|
5th Michigan Cavalry
The 5th Michigan Cavalry Regiment was a cavalry regiment that served in the Union Army during the American Civil War. It was a part of the famed Michigan Brigade, commanded for a time by Brigadier General George Armstrong Custer. Service Organized in Detroit, Michigan, the 5th Michigan Cavalry was mustered into service on August 30, 1862, and left for Washington, D.C., on December 4 of that year. The regiment served in the defenses of the capital until June 1863, when it joined the Cavalry Corps of the Army of the Potomac. Over the next month, the 5th Michigan Cavalry took part in several major battles, including the Battle of Hanover on June 30, the Battle of Gettysburg from July 1 to July 3, and the Battle of Williamsport from July 6 to July 14. The regiment then participated in a series of smaller engagements followed by the Battle of Mine Run from November 26 to December 2. Early in 1864 came the Battle of Morton's Ford, on February 6 and 7, and three months later the Over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (American Civil War)
During the American Civil War, the Union, also known as the North, referred to the United States led by President Abraham Lincoln. It was opposed by the secessionist Confederate States of America (CSA), informally called "the Confederacy" or "the South". The Union is named after its declared goal of preserving the United States as a constitutional union. "Union" is used in the U.S. Constitution to refer to the founding formation of the people, and to the states in union. In the context of the Civil War, it has also often been used as a synonym for "the northern states loyal to the United States government;" in this meaning, the Union consisted of 20 free states and five border states. The Union Army was a new formation comprising mostly state units, together with units from the regular U.S. Army. The border states were essential as a supply base for the Union invasion of the Confederacy, and Lincoln realized he could not win the war without control of them, especially Maryla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michigan Brigade
The Michigan Brigade, sometimes called the Wolverines, the Michigan Cavalry Brigade or Custer's Brigade, was a brigade of cavalry in the volunteer Union Army during the latter half of the American Civil War. Composed primarily of the 1st Michigan Cavalry, 5th Michigan Cavalry, 6th Michigan Cavalry and 7th Michigan Cavalry, the Michigan Brigade fought in every major campaign of the Army of the Potomac from the Battle of Gettysburg in July 1863 to the Confederate surrender at Appomattox Court House in April 1865. The brigade first gained fame during the Gettysburg Campaign under the command of youthful Brigadier General George Armstrong Custer. After the war, several men associated with the brigade joined the 7th U.S. Cavalry Regiment and later fought again under Custer in the Old West frontier. Service record Organization and the Gettysburg Campaign The Michigan Cavalry Brigade was created on December 12, 1862, at Washington, D.C. It originally consisted of the 5th, 6th and 7th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cold Harbor
The Battle of Cold Harbor was fought during the American Civil War near Mechanicsville, Virginia, from May 31 to June 12, 1864, with the most significant fighting occurring on June 3. It was one of the final battles of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant's Overland Campaign, and is remembered as one of American history's bloodiest, most lopsided battles. Thousands of Union soldiers were killed or wounded in a hopeless frontal assault against the fortified positions of Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's army. On May 31, as Grant's army once again swung around the right flank of Lee's army, Union cavalry seized the crossroads of Old Cold Harbor, about 10 miles northeast of the Confederate capital of Richmond, Virginia, holding it against Confederate attacks until the Union infantry arrived. Both Grant and Lee, whose armies had suffered enormous casualties in the Overland Campaign, received reinforcements. On the evening of June 1, the Union VI Corps and XVIII Corps arrived and assaul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Totopotomoy Creek
The Battle of Totopotomoy Creek , also called the Battle of Bethesda Church, Crumps Creek, Shady Grove Road, and Hanovertown, was a battle fought in Hanover County, Virginia on May 28–30, 1864, as part of Union Lt. Gen. Ulysses Grant's Overland Campaign against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia. As Grant continued his attempts to maneuver around Lee's right flank and lure him into a general battle in the open, Lee saw an opportunity to attack the advancing V Corps, under Maj. Gen. Gouverneur K. Warren with the Second Corps of Lt. Gen. Jubal Early. Early's divisions under Maj. Gens. Robert E. Rodes and Stephen Dodson Ramseur drove the Union troops back to Shady Grove Road, but Ramseur's advance was stopped by a fierce stand of infantry and artillery fire. Grant ordered his other corps commanders to conduct a supporting attack along the entire Confederate line, which was entrenched behind Totopotomoy Creek, but only the II Corps of Maj. Gen. Winfie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overland Campaign
The Overland Campaign, also known as Grant's Overland Campaign and the Wilderness Campaign, was a series of battles fought in Virginia during May and June 1864, in the American Civil War. Lt. Gen. Ulysses S. Grant, general-in-chief of all Union armies, directed the actions of the Army of the Potomac, commanded by Maj. Gen. George G. Meade, and other forces against Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee's Army of Northern Virginia. Although Grant suffered severe losses during the campaign, it was a strategic Union victory. It inflicted proportionately higher losses on Lee's army and maneuvered it into a siege at Richmond and Petersburg, Virginia, in just over eight weeks. Crossing the Rapidan River on May 4, 1864, Grant sought to defeat Lee's army by quickly placing his forces between Lee and Richmond and inviting an open battle. Lee surprised Grant by attacking the larger Union army in the Battle of the Wilderness (May 5–7), resulting in many casualties on both sides. Unlike his pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Morton's Ford
The Battle of Morton's Ford was a battle of the American Civil War, fought February 6–7, 1864. To distract attention from a planned cavalry-infantry raid up the Virginia Peninsula on Richmond, the Union Army of the Potomac forced several crossings of the Rapidan River on February 6, 1864. Units of the II Corps under Maj. Gen. John C. Caldwell crossed at Morton's Ford, the I Corps at Raccoon Ford, and Union cavalry at Robertson's Ford. Confederate Lt. Gen. Richard S. Ewell's Corps of the Army of Northern Virginia resisted the crossings, with sporadic fighting and the most severe fighting at Morton's Ford. By February 7, 1864, the attacks had stalled, and the Union army withdrew during the night, with the results of the battle inconclusive. Background Union Major General Benjamin Butler, commanding the Army of the James in Fort Monroe, learned that General Robert E. Lee had detached a small portion of the Army of Northern Virginia to North Carolina. Convinced that Lee ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Park Service
The National Park Service (NPS) is an agency of the United States federal government within the U.S. Department of the Interior that manages all national parks, most national monuments, and other natural, historical, and recreational properties with various title designations. The U.S. Congress created the agency on August 25, 1916, through the National Park Service Organic Act. It is headquartered in Washington, D.C., within the main headquarters of the Department of the Interior. The NPS employs approximately 20,000 people in 423 individual units covering over 85 million acres in all 50 states, the District of Columbia, and US territories. As of 2019, they had more than 279,000 volunteers. The agency is charged with a dual role of preserving the ecological and historical integrity of the places entrusted to its management while also making them available and accessible for public use and enjoyment. History Yellowstone National Park was created as the first national par ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
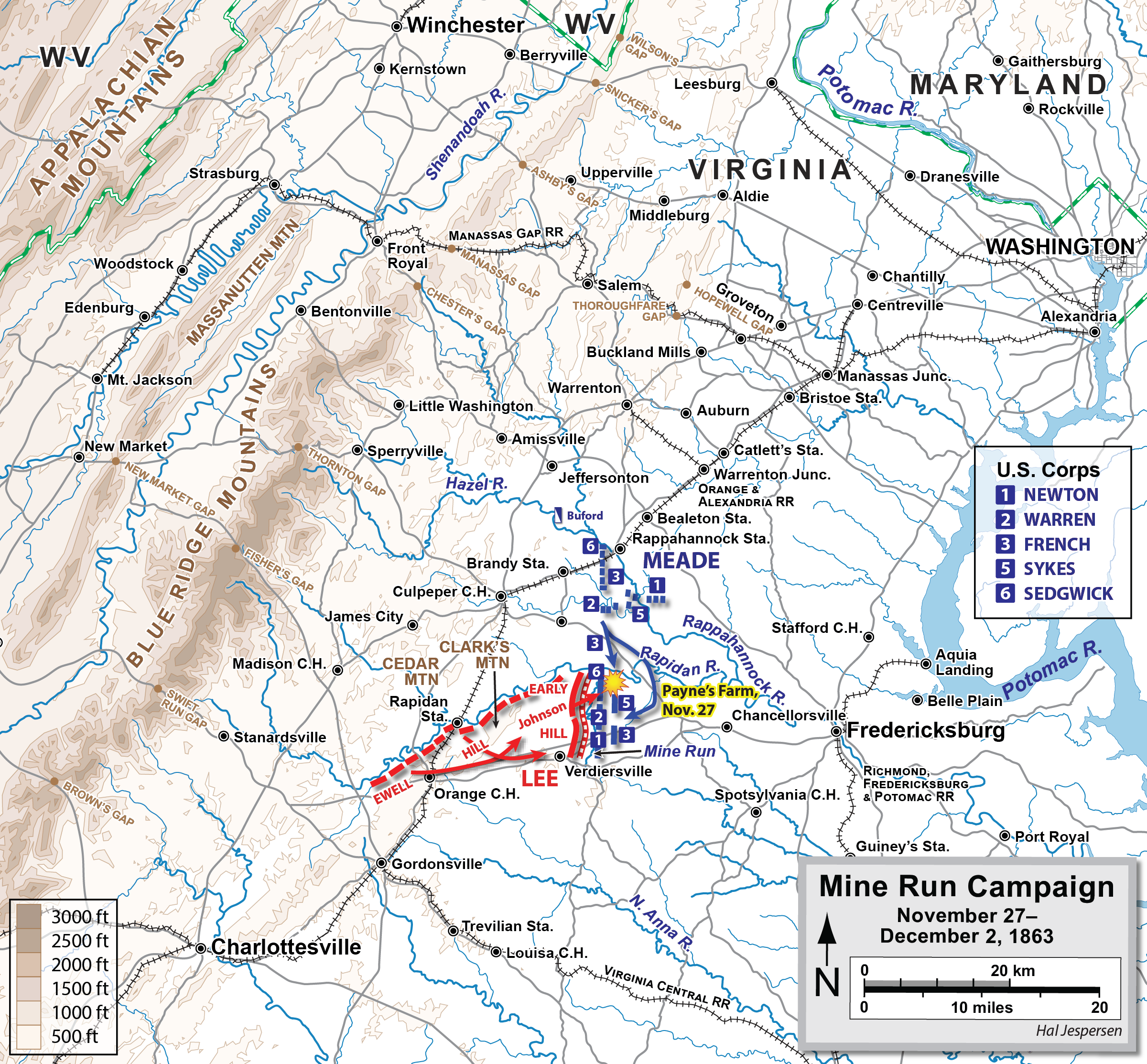
Battle Of Mine Run
The Battle of Mine Run, also known as Payne's Farm, or New Hope Church, or the Mine Run campaign (November 27 – December 2, 1863), was conducted in Orange County, Virginia, in the American Civil War. An unsuccessful attempt of the Union Army of the Potomac to defeat the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia, it was marked by false starts and low casualties and ended hostilities in the Eastern Theater for the year. Background After the Battle of Gettysburg in July, Confederate Gen. Robert E. Lee and his command retreated back across the Potomac River into Virginia. Union commander Maj. Gen. George G. Meade was widely criticized for failing to pursue aggressively and defeat Lee's army. Meade planned new offensives in Virginia for the fall. His first attempt was a series of inconclusive duels and maneuvers in October and November known as the Bristoe campaign. In late November, Meade attempted to steal a march through the Wilderness of Spotsylvania and strike the rig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
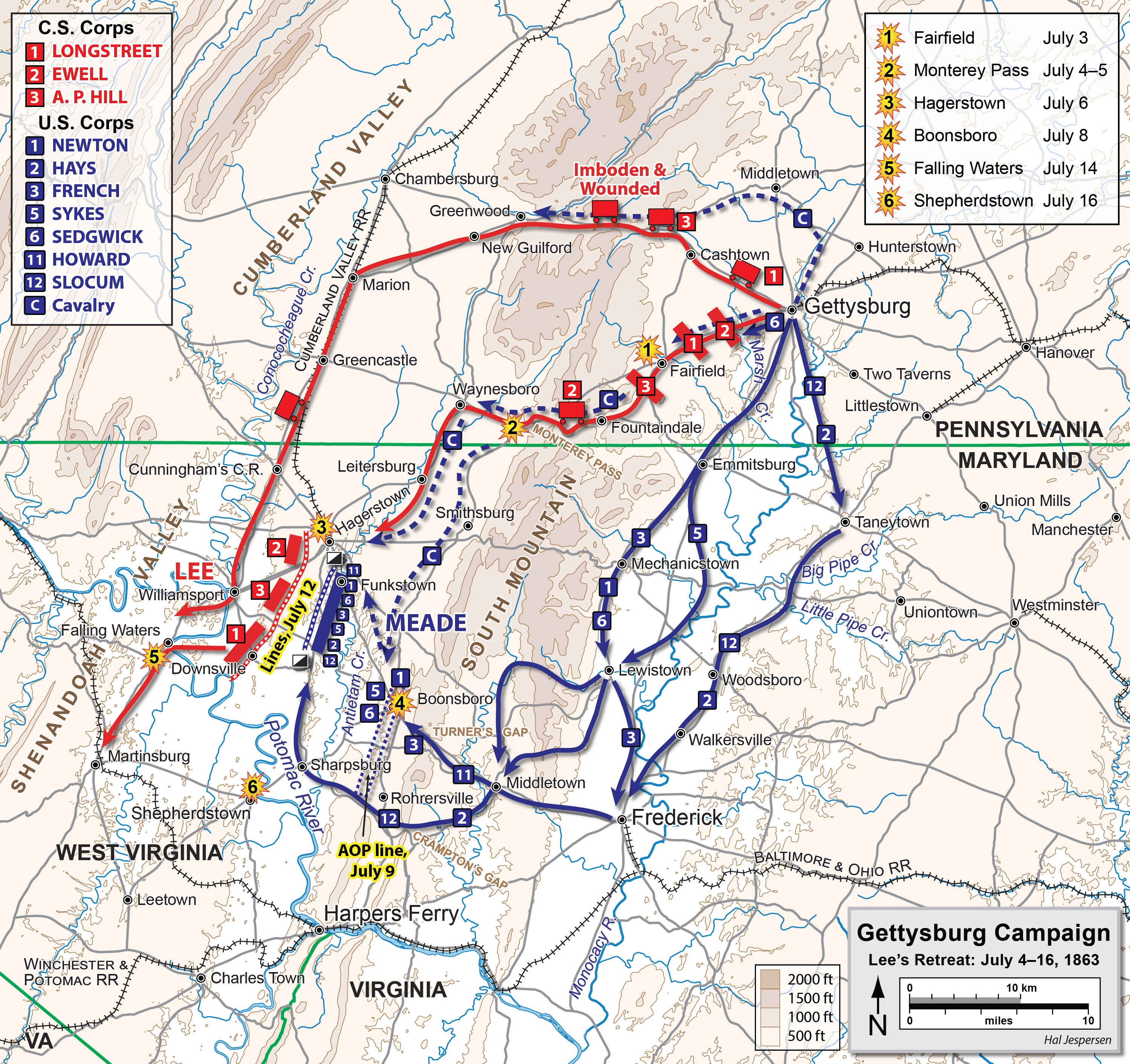
Battle Of Williamsport
The Battle of Williamsport, also known as the Battle of Hagerstown or Falling Waters, took place from July 6 to July 16, 1863, in Washington County, Maryland, as part of the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War. It is not to be confused with the fighting at Hoke's Run which was also known as the Battle of Falling Waters. During the night of July 4–July 5, Gen. Robert E. Lee's battered Confederate army began its retreat from Gettysburg, moving southwest on the Fairfield Road toward Hagerstown and Williamsport, screened by Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart's cavalry. The Union infantry followed cautiously the next day, converging on Middletown, Maryland. By July 7, Brig. Gen. John D. Imboden stopped Brig. Gen. John Buford's Union cavalry from occupying Williamsport and destroying Confederate trains. On July 6, Brig. Gen. Judson Kilpatrick's cavalry division drove two Confederate cavalry brigades through Hagerstown before being forced to retire by the arrival of the rest of St ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Hanover
The Battle of Hanover took place on June 30, 1863, in Hanover in southwestern York County, Pennsylvania, as part of the Gettysburg Campaign of the American Civil War. Maj. Gen. J.E.B. Stuart's Confederate cavalry, which was riding north to get around the Union Army of the Potomac, attacked a Federal cavalry regiment, driving it through the streets of Hanover. Brig. Gen. Elon Farnsworth's brigade arrived and counterattacked, routing the Confederate vanguard and nearly capturing Stuart himself. Stuart soon counterattacked. Reinforced by Brig. Gen. George A. Custer's Michigan Brigade, Farnsworth held his ground, and a stalemate ensued. Stuart was forced to continue north and east to get around the Union cavalry, further delaying his attempt to rejoin Robert E. Lee's army, which was then concentrating at Cashtown Gap west of Gettysburg. Background As Robert E. Lee moved his Army of Northern Virginia northward in June 1863 through the Shenandoah Valley towards Pennsylvania, porti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Army Of The Potomac
The Army of the Potomac was the principal Union Army in the Eastern Theater of the American Civil War. It was created in July 1861 shortly after the First Battle of Bull Run and was disbanded in June 1865 following the surrender of the Confederate Army of Northern Virginia in April. History The Army of the Potomac was created in 1861 but was then only the size of a corps (relative to the size of Union armies later in the war). Its nucleus was called the Army of Northeastern Virginia, under Brig. Gen. Irvin McDowell, and it was the army that fought (and lost) the war's first major battle, the First Battle of Bull Run. The arrival in Washington, D.C., of Maj. Gen. George B. McClellan dramatically changed the makeup of that army. McClellan's original assignment was to command the Division of the Potomac, which included the Department of Northeast Virginia under McDowell and the Department of Washington under Brig. Gen. Joseph K. Mansfield. On July 26, 1861, the Department of the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cavalry Corps (Union Army)
Two corps of the Union Army were called Cavalry Corps during the American Civil War. One served with the Army of the Potomac; the other served in the various armies of the western theater of the war. Overview In contrast to the Confederacy, which early on spawned such brilliant cavalry leaders as J.E.B. Stuart, Nathan B. Forrest, and John S. Mosby, the Union high command initially failed to understand the proper way to use cavalry during the early stages of the war. At the time, cavalry units in the Union armies were generally directly attached to infantry corps, divisions, and "wings" to be used as "shock troops," and essentially played minimal roles in early Civil War campaigns. The Union cavalry was disgraced by Stuart's raids during the Peninsular, Northern Virginia, and Maryland Campaigns, where Stuart was able to ride around the Union Army of the Potomac with feeble resistance from the scant Federal cavalry. The Federals rarely even used cavalry as scouts or raiders in the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |







.png)