J.R. Jayewardene on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Junius Richard Jayewardene ( si, ජුනියස් රිචඩ් ජයවර්ධන, ta, ஜூனியஸ் ரிச்சட் ஜயவர்தனா; 17 September 1906 – 1 November 1996), commonly abbreviated in
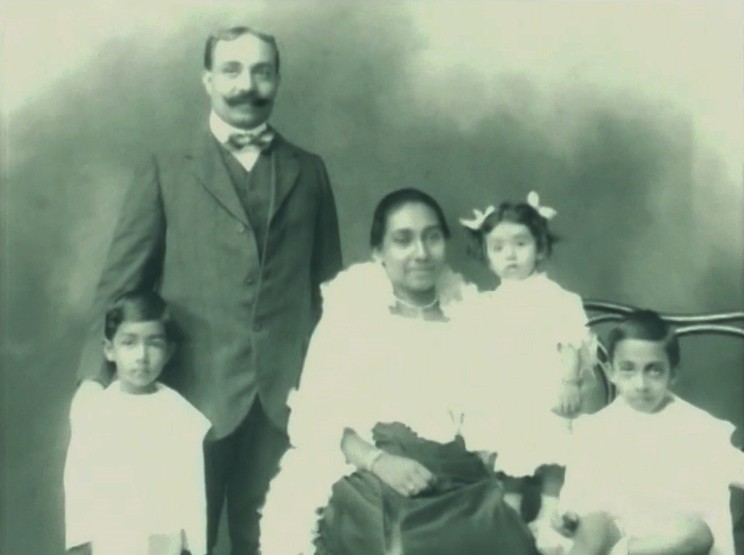
Following the family tradition, Jayewardene entered the
 Jayewardene was attracted to national politics in his student years and developed strong nationalist views. He converted from
Jayewardene was attracted to national politics in his student years and developed strong nationalist views. He converted from
 The United National Party won the next election in 1965 and formed a
The United National Party won the next election in 1965 and formed a
 Tapping into growing anger with the SLFP government, Jayewardene led the UNP to a crushing victory in the 1977 election. The UNP won a staggering five-sixths of the seats in parliament—a total that was magnified by the first-past-the-post system, and one of the most lopsided victories ever recorded for a democratic election. Having been elected to parliament from the Colombo West Electoral District, Jayewardene became Prime Minister and Jayewardene cabinet, formed a new government.
Tapping into growing anger with the SLFP government, Jayewardene led the UNP to a crushing victory in the 1977 election. The UNP won a staggering five-sixths of the seats in parliament—a total that was magnified by the first-past-the-post system, and one of the most lopsided victories ever recorded for a democratic election. Having been elected to parliament from the Colombo West Electoral District, Jayewardene became Prime Minister and Jayewardene cabinet, formed a new government.
 In contrast with his predecessor, Sirimavo Bandaranaike, Jayewardena's foreign policy was aligned with American policies (earning him the nickname 'Yankie Dickie') much to the chagrin of India. Before Jayewardena's ascendency into the presidency, Sri Lanka had doors widely open to neighboring India. Jayewardena's tenure in the office restricted the doors to India a number of times; once an American company tender was granted over an Indian company tender.
In contrast with his predecessor, Sirimavo Bandaranaike, Jayewardena's foreign policy was aligned with American policies (earning him the nickname 'Yankie Dickie') much to the chagrin of India. Before Jayewardena's ascendency into the presidency, Sri Lanka had doors widely open to neighboring India. Jayewardena's tenure in the office restricted the doors to India a number of times; once an American company tender was granted over an Indian company tender.
 On the economic front, Jayewardene's legacy is decisively a positive one. His economic policies are often credited with saving the Sri Lankan economy from ruin. For thirty years after independence, Sri Lanka had struggled in vain with slow growth and high unemployment. By opening up the country for extensive foreign investments, lifting price controls and promoting private enterprise (which had taken a heavy hit because of the policies of the preceding administration), Jayewardene ensured that the island maintained healthy growth despite the civil war. William K. Steven of The New York Times observes,
On the economic front, Jayewardene's legacy is decisively a positive one. His economic policies are often credited with saving the Sri Lankan economy from ruin. For thirty years after independence, Sri Lanka had struggled in vain with slow growth and high unemployment. By opening up the country for extensive foreign investments, lifting price controls and promoting private enterprise (which had taken a heavy hit because of the policies of the preceding administration), Jayewardene ensured that the island maintained healthy growth despite the civil war. William K. Steven of The New York Times observes, ''President Jayawardene's economic policies were credited with transforming the economy from one of scarcity to one of abundance.''
On the ethnic question, Jayewardene's legacy is bitterly divisive. When he took office, ethnic tensions were present in the country but were not overtly volatile. But relations between the two ethnicities heavily deteriorated during his administration and his response to these tensions and the signs of conflict has been heavily criticized. President Jayewardene saw these differences between the Sinhalese and Tamils as being ''an unbridgeable gap'' . Jayewardene said in an interview with the Daily Telegraph, 11 July 1983, "Really, if I starve the Tamils out, the Sinhala people will be happy" in reference to the widespread anti-Tamil sentiments among the Sinhalese at that time.
Highly respected in Japan for his call for peace and reconciliation with post-war Japan at the Treaty of San Francisco, Peace Conference in San Francisco in 1951, a statue of Jayewardene was erected at Kōtoku-in, the Kamakura Temple in the Kanagawa Prefecture in A visionary strategist
/ref>
The JAYEWARDENE Ancestry
The Statesman Misunderstood
Humble son of a humble President
Website of the Parliament of Sri Lanka
Official Website of United National Party (UNP)
J.R. Jayewardene Centre
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080918034319/http://www.sundayobserver.lk/2008/09/14/new24.asp J.R. Jayewardene by Ananda Kannangara]
President JRJ and the Export Processing Zone By K. Godage
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jayewardene, Junius Richard J. R. Jayewardene, 1906 births 1996 deaths Presidents of Sri Lanka Prime Ministers of Sri Lanka Finance ministers of Sri Lanka Leaders of the United National Party Sri Lankan Buddhists Leaders of the Opposition (Sri Lanka) Sinhalese lawyers Sri Lankan cricketers Sri Lankan anti-communists Sinhalese nationalists Alumni of Bishop's College, Colombo Alumni of Royal College, Colombo Alumni of University of London Worldwide Alumni of the University of London Alumni of the Ceylon University College Converts to Buddhism Members of the 1st Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 2nd Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 4th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 5th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 6th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 7th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 8th Parliament of Sri Lanka Sinhalese politicians People of British Ceylon People from Colombo Alumni of Sri Lanka Law College Defence ministers of Sri Lanka Agriculture ministers of Sri Lanka Housing ministers of Sri Lanka Local government and provincial councils ministers of Sri Lanka Jayewardene family, JR Secretaries-General of the Non-Aligned Movement 20th-century Sri Lankan lawyers Parliamentary secretaries of Ceylon Candidates in the 1982 Sri Lankan presidential election Higher education ministers of Sri Lanka Ceylonese people of World War II Chief Government Whips (Sri Lanka) Colombo municipal councillors Deaths from cancer in Sri Lanka Deaths from colorectal cancer People of the Sri Lankan Civil War Indian Peace Keeping Force
Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
as J.R., was the leader of Sri Lanka from 1977 to 1989, serving as Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is not ...
from 1977 to 1978 and as the second President of Sri Lanka
The President of Sri Lanka ( si, ශ්රී ලංකා ජනාධිපති ''Śrī Laṃkā Janādhipathi''; ta, இலங்கை சனாதிபதி ''Ilankai janātipati'') is the head of state and head of government of t ...
from 1978 to 1989. He was a leader of the nationalist movement in Ceylon
Sri Lanka (, ; si, ශ්රී ලංකා, Śrī Laṅkā, translit-std=ISO (); ta, இலங்கை, Ilaṅkai, translit-std=ISO ()), formerly known as Ceylon and officially the Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka, is an ...
(now Sri Lanka) who served in a variety of cabinet positions in the decades following independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the statu ...
. A longtime member of the United National Party
The United National Party, often abbreviated as UNP ( si, එක්සත් ජාතික පක්ෂය, translit=Eksath Jāthika Pakshaya, ta, ஐக்கிய தேசியக் கட்சி, translit=Aikkiya Tēciyak Kaṭci), ...
, he led it to a landslide victory in 1977 and served as Prime Minister for half a year before becoming the country's first executive president under an amended constitution.
A controversial figure in the history of Sri Lanka
The history of Sri Lanka is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions, comprising the areas of South Asia, Southeast Asia and Indian Ocean.
The early human remains found on the island of Sri La ...
, while the open economic system he introduced in 1978 brought the country out of the economic turmoil Sri Lanka was facing as the result of the preceding closed economic policies, Jayawardene's actions, including his response to the Black July riots of 1983, have been accused of contributing to the beginnings of the Sri Lankan Civil War.
Early Life and Marriage
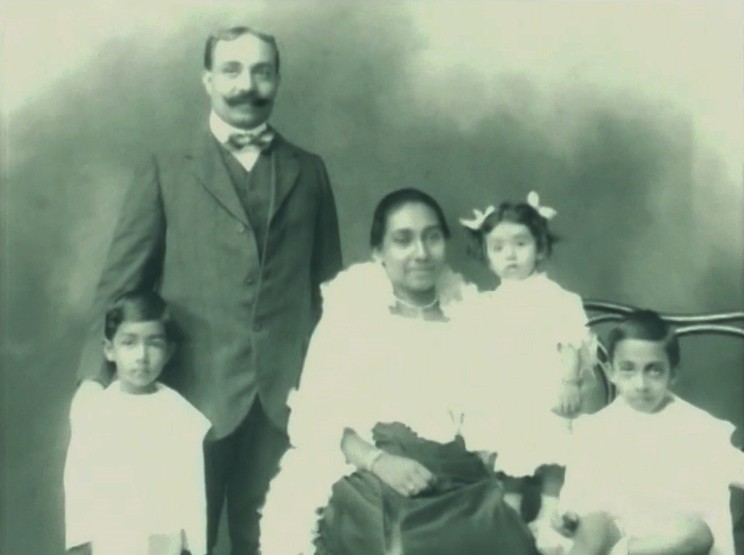
Childhood
Born inColombo
Colombo ( ; si, කොළඹ, translit=Koḷam̆ba, ; ta, கொழும்பு, translit=Koḻumpu, ) is the executive and judicial capital and largest city of Sri Lanka by population. According to the Brookings Institution, Colombo me ...
to a prominent Ceylonese family with a strong association with the legal profession, Jayewardene was the eldest of twelve children, of Hon. Justice Eugene Wilfred Jayewardene
Justice Eugene Wilfred Jayewardene, King's Counsel, KC (Sinhala language, Sinhala:යුජින් විල්ෆ්රඩ් ජයවර්ධන; 11 June 1874 – 23 November 1932) was a Ceylonese (Sri Lankan) judge, lawyer and politici ...
KC, a prominent lawyer and Agnes Helen Don Philip Wijewardena daughter of Muhandiram
Muhandiram ( si, මුහන්දිරම්, ta, முகாந்திரம்) was a post in the native headmen system in the lower-country (coastal districts) of Ceylon (Sri Lanka) during the colonial era. It was awarded as a title o ...
Tudugalage Don Philip Wijewardena a wealthy timber merchant. He was known as Dickie within his family. His younger brothers included Hector Wilfred Jayewardene
Deshamanya Hector Wilfred "Harry" Jayewardene, QC (November 3, 1916 - April 20, 1990) was a prominent Sri Lankan lawyer. In 1979 he was chairman of a UNESCO conference on human rights in Bangkok and later chairman of the Sri Lanka Foundation Ins ...
, QC and Rolly Jayewardene, FRCP. His uncles were the Colonel Theodore Jayewardene, Justice Valentine Jayewardene and the Press Baron D. R. Wijewardena
Don Richard Wijewardena ( Sinhala:දොන් රිච්ඩ් විජෙවර්ධන) (23 February 1886 – 13 June 1950) was a Sri Lankan press baron who was involved in the Sri Lankan independence movement. A successful entrepreneur ...
. Raised by an English nanny, he received his primary education at Bishop's College, Colombo
Bishop's College in Colombo, Sri Lanka, is a private girls' school founded by the Anglican Church of Ceylon in February 1875.
Description
Bishop's College is a private fee-levying Anglican girls' school in Sri Lanka with about 1900 students at al ...
.
Education and Early Career
Jayewardene gained admission toRoyal College, Colombo
Royal College, Colombo is a selective entry boys' school located in Cinnamon Gardens, Colombo, Sri Lanka. Started as a private school by Rev Joseph Marsh in 1835, it was established as the Colombo Academy by Sir Robert Wilmot-Horton in Janua ...
for his secondary education. There he excelled in sports, played for the college cricket
Cricket is a bat-and-ball game played between two teams of eleven players on a field at the centre of which is a pitch with a wicket at each end, each comprising two bails balanced on three stumps. The batting side scores runs by striki ...
team, debuting in the Royal-Thomian series in 1925; captained the rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
team in 1924 at the annual "Royal-Trinity Encounter" (which later became known as the Bradby Shield Encounter
The Bradby Shield Encounter - commonly known as "The Bradby" - is the pinnacle of Sri Lanka's school rugby union season. It is played annually between two of the most prominent boys’ schools in the country and traditional rivals Royal College, C ...
); he was the vice captain of the football team in 1924; and was a member of the boxing team winning sports colours. He was a Senior Cadet; Captain, Debating Team; Editor, College Magazine; first Secretary in Royal College Social Services League in 1921 and he became the head prefect
Head boy and head girl are student leadership roles in schools, representing the school's entire student body. They are normally the most senior prefects in the school. The terms are commonly used in the British education system as well as in Aus ...
in 1925. In later life, he served as president, Board of Control for Cricket in Sri Lanka
Sri Lanka Cricket (SLC) is the governing body for cricket in Sri Lanka. It was first registered with the Sri Lankan Ministry of Sports as the Board of Cricket for Sri Lanka (BCCSL) on 30 June 1975 as a national sports body. The board was renamed ...
; President, Sinhalese Sports Club
The Singhalese Sports Club (SSC) is a first-class cricket club in Sri Lanka. Singhalese is the most successful club in Sri Lankan domestic cricket, having won the Premier Trophy a record 32 times to 2017. Although the name is correctly spelt wi ...
; and Secretary, Royal College Union
The Royal College Union (RCU) is the alumni association of the Royal College Colombo. Founded in 1891 as a society for alumni of the college, it is the oldest such alumni society in Sri Lanka. The Royal College Union was set up to further the ...
.Remembering the most dominant Lankan political figureFollowing the family tradition, Jayewardene entered the
University College, Colombo
Ceylon University College was a public university college in Ceylon. Established in 1921, it was Ceylon's first attempt at university education. The college didn't award degrees under its own name but prepared students to sit the University of Lo ...
in 1926 pursuing the Advocate's course, reading English, Latin, Logic and Economics for two years, after which he entered Ceylon Law College
Sri Lanka Law College (abbreviated as SLLC), formerly known as Ceylon Law College, is a law college, and the only legal institution where one can enroll as a attorney-at-law in Sri Lanka. It was established in 1874, under the then Council of Legal ...
in 1928. He formed the College Union based on that of the Oxford Union
The Oxford Union Society, commonly referred to simply as the Oxford Union, is a debating society in the city of Oxford England, whose membership is drawn primarily from the University of Oxford. Founded in 1823, it is one of Britain's oldest ...
with assistance of S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike
Solomon West Ridgeway Dias Bandaranaike ( si, සොලොමන් වෙස්ට් රිජ්වේ ඩයස් බණ්ඩාරනායක; ta, சாலமன் வெஸ்ட் ரிட்ஜ்வே டயஸ் ப� ...
who had recently return to Ceylon. At the Ceylon Law College he won the Hector Jayewardene Gold Medal and the Walter Pereira Prize in 1929. During this time he worked as his father's Private Secretary
A private secretary (PS) is a civil servant in a governmental department or ministry, responsible to a secretary of state or minister; or a public servant in a royal household, responsible to a member of the royal family.
The role exists in t ...
, while latter served as a Puisne Justice of Supreme Court of Ceylon and in July 1929, he joined three others in forming a dining club
A dining club (UK) or eating club (US) is a social group, usually requiring membership (which may, or may not be available only to certain people), which meets for dinners and discussion on a regular basis. They may also often have guest speakers. ...
they called ''The Honorable Society of Pushcannons'', which was later renamed as the ''Priya Sangamaya''. In 1931, he passed his advocate
An advocate is a professional in the field of law. Different countries' legal systems use the term with somewhat differing meanings. The broad equivalent in many English law–based jurisdictions could be a barrister or a solicitor. However, ...
s exams, starting his legal practice in the unofficial bar.
Marriage
On 28 February 1935, Jayewardene married the heiress Miss Elina Bandara Rupasinghe, only daughter of Nancy Margaret Suriyabandara and Gilbert Leonard Rupasinghe, a notary public turned successful businessmen. Their only child Ravindra "Ravi" Vimal Jayewardene was born the year after. Having originally settled at Jayewardene's parents houseVaijantha
Vaijantha, was the childhood home of J. R. Jayewardene former President of Sri Lanka in Colombo, Sri Lanka. Today it houses the J.R. Jayewardene Centre
It was built by Jayewardene's father Hon. Justice Eugene Wilfred Jayewardene KC, a Chief Jus ...
, the Jayewardene's moved to their own house Braemar
Braemar is a village in Aberdeenshire, Scotland, around west of Aberdeen in the Highlands. It is the closest significantly-sized settlement to the upper course of the River Dee sitting at an elevation of .
The Gaelic ''Bràigh Mhàrr'' prop ...
in 1938, where they remained the rest of their lives, when not holidaying at their holiday home
A holiday cottage, holiday home, vacation home, or vacation property is accommodation used for holiday vacations, corporate travel, and temporary housing often for less than 30 days. Such properties are typically small homes, such as cottage ...
in Mirissa
Mirissa ( si, මිරිස්ස, translit=Mirissa; ta, மிரிஸ்ஸ, translit=Miris'sa) is a small town on the south coast of Sri Lanka, located in the Matara District of the Southern Province. It is approximately south of Colombo ...
.
Early Political Career
 Jayewardene was attracted to national politics in his student years and developed strong nationalist views. He converted from
Jayewardene was attracted to national politics in his student years and developed strong nationalist views. He converted from Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
to Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
and adopted the national dress as his formal attire.
Jayewardene did not practice law for long. In 1943 he gave up his full time legal practice to become an activist in the Ceylon National Congress
The Ceylon National Congress ( Sinhala: ලංකා ජාතික කොන්ග්රසය ''Lanka Jathika Kongrasaya'') (CNC) was a Nationalist political party which was formed in Ceylon on 11 December 1919. It was founded after national ...
(CNC), which provided the organizational platform for Ceylon's nationalist movement (the island was officially renamed Sri Lanka in 1972). He became its Joint Secretary with Dudley Senanayake
Dudley Shelton Senanayake ( Sinhala: ඩඩ්ලි ශෙල්ටන් සේනානායක: ta, டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா; 19 June 1911 – 13 April 1973), was a Sri Lankan statesman who served as Prime Mi ...
in 1939 and in 1940 he was elected to the Colombo Municipal Council
The Colombo Municipal Council is the municipal governing body of Colombo, the largest city and financial centre in Sri Lanka. It consists of a directly elected executive Mayor of Colombo, current elect is Rosy Senanayake, and 119 elected 119 muni ...
from the New Bazaar Ward.
State Council
He was elected to the colonial legislature, theState Council State Council may refer to:
Government
* State Council of the Republic of Korea, the national cabinet of South Korea, headed by the President
* State Council of the People's Republic of China, the national cabinet and chief administrative auth ...
in 1943 by winning the Kelaniya by-election following the resignation of incumbent D. B. Jayatilaka
Sir Don Baron Jayatilaka, Knight Commander of the Most Excellent Order of the British Empire, KBE (Sinhala language, Sinhala:ශ්රීමත් දොන් බාරොන් ජයතිලක; 13 February 1868 – 29 May 1944) known as ...
. His victory is credited to his use of an anti-Christian campaign against his opponent the nationalist E. W. Perera
Edward Walter Perera (11 December 1875 – 15 February 1953) was a Ceylonese (Sri Lankan) barrister, politician and freedom fighter. He was known as the "Lion of Kotte" and was a prominent figure in the Sri Lankan independence movement, served ...
. During World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, Jayewardene, along with other nationalists, contacted the Japanese and discussed a rebellion to drive the British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
from the island. In 1944, Jayewardene moved a motion in the State Council that Sinhala alone should replace English as the official language.
First Finance Minister of Ceylon
After joining theUnited National Party
The United National Party, often abbreviated as UNP ( si, එක්සත් ජාතික පක්ෂය, translit=Eksath Jāthika Pakshaya, ta, ஐக்கிய தேசியக் கட்சி, translit=Aikkiya Tēciyak Kaṭci), ...
on its formation in 1946 as a founder member, he was reelected from the Kelaniya electorate in the 1st parliamentary election and was appointed by D. S. Senanayake
Don Stephen Senanayake ( si, දොන් ස්ටීවන් සේනානායක,; ta, டி. எஸ். சேனநாயக்கா; 21 October 1884 – 22 March 1952) was a Ceylonese statesman. He was the first Prime Mi ...
as the Minister of Finance
A finance minister is an executive or cabinet position in charge of one or more of government finances, economic policy and financial regulation.
A finance minister's portfolio has a large variety of names around the world, such as "treasury", " ...
in the island's first Cabinet in 1947. Initiating post-independence reforms, he was instrumental in the establishment of the Central Bank of Ceylon
The Central Bank of Sri Lanka ( CBSL; si, ශ්රී ලංකා මහ බැංකුව, Sri Lanka Maha Bankuwa) is the monetary authority of Sri Lanka. It was established in 1950 under the Monetary Law Act No.58 of 1949 (MLA), it is a ...
under the guidance of the American economist John Exter
John Exter (September 17, 1910 – February 28, 2006) was an American economist, member of the Board of Governors of the United States Federal Reserve System, and founder of the Central Bank of Sri Lanka. He is also known for creating ''Exter's Py ...
. In 1951 Jayewardene was a member of the committee to select a National Anthem for Sri Lanka headed by Sir Edwin Wijeyeratne
Sir Edwin Aloysius Perera Wijeyeratne ( Sinhala: ශ්රිමත් එඩ්වින් ඇලෝසියස් පෙරේරා විජයරත්න) (8 January 1889 – 19 October 1968), known as ''Edwin Wijeyeratne'', was a Sr ...
. The following year he was elected as the President of the Board of Control for Cricket in Ceylon. He played a major role in re-admitting Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
to the world community at the San Francisco Conference
The United Nations Conference on International Organization (UNCIO), commonly known as the San Francisco Conference, was a convention of delegates from 50 Allied nations that took place from 25 April 1945 to 26 June 1945 in San Francisco, Calif ...
. Jayewardene struggled to balance the budget, faced with mounting government expenditures, particularly for rice subsidies. He was re-elected in 1952 parliamentary election and remained as finance minister.
Minister of Agriculture and Food
His 1953 proposal to cut the subsidies on which many poor people depended on for survival provoked fierce opposition and the 1953 Hartal campaign, and had to be called off. Following the resignation of Prime MinisterDudley Senanayake
Dudley Shelton Senanayake ( Sinhala: ඩඩ්ලි ශෙල්ටන් සේනානායක: ta, டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா; 19 June 1911 – 13 April 1973), was a Sri Lankan statesman who served as Prime Mi ...
after the 1953 Hartal, the new Prime Minister Sir John Kotelawala
General Sir John Lionel Kotelawala ( si, ශ්රිමත් ජෝන් ලයනල් කොතලාවල; 4 April 1897 – 2 October 1980) was a Sri Lankan statesman, who served as the 3rd Prime Minister of Ceylon (Sri Lanka) fro ...
appointed Jayewardene as Minister of Agriculture and Food and Leader of the House.
Defeat and Opposition
Prime Minister Sir John Kotelawala called for early elections in 1956 with confidence that the United National Party would win the election. The 1956 parliamentary election saw the United National Party suffering a crushing defeat at the hands of the socialist and nationalist coalition led by theSri Lanka Freedom Party
The Sri Lanka Freedom Party ( si, ශ්රී ලංකා නිදහස් පක්ෂය, translit=Śrī Laṁkā Nidahas Pakṣaya; ta, இலங்கை சுதந்திரக் கட்சி, translit=Ilaṅkai Cutantirak Ka� ...
headed by S. W. R. D. Bandaranaike
Solomon West Ridgeway Dias Bandaranaike ( si, සොලොමන් වෙස්ට් රිජ්වේ ඩයස් බණ්ඩාරනායක; ta, சாலமன் வெஸ்ட் ரிட்ஜ்வே டயஸ் ப� ...
. Jayewardene himself lost his parliamentary seat in Kelaniya to R. G. Senanayake
Richard Gotabhaya Senanayake (4 November 1911 – 22 December 1970; popularly known as R.G. Senanayake) was a Sri Lankan politician. He was Minister of Trade and Commerce during the period 1952-56 and 1956-60. He was elected a Member of Parliamen ...
, who had contested both his own constituency Dambadeniya and Jayewardene's constituency of Kelaniya with the objective of defeating the latter after he had forced Senanayake out of the party.
Having lost his seat in parliament, Jayewardene pushed the party to accommodate nationalism and endorse the Sinhala Only Act
The Official Language Act (No. 33 of 1956), commonly referred to as the Sinhala Only Act, was an act passed in the Parliament of Ceylon in 1956. The act replaced English with Sinhala as the sole official language of Ceylon, with the exclusion ...
, which was bitterly opposed by the island's minorities. When Bandaranaike came to an agreement with S.J.V. Chelvanayagam
Samuel James Veluppillai Chelvanayakam ( ta, சாமுவேல் ஜேம்ஸ் வேலுப்பிள்ளை செல்வநாயகம், translit=Cāmuvēl Jēms Vēluppiḷḷai Celvanāyakam; 31 March 1898 – 26 Ap ...
in 1957, to solve the outstanding problems of the minorities, Jayawardene led a "March on Kandy" against it, but was stopped at Imbulgoda S. D. Bandaranayake
Samuel Dias Bandaranayake (1 December 1917 – 3 June 2014) was a Sri Lankan socialist politician and a member of parliament representing Gampaha.
Early life and education
Born to a wealthy family, his father was Conrad Peter Dias Bandaranaya ...
. The U.N.P.'s official organ the ''Siyarata'' subsequently ran several anti-Tamil articles, including a poem,containing an exhortation to kill Tamils in almost every line.
Throughout the 1960s Jayewardene clashed over this issue with party leader Dudley Senanayake
Dudley Shelton Senanayake ( Sinhala: ඩඩ්ලි ශෙල්ටන් සේනානායක: ta, டட்லி சேனநாயக்கா; 19 June 1911 – 13 April 1973), was a Sri Lankan statesman who served as Prime Mi ...
. Jayewardene felt the UNP should be willing to play the ethnic card, even if it meant losing the support of ethnic minorities.
Minister of Finance
Jayewardene became the Vice President and Chief Organizer of the United National Party, which achieved a narrow win in the March 1960 parliamentary election, forming a government under Dudley Senanayake. Jayewardene having been elected to parliament once again from the Kelaniya electorate was appointed once again as Minister of Finance. The government lasted only three months and lost the July 1960 parliamentary election to the a new coalition lead by Bandaranayake's widow. Jayewardene remained in parliament in the opposition having been elected from the Colombo South electorate.Minister of State
 The United National Party won the next election in 1965 and formed a
The United National Party won the next election in 1965 and formed a national government A national government is the government of a nation.
National government or
National Government may also refer to:
* Central government in a unitary state, or a country that does not give significant power to regional divisions
* Federal governme ...
with the Sri Lanka Freedom Socialist Party
Sri Lanka Freedom Socialist Party was a political party in Sri Lanka. SLFSP was formed in 1964 by C. P. de Silva when he broke away from the Sri Lanka Freedom Party. In the 1965 elections, SLFSP contested in coalition with the United National Part ...
led by C. P. de Silva
Charles Percival de Silva (16 April 1912 – 9 October 1972) was a leading Sri Lankan politician and civil servant. He had served as the Minister of Finance, Minister of Lands, Land Development and Agriculture; and Minister of Power and Ir ...
. Jayewardene was reelected from the Colombo South electorate uncontested and was appointed Chief Government Whip
The Chief Whip is a political leader whose task is to enforce the whipping system, which aims to ensure that legislators who are members of a political party attend and vote on legislation as the party leadership prescribes.
United Kingdom
...
. Senanayake appointed Jayewardene to his cabinet as Minister of State and Parliamentary Secretary to the Minister of Defence and External Affairs thereby becoming the ''de-facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' deputy prime minister
A deputy prime minister or vice prime minister is, in some countries, a government minister who can take the position of acting prime minister when the prime minister is temporarily absent. The position is often likened to that of a vice president, ...
. No government had given serious thought to the development of the tourism industry as an economically viable venture until the United National Party came to power in 1965 and the subject came under the purview of J. R. Jayewardene. Jayewardene saw tourism as a great industry capable of earning foreign exchange, providing avenues of mass employment, and creating a workforce which commanded high employment potential globally. He was determined to place this industry on a solid foundation, providing it a 'conceptional base and institutional support.' This was necessary to bring dynamism and cohesiveness into an industry, shunned by leaders in the past, ignored by investors who were inhibited by the lack of incentive to invest in projects which were uncertain of a satisfactory return. Jayewardene considered it essential for the government to give that assurance and with this objective in view he tabled the Ceylon Tourist Board Act No 10 of 1966 followed by Ceylon Hotels Corporation Act No 14 of 1966. At present the tourism industry in Sri Lanka is major foreign exchange earner with tourist resorts in almost all cities and an annual turnover of over 500,000 tourists are enjoying the tropical climes and beautiful beaches.
Leader of the Opposition
In the general election of 1970 the UNP suffered a major defeat, when the SLFP and its newly formed coalition of leftist parties won almost 2/3 of the parliamentary seats. Once again elected to parliament J. R. Jayewardene took over as opposition leader and de facto leader of the UNP due to the ill health of Dudley Senanayake. After Senanayake's death in 1973, Jayewardene succeeded him as UNP leader. He gave the SLFP government his fullest support during the 1971 JVP Insurrection (even though his son was arrested by the police without charges) and in 1972 when the new constitution was enacted proclaiming Ceylon a republic. However he opposed the government in many moves, which he saw as short sighted and damaging for the country's economy in the long run. These included the adaptation of the closed economy and nationalization of many private business and lands. In 1976 he resigned from his seat in parliament in protest, when the government used its large majority in parliament to extend the duration of the government by two more years at the end of its six-year term without holding a general election or a referendum requesting public approval.Prime Minister
 Tapping into growing anger with the SLFP government, Jayewardene led the UNP to a crushing victory in the 1977 election. The UNP won a staggering five-sixths of the seats in parliament—a total that was magnified by the first-past-the-post system, and one of the most lopsided victories ever recorded for a democratic election. Having been elected to parliament from the Colombo West Electoral District, Jayewardene became Prime Minister and Jayewardene cabinet, formed a new government.
Tapping into growing anger with the SLFP government, Jayewardene led the UNP to a crushing victory in the 1977 election. The UNP won a staggering five-sixths of the seats in parliament—a total that was magnified by the first-past-the-post system, and one of the most lopsided victories ever recorded for a democratic election. Having been elected to parliament from the Colombo West Electoral District, Jayewardene became Prime Minister and Jayewardene cabinet, formed a new government.
Presidency
Shortly thereafter, he amended the Sri Lankan Constitution of 1972, constitution of 1972 to make the presidency an executive post. The provisions of the amendment automatically made the incumbent prime minister—himself—president, and he was sworn in as president on 4 February 1978. He passed a Constitution of Sri Lanka, new constitution on 31 August 1978 which came into operation on 7 September of the same year, which granted the president sweeping—and according to some critics, almost dictatorial—powers. He moved the legislative capital from Colombo to Sri Jayawardanapura Kotte. He had likely SLFP presidential nominee Sirimavo Bandaranaike stripped of her civic rights and barred from running for office for six years, based her decision in 1976 to extend the term of parliament. This ensured that the SLFP would be unable to field a strong candidate against him in the 1982 Sri Lankan presidential election, 1982 election, leaving his path to victory clear. This election was held under the 3rd amendment to the constitution which empowered the president to hold a Presidential Election anytime after the expiration of four years of his first term. He held a referendum to cancel the 1983 parliamentary elections, and allow the 1977 parliament to continue until 1989. He also passed a constitutional amendment barring from Parliament any MP who supported separatism; this effectively eliminated the main opposition party, the Tamil United Liberation Front.Economy
There was a complete turnaround in economic policy under him as the previous policies had led to economic stagnation. He opened the heavily state-controlled economy to market forces, which many credit with subsequent economic growth. He opened up the economy and introduced more Economic liberalism, liberal economic policies emphasizing private sector led development. Policies were changed to create an environment conducive to foreign and local investment, with the objective of promoting export led growth shifting from previous policies of import substitution. To facilitate export oriented enterprises and to administer Export Processing Zones the Greater Colombo Economic Commission was established. Food subsidies were curtailed and targeted through a Food Stamps Scheme extended to the poor. The system of rice rationing was abolished. The Floor Price Scheme and the Fertilizer Subsidy Scheme were withdrawn. New welfare schemes, such as free school books and the Mahapola Higher Education Scholarship Trust Fund, Mahapola Scholarship Programme, were introduced. The rural credit programme expanded with the introduction of the New Comprehensive Rural Credit Scheme and several other medium and long-term credit schemes aimed at small farmers and the Self-employment, self-employed. He also launched large scale infrastructure development projects. He launched an extensive housing development program to meet housing shortages in urban and rural areas. The Mahaweli Development programme, Accelerated Mahaweli Programme built new reservoirs and large hydropower projects such as the Kotmale Dam, Kotmale, Victoria Dam (Sri Lanka), Victoria, Randenigala Dam, Randenigala, Rantembe Dam, Rantembe and Ulhitiya. Several Trans Basin Canals were also built to divert water to the Dry Zone.Conservation
His administration launched several wildlife conservation initiatives. This included stopping commercial logging in rain forests such as Sinharaja Forest Reserve which was designated a World Biosphere Reserve in 1978 and a World Heritage Site in 1988.Tamil Militancy and Civil War
Jayewardene moved to crack down on the growing activity of List of Tamil militant groups, Tamil militant groups active since the mid-1970s. He passed the Prevention of Terrorism Act (Sri Lanka), Prevention of Terrorism Act in 1979, giving police sweeping powers to arrest and detain. This only escalated the ethnic tensions. Jayewardene claimed he needed overwhelming power to deal with the militants. After the Sri Lankan riots of 1977, 1977 riots, the government made one concession to the Tamils; it lifted the policy of standardization for university admission that had driven many Tamil youths into militancy. The concession was regarded by the militants as too little and too late, and violent attacks continued, culminating in the ambush of Four Four Bravo which led to the Black July, Black July riots. Black July riots transformed the militancy into a civil war, with the swelling of ranks of the militant groups. By 1987, the LTTE had emerged as the dominant of the Tamil militant groups and had a free hand over the Jaffna Peninsula, limiting government activities in that region. Jayewardene's administration responded with a massive military operation codenamed Vadamarachchi Operation, Operation Liberation to eliminate the LTTE leadership. Jayewardene had to halt the offensive after pressure from India pushed for a negotiated solution to the conflict after executing Operation Poomalai. Jayewardene and Indian Prime Minister Rajiv Gandhi finally concluded the Indo-Sri Lanka Accord, which provided for devolution of powers to Tamil dominated regions, an IPKF, Indian peacekeeping force in the north, and the demobilization of the LTTE. The LTTE rejected the accord, as it fell short of even an autonomous state. The provincial councils suggested by India did not have powers to control revenue, policing, or government-sponsored Sinhalese people, Sinhala settlements in Tamil provinces. Sinhala nationalists were outraged by both the devolution and the presence of foreign troops on Sri Lankan soil. An 1987 grenade attack in the Sri Lankan Parliament, attempt was made on Jayewardene's life in 1987 as a result of his signing of the accord. Young, deprived Sinhalese soon rose in a Insurrection 1987-89, revolt, organized by the Janatha Vimukthi Peramuna (JVP) which was eventually put down by the government by 1989.Foreign Policy
 In contrast with his predecessor, Sirimavo Bandaranaike, Jayewardena's foreign policy was aligned with American policies (earning him the nickname 'Yankie Dickie') much to the chagrin of India. Before Jayewardena's ascendency into the presidency, Sri Lanka had doors widely open to neighboring India. Jayewardena's tenure in the office restricted the doors to India a number of times; once an American company tender was granted over an Indian company tender.
In contrast with his predecessor, Sirimavo Bandaranaike, Jayewardena's foreign policy was aligned with American policies (earning him the nickname 'Yankie Dickie') much to the chagrin of India. Before Jayewardena's ascendency into the presidency, Sri Lanka had doors widely open to neighboring India. Jayewardena's tenure in the office restricted the doors to India a number of times; once an American company tender was granted over an Indian company tender.
Post-presidency
Jayewardene retired from politics in 1989 after his second term as president at the age of 82; his successor Ranasinghe Premadasa was formally inaugurated on 2 January 1989. He did not re-enter politics during his retirement even after the assassination of Premadasa in 1993.Death
Jayewardene died of colon cancer, on 1 November 1996, aged 90, at a hospital in Colombo. He was survived by his wife, Elina Jayewardene, Elina, and his son, Ravi Jayewardene, Ravi.Legacy
 On the economic front, Jayewardene's legacy is decisively a positive one. His economic policies are often credited with saving the Sri Lankan economy from ruin. For thirty years after independence, Sri Lanka had struggled in vain with slow growth and high unemployment. By opening up the country for extensive foreign investments, lifting price controls and promoting private enterprise (which had taken a heavy hit because of the policies of the preceding administration), Jayewardene ensured that the island maintained healthy growth despite the civil war. William K. Steven of The New York Times observes,
On the economic front, Jayewardene's legacy is decisively a positive one. His economic policies are often credited with saving the Sri Lankan economy from ruin. For thirty years after independence, Sri Lanka had struggled in vain with slow growth and high unemployment. By opening up the country for extensive foreign investments, lifting price controls and promoting private enterprise (which had taken a heavy hit because of the policies of the preceding administration), Jayewardene ensured that the island maintained healthy growth despite the civil war. William K. Steven of The New York Times observes, Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north ...
in his honor./ref>
J.R. Jayewardene Centre
In 1988, the J.R. Jayewardene Centre was established by the J.R. Jayewardene Centre Act No. 77 of 1988 by Parliament at the childhood home of J. R. Jayewardene Dharmapala Mawatha, Colombo. It serves as archive for J.R. Jayewardene's personal library and papers as well as papers, records from the Presidential Secretariat (Sri Lanka), Presidential Secretariat and gifts he received in his tenure as president.Further reading
* De Silva, K. M., & Wriggins, W. H. (1988), ''J.R. Jayewardene of Sri Lanka: a political biography'', University of Hawaii Press * Jayewardene, J. R. (1988), ''My quest for peace: a collection of speeches on international affairs'', * Dissanayaka, T. D. S. A. (1977), ''J.R. Jayewardene of Sri Lanka: the inside story of how the Prime Minister led the UNP to victory in 1977'', Swastika Press * *See also
* Jayewardene cabinet * Braemar, Colombo *Vaijantha
Vaijantha, was the childhood home of J. R. Jayewardene former President of Sri Lanka in Colombo, Sri Lanka. Today it houses the J.R. Jayewardene Centre
It was built by Jayewardene's father Hon. Justice Eugene Wilfred Jayewardene KC, a Chief Jus ...
* List of political families in Sri Lanka
* 1987 grenade attack in the Sri Lankan Parliament
References
External links
The JAYEWARDENE Ancestry
The Statesman Misunderstood
Humble son of a humble President
Website of the Parliament of Sri Lanka
Official Website of United National Party (UNP)
J.R. Jayewardene Centre
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20080918034319/http://www.sundayobserver.lk/2008/09/14/new24.asp J.R. Jayewardene by Ananda Kannangara]
President JRJ and the Export Processing Zone By K. Godage
{{DEFAULTSORT:Jayewardene, Junius Richard J. R. Jayewardene, 1906 births 1996 deaths Presidents of Sri Lanka Prime Ministers of Sri Lanka Finance ministers of Sri Lanka Leaders of the United National Party Sri Lankan Buddhists Leaders of the Opposition (Sri Lanka) Sinhalese lawyers Sri Lankan cricketers Sri Lankan anti-communists Sinhalese nationalists Alumni of Bishop's College, Colombo Alumni of Royal College, Colombo Alumni of University of London Worldwide Alumni of the University of London Alumni of the Ceylon University College Converts to Buddhism Members of the 1st Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 2nd Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 4th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 5th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 6th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 7th Parliament of Ceylon Members of the 8th Parliament of Sri Lanka Sinhalese politicians People of British Ceylon People from Colombo Alumni of Sri Lanka Law College Defence ministers of Sri Lanka Agriculture ministers of Sri Lanka Housing ministers of Sri Lanka Local government and provincial councils ministers of Sri Lanka Jayewardene family, JR Secretaries-General of the Non-Aligned Movement 20th-century Sri Lankan lawyers Parliamentary secretaries of Ceylon Candidates in the 1982 Sri Lankan presidential election Higher education ministers of Sri Lanka Ceylonese people of World War II Chief Government Whips (Sri Lanka) Colombo municipal councillors Deaths from cancer in Sri Lanka Deaths from colorectal cancer People of the Sri Lankan Civil War Indian Peace Keeping Force