Instep on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The foot ( : feet) is an

 The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26
The human foot is a strong and complex mechanical structure containing 26
 *
*
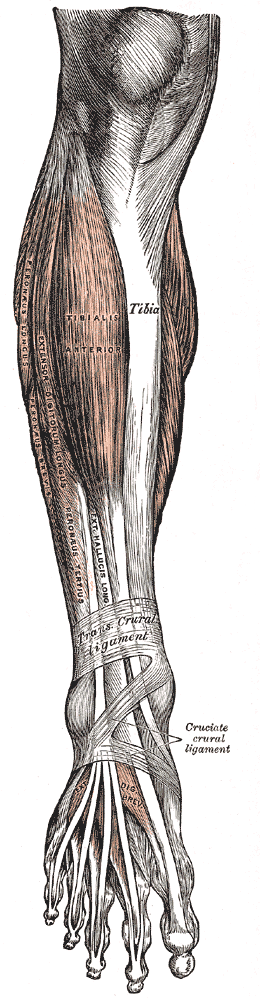 All muscles originating on the lower leg except the
All muscles originating on the lower leg except the
 An individual who underpronates also initially strikes the ground on the lateral side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus, the foot will not roll far enough in a medial direction. The weight is distributed unevenly across the metatarsus, with excessive weight borne on the
An individual who underpronates also initially strikes the ground on the lateral side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus, the foot will not roll far enough in a medial direction. The weight is distributed unevenly across the metatarsus, with excessive weight borne on the
anatomical
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having its ...
structure found in many vertebrate
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxon, taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with vertebral column, backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the ...
s. It is the terminal portion of a limb
Limb may refer to:
Science and technology
* Limb (anatomy), an appendage of a human or animal
*Limb, a large or main branch of a tree
*Limb, in astronomy, the curved edge of the apparent disk of a celestial body, e.g. lunar limb
*Limb, in botany, ...
which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many animals with feet, the foot is a separate organ at the terminal part of the leg
A leg is a weight-bearing and locomotive anatomical structure, usually having a columnar shape. During locomotion, legs function as "extensible struts". The combination of movements at all joints can be modeled as a single, linear element c ...
made up of one or more segments or bones, generally including claws or nails.
Etymology
The word "foot", in the sense of meaning the "terminal part of the leg of a vertebrate animal" comes from "Old English fot "foot," from Proto-Germanic *fot (source also of Old Frisian fot, Old Saxon fot, Old Norse fotr, Danish fod, Swedish fot, Dutch voet, Old High German fuoz, German Fuß, Gothic fotus "foot"), fromPIE
A pie is a baked dish which is usually made of a pastry dough casing that contains a filling of various sweet or savoury ingredients. Sweet pies may be filled with fruit (as in an apple pie), nuts ( pecan pie), brown sugar ( sugar pie), swe ...
root *ped- "foot".
The "plural form feet is an instance of i-mutation."
Structure

bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, an ...
s, 33 joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
(20 of which are actively articulated), and more than a hundred muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are Organ (biology), organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other ...
s, tendon
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its ability ...
s, and ligaments.Podiatry Channel, ''Anatomy of the foot and ankle'' The joints of the foot are the ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular ...
and subtalar joint
In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the
talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus.
The joint is classed structurally as a synovial joint, and functionally as a pla ...
and the interphalangeal joints of the foot
The interphalangeal joints of the foot are between the phalanx bones of the toes in the feet.
Since the great toe only has two phalanx bones (proximal and distal phalanges), it only has one interphalangeal joint, which is often abbreviated as ...
. An anthropometric study of 1197 North American adult Caucasian males (mean age 35.5 years) found that a man's foot length was 26.3 cm with a standard deviation of 1.2 cm.
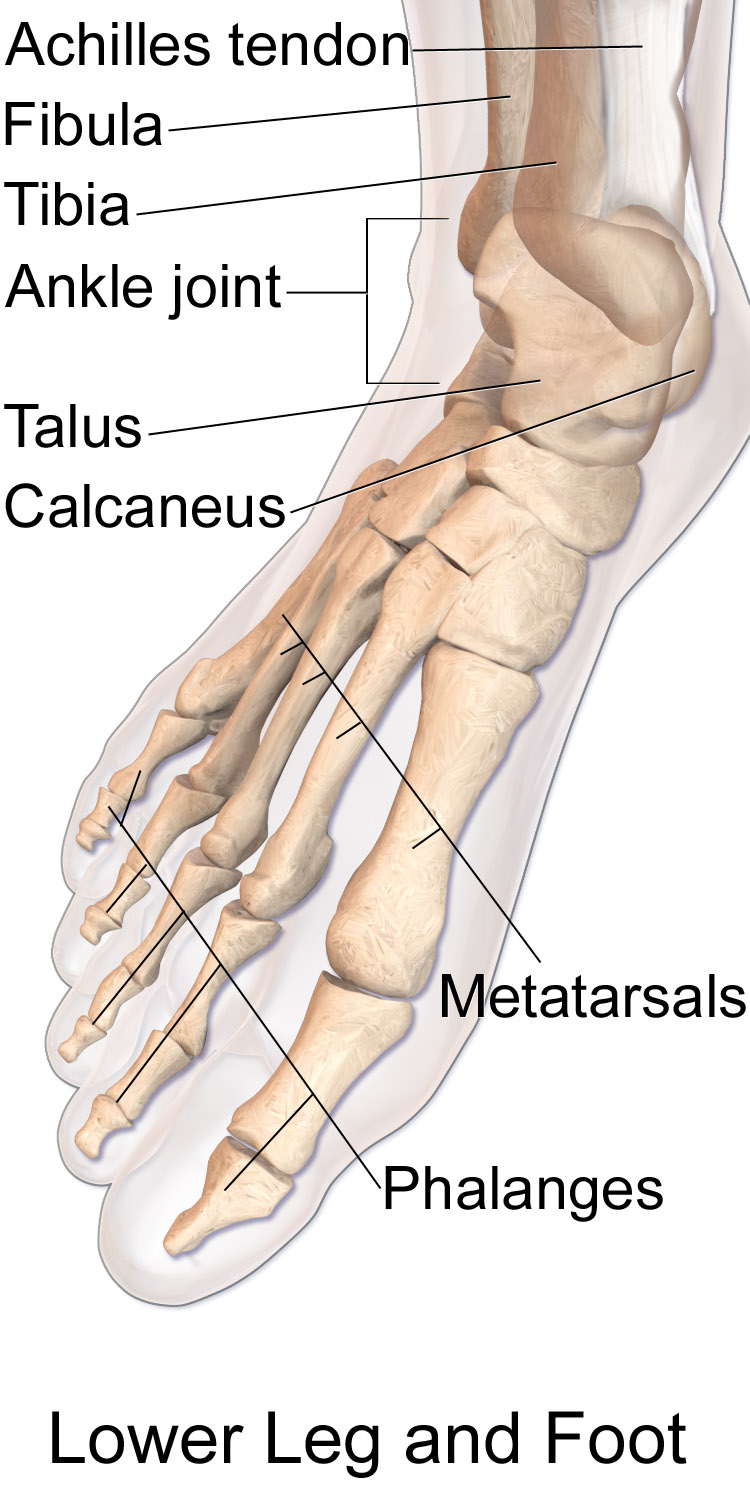
The foot can be subdivided into the hindfoot, the midfoot, and the forefoot:
The ''hindfoot'' is composed of the talus (or ankle bone) and the calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
...
(or heel bone). The two long bones of the lower leg, the tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
and fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a human leg, leg bone on the Lateral (anatomy), lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long ...
, are connected to the top of the talus to form the ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular ...
. Connected to the talus at the subtalar joint
In human anatomy, the subtalar joint, also known as the
talocalcaneal joint, is a joint of the foot. It occurs at the meeting point of the talus and the calcaneus.
The joint is classed structurally as a synovial joint, and functionally as a pla ...
, the calcaneus, the largest bone of the foot, is cushioned underneath by a layer of fat.
The five irregular bones of the ''midfoot'', the cuboid
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. Cuboid means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a cu ...
, navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.
Human anatomy
The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the ...
, and three cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedg ...
bones, form the arches of the foot
The arches of the foot, formed by the tarsal and metatarsal bones, strengthened by ligaments and tendons, allow the foot to support the weight of the body in the erect posture with the least weight.
They are categorized as longitudinal and tran ...
which serves as a shock absorber. The midfoot is connected to the hind- and fore-foot by muscles and the plantar fascia
The plantar fascia is the thick connective tissue (aponeurosis) which supports the arch on the bottom (plantar side) of the foot. It runs from the tuberosity of the calcaneus (heel bone) forward to the heads of the metatarsal bones (the bone be ...
.
The ''forefoot'' is composed of five toes and the corresponding five proximal long bones forming the metatarsus
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the med ...
. Similar to the fingers of the hand, the bones of the toes are called phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones ...
and the big toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''planti ...
has two phalanges while the other four toes have three phalanges each. The joints between the phalanges are called interphalangeal and those between the metatarsus and phalanges are called metatarsophalangeal
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones (proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an ellipt ...
(MTP).
Both the midfoot and forefoot constitute the ''dorsum'' (the area facing upward while standing) and the ''planum'' (the area facing downward while standing).
The ''instep'' is the arched part of the top of the foot between the toes and the ankle.
Bones
 *
* tibia
The tibia (; ), also known as the shinbone or shankbone, is the larger, stronger, and anterior (frontal) of the two bones in the leg below the knee in vertebrates (the other being the fibula, behind and to the outside of the tibia); it connects ...
, fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a human leg, leg bone on the Lateral (anatomy), lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long ...
* tarsus (7): talus, calcaneus
In humans and many other primates, the calcaneus (; from the Latin ''calcaneus'' or ''calcaneum'', meaning heel) or heel bone is a bone of the tarsus of the foot which constitutes the heel. In some other animals, it is the point of the hock.
...
, cuneiformes (3), cuboid
In geometry, a cuboid is a hexahedron, a six-faced solid. Its faces are quadrilaterals. Cuboid means "like a cube", in the sense that by adjusting the length of the edges or the angles between edges and faces a cuboid can be transformed into a cu ...
, and navicular
The navicular bone is a small bone found in the feet of most mammals.
Human anatomy
The navicular bone in humans is one of the tarsal bones, found in the foot. Its name derives from the human bone's resemblance to a small boat, caused by the ...
* metatarsus
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the med ...
(5): first
First or 1st is the ordinal form of the number one (#1).
First or 1st may also refer to:
*World record, specifically the first instance of a particular achievement
Arts and media Music
* 1$T, American rapper, singer-songwriter, DJ, and reco ...
, second, third
Third or 3rd may refer to:
Numbers
* 3rd, the ordinal form of the cardinal number 3
* , a fraction of one third
* 1⁄60 of a ''second'', or 1⁄3600 of a ''minute''
Places
* 3rd Street (disambiguation)
* Third Avenue (disambiguation)
* Hi ...
, fourth, and fifth metatarsal bone
The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.
A ...
* phalanges
The phalanges (singular: ''phalanx'' ) are digital bones in the hands and feet of most vertebrates. In primates, the thumbs and big toes have two phalanges while the other digits have three phalanges. The phalanges are classed as long bones ...
(14)
There can be many sesamoid bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be prese ...
s near the metatarsophalangeal joints, although they are only regularly present in the distal portion of the first metatarsal bone
The first metatarsal bone is the bone in the foot just behind the big toe. The first metatarsal bone is the shortest of the metatarsal bones and by far the thickest and strongest of them.
Like the four other metatarsals, it can be divided into t ...
.Platzer 2004, p. 220
Arches
The human foot has twolongitudinal
Longitudinal is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
* Longitude
** Line of longitude, also called a meridian
* Longitudinal engine, an internal combustion engine in which the crankshaft is oriented along the long axis of the vehicle, ...
arches and a transverse arch maintained by the interlocking shapes of the foot bones, strong ligaments, and pulling muscles during activity. The slight mobility of these arches when weight is applied to and removed from the foot makes walking and running more economical in terms of energy. As can be examined in a footprint, the medial longitudinal arch curves above the ground. This arch stretches from the heel bone over the "keystone" ankle bone to the three medial metatarsals. In contrast, the lateral longitudinal arch is very low. With the cuboid serving as its keystone, it redistributes part of the weight to the calcaneus and the distal end of the fifth metatarsal. The two longitudinal arches serve as pillars for the transverse arch which run obliquely across the tarsometatarsal joints. Excessive strain on the tendons and ligaments of the feet can result in fallen arches or flat feet
Flat feet (also called pes planus or fallen arches) is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Sometimes children are born ...
.Mareb-Hoehn 2007, pp. 244–45
Muscles
The muscles acting on the foot can be classified intoextrinsic muscles
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.
Types
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, a ...
, those originating on the anterior or posterior aspect of the lower leg, and intrinsic muscles
Anatomical terminology is used to uniquely describe aspects of skeletal muscle, cardiac muscle, and smooth muscle such as their actions, structure, size, and location.
Types
There are three types of muscle tissue in the body: skeletal, smooth, ...
, originating on the dorsal (top) or plantar (base) aspects of the foot.
Extrinsic
 All muscles originating on the lower leg except the
All muscles originating on the lower leg except the popliteus muscle
The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the gait cycle (one with the foot in contact with the ground). In open chain movements ...
are attached to the bones of the foot. The tibia and fibula and the interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
The interosse ...
separate these muscles into anterior and posterior groups, in their turn subdivided into subgroups and layers.Platzer 2004, p. 256
=''Anterior group''
= ''Extensor group'': thetibialis anterior
The tibialis anterior muscle is a muscle in humans that originates along the upper two-thirds of the lateral (outside) surface of the tibia and inserts into the medial cuneiform and first metatarsal bones of the foot. It acts to dorsiflex and inve ...
originates on the proximal half of the tibia and the interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
The interosse ...
and is inserted near the tarsometatarsal joint
The tarsometatarsal joints (Lisfranc joints) are arthrodial joints in the foot
The foot ( : feet) is an anatomical structure found in many vertebrates. It is the terminal portion of a limb which bears weight and allows locomotion. In many anim ...
of the first digit. In the non-weight-bearing leg, the tibialis anterior dorsiflexes the foot and lift its medial edge (supination
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
). In the weight-bearing leg, it brings the leg toward the back of the foot, like in rapid walking. The extensor digitorum longus
The extensor digitorum longus is a pennate muscle, situated at the lateral part of the front of the leg.
Origin and insertion
It arises from the lateral condyle of the tibia; from the upper three-quarters of the anterior surface of the body of ...
arises on the lateral tibial condyle and along the fibula, and is inserted on the second to fifth digits and proximally on the fifth metatarsal. The extensor digitorum longus acts similar to the tibialis anterior except that it also dorsiflexes the digits. The extensor hallucis longus
The extensor hallucis longus muscle is a thin skeletal muscle, situated between the tibialis anterior and the extensor digitorum longus. It extends the big toe and dorsiflects the foot. It also assists with foot eversion and inversion.
Struct ...
originates medially on the fibula and is inserted on the first digit. It dorsiflexes the big toe and also acts on the ankle in the unstressed leg. In the weight-bearing leg, it acts similarly to the tibialis anterior.Platzer 2004, p. 258
''Peroneal group'': the peroneus longus
In human anatomy, the fibularis longus (also known as peroneus longus) is a superficial muscle in the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to extend the foot downwar ...
arises on the proximal aspect of the fibula and peroneus brevis
In human anatomy, the fibularis brevis (or peroneus brevis) is a muscle that lies underneath the fibularis longus within the lateral compartment of the leg. It acts to tilt the sole of the foot away from the midline of the body (eversion) and to ...
below it. Together, their tendons pass behind the lateral malleolus
A malleolus is the bony prominence on each side of the human ankle.
Each leg is supported by two bones, the tibia on the inner side (medial) of the leg and the fibula on the outer side (lateral) of the leg. The medial malleolus is the promine ...
. Distally, the peroneus longus crosses the plantar side of the foot to reach its insertion on the first tarsometatarsal joint, while the peroneus brevis reaches the proximal part of the fifth metatarsal. These two muscles are the strongest pronators and aid in plantar flexion. The peroneus longus also acts like a bowstring that braces the transverse arch of the foot.Platzer 2004, p. 260
=''Posterior group''
= The ''superficial layer'' of posterior leg muscles is formed by thetriceps surae
The triceps surae consists of two muscles located at the calf – the two-headed gastrocnemius and the soleus. These muscles both insert into the calcaneus, the bone of the heel of the human foot, and form the major part of the muscle of the pos ...
and the plantaris
The plantaris is one of the superficial muscles of the superficial posterior compartment of the leg, one of the fascial compartments of the leg.
It is composed of a thin muscle belly and a long thin tendon. While not as thick as the achilles te ...
. The triceps surae consists of the soleus
In humans and some other mammals, the soleus is a powerful muscle in the back part of the lower leg (the calf). It runs from just below the knee to the heel, and is involved in standing and walking. It is closely connected to the gastrocnemius m ...
and the two heads of the gastrocnemius
The gastrocnemius muscle (plural ''gastrocnemii'') is a superficial two-headed muscle that is in the back part of the lower leg of humans. It runs from its two heads just above the knee to the heel, a three joint muscle (knee, ankle and subtalar ...
. The heads of gastrocnemius arise on the femur
The femur (; ), or thigh bone, is the proximal bone of the hindlimb in tetrapod vertebrates. The head of the femur articulates with the acetabulum in the pelvic bone forming the hip joint, while the distal part of the femur articulates wit ...
, proximal to the condyles, and the soleus arises on the proximal dorsal parts of the tibia and fibula. The tendons of these muscles merge to be inserted onto the calcaneus as the Achilles tendon
The Achilles tendon or heel cord, also known as the calcaneal tendon, is a tendon at the back of the lower leg, and is the thickest in the human body. It serves to attach the plantaris, gastrocnemius (calf) and soleus muscles to the calcane ...
. The plantaris originates on the femur proximal to the lateral head of the gastrocnemius and its long tendon is embedded medially into the Achilles tendon. The triceps surae is the primary plantar flexor. Its strength becomes most obvious during ballet dancing. It is fully activated only with the knee extended, because the gastrocnemius is shortened during flexion of the knee. During walking it not only lifts the heel, but also flexes the knee, assisted by the plantaris.Platzer 2004, p. 262
In the ''deep layer'' of posterior muscles, the tibialis posterior
The tibialis posterior muscle is the most central of all the leg muscles, and is located in the deep posterior compartment of the leg. It is the key stabilizing muscle of the lower leg.
Structure
The tibialis posterior muscle originates on th ...
arises proximally on the back of the interosseous membrane
An interosseous membrane is a thick dense fibrous sheet of connective tissue that spans the space between two bones, forming a type of syndesmosis joint.
Interosseous membranes in the human body:
* Interosseous membrane of forearm
The interosse ...
and adjoining bones, and divides into two parts in the sole of the foot to attach to the tarsus. In the non-weight-bearing leg, it produces plantar flexion and supination, and, in the weight-bearing leg, it proximates the heel to the calf. The flexor hallucis longus
The flexor hallucis longus muscle (FHL) is one of the three deep muscles of the posterior compartment of the leg that attaches to the plantar surface of the distal phalanx of the great toe. The other deep muscles are the flexor digitorum longus ...
arises on the back of the fibula on the lateral side, and its relatively thick muscle belly extends distally down to the flexor retinaculum where it passes over to the medial side to stretch across the sole to the distal phalanx of the first digit. The popliteus
The popliteus muscle in the leg is used for unlocking the knees when walking, by laterally rotating the femur on the tibia during the closed chain portion of the gait cycle (one with the foot in contact with the ground). In open chain movements ...
is also part of this group, but, with its oblique course across the back of the knee, does not act on the foot.Platzer 2004, p. 264
Intrinsic
On the top of the foot, the tendons ofextensor digitorum brevis
The extensor digitorum brevis muscle (sometimes EDB) is a muscle on the upper surface of the foot that helps extend digits 2 through 4.
Structure
The muscle originates from the forepart of the upper and lateral surface of the calcaneus (in front ...
and extensor hallucis brevis
The extensor hallucis brevis is a muscle on the top of the foot that helps to extend the big toe.
Structure
The extensor hallucis brevis is essentially the medial part of the extensor digitorum brevis muscle. Some anatomists have debated wheth ...
lie deep in the system of long extrinsic extensor tendons. They both arise on the calcaneus and extend into the dorsal aponeurosis
An aponeurosis (; plural: ''aponeuroses'') is a type or a variant of the deep fascia, in the form of a sheet of pearly-white fibrous tissue that attaches sheet-like muscles needing a wide area of attachment. Their primary function is to join muscl ...
of digits one to four, just beyond the penultimate joints. They act to dorsiflex the digits.Platzer 2004, p. 268 Similar to the intrinsic muscles of the hand, there are three groups of muscles in the ''sole of foot'', those of the first and last digits, and a central group:
''Muscles of the big toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''planti ...
'': the abductor hallucis stretches medially along the border of the sole, from the calcaneus to the first digit. Below its tendon, the tendons of the long flexors pass through the tarsal canal. The abductor hallucis is an abductor and a weak flexor, and also helps maintain the arch of the foot. The flexor hallucis brevis
A flexor is a muscle that flexes a joint. In anatomy, flexion (from the Latin verb ''flectere'', to bend) is a joint movement that decreases the angle between the bones that converge at the joint. For example, one’s elbow joint flexes when one ...
arises on the medial cuneiform bone and related ligaments and tendons. An important plantar flexor, it is crucial to ballet dancing. Both these muscles are inserted with two heads proximally and distally to the first metatarsophalangeal joint
The metatarsophalangeal joints (MTP joints), also informally known as toe knuckles, are the joints between the metatarsal bones of the foot and the proximal bones ( proximal phalanges) of the toes. They are condyloid joints, meaning that an el ...
. The adductor hallucis
The Adductor hallucis (Adductor obliquus hallucis) arises by two heads—oblique and transverse and is responsible for adducting the big toe. It has two heads, both are innervated by the lateral plantar nerve.
Structure Oblique head
The ''oblique ...
is part of this group, though it originally formed a separate system (see Contrahens). It has two heads, the oblique head originating obliquely across the central part of the midfoot, and the transverse head originating near the metatarsophalangeal joints of digits five to three. Both heads are inserted into the lateral sesamoid bone
In anatomy, a sesamoid bone () is a bone embedded within a tendon or a muscle. Its name is derived from the Arabic word for 'sesame seed', indicating the small size of most sesamoids. Often, these bones form in response to strain, or can be prese ...
of the first digit. The adductor hallucis acts as a tensor of the plantar arches and also adducts the big toe and might plantar flex the proximal phalanx.Platzer 2004, pp. 270–72
''Muscles of the little toe
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''plan ...
'': Stretching laterally from the calcaneus to the proximal phalanx of the fifth digit, the abductor digiti minimi form the lateral margin of the foot and are the largest of the muscles of the fifth digit. Arising from the base of the fifth metatarsal, the flexor digiti minimi is inserted together with abductor on the first phalanx. Often absent, the opponens digiti minimi
The opponens digiti minimi (opponens digiti quinti in older texts) is a muscle in the hand. It is of a triangular form, and placed immediately beneath the palmaris brevis, abductor digiti minimi and flexor digiti minimi brevis. It is one of th ...
originates near the cuboid bone and is inserted on the fifth metatarsal bone. These three muscles act to support the arch of the foot and to plantar flex the fifth digit.Platzer 2004, p. 272
''Central muscle group'': The four lumbricals arise on the medial side of the tendons of flexor digitorum longus
The flexor digitorum longus muscle is situated on the tibial side of the leg. At its origin it is thin and pointed, but it gradually increases in size as it descends. It serves to flex the second, third, fourth, and fifth toes.
Structure
The fl ...
and are inserted on the medial margins of the proximal phalanges. The quadratus plantae
The quadratus plantae (flexor accessorius) is separated from the muscles of the first layer by the lateral plantar vessels and nerve. It acts to aid in flexing the 2nd to 5th toes (offsetting the oblique pull of the flexor digitorum longus) and is ...
originates with two slips from the lateral and medial margins of the calcaneus and inserts into the lateral margin of the flexor digitorum tendon. It is also known as the flexor accessorius. The flexor digitorum brevis
The flexor digitorum brevis is a muscle which lies in the middle of the sole of the foot, immediately above the central part of the plantar aponeurosis, with which it is firmly united.
Its deep surface is separated from the lateral plantar ve ...
arises inferiorly on the calcaneus and its three tendons are inserted into the middle phalanges of digits two to four (sometimes also the fifth digit). These tendons divide before their insertions and the tendons of flexor digitorum longus pass through these divisions. Flexor digitorum brevis flexes the middle phalanges. It is occasionally absent. Between the toes, the dorsal
Dorsal (from Latin ''dorsum'' ‘back’) may refer to:
* Dorsal (anatomy), an anatomical term of location referring to the back or upper side of an organism or parts of an organism
* Dorsal, positioned on top of an aircraft's fuselage
* Dorsal co ...
and plantar interossei stretch from the metatarsals to the proximal phalanges of digits two to five. The plantar interossei adduct and the dorsal interossei abduct these digits, and are also plantar flexors at the metatarsophalangeal joints.Platzer 2004, p. 274
Clinical significance
Due to their position and function, feet are exposed to avariety
Variety may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Entertainment formats
* Variety (radio)
* Variety show, in theater and television
Films
* ''Variety'' (1925 film), a German silent film directed by Ewald Andre Dupont
* ''Variety'' (1935 film), ...
of potential infection
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable d ...
s and injuries
An injury is any physiological damage to living tissue caused by immediate physical stress. An injury can occur intentionally or unintentionally and may be caused by blunt trauma, penetrating trauma, burning, toxic exposure, asphyxiation, or ...
, including athlete's foot
Athlete's foot, known medically as ''tinea pedis'', is a common skin infection of the feet caused by a fungus. Signs and symptoms often include itching, scaling, cracking and redness. In rare cases the skin may blister. Athlete's foot fungus ...
, bunion
A bunion, also known as hallux valgus, is a deformity of the joint connecting the big toe to the foot. The big toe often bends towards the other toes and the joint becomes red and painful. The onset of bunions is typically gradual. Complicati ...
s, ingrown toenails, Morton's neuroma
Morton's neuroma is a benign neuroma of an intermetatarsal plantar nerve, most commonly of the second and third intermetatarsal spaces (between the second/third and third/fourth metatarsal heads; the first is of the big toe), which results in t ...
, plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis or plantar heel pain (PHP) is a disorder of the plantar fascia, which is the connective tissue which supports the arch of the foot. It results in pain in the heel and bottom of the foot that is usually most severe with the ...
, plantar wart
A plantar wart, or verruca vulgaris, is a wart occurring on the bottom of the foot or toes. Its color is typically similar to that of the skin. Small black dots often occur on the surface. One or more may occur in an area. They may result in pain ...
s, and stress fracture
A stress fracture is a fatigue-induced bone fracture caused by repeated stress over time. Instead of resulting from a single severe impact, stress fractures are the result of accumulated injury from repeated submaximal loading, such as running or ...
s. In addition, there are several genetic disorder
A genetic disorder is a health problem caused by one or more abnormalities in the genome. It can be caused by a mutation in a single gene (monogenic) or multiple genes (polygenic) or by a chromosomal abnormality. Although polygenic disorde ...
s that can affect the shape and function of the feet, including clubfoot
Clubfoot is a birth defect where one or both feet are rotated inward and downward. Congenital clubfoot is the most common congenital malformation of the foot with an incidence of 1 per 1000 births. In approximately 50% of cases, clubfoot aff ...
or flat feet
Flat feet (also called pes planus or fallen arches) is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Sometimes children are born ...
.
This leaves humans more vulnerable to medical problems that are caused by poor leg and foot alignments. Also, the wearing of shoes, sneakers and boots can impede proper alignment and movement within the ankle and foot. For example, high-heeled shoe
High-heeled shoes, also known as high heels, are a type of shoe with an angled sole. The heel in such shoes is raised above the ball of the foot. High heels cause the legs to appear longer, make the wearer appear taller, and accentuate th ...
s are known to throw off the natural weight balance (this can also affect the lower back). For the sake of posture, flat soles with no heels are advised.
A doctor
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
* ...
who specializes in the treatment of the feet practices podiatry
Podiatry () or podiatric medicine () is a branch of medicine devoted to the study, diagnosis, medical and surgical treatment of disorders of the foot, ankle, and leg.
A Doctor of Podiatric Medicine (DPM), or a podiatrist, is a healthcare ...
and is called a podiatrist. A pedorthist A pedorthist is a professional who has specialized training to modify footwear and employ supportive devices to address conditions which affect the feet and lower limbs. They are trained in the assessment of lower limb anatomy and biomechanics, and ...
specializes in the use and modification of footwear to treat problems related to the lower limbs.
Fractures of the foot include:
*Lisfranc fracture
A Lisfranc injury, also known as Lisfranc fracture, is an injury of the foot in which one or more of the metatarsal bones are displaced from the tarsus.
The injury is named after Jacques Lisfranc de St. Martin, a French surgeon and gynecologis ...
– in which one or all of the metatarsal
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the med ...
s are displaced from the tarsus
*Jones fracture
A Jones fracture is a broken bone in a specific part of the fifth metatarsal of the foot between the base and middle part that is known for its high rate of delayed healing or nonunion. It results in pain near the midportion of the foot on the ...
– a fracture of the fifth metatarsal
The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.
As ...
* March fracture – a fracture of the distal third of one of the metatarsals occurring because of recurrent stress
*Calcaneal fracture
A calcaneal fracture is a break of the calcaneus (heel bone). Symptoms may include pain, bruising, trouble walking, and deformity of the heel. It may be associated with breaks of the hip or back.
It usually occurs when a person lands on thei ...
*Broken toe }
A broken toe is a type of bone fracture. Symptoms include pain when the toe is touched near the break point, or compressed along its length (as if gently stubbing the toe). There may be bruising, swelling, stiffness, or displacement of the broke ...
– a fracture of a phalanx
*Cuneiform fracture – Due to the ligamentous support of the midfoot, isolated cuneiform fractures are rare.
Pronation
In anatomy,pronation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
is a rotational movement of the forearm (at the radioulnar joint) or foot (at the subtalar and talocalcaneonavicular joints). Pronation of the foot refers to how the body distributes weight as it cycles through the gait
Gait is the pattern of movement of the limbs of animals, including humans, during locomotion over a solid substrate. Most animals use a variety of gaits, selecting gait based on speed, terrain, the need to maneuver, and energetic efficiency. ...
. During the gait cycle the foot can pronate in many different ways based on rearfoot and forefoot function. Types of pronation include neutral pronation, underpronation (supination), and overpronation.
;Neutral pronation
An individual who neutrally pronates initially strikes the ground on the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus
The metatarsal bones, or metatarsus, are a group of five long bones in the foot, located between the tarsal bones of the hind- and mid-foot and the phalanges of the toes. Lacking individual names, the metatarsal bones are numbered from the med ...
, the foot will roll in a medial
Medial may refer to:
Mathematics
* Medial magma, a mathematical identity in algebra Geometry
* Medial axis, in geometry the set of all points having more than one closest point on an object's boundary
* Medial graph, another graph that re ...
direction, such that the weight is distributed evenly across the metatarsus. In this stage of the gait, the knee
In humans and other primates, the knee joins the thigh with the human leg, leg and consists of two joints: one between the femur and tibia (tibiofemoral joint), and one between the femur and patella (patellofemoral joint). It is the largest join ...
will generally, but not always, track directly over the hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''pla ...
.
This rolling inward motion as the foot progresses from heel to toe is the way that the body naturally absorbs shock. Neutral pronation is the most ideal, efficient type of gait when using a heel strike gait; in a forefoot strike, the body absorbs shock instead via flexion of the foot.
;Overpronation
As with a neutral pronator, an individual who overpronates initially strikes the ground on the lateral side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus, however, the foot will roll too far in a medial direction, such that the weight is distributed unevenly across the metatarsus, with excessive weight borne on the hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''pla ...
. In this stage of the gait, the knee will generally, but not always, track inward.
An overpronator does not absorb shock efficiently. Imagine someone jumping onto a diving board, but the board is so flimsy that when it is struck, it bends and allows the person to plunge straight down into the water instead of back into the air. Similarly, an overpronator's arches will collapse, or the ankles will roll inward (or a combination of the two) as they cycle through the gait. An individual whose bone structure involves external rotation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
at the hip
In vertebrate anatomy, hip (or "coxa"Latin ''coxa'' was used by Celsus in the sense "hip", but by Pliny the Elder in the sense "hip bone" (Diab, p 77) in medical terminology) refers to either an anatomical region or a joint.
The hip region ...
, knee, or ankle
The ankle, or the talocrural region, or the jumping bone (informal) is the area where the foot and the leg meet. The ankle includes three joints: the ankle joint proper or talocrural joint, the subtalar joint, and the inferior tibiofibular ...
will be more likely to overpronate than one whose bone structure has internal rotation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
or central alignment. An individual who overpronates tends to wear down their running shoes on the medial (inside) side of the shoe toward the toe area.
When choosing a running or walking shoe, a person with overpronation can choose shoes that have good inside support—usually by strong material at the inside sole and arch of the shoe. It is usually visible. The inside support area is marked by strong greyish material to support the weight when a person lands on the outside foot and then roll onto the inside foot.
;Underpronation (supination)
 An individual who underpronates also initially strikes the ground on the lateral side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus, the foot will not roll far enough in a medial direction. The weight is distributed unevenly across the metatarsus, with excessive weight borne on the
An individual who underpronates also initially strikes the ground on the lateral side of the heel. As the individual transfers weight from the heel to the metatarsus, the foot will not roll far enough in a medial direction. The weight is distributed unevenly across the metatarsus, with excessive weight borne on the fifth metatarsal
The fifth metatarsal bone is a long bone in the foot, and is palpable along the distal outer edges of the feet. It is the second smallest of the five metatarsal bones. The fifth metatarsal is analogous to the fifth metacarpal bone in the hand.
As ...
, toward the lateral side of the foot. In this stage of the gait, the knee will generally, but not always, track laterally of the hallux
Toes are the digits (fingers) of the foot of a tetrapod. Animal species such as cats that walk on their toes are described as being ''digitigrade''. Humans, and other animals that walk on the soles of their feet, are described as being ''pla ...
.
Like an overpronator, an underpronator does not absorb shock efficiently – but for the opposite reason. The underpronated foot is like a diving board that, instead of failing to spring someone in the air because it is too flimsy, fails to do so because it is too rigid. There is virtually no give. An underpronator's arches or ankles don't experience much motion as they cycle through the gait. An individual whose bone structure involves internal rotation
Motion, the process of movement, is described using specific anatomical terms. Motion includes movement of organs, joints, limbs, and specific sections of the body. The terminology used describes this motion according to its direction relativ ...
at the hip, knee, or ankle will be more likely to underpronate than one whose bone structure has external rotation or central alignment. Usually – but not always – those who are bow-legged
Genu varum (also called bow-leggedness, bandiness, bandy-leg, and tibia vara) is a varus deformity marked by (outward) bowing at the knee, which means that the lower leg is angled inward ( medially) in relation to the thigh's axis, giving the ...
tend to underpronate. An individual who underpronates tends to wear down their running shoes on the lateral (outside) side of the shoe toward the rear of the shoe in the heel area.
Society and culture
Humans usually wearshoe
A shoe is an item of footwear intended to protect and comfort the Foot, human foot. They are often worn with a sock. Shoes are also used as an item of decoration and fashion. The design of shoes has varied enormously through time and from cult ...
s or similar footwear for protection from hazards when walking outside. There are a number of contexts where it is considered inappropriate to wear shoes. Some people consider it rude to wear shoes into a house and a Māori
Māori or Maori can refer to:
Relating to the Māori people
* Māori people of New Zealand, or members of that group
* Māori language, the language of the Māori people of New Zealand
* Māori culture
* Cook Islanders, the Māori people of the Co ...
Marae
A ' (in New Zealand Māori, Cook Islands Māori, Tahitian), ' (in Tongan), ' (in Marquesan) or ' (in Samoan) is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term ...
should only be entered with bare feet.
Foot fetishism
Foot fetishism, also known as foot partialism or podophilia, is a pronounced sexual interest in feet. It is the most common form of sexual fetishism for otherwise non-sexual objects or body parts.
Characteristics and related fetishes
Foot f ...
is the most common sexual fetish.
Other animals
Apaw
A paw is the soft foot-like part of a mammal, generally a quadruped, that has claws.
Common characteristics
The paw is characterised by thin, pigmented, keratinised, hairless epidermis covering subcutaneous collagenous and adipose tissue, ...
is the soft foot of a mammal, generally a quadruped, that has claws or nails (e.g., a cat or dog's paw). A hard foot is called a hoof
The hoof (plural: hooves) is the tip of a toe of an ungulate mammal, which is covered and strengthened with a thick and horny keratin covering. Artiodactyls are even-toed ungulates, species whose feet have an even number of digits, yet the ru ...
. Depending on style of locomotion, animals can be classified as plantigrade
151px, Portion of a human skeleton, showing plantigrade habit
In terrestrial animals, plantigrade locomotion means walking with the toes and metatarsals flat on the ground. It is one of three forms of locomotion adopted by terrestrial mammals. ...
(sole walking), digitigrade
In terrestrial vertebrates, digitigrade () locomotion is walking or running on the toes (from the Latin ''digitus'', 'finger', and ''gradior'', 'walk'). A digitigrade animal is one that stands or walks with its toes (metatarsals) touching the groun ...
(toe walking), or unguligrade
Ungulates ( ) are members of the diverse clade Ungulata which primarily consists of large mammals with hooves. These include odd-toed ungulates such as horses, rhinoceroses, and tapirs; and even-toed ungulates such as cattle, pigs, giraffes, c ...
(nail walking).
The metatarsals are the bones that make up the main part of the foot in humans, and part of the leg in large animals or paw in smaller animals. The number of metatarsals are directly related to the mode of locomotion with many larger animals having their digits reduced to two (elk
The elk (''Cervus canadensis''), also known as the wapiti, is one of the largest species within the deer family, Cervidae, and one of the largest terrestrial mammals in its native range of North America and Central and East Asia. The com ...
, cow
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
, sheep
Sheep or domestic sheep (''Ovis aries'') are domesticated, ruminant mammals typically kept as livestock. Although the term ''sheep'' can apply to other species in the genus ''Ovis'', in everyday usage it almost always refers to domesticated sh ...
) or one (horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million ...
). The metatarsal bones of feet and paws are tightly grouped compared to, most notably, the human hand where the thumb metacarpal diverges from the rest of the metacarpus.France 2008, p. 537
Metaphorical and cultural usage
The word "foot" is used to refer to a "...linear measure was in Old English (the exact length has varied over time), this being considered the length of a man's foot; a unit of measure used widely and anciently. In this sense the plural is often foot. The current inch and foot are implied from measurements in 12c." The word "foot" also has a musical meaning; a "...metrical foot (late Old English, translating Latin pes, Greek pous in the same sense) is commonly taken to represent one rise and one fall of a foot: keeping time according to some, dancing according to others." The word "foot" was used in Middle English to mean "a person" (c. 1200). The expression "...to put one's best foot foremost first recorded 1849 (Shakespeare has the better foot before, 1596)". The expression to "...put one's foot in (one's) mouth "say something stupid" was first used in 1942. The expression "put (one's) foot in something" meaning to "make a mess of it" was used in 1823. The word "footloose" was first used in the 1690s, meaning "free to move the feet, unshackled"; the more "figurative sense of "free to act as one pleases" was first used in 1873. Like "footloose", "flat-footed" at first had its obvious literal meaning (in 1600, it meant "with flat feet") but by 1912 it meant "unprepared" (U.S. baseball slang).See also
*Ball (foot)
The ball of the foot is the padded portion of the sole between the toes and the arch, underneath the heads of the metatarsal bones.
In comparative foot morphology, the ball is most analogous to the metacarpal (forepaw) or metatarsal (hindpa ...
*Barefoot
Barefoot is the state of not wearing any footwear.
There are health benefits and some risks associated with going barefoot. Shoes, while they offer protection, can limit the flexibility, strength, and mobility of the foot and can lead to ...
*Comparison of orthotics
Comparison of orthotics stem from podiatrists having molded custom orthotics to address patients' foot malformations. Over the years they have developed numerous means to create the basis for their molds, plaster casts, foam box impressions, or thr ...
*Flat feet
Flat feet (also called pes planus or fallen arches) is a postural deformity in which the arches of the foot collapse, with the entire sole of the foot coming into complete or near-complete contact with the ground. Sometimes children are born ...
*Foot binding
Foot binding, or footbinding, was the Chinese custom of breaking and tightly binding the feet of young girls in order to change their shape and size. Feet altered by footbinding were known as lotus feet, and the shoes made for these feet were kno ...
*Foot fetishism
Foot fetishism, also known as foot partialism or podophilia, is a pronounced sexual interest in feet. It is the most common form of sexual fetishism for otherwise non-sexual objects or body parts.
Characteristics and related fetishes
Foot f ...
* Foot gymnastics
*Gait analysis
Gait analysis is the systematic study of animal locomotion, more specifically the study of human motion, using the eye and the brain of observers, augmented by instrumentation for measuring body movements, body mechanics, and the activity of the ...
* Heel
* Pedobarography (foot pressure analysis)
*Pes cavus
Pes cavus, also known as high arch, is a human foot type in which the sole of the foot is distinctly hollow when bearing weight. That is, there is a fixed plantar flexion of the foot. A high arch is the opposite of a flat foot and is somewha ...
*Runner's toe
A subungual hematoma is a collection of blood (hematoma) underneath a toenail or fingernail. It can be extremely painful for an injury of its size, although otherwise it is not a serious medical condition.
Nature
A laceration of the nail bed c ...
, repetitive injury seen in runners
*Sole (foot)
The sole is the bottom of the foot.
In humans the sole of the foot is anatomically referred to as the plantar aspect.
Structure
The glabrous skin on the sole of the foot lacks the hair and pigmentation found elsewhere on the body, and it ...
*Squatting position
Squatting is a versatile posture where the weight of the body is on the feet but the knees and hips are bent. In contrast, sitting involves taking the weight of the body, at least in part, on the buttocks against the ground or a horizontal object ...
References
Bibliography
* * * *External links
* {{Authority control Human body