottish border at the confluence of the rivers River Eden, Cumbria, Eden, River C ...
, hoping to find Ewell. He lobbed a few shells into town during the early evening of July 1 and burned the Carlisle Barracks
Carlisle Barracks is a United States Army facility located in Carlisle, Pennsylvania. The site of the U.S. Army War College, it is the nation's second-oldest active military base. The first structures were built in 1757, during the French and In ...
before withdrawing to the south towards Gettysburg. He and the bulk of his command reached Lee at Gettysburg the afternoon of July 2. He ordered Wade Hampton to cover the left rear of the Confederate battle lines, and Hampton fought with Brig. Gen. George Armstrong Custer at the Battle of Hunterstown
The Battle of Hunterstown was an American Civil War skirmish at Beaverdam Creek near Hunterstown, Pennsylvania, on July 2, 1863, in which Wade Hampton's Confederate cavalry withdrew after engaging George Armstrong Custer's and Elon Farnsworth' ...
before joining Stuart at Gettysburg.
Gettysburg and its aftermath
When Stuart arrived at Gettysburg on the afternoon of July 2—bringing with him the caravan of captured Union supply wagons—he received a rare rebuke from Lee. No one witnessed the private meeting between Lee and Stuart, but reports circulated at headquarters that Lee's greeting was "abrupt and frosty." ColonelEdward Porter Alexander
Edward Porter Alexander (May 26, 1835 – April 28, 1910) was an American military engineer, railroad executive, planter, and author. He served first as an officer in the United States Army and later, during the American Civil War (1861–1865) ...
wrote, "Although Lee said only, 'Well, General, you are here at last,' his manner implied rebuke, and it was so understood by Stuart." On the final day of the battle, Stuart was ordered to move into the enemy's rear and disrupt its line of communications at the same time Pickett's Charge was sent against the Union positions on Cemetery Ridge
Cemetery Ridge is a geographic feature in Gettysburg National Military Park, south of the town of Gettysburg, Pennsylvania, that figured prominently in the Battle of Gettysburg, July 1 to July 3, 1863. It formed a primary defensive position for the ...
, but his attack on East Cavalry Field was repelled by Union cavalry under Brig. Gens. David Gregg and George Custer
George Armstrong Custer (December 5, 1839 – June 25, 1876) was a United States Army officer and cavalry commander in the American Civil War and the American Indian Wars.
Custer graduated from West Point in 1861 at the bottom of his class, b ...
.
During the retreat from Gettysburg
The Confederate Army of Northern Virginia began its Retreat from Gettysburg on July 4, 1863. Following General Robert E. Lee's failure to defeat the Union Army at the Battle of Gettysburg (July 1–3, 1863), he ordered a retreat through Mary ...
, Stuart devoted his full attention to supporting the army's movement, successfully screening against aggressive Union cavalry pursuit and escorting thousands of wagons with wounded men and captured supplies over difficult roads and through inclement weather. Numerous skirmishes and minor battles occurred during the screening and delaying actions of the retreat. Stuart's men were the final units to cross the Potomac River, returning to Virginia in "wretched condition—completely worn out and broken down."
The Gettysburg Campaign was the most controversial of Stuart's career. He became one of the scapegoats
Scapegoating is the practice of singling out a person or group for unmerited blame and consequent negative treatment. Scapegoating may be conducted by individuals against individuals (e.g. "he did it, not me!"), individuals against groups (e.g., ...
(along with James Longstreet) blamed for Lee's loss at Gettysburg by proponents of the postbellum Lost Cause movement, such as Jubal Early. This was fueled in part by opinions of less partisan writers, such as Stuart's subordinate, Thomas L. Rosser
Thomas Lafayette "Tex" Rosser (October 15, 1836 – March 29, 1910) was a Confederate major general during the American Civil War, and later a railroad construction engineer and in 1898 a brigadier general of volunteers in the United States Army ...
, who stated after the war that Stuart did, "on this campaign, ''undoubtedly'', make the fatal blunder which lost us the battle of Gettysburg." In General Lee's report on the campaign, he wrote
One of the most forceful postbellum defenses of Stuart was by Col. John S. Mosby
John Singleton Mosby (December 6, 1833 – May 30, 1916), also known by his nickname "Gray Ghost", was a Confederate army cavalry battalion commander in the American Civil War. His command, the 43rd Battalion, Virginia Cavalry, known as Mosby's ...
, who had served under him during the campaign and was fiercely loyal to the late general, writing, "He made me all that I was in the war. ... But for his friendship I would never have been heard of." He wrote numerous articles for popular publications and published a book length treatise in 1908, a work that relied on his skills as a lawyer to refute categorically all of the claims laid against Stuart.
Historians remain divided on how much the defeat at Gettysburg was due to Stuart’s failure to keep Lee informed. Edward G. Longacre argues that Lee deliberately gave Stuart wide discretion in his orders. Edwin B. Coddington refers to the "tragedy" of Stuart in the Gettysburg Campaign and judges that when Fitzhugh Lee raised the question of "whether Stuart exercised the discretion ''undoubtedly given to him, judiciously''," the answer is no. Agreeing that Stuart's absence permitted Lee to be surprised at Gettysburg, Coddington points out that the Union commander was just as surprised. Eric J. Wittenberg and J. David Petruzzi have concluded that there was "plenty of blame to go around" and the fault should be divided between Stuart, the lack of specificity in Lee's orders, and Richard S. Ewell, who might have tried harder to link up with Stuart northeast of Gettysburg. Jeffry D. Wert
Jeffry D. Wert (born May 8, 1946) is an American historian and author specializing in the American Civil War. He has written several books on the subject, which have been published in multiple languages and countries.
Early life
Jeffry Wert's int ...
acknowledges that Lee, his officers, and fighting by the Army of the Potomac bear the responsibility for the Confederate loss at Gettysburg, but states that "Stuart failed Lee and the army in the reckoning at Gettysburg. ... Lee trusted him and gave him discretion, but Stuart acted injudiciously."
Although Stuart was not reprimanded or disciplined in any official way for his role in the Gettysburg campaign, it is noteworthy that his appointment to corps command on September 9, 1863, did not carry with it a promotion to lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on the ...
. Edward Bonekemper wrote that since all other corps commanders in the Army of Northern Virginia carried this rank, Lee's decision to keep Stuart at major general rank, while at the same time promoting Stuart's subordinates Wade Hampton Wade Hampton may refer to the following people:
People
*Wade Hampton I (1752–1835), American soldier in Revolutionary War and War of 1812 and U.S. congressman
*Wade Hampton II (1791–1858), American plantation owner and soldier in War of 1812
*W ...
and Fitzhugh Lee to major generals, could be considered an implied rebuke. Wert wrote that there is no evidence Lee considered Stuart's performance during the Gettysburg Campaign and that it is "more likely that Lee thought the responsibilities in command of a cavalry corps did not equal those of an infantry corps."

Fall 1863 and the 1864 Overland Campaign
Lee reorganized his cavalry on September 9, creating a Cavalry Corps for Stuart with two divisions of three brigades each. In the Bristoe Campaign, Stuart was assigned to lead a broad turning movement in an attempt to get into the enemy's rear, but General Meade skillfully withdrew his army without leaving Stuart any opportunities to take advantage of. On October 13, Stuart blundered into the rear guard of the UnionIII Corps 3rd Corps, Third Corps, III Corps, or 3rd Army Corps may refer to:
France
* 3rd Army Corps (France)
* III Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* III Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of th ...
near Warrenton, resulting in the First Battle of Auburn. Ewell's corps was sent to rescue him, but Stuart hid his troopers in a wooded ravine until the unsuspecting III Corps moved on, and the assistance was not necessary. As Meade withdrew towards Manassas Junction, brigades from the Union II Corps 2nd Corps, Second Corps, or II Corps may refer to:
France
* 2nd Army Corps (France)
* II Cavalry Corps (Grande Armée), a cavalry unit of the Imperial French Army during the Napoleonic Wars
* II Corps (Grande Armée), a unit of the Imperial French ...
fought a rearguard action against Stuart's cavalry and the infantry of Brig. Gen. Harry Hays's division near Auburn on October 14. Stuart's cavalry boldly bluffed Warren's infantry and escaped disaster. After the Confederate repulse at Bristoe Station and an aborted advance on Centreville, Stuart's cavalry shielded the withdrawal of Lee's army from the vicinity of Manassas Junction. Judson Kilpatrick's Union cavalry pursued Stuart's cavalry along the Warrenton Turnpike, but were lured into an ambush near Chestnut Hill and routed. The Federal troopers were scattered and chased five miles (eight km) in an affair that came to be known as the "Buckland Races". The Southern press began to mute its criticism of Stuart following his successful performance during the fall campaign.
The Overland Campaign, Lt. Gen.
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star rank, three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in ...
Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union Ar ...
's offensive against Lee in the spring of 1864, began at the Battle of the Wilderness
The Battle of the Wilderness was fought on May 5–7, 1864, during the American Civil War. It was the first battle of Lieutenant General Ulysses S. Grant's 1864 Virginia Overland Campaign against General Robert E. Lee and the Confederate Arm ...
, where Stuart aggressively pushed Thomas L. Rosser's Laurel Brigade into a fight against George Custer's better-armed Michigan Brigade, resulting in significant losses. General Lee sent a message to Stuart: "It is very important to save your Cavalry & not wear it out. ... You must use your good judgment to make any attack which may offer advantages." As the armies maneuvered toward their next confrontation at Spotsylvania Court House
The Battle of Spotsylvania Court House, sometimes more simply referred to as the Battle of Spotsylvania (or the 19th-century spelling Spottsylvania), was the second major battle in Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant and Maj. Gen. George G. Meade's 1864 ...
, Stuart's cavalry fought delaying actions against the Union cavalry. His defense at Laurel Hill, also directing the infantry of Brig. Gen. Joseph B. Kershaw
Joseph Brevard Kershaw (January 5, 1822 – April 13, 1894) was a prominent South Carolina planter and slaveholder. He was also a lawyer, judge, and a Confederate general in the American Civil War.
Early life
Kershaw was born on January 5, 1822 ...
, skillfully delayed the advance of the Federal army for nearly 5 critical hours.
Yellow Tavern and death
The commander of the Army of the Potomac, Maj. Gen. George Meade, and his cavalry commander, Maj. Gen.Philip Sheridan
General of the Army Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close as ...
, quarreled about the Union cavalry's performance in the first two engagements of the Overland Campaign. Sheridan heatedly asserted that he wanted to "concentrate all of cavalry, move out in force against Stuart's command, and whip it." Meade reported the comments to Grant, who replied, "Did Sheridan say that? Well, he generally knows what he is talking about. Let him start right out and do it." Sheridan immediately organized a raid against Confederate supply and railroad lines close to Richmond, which he knew would bring Stuart to battle.
Sheridan moved aggressively to the southeast, crossing the North Anna River
The North Anna River is a principal tributary of the Pamunkey River, about long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 in central Virginia in the United States. ...
and seizing Beaver Dam Station on the Virginia Central Railroad, where his men captured a train, liberating 3,000 Union prisoners and destroying more than one million rations and medical supplies destined for Lee's army. Stuart dispatched a force of about 3,000 cavalrymen to intercept Sheridan's cavalry, which was more than three times their numbers. As he rode in pursuit, accompanied by his aide, Maj. Andrew R. Venable, they were able to stop briefly along the way to be greeted by Stuart's wife, Flora, and his children, Jimmie and Virginia. Venable wrote of Stuart, "He told me he never expected to live through the war, and that if we were conquered, that he did not want to live."
The Battle of Yellow Tavern occurred May 11, at an abandoned inn located north of Richmond. The Confederate troops resisted from the low ridgeline bordering the road to Richmond, fighting for over three hours. After receiving a scouting report from Texas Jack Omohundro
John Baker Omohundro (July 27, 1846 – June 28, 1880), also known as "Texas Jack", was an American frontier scout, actor, and cowboy. Born in rural Virginia, he served the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. He late ...
, Stuart led a countercharge and pushed the advancing Union troopers back from the hilltop. Stuart, on horseback, shouted encouragement from in front of Company K of the 1st Virginia Cavalry
The 1st Virginia Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment raised in Virginia for service in the Confederate States Army during the American Civil War. It fought mostly with the Army of Northern Virginia.
Organization
The 1st Virginia Cavalry com ...
while firing his revolver at the Union troopers.
As the 5th Michigan Cavalry streamed in retreat past Stuart, a dismounted Union private, 44-year-old John A. Huff, turned and shot Stuart with his .44-caliber revolver from a distance of 10–30 yards. Huff's bullet struck Stuart in the left side. It then sliced through his stomach and exited his back, one inch to the right of his spine. Stuart fell into the arms of Company K's commander Gus W. Dorsey
Gustavus Warfield Dorsey (April 20, 1839 – September 6, 1911) was a cavalry commander during the American Civil War for the Confederacy. When famed cavalry commander Jeb Stuart was shot at the Battle of Yellow Tavern and mortally wounded, ...
. Dorsey caught him and took him from his horse. Stuart told him: "Dorsey...save your men." Dorsey refused to leave him and brought Stuart to the rear.
 He suffered great pain as an ambulance took him to Richmond to await his wife's arrival at the home of Dr. Charles Brewer, his brother-in-law. As he was being driven from the field in an ambulance wagon, Stuart noticed disorganized ranks of retreating men and called out to them his last words on the battlefield: "Go back, go back, and do your duty, as I have done mine, and our country will be safe. Go back, go back! I had rather die than be whipped."McClellan, Henry B. I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press.
Stuart ordered his sword and spurs be given to his son. As his aide Major McClellan left his side, Confederate President Jefferson Davis came in, took General Stuart's hand, and asked, "General, how do you feel?" Stuart answered "Easy, but willing to die, if God and my country think I have fulfilled my destiny and done my duty." His last whispered words were: "I am resigned; God's will be done." He died at 7:38 p.m. on May 12, the following day, before Flora Stuart reached his side. He was 31 years old. Stuart was buried in Richmond's Hollywood Cemetery. Upon learning of Stuart's death, General Lee is reported to have said that he could hardly keep from weeping at the mere mention of Stuart's name and that Stuart had never given him a bad piece of information. John Huff, the private who had fatally wounded Stuart, was killed in action just a few weeks later at the
He suffered great pain as an ambulance took him to Richmond to await his wife's arrival at the home of Dr. Charles Brewer, his brother-in-law. As he was being driven from the field in an ambulance wagon, Stuart noticed disorganized ranks of retreating men and called out to them his last words on the battlefield: "Go back, go back, and do your duty, as I have done mine, and our country will be safe. Go back, go back! I had rather die than be whipped."McClellan, Henry B. I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press.
Stuart ordered his sword and spurs be given to his son. As his aide Major McClellan left his side, Confederate President Jefferson Davis came in, took General Stuart's hand, and asked, "General, how do you feel?" Stuart answered "Easy, but willing to die, if God and my country think I have fulfilled my destiny and done my duty." His last whispered words were: "I am resigned; God's will be done." He died at 7:38 p.m. on May 12, the following day, before Flora Stuart reached his side. He was 31 years old. Stuart was buried in Richmond's Hollywood Cemetery. Upon learning of Stuart's death, General Lee is reported to have said that he could hardly keep from weeping at the mere mention of Stuart's name and that Stuart had never given him a bad piece of information. John Huff, the private who had fatally wounded Stuart, was killed in action just a few weeks later at the Battle of Haw's Shop
The Battle of Haw's Shop or Enon Church was fought on May 28, 1864, in Hanover County, Virginia, as part of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia during the Amer ...
.
Flora wore the black of mourning for the remainder of her life, and never remarried. She lived in Saltville, Virginia, for 15 years after the war, where she opened and taught at a school in a log cabin. She worked from 1880 to 1898 as principal of the Virginia Female Institute in Staunton, Virginia
Staunton ( ) is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 25,750. In Virginia, independent cities a ...
, a position for which Robert E. Lee had recommended her before his death ten years earlier. In 1907, the institute was renamed Stuart Hall School in her honor. Upon the death of her daughter Virginia, from complications in childbirth in 1898, Flora resigned from the institute and moved to Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia Be ...
, where she helped Virginia's widower, Robert Page Waller, in raising her grandchildren. She died in Norfolk on May 10, 1923, after striking her head in a fall on a city sidewalk. She is buried alongside her husband and their daughter, Little Flora, in Hollywood Cemetery in Richmond.
Legacy and memorials
 Like his intimate friend,
Like his intimate friend, Stonewall Jackson
Thomas Jonathan "Stonewall" Jackson (January 21, 1824 – May 10, 1863) was a Confederate general during the American Civil War, considered one of the best-known Confederate commanders, after Robert E. Lee. He played a prominent role in nearl ...
, General J.E.B. Stuart was a legendary figure and is considered one of the greatest cavalry commanders in American history. His friend from his federal army days, Union Maj. Gen. John Sedgwick, said that Stuart was "the greatest cavalry officer ever foaled in America." Jackson and Stuart, both of whom were killed in battle, had colorful public images, although the latter's seems to have been more deliberately crafted. Wert wrote about Stuart:
Stuart's birthplace, Laurel Hill, located in Patrick County, Virginia
Patrick County is a county located on the central southern border of the Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 census, the population was 17,608. Its county seat is Stuart. It is located within both the rolling hills and valleys of the Pie ...
, was purchased by the J.E.B. Stuart Birthplace Preservation Trust, Inc., in 1992 to preserve and interpret it. In December 2006, a personal Confederate battle flag, sewn by Flora Stuart, was sold in a Heritage
Heritage may refer to:
History and society
* A heritage asset is a preexisting thing of value today
** Cultural heritage is created by humans
** Natural heritage is not
* Heritage language
Biology
* Heredity, biological inheritance of physical c ...
Auction for a world-record price for any Confederate flag, for $956,000 (including buyer's premium). The 34-inch by 34-inch flag was hand-sewn for Stuart by Flora in 1862, and Stuart carried it into some of his most famous battles.
A statue of Stuart, by sculptor Frederick Moynihan
Frederick Moynihan was an American sculptor, born on the Isle of Guernsey in 1843. He died in his New York City studio on January 9, 1910.
Moynihan studied at the Royal Academy of Arts in London before immigrating to the United States. He is b ...
, used to occupy a space on Richmond's Monument Avenue at Stuart Circle. Originally dedicated in 1907, the statue was removed on July 7, 2020.

Named after Stuart
U.S. Route 58, in Virginia, is named the "J.E.B. Stuart Highway". In 1884 the town of Taylorsville, Virginia, was renamedStuart
Stuart may refer to:
Names
* Stuart (name), a given name and surname (and list of people with the name) Automobile
*Stuart (automobile)
Places
Australia Generally
*Stuart Highway, connecting South Australia and the Northern Territory
Northe ...
. The British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
named two models of American-made World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
tanks, the M3 and M5, the Stuart tank
The M3 Stuart/Light Tank M3, was an American light tank of World War II. An improved version of the tank entered service as the M5 in 1942 to be supplied to British and other Commonwealth forces under lend-lease prior to the entry of the U.S. ...
in General Stuart's honor.
Schools
A middle school inJacksonville, Florida
Jacksonville is a city located on the Atlantic coast of northeast Florida, the most populous city proper in the state and is the largest city by area in the contiguous United States as of 2020. It is the seat of Duval County, with which the ...
is named for him. A high school
A secondary school describes an institution that provides secondary education and also usually includes the building where this takes place. Some secondary schools provide both '' lower secondary education'' (ages 11 to 14) and ''upper seconda ...
named after him on Munson's Hill
Munson's Hill is a geographic eminence located in eastern Fairfax County, Virginia. Its summit rises to above sea level.
Location and name
Munson's Hill is located at .
The hill is adjacent to Upton's Hill (410 ft) on its north. It is ...
in Falls Church, Virginia
Falls Church is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the population was 14,658. Falls Church is included in the Wash ...
, opened in 1959. In early 2017, Fairfax County Public Schools established an Ad Hoc Working Committee to assist the Fairfax County School Board in determining whether to rename the Stuart High School in Virginia, in response to suggestions from students and local community members that FCPS should not continue to honor a Confederate general who fought in support of a cause dedicated to maintaining the institution of slavery in Virginia and other states. The creation of the committee followed the circulation of a petition started by actress Julianne Moore and Bruce Cohen
Bruce L. Cohen (born September 23, 1961) is a film, television, and theater producer.
Biography
Cohen was born to a Jewish family and raised in Falls Church, Virginia.United States Supreme Court Justice
 *Stuart, along with his warhorse Skylark, is featured prominently in the novel ''
*Stuart, along with his warhorse Skylark, is featured prominently in the novel ''
''The Life and Campaigns of Major-General J.E.B. Stuart: Commander of the Cavalry of the Army of Northern Virginia.''
Boston: Houghton, Mifflin and Company, 1885. * McClellan, Henry B. ''I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart''. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press. * Mosby, John Singleton
''Mosby's Reminiscences and Stuart's Cavalry Campaigns''
New York: Dodd, Mead & Company, 1887. . * Perry, Thomas D
''Laurel Hill Teachers' Guide''
2005. * Petruzzi, J. David, and Steven Stanley. ''The Complete Gettysburg Guide''. New York: Savas Beatie, 2009. . * Wittenberg, Eric J., J. David Petruzzi, and Michael F. Nugent. ''One Continuous Fight: The Retreat from Gettysburg and the Pursuit of Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, July 4–14, 1863''. New York: Savas Beatie, 2008. .
Flora Stuart
Wife Of Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart
Laurel Hill – Stuart's BirthplaceJ. E. B. Stuart in ''Encyclopedia Virginia''Stuart A. Rose Manuscript, Archives, and Rare Book LibraryJeb Stuart letters, 1861
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stuart, James Ewell Brown 1833 births 1864 deaths American slave owners Army of Northern Virginia Confederate States Army major generals United States Army officers People of Virginia in the American Civil War United States Military Academy alumni Confederate States of America military personnel killed in the American Civil War American people of Scotch-Irish descent People from Patrick County, Virginia Burials at Hollywood Cemetery (Richmond, Virginia) Cavalry commanders Deaths by firearm in Virginia Witnesses to John Brown's execution
Thurgood Marshall
Thurgood Marshall (July 2, 1908 – January 24, 1993) was an American civil rights lawyer and jurist who served as an associate justice of the Supreme Court of the United States from 1967 until 1991. He was the Supreme Court's first African-A ...
.
On July 27, 2017, the Fairfax County School Board approved a measure to change the school name no later than the start of the 2019 school year. The measure asked that "Stuart High School" be considered as a possibility for the new name. On October 27, 2017, the Fairfax County School Board voted to change the name of J.E.B. Stuart High School to "Justice High School." Board member Sandy Evans from the Mason District said that the name will honor Justice Thurgood Marshall, civil rights leader Barbara Rose Johns
Barbara Rose Johns Powell (March 6, 1935 – September 28, 1991) was a leader in the American civil rights movement. On April 23, 1951, at the age of 16, Powell led a student strike for equal education at R.R. Moton High School in Farmville ...
, U.S. Army officer Louis Gonzaga Mendez Jr.
Colonel Louis Gonzaga Mendez Jr. (July 14, 1915 – September 19, 2001) was a highly decorated United States Army officer of the 82nd Airborne Division who in June 1944, as commander of the 3rd Battalion, 508th Parachute Infantry Regiment dur ...
, and all those who have fought for justice and equality.
On June 18, 2018, the school board for Richmond Public Schools
Richmond Public Schools is a public school district located in the independent city of Richmond, Virginia. It is occasionally described locally as Richmond City Public Schools to emphasize its connection to the independent city rather than the ...
in Richmond, Virginia voted 6–1 to rename J. E. B. Stuart Elementary School to Barack Obama Elementary School. On June 12, 2018, students of the school were given the opportunity to narrow down the choices for renaming the school from seven to three. Northside Elementary received 190 votes, Barack Obama Elementary earned 166 votes, and Wishtree Elementary received 127 votes. From there, the administration of Richmond Public Schools recommended to the school board that it rename the school after Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the U ...
. Superintendent Jason Kamras said, "It's incredibly powerful that in the capital of the Confederacy, where we had a school named for an individual who fought to maintain slavery, that now we're renaming that school after the first black president. A lot of our kids, and our kids at J. E. B. Stuart, see themselves in Barack Obama." The student population of the newly named Barack Obama Elementary School is made up of more than 90 percent African-American children.
Stuart Hall School is a Staunton, Virginia
Staunton ( ) is an independent city (United States), independent city in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), U.S. Commonwealth of Virginia. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 25,750. In Virginia, independent cities a ...
, co-educational school for students from pre-kindergarten to Grade 12, and it offers a boarding program from Grades 8 to 12. It was renamed in 1907 in honor of its most famous headmistress Mrs. Gen. Flora Cooke Stuart, the widow of Confederate cavalry leader Maj. Gen. J. E. B. Stuart.
In art and popular culture
Films
* Joseph Fuqua played Stuart in the films '' Gettysburg'' and '' Gods and Generals''. *Errol Flynn
Errol Leslie Thomson Flynn (20 June 1909 – 14 October 1959) was an Australian-American actor who achieved worldwide fame during the Golden Age of Hollywood. He was known for his romantic swashbuckler roles, frequent partnerships with Olivia ...
played Stuart in the movie ''Santa Fe Trail
The Santa Fe Trail was a 19th-century route through central North America that connected Franklin, Missouri, with Santa Fe, New Mexico. Pioneered in 1821 by William Becknell, who departed from the Boonslick region along the Missouri River, th ...
'', depicting his antebellum life, confronting John Brown in Kansas and at Harper's Ferry. The movie has become infamous for its many historical inaccuracies, one of which was that Stuart, George Armstrong Custer (portrayed by Ronald Reagan
Ronald Wilson Reagan ( ; February 6, 1911June 5, 2004) was an American politician, actor, and union leader who served as the 40th president of the United States from 1981 to 1989. He also served as the 33rd governor of California from 1967 ...
in the film), and Philip Sheridan
General of the Army Philip Henry Sheridan (March 6, 1831 – August 5, 1888) was a career United States Army officer and a Union general in the American Civil War. His career was noted for his rapid rise to major general and his close as ...
were firm friends and all attended West Point together in 1854.
Television
* Jeb Stuart was evoked byG.I. Joe
''G.I. Joe'' is an American media franchise and a line of action figures owned and produced by the toy company Hasbro. The initial product offering represented four of the branches of the U.S. armed forces with the Action Soldier ( U.S. Army), Ac ...
character, Cross Country, in the third episode of the mini-series, "Arise Serpentor, Arise".
* Jeb Stuart is mentioned by the Baladeer in Season four, episode 10 of the TV Series, The Dukes of Hazzard.
* A limited television series based on the novel ''The Good Lord Bird
''The Good Lord Bird'' is a 2013 novel by James McBride about Henry Shackleford, an enslaved person, who unites with John Brown in Brown's abolitionist mission. The novel won the National Book Award for Fiction in 2013 and received generally po ...
'' was released, with Wyatt Russell as Stuart.
*The ghost of Jeb Stuart appears driving a tank in the animated series Batman: The Brave and the Bold in season 2, episode 18: The Menance of the Madniks.
Literature
 *Stuart, along with his warhorse Skylark, is featured prominently in the novel ''
*Stuart, along with his warhorse Skylark, is featured prominently in the novel ''Traveller
Traveler(s), traveller(s), The Traveler(s), or The Traveller(s) may refer to:
People Generic terms
*One engaged in travel
*Explorer, one who searches for the purpose of discovery of information or resources
*Nomad, a member of a community withou ...
'' by Richard Adams
Richard George Adams (9 May 1920 – 24 December 2016) was an English novelist and writer of the books ''Watership Down'', ''Maia'', ''Shardik'' and ''The Plague Dogs''. He studied modern history at university before serving in the British Army ...
.
*In the alternate history
Alternate history (also alternative history, althist, AH) is a genre of speculative fiction of stories in which one or more historical events occur and are resolved differently than in real life. As conjecture based upon historical fact, altern ...
novel ''Gray Victory
''Gray Victory'' is a 1988 alternate history novel by Robert Skimin, taking place in an alternate 1866 where the Confederacy won its independence.
Plot introduction
The first point of divergence occurs during the American Civil War in May 1864, ...
'' (1988), author Robert Skimin Robert Skimin (July 30, 1929 in Belden, Ohio – May 9, 2011 in El Paso, Texas) was a U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and i ...
depicts Stuart surviving his wound from the battle of Yellow Tavern. After the war, in which the Confederacy emerges victorious, he faces a court of inquiry over his actions at the Battle of Gettysburg.
*In Harry Turtledove's 1992 alternate-history novel '' The Guns of the South'', Stuart features as one of Lee's generals as the AWB bring back AK-47 rifles from 2014 to 1864. Men under Stuart's command are the first Confederate troops to use the AK-47 in battle. Stuart is so impressed with the new rifle that he sells his personal LeMat Revolver and replaces it with an AK-47.
*In Harry Turtledove's alternate-history novel ''How Few Remain
''How Few Remain'' is a 1997 alternate history novel by Harry Turtledove. It is the first part of the Southern Victory saga, which depicts a world in which the Confederate States of America won the American Civil War. It is similar to his earlier ...
'', Stuart is the commanding Confederate general in charge of the occupation and defense of the recently purchased Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
provinces of Sonora
Sonora (), officially Estado Libre y Soberano de Sonora ( en, Free and Sovereign State of Sonora), is one of the 31 states which, along with Mexico City, comprise the Administrative divisions of Mexico, Federal Entities of Mexico. The state is d ...
and Chihuahua Chihuahua may refer to:
Places
*Chihuahua (state), a Mexican state
**Chihuahua (dog), a breed of dog named after the state
**Chihuahua cheese, a type of cheese originating in the state
**Chihuahua City, the capital city of the state
**Chihuahua Mun ...
in 1881. This is the first volume of the Southern Victory
The ''Southern Victory'' series or Timeline-191 is a series of eleven alternate history novels by author Harry Turtledove, beginning with ''How Few Remain'' (1997) and published over a decade. The period addressed in the series begins during the ...
series, where the US and CSA fight each other repeatedly in the 19th and 20th centuries. Stuart's son and grandson also appear in these novels. Turtledove, Harry, ''How Few Remain, Volume 1'', Random House, Inc., 1998, , p. 45.
*Several short stories in Barry Hannah
Barry Hannah (April 23, 1942 – March 1, 2010) was an American novelist and short story writer from Mississippi.Kellogg, Carolyn (March 2, 2010)"Author Barry Hannah, 67, has died" ''Los Angeles Times''. Retrieved May 18, 2013. Hannah was born in ...
's collection ''Airships'' feature Stuart as a character.
*Stuart's route to Gettysburg is the impetus for the sci-fi-ish book ''An End to Bugling'' by Edmund G. Love.
*Stuart is also a character in L. M. Elliott
L.M. Elliott is the pen name of Laura Malone Elliott. She was born on September 17, 1957, not far from Washington, DC. She is the award-winning author of more than a dozen young adult novels, including '' Under a War-Torn Sky'' (2001), ''Give Me L ...
's ''Annie, Between the States''.
*J. E. B. Stuart is a character in the historical adventure novel ''Flashman and the Angel of the Lord
''Flashman and the Angel of the Lord'' is a 1994 novel by George MacDonald Fraser. It is the tenth of the Flashman novels.
Plot introduction
Presented within the frame of the supposedly discovered historical Flashman Papers, this book describe ...
'' by George MacDonald Fraser featuring Stuart's early-career role in the US Army at John Brown's raid on Harpers Ferry
John is a common English name and surname:
* John (given name)
* John (surname)
John may also refer to:
New Testament
Works
* Gospel of John, a title often shortened to John
* First Epistle of John, often shortened to 1 John
* Second E ...
.
*In the long-running comic book ''G.I. Combat
''G.I. Combat'' was an American comics anthology featuring war stories. It was published from 1952 until 1956 by Quality Comics, followed by DC Comics until its final issue in 1987. In 2012 it was briefly revived.
Publication history
The focu ...
'', featuring "The Haunted Tank
The Haunted Tank is a comic book feature that appeared in the DC Comics anthology war title ''G.I. Combat'' from 1961 through 1987.
Publication history
The Haunted Tank was created by writer and editor Robert Kanigher and artist Russ Heath in ' ...
", published by DC Comics
DC Comics, Inc. (doing business as DC) is an American comic book publisher and the flagship unit of DC Entertainment, a subsidiary of Warner Bros. Discovery.
DC Comics is one of the largest and oldest American comic book companies, with thei ...
from the 1960s through the late 1980s, the ghost of General Stuart guided a tank crew (the tank being, at first, a Stuart, later a Sherman) commanded by his namesake, Lt. Jeb Stuart.
Music
*''Southern Troopers Song, Dedicated to Gen'l. J. E. B. Stuart and his gallant Soldiers'' *"When I Was On Horseback," a song on the folk group Arborea's album ''Fortress of the Sun'' (2013), features lyrics that refer to Stuart's death near Richmond, Virginia.See also
* List of American Civil War generals (Confederate)Notes
References
Books
* Bonekemper, Edward H., III. ''How Robert E. Lee Lost the Civil War''. Fredericksburg, VA: Sergeant Kirkland's Press, 1998. . * Coddington, Edwin B. ''The Gettysburg Campaign; a study in command''. New York: Scribner's, 1968. . * Davis, Burke. ''Jeb Stuart: The Last Cavalier''. New York: Random House, 1957. . * Eicher, John H., andDavid J. Eicher
David John Eicher (born August 7, 1961) is an American editor, writer, and popularizer of astronomy and space. He has been editor-in-chief of ''Astronomy'' magazine since 2002. He is author, coauthor, or editor of 23 books on science and American ...
. ''Civil War High Commands''. Stanford, CA: Stanford University Press, 2001. .
* Longacre, Edward G. ''The Cavalry at Gettysburg: A Tactical Study of Mounted Operations during the Civil War's Pivotal Campaign, 9 June–14 July 1863''. Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press, 1986. .
* Longacre, Edward G. ''Lee's Cavalrymen: A History of the Mounted Forces of the Army of Northern Virginia''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2002. .
* Perry, Thomas D. ''J. E. B. Stuart's Birthplace: The History of the Laurel Hill Farm''. Ararat, VA: Laurel Hill Publishing, 2008. .
* Peterson, Alexander Duncan Campbell. ''Schools Across Frontiers: The Story of the International Baccalaureate and the United World Colleges''. La Salle, IL: Open Court Publishing, 2003. .
* Rhea, Gordon C. ''The Battles for Spotsylvania Court House and the Road to Yellow Tavern, May 7–12, 1864''. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1997. .
* Robertson, James I., Jr. ''Stonewall Jackson: The Man, The Soldier, The Legend''. New York: Simon & Schuster Macmillan, 1997. .
* Salmon, John S. ''The Official Virginia Civil War Battlefield Guide''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2001. .
* Sears, Stephen W. ''Chancellorsville''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 1996. .
* Sears, Stephen W. ''Gettysburg''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin, 2003. .
* Sifakis, Stewart. ''Who Was Who in the Civil War.'' New York: Facts On File, 1988. .
* Smith, Derek. ''The Gallant Dead: Union & Confederate Generals Killed in the Civil War''. Mechanicsburg, PA: Stackpole Books, 2005. .
* Starr, Steven. ''The Union Cavalry in the Civil War: The War in the East from Gettysburg to Appomattox, 1863–1865''. Volume 2. Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 2007. Originally published 1981. .
* Thomas, Emory M. ''Bold Dragoon: The Life of J.E.B. Stuart''. Norman: University of Oklahoma Press, 1986. .
* Warner, Ezra J. ''Generals in Gray: Lives of the Confederate Commanders.'' Baton Rouge: Louisiana State University Press, 1959. .
* Wert, Jeffry D. ''Cavalryman of the Lost Cause: A Biography of J.E.B. Stuart''. New York: Simon & Schuster, 2008. .
* Wittenberg, Eric J., and J. David Petruzzi. ''Plenty of Blame to Go Around: Jeb Stuart's Controversial Ride to Gettysburg''. New York: Savas Beatie, 2006. .
Further reading
* Brown, Kent Masterson. ''Retreat from Gettysburg: Lee, Logistics, & the Pennsylvania Campaign''. Chapel Hill: University of North Carolina Press, 2005. . * Laino, Philip, ''Gettysburg Campaign Atlas''. 2nd ed. Dayton, OH: Gatehouse Press 2009. . * McClellan, H B''The Life and Campaigns of Major-General J.E.B. Stuart: Commander of the Cavalry of the Army of Northern Virginia.''
Boston: Houghton, Mifflin and Company, 1885. * McClellan, Henry B. ''I Rode with Jeb Stuart: The Life and Campaigns of Maj. Gen. Jeb Stuart''. Edited by Burke Davis. New York: Da Capo Press, 1994. . First published 1958 by Indiana University Press. * Mosby, John Singleton
''Mosby's Reminiscences and Stuart's Cavalry Campaigns''
New York: Dodd, Mead & Company, 1887. . * Perry, Thomas D
''Laurel Hill Teachers' Guide''
2005. * Petruzzi, J. David, and Steven Stanley. ''The Complete Gettysburg Guide''. New York: Savas Beatie, 2009. . * Wittenberg, Eric J., J. David Petruzzi, and Michael F. Nugent. ''One Continuous Fight: The Retreat from Gettysburg and the Pursuit of Lee's Army of Northern Virginia, July 4–14, 1863''. New York: Savas Beatie, 2008. .
External links
Flora Stuart
Wife Of Confederate General J.E.B. Stuart
Laurel Hill – Stuart's Birthplace
{{DEFAULTSORT:Stuart, James Ewell Brown 1833 births 1864 deaths American slave owners Army of Northern Virginia Confederate States Army major generals United States Army officers People of Virginia in the American Civil War United States Military Academy alumni Confederate States of America military personnel killed in the American Civil War American people of Scotch-Irish descent People from Patrick County, Virginia Burials at Hollywood Cemetery (Richmond, Virginia) Cavalry commanders Deaths by firearm in Virginia Witnesses to John Brown's execution