Industry in Brazil on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in
Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in


 Most large industry is concentrated in the south and south east. The north east is traditionally the poorest part of Brazil, but it is beginning to attract new investment.
Brazil has the third best advanced industrial sector in
Most large industry is concentrated in the south and south east. The north east is traditionally the poorest part of Brazil, but it is beginning to attract new investment.
Brazil has the third best advanced industrial sector in
/ref> Despite being, in 2018, the eighth largest vehicle producer in the world, Brazil didn't even have a national industry. The last Brazilian industry was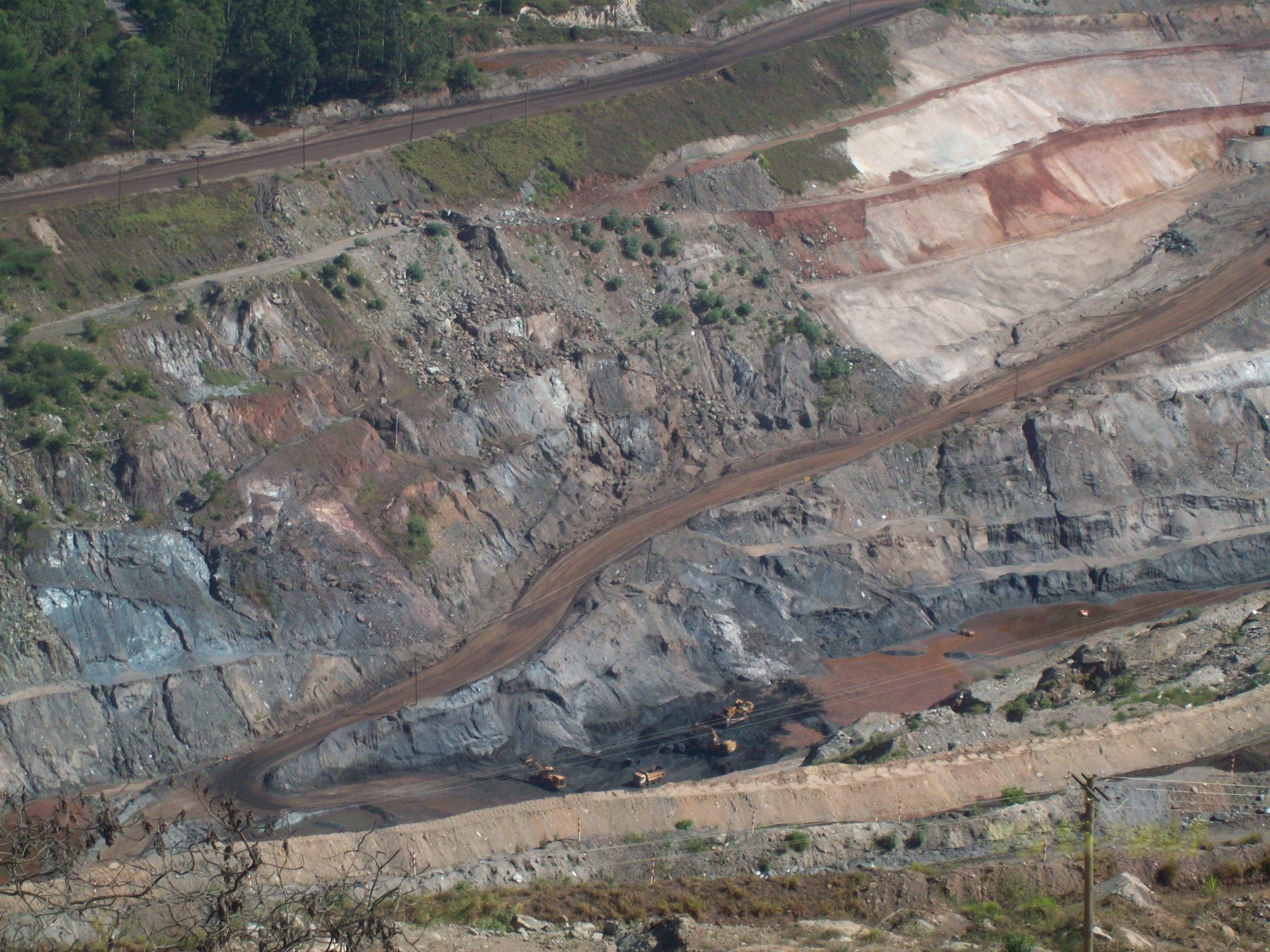

 In 2016, substances in the metallic class accounted for about 77% of the total value of Brazilian commercialized mineral production. Among these substances, eight correspond to 98.6% of the value:
In 2016, substances in the metallic class accounted for about 77% of the total value of Brazilian commercialized mineral production. Among these substances, eight correspond to 98.6% of the value:
/ref> In 2017, in the Southeast Region, the numbers were as follows: Minas Gerais was the country's largest producer of
/ref> In 2017, in terms of production traded throughout the Northern Region, in the In
In  In the
In the
/ref> The
The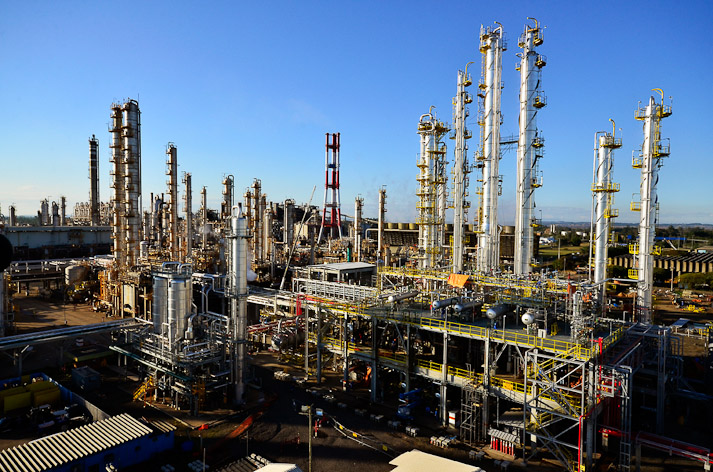  In 2011, Brazil had the 6th largest
In 2011, Brazil had the 6th largest 
 In
In  In
In  In the leather-footwear sector (
In the leather-footwear sector ( In
In  In
In
/ref> The technological center of Curitiba has companies such as In the
In the  In the
In the

 Southeast, South and Midwest are responsible for 80% of the national industrial GDP, as shown below:
Southeast, South and Midwest are responsible for 80% of the national industrial GDP, as shown below:
/ref> In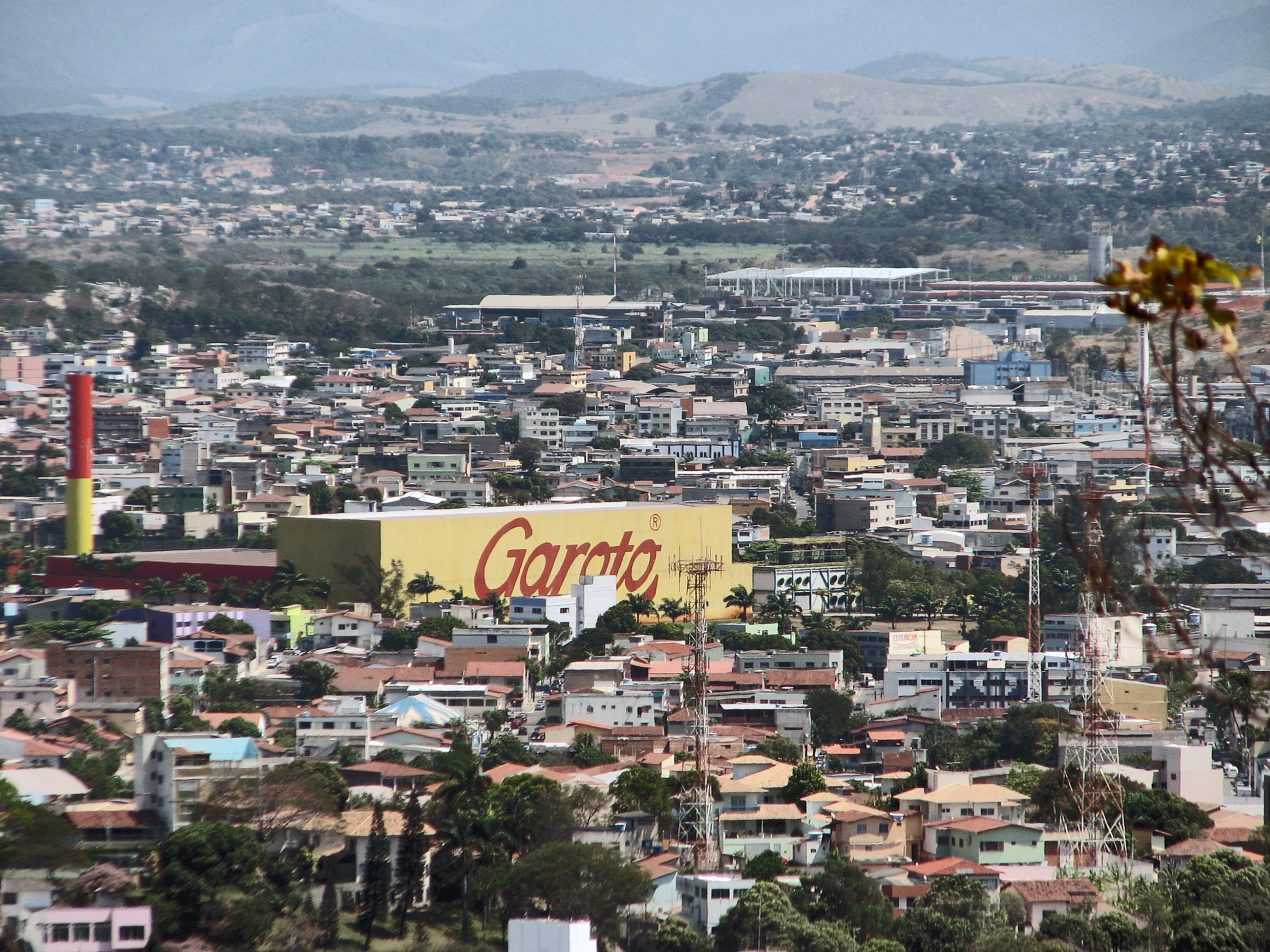
 The
The
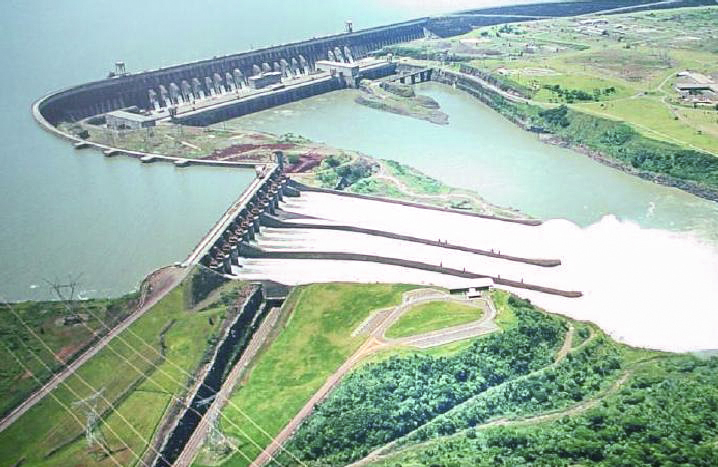



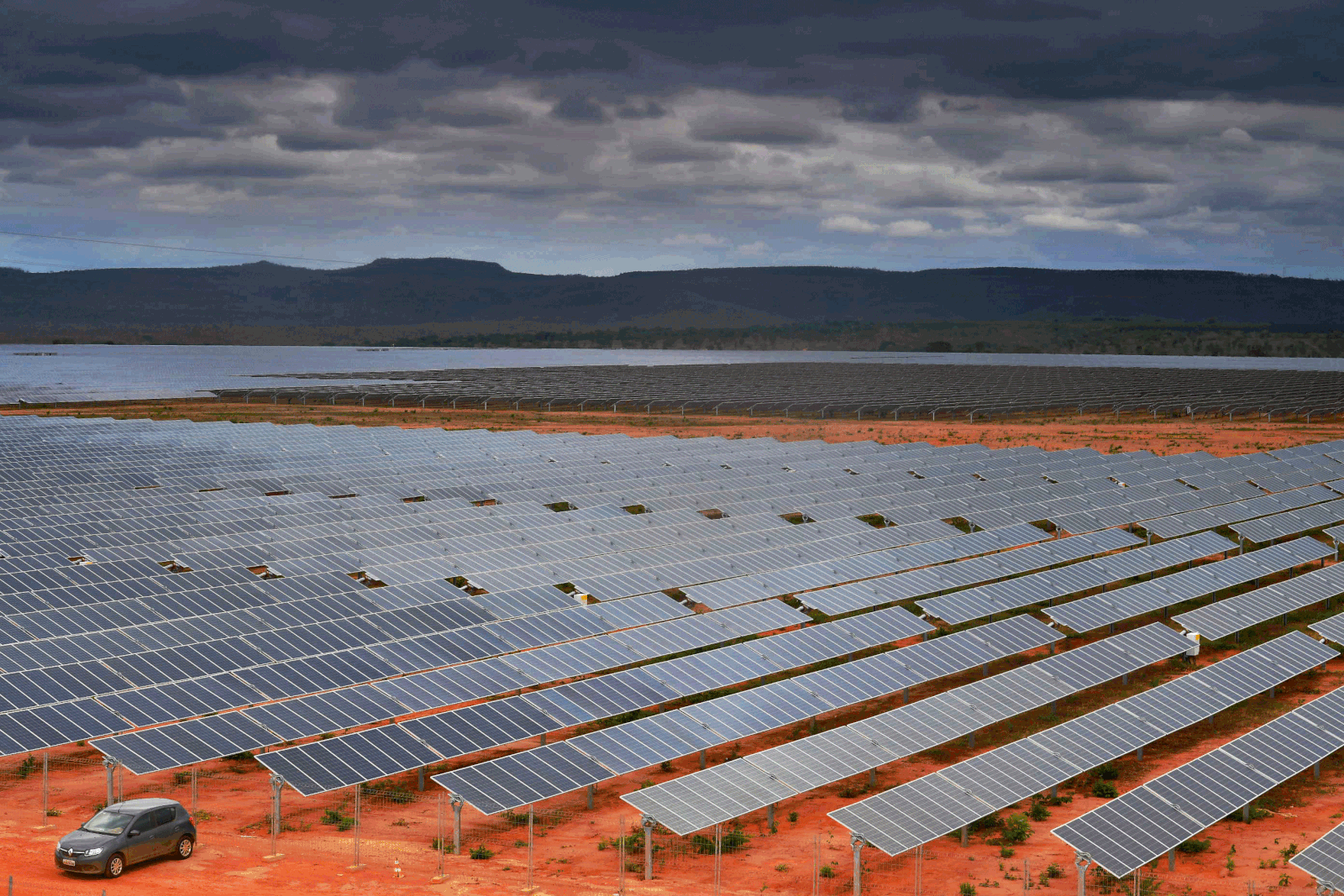 The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.Matriz Energética e Elétrica
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.Matriz Energética e Elétrica
/ref> In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix is composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%. In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of installed capacity, more than 75% from renewable sources (the majority,
/ref> Brazil is one of the 10 largest wind energy producers in the world (8th place in 2019, with 2.4% of world production). Brazil also has 3 atomic plants. In
/ref> * ''production:'' 380 TWh (2004) * ''consumption: ''391 TWh (2004) Electricity - production by source: (2004) * ''other sources:'' 9% * ''hydroelectric:'' 83% * c''onventional thermal:'' 4% * ''nuclear:'' 4% Oil: * ''production:'' 2.165 million barrel/day (2006) * ''consumption:'' 2.216 million barrel/day (2006) * ''imports:'' 0.051 million barrel/day (2006) * ''proven reserves:'' 11.2 billion barrels (2006) * ''refinery capacity:'' 1.908 million barrel/day (2006) Natural gas: * ''production:'' 9.88 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''consumption:'' 19.34 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''imports:'' 9.45 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''proven reserves:'' 326 billion cubic kilometers (2006)
 Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in
Brazilian industry has its earliest origin in workshop
Beginning with the Industrial Revolution era, a workshop may be a room, rooms or building which provides both the area and tools (or machinery) that may be required for the manufacture or repair of manufactured goods. Workshops were the only ...
s dating from the beginning of the 19th century. Most of the country's industrial establishments appeared in the Brazilian southeast (mainly in the provinces of Rio de Janeiro, Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
and, later, São Paulo), and, according to the Commerce, Agriculture, Factories and Navigation Joint, 77 establishments registered between 1808 and 1840 were classified as "factories" or "manufacturers". However, most, about 56 establishments, would be considered workshops by today's standards, directed toward the production of soap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
and tallow candles, snuff
Snuff may refer to:
Tobacco
* Snuff (tobacco), fine-ground tobacco, sniffed into the nose
** Moist snuff or dipping tobacco
** Creamy snuff, an Indian tobacco paste
Media and entertainment
* Snuff film, a type of film that shows a murder
Literat ...
, spinning
Spin or spinning most often refers to:
* Spinning (textiles), the creation of yarn or thread by twisting fibers together, traditionally by hand spinning
* Spin, the rotation of an object around a central axis
* Spin (propaganda), an intentionally b ...
and weaving
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal th ...
, food
Food is any substance consumed by an organism for nutritional support. Food is usually of plant, animal, or fungal origin, and contains essential nutrients, such as carbohydrates, fats, proteins, vitamins, or minerals. The substance is inge ...
s, melting of iron and metals, wool
Wool is the textile fibre obtained from sheep and other mammals, especially goats, rabbits, and camelids. The term may also refer to inorganic materials, such as mineral wool and glass wool, that have properties similar to animal wool.
As ...
and silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the coc ...
, amongst others. They used both slaves and free laborers.
There were twenty establishments that could be considered in fact manufacturers
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range ...
, and of this total, thirteen were created between the years 1831 and 1840. All were, however, of small size and resembled large workshops more than proper factories. Still, the manufactured goods
Manufacturing is the creation or production of goods with the help of equipment, labor, machines, tools, and chemical or biological processing or formulation. It is the essence of secondary sector of the economy. The term may refer to a range ...
were quite diverse: hat
A hat is a head covering which is worn for various reasons, including protection against weather conditions, ceremonial reasons such as university graduation, religious reasons, safety, or as a fashion accessory. Hats which incorporate mecha ...
s, comb
A comb is a tool consisting of a shaft that holds a row of teeth for pulling through the hair to clean, untangle, or style it. Combs have been used since prehistoric times, having been discovered in very refined forms from settlements dating ba ...
s, farrier
A farrier is a specialist in equine hoof care, including the trimming and balancing of horses' hooves and the placing of shoes on their hooves, if necessary. A farrier combines some blacksmith's skills (fabricating, adapting, and adjus ...
y and sawmill
A sawmill (saw mill, saw-mill) or lumber mill is a facility where logs are cut into lumber. Modern sawmills use a motorized saw to cut logs lengthwise to make long pieces, and crosswise to length depending on standard or custom sizes (dimensi ...
s, spinning and weaving, soap and candles, glass
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
es, carpet
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester hav ...
s, oil
An oil is any nonpolar chemical substance that is composed primarily of hydrocarbons and is hydrophobic (does not mix with water) & lipophilic (mixes with other oils). Oils are usually flammable and surface active. Most oils are unsaturated ...
, etc. Probably because of the instability of the regency period
The Regency era of British history officially spanned the years 1811 to 1820, though the term is commonly applied to the longer period between and 1837. King George III succumbed to mental illness in late 1810 and, by the Regency Act 1811, h ...
, only nine of these establishments were still functioning in 1841, but these nine were large
Large means of great size.
Large may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Arbitrarily large, a phrase in mathematics
* Large cardinal, a property of certain transfinite numbers
* Large category, a category with a proper class of objects and morphisms (or ...
and could be considered to "presage a new era for manufactures".
The advent of manufacturing before the 1840s was extremely limited, due to the self-sufficiency of the rural regions, where farms producing coffee and sugar cane also produced their own food, clothes, equipment, etc., the lack of capital
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
, and high costs of production
Production may refer to:
Economics and business
* Production (economics)
* Production, the act of manufacturing goods
* Production, in the outline of industrial organization, the act of making products (goods and services)
* Production as a stati ...
that made it impossible for Brazilian manufacturers to compete with foreign products. Costs were high because most raw materials were import
An import is the receiving country in an export from the sending country. Importation and exportation are the defining financial transactions of international trade.
In international trade, the importation and exportation of goods are limited ...
ed, even though some of the plants
Plants are predominantly Photosynthesis, photosynthetic eukaryotes of the Kingdom (biology), kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all curr ...
already used machine
A machine is a physical system using Power (physics), power to apply Force, forces and control Motion, movement to perform an action. The term is commonly applied to artificial devices, such as those employing engines or motors, but also to na ...
s.
From a colony whose aim was to export primary goods (sugar, gold and cotton), Brazil has managed to create a diversified industrial base in the 20th century. The steel industry is a prime example of that, with Brazil being the 9th largest producer of steel in 2018, and the 5th largest steel net exporter in 2018. Gerdau
Gerdau is the largest producer of long steel in the Americas, with steel mills in Brazil, Argentina, Canada, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Mexico, Peru, United States, Uruguay and Venezuela. Currently, Gerdau has an installed capacity of 26 mill ...
is the largest producer of long steel in the Americas, owning 337 industrial and commercial units and more than 45,000 employees across 14 countries. Brazil is also a key player in the aircraft market: Embraer
Embraer S.A. () is a Brazilian multinational aerospace manufacturer that produces commercial, military, executive and agricultural aircraft, and provides aeronautical services. It was founded in 1969 in São José dos Campos, São Paulo, where i ...
is the third largest producer of civil aircraft
Civil aviation is one of two major categories of flying, representing all non-military and non-state aviation, both private and commercial. Most of the countries in the world are members of the International Civil Aviation Organization and work ...
right after Boeing
The Boeing Company () is an American multinational corporation that designs, manufactures, and sells airplanes, rotorcraft, rockets, satellites, telecommunications equipment, and missiles worldwide. The company also provides leasing and product ...
and Airbus
Airbus SE (; ; ; ) is a European Multinational corporation, multinational aerospace corporation. Airbus designs, manufactures and sells civil and military aerospace manufacturer, aerospace products worldwide and manufactures aircraft througho ...
.
1840s–1860s
The promulgation of the Alves Brancotariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
modified this picture. This tariff succeeded in increasing state revenues and stimulating the growth of national industry. The sudden proliferation of capital was directed to investments in urban services, transports, commerce, banks, industries, etc. Most of the capital invested in industry was directed toward textiles. With unprecedented industrial growth, multiple manufacturing establishments appeared, dedicated to such diverse products as smelting of iron and metal, machinery, soap and candles, glasses, beer, vinegar, gallons of gold and silver, shoes, hats and cotton fabric.
One of the main establishments created at this period was the metallurgical factory ''Ponta da Areia'' (in English: Sand Tip), in the city of Niterói
Niterói (, ) is a Municipalities of Brazil, municipality of the state of Rio de Janeiro (state), Rio de Janeiro in the Southeast Region, Brazil, southeast region of Brazil. It lies across Guanabara Bay facing the city of Rio de Janeiro and forms ...
, that also constructed steamship
A steamship, often referred to as a steamer, is a type of steam-powered vessel, typically ocean-faring and seaworthy, that is propelled by one or more steam engines that typically move (turn) propellers or paddlewheels. The first steamships ...
s.Vainfas, p. 374 It is likely that the textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturi ...
benefited most by the virtue of being the oldest in the country. It first appeared in 1826, in the city of Recife
That it may shine on all ( Matthew 5:15)
, image_map = Brazil Pernambuco Recife location map.svg
, mapsize = 250px
, map_caption = Location in the state of Pernambuco
, pushpin_map = Brazil#South A ...
, capital of the province of Pernambuco
Pernambuco () is a state of Brazil, located in the Northeast region of the country. With an estimated population of 9.6 million people as of 2020, making it seventh-most populous state of Brazil and with around 98,148 km², being the 19 ...
. The textile sector was quite dynamic in the monarchic period and received large investments until 1890, when it entered into decline. Various modernizations occurred, principally between 1840 and 1860, when factories with a high level of technological capability were created, able to compete with other major international centers. Other improvements came with the establishment of factories and forges geared for the production of equipment and pieces for textile manufacture. And now Brazil ranks second in the world's largest producer of denim, the third – for the production of knitted fabrics, the fifth – for the manufacture of clothing and seventh – for the production of yarns and fibers. The concentration of industry that emerged in the province of Bahia considerably expanded its economic scope, reaching the south of Ceará
Ceará (, pronounced locally as or ) is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northeastern part of the country, on the Atlantic coast. It is the eighth-largest Brazilian State by population and the 17th by area. It is also one of the ...
, Piauí
Piaui (, ) is one of the states of Brazil, located in the country's Northeast Region. The state has 1.6% of the Brazilian population and produces 0.7% of the Brazilian GDP.
Piaui has the shortest coastline of any coastal Brazilian state at 66&n ...
and even Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
.
The extinction of the traffic in African slaves in 1850, contrary to what many authors allege, did not "liberate" credit for industrial development. That claim has no documentary basis whatever.Vainfas, p. 375 On the contrary, capital employed in the trade had already been directed to sectors such as enterprises of urban services, transport, banking and trade. But it is possible that there was an indirect contribution to the growth of the industrial sector through banking loans. In 1850, there were 50 factories
A factory, manufacturing plant or a production plant is an industrial facility, often a complex consisting of several buildings filled with machinery, where workers manufacture items or operate machines which process each item into another. T ...
with a capital of at least Rs 7.000:000$000.Vianna, p. 496
The imperial government created several incentives for the industrialization of the country. The earliest of these date from the reign of Dom Dom or DOM may refer to:
People and fictional characters
* Dom (given name), including fictional characters
* Dom (surname)
* Dom La Nena (born 1989), stage name of Brazilian-born cellist, singer and songwriter Dominique Pinto
* Dom people, an et ...
Pedro I, through awards of government grants. The first establishment to receive such a grant was the ''Fábrica das Chitas'' (in English: Chitas Factory), devoted to paper and printing, by a decree of 26 June 1826. The practice was resumed in the 1840s, when new industrial establishments received subsidies. in 1857, seven factories benefited from this practice of incentives, among them, the ''Ponta da Areia'' mentioned above and that was owned by Irineu Evangelista de Sousa Irineu is the Portuguese version of the name Irenaeus.
This name is borne by:
People
*Irineu Calixto Couto
*Irineu Evangelista de Sousa
*Victor Irineu de Souza
Victor Irineu de Souza (born 3 April 1989 in Belo Horizonte), or simply Victor, is ...
(later Viscount of Mauá). One of the criteria for the granting of these subsidies was the exclusive employment of free workers.
The goal, then, was not only the transition from the old colonial economic system to that of the modern capitalist, but also from slave labor to free. Other incentives arose, such as the decree of 8 August 1846 that exempted manufactured products from certain transport taxes (internally as well as externally), shielded from military recruitment a specific number of employees of industrial establishments and eliminated tariffs on parts and machinery imported for textile factories. The following year in June, a new decree stated that all industrial establishments on national soil would be free of taxes on imported raw materials. Thus, production costs of domestic industry dropped considerably, allowing it to compete with foreign products. The Alves Branco tariff underwent modification in 1857, reducing to 15% the tax on imported products.Sodré, p. 200 Later, under the Rio Branco cabinet at the beginning of the 1870s, the tariff on foreign products was newly raised to 40%, and new raw materials were exempted from import taxes.
1860s–1880s
At the end of the 1860s, came a new industrial surge caused by two armed conflicts: theAmerican Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by states th ...
and the Paraguayan War
The Paraguayan War, also known as the War of the Triple Alliance, was a South American war that lasted from 1864 to 1870. It was fought between Paraguay and the Triple Alliance of Argentina, the Empire of Brazil, and Uruguay. It was the deadlies ...
. U.S. production of cotton was interrupted by the blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are le ...
by Union forces of the Confederacy. The second resulted in the emission of currency and an increase in import tariff
A tariff is a tax imposed by the government of a country or by a supranational union on imports or exports of goods. Besides being a source of revenue for the government, import duties can also be a form of regulation of foreign trade and poli ...
s to cover the costs of war. This resulted in a great stimulus not only for the textile industry, but also for other sectors, such as chemicals, cigars, glass, paper, leather, and optical and nautical instruments.
During the 1870s, the decline of the coffee region of the Paraíba Valley
The Paraíba Valley ( pt, Vale do Paraíba) is a landform that encompasses the regions: Paraíba Valley Metropolitan Region and Northern Coast, in the state of São Paulo and Sul-Fluminense Region, in the state of Rio de Janeiro, which stands out ...
and in some areas of sugar production, caused many plantation owners to invest not only in the cotton textile industry, but also in other manufacturing sectors. Deployment of a railway network throughout the national territory also stimulated the emergence of new industrial activities, mainly in São Paulo. Industry experienced a major impetus in this period. From the 1870s onward, the great expansion of industrialization became a constant in Brazil. In 1866, there were nine textile factories with 795 workers.Graça Filho, p. 80 In 1881, there were 46 textile factories through the country: 12 in Bahia; 11 in Rio de Janeiro; nine in São Paulo; nine in Minas Gerais; and five in other provinces. The number of establishments diminished a little by 1885 to 42 textile factories with 3,172 workers. However, the drop did not impede overall growth in the sector up to 1889.
In 1880 the Industrial Association was established, with its first board elected the following year. It supported new industrial incentives and propagandized against the defenders of an essentially agricultural Brazil. 9.6% of the capital of the Brazilian economy was directed to industry by 1884, and by 1885, 11.2%. This figure dropped sharply during the republican period, falling to 5% between 1895 and 1899, and improved slightly to 6% between 1900 and 1904. Still, it took many years to return to the level that prevailed during the Empire. At the time of its downfall in 1889, monarchical Brazil had 636 factories (representing an annual rate of increase of 6.74% from 1850) with a capital of Rs 401.630:600$000 (annual growth rate of 10.94% since 1850). Of this amount, 60% were employed in the textile sector, 15% in food, 10% in the chemical
A chemical substance is a form of matter having constant chemical composition and characteristic properties. Some references add that chemical substance cannot be separated into its constituent elements by physical separation methods, i.e., wi ...
, 4% in timber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
, 3.5% in clothing
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural ...
and 3% in metallurgy
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
.
Brazilian industrial sector

 Most large industry is concentrated in the south and south east. The north east is traditionally the poorest part of Brazil, but it is beginning to attract new investment.
Brazil has the third best advanced industrial sector in
Most large industry is concentrated in the south and south east. The north east is traditionally the poorest part of Brazil, but it is beginning to attract new investment.
Brazil has the third best advanced industrial sector in The Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. Accounting for one-third of GDP, Brazil's diverse industries range from automobiles, steel and petrochemicals to computers, aircraft, and consumer durables. With the increased economic stability provided by the Plano Real, Brazilian and multinational businesses have invested heavily in new equipment and technology, a large proportion of which has been purchased from U.S. firms.
Brazil has a diverse and sophisticated services industry as well. During the early 1990s, the banking sector accounted for as much as 16% of GDP. Although undergoing a major overhaul, Brazil's financial services industry provides local businesses with a wide range of products and is attracting numerous new entrants, including U.S. financial firms. The São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
and Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
stock exchanges are undergoing a consolidation and the reinsurance sector is about to be privatized.
In 2019, Brazil's secondary (industrial) sector represented only 11% of Brazil's economic activity. In the 1990s, activity accounted for more than 15% of GDP. In 1970, the participation was 21.4%. The Brazilian industry is one of those that showed the most decline in the world in almost 50 years. The deindustrialization of the Brazilian economy is very particular and happened very early, as it is normal for the industry to lose space when the per capita income of families starts to grow, since they consume more services and less goods, however, in Brazil, they do not a high per capita income was reached and the country did not get rich enough for the productive structure to migrate so quickly. With that, the country is stuck. The stagnation of the sector partly explains the slow resumption of the labor market in the country. The solution to the problem, according to experts, would be more financing mechanisms, solving bottlenecks in the national infrastructure and in the tax system to leverage the industry again and make Brazil more competitive. Brazil is the ninth industrial park in the world.
In 2017, the Southeast was responsible for 58% of the value of industrial transformation in Brazil, followed by the South (19.6%), Northeast (9.9%), North (6.9%) and Midwest (5.6%).
In Brazil, the automotive sector represents close to 22% of industrial GDP. The ABC Region in São Paulo is the first center and largest automobile hub in Brazil. When the country's manufacturing was practically restricted to ABC, the State accounted for 74.8% of Brazilian production in 1990. In 2017, this index decreased to 46.6%, and in 2019, to 40.1%, due to a phenomenon of internalization of the production of vehicles in Brazil, driven by factors such as unions, which made the payroll and labor charges excessive, discouraged investments and favored the search for new cities. The development of ABC cities has also helped to curb attractiveness, due to rising real estate costs, and a greater density of residential areas. The area around Porto Real
Porto Real () is a municipality located in the Brazilian state of Rio de Janeiro. Its population was 19,974 (2020) and its area is 50.9 km2.IBGE
The Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics ( pt, Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia ...
, in Rio de Janeiro was already the second largest pole in 2017, but in 2019 it fell to 4th place, behind Paraná (15%) and Minas Gerais (10.7%). In the Southeast, São Paulo has plants from GM, Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German Automotive industry, motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a ...
, Ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
, Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a product ...
, Toyota
is a Japanese multinational automotive manufacturer headquartered in Toyota City, Aichi, Japan. It was founded by Kiichiro Toyoda and incorporated on . Toyota is one of the largest automobile manufacturers in the world, producing about 10 ...
, Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate ("chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai ...
, Mercedes-Benz
Mercedes-Benz (), commonly referred to as Mercedes and sometimes as Benz, is a German luxury and commercial vehicle automotive brand established in 1926. Mercedes-Benz AG (a Mercedes-Benz Group subsidiary established in 2019) is headquartere ...
, Scania
Scania, also known by its native name of Skåne (, ), is the southernmost of the historical provinces of Sweden, provinces (''landskap'') of Sweden. Located in the south tip of the geographical region of Götaland, the province is roughly conte ...
and Caoa. Rio de Janeiro has Nissan
, trade name, trading as Nissan Motor Corporation and often shortened to Nissan, is a Japanese multinational corporation, multinational Automotive industry, automobile manufacturer headquartered in Nishi-ku, Yokohama, Japan. The company sells ...
, Land Rover
Land Rover is a British brand of predominantly four-wheel drive, off-road capable vehicles, owned by multinational car manufacturer Jaguar Land Rover (JLR), since 2008 a subsidiary of India's Tata Motors. JLR currently builds Land Rovers ...
, Citroen/Peugeot and MAN
A man is an adult male human. Prior to adulthood, a male human is referred to as a boy (a male child or adolescent). Like most other male mammals, a man's genome usually inherits an X chromosome from the mother and a Y chromos ...
plants. Minas Gerais has Fiat
Fiat Automobiles S.p.A. (, , ; originally FIAT, it, Fabbrica Italiana Automobili di Torino, lit=Italian Automobiles Factory of Turin) is an Italian automobile manufacturer, formerly part of Fiat Chrysler Automobiles, and since 2021 a subsidiary ...
and Iveco
IVECO, an acronym for Industrial Vehicles Corporation, is an Italian multinational transport vehicle manufacturing company. It designs and builds light, medium, and heavy commercial vehicles. The name IVECO first appeared in 1975 after a merger o ...
factories. In the South, Paraná has Volkswagen
Volkswagen (),English: , . abbreviated as VW (), is a German Automotive industry, motor vehicle manufacturer headquartered in Wolfsburg, Lower Saxony, Germany. Founded in 1937 by the German Labour Front under the Nazi Party and revived into a ...
, Renault
Groupe Renault ( , , , also known as the Renault Group in English; legally Renault S.A.) is a French multinational automobile manufacturer established in 1899. The company produces a range of cars and vans, and in the past has manufactured ...
, Audi
Audi AG () is a German automotive manufacturer of luxury vehicles headquartered in Ingolstadt, Bavaria, Germany. As a subsidiary of its parent company, the Volkswagen Group, Audi produces vehicles in nine production facilities worldwide.
Th ...
, Volvo
The Volvo Group ( sv, Volvokoncernen; legally Aktiebolaget Volvo, shortened to AB Volvo, stylized as VOLVO) is a Swedish multinational manufacturing corporation headquartered in Gothenburg. While its core activity is the production, distributio ...
and DAF factories; Santa Catarina has GM and BMW plants and Rio Grande do Sul, a GM plant. In the Midwest, Goiás has Mitsubishi
The is a group of autonomous Japanese multinational companies in a variety of industries.
Founded by Yatarō Iwasaki in 1870, the Mitsubishi Group historically descended from the Mitsubishi zaibatsu, a unified company which existed from 1870 ...
, Suzuki
is a Japan, Japanese multinational corporation headquartered in Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Japan. Suzuki manufactures automobiles, motorcycles, All-terrain vehicle, all-terrain vehicles (ATVs), outboard motor, outboard marine engines, wheelchairs ...
and Hyundai Hyundai is a South Korean industrial conglomerate ("chaebol"), which was restructured into the following groups:
* Hyundai Group, parts of the former conglomerate which have not been divested
** Hyundai Mobis, Korean car parts company
** Hyundai ...
factories. In the Northeast, Bahia has a Ford
Ford commonly refers to:
* Ford Motor Company, an automobile manufacturer founded by Henry Ford
* Ford (crossing), a shallow crossing on a river
Ford may also refer to:
Ford Motor Company
* Henry Ford, founder of the Ford Motor Company
* Ford F ...
factory and Pernambuco has a Jeep
Jeep is an American automobile marque, now owned by multi-national corporation Stellantis. Jeep has been part of Chrysler since 1987, when Chrysler acquired the Jeep brand, along with remaining assets, from its previous owner American Moto ...
factory.O novo mapa das montadoras/ref> Despite being, in 2018, the eighth largest vehicle producer in the world, Brazil didn't even have a national industry. The last Brazilian industry was
Gurgel
Gurgel Motores () was a Brazilian automobile manufacturer, named after its founder João do Amaral Gurgel. The company was founded in 1969 and first specialised in buggies and off-road vehicles. Early models were fiberglass bodies installed on V ...
.
In 2017, the main manufacturers of tractors in Brazil were John Deere
Deere & Company, doing business as John Deere (), is an American corporation that manufactures agricultural machinery, heavy equipment, forestry machinery, diesel engines, drivetrains (axles, transmissions, gearboxes) used in heavy equipment, ...
, New Holland, Massey Ferguson
Massey Ferguson Limited is an American agricultural machinery manufacturer. The company was established in 1953 through the merger of farm equipment makers Massey-Harris of Canada and the Ferguson Company of the United Kingdom. It was based in T ...
, Valtra
Valtra is an agricultural machinery manufacturer based in Äänekoski, Finland. Valtra's products include tractors, combine harvesters, sugar cane harvesters, self-propelled sprayers and seed drills. Valtra has been part of the American AGCO Cor ...
, Case IH
Case IH is an American agricultural machinery manufacturer. It was created in 1985 when Tenneco bought selected assets of the agricultural division from International Harvester and merged it into its J.I. Case Company (IH then became Navistar).To ...
and the Brazilian Agrale
Agrale, previously called AGRISA, is a Brazilian vehicle manufacturer. Established in 1962, it is based in Caxias do Sul in the state of Rio Grande do Sul. Agrale manufactures tractors, commercial vehicles, military vehicles, bus, chassis ...
. All have factories in the Southeast, basically in São Paulo.
The mineral extractive industry represents 15% of the GDP of Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
. In the state, this sector corresponds almost entirely to the exploration and production of oil and gas
A fossil fuel is a hydrocarbon-containing material formed naturally in the Earth's crust from the remains of dead plants and animals that is extracted and burned as a fuel. The main fossil fuels are coal, oil, and natural gas. Fossil fuels ...
, which reflects its importance for the economy of Rio de Janeiro. The transformation industry represents 6% of the State's GDP. In 2019, Rio de Janeiro was the largest producer of oil and natural gas in Brazil, with 71% of the total volume produced. São Paulo comes in 2nd place, with an 11.5% share of total production. Espírito Santo was the third largest producer state, with 9.4%.

aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
, niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
and gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
. Highlight for the significant participation of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
in this amount, whose production is mainly concentrated in the states of Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
and Pará
Pará is a Federative units of Brazil, state of Brazil, located in northern Brazil and traversed by the lower Amazon River. It borders the Brazilian states of Amapá, Maranhão, Tocantins (state), Tocantins, Mato Grosso, Amazonas (Brazilian state) ...
. According to the National Department of Mineral Production (DNPM), in 2011 there were 8,870 mining companies in the country, and in the Southeast region, this number reached 3,609, about 40% of the total. In the Southeast region, iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
and bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
, in the Quadrilátero Ferrífero; niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
and phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phospho ...
in Araxá
Araxá () is a municipality in Western Minas Gerais state, Brazil. Its estimated population by IBGE (Brazilian Institute of Geography and Statistics) in 2020 is 107,337 inhabitants and the area of the municipality is , with making up the urban p ...
; gemstones
A gemstone (also called a fine gem, jewel, precious stone, or semiprecious stone) is a piece of mineral crystal which, in cut and polished form, is used to make jewelry or other adornments. However, certain rocks (such as lapis lazuli, opal, an ...
, in Governador Valadares
Governador Valadares is a Brazilian municipality in the countryside of Minas Gerais. In 2020, its population was 281,046 inhabitants, thus being the ninth most populated city in the state. It is an economical axis of the middle valley of the Doce R ...
; and graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on large ...
, in Salto da Divisa
Salto da Divisa is a municipality in the northeast of the Brazilian state of Minas Gerais. Its population in 2020 was 7,012 inhabitants in a total area of 943.647 km2. It is the easternmost municipality of Minas Gerais
Salto da Divisa belong ...
, all in the state of Minas Gerais; in addition to aggregates, in São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro, and ornamental rocks, in Espírito Santo. The income of the mining sector in Brazil was R$153.4 billion in 2019. Exports were U$32.5 billion. The country's iron ore production was 410 million tons in 2019. Brazil is the second largest global iron ore exporter and has the second position in the reserve ranking: under Brazilian soil there are at least 29 billion tons. The largest reserves are currently in the states of Minas Gerais and Pará. According to data from 2013, Minas Gerais is the largest Brazilian mining state. With mining activity in more than 250 municipalities, and more than 300 mines in operation, the state has 40 of the 100 largest mines in Brazil. In addition, of the 10 largest mining municipalities, seven are in Minas, with Itabira
Itabira is a Brazilian municipality and a major city in the state of Minas Gerais. The city belongs to the Belo Horizonte metropolitan area mesoregion and to the Itabira microregion.
It is currently the twenty-fourth largest city in the state in ...
being the largest in the country. It is also responsible for approximately 53% of the Brazilian production of metallic minerals and 29% of the total minerals, in addition to extracting over 160 million tons/year of iron ore. Vale S.A. is the main company active in the production of iron ore in the state. The state is the largest employer in the mineral activity (53,791 workers in 2011). São Paulo, the second largest employer, had 19 thousand employees in the sector this year.O peso da mineração na Região Sudeste/ref> In 2017, in the Southeast Region, the numbers were as follows: Minas Gerais was the country's largest producer of
iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
(277 million tons at a value of R$37.2 billion), gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
(29.3 tons at a value of R$3.6 billion), zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
(400 thousand tons at a value of R$351 million) and niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
(in the form of pyrochlorine) (131 thousand tons at a value of R$254 million). In addition, Minas was the 2nd largest producer of aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
(bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
) (1.47 million tons at a value of R$105 million), 3rd of manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
(296 thousand tons at a value of R$32 million) and 5º of tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
(206 tons at a value of R$4.7 million). Minas Gerais had 47.19% of the value of mineral production traded in Brazil, with R$41.7 billion.Anuário Mineral Brasileiro 2018/ref> In 2017, in terms of production traded throughout the Northern Region, in the
iron ore
Iron ores are rocks and minerals from which metallic iron can be economically extracted. The ores are usually rich in iron oxides and vary in color from dark grey, bright yellow, or deep purple to rusty red. The iron is usually found in the fo ...
sector, Pará was the 2nd largest national producer, with 169 million tons (of the 450 million produced by the country), at a value of R$25.5 billion. Amapá produced 91.5 thousand tons. In copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, Pará produced almost 980 thousand tons (of the 1.28 million tons in Brazil), at a value of R$6.5 billion. In aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
(bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
), Pará carried out almost all Brazilian production (34.5 of 36.7 million tons) at a value of R$3 billion. In manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
, Pará produced a large part of Brazilian production (2.3 of 3.4 million tons) at a value of R$1 billion. In gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, Pará was the 3rd largest Brazilian producer, with 20 tons at a value of R$940 million. Amapá produced 4.2 tons at a value of R$540 million. Rondônia produced 1 ton at a value of R$125 million. In nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
, Goiás and Pará are the only two producers in the country, with Pará being the 2nd in production, having obtained 90 thousand tons at a value of R$750 million. In tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
, the state of Amazonas was the largest producer (14.8 thousand tons, at a value of R$347 million), Rondônia
Rondônia () is one of the 26 states of Brazil, located in the northern subdivision of the country (central-western part). To the west is a short border with the state of Acre, to the north is the state of Amazonas, in the east is Mato Grosso, ...
was the 2nd largest producer (10,9 thousand tons, at a value of R$333 million) and Pará the 3rd largest producer (4.4 thousand tons, at a value of R$114 million). There was also production of niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
(in the form of columbita-tantalita) in Amazonas (8.8 thousand tons at R$44 million) and Rondônia (3.5 thousand tons at R$24 million), and zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
in gross form in Rondônia (26 thousand tons at R$27 million). Pará had 42.93% of the value of commercialized mineral production in Brazil, with almost R$38 billion, Amapá had 0.62% of the value, with R$551 million, Rondônia had 0.62% of the value, with R$544 million, Amazonas had 0.45% of the amount with R$396 million, and Tocantins had 0.003% of the amount with R$2.4 million. In the Midwest Region, Goiás
Goiás () is a Brazilian state located in the Center-West region. Goiás borders the Federal District and the states of (from north clockwise) Tocantins, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso. The state capital is Goiânia. ...
stands out, with 4.58% of the national mineral participation (3rd place in the country). In 2017, at nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow to ...
, Goiás and Pará are the only two producers in the country, Goiás being the 1st in production, having obtained 154 thousand tons at a value of R$1.4 billion. In copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, it was the 2nd largest producer in the country, with 242 thousand tons, at a value of R$1.4 billion. In gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, it was the 4th largest producer in the country, with 10.2 tons, at a value of R$823 million. In niobium
Niobium is a chemical element with chemical symbol Nb (formerly columbium, Cb) and atomic number 41. It is a light grey, crystalline, and ductile transition metal. Pure niobium has a Mohs hardness rating similar to pure titanium, and it has sim ...
(in the form of pyrochlorine), it was the 2nd largest producer in the country, with 27 thousand tons, at a value of R$312 million. In aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It has ...
(bauxite
Bauxite is a sedimentary rock with a relatively high aluminium content. It is the world's main source of aluminium and gallium. Bauxite consists mostly of the aluminium minerals gibbsite (Al(OH)3), boehmite (γ-AlO(OH)) and diaspore (α-AlO(O ...
), it was the 3rd largest producer in the country, with 766 thousand tons, at a value of R$51 million. Still in 2017, in the Midwest, Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – lit. "Thick Bush") is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.
Neighboring ...
had 1.15% of the national mineral participation (5th place in the country) and Mato Grosso do Sul
Mato Grosso do Sul () is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are (from north clockwise) Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and ...
had 0.71% of the national mineral participation (6th place in the country). Mato Grosso had production of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
(8.3 tons at a value of R$1 billion) and tin
Tin is a chemical element with the symbol Sn (from la, stannum) and atomic number 50. Tin is a silvery-coloured metal.
Tin is soft enough to be cut with little force and a bar of tin can be bent by hand with little effort. When bent, t ...
(536 tons at a value of R$16 million). Mato Grosso do Sul had production of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in f ...
(3.1 million tons at a value of R$324 million) and manganese
Manganese is a chemical element with the symbol Mn and atomic number 25. It is a hard, brittle, silvery metal, often found in minerals in combination with iron. Manganese is a transition metal with a multifaceted array of industrial alloy use ...
(648 thousand tons at a value of R$299 million). In Northeast Region, Bahia
Bahia ( , , ; meaning "bay") is one of the 26 Federative units of Brazil, states of Brazil, located in the Northeast Region, Brazil, Northeast Region of the country. It is the fourth-largest Brazilian state by population (after São Paulo (sta ...
stands out, with 1.68% of the national mineral participation (4th place in the country). In 2017, at gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile met ...
, it produced 6.2 tons, at a value of R$730 million. At copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, it produced 56 thousand tons, at a value of R$404 million. At chrome, it produced 520 thousand tons, at a value of R$254 million. In vanadium
Vanadium is a chemical element with the symbol V and atomic number 23. It is a hard, silvery-grey, malleable transition metal. The elemental metal is rarely found in nature, but once isolated artificially, the formation of an oxide layer ( pas ...
, it produced 358 thousand tons, at a value of R$91 million.
 In
In steel industry
Steel is an alloy made up of iron with added carbon to improve its strength and fracture resistance compared to other forms of iron. Many other elements may be present or added. Stainless steels that are corrosion- and oxidation-resistant ty ...
, Brazilian crude steel production was 32.2 million tons in 2019. Minas Gerais accounted for 32.3% of the volume produced in the period, with 10.408 million tons. The other largest steel centers in Brazil in 2019 were: Rio de Janeiro (8.531 million tons), Espírito Santo (6.478 million tons) and São Paulo (2.272 million tons). National production of rolled products was 22.2 million tons, and that of semi-finished products for sales totaled 8.8 million tons. Exports reached 12.8 million tons, or US $7.3 billion. Among the largest steel companies in the Southeast are Gerdau
Gerdau is the largest producer of long steel in the Americas, with steel mills in Brazil, Argentina, Canada, Colombia, Dominican Republic, Mexico, Peru, United States, Uruguay and Venezuela. Currently, Gerdau has an installed capacity of 26 mill ...
, CSN ''CSN'' may refer to:
Companies
* CSN Stores, former name of Wayfair, American e-commerce company
* CSN International (Christian Satellite Network), religious radio broadcaster based on radio station KAWZ in Twin Falls, Idaho
* ''Centrala Studies ...
, Ternium Brasil, Usiminas
Usiminas is one of the largest producers of steel in the Americas, with major steel mills in Brazil with a total capacity of 9.5 million metric tons of steel per year. The company accounts for 28% of total steel output in Brazil.
Usiminas has an ...
and Aperam South America
Aperam South America, old Acesita and ArcelorMittal Timóteo, is the biggest Brazilian manufacturer of specialty steels. Headquartered in Belo Horizonte, Minas Gerais, the company is a supplier of stainless, silicon and special carbon steels. Ap ...
.
 In the
In the paper
Paper is a thin sheet material produced by mechanically or chemically processing cellulose fibres derived from wood, rags, grasses or other vegetable sources in water, draining the water through fine mesh leaving the fibre evenly distributed ...
and cellulose
Cellulose is an organic compound with the formula , a polysaccharide consisting of a linear chain of several hundred to many thousands of β(1→4) linked D-glucose units. Cellulose is an important structural component of the primary cell wall ...
sector, Brazilian pulp production was 19.691 million tons in 2019. The country exported US $7.48 billion in pulp this year, US $3.25 billion only to China. Brazilian forest-based industry exports totaled US $9.7 billion (US $7.48 billion in cellulose, US $2 billion in paper and US $265 million in wood panels). Paper production was 10.535 million tons in 2019. The country exported 2.163 million tons. In 2016, the paper and cellulose industry in the South of the country represented 33% of the national total. This year, Paraná was the national leader in the production of roundwood (mainly eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as euca ...
) for the pulp and paper industry (15.9 million m³); Brazil was the second country that produced the most cellulose in the world and the eighth in the production of paper. The city that most produced these woods in Brazil was Telêmaco Borba
Telêmaco Borba is a municipality in the state of Paraná in the Southern Region of Brazil.
Telêmaco Borba is known as the "capital of paper" (Capital do Papel) and "capital of wood" (Capital da Madeira) due to the importance of paper and wood ...
(PR), and the 5th largest was Ortigueira
Ortigueira is a seaport and municipality in the province of A Coruña (province), A Coruña the autonomous community of Galicia, Spain, Galicia in northwestern Spain. It belongs to the Comarcas of Galicia, comarca of Ortegal. It is located on th ...
(PR).São Mateus é o 6º maior produtor de madeira em tora para papel e celulose no país, diz IBGE/ref>
Espírito Santo
Espírito Santo (, , ; ) is a state in southeastern Brazil. Its capital is Vitória, and its largest city is Serra. With an extensive coastline, the state hosts some of the country's main ports, and its beaches are significant tourist attra ...
stands out in this sector. In 2018, U $920 million were traded in the sale of cellulose to the foreign market, the third strongest Espírito Santo product in the export balance. In 2016, the top five states producing logs for paper and cellulose (mainly eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as euca ...
) were: Paraná (15.9 million m³), São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
(14.7 million m³), Bahia (13.6 million m³), Mato Grosso do Sul (9.9 million m³) and Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
(7.8 million m³). Together, they correspond to 72.7% of the national production of 85.1 million m³. Espírito Santo, 9th place, had a production of 4.1 million m³. São Mateus, in the North of Espírito Santo, was the best placed city in the Southeast, as the 6th largest producer of roundwood for paper and cellulose in the country. The ten largest producing municipalities had 22.9% of the country's production. They were the cities of Telêmaco Borba (PR), Três Lagoas (MS), Caravelas (BA), Mucuri (BA), Ortigueira (PR), São Mateus (ES), Dom Eliseu (PR), Nova Viçosa (BA), Water Clara (MS) and Ribas do Rio Pardo (MS).
 The
The shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to befor ...
sector of Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
is one of the most important in the country, but it has already had two major historical crises: one in the 1980s, when it went bankrupt, and another that started in 2014, both due to the country's economic situation: between 2014 and 2016, the Brazilian shipbuilding industry lost 49% of its employed people. The drop of about 30 thousand vacancies was concentrated in the state of Rio de Janeiro, which closed around 23 thousand jobs in the same period. From 31.2 thousand employed in 2014, the number dropped to just 8 thousand in 2016. The gross real value of industrial production also fell 71%, from R $6.8 billion in 2014, to R $1.97 billion in 2016. However, at the end of 2019, the return of the pre-salt began to re-boost the naval sector: maintenance and repair activities pointed to increased demand for the coming years.
 In 2011, Brazil had the 6th largest
In 2011, Brazil had the 6th largest chemical industry
The chemical industry comprises the companies that produce industrial chemicals. Central to the modern world economy, it converts raw materials (oil, natural gas, air, water, metals, and minerals) into more than 70,000 different products. The ...
in the world, with net sales of US $157 billion, or 3.1% of world sales. At that time, there were 973 factories for chemical products for industrial use. They are concentrated in the Southeast Region, mainly in São Paulo. The chemical industry contributed 2.7% to Brazilian GDP in 2012 and established itself as the fourth largest sector in the manufacturing industry. Despite registering one of the largest sales in the sector in the world, the Brazilian chemical industry, in 2012 and 2013, saw a strong transfer of production abroad, with a drop in national industrial production and an increase in imports. One third of consumption in the country was served by imports. 448 products stopped being manufactured in Brazil between 1990 and 2012. This resulted in the stoppage of 1,710 production lines. In 1990, the share of imported products in Brazilian consumption was only 7%, in 2012 it was 30%. The main companies in the sector in Brazil are: Braskem
Braskem is a Brazilian petrochemical company headquartered in São Paulo. The company is the largest petrochemical company in Latin America and has become a major player in the international petrochemical market (8th largest resin producer worldw ...
, BASF
BASF Societas Europaea, SE () is a German multinational corporation, multinational chemical company and the List of largest chemical producers, largest chemical producer in the world. Its headquarters is located in Ludwigshafen, Germany.
The ...
, Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of busi ...
, among others. In 2018, the Brazilian chemical sector was the eighth largest in the world, accounting for 10% of the national industrial GDP and 2.5% of the total GDP. In 2020, imports will occupy 43% of the domestic demand for chemicals. Since 2008, the average use of capacity in the Brazilian chemical industry has been at a level considered low, ranging between 70 and 83%.

 In
In Food industry
The food industry is a complex, global network of diverse businesses that supplies most of the food consumed by the world's population. The food industry today has become highly diversified, with manufacturing ranging from small, traditiona ...
, In 2019, Brazil was the 2nd largest exporter of processed foods in the world, with a value of U $34.1 billion in exports. The Brazilian food and beverage industry's revenue in 2019 was R $699.9 billion, 9.7% of the country's Gross Domestic Product. In 2015, the industrial food and beverage sector in Brazil comprised 34,800 companies (not counting bakeries), the vast majority of which were small. These companies employed more than 1,600,000 workers, making the food and beverage industry the largest employer in the manufacturing industry. There are around 570 large companies in Brazil, which concentrate a good part of the total industry revenue. The top 50 were: JBS, Ambev, Bunge, BRF, Cargill
Cargill, Incorporated, is a privately held American global food corporation based in Minnetonka, Minnesota, and incorporated in Wilmington, Delaware. Founded in 1865, it is the largest privately held corporation in the United States in ter ...
, Marfrig
Marfrig is the second largest Brazilian food processing company, after JBS. The company is headquartered in São Paulo. The company has an operational base in 22 countries, exporting to over 100, and is the second-largest beef producer in the wor ...
, LDC do Brasil, Amaggi, Minerva Foods, Coca Cola Femsa, Aurora
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
, Vigor
Vigor or vigour may refer to:
Companies
* Vigor S.A., a Brazilian food company
* Vigor Industrial, an American shipbuilding, ship repair, and industrial service provider in the Pacific Northwest and Alaska
** Vigor Shipyards, four shipyards in Was ...
, M.Dias Branco, Camil Alimentos, Solar.Br, Granol, Caramuru Alimentos, Bianchini, Copacol
Copacol is a Brazilian meat and food processor with its headquarters in Cafelândia, Paraná.
External linksofficial site
Meat companies of Brazil
Companies based in Paraná (state)
Cooperatives in Brazil
{{Brazil-company-stub ...
, Citrosuco, Três Corações Alimentos S.A., Itambé, Ajinomoto
is a Japanese multinational food and biotechnology corporation which produces seasonings, interlayer insulating materials for semiconductor packages for use in personal computers, cooking oils, frozen foods, beverages, sweeteners, amino acids, an ...
, Algar Agro, Piracanjuba
Piracanjuba () is a municipality in southeastern Goiás state, Brazil. It is a big producer of orchids, milk products, and soybeans. ''Piracanjuba is also the name of a fish (Brycon orbignyanus) common to the waters of the Plata River basin.''
...
, Vonpar, Agrex, Frimesa, GTFoods Group, Grupo Simões, Elebat Alimentos, Garoto
Chocolates Garoto S.A. is a Brazilian chocolate manufacturer. Its headquarters are located in Vila Velha, Espírito Santo. The company was founded in 1929 by German immigrant Heinrich Meyerfreund and acquired by Nestlé in 2002.
History
Early ...
, Pif Paf Alimentos, J. Macêdo, Frigol, Josapar, Olfar Alimento e Energia, Embaré, Alibem, Dalia Alimentos, Asa Participações, Cacique
A ''cacique'' (Latin American ; ; feminine form: ''cacica'') was a tribal chieftain of the Taíno people, the indigenous inhabitants at European contact of the Bahamas, the Greater Antilles, and the northern Lesser Antilles. The term is a Spa ...
, Frisa, Arroz Brejeiro, Gomes da Costa
Manuel de Oliveira Gomes da Costa , commonly known as Manuel Gomes da Costa () or just Gomes da Costa (14 January 1863 – 17 December 1929), was a Portuguese army officer and politician, the tenth president of Portugal and the second of ...
, Pamplona
Pamplona (; eu, Iruña or ), historically also known as Pampeluna in English, is the capital city of the Chartered Community of Navarre, in Spain. It is also the third-largest city in the greater Basque cultural region.
Lying at near above ...
, Moinhos Cruzeiro do Sul, Better Beef, SSA Alimentos and Correcta.
 In
In Pharmaceutical industry
The pharmaceutical industry discovers, develops, produces, and markets drugs or pharmaceutical drugs for use as medications to be administered to patients (or self-administered), with the aim to cure them, vaccinate them, or alleviate symptoms. ...
, most companies in Brazil have been based in Rio de Janeiro and São Paulo for a long time. In 2019, the situation was that, due to the tax advantages offered in states like Pernambuco, Goiás and Minas Gerais, companies were leaving RJ and SP, and going to these states. At the time, the more than 110 companies associated with Sinfar-RJ fell to just 49. Rio de Janeiro, at this time, represented the most expensive state for pharmaceutical production, with its ICMS at 20%. Even in 2019, the Rio de Janeiro industrial park had revenues of almost R $8 billion and an 11% share in the Brazilian pharmaceutical market. In the Jacarepaguá
Jacarepaguá (), with a land area of , is a neighborhood situated in the West Zone of Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. In 2010, it had a population of 157,326. The name comes from the indigenous name of the location, "shallow pond of caymans", yakaré (c ...
neighborhood, there are several pharmaceutical industries, such as GSK, Roche
F. Hoffmann-La Roche AG, commonly known as Roche, is a Swiss multinational healthcare company that operates worldwide under two divisions: Pharmaceuticals and Diagnostics. Its holding company, Roche Holding AG, has shares listed on the SIX S ...
, Merck
Merck refers primarily to the German Merck family and three companies founded by the family, including:
* the Merck Group, a German chemical, pharmaceutical and life sciences company founded in 1668
** Merck Serono (known as EMD Serono in the Unite ...
, Servier
Servier Laboratories (French: Laboratoires Servier, often abbreviated to Servier) is an international pharmaceutical company governed by a non-profit foundation, with its headquarters in France (Suresnes).
The consolidated turnover for the 2018 ...
and Abbott. In 2017, Brazil was considered the sixth largest pharmaceutical market in the world. Drug sales in pharmacies reached around R $57 billion (US $17.79 billion) in the country. The pharmaceutical market in Brazil had 241 laboratories regularized and authorized for the sale of medicines. Of these, the majority (60%) have national capital. Multinational companies held about 52.44% of the market, with 34.75% in marketed packaging. Brazilian laboratories represent 47.56% of the market in sales and 65.25% in boxes sold. In the distribution of drug sales by state, São Paulo occupied the first position: the São Paulo drug industry had a turnover of R $53.3 billion, 76.8% of total sales across the country. Just behind came Rio de Janeiro, which had revenues of approximately R $7.8 billion. The pharmaceutical industry's exports reached US $1.247 billion in 2017. The companies that most profited from the sale of medicines in the country in 2015 were EMS, Hypermarcas
Hypera Pharma (formerly known as Hypermarcas) is a Brazilian multinational pharmaceutical
company headquartered in São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for ' Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the stat ...
(NeoQuímica), Sanofi
Sanofi S.A. is a French multinational pharmaceutical and healthcare company headquartered in Paris, France. Originally, the corporation was established in 1973 and merged with Synthélabo in 1999 to form Sanofi-Synthélabo. In 2004, Sanofi-Syn ...
(Medley), Novartis
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
, Aché
The Aché ( ) are an indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous people of Paraguay. They are hunter-gatherers living in eastern Paraguay.
From the earliest Jesuit accounts of the Aché in the 17th century until their peaceful outside contac ...
, Eurofarma, Takeda
is a Japanese family name.1990 Census Name Files< ...
, Bayer
Bayer AG (, commonly pronounced ; ) is a German multinational corporation, multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company and one of the largest pharmaceutical companies in the world. Headquartered in Leverkusen, Bayer's areas of busi ...
, Pfizer
Pfizer Inc. ( ) is an American multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology corporation headquartered on 42nd Street in Manhattan, New York City. The company was established in 1849 in New York by two German entrepreneurs, Charles Pfizer ...
and GSK.
Footwear industry
Footwear refers to garments worn on the feet, which typically serves the purpose of protection against adversities of the environment such as wear from ground textures and temperature. Footwear in the manner of shoes therefore primarily serves th ...
), in 2019 Brazil produced 972 million pairs. Exports were around 10%, reaching almost 125 million pairs. Brazil is in the 4th position among the world producers, behind China (who produces more than 10 billion pairs), India and Vietnam, and in 11th place among the biggest exporters. Of the pairs produced, 49% were made of plastic or rubber, 28.8% were made of synthetic laminate and only 17.7% were made of leather. The largest pole in Brazil is located in Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, , ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative_units_of_Brazil#List, fifth-most-populous state and the List of Brazilian st ...
(region of Vale dos Sinos, in 25 cities around Novo Hamburgo
Novo Hamburgo (Portuguese for ''New Hamburg''; german: Neu-Hamburg) is a municipality in the southernmost Brazilian state of Rio Grande do Sul, located in the metropolitan area of Porto Alegre, the state capital. As of 2020, its population was 247, ...
). The Brazilian state that most exports the product is Rio Grande do Sul: in 2019 it exported US $448.35 million. The majority of the product goes to United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territorie ...
, Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
and France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. Domestic consumption absorbs a large part of production. The state has or created some of the most important factories in Brazil in the sector. São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
has important footwear hubs, such as that of the city of Franca
Franca is a municipality in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The city is located in the northeastern portion of the state, distant 401 km (249 mi) from the state capital (São Paulo), and 676 km (420 mi) from Brasilia. It covers a total area of ...
, specialized in men's shoes, in the city of Jaú
Jaú is a municipality in the center of the state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo, in Brazil. The population is 151,881 (2020 est.) in an area of . The elevation is . The city takes its name from the native fish species ''Gilded catfish, jau''.
...
, specialized in women's shoes and in the city of Birigui
Birigui is a city in the state of São Paulo, Brazil. The city is located on the northwest of the state and has 124,883 inhabitants (IBGE/2020) and 530.9 km2 of area.
The name ''Birigui'' comes from the Tupi–Guarani language and means "l ...
, specialized in children's shoes. Jaú, Franca and Birigui represent 92% of the footwear production in the State of São Paulo. Birigui has 350 companies, which generate about 13 thousand jobs, producing 45.9 million pairs per year. 52% of children's shoes in the country are produced in this city. From Birigui came most of the most famous children's shoe factories in the country. Jaú has 150 factories that produce about 130 thousand pairs of women's shoes per day. The footwear sector in Franca has around 550 companies and employs around 20,000 employees. Most of the most famous men's shoe factories in the country came from São Paulo. Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
has a polo specialized in cheap shoes and falsified tennis in Nova Serrana
Nova Serrana is a municipality in the state of Minas Gerais in the Southeast region of Brazil.
See also
*List of municipalities in Minas Gerais
This is a list of the municipalities in the state of Minas Gerais (MG), located in the Southeast Re ...
. The city has about 830 industries, which in 2017 produced around 110 million pairs. However, in general, the Brazilian industry has been struggling to compete with Chinese footwear, which is unbeatable in price due to the difference in tax collection from one country to another, apart from the absence of heavy Brazilian labor taxes in China, and the Brazilian businessman has had to invest in value-added products, combining quality and design, in order to survive. Some of the most famous companies in the country are Beira Rio, Grendene, Ortopé, Piccadilly
Piccadilly () is a road in the City of Westminster, London, to the south of Mayfair, between Hyde Park Corner in the west and Piccadilly Circus in the east. It is part of the A4 road that connects central London to Hammersmith, Earl's Court, ...
, Usaflex, Vulcabrás, Alpargatas and Rainha.
 In
In Textile industry
The textile industry is primarily concerned with the design, production and distribution of yarn, cloth and clothing. The raw material may be natural, or synthetic using products of the chemical industry.
Industry process
Cotton manufacturi ...
, Brazil, despite being among the 5 largest producers in the world in 2013, and being representative in the consumption of textiles and clothing, has very little insertion in global trade. In 2015, Brazilian imports ranked 25th in the ranking (US $5.5 billion). And in exports, it was only 40th in the world ranking. Brazil's participation in the world trade in textiles and clothing is only 0.3%, due to the difficulty of competing in price with producers in India and mainly in China. The gross value of production, which includes consumption of intermediate goods and services, by the Brazilian textile industry corresponded to almost R $40 billion in 2015, 1.6% of the gross value of Industrial Production in Brazil. The Southeast has 48.29% of production, the South has 32.65% and the Northeast, 16.2%. Midwest (2.5%) and North (0.4%) are not very representative in this activity. São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
(37.4%) is the largest producer. Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
has 8.51% (3rd largest production in the country, behind Santa Catarina). There are 260 thousand people employed in this activity in the country, 128 thousand in the Southeast. Among the main textile clusters in Brazil, the Vale do Itajaí (SC), the Metropolitan Region of São Paulo (SP) and Campinas (SP) stand out. Together, these three mesoregions are responsible for 36% of formal jobs in this industry. There were 2,983 textile companies in Brazil in 2015. In 2015, Santa Catarina was the 2nd largest textile and clothing employer in Brazil. It occupied the national leadership in the manufacture of pillows and is the largest producer in Latin America and the second in the world in woven labels. It is the largest exporter in the country of toilet / kitchen clothes, cotton terry cloth fabrics and cotton knit shirts. Some of the most famous companies in the region are Hering, Malwee, Karsten and Haco.
 In
In Electronics industry
The electronics industry is the economic sector that produces electronic devices. It emerged in the 20th century and is today one of the largest global industries. Contemporary society uses a vast array of electronic devices built-in automated or ...
, the turnover of industries in Brazil reached R $153.0 billion in 2019, about 3% of the national GDP. The number of employees in the sector was 234.5 thousand people. Exports were US $5.6 billion, and the country's imports were US $32.0 billion. Brazil, despite its efforts over the decades to get rid of the dependence on technology imports, has not yet managed to reach this level. Imports are concentrated in expensive components, such as processors, microcontrollers, memories, under-mounted magnetic disks, lasers, LED and LCD. Cables for telecommunication and electricity distribution, wires, optical fibers and connectors are manufactured in the country. Brazil has two large electro-electronic production hubs, located in the Metropolitan Region of Campinas
Campinas (, ''Plains'' or ''Meadows'') is a Brazilian municipality in São Paulo State, part of the country's Southeast Region. According to the 2020 estimate, the city's population is 1,213,792, making it the fourteenth most populous Brazilian ...
, in the State of São Paulo, and in Free Economic Zone of Manaus
The Free Economic Zone of Manaus ( pt, Zona Franca de Manaus, - ZFM) is a free economic zone in the city of Manaus, the capital of the State of Amazonas, Northern Brazil. The initial idea, a free trade port in Manaus, came from Deputy Francisco ...
, in the State of Amazonas. There are large internationally renowned technology companies, as well as part of the industries that participate in its supply chain. The country also has other smaller centers, such as the municipalities of São José dos Campos
São José dos Campos (, meaning Saint Joseph of the Fields) is a major city and the seat of the Municipalities of Brazil, municipality of the same name in the state of São Paulo (state), São Paulo, Brazil. One of the leading industrial and res ...
and São Carlos
São Carlos (Saint Charles, in English, ; named after Saint Charles Borromeo) is a Brazilian municipality in the interior of the state of São Paulo, 254 kilometers from the city of São Paulo. With a population of 254,484 inhabitants, it is th ...
, in the State of São Paulo; the municipality of Santa Rita do Sapucaí
Santa Rita do Sapucaí () is a municipality situated in the southernmost part of the State of Minas Gerais. The city is known as the "electronic valley", since it has plenty of electronic industries, and both a technical school ( ETE - Escola Téc ...
, in the State of Minas Gerais; Recife
That it may shine on all ( Matthew 5:15)
, image_map = Brazil Pernambuco Recife location map.svg
, mapsize = 250px
, map_caption = Location in the state of Pernambuco
, pushpin_map = Brazil#South A ...
, capital of Pernambuco; and Curitiba
Curitiba () is the capital and largest city in the state of Paraná (state), Paraná in Brazil. The city's population was 1,948,626 , making it the List of cities in Brazil by population, eighth most populous city in Brazil and the largest in ...
, capital of Paraná. In Campinas there are industrial units from groups such as General Electric
General Electric Company (GE) is an American multinational conglomerate founded in 1892, and incorporated in New York state and headquartered in Boston. The company operated in sectors including healthcare, aviation, power, renewable energ ...
, Samsung
The Samsung Group (or simply Samsung) ( ko, 삼성 ) is a South Korean multinational manufacturing conglomerate headquartered in Samsung Town, Seoul, South Korea. It comprises numerous affiliated businesses, most of them united under the ...
, HP and Foxconn
Hon Hai Precision Industry Co., Ltd., trading as Hon Hai Technology Group in China and Taiwan and Foxconn internationally, is a Taiwanese multinational electronics contract manufacturer established in 1974 with headquarters in Tucheng, New T ...
, a manufacturer of products from Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple fruit tree, trees are agriculture, cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, wh ...
and Dell
Dell is an American based technology company. It develops, sells, repairs, and supports computers and related products and services. Dell is owned by its parent company, Dell Technologies.
Dell sells personal computers (PCs), servers, data ...
. São José dos Campos, is focused on the aviation industry. This is where the headquarters of Embraer
Embraer S.A. () is a Brazilian multinational aerospace manufacturer that produces commercial, military, executive and agricultural aircraft, and provides aeronautical services. It was founded in 1969 in São José dos Campos, São Paulo, where i ...
is located, a Brazilian company that is the third largest aircraft manufacturer in the world, after Boeing and Airbus. In Santa Rita do Sapucaí, 8 thousand jobs are linked to the sector, with more than 120 companies. Most produce equipment for the telecommunications industry, such as converters (set-top Box), including those used in the transmission of the digital TV system.A indústria eletroeletrônica do Brasil – Levantamento de dados/ref> The technological center of Curitiba has companies such as
Siemens
Siemens AG ( ) is a German multinational conglomerate corporation and the largest industrial manufacturing company in Europe headquartered in Munich with branch offices abroad.
The principal divisions of the corporation are ''Industry'', '' ...
and Positivo Informatics. In all, 87 companies and 16 thousand employees work at Tecnoparque, an area of 127 thousand square meters created by state law in 2007. Tecnoparque can grow up to 400 thousand square meters and receive up to four times the number of workers it has today, reaching 68 thousand people.
 In the
In the household appliances
A major appliance, also known as a large domestic appliance or large electric appliance or simply a large appliance, large domestic, or large electric, is a non-portable or semi-portable machine used for routine housekeeping tasks such as cookin ...
industry, sales of so-called "white line" equipment (refrigerator, air conditioning and others) were 12.9 million units in 2017. The sector had its peak sales in 2012, with 18.9 million units. The brands that sold the most were Brastemp, Electrolux
Electrolux AB () is a Swedish multinational home appliance manufacturer, headquartered in Stockholm. It is consistently ranked the world's second largest appliance maker by units sold, after Whirlpool.
Electrolux products sell under a variety ...
, Consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throug ...
and Philips
Koninklijke Philips N.V. (), commonly shortened to Philips, is a Dutch multinational conglomerate corporation that was founded in Eindhoven in 1891. Since 1997, it has been mostly headquartered in Amsterdam, though the Benelux headquarters i ...
. Brastemp is originally from São Bernardo do Campo-SP. Consul is originally from Santa Catarina, having merged with Brastemp and today being part of the multinational Whirlpool Corporation
The Whirlpool Corporation is an American multinational manufacturer and marketer of home appliances, headquartered in Benton Charter Township, Michigan, United States. The Fortune 500 company has annual revenue of approximately $21 billion, ...
. Another famous brand from the South was Prosdócimo, founded in Curitiba, which was sold to Electrolux
Electrolux AB () is a Swedish multinational home appliance manufacturer, headquartered in Stockholm. It is consistently ranked the world's second largest appliance maker by units sold, after Whirlpool.
Electrolux products sell under a variety ...
.
In the small appliances
A small domestic appliance, also known as a small electric appliance or minor appliance or simply a small appliance, small domestic or small electric, is a portable or semi-portable machine, generally used on table-tops, counter-tops or oth ...
sector, Brazil has two famous companies: Arno
The Arno is a river in the Tuscany region of Italy. It is the most important river of central Italy after the Tiber.
Source and route
The river originates on Monte Falterona in the Casentino area of the Apennines, and initially takes a s ...
, which was 70 years in São Paulo, and today its factory is located in Itatiaia
Itatiaia () is a Brazilian municipality of the state of Rio de Janeiro. It is located at an altitude of . Its population was 32,064 in 2020 and its area is .
The oldest Brazilian national park, Itatiaia National Park (Parque Nacional do Itatiaia, ...
-RJ; and Britânia
Britânia is a municipality in northwestern Goiás state, Brazil. The population was 5,797 (2020) in a total area of 1461.2 km2.
Municipal boundaries
Municipal boundaries:
*North: Aruanã
*South: Jussara
*East: Itapirapuã and Aruanã
*W ...
, originally from Curitiba-PR.
 In the
In the metallurgical
Metallurgy is a domain of materials science and engineering that studies the physical and chemical behavior of metallic elements, their inter-metallic compounds, and their mixtures, which are known as alloys.
Metallurgy encompasses both the sc ...
business, the South has one of the most famous companies in the country, Tramontina, originally from Rio Grande do Sul and famous manufacturer of knives, pans, shovels and various utensils, which has more than 8,500 employees and 10 manufacturing units. Other famous companies in the South are Marcopolo
Thor (previously known as Marcopolo) is a family of satellites designed, launched and tested by Hughes Space and Communications (now part of Boeing Satellite Systems) for British Satellite Broadcasting (BSB), and were used for Britain's Dire ...
, a manufacturer of bus bodies, which had a market value of R $2.782 billion in 2015, and Randon, a group of 9 companies specialized in solutions for the transportation, which brings together manufacturers of vehicles, auto parts, and road equipment - employs around 11,000 people and recorded gross sales in 2017 of R $4.2 billion.
Another important industry, based in Rio de Janeiro, is White Martins, which deals with the manufacture of industrial and medical gases, such as oxygen cylinders. It is a supplier of all Brazilian petrochemical hubs and one of the largest suppliers to the steel industry. The company also has a strong presence in the metal-mechanic, food, beverage, environment and small consumer segment, in the medical-hospital sector and in the natural gas area.
By state and region

 Southeast, South and Midwest are responsible for 80% of the national industrial GDP, as shown below:
Southeast, South and Midwest are responsible for 80% of the national industrial GDP, as shown below:
São Paulo
São Paulo (, ; Portuguese for 'Saint Paul') is the most populous city in Brazil, and is the capital of the state of São Paulo, the most populous and wealthiest Brazilian state, located in the country's Southeast Region. Listed by the GaWC a ...
in 2017 had an industrial GDP of R $378.7 billion, equivalent to 31.6% of the national industry and employing 2,859,258 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (18.7%), Food (12.7%), Chemicals (8.4%), Public Utility Industrial Services, such as Electricity and Water (7.9%) and Motor Vehicles (7.0%). These 5 sectors concentrate 54.7% of the state's industry.
Minas Gerais
Minas Gerais () is a state in Southeastern Brazil. It ranks as the second most populous, the third by gross domestic product (GDP), and the fourth largest by area in the country. The state's capital and largest city, Belo Horizonte (literally ...
had in 2017 an industrial GDP of R $128.4 billion, equivalent to 10.7% of the national industry. It employs 1,069,469 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (17.9%), Extraction of Metallic Minerals (15.2%), Food (13.4%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (10.8%) and Metallurgy (10.5%). These 5 sectors concentrate 67.8% of the state's industry.Minas Gerais Industry Profile/ref> In
Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
in 2017 had an industrial GDP of R $104.6 billion, equivalent to 8.7% of the national industry and employing 556,283 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors in Rio are: Construction (22.6%), Extraction of Oil and Natural Gas (22.3%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (14.3%), Petroleum Products and Biofuels (14.1%) and Chemicals (3.6%). These 5 sectors concentrate 76.9% of the state's industry.
Paraná had an industrial GDP of R $92.8 billion in 2017, equivalent to 7.8% of the national industry. It employs 763,064 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Food (19.1%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (18.5%), Construction (17.3%), Motor Vehicles (8.1%), and Petroleum Derivatives and Biofuels (5.7%). These 5 sectors concentrate 68.7% of the state's industry.
In 2017, Rio Grande do Sul
Rio Grande do Sul (, , ; "Great River of the South") is a Federative units of Brazil, state in the South Region, Brazil, southern region of Brazil. It is the Federative_units_of_Brazil#List, fifth-most-populous state and the List of Brazilian st ...
had an industrial GDP of R $82.1 billion, equivalent to 6.9% of the national industry. It employs 762,045 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (18.2%), Food (15.4%), Industrial Public Utility Services, such as Electricity and Water (9.8%), Chemicals (6.8%), and Machinery and Equipment (6.6%). These 5 sectors concentrate 56.8% of the state's industry.
Santa Catarina had an industrial GDP of R $63.2 billion in 2017, equivalent to 5.3% of the national industry. It employs 761,072 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (17.9%), Food (15.9%), Clothing (7.4%), Industrial Public Utility Services, such as Electricity and Water (6.9%), and Textiles (6.0%). These 5 sectors concentrate 54.1% of the state's industry.
Goiás
Goiás () is a Brazilian state located in the Center-West region. Goiás borders the Federal District and the states of (from north clockwise) Tocantins, Bahia, Minas Gerais, Mato Grosso do Sul and Mato Grosso. The state capital is Goiânia. ...
had in 2017 an industrial GDP of R $37.1 billion, equivalent to 3.1% of the national industry. It employs 302,952 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (25.6%), Food (25.2%), Industrial Public Utility Services, such as Electricity and Water (17.2%) and Petroleum Products and Biofuels (7.4%) and Chemicals (3.7%). These 5 sectors concentrate 79.1% of the state's industry.

Espírito Santo
Espírito Santo (, , ; ) is a state in southeastern Brazil. Its capital is Vitória, and its largest city is Serra. With an extensive coastline, the state hosts some of the country's main ports, and its beaches are significant tourist attra ...
in 2017 had an industrial GDP of R $21.3 billion, equivalent to 1.8% of the national industry. It employs 168,357 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Extraction of Oil and Natural Gas (23.0%), Construction (20.5%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (12.3%), Metallurgy (7.5%) and Pulp and Paper (6.6%). These 5 sectors concentrate 69.9% of the state's industry.
Mato Grosso do Sul
Mato Grosso do Sul () is one of the Midwestern states of Brazil. Neighboring Brazilian states are (from north clockwise) Mato Grosso, Goiás, Minas Gerais, São Paulo and Paraná. It also borders the countries of Paraguay, to the southwest, and ...
had an industrial GDP of R $19.1 billion in 2017, equivalent to 1.6% of the national industry. It employs 122,162 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Public Utility Industrial Services, such as Electricity and Water (23.2%), Construction (20.8%), Food (15.8%), Pulp and Paper (15.1%) and Petroleum Derivatives and Biofuels (12.5%). These 5 sectors concentrate 87.4% of the state's industry.
Mato Grosso
Mato Grosso ( – lit. "Thick Bush") is one of the states of Brazil, the third largest by area, located in the Central-West region. The state has 1.66% of the Brazilian population and is responsible for 1.9% of the Brazilian GDP.
Neighboring ...
had an industrial GDP of R $17.0 billion in 2017, equivalent to 1.4% of the national industry. It employs 141,121 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (32.0%), Food (27.9%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (18.6%), Beverages (4.5%) and Oil Products Oil and Biofuels (3.9%). These 5 sectors concentrate 86.9% of the state's industry.
 The
The Federal District
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they e ...
had an industrial GDP of R $8.4 billion in 2017, equivalent to 0.7% of the national industry. It employs 82,163 workers in the industry. The main industrial sectors are: Construction (53.4%), Industrial Services of Public Utility, such as Electricity and Water (22.2%), Food (7.2%), Beverages (6.0%) and Non-minerals -metallics (3.0%). These 5 sectors concentrate 91.8% of the state's industry.
In Northeast Region, Bahia has 4.4% of the national industrial GDP, Pernambuco 2.7%, Ceará 1.9%, Maranhão 1.1%, Rio Grande do Norte 0.9%, Paraíba 0.7%, Sergipe 0.6%, Alagoas 0.5% and Piauí 0.4%, num overall total of approximately 13.2%.
In the Northern Region, Pará has 3.7% of the national industrial GDP, Amazonas 2.2%, Rondônia 0.7%, Tocantins 0.4%, Amapá 0.1%, Acre 0.1% and Roraima 0.1%, in an overall total of approximately 7.3%.
Energy



 The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.Matriz Energética e Elétrica
The main characteristic of the Brazilian energy matrix is that it is much more renewable than that of the world. While in 2019 the world matrix was only 14% made up of renewable energy, Brazil's was at 45%. Petroleum and oil products made up 34.3% of the matrix; sugar cane derivatives, 18%; hydraulic energy, 12.4%; natural gas, 12.2%; firewood and charcoal, 8.8%; varied renewable energies, 7%; mineral coal, 5.3%; nuclear, 1.4%, and other non-renewable energies, 0.6%.Matriz Energética e Elétrica/ref> In the electric energy matrix, the difference between Brazil and the world is even greater: while the world only had 25% of renewable electric energy in 2019, Brazil had 83%. The Brazilian electric matrix is composed of: hydraulic energy, 64.9%; biomass, 8.4%; wind energy, 8.6%; solar energy, 1%; natural gas, 9.3%; oil products, 2%; nuclear, 2.5%; coal and derivatives, 3.3%. In total electricity generation, in 2019 Brazil reached 170,000 megawatts of installed capacity, more than 75% from renewable sources (the majority,
hydroelectric plants
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
). In 2019, Brazil had 217 hydroelectric plants in operation, with an installed capacity of 98,581 MW, 60.16% of the country's energy generation. Brazil is one of the 5 largest hydroelectric energy producers in the world (2nd place in 2017).
In 2013, the Southeast used about 50% of the load of the National Integrated System (SIN), being the main energy consuming region in the country. The region's installed electricity generation capacity totaled almost 42,500 MW, which represented about a third of Brazil's generation capacity. The hydroelectric
Hydroelectricity, or hydroelectric power, is electricity generated from hydropower (water power). Hydropower supplies one sixth of the world's electricity, almost 4500 TWh in 2020, which is more than all other renewable sources combined and ...
generation represented 58% of the installed capacity in the region, with the remaining 42% basically corresponding to the thermoelectric
The thermoelectric effect is the direct conversion of temperature differences to electric voltage and vice versa via a thermocouple. A thermoelectric device creates a voltage when there is a different temperature on each side. Conversely, when ...
generation. São Paulo accounted for 40% of this capacity; Minas Gerais by about 25%; Rio de Janeiro by 13.3%; and Espírito Santo for the rest. Among the renewable sources for thermoelectric generation, sugar cane biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
stands out, with more than 6,300 MW of capacity, distributed in more than 230 plants. Among the non-renewable sources, natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
, with almost 6,300 MW, thermonuclear generation, with 2,000 MW, and oil products, with 1,100 MW.
The South Region has the Itaipu Dam
The Itaipu Dam ( pt, Barragem de Itaipu , es, Represa de Itaipú ) is a hydroelectric dam on the Paraná River located on the border between Brazil and Paraguay. The construction of the dam was first contested by Argentina, but the negotiations ...
, which was the largest hydroelectric plant in the world for several years, until the inauguration of the Three Gorges Dam
The Three Gorges Dam is a hydroelectric gravity dam that spans the Yangtze River by the town of Sandouping, in Yiling District, Yichang, Hubei province, central China, downstream of the Three Gorges. The Three Gorges Dam has been the world ...
in China. The region is also the only one in the country that produces coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
and oil shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitute ...
.
Northern Brazil has large hydroelectric plants such as Belo Monte and Tucuruí
Tucuruí is a municipality in the state of Pará in the Northern region of Brazil.
The city is served by Tucuruí Airport.
The name Tucuruí is a Tupi word that means "river of ants" or "river of locusts". It's the concatenation of two tupi word ...
, which produce much of the national energy.
Brazil's hydroelectric potential has not yet been fully explored, so the country still has the capacity to build several renewable energy plants in its territory.
In the Northeast region, the installation of wind farms
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few h ...
is multiplying. In 2019, it was estimated that the country had an estimated wind power generation potential of around 522 GW (this, only onshore), enough energy to meet three times the country's current demand. according to ONS, total installed capacity of wind power
Wind power or wind energy is mostly the use of wind turbines to electricity generation, generate electricity. Wind power is a popular, sustainable energy, sustainable, renewable energy source that has a much smaller Environmental impact of wi ...
was 21 GW, with average capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is de ...
of 58%. While the world average wind production capacity factors is 24.7%, there are areas in Northern Brazil, specially in Bahia State, where some wind farms record with average capacity factors over 60%; the average capacity factor in the Northeast Region is 45% in the coast and 49% in the interior. In 2019, wind energy represented 9% of the energy generated in the country.Quantas usinas geradoras de energia temos no Brasil?/ref> Brazil is one of the 10 largest wind energy producers in the world (8th place in 2019, with 2.4% of world production). Brazil also has 3 atomic plants. In
Angra dos Reis
Angra dos Reis (; Portuguese for ''cove'' or ''bay of the Kings'') is a Brazilian municipality located in the southern part of the state of Rio de Janeiro. The city is located by the sea and includes in its territory many offshore islands, the l ...
, in the state of Rio de Janeiro
Rio de Janeiro ( , , ; literally 'River of January'), or simply Rio, is the capital of the state of the same name, Brazil's third-most populous state, and the second-most populous city in Brazil, after São Paulo. Listed by the GaWC as a b ...
, is the Central Nuclear Almirante Álvaro Alberto, a complex formed by the group of nuclear plants
A nuclear power plant (NPP) is a thermal power station in which the heat source is a nuclear reactor. As is typical of thermal power stations, heat is used to generate steam that drives a steam turbine connected to a generator that produces e ...
'' 'Angra 1' '', '' 'Angra 2' '' and '' 'Angra 3' '' (under construction), owned by Eletronuclear
Eletrobras (, full name: Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A.) is a major Brazilian electric utilities company. The company's headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro.
It is Latin America's biggest power utility company, tenth largest in the wo ...
, a subsidiary of Eletrobras
Eletrobras (, full name: Centrais Elétricas Brasileiras S.A.) is a major Brazilian electric utilities company. The company's headquarters are located in Rio de Janeiro.
It is Latin America's biggest power utility company, tenth largest in the wo ...
. The complex produces three percent of the National Interconnected System electricity consumption. The total power of the plants is 2007 MW, of which 657 MW in Angra 1 and 1350 MW in Angra 2. Additionally, the Angra 3 nuclear plant, which will have a capacity of 1405 MW, is under construction.
according to ONS, total installed capacity of photovoltaic solar
Photovoltaics (PV) is the conversion of light into electricity using semiconducting materials that exhibit the photovoltaic effect, a phenomenon studied in physics, photochemistry, and electrochemistry. The photovoltaic effect is commercially us ...
was 14 GW, with average capacity factor
The net capacity factor is the unitless ratio of actual electrical energy output over a given period of time to the theoretical maximum electrical energy output over that period. The theoretical maximum energy output of a given installation is de ...
of 23%. Some of the most irradiated
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve ...
Brazilian States are MG ("Minas Gerais"), BA ("Bahia") and GO (Goiás), which have indeed world irradiation
Irradiation is the process by which an object is exposed to radiation. The exposure can originate from various sources, including natural sources. Most frequently the term refers to ionizing radiation, and to a level of radiation that will serve ...
level records. In 2019, solar power represented 1.27% of the energy generated in the country. In 2020, Brazil was the 14th country in the world in terms of installed solar power (7.8 GW).
In 2020, Brazil was the 2nd largest country in the world in the production of energy through biomass
Biomass is plant-based material used as a fuel for heat or electricity production. It can be in the form of wood, wood residues, energy crops, agricultural residues, and waste from industry, farms, and households. Some people use the terms bi ...
(energy production from solid biofuels and renewable waste), with 15,2 GW installed.
Cars
Brazilian automobile production began in 1957, with an initial production of 1,166 units in the first year. Most production is concentrated in the states of São Paulo, Minas Gerais and Paraná. Theautomotive industry in Brazil
The Brazilian automotive industry is coordinated by the ''Associação Nacional dos Fabricantes de Veículos Automotores'' (Anfavea), created in 1956, which includes automakers (cars, light vehicles, trucks, buses and agriculture machines) w ...
boomed after ex-president Fernando Collor de Mello
Fernando Affonso Collor de Mello (; born 12 August 1949) is a Brazilian politician who served as the 32nd president of Brazil from 1990 to 1992, when he resigned in a failed attempt to stop his impeachment trial by the Brazilian Senate. Coll ...
opened up the market in 1990, but high production costs, high taxes and technology deficits are barriers that Brazil is still struggling to defeat.
Brazil's automotive industry has been displaying impressive two-digit growth over the last years, totaling revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive reven ...
s over USD 100 billion by the end of 2010. These figures secured Brazil the fourth position amongst the largest car markets in the world (one position ahead of Germany). The industry generates 1.5 million jobs.
The perspective of a steady development of the industry is attracting billions in investments to the country. BMW announced in December 2011 plans to set up a plant in São Paulo, and by 2014 Chinese manufacturer JAC Motors
JAC Motors (; officially Anhui Jianghuai Automobile Co., Ltd.) is a Chinese automobile and commercial vehicle manufacturer.
was to officially start production on the assembly line being built in Bahia state.
Petroleum
The northeast shore of theBay of All Saints
The Bay of All Saints ( pt, Baía de Todos os Santos), also known as All Saints' Bay and Todos os Santos Bay, is the principal bay of the Brazilian state of Bahia, to which it gave its name. It sits on the eastern coast of Brazil, surrounding pa ...
was home to Brazil's first active oil field
A petroleum reservoir or oil and gas reservoir is a subsurface accumulation of hydrocarbons contained in porous or fractured rock formations.
Such reservoirs form when kerogen (ancient plant matter) is created in surrounding rock by the presence ...
s. The municipality of São Francisco do Conde
São Francisco do Conde is a municipality in the state of Bahia in the North-East region of Brazil. São Francisco do Conde covers , and has a population of 40,245 with a population density of 150 inhabitants per square kilometer. It is located f ...
at the north of the bay remains a port serving the refineries
A refinery is a production facility composed of a group of chemical engineering unit processes and unit operations refining certain materials or converting raw material into products of value.
Types of refineries
Different types of refineries ar ...
at . The bay is dredge
Dredging is the excavation of material from a water environment. Possible reasons for dredging include improving existing water features; reshaping land and water features to alter drainage, navigability, and commercial use; constructing da ...
d from the port to the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
to remain open to shipping.
Statistics
Electricity:Brazil Energy Data, Statistics and Analysis - Oil, gas, electricity, coal/ref> * ''production:'' 380 TWh (2004) * ''consumption: ''391 TWh (2004) Electricity - production by source: (2004) * ''other sources:'' 9% * ''hydroelectric:'' 83% * c''onventional thermal:'' 4% * ''nuclear:'' 4% Oil: * ''production:'' 2.165 million barrel/day (2006) * ''consumption:'' 2.216 million barrel/day (2006) * ''imports:'' 0.051 million barrel/day (2006) * ''proven reserves:'' 11.2 billion barrels (2006) * ''refinery capacity:'' 1.908 million barrel/day (2006) Natural gas: * ''production:'' 9.88 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''consumption:'' 19.34 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''imports:'' 9.45 billion cubic kilometers (2006) * ''proven reserves:'' 326 billion cubic kilometers (2006)
References
Bibliography
* Furtado, Celso. ''Formação econômica do Brasil''. (http://www.afoiceeomartelo.com.br/posfsa/Autores/Furtado,%20Celso/Celso%20Furtado%20-%20Forma%C3%A7%C3%A3o%20Econ%C3%B4mica%20do%20Brasil.pdf) * Prado Junior, Caio. ''História econômica do Brasil''. (http://www.afoiceeomartelo.com.br/posfsa/Autores/Prado%20Jr,%20Caio/Historia%20Economica%20do%20Brasil.pdf) *Graça Filho, Afonso de Alencastro. ''A economia do Império brasileiro''. São Paulo: Atual, 2004. *Scantimburgo, João de. ''O Poder Moderador''. São Paulo: Secretaria de Estado da Cultura, 1980. *Silva, Hélio. ''1889 - A república não esperou o amanhecer''. Porto Alegre: L&PM, 2005. *Sodré, Nelson Werneck. ''Panorama do Segundo Império'', 2. ed. Rio de Janeiro: GRAPHIA, 2004. *Szmrecsány, Tamás ''and'' Lapa, José Roberto do Amaral. ''História Econômica da Independência e do Império'', 2. ed. São Paulo: USP, 2002. *Vainfas, Ronaldo. ''Dicionário do Brasil Imperial''. Rio de Janeiro: Objetiva, 2002. *15. ed. São Paulo: Melhoramentos, 1994. {{DEFAULTSORT:Industry In Brazil