Italian Swiss People on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The four national languages of Switzerland are German,
 The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) constitutes about 65% of
The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) constitutes about 65% of  By the Middle Ages, a marked difference had developed within the German-speaking part of Switzerland between the rural cantons (Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Glarus, Zug, Appenzell, Schaffhausen) and the city cantons (Lucerne, Berne, Zurich, Solothurn, Fribourg, Basel, St. Gallen), divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant, and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, when all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farmhouses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
In addition to this more widespread notion of Swiss German dialect, there is also Walser German, another
By the Middle Ages, a marked difference had developed within the German-speaking part of Switzerland between the rural cantons (Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Glarus, Zug, Appenzell, Schaffhausen) and the city cantons (Lucerne, Berne, Zurich, Solothurn, Fribourg, Basel, St. Gallen), divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant, and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, when all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farmhouses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
In addition to this more widespread notion of Swiss German dialect, there is also Walser German, another
 Romandy (french: Romandie, la Suisse romande, german: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz, it, Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of
Romandy (french: Romandie, la Suisse romande, german: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz, it, Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of
 Italian Switzerland ( it, Svizzera italiana, rm, Svizra taliana, french: Suisse italienne, german: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of
Italian Switzerland ( it, Svizzera italiana, rm, Svizra taliana, french: Suisse italienne, german: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of
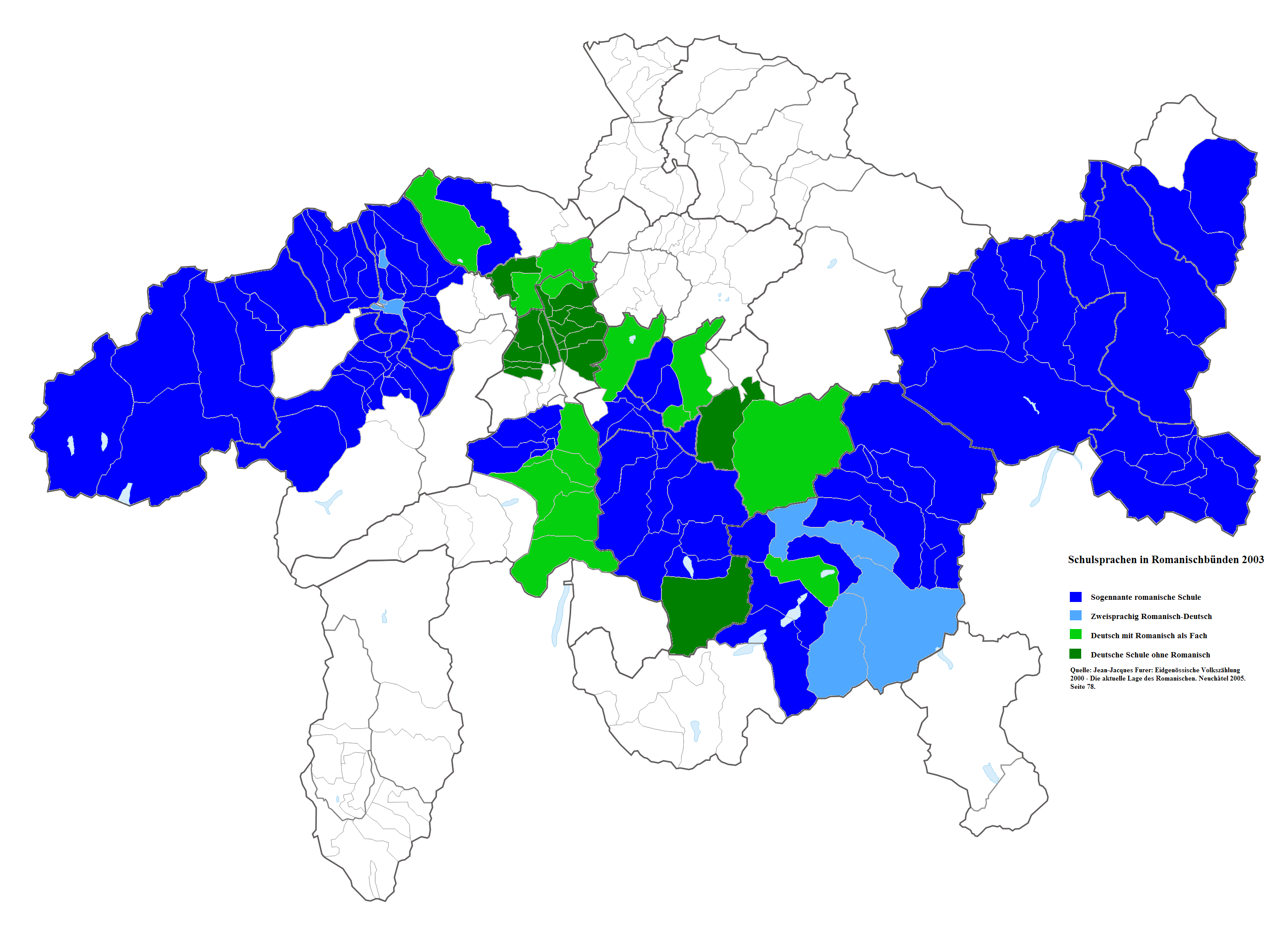 Romansh is an official language in the trilingual Canton of Grisons, where the municipalities in turn are free to specify their own official languages.
Romansh has been recognized as one of four "national languages" by the
Romansh is an official language in the trilingual Canton of Grisons, where the municipalities in turn are free to specify their own official languages.
Romansh has been recognized as one of four "national languages" by the
French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Italian, and Romansh. German, French, and Italian maintain equal status as official languages at the national level within the Federal Administration of the Swiss Confederation, while Romansh is used in dealings with people who speak it. Latin is occasionally used in some formal contexts, particularly to denote the country (''Confederatio Helvetica)''.
In 2020, 62.3% of the population of Switzerland were native speakers of German (either Swiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
or Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
) at home; 22.8% French (mostly Swiss French, but including some Franco-Provençal dialects); 8% Italian (mostly Swiss Italian, but including Lombard); and 0.5% Romansh. The German region (''Deutschschweiz'') is roughly in the east, north, and centre; the French part (''la Romandie'') in the west; and the Italian area (''Svizzera italiana'') in the south. There remains a small Romansh-speaking native population in Grisons
The Grisons () or Graubünden,Names include:
*german: (Kanton) Graubünden ;
* Romansh:
** rm, label= Sursilvan, (Cantun) Grischun
** rm, label=Vallader, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label= Puter, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label=Surmiran, (Cant ...
in the east. The cantons of Fribourg, Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
, and Valais are officially bilingual; Grisons
The Grisons () or Graubünden,Names include:
*german: (Kanton) Graubünden ;
* Romansh:
** rm, label= Sursilvan, (Cantun) Grischun
** rm, label=Vallader, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label= Puter, (Chantun) Grischun
** rm, label=Surmiran, (Cant ...
is officially trilingual.
History
The main languages of Swiss residents from 1950 to 2015, in percentages, were as follows: In 2012, for the first time, respondents could indicate more than one language, causing the percentages to exceed 100%.National languages and linguistic regions
German

 The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) constitutes about 65% of
The German-speaking part of Switzerland (german: Deutschschweiz, french: Suisse alémanique, it, Svizzera tedesca, rm, Svizra tudestga) constitutes about 65% of Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
(North Western Switzerland, Eastern Switzerland, Central Switzerland, most of the Swiss Plateau and the greater part of the Swiss Alps
The Alpine region of Switzerland, conventionally referred to as the Swiss Alps (german: Schweizer Alpen, french: Alpes suisses, it, Alpi svizzere, rm, Alps svizras), represents a major natural feature of the country and is, along with the Swiss ...
).
In seventeen of the Swiss cantons, German is the only official language (Aargau
Aargau, more formally the Canton of Aargau (german: Kanton Aargau; rm, Chantun Argovia; french: Canton d'Argovie; it, Canton Argovia), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven districts and its capita ...
, Appenzell Ausserrhoden
Appenzell Ausserrhoden (; in English sometimes Appenzell Outer Rhodes) (german: Kanton Appenzell Ausserrhoden; rm, Chantun Appenzell Dadora; french: Canton d'Appenzell Rhodes-Extérieures; it, Canton Appenzello Esterno) is one of the 26 canton ...
, Appenzell Innerrhoden
Appenzell Innerrhoden (; in English sometimes Appenzell Inner-Rhodes) (german: Kanton Appenzell Innerrhoden rm, Chantun Appenzell Dadens; french: Canton d'Appenzell Rhodes-Intérieures; it, Canton Appenzello Interno) is one of the 26 cantons ...
, Basel-Stadt
Basel-Stadt or Basel-City (german: Kanton ; rm, Chantun Basilea-Citad; french: Canton de Bâle-Ville; it, Canton Basilea Città) is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of three municipalities with Basel as t ...
, Basel-Landschaft, Glarus, Luzern
, neighboring_municipalities= Adligenswil, Ebikon, Emmen, Horw, Kriens, Malters, Meggen, Neuenkirch
Lucerne ( , ; High Alemannic: ''Lozärn'') or Luzern ()Other languages: gsw, Lozärn, label=Lucerne German; it, Lucerna ; rm, Lucerna . is a ...
, Nidwalden
Nidwalden, also Nidwald (german: Kanton Nidwalden, ; rm, Chantun Sutsilvania; french: Canton de Nidwald; it, Canton Nidvaldo) is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eleven municipalities and the seat of the ...
, Obwalden
Obwalden, also Obwald (german: Kanton Obwalden, rm, Chantun Sursilvania; french: Canton d'Obwald; it, Canton Obvaldo), is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of seven municipalities and the seat of the govern ...
, Schaffhausen, Schwyz, Solothurn, St. Gallen, Thurgau, Uri Uri may refer to:
Places
* Canton of Uri, a canton in Switzerland
* Úri, a village and commune in Hungary
* Uri, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province
* Uri, Jammu and Kashmir, a town in India
* Uri (island), an island off Malakula Islan ...
, Zug, and Zürich).
In the cantons of Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
, Fribourg and Valais, French is co-official; in the trilingual canton of Graubünden, more than half of the population speaks German, while the rest speak Romansh or Italian. In each case, all languages are official languages of the respective canton.
While the French-speaking Swiss prefer to call themselves ''Romands'' and their part of the country is the Romandy, the German-speaking Swiss used to (and, colloquially, still do) refer to the French-speaking Swiss as "Welsche", and to their area as ''Welschland'', which has the same etymology as the English Welsh (see '' Walha''). In Germany, ''Welsch'' and ''Welschland'' refer to Italy; there, the term is antiquated, rarely used, and somewhat disparaging. Research shows that individuals with a French-sounding name in the German-speaking part suffer from social discrimination.
Nevertheless, in 2017, 11.1%, or about 920,600 of the Swiss residents speak Standard German
Standard High German (SHG), less precisely Standard German or High German (not to be confused with High German dialects, more precisely Upper German dialects) (german: Standardhochdeutsch, , or, in Switzerland, ), is the standardized variety ...
("Hochdeutsch") at home, but this statistic is probably mainly due to German (and Austrian) immigrants.
 By the Middle Ages, a marked difference had developed within the German-speaking part of Switzerland between the rural cantons (Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Glarus, Zug, Appenzell, Schaffhausen) and the city cantons (Lucerne, Berne, Zurich, Solothurn, Fribourg, Basel, St. Gallen), divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant, and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, when all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farmhouses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
In addition to this more widespread notion of Swiss German dialect, there is also Walser German, another
By the Middle Ages, a marked difference had developed within the German-speaking part of Switzerland between the rural cantons (Uri, Schwyz, Unterwalden, Glarus, Zug, Appenzell, Schaffhausen) and the city cantons (Lucerne, Berne, Zurich, Solothurn, Fribourg, Basel, St. Gallen), divided by views about trade and commerce. After the Reformation, all cantons were either Catholic or Protestant, and the denominational influences on culture added to the differences. Even today, when all cantons are somewhat denominationally mixed, the different historical denominations can be seen in the mountain villages, where Roman Catholic Central Switzerland abounds with chapels and statues of saints, and the farmhouses in the very similar landscape of the Protestant Bernese Oberland show Bible verses carved on the housefronts instead.
In addition to this more widespread notion of Swiss German dialect, there is also Walser German, another Highest Alemannic
Highest Alemannic is a branch of Alemannic German and is often considered to be part of the German language, even though mutual intelligibility with Standard German and other non-Alemannic German dialects is very limited.
Highest Alemannic dialect ...
speech brought by Walser emigrants from Valais.
Because the largest part of Switzerland is German-speaking, many French, Italian, and Romansh speakers migrate to the rest of Switzerland, and the children of those non-German-speaking Swiss-born within the rest of Switzerland speak German.
French
 Romandy (french: Romandie, la Suisse romande, german: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz, it, Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of
Romandy (french: Romandie, la Suisse romande, german: Romandie, Welschland, Welschschweiz, or in some contexts: Westschweiz, it, Svizzera romanda) is the French-speaking part of Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
. It covers the area of the cantons of Geneva, Vaud, Neuchâtel
, neighboring_municipalities= Auvernier, Boudry, Chabrey (VD), Colombier, Cressier, Cudrefin (VD), Delley-Portalban (FR), Enges, Fenin-Vilars-Saules, Hauterive, Saint-Blaise, Savagnier
, twintowns = Aarau (Switzerland), Besançon (France), ...
, and Jura as well as the French-speaking parts of the cantons of Bern
german: Berner(in)french: Bernois(e) it, bernese
, neighboring_municipalities = Bremgarten bei Bern, Frauenkappelen, Ittigen, Kirchlindach, Köniz, Mühleberg, Muri bei Bern, Neuenegg, Ostermundigen, Wohlen bei Bern, Zollikofen
, website ...
(German-speaking majority), Valais (French-speaking majority), and Fribourg (French-speaking majority). 1.9 million people (or 24.4% of the Swiss population) live in Romandy.
Standard Swiss French and the French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
of France are highly mutually intelligible, though some differences exist. For example, like most Francophone Belgians, speakers of Swiss French use ''septante'' (seventy) instead of ''soixante-dix'' (literally, "sixty ten") and ''nonante'' (ninety) instead of "quatre-vingt-dix" ("four twenty ten"). In the cantons of Vaud, Valais and Fribourg, speakers use ''huitante'' (eighty) instead of "quatre-vingts" (four twenties) used in the rest of the French-speaking world
French language, French became an international language in the Middle Ages, when the power of the Kingdom of France made it the second Lingua franca, international language, alongside Latin. This status continued to grow into the 18th century, ...
; the cantons of Geneva, Bern and Jura use "quatre-vingts". " Sou" is used throughout Romandy for a 5-centime coin, as is "tune" (or "thune") when referring to a 5-Swiss-franc piece.
Historically, the vernacular language used by inhabitants of most parts of Romandy was Franco-Provençal. Franco-Provençal (also called Arpitan) is a language sometimes considered to be halfway between the langue d'oïl (the historical language of northern France and ancestor of French) and Occitan (the langue d'oc, spoken in southern France). Standard French and Franco-Provençal/Arpitan, linguistically, are distinct and mutual intelligibility is limited. Increasingly, Franco-Provençal/Arpitan is used only by members of the older generations. In parts of Jura Franc-Comtois
Frainc-Comtou (french: franc-comtois) is a Romance language of the '' langues d'oïl'' language family spoken in the Franche-Comté region of France and in the Canton of Jura and Bernese Jura in Switzerland.
Sample vocabulary
References
Bi ...
dialects are also spoken; these belong to the same Oïl bloc as Standard French.
The term ''Romandy'' does not formally exist in the political system, but is used to distinguish and unify the French-speaking population of Switzerland. The television channel Télévision Suisse Romande (TSR) serves the ''Romande'' community across Switzerland and worldwide through TV5Monde.
Italian
 Italian Switzerland ( it, Svizzera italiana, rm, Svizra taliana, french: Suisse italienne, german: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of
Italian Switzerland ( it, Svizzera italiana, rm, Svizra taliana, french: Suisse italienne, german: italienische Schweiz) is the Italian-speaking part of Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
, which includes the canton of Ticino and the southern part of Grisons. Italian is also spoken in the Gondo Valley (leading to the Simplon Pass, on the southern part of the watershed) in Valais. The traditional vernacular of this region is the Lombard language, specifically its Ticinese dialect.
The linguistic region covers an area of about 3,500 km2 and has a total population of around 350,000, with the number of Italophones residing in Switzerland being 545,274 (about 7% of the Swiss population).
The proportion of Italian-speaking inhabitants had been decreasing since the 1970s, after reaching a high of 12% of the population during the same decade. This was entirely because of the reduced number of immigrants from Italy to Switzerland. However it has increased again during the last decade.
Romansh
Swiss Federal Constitution
The Federal Constitution of the Swiss Confederation (SR 10; german: Bundesverfassung der Schweizerischen Eidgenossenschaft (BV); french: Constitution fédérale de la Confédération suisse (Cst.); it, Costituzione federale della Confederaz ...
since 1938. It was also declared an "official language" of the Confederation in 1996, meaning that Romansh speakers may use their language for correspondence with the federal government and expect to receive a Romansh response. Although Romansh is split into several dialects, the federal and cantonal authorities use the standardized version (''Romansh Grischun'') exclusively.
Romansh speakers remain predominant in the Surselva
Surselva Region is one of the eleven administrative districts in the canton of Graubünden in Switzerland. It was created on 1 January 2017 as part of a reorganization of the canton.Albula Region, and the Engiadina Bassa/Val Müstair Region.
 To avoid having to translate the name of Switzerland into the four national languages, Latin is used on the coins of the Swiss franc ('' Helvetia'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on
To avoid having to translate the name of Switzerland into the four national languages, Latin is used on the coins of the Swiss franc ('' Helvetia'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on
Swiss Germanswiss-linguistics.com
Information portal on current linguistic research in Switzerland
sieps.ch
Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities
Pimsleur Swiss German
Pimsleur Swiss German Course {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of Switzerland Linguistic Geography of Switzerland af:Romandie als:Romandie cs:Romandie it:Svizzera Italiana nn:Romandie pl:Romandia sv:Romandiet
Other languages
Besides the national languages and the many varieties ofSwiss German
Swiss German (Standard German: , gsw, Schwiizerdütsch, Schwyzerdütsch, Schwiizertüütsch, Schwizertitsch Mundart,Because of the many different dialects, and because there is no defined orthography for any of them, many different spelling ...
, several regional Romance languages are spoken natively in Switzerland: Franco-Provençal and Lombard.
About 20,000 Romani
Romani may refer to:
Ethnicities
* Romani people, an ethnic group of Northern Indian origin, living dispersed in Europe, the Americas and Asia
** Romani genocide, under Nazi rule
* Romani language, any of several Indo-Aryan languages of the Roma ...
speak Sinte, an Indic language Indic languages may refer to:
* Indo-Aryan languages, a subgroup of the Indo-European languages spoken mainly in the north of the Indian subcontinent
* Languages of the Indian subcontinent, all the indigenous languages of the region regardless of la ...
.
While learning one of the other national languages at school is important, many Swiss nowadays find it easier to use English as a lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
even with other Swiss people of different linguistic backgrounds.
Five sign languages are used: Swiss-German, French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
, Italian, Austrian, and German.
Neo-Latin
 To avoid having to translate the name of Switzerland into the four national languages, Latin is used on the coins of the Swiss franc ('' Helvetia'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on
To avoid having to translate the name of Switzerland into the four national languages, Latin is used on the coins of the Swiss franc ('' Helvetia'' or ''Confoederatio Helvetica'') and on Swiss stamps
This is a survey of the postage stamps and postal history of Switzerland.
History
The first stamps used in Switzerland were issued by the cantons of Zürich (1843), Geneva (1843) and Basel (1845) for their own use, with the first federal ...
(''Helvetia''). The country code top-level domain for Switzerland on the internet is .ch
.ch is the country code top-level domain (ccTLD) for Switzerland in the Domain Name System of the Internet. Made available in 1987, only two years after .com, it is administered by SWITCH Information Technology Services.
The domain ''ch'', as ...
, the abbreviation of the Latin name, ''Confoederatio Helvetica'' (Swiss Confederation); similarly, the International vehicle registration code for Swiss automobiles is "CH". The Federal Palace of Switzerland bears the inscription '.
To have a unique name across the country (without favoring German, French or any other language), several Swiss foundations and associations have Latin names, such as Pro Helvetia, Pro Infirmis, Pro Juventute, Pro Natura, Pro Patria, Pro Senectute, Pro Specie Rara, etc.
See also
*Swiss people
The Swiss people (german: die Schweizer, french: les Suisses, it, gli Svizzeri, rm, ils Svizzers) are the citizens of Switzerland or people of Swiss abroad, Swiss ancestry.
The number of Swiss nationality law, Swiss nationals has grown from ...
* Demographics of Switzerland
* Röstigraben, referring to the asserted difference in mentality between German Swiss and the French-speaking Romands
* Swiss literature
As there is no dominant national language, the four main languages of French, Italian, German and Romansch form the four branches which make up a literature of Switzerland. The original Swiss Confederation, from its foundation in 1291 up to 1 ...
* List of multilingual countries and regions
Notes
References
External links
Swiss German
Information portal on current linguistic research in Switzerland
sieps.ch
Information Services on Swiss Private Schools and Universities
Pimsleur Swiss German
Pimsleur Swiss German Course {{DEFAULTSORT:Languages of Switzerland Linguistic Geography of Switzerland af:Romandie als:Romandie cs:Romandie it:Svizzera Italiana nn:Romandie pl:Romandia sv:Romandiet