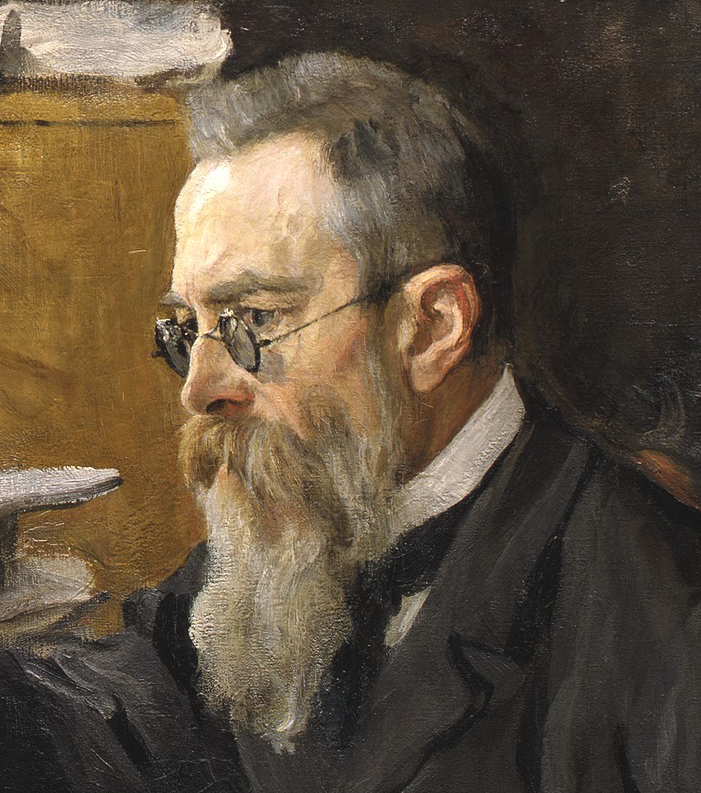
Igor Stravinsky (1962) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and United States citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of the 20th century and a pivotal figure in
 Stravinsky was born on 17 June 1882 in the town of Oranienbaum (now Lomonosov), on the southern coast of the
Stravinsky was born on 17 June 1882 in the town of Oranienbaum (now Lomonosov), on the southern coast of the
 In 1902, Stravinsky met Vladimir Rimsky-Korsakov, a fellow student at the University of Saint Petersburg and the youngest son of
In 1902, Stravinsky met Vladimir Rimsky-Korsakov, a fellow student at the University of Saint Petersburg and the youngest son of
 By 1909, Stravinsky had composed two more pieces, ''
By 1909, Stravinsky had composed two more pieces, '' In April 1914, Stravinsky and his family returned to Clarens. Stravinsky was ineligible for military service in the
In April 1914, Stravinsky and his family returned to Clarens. Stravinsky was ineligible for military service in the
 In May 1921, Stravinsky and his family moved to
In May 1921, Stravinsky and his family moved to
modernist music
In music, modernism is an aesthetic stance underlying the period of change and development in musical language that occurred around the turn of the 20th century, a period of diverse reactions in challenging and reinterpreting older categories o ...
.
Stravinsky's father was an established bass opera singer, and Stravinsky grew up taking piano and music theory lessons. While studying law at the University of Saint Petersburg
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the ...
, he met Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
and studied under him until Rimsky-Korsakov's death in 1908. Stravinsky met the impresario
An impresario (from the Italian ''impresa'', "an enterprise or undertaking") is a person who organizes and often finances concerts, plays, or operas, performing a role in stage arts that is similar to that of a film or television producer.
Hist ...
Sergei Diaghilev
Sergei Pavlovich Diaghilev ( ; rus, Серге́й Па́влович Дя́гилев, , sʲɪˈrɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪdʑ ˈdʲæɡʲɪlʲɪf; 19 August 1929), usually referred to outside Russia as Serge Diaghilev, was a Russian art critic, pat ...
soon after, who commissioned Stravinsky to write three ballets: ''The Firebird
''The Firebird'' (french: L'Oiseau de feu, link=no; russian: Жар-птица, Zhar-ptitsa, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral concert work by the Russian composer Igor Stravinsky. It was written for the 1910 Paris season of Sergei Diaghilev's ...
'' (1910), ''Petrushka
Petrushka ( rus, Петру́шка, p=pʲɪtˈruʂkə, a=Ru-петрушка.ogg) is a stock character of Russian folk puppetry. Italian puppeteers introduced it in the first third of the 19th century. While most core characters came from Italy ...
'' (1911), and ''The Rite of Spring
''The Rite of Spring''. Full name: ''The Rite of Spring: Pictures from Pagan Russia in Two Parts'' (french: Le Sacre du printemps: tableaux de la Russie païenne en deux parties) (french: Le Sacre du printemps, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral ...
'' (1913), the last of which brought him international fame after the near-riot at the premiere, and changed the way composers understood rhythmic structure.
Stravinsky's compositional career is divided into three periods: his Russian period (1913–1920), his neoclassical period (1920–1951), and his serial period (1954–1968). Stravinsky's Russian period was characterised by influence from Russian styles and folklore. '' Renard'' (1916) and ''Les noces
''Les Noces'' (French for The Wedding; russian: Свадебка, ''Svadebka'') is a ballet and orchestral concert work composed by Igor Stravinsky for percussion, pianists, chorus, and vocal soloists. The composer gave it the descriptive title " ...
'' (1923) were based on Russian folk poetry, and works like ''L'Histoire du soldat
' (''The Soldier's Tale'') is a theatrical work "to be read, played, and danced" () by three actors and one or several dancers, accompanied by a septet of instruments. Conceived by Igor Stravinsky and Swiss writer C. F. Ramuz, the piece was bas ...
'' blended these folktales with popular musical structures, like the tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
, waltz
The waltz ( ), meaning "to roll or revolve") is a ballroom and folk dance, normally in triple ( time), performed primarily in closed position.
History
There are many references to a sliding or gliding dance that would evolve into the wa ...
, rag
Rag, rags, RAG or The Rag may refer to:
Common uses
* Rag, a piece of old cloth
* Rags, tattered clothes
* Rag (newspaper), a publication engaging in tabloid journalism
* Rag paper, or cotton paper
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Rags'' (1915 ...
, and chorale
Chorale is the name of several related musical forms originating in the music genre of the Lutheran chorale:
* Hymn tune of a Lutheran hymn (e.g. the melody of "Wachet auf, ruft uns die Stimme"), or a tune in a similar format (e.g. one of the t ...
. His neoclassical period exhibited themes and techniques from the classical period, like the use of the sonata form in his Octet
Octet may refer to:
Music
* Octet (music), ensemble consisting of eight instruments or voices, or composition written for such an ensemble
** String octet, a piece of music written for eight string instruments
*** Octet (Mendelssohn), 1825 compos ...
(1923) and use of Greek mythological
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the origin and nature of the world, the lives and activities of d ...
themes in works like ''Apollon musagète
''Apollo'' (originally ''Apollon musagète'' and variously known as ''Apollo musagetes'', ''Apolo Musageta'', and ''Apollo, Leader of the Muses'') is a neoclassical ballet in two ''tableaux'' composed between 1927 and 1928 by Igor Stravinsky. ...
'' (1927), ''Oedipus rex
''Oedipus Rex'', also known by its Greek title, ''Oedipus Tyrannus'' ( grc, Οἰδίπους Τύραννος, ), or ''Oedipus the King'', is an Athenian tragedy by Sophocles that was first performed around 429 BC. Originally, to the ancient Gr ...
'' (1927), and ''Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
'' (1935). In his serial period, Stravinsky turned towards compositional techniques from the Second Viennese School
The Second Viennese School (german: Zweite Wiener Schule, Neue Wiener Schule) was the group of composers that comprised Arnold Schoenberg and his pupils, particularly Alban Berg and Anton Webern, and close associates in early 20th-century Vienna. ...
like Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (, ; ; 13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian-American composer, music theorist, teacher, writer, and painter. He is widely considered one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was as ...
's twelve-tone technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition first devised by Austrian composer Josef Matthias Hauer, who published his "law o ...
. ''In Memoriam Dylan Thomas'' (1954) was the first of his compositions to be fully based on the technique, and ''Canticum Sacrum
''Canticum Sacrum ad Honorem Sancti Marci Nominis'' is a 17-minute choral-orchestral piece composed in 1955 by Igor Stravinsky (1882–1971) in tribute "To the City of Venice, in praise of its Patron Saint, the Blessed Mark, Apostle." The piec ...
'' (1956) was his first to be based on a tone row
In music, a tone row or note row (german: Reihe or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets ar ...
. Stravinsky's last major work was the ''Requiem Canticles
''Requiem Canticles'' is a 15-minute composition by Igor Stravinsky, for contralto and bass soli, chorus, and orchestra. Stravinsky completed the work in 1966, and it received its first performance that same year.
The work is a partial setting o ...
'' (1966), which was performed at his funeral.
While some composers and academics of the time disliked the avant-garde nature of Stravinsky's music, particularly ''The Rite of Spring'', later writers recognized his importance to the development of modernist music. Stravinsky's revolutions of rhythm and modernism influenced composers like Aaron Copland
Aaron Copland (, ; November 14, 1900December 2, 1990) was an American composer, composition teacher, writer, and later a conductor of his own and other American music. Copland was referred to by his peers and critics as "the Dean of American Com ...
, Philip Glass
Philip Glass (born January 31, 1937) is an American composer and pianist. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential composers of the late 20th century. Glass's work has been associated with minimal music, minimalism, being built up fr ...
, Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as H ...
, and Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 1925 – 5 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war Western classical music.
Born in Mont ...
, all of whom "felt impelled to face the challenges set by 'The Rite of Spring''" as George Benjamin wrote in ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
''. In 1998, ''Time'' magazine named Stravinsky one of the 100 most influential people
''Time'' 100 (often stylized as ''TIME'' 100) is an annual listicle of the 100 most influential people in the world, assembled by the American news magazine ''Time''. First published in 1999 as the result of a debate among American academics, po ...
of the century. Stravinsky died of pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
on 6 April 1971 in New York City.
Biography
Early life, 1882–1901
 Stravinsky was born on 17 June 1882 in the town of Oranienbaum (now Lomonosov), on the southern coast of the
Stravinsky was born on 17 June 1882 in the town of Oranienbaum (now Lomonosov), on the southern coast of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and E ...
, west of Saint Petersburg. His father, Fyodor Ignatievich Stravinsky, was an established bass
Bass or Basses may refer to:
Fish
* Bass (fish), various saltwater and freshwater species
Music
* Bass (sound), describing low-frequency sound or one of several instruments in the bass range:
** Bass (instrument), including:
** Acoustic bass gui ...
opera singer in the Kiev Opera
The Kyiv Opera group was formally established in the summer of 1867, and is the third oldest in Ukraine, after Odessa Opera and Lviv Opera.
The Kyiv Opera Company perform at the National Opera House of Ukraine named after Taras Shevchenko in ...
and the Mariinsky Theatre
The Mariinsky Theatre ( rus, Мариинский театр, Mariinskiy teatr, also transcribed as Maryinsky or Mariyinsky) is a historic theatre of opera and ballet in Saint Petersburg, Russia. Opened in 1860, it became the preeminent music th ...
in Saint Petersburg and his mother, Anna Kirillovna Stravinskaya (''née'' Kholodovskaya; 1854–1939), a native of Kiev, was one of four daughters of a high-ranking official in the Kiev Ministry of Estates. Igor was the third of their four sons; his brothers were Roman, Yury, and Gury. The Stravinsky family was of Polish and Russian heritage, descended "from a long line of Polish grandees, senators and landowners". It is traceable to the 17th and 18th centuries to the bearers of the Sulima and Strawiński coat of arms. The original family surname was Sulima-Strawiński; the name "Stravinsky" originated from the word "Strava", one of the variants of the Streva river in Lithuania.
On 10 August 1882, Stravinsky was baptised
Baptism (from grc-x-koine, βάπτισμα, váptisma) is a form of ritual purification—a characteristic of many religions throughout time and geography. In Christianity, it is a Christian sacrament of initiation and adoption, almost inv ...
at Nikolsky Cathedral in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. Stravinsky's first school was the Second Saint Petersburg Gymnasium, where he stayed until his mid-teens. Then, he moved to Gourevitch Gymnasium, a private school, where he studied history, mathematics, and languages (Latin, Greek, French, German, Slavonic, and his native Russian). Stravinsky expressed his general distaste for schooling and recalled being a lonely pupil: "I never came across anyone who had any real attraction for me."
At around eight years old, he attended a performance of Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky's ballet '' The Sleeping Beauty'' at the Mariinsky Theatre, which began a lifelong interest in ballets and Tchaikovsky
Pyotr Ilyich Tchaikovsky , group=n ( ; 7 May 1840 – 6 November 1893) was a Russian composer of the Romantic period. He was the first Russian composer whose music would make a lasting impression internationally. He wrote some of the most popu ...
. Stravinsky took to music at an early age and began regular piano lessons at age nine, followed by tuition in music theory
Music theory is the study of the practices and possibilities of music. ''The Oxford Companion to Music'' describes three interrelated uses of the term "music theory". The first is the "rudiments", that are needed to understand music notation (ke ...
and composition. By age fourteen, Stravinsky mastered Mendelssohn
Jakob Ludwig Felix Mendelssohn Bartholdy (3 February 18094 November 1847), born and widely known as Felix Mendelssohn, was a German composer, pianist, organist and conductor of the early Romantic music, Romantic period. Mendelssohn's compositi ...
's Piano Concerto No. 1, and at age fifteen finished a piano reduction of a string quartet by Alexander Glazunov
Alexander Konstantinovich Glazunov; ger, Glasunow (, 10 August 1865 – 21 March 1936) was a Russian composer, music teacher, and conductor of the late Russian Romantic period. He was director of the Saint Petersburg Conservatory between 1905 ...
, who reportedly considered Stravinsky unmusical and thought little of his skills.
Education and first compositions, 1901–1909
Despite Stravinsky's enthusiasm and ability in music, his parents expected him to study law. In 1901, he enrolled at theUniversity of Saint Petersburg
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the ...
, studying criminal law and legal philosophy, but attendance at lectures was optional and he estimated that he turned up to fewer than fifty classes in his four years of study.
 In 1902, Stravinsky met Vladimir Rimsky-Korsakov, a fellow student at the University of Saint Petersburg and the youngest son of
In 1902, Stravinsky met Vladimir Rimsky-Korsakov, a fellow student at the University of Saint Petersburg and the youngest son of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov
Nikolai Andreyevich Rimsky-Korsakov . At the time, his name was spelled Николай Андреевичъ Римскій-Корсаковъ. la, Nicolaus Andreae filius Rimskij-Korsakov. The composer romanized his name as ''Nicolas Rimsk ...
. Nikolai at that time was arguably the leading Russian composer, and he was a professor at Saint Petersburg Conservatory
The N. A. Rimsky-Korsakov Saint Petersburg State Conservatory (russian: Санкт-Петербургская государственная консерватория имени Н. А. Римского-Корсакова) (formerly known as th ...
. Stravinsky wished to meet him to discuss his musical aspirations. He spent the summer of 1902 with Rimsky-Korsakov and his family in Heidelberg
Heidelberg (; Palatine German language, Palatine German: ''Heidlberg'') is a city in the States of Germany, German state of Baden-Württemberg, situated on the river Neckar in south-west Germany. As of the 2016 census, its population was 159,914 ...
, Germany. Rimsky-Korsakov suggested to Stravinsky that he should not enter the Saint Petersburg Conservatory but continue private lessons in theory.
By the time of his father's death in 1902, Stravinsky was spending more time studying music than law. His decision to pursue music full time was helped when the university was closed for two months in 1905 in the aftermath of Bloody Sunday
Bloody Sunday may refer to:
Historical events Canada
* Bloody Sunday (1923), a day of police violence during a steelworkers' strike for union recognition in Sydney, Cape Breton Island, Nova Scotia
* Bloody Sunday (1938), police violence agai ...
, which prevented him from taking his final law exams. In April 1906, Stravinsky received a half-course diploma and concentrated on music thereafter. In 1905, he had begun studying with Rimsky-Korsakov twice a week and came to regard him as a second father. These lessons continued until Rimsky-Korsakov's death in 1908. Stravinsky completed his first composition during this time, the Symphony in E-flat, catalogued as Opus
''Opus'' (pl. ''opera'') is a Latin word meaning "work". Italian equivalents are ''opera'' (singular) and ''opere'' (pl.).
Opus or OPUS may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Music
* Opus number, (abbr. Op.) specifying order of (usually) publicatio ...
1. In 1908, soon after Rimsky-Korsakov's death, Stravinsky composed '' Funeral Song'', Op. 5, which was performed once and then considered lost until its re-discovery in 2015.
In August 1905, Stravinsky became engaged to his first cousin, Yekaterina Gavrilovna Nosenko. In spite of the Orthodox Church
Orthodox Church may refer to:
* Eastern Orthodox Church
* Oriental Orthodox Churches
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church
* Orthodox Presbyterian Church of New Zealand
* State church of the Roman Empire
* True Orthodox church
See also
* Orthodox (dis ...
's opposition to marriage between first cousins, the couple married on 23 January 1906. They lived in the family's residence at 66 Krukov Canal in Saint Petersburg before they moved into a new home in Ustilug
Ustylúh (, , yi, אוסטילע ''Ustile'') is a town in Volodymyr Raion, Volyn Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the east side of the Ukrainian-Polish border, and 8 miles (13 km) west of Volodymyr (city), Volodymyr. Population:
Igor Str ...
, which Stravinsky designed and built, chosen because Stravinsky had spent many summers there as a child with his father-in-law. Stravinsky worked on many of his early compositions there, including ''Funeral Song'', the revision of ''Feu d'artifice
''Feu d'artifice'', Op. 4 (''Fireworks'', russian: Фейерверк, ) is a composition by Igor Stravinsky, written in 1908 and described by the composer as a "short orchestral fantasy." It usually takes less than four minutes to perform.
C ...
'', ''The Nightingale
The common nightingale is a songbird found in Eurasia.
Nightingale may also refer to:
Birds
* Thrush nightingale, a songbird found in Eurasia
* Red-billed leiothrix, a songbird of the Indian Subcontinent
Literature
* "Nightingale" (short sto ...
'', and some parts of ''The Rite of Spring
''The Rite of Spring''. Full name: ''The Rite of Spring: Pictures from Pagan Russia in Two Parts'' (french: Le Sacre du printemps: tableaux de la Russie païenne en deux parties) (french: Le Sacre du printemps, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral ...
''. It is now a museum with documents, letters, and photographs on display, and an annual Stravinsky Festival takes place in the nearby town of Lutsk
Lutsk ( uk, Луцьк, translit=Lutsk}, ; pl, Łuck ; yi, לוצק, Lutzk) is a city on the Styr River in northwestern Ukraine. It is the administrative center of the Volyn Oblast (province) and the administrative center of the surrounding Luts ...
. The couple had two children, Fyodor
Fyodor, Fedor (russian: Фёдор) or Feodor is the Russian form of the name "Theodore" meaning “God’s Gift”. Fedora () is the feminine form. Fyodor and Fedor are two English transliterations of the same Russian name.
It may refer to:
Giv ...
and Ludmila, who were born in 1907 and 1908, respectively.
Ballets for Diaghilev and international fame, 1909–1920
 By 1909, Stravinsky had composed two more pieces, ''
By 1909, Stravinsky had composed two more pieces, ''Scherzo fantastique
''Scherzo fantastique'', op. 3, composed in 1908, is the second purely orchestral work by Igor Stravinsky (preceded by the Symphony in E-flat (Stravinsky), Symphony in E-flat op.1). Despite the composer's later description of the work as "a piece ...
'', Op. 3, and ''Feu d'artifice
''Feu d'artifice'', Op. 4 (''Fireworks'', russian: Фейерверк, ) is a composition by Igor Stravinsky, written in 1908 and described by the composer as a "short orchestral fantasy." It usually takes less than four minutes to perform.
C ...
'' (''Fireworks''), Op. 4. In February of that year, both were performed in Saint Petersburg at a concert that marked a turning point in Stravinsky's career. In the audience was Sergei Diaghilev
Sergei Pavlovich Diaghilev ( ; rus, Серге́й Па́влович Дя́гилев, , sʲɪˈrɡʲej ˈpavləvʲɪdʑ ˈdʲæɡʲɪlʲɪf; 19 August 1929), usually referred to outside Russia as Serge Diaghilev, was a Russian art critic, pat ...
, a Russian impresario
An impresario (from the Italian ''impresa'', "an enterprise or undertaking") is a person who organizes and often finances concerts, plays, or operas, performing a role in stage arts that is similar to that of a film or television producer.
Hist ...
and owner of the Ballets Russes
The Ballets Russes () was an itinerant ballet company begun in Paris that performed between 1909 and 1929 throughout Europe and on tours to North and South America. The company never performed in Russia, where the Revolution disrupted society. A ...
who was struck with Stravinsky's compositions. He commissioned Stravinsky to write some orchestrations for the 1909 ballet season, which were finished by April of that year. While planning for the 1910 ballet season, Diaghilev wished to stage a new ballet from fresh talent that was based on the Russian fairytale of the Firebird
Firebird and fire bird may refer to:
Mythical birds
* Phoenix (mythology), sacred firebird found in the mythologies of many cultures
* Bennu, Egyptian firebird
* Huma bird, Persian firebird
* Firebird (Slavic folklore)
Bird species
''Various spe ...
. After Anatoly Lyadov
Anatoly Konstantinovich Lyadov (russian: Анато́лий Константи́нович Ля́дов; ) was a Russian composer, teacher, and conductor (music), conductor.
Biography
Lyadov was born in 1855 in Saint Petersburg, St. Petersbur ...
was given the task of composing the score, he informed Diaghilev that he needed about one year to complete it. Diaghilev then asked the 28-year-old Stravinsky, who had already begun work on the score in anticipation of the commission. At about 50 minutes in length, ''The Firebird
''The Firebird'' (french: L'Oiseau de feu, link=no; russian: Жар-птица, Zhar-ptitsa, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral concert work by the Russian composer Igor Stravinsky. It was written for the 1910 Paris season of Sergei Diaghilev's ...
'' was revised by Stravinsky into concert suites in 1919 and 1945.
''The Firebird'' premiered at the Opera de Paris
The Paris Opera (, ) is the primary opera and ballet company of France. It was founded in 1669 by Louis XIV as the , and shortly thereafter was placed under the leadership of Jean-Baptiste Lully and officially renamed the , but continued to be ...
on 25 June 1910 to widespread critical acclaim and Stravinsky became an overnight sensation. As his wife was pregnant, the Stravinskys spent the summer in La Baule
La Baule-Escoublac (; br, Ar Baol-Skoubleg, ), commonly referred to as La Baule, is a communes of France, commune in the Loire-Atlantique departments of France, department, Pays de la Loire, western France.
A century-old seaside resort in southe ...
in western France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
. In September, they moved to Clarens, Switzerland, where their second son, Soulima, was born. The family would spend their summers in Russia and winters in Switzerland until 1914. Diaghilev commissioned Stravinsky to score a second ballet for the 1911 Paris season. The result was ''Petrushka
Petrushka ( rus, Петру́шка, p=pʲɪtˈruʂkə, a=Ru-петрушка.ogg) is a stock character of Russian folk puppetry. Italian puppeteers introduced it in the first third of the 19th century. While most core characters came from Italy ...
'', based on the Russian folk tale featuring the titular character
The title character in a narrative work is one who is named or referred to in the title of the work. In a performed work such as a play or film, the performer who plays the title character is said to have the title role of the piece. The title of ...
, a puppet, who falls in love with another, a ballerina. Though it failed to capture the immediate reception that ''The Firebird'' had following its premiere at Théâtre du Châtelet
The Théâtre du Châtelet () is a theatre and opera house, located in the place du Châtelet in the 1st arrondissement of Paris, France.
One of two theatres (the other being the Théâtre de la Ville) built on the site of a ''châtelet'', a s ...
in June 1911, the production continued Stravinsky's success.
It was Stravinsky's third ballet for Diaghilev, ''The Rite of Spring
''The Rite of Spring''. Full name: ''The Rite of Spring: Pictures from Pagan Russia in Two Parts'' (french: Le Sacre du printemps: tableaux de la Russie païenne en deux parties) (french: Le Sacre du printemps, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral ...
'', that caused a sensation among critics, fellow composers, and concertgoers. Based on an idea thought up by Stravinsky while composing ''Firebird'', the production features a series of primitive pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. ...
rituals celebrating the advent of spring. Stravinsky's score contained many novel features for its time, including experiments in tonality, metre, rhythm, stress and dissonance. The radical nature of the music and choreography caused a near-riot at its premiere at the Théâtre des Champs-Élysées
The Théâtre des Champs-Élysées () is an entertainment venue standing at 15 avenue Montaigne in Paris. It is situated near Avenue des Champs-Élysées, from which it takes its name. Its eponymous main hall may seat up to 1,905 people, while th ...
on 29 May 1913.
Shortly after the premiere, Stravinsky contracted typhoid
Typhoid fever, also known as typhoid, is a disease caused by '' Salmonella'' serotype Typhi bacteria. Symptoms vary from mild to severe, and usually begin six to 30 days after exposure. Often there is a gradual onset of a high fever over several ...
from eating bad oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not al ...
s and he was confined to a Paris nursing home. He left in July 1913 and returned to Ustilug. For the rest of the summer he focused on his first opera, ''The Nightingale
The common nightingale is a songbird found in Eurasia.
Nightingale may also refer to:
Birds
* Thrush nightingale, a songbird found in Eurasia
* Red-billed leiothrix, a songbird of the Indian Subcontinent
Literature
* "Nightingale" (short sto ...
'', based on a story
''A Story'' is an album by Yoko Ono, recorded in 1974, during the "lost weekend" sessions in which John Lennon produced ''Walls and Bridges''. It was unreleased until the 1992 box set ''Onobox'', which featured material from ''A Story'' on dis ...
by Hans Christian Andersen
Hans Christian Andersen ( , ; 2 April 1805 – 4 August 1875) was a Danish author. Although a prolific writer of plays, travelogues, novels, and poems, he is best remembered for his literary fairy tales.
Andersen's fairy tales, consisti ...
, which Stravinsky had started in 1908. On 15 January 1914, Stravinsky and Nosenko had their fourth child, Marie Milène (or Maria Milena). After her delivery, Nosenko was discovered to have tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
and was committed to a sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal, make healthy'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, are antiquated names for specialised hospitals, for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often ...
in Leysin
Leysin is a municipality of the canton of Vaud in the Aigle district of Switzerland. It is first mentioned around 1231–32 as ''Leissins'', in 1352 as ''Leisins''.
Located in the Vaud Alps, Leysin is a sunny alpine resort village at the easter ...
in the Alps. Stravinsky took up residence nearby, where he completed ''The Nightingale''. The work premiered in Paris in May 1914, after the Moscow Free Theatre had commissioned the piece for 10,000 roubles
The ruble (American English) or rouble (Commonwealth English) (; rus, рубль, p=rublʲ) is the currency unit of Belarus and Russia. Historically, it was the currency of the Russian Empire and of the Soviet Union.
, currencies named ''rub ...
but soon became bankrupt. Diaghilev agreed that the Ballets Russes to stage it. The opera had only lukewarm success with the public and the critics, apparently because its delicacy did not meet their expectations following the tumultuous ''Rite of Spring''. However, composers including Maurice Ravel
Joseph Maurice Ravel (7 March 1875 – 28 December 1937) was a French composer, pianist and conductor. He is often associated with Impressionism along with his elder contemporary Claude Debussy, although both composers rejected the term. In ...
, Béla Bartók
Béla Viktor János Bartók (; ; 25 March 1881 – 26 September 1945) was a Hungarian composer, pianist, and ethnomusicologist. He is considered one of the most important composers of the 20th century; he and Franz Liszt are regarded as H ...
, and Reynaldo Hahn
Reynaldo Hahn (; 9 August 1874 – 28 January 1947) was a Venezuelan-born French composer, conductor, music critic, and singer. He is best known for his songs – ''mélodies'' – of which he wrote more than 100.
Hahn was born in Caracas b ...
found much to admire in the score's craftsmanship, even claiming to detect the influence of Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (, ; ; 13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian-American composer, music theorist, teacher, writer, and painter. He is widely considered one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was as ...
.
 In April 1914, Stravinsky and his family returned to Clarens. Stravinsky was ineligible for military service in the
In April 1914, Stravinsky and his family returned to Clarens. Stravinsky was ineligible for military service in the World War
A world war is an international conflict which involves all or most of the world's major powers. Conventionally, the term is reserved for two major international conflicts that occurred during the first half of the 20th century, World WarI (1914 ...
due to his history of typhoid. Stravinsky managed a short visit to Ustilug to retrieve personal items just before borders were closed. In June 1915, he and his family moved from Clarens to Morges
Morges (; la, Morgiis, plural, probably ablative, else dative; frp, Môrges) is a municipality in the Swiss canton of Vaud and the seat of the district of Morges. It is located on Lake Geneva.
History
Morges is first mentioned in 1288 as ' ...
, a town six miles from Lausanne on the shore of Lake Geneva
, image = Lake Geneva by Sentinel-2.jpg
, caption = Satellite image
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = Switzerland, France
, coords =
, lake_type = Glacial lak ...
. The family lived there (at three different addresses), until 1920. In December 1915, Stravinsky made his conducting debut at two concerts in aid of the Red Cross
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a Humanitarianism, humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million Volunteering, volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure re ...
with ''The Firebird''. The war and subsequent Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution was a period of Political revolution (Trotskyism), political and social revolution that took place in the former Russian Empire which began during the First World War. This period saw Russia abolish its monarchy and ad ...
in 1917 made it impossible for Stravinsky to return to his homeland.
Stravinsky began to struggle financially in the late 1910s. When Russia (and its successor, the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
) did not adhere to the Berne Convention
The Berne Convention for the Protection of Literary and Artistic Works, usually known as the Berne Convention, was an international assembly held in 1886 in the Swiss city of Bern by ten European countries with the goal to agree on a set of leg ...
and the aftermath of World War I
The aftermath of World War I saw drastic political, cultural, economic, and social change across Eurasia, Africa, and even in areas outside those that were directly involved. Four empires collapsed due to the war, old countries were abolished, ne ...
left countries in ruin, royalties
A royalty payment is a payment made by one party to another that owns a particular asset, for the right to ongoing use of that asset. Royalties are typically agreed upon as a percentage of gross or net revenues derived from the use of an asset o ...
for performances of Stravinsky's pieces stopped coming. Stravinsky, seeking financial assistance, approached the Swiss philanthropist Werner Reinhart, who agreed to sponsor him and largely underwrite the first performance of ''L'Histoire du soldat
' (''The Soldier's Tale'') is a theatrical work "to be read, played, and danced" () by three actors and one or several dancers, accompanied by a septet of instruments. Conceived by Igor Stravinsky and Swiss writer C. F. Ramuz, the piece was bas ...
'' in September 1918. In gratitude, Stravinsky dedicated the work to Reinhart and gave him the original manuscript. Reinhart supported Stravinsky further when he funded a series of concerts of his chamber music in 1919. In gratitude to his benefactor, Stravinsky dedicated his ''Three Pieces for Solo Clarinet
''Three Pieces for Solo Clarinet'' is a solo instrumental work by Igor Stravinsky. The work was composed in 1918. It was published in 1919, shortly after the completion of his Suite from ''L'Histoire du Soldat'', as a thank-you gift to the philanth ...
'' to Reinhart, who was an amateur clarinettist. Stravinsky travelled to Paris to attend the premiere of ''Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
'' by the Ballets Russes on 15 May 1920, returning to Switzerland afterwards.
Life in France, 1920–1939
In June 1920, Stravinsky and his family left Switzerland for France, first settling inCarantec
Carantec (; br, Karanteg) is a commune in the Finistère department of Brittany in north-western France.
Carantec is located on the coast of the English Channel. It contains a small island within its boundaries, Île Callot, which can be reache ...
for the summer while they sought a permanent home in Paris.
They soon heard from the couturière
''Haute couture'' (; ; French for 'high sewing', 'high dressmaking') is the creation of exclusive custom-fitted high-end fashion design that is constructed by hand from start-to-finish. Beginning in the mid-nineteenth century, Paris became th ...
Coco Chanel
Gabrielle Bonheur "Coco" Chanel ( , ; 19 August 1883 – 10 January 1971) was a French fashion designer and businesswoman. The founder and namesake of the Chanel brand, she was credited in the post-World War I era with popularizing a sporty, c ...
, who invited the family to live in her Paris mansion until they had found their own residence. The Stravinskys accepted and arrived in September. Stravinsky and Chanel quickly became lovers, but the affair was short and ended in May 1921. She helped secure a guarantee for a revival production of ''The Rite of Spring'' by the Ballets Russes from December 1920 with an anonymous gift to Diaghilev that was claimed to be worth 300,000 franc
The franc is any of various units of currency. One franc is typically divided into 100 centimes. The name is said to derive from the Latin inscription ''francorum rex'' (Style of the French sovereign, King of the Franks) used on early France, ...
s.
In 1920, Stravinsky signed a contract with the French piano manufacturing company Pleyel
Ignace Joseph Pleyel (; ; 18 June 1757 – 14 November 1831) was an Austrian-born French composer, music publisher and piano builder of the Classical period.
Life Early years
He was born in in Lower Austria, the son of a schoolmaster named Ma ...
. As part of the deal, Stravinsky transcribed most of his compositions for their player piano
A player piano (also known as a pianola) is a self-playing piano containing a pneumatic or electro-mechanical mechanism, that operates the piano action via programmed music recorded on perforated paper or metallic rolls, with more modern i ...
, the Pleyela. The company helped collect Stravinsky's mechanical royalties
A royalty payment is a payment made by one party to another that owns a particular asset, for the right to ongoing use of that asset. Royalties are typically agreed upon as a percentage of gross or net revenues derived from the use of an asset o ...
for his works and provided him with a monthly income. In 1921, he was given studio space at their Paris headquarters where he worked and entertained friends and acquaintances. The piano rolls were not recorded, but were instead marked up from a combination of manuscript fragments and handwritten notes by Jacques Larmanjat, musical director of Pleyel's roll department. During the 1920s, Stravinsky recorded Duo-Art
Duo-Art was one of the leading reproducing piano technologies of the early 20th century, the others being American Piano Company (Ampico), introduced in 1913 too, and Welte-Mignon in 1905. These technologies flourished at that time because of th ...
piano rolls for the Aeolian Company The Aeolian Company was a musical-instrument making firm whose products included player organs, pianos, sheet music, records and phonographs. Founded in 1887, it was at one point the world's largest such firm. During the mid 20th century, it surpas ...
in London and New York City.
Stravinsky met Vera Sudeikin in Paris in February 1921, while she was married to the painter and stage designer
Scenic design (also known as scenography, stage design, or set design) is the creation of theatrical, as well as film or television scenery. Scenic designers come from a variety of artistic backgrounds, but in recent years, are mostly trained ...
Serge Sudeikin
Sergey Yurievich Sudeikin, also known as Serge Soudeikine (19 March 1882 in Smolensk – 12 August 1946 in Nyack, New York), was a Russian artist and set-designer associated with the Ballets Russes and the Metropolitan Opera.
Biography
Having ...
, and they began an affair
An affair is a sexual relationship, romantic friendship, or passionate attachment in which at least one of its participants has a formal or informal commitment to a third person who may neither agree to such relationship nor even be aware of i ...
that led to Vera Sudeikin leaving her husband in the spring of 1922.
 In May 1921, Stravinsky and his family moved to
In May 1921, Stravinsky and his family moved to Anglet
Anglet (; , eu, Angelu )ANGELU
 On the same day Stravinsky became an American citizen, he arranged for
On the same day Stravinsky became an American citizen, he arranged for
 In March 1967, Stravinsky conducted ''L'Histoire du soldat'' with the
In March 1967, Stravinsky conducted ''L'Histoire du soldat'' with the  On 18 March 1971, Stravinsky was taken to
On 18 March 1971, Stravinsky was taken to
 After the premiere of ''Scherzo fantastique'' and ''Feu d'artifice'' attracted the attention of Diaghilev, he commissioned Stravinsky to orchestrate Chopin's Nocturne in A-flat major and Grande valse brillante in E-flat major for the new ballet ''
After the premiere of ''Scherzo fantastique'' and ''Feu d'artifice'' attracted the attention of Diaghilev, he commissioned Stravinsky to orchestrate Chopin's Nocturne in A-flat major and Grande valse brillante in E-flat major for the new ballet ''

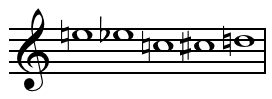 Stravinsky first experimented with non-twelve-tone serial techniques in vocal and chamber works such as the
Stravinsky first experimented with non-twelve-tone serial techniques in vocal and chamber works such as the  Influence from other composers can be seen throughout this period. Stravinsky was heavily influenced by Schoenberg, not only in his use of the twelve-tone technique, but also in the distinctly "Schoenbergian" instrumentation of the Septet and the "Stravinskian interpretation of Schoenberg's ''
Influence from other composers can be seen throughout this period. Stravinsky was heavily influenced by Schoenberg, not only in his use of the twelve-tone technique, but also in the distinctly "Schoenbergian" instrumentation of the Septet and the "Stravinskian interpretation of Schoenberg's ''
 Stravinsky had a number of dissenters throughout his career, particularly regarding his later works. In 1935, the American composer
Stravinsky had a number of dissenters throughout his career, particularly regarding his later works. In 1935, the American composer
DICTECO
* A
DICTECO
* * A
DICTECO
* A
SCRIBD
* * A
DICTECO
* A
DICTECO
* Translated in English, 1936, as ''An Autobiography''. * * *
Facsimile
Shortened at * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
The Stravinsky Foundation
website * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Stravinsky, Igor 1882 births 1971 deaths 20th-century American composers 20th-century American conductors (music) 20th-century American male musicians 20th-century American pianists 20th-century classical composers 20th-century classical pianists 20th-century French composers 20th-century French conductors (music) 20th-century French male classical pianists 20th-century French male musicians Academic staff of the École Normale de Musique de Paris American classical composers American classical pianists American male classical composers American male classical pianists American male conductors (music) American opera composers American people of Polish descent American people of Russian descent Ballets Russes composers Burials at Isola di San Michele Composers for piano Naturalized citizens of France French classical composers French classical pianists French male classical composers French male classical pianists French people of Polish descent French people of Russian descent Grammy Award winners Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award winners Honorary Members of the Royal Philharmonic Society Emigrants from the Russian Empire to France Emigrants from the Russian Empire to Switzerland Emigrants from the Russian Empire to the United States Jazz-influenced classical composers Male opera composers Modernist composers Neoclassical composers People from Lomonosov People from Petergofsky Uyezd Pupils of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov Ragtime composers Recipients of the Léonie Sonning Music Prize Royal Philharmonic Society Gold Medallists Russian anti-communists Russian classical pianists Russian male conductors (music) Russian male classical composers Russian opera composers Russian Orthodox Christians from the United States Russian people of Polish descent Twelve-tone and serial composers
Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Cana ...
border. Their stay was short-lived as by autumn, they had settled to nearby Biarritz
Biarritz ( , , , ; Basque also ; oc, Biàrritz ) is a city on the Bay of Biscay, on the Atlantic coast in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in the French Basque Country in southwestern France. It is located from the border with Spain. ...
and Stravinsky completed his ''Trois mouvements de Petrouchka
''Trois mouvements de Petrouchka'' or ''Three Movements from Petrushka'' is an arrangement for piano of music from the ballet ''Petrushka'' by the composer Igor Stravinsky for the pianist Arthur Rubinstein.
History
Sergei Diaghilev, who had commi ...
'', a piano transcription
In music, a reduction is an arrangement or transcription of an existing score or composition in which complexity is lessened to make analysis, performance, or practice easier or clearer; the number of parts may be reduced or rhythm may be si ...
of excerpts from ''Petrushka'' for Artur Rubinstein
Arthur Rubinstein ( pl, Artur Rubinstein; 28 January 188720 December 1982) was a Polish-American pianist.
. Diaghilev then requested orchestrations for a revival production of Tchaikovsky's ''The Sleeping Beauty''. From then until his wife's death in 1939, Stravinsky led a double life, dividing his time between his family in Anglet, and Vera Sudeikin in Paris and on tour. Nosenko reportedly bore her husband's situation "with a mixture of magnanimity, bitterness, and compassion".
In June 1923, Stravinsky's ballet ''Les noces
''Les Noces'' (French for The Wedding; russian: Свадебка, ''Svadebka'') is a ballet and orchestral concert work composed by Igor Stravinsky for percussion, pianists, chorus, and vocal soloists. The composer gave it the descriptive title " ...
'' premiered in Paris and performed by the Ballets Russes. In the following month, he started to receive money from an anonymous patron from the US who insisted on remaining anonymous and only identified themselves as "Madame". They promised to send him $6,000 in the course of three years, and sent Stravinsky an initial cheque
A cheque, or check (American English; see spelling differences) is a document that orders a bank (or credit union) to pay a specific amount of money from a person's account to the person in whose name the cheque has been issued. The pers ...
for $1,000. Stravinsky's later student Robert Craft
Robert Lawson Craft (October 20, 1923 – November 10, 2015) was an American conductor and writer. He is best known for his intimate professional relationship with Igor Stravinsky, on which Craft drew in producing numerous recordings and books.
...
believed that the patron was the famed conductor Leopold Stokowski
Leopold Anthony Stokowski (18 April 1882 – 13 September 1977) was a British conductor. One of the leading conductors of the early and mid-20th century, he is best known for his long association with the Philadelphia Orchestra and his appeara ...
, whom Stravinsky had recently met, and theorised that the conductor wanted to win Stravinsky over to visit the US.
In September 1924, Stravinsky bought a new home in Nice
Nice ( , ; Niçard: , classical norm, or , nonstandard, ; it, Nizza ; lij, Nissa; grc, Νίκαια; la, Nicaea) is the prefecture of the Alpes-Maritimes department in France. The Nice agglomeration extends far beyond the administrative c ...
. Here, the composer re-evaluated his religious beliefs and reconnected with his Christian faith with help from a Russian priest, Father Nicholas. He also thought of his future, and used the experience of conducting the premiere of his Octet
Octet may refer to:
Music
* Octet (music), ensemble consisting of eight instruments or voices, or composition written for such an ensemble
** String octet, a piece of music written for eight string instruments
*** Octet (Mendelssohn), 1825 compos ...
at one of Serge Koussevitzky
Sergei Alexandrovich KoussevitzkyKoussevitzky's original Russian forename is usually transliterated into English as either "Sergei" or "Sergey"; however, he himself adopted the French spelling "Serge", using it in his signature. (SeThe Koussevit ...
's concerts the year before to build on his career as a conductor. Koussevitzky asked Stravinsky to compose a new piece for one of his upcoming concerts; Stravinsky agreed to a piano concerto. The ''Concerto for Piano and Wind Instruments The Concerto for Piano and Wind Instruments was written by Igor Stravinsky in Paris in 1923–24. This work was revised in 1950.
It was composed four years after the '' Symphonies of Wind Instruments'', which he wrote upon his arrival in Paris afte ...
'' was first performed in May 1924 with Stravinsky as the soloist. The piece was a success, and Stravinsky secured himself the exclusive rights to perform the work for the next five years. Stravinsky visited Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a ''nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the north ...
six times, and the first time, in 1924, after holding three concerts with the Pau Casals Orchestra at the Gran Teatre del Liceu
Gran may refer to:
People
*Grandmother, affectionately known as "gran"
* Gran (name)
Places
* Gran, the historical German name for Esztergom, a city and the primatial metropolitan see of Hungary
* Gran, Norway, a municipality in Innlandet coun ...
, he said, "Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within ci ...
will be unforgettable for me. What I liked most was the cathedral
A cathedral is a church that contains the '' cathedra'' () of a bishop, thus serving as the central church of a diocese, conference, or episcopate. Churches with the function of "cathedral" are usually specific to those Christian denomination ...
and the sardana
The ''sardana'' (; plural ''sardanes'' in Catalan) is a Catalan musical genre typical of Catalan culture and danced in circle following a set of steps. The dance was originally from the Empordà region, but started gaining popularity throughout ...
s". Following a European tour through the latter half of 1924, Stravinsky completed his first US tour in early 1925, which spanned two months. It opened with Stravinsky conducting an all-Stravinsky programme at Carnegie Hall
Carnegie Hall ( ) is a concert venue in Midtown Manhattan in New York City. It is at 881 Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh Avenue, occupying the east side of Seventh Avenue between West 56th Street (Manhattan), 56th and 57th Street (Manhatta ...
.
In 1926, Stravinsky rejoined the Orthodox Church, having been moved by a ceremony at the Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua
The Pontifical Basilica of Saint Anthony of Padua ( it, Basilica Pontificia di Sant'Antonio di Padova) is a Catholic church and minor basilica in Padua, Veneto, Northern Italy, dedicated to St. Anthony of Padua.
Although the basilica is visi ...
while on a spring concert tour. In May 1927, Stravinsky's opera
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librett ...
-oratorio
An oratorio () is a large musical composition for orchestra, choir, and soloists. Like most operas, an oratorio includes the use of a choir, soloists, an instrumental ensemble, various distinguishable characters, and arias. However, opera is mus ...
''Oedipus Rex
''Oedipus Rex'', also known by its Greek title, ''Oedipus Tyrannus'' ( grc, Οἰδίπους Τύραννος, ), or ''Oedipus the King'', is an Athenian tragedy by Sophocles that was first performed around 429 BC. Originally, to the ancient Gr ...
'' premiered in Paris. The funding of its production was largely provided by Winnaretta Singer, Princesse Edmond de Polignac, who paid 12,000 francs for a private preview of the piece at her house. Stravinsky gave the money to Diaghilev to help finance the public performances. The premiere at the Théâtre Sarah-Bernhardt received a negative reaction, believed by the painter Boris Grigoriev
Boris Grigoriev (russian: Бори́с Дми́триевич Григо́рьев; 11 July 1886 – 7 February 1939) was a painter, graphic artist, and writer.
Biography
Grigoriev was born in Rybinsk and studied at the Stroganov Art School ...
to be due to its tameness compared to ''The Firebird'', which irked Stravinsky, who had started to become annoyed at the public's fixation on his early ballets. In the summer of 1927, Stravinsky received a commission from Elizabeth Sprague Coolidge
Elizabeth Sprague Coolidge aka Liz Coolidge (30 October 1864 – 4 November 1953), born Elizabeth Penn Sprague, was an American pianist and patron of music, especially of chamber music.
Biography
Elizabeth Sprague Coolidge's father was a we ...
, his first from the US. A wealthy patron of music, Coolidge requested a thirty-minute ballet score for a festival to be held at the Library of Congress
The Library of Congress (LOC) is the research library that officially serves the United States Congress and is the ''de facto'' national library of the United States. It is the oldest federal cultural institution in the country. The library is ...
, for a $1,000 fee. Stravinsky accepted and wrote ''Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
'', which premiered in 1928.
After Diaghilev's death in 1929, Stravinsky continued touring across Europe, playing the premiere of his Capriccio for Piano and Orchestra
The Capriccio for Piano and Orchestra was written by Igor Stravinsky in Nice between 1926 and 1929. The score was revised in 1949.
Stravinsky designed the Capriccio to be a virtuosic vehicle which would allow him to earn a living from playing th ...
at the Salle Pleyel
The Salle Pleyel (, meaning "Pleyel Hall") is a concert hall in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France, designed by acoustician Gustave Lyon together with architect Jacques Marcel Auburtin, who died in 1926, and the work was completed in 1927 by ...
on 6 December and performing it in many European towns afterwards. Stravinsky toured for most of 1930 to 1933, also composing his '' Symphonies of Wind Instruments'' upon a commission from the Boston Symphony Orchestra
The Boston Symphony Orchestra (BSO) is an American orchestra based in Boston, Massachusetts. It is the second-oldest of the five major American symphony orchestras commonly referred to as the " Big Five". Founded by Henry Lee Higginson in 1881, ...
and his Violin Concerto in D for Samuel Dushkin
Samuel Dushkin (December 13, 1891 – June 24, 1976) was an American violinist, composer, and pedagogue of Polish birth and Jewish origin.
Dushkin was born in Suwałki, Poland. He studied at the Conservatoire de Paris, as well as with Leopold ...
. After touring the latter with Dushkin, Stravinsky was inspired to transcribe some of his works for violin and piano, later touring these transcriptions at "recitals" with Dushkin. On 30 May 1934, the Stravinskys acquired French nationality
French nationality law is historically based on the principles of ''jus soli'' (Latin for "right of soil") and ''jus sanguinis'', according to Ernest Renan's definition, in opposition to the German definition of nationality, ''jus sanguinis'' ( ...
by naturalization. Later in that year, they moved to a house on the Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré
The Rue du Faubourg Saint-Honoré () is a street located in the 8th arrondissement of Paris, France. Relatively narrow and nondescript, especially in comparison to the nearby Avenue des Champs-Élysées, it is cited as being one of the most luxu ...
in Paris, where they stayed for five years. The composer used his citizenship to publish his memoir
A memoir (; , ) is any nonfiction narrative writing based in the author's personal memories. The assertions made in the work are thus understood to be factual. While memoir has historically been defined as a subcategory of biography or autobi ...
s in French, entitled ''Chroniques de ma Vie'' in 1935. His only composition of that year was the '' Concerto for Two Solo Pianos'', which was written for himself and his son Sviatoslav using a special double piano that Pleyel had built. The pair completed a tour of Europe and South America in 1936. In April 1937, he directed his three-part ballet '' Jeu de cartes'', a commission for Lincoln Kirstein
Lincoln Edward Kirstein (May 4, 1907 – January 5, 1996) was an American writer, impresario, art connoisseur, philanthropist, and cultural figure in New York City, noted especially as co-founder of the New York City Ballet. He developed and sus ...
's ballet company in New York City with choreography by George Balanchine
George Balanchine (;
Various sources:
*
*
*
* born Georgiy Melitonovich Balanchivadze; ka, გიორგი მელიტონის ძე ბალანჩივაძე; January 22, 1904 (O. S. January 9) – April 30, 1983) was ...
.
Upon his return to Europe, Stravinsky left Paris for Annemasse
Annemasse (; Arpitan: ''Anemâsse'') is a commune in the Haute-Savoie department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes region in Eastern France. Even though it covers a relatively small territory (4.98 km2 or 1.92 sq mi), it is Haute-Savoie's second ...
near the Swiss border to be near his family, after his wife and daughters Ludmila and Milena had contracted tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in ...
and were in a sanatorium
A sanatorium (from Latin '' sānāre'' 'to heal, make healthy'), also sanitarium or sanitorium, are antiquated names for specialised hospitals, for the treatment of specific diseases, related ailments and convalescence. Sanatoriums are often ...
. Ludmila died in late 1938, followed by his wife of 33 years, in March 1939. Stravinsky himself spent five months in hospital at Sancellemoz
Sancellemoz is a sanatorium in the town of Passy, in Haute-Savoie, eastern France. Professor Marie Curie
Marie Salomea Skłodowska–Curie ( , , ; born Maria Salomea Skłodowska, ; 7 November 1867 – 4 July 1934) was a Polish and natur ...
, during which time his mother also died. During his later years in Paris, Stravinsky had developed professional relationships with key people in the United States: he was already working on his Symphony in C for the Chicago Symphony Orchestra
The Chicago Symphony Orchestra (CSO) was founded by Theodore Thomas in 1891. The ensemble makes its home at Orchestra Hall in Chicago and plays a summer season at the Ravinia Festival. The music director is Riccardo Muti, who began his tenure ...
and he had agreed to accept the Charles Eliot Norton Chair of Poetry of 1939–1940 at Harvard University
Harvard University is a private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Founded in 1636 as Harvard College and named for its first benefactor, the Puritan clergyman John Harvard, it is the oldest institution of higher le ...
and while there, deliver six lectures on music as part of the prestigious Charles Eliot Norton Lectures
The Charles Eliot Norton Professorship of Poetry at Harvard University was established in 1925 as an annual lectureship in "poetry in the broadest sense" and named for the university's former professor of fine arts. Distinguished creative figures ...
.
Life in the United States, 1939–1971
Early US years, 1939–1945
Stravinsky arrived in New York City on 30 September 1939 and headed forCambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston, ...
, to fulfil his engagements at Harvard. During his first two months in the US, Stravinsky stayed at Gerry's Landing, the home of art historian Edward W. Forbes
Edward Waldo Forbes (1873-1969) was an American art historian. He was the Director of the Fogg Art Museum at Harvard University from 1909 to 1944.
Early life
Edward Waldo Forbes, of the Forbes family, was born on July 16, 1873 on Naushon Island ...
. Vera Sudeikin arrived in January 1940 and the couple married on 9 March in Bedford, Massachusetts
Bedford is a town in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. The population of Bedford was 14,383 at the time of the 2020 United States Census.
History
''The following compilation comes from Ellen Abrams (1999) based on information ...
. After a period of travel, the two moved into a home in Beverly Hills, California
Beverly Hills is a city located in Los Angeles County, California. A notable and historic suburb of Greater Los Angeles, it is in a wealthy area immediately southwest of the Hollywood Hills, approximately northwest of downtown Los Angeles. B ...
, before they settled in Hollywood
Hollywood usually refers to:
* Hollywood, Los Angeles, a neighborhood in California
* Hollywood, a metonym for the cinema of the United States
Hollywood may also refer to:
Places United States
* Hollywood District (disambiguation)
* Hollywood, ...
from 1941. Stravinsky felt the warmer Californian climate would benefit his health. Stravinsky had adapted to life in France, but moving to America at the age of 58 was a very different prospect. For a while, he maintained a circle of contacts and émigré
An ''émigré'' () is a person who has emigrated, often with a connotation of political or social self-exile. The word is the past participle of the French ''émigrer'', "to emigrate".
French Huguenots
Many French Huguenots fled France followi ...
friends from Russia, but he eventually found that this did not sustain his intellectual and professional life. He was drawn to the growing cultural life of Los Angeles, especially during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, when writers, musicians, composers, and conductors settled in the area. The music critic Bernard Holland
Bernard Holland (born 1933) is an American music critic. He served on the staff of ''The New York Times'' from 1981 until 2008 and held the post of chief music critic from 1995, contributing 4,575 articles to the newspaper. He then became the Nati ...
claimed Stravinsky was especially fond of British writers, who visited him in Beverly Hills, like W. H. Auden
Wystan Hugh Auden (; 21 February 1907 – 29 September 1973) was a British-American poet. Auden's poetry was noted for its stylistic and technical achievement, its engagement with politics, morals, love, and religion, and its variety in ...
, Christopher Isherwood
Christopher William Bradshaw Isherwood (26 August 1904 – 4 January 1986) was an Anglo-American novelist, playwright, screenwriter, autobiographer, and diarist. His best-known works include '' Goodbye to Berlin'' (1939), a semi-autobiographical ...
, and later Dylan Thomas
Dylan Marlais Thomas (27 October 1914 – 9 November 1953) was a Welsh poet and writer whose works include the poems "Do not go gentle into that good night" and "And death shall have no dominion", as well as the "play for voices" ''Under ...
: "They shared the composer's taste for hard spirits – especially Aldous Huxley, with whom Stravinsky spoke in French." Stravinsky and Huxley had a tradition of Saturday lunches for west coast avant-garde and luminaries.
In 1940, Stravinsky completed his ''Symphony in C'' and conducted the Chicago Symphony Orchestra at its premiere later that year. At this time, Stravinsky began to associate himself with film music
A film score is original music written specifically to accompany a film. The score comprises a number of orchestral, instrumental, or choral pieces called cues, which are timed to begin and end at specific points during the film in order to e ...
; the first major film to use his music was Walt Disney
Walter Elias Disney (; December 5, 1901December 15, 1966) was an American animator, film producer and entrepreneur. A pioneer of the American animation industry, he introduced several developments in the production of cartoons. As a film p ...
's animated feature ''Fantasia
Fantasia International Film Festival (also known as Fantasia-fest, FanTasia, and Fant-Asia) is a film festival that has been based mainly in Montreal since its founding in 1996. Regularly held in July of each year, it is valued by both hardcore ...
'' (1940) which includes parts of ''The Rite of Spring'' rearranged by Leopold Stokowski to a segment depicting the history of Earth
The history of Earth concerns the development of planet Earth from its formation to the present day. Nearly all branches of natural science have contributed to understanding of the main events of Earth's past, characterized by constant geologi ...
and the age of dinosaur
Dinosaurs are a diverse group of reptiles of the clade Dinosauria. They first appeared during the Triassic period, between 243 and 233.23 million years ago (mya), although the exact origin and timing of the evolution of dinosaurs is t ...
s. Orson Welles
George Orson Welles (May 6, 1915 – October 10, 1985) was an American actor, director, producer, and screenwriter, known for his innovative work in film, radio and theatre. He is considered to be among the greatest and most influential f ...
urged Stravinsky to write the score for ''Jane Eyre
''Jane Eyre'' ( ; originally published as ''Jane Eyre: An Autobiography'') is a novel by the English writer Charlotte Brontë. It was published under her pen name "Currer Bell" on 19 October 1847 by Smith, Elder & Co. of London. The first ...
'' (1943), but negotiations broke down; a piece used in one of the film's hunting scenes was used in Stravinsky's orchestral work ''Ode
An ode (from grc, ᾠδή, ōdḗ) is a type of lyric poetry. Odes are elaborately structured poems praising or glorifying an event or individual, describing nature intellectually as well as emotionally. A classic ode is structured in three majo ...
'' (1943). An offer to score '' The Song of Bernadette'' (1943) also fell through; Stravinsky considered the terms were too much in the producer's favour. Music he had written for the film was later used in his ''Symphony in Three Movements
The Symphony in Three Movements is a work by Russian expatriate composer Igor Stravinsky. Stravinsky wrote the symphony from 1942–45 on commission by the Philharmonic Symphony Society of New York. It was premièred by the New York Philharmoni ...
''.
Stravinsky's unconventional dominant seventh chord
In music theory, a dominant seventh chord, or major minor seventh chord, is a seventh chord, usually built on the fifth degree of the major scale, and composed of a root, major third, perfect fifth, and minor seventh. Thus it is a major triad tog ...
in his arrangement of the "Star-Spangled Banner
"The Star-Spangled Banner" is the national anthem of the United States. The lyrics come from the "Defence of Fort M'Henry", a poem written on September 14, 1814, by 35-year-old lawyer and amateur poet Francis Scott Key after witnessing the bo ...
" led to an incident with the Boston police
The Boston Police Department (BPD), dating back to 1854, holds the primary responsibility for law enforcement and investigation within the city of Boston, Massachusetts. It is the oldest municipal police department in the United States. The ...
on 15 January 1944, and he was warned that the authorities could impose a $100 fine upon any "re-arrangement of the national anthem in whole or in part". The police, as it turned out, were wrong. The law in question forbade using the national anthem "as dance music, as an exit march, or as a part of a medley of any kind", but the incident soon established itself as a myth, in which Stravinsky was supposedly arrested, held in custody for several nights, and photographed for police records.
On 28 December 1945, the Stravinskys became naturalised
Naturalization (or naturalisation) is the legal act or process by which a non-citizen of a country may acquire citizenship or nationality of that country. It may be done automatically by a statute, i.e., without any effort on the part of the i ...
US citizens
Citizenship of the United States is a legal status that entails Americans with specific rights, duties, protections, and benefits in the United States. It serves as a foundation of fundamental rights derived from and protected by the Constituti ...
. Their sponsor and witness was the actor Edward G. Robinson
Edward G. Robinson (born Emanuel Goldenberg; December 12, 1893January 26, 1973) was a Romanian-American actor of stage and screen, who was popular during the Hollywood's Golden Age. He appeared in 30 Broadway plays and more than 100 films duri ...
.
Last major works, 1945–1966
 On the same day Stravinsky became an American citizen, he arranged for
On the same day Stravinsky became an American citizen, he arranged for Boosey & Hawkes
Boosey & Hawkes is a British music publisher purported to be the largest specialist classical music publisher in the world. Until 2003, it was also a major manufacturer of brass, string and woodwind musical instruments.
Formed in 1930 throu ...
to publish rearrangements of several of his compositions and used his newly acquired American citizenship to secure a copyright on the material, thus allowing him to earn money from them. The five-year contract was finalised and signed in January 1947 which included a guarantee of $10,000 per for the first two years, then $12,000 for the remaining three.
In late 1945, Stravinsky received a commission from Europe, his first since '' Perséphone'', in the form of a string piece for the 20th anniversary for Paul Sacher
Paul Sacher (28 April 190626 May 1999) was a Swiss conductor, patron and billionaire businessperson. At the time of his death Sacher was majority shareholder of pharmaceutical company Hoffmann-La Roche and was considered the third richest person i ...
's Basle Chamber Orchestra. The '' Concerto in D'' premiered in 1947. In January 1946, Stravinsky conducted the premiere of his ''Symphony in Three Movements'' at Carnegie Hall
Carnegie Hall ( ) is a concert venue in Midtown Manhattan in New York City. It is at 881 Seventh Avenue (Manhattan), Seventh Avenue, occupying the east side of Seventh Avenue between West 56th Street (Manhattan), 56th and 57th Street (Manhatta ...
in New York City. It marked his first premiere in the US. In 1947, Stravinsky was inspired to write his English-language opera ''The Rake's Progress
''The Rake's Progress'' is an English-language opera from 1951 in three acts and an epilogue by Igor Stravinsky. The libretto, written by W. H. Auden and Chester Kallman, is based loosely on the eight paintings and engravings ''A Rake's Progres ...
'' by a visit to a Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
exhibition of the same-titled series of paintings by the eighteenth-century British artist William Hogarth
William Hogarth (; 10 November 1697 – 26 October 1764) was an English painter, engraver, pictorial satirist, social critic, editorial cartoonist and occasional writer on art. His work ranges from realistic portraiture to comic strip-like s ...
, which tells the story of a fashionable wastrel descending into ruin. W. H. Auden and writer Chester Kallman
Chester Simon Kallman (January 7, 1921 – January 18, 1975) was an American poet, librettist, and translator, best known for collaborating with W. H. Auden on opera librettos for Igor Stravinsky and other composers.
Life
Kallman was born in ...
worked on the libretto
A libretto (Italian for "booklet") is the text used in, or intended for, an extended musical work such as an opera, operetta, masque, oratorio, cantata or Musical theatre, musical. The term ''libretto'' is also sometimes used to refer to the t ...
. The opera premiered in 1951 and marks the final work of Stravinsky's neoclassical period. While composing ''The Rake's Progress'', Stravinsky met Robert Craft
Robert Lawson Craft (October 20, 1923 – November 10, 2015) was an American conductor and writer. He is best known for his intimate professional relationship with Igor Stravinsky, on which Craft drew in producing numerous recordings and books.
...
, whom Stravinsky invited to his home in Hollywood as a personal assistant. Craft soon became Stravinsky's "closest friend, his confident, amanuensis, spokesman and fellow conductor," as Jay Harrison wrote in the ''New York Herald Tribune
The ''New York Herald Tribune'' was a newspaper published between 1924 and 1966. It was created in 1924 when Ogden Mills Reid of the ''New-York Tribune'' acquired the ''New York Herald''. It was regarded as a "writer's newspaper" and competed ...
''. Craft encouraged the composer to explore serial music
In music, serialism is a method of Musical composition, composition using series of pitches, rhythms, dynamics, timbres or other elements of music, musical elements. Serialism began primarily with Arnold Schoenberg's twelve-tone technique, thou ...
and the composers of the Second Viennese School
The Second Viennese School (german: Zweite Wiener Schule, Neue Wiener Schule) was the group of composers that comprised Arnold Schoenberg and his pupils, particularly Alban Berg and Anton Webern, and close associates in early 20th-century Vienna. ...
, beginning Stravinsky's third and final distinct musical period, which lasted until his death.
In 1953, Stravinsky agreed to compose a new opera with a libretto by Dylan Thomas, which detailed the recreation of the world after one man and one woman remained on Earth after a nuclear disaster
A nuclear and radiation accident is defined by the International Atomic Energy Agency (IAEA) as "an event that has led to significant consequences to people, the environment or the facility. Examples include radiation poisoning, lethal effects ...
. Development on the project came to a sudden end following Thomas's death in November of that year. Stravinsky completed ''In Memoriam Dylan Thomas'', a piece for tenor, string quartet, and four trombones, in 1954. Stravinsky composed his cantata ''Canticum Sacrum
''Canticum Sacrum ad Honorem Sancti Marci Nominis'' is a 17-minute choral-orchestral piece composed in 1955 by Igor Stravinsky (1882–1971) in tribute "To the City of Venice, in praise of its Patron Saint, the Blessed Mark, Apostle." The piec ...
'' for the International Festival of Contemporary Music in Venice, to which he dedicated the work, and it premiered on 13 September 1956. The work inspired the Norddeutscher Rundfunk
Norddeutscher Rundfunk (NDR; ''Northern German Broadcasting'') is a public broadcasting, public radio and television broadcaster, based in Hamburg. In addition to the city-state of Hamburg, NDR broadcasts for the German states of Lower Saxony, M ...
to commission the musical setting '' Threni'' in 1957, which was premiered by their orchestra and chorus
Chorus may refer to:
Music
* Chorus (song) or refrain, line or lines that are repeated in music or in verse
* Chorus effect, the perception of similar sounds from multiple sources as a single, richer sound
* Chorus form, song in which all verse ...
on 23 September 1958. In 1959, Craft interviewed Stravinsky for an article titled ''Answers to 35 Questions'', in which Stravinsky corrected a number of myths surrounding him and discussed his relationships with many of his collaborators. The article was later expanded into a book, and over the next four years, three more books of this fashion were published due to Craft's initiative.
In 1961, the Stravinskys and Craft travelled to London, Zürich
Zürich () is the list of cities in Switzerland, largest city in Switzerland and the capital of the canton of Zürich. It is located in north-central Switzerland, at the northwestern tip of Lake Zürich. As of January 2020, the municipality has 43 ...
and Cairo on their way to Australia where Stravinsky and Craft conducted all-Stravinsky concerts in Sydney and Melbourne. They returned to California via New Zealand, Tahiti, and Mexico. In January 1962, during his tour's stop in Washington, D.C.
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan, ...
, Stravinsky attended a dinner at the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in 1800. ...
with President John F. Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until his assassination i ...
in honour of his 80th birthday, where he received a special medal for "the recognition his music has achieved throughout the world". In September 1962, Stravinsky returned to Russia for the first time since 1914, accepting an invitation from the Union of Soviet Composers
The Union of Russian Composers (formerly the Union of Soviet Composers, Order of Lenin Union of Composers of USSR () (1932- ), and Union of Soviet Composers of the USSR) is a state-created organization for musicians and musicologists created in 193 ...
to conduct six performances in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
and Leningrad
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
. During the three-week visit he met with Soviet Premier Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
and several leading Soviet composers, including Dmitri Shostakovich
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich, , group=n (9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his Symphony No. 1 (Shostakovich), First Symphony in 1926 and was regarded throug ...
and Aram Khachaturian
Aram Ilyich Khachaturian (; rus, Арам Ильич Хачатурян, , ɐˈram ɨˈlʲjitɕ xətɕɪtʊˈrʲan, Ru-Aram Ilyich Khachaturian.ogg; hy, Արամ Խաչատրյան, ''Aram Xačʿatryan''; 1 May 1978) was a Soviet and Armenian ...
. Stravinsky did not return to his Hollywood home until December 1962 in what was almost eight months of continual travelling. Following the assassination of Kennedy in 1963, Stravinsky completed his '' Elegy for J.F.K.'' in the following year. The two-minute work took the composer two days to write.
By early 1964, the long periods of travel started to affect Stravinsky's health. His case of polycythemia
Polycythemia (also known as polycythaemia) is a laboratory finding in which the hematocrit (the volume percentage of red blood cells in the blood) and/or hemoglobin concentration are increased in the blood. Polycythemia is sometimes called erythr ...
worsened and his friends noticed that his movements and speech had slowed. In 1965, Stravinsky agreed to have David Oppenheim produce a documentary film
A documentary film or documentary is a non-fictional film, motion-picture intended to "document reality, primarily for the purposes of instruction, education or maintaining a Recorded history, historical record". Bill Nichols (film critic), Bil ...
about himself for the CBS
CBS Broadcasting Inc., commonly shortened to CBS, the abbreviation of its former legal name Columbia Broadcasting System, is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the CBS Entertainmen ...
network. It involved a film crew following the composer at home and on tour that year, and he was paid $10,000 for the production. The documentary includes Stravinsky's visit to Les Tilleuls, the house in Clarens where he wrote the majority of ''The Rite of Spring''. The crew asked Soviet authorities for permission to film Stravinsky returning to his hometown of Ustilug, but the request was denied. In 1966, Stravinsky completed his last major work, the ''Requiem Canticles
''Requiem Canticles'' is a 15-minute composition by Igor Stravinsky, for contralto and bass soli, chorus, and orchestra. Stravinsky completed the work in 1966, and it received its first performance that same year.
The work is a partial setting o ...
''. His final attempt at composition, '' Two Sketches for a Sonata'', existed in a manuscript of short piano fragments. The sketches were published by Boosey & Hawkes in 2021.
Final years and death, 1967–1971
 In March 1967, Stravinsky conducted ''L'Histoire du soldat'' with the
In March 1967, Stravinsky conducted ''L'Histoire du soldat'' with the Seattle Opera
Seattle Opera is an opera company based in Seattle, Washington. It was founded in 1963 by Glynn Ross, who served as its first general director until 1983. The company's season runs from August through late May, comprising five or six operas of ...
. By this time, Stravinsky's typical performance fee had grown to $10,000. However, after Stravinsky's conducting became "erratic" and "vague" as one reviewer described it, Craft cancelled all concerts that required Stravinsky to fly. An exception to this was a concert at Massey Hall
Massey Hall is a performing arts theatre in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. Opened in 1894, it is known for its outstanding acoustics and was the long-time hall of the Toronto Symphony Orchestra. An intimate theatre, it was originally designed to seat ...
in Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the most populous city in Canada and the fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the ancho ...
in May 1967, where he conducted the relatively physically undemanding ''Pulcinella'' suite with the Toronto Symphony Orchestra
The Toronto Symphony Orchestra (TSO) is a Canadian orchestra based in Toronto, Ontario. Founded in 1906, the TSO gave regular concerts at Massey Hall until 1982, and since then has performed at Roy Thomson Hall. The TSO also manages the Toronto ...
. Unbeknownst to him, it was his final performance as conductor. While backstage at the venue, Stravinsky informed Craft that he believed he had suffered a stroke
A stroke is a medical condition in which poor blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and hemorrhagic, due to bleeding. Both cause parts of the brain to stop functionin ...
. In August 1967, Stravinsky was hospitalised in Hollywood for bleeding stomach ulcers
Peptic ulcer disease (PUD) is a break in the inner lining of the stomach, the first part of the small intestine, or sometimes the lower esophagus. An ulcer in the stomach is called a gastric ulcer, while one in the first part of the intestines ...
and thrombosis
Thrombosis (from Ancient Greek "clotting") is the formation of a blood clot inside a blood vessel, obstructing the flow of blood through the circulatory system. When a blood vessel (a vein or an artery) is injured, the body uses platelets (thro ...
which required a blood transfusion
Blood transfusion is the process of transferring blood products into a person's circulation intravenously. Transfusions are used for various medical conditions to replace lost components of the blood. Early transfusions used whole blood, but mo ...
.
By 1968, Stravinsky had recovered enough to resume touring across the US with him in the audience while Craft took to the conductor's post for the majority of the concerts. In May 1968, Stravinsky completed the piano arrangement of two songs by Hugo Wolf
Hugo Philipp Jacob Wolf (13 March 1860 – 22 February 1903) was an Austrian composer of Slovene origin, particularly noted for his art songs, or Lieder. He brought to this form a concentrated expressive intensity which was unique in late Ro ...
for a small orchestra. In October, the Stravinskys and Craft travelled to Zürich to sort out business matters with Stravinsky's family. The three considered relocating to Switzerland as they had become increasingly less fond of Hollywood, but they decided against it and returned to the US.
In October 1969, after close to three decades in California and Stravinsky being denied to travel overseas by his doctors due to ill health, the Stravinskys secured a two-year lease for a luxury three bedroom apartment in Essex House in New York City. Craft moved in with them, effectively putting his career on hold to care for the ailing composer. Among Stravinsky's final projects was orchestrating two preludes from Bach's ''The Well-Tempered Clavier
''The Well-Tempered Clavier'', BWV 846–893, consists of two sets of preludes and fugues in all 24 major and minor keys for keyboard by Johann Sebastian Bach. In the composer's time, ''clavier'', meaning keyboard, referred to a variety of in ...
'', but it was never completed. In June 1970, he travelled to Évian-les-Bains
Évian-les-Bains (), or simply Évian ( frp, Èvian, , or ), is a Communes of France, commune in the northern part of the Haute-Savoie Departments of France, department in the Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes Regions of France, region, Southeastern France. ...
by Lake Geneva where he reunited with his eldest son Fyodor and niece Xenia.
 On 18 March 1971, Stravinsky was taken to
On 18 March 1971, Stravinsky was taken to Lenox Hill Hospital
Lenox Hill Hospital (LHH) is a nationally ranked 450-bed non-profit, tertiary, research and academic medical center located on the Upper East Side of Manhattan in New York City, servicing the tri-state area. LHH is one of the region's many unive ...
with pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema, also known as pulmonary congestion, is excessive edema, liquid accumulation in the parenchyma, tissue and pulmonary alveolus, air spaces (usually alveoli) of the lungs. It leads to impaired gas exchange and may cause hypoxemia an ...
where he stayed for ten days. On 29 March, he moved into a newly furnished apartment at 920 Fifth Avenue
Fifth Avenue is a major and prominent thoroughfare in the borough of Manhattan in New York City. It stretches north from Washington Square Park in Greenwich Village to West 143rd Street in Harlem. It is one of the most expensive shopping stre ...
, his first city apartment since living in Paris in 1939. After a period of well-being, the edema returned on 4 April and Vera Stravinsky insisted that medical equipment should be installed in the apartment. Stravinsky soon stopped eating and drinking and died at 5:20 a.m. on 6 April at the age of 88. The cause on his death certificate is heart failure
Heart failure (HF), also known as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a syndrome, a group of signs and symptoms caused by an impairment of the heart's blood pumping function. Symptoms typically include shortness of breath, excessive fatigue, a ...
. A funeral service was held three days later at Frank E. Campbell Funeral Chapel
The Frank E. Campbell Funeral Chapel is a funeral home located on Madison Avenue at 81st Street in Manhattan. Founded in 1898 as Frank E. Campbell Burial and Cremation Company, the company is now owned by Service Corporation International. The fun ...
.
In accordance with his wishes, he was buried in the Russian corner of the cemetery island of San Michele in Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, several yards from the tomb of Sergei Diaghilev, having been brought there by gondola
The gondola (, ; vec, góndoła ) is a traditional, flat-bottomed Venetian rowing boat, well suited to the conditions of the Venetian lagoon. It is typically propelled by a gondolier, who uses a rowing oar, which is not fastened to the hull ...
after a service at Santi Giovanni e Paolo led by Cherubin Malissianos, Archimandrite
The title archimandrite ( gr, ἀρχιμανδρίτης, archimandritēs), used in Eastern Christianity, originally referred to a superior abbot (''hegumenos'', gr, ἡγούμενος, present participle of the verb meaning "to lead") who ...
of the Greek Orthodox Church
The term Greek Orthodox Church (Greek: Ἑλληνορθόδοξη Ἐκκλησία, ''Ellinorthódoxi Ekklisía'', ) has two meanings. The broader meaning designates "the entire body of Orthodox (Chalcedonian) Christianity, sometimes also call ...
. During the service, his ''Requiem Canticles
''Requiem Canticles'' is a 15-minute composition by Igor Stravinsky, for contralto and bass soli, chorus, and orchestra. Stravinsky completed the work in 1966, and it received its first performance that same year.
The work is a partial setting o ...
'' and organ music by Andrea Gabrieli
Andrea Gabrieli (1532/1533Bryant, Grove online – August 30, 1585) was an Italian composer and organist of the late Renaissance. The uncle of the somewhat more famous Giovanni Gabrieli, he was the first internationally renowned member of the Ven ...
were performed.
Music
Most of Stravinsky's student works were composed for assignments from his teacher Rimsky-Korsakov, being mainly influenced by Rimsky-Korsakov and other Russian composers. Stravinsky's first three ballets, ''The Firebird
''The Firebird'' (french: L'Oiseau de feu, link=no; russian: Жар-птица, Zhar-ptitsa, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral concert work by the Russian composer Igor Stravinsky. It was written for the 1910 Paris season of Sergei Diaghilev's ...
'', ''Petrushka
Petrushka ( rus, Петру́шка, p=pʲɪtˈruʂkə, a=Ru-петрушка.ogg) is a stock character of Russian folk puppetry. Italian puppeteers introduced it in the first third of the 19th century. While most core characters came from Italy ...
'', and ''The Rite of Spring
''The Rite of Spring''. Full name: ''The Rite of Spring: Pictures from Pagan Russia in Two Parts'' (french: Le Sacre du printemps: tableaux de la Russie païenne en deux parties) (french: Le Sacre du printemps, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral ...
'', were the beginning of his international fame and deviation from the conservative Saint Petersburg life. Stravinsky's music is often divided into three periods of composition: his Russian period (1913–1920), where he was greatly influenced by Russian folklore and style; his neoclassical period (1920–1951), where Stravinsky turned towards techniques and themes from the Classical period; and his serial period (1954–1968), where Stravinsky used serial composition techniques pioneered by composers of the Second Viennese School
The Second Viennese School (german: Zweite Wiener Schule, Neue Wiener Schule) was the group of composers that comprised Arnold Schoenberg and his pupils, particularly Alban Berg and Anton Webern, and close associates in early 20th-century Vienna. ...
.
Student works, 1898–1907
Stravinsky's time before meeting Diaghilev was spent learning from Rimsky-Korsakov and his collaborators. Only three works survive from before Stravinsky met Rimsky-Korsakov in August 1902: "Tarantella
() is a group of various southern Italian folk dances originating in the regions of Calabria, Campania and Puglia. It is characterized by a fast upbeat tempo, usually in time (sometimes or ), accompanied by tambourines. It is among the mo ...
" (1898), Scherzo in G minor (1902), and ''The Storm Cloud'', the first two being works for piano and the last for voice and piano. Stravinsky's first assignment from Rimsky-Korsakov was the four-movement Piano Sonata in F minor, which was also his first work to be performed in public. Rimsky-Korsakov often gave Stravinsky the task of orchestrating various works to allow him to analyze the works' form and structure. A number of Stravinsky's student compositions were performed at Rimsky-Korsakov's gatherings at his home; these include a set of bagatelles
Bagatelle (from the Château de Bagatelle) is a billiards-derived indoor table game, the object of which is to get a number of balls (set at nine in the 19th century) past wooden pins (which act as obstacles) into holes that are guarded by wooden ...
, a "chanson comique", and a cantata, showing the use of classical musical techniques that would later define Stravinsky's neoclassical period. Stephen Walsh described this time in Stravinsky's musical career as "aesthetically cramped" due to the "cynical conservatism" of Rimsky-Korsakov and his music. Rimsky-Korsakov thought the Symphony in E-flat (1907) was swayed too much by Glazunov's style, and disliked the modernist influence on ''Faun and Shepherdess'' (1907).
First three ballets, 1910–1913
 After the premiere of ''Scherzo fantastique'' and ''Feu d'artifice'' attracted the attention of Diaghilev, he commissioned Stravinsky to orchestrate Chopin's Nocturne in A-flat major and Grande valse brillante in E-flat major for the new ballet ''
After the premiere of ''Scherzo fantastique'' and ''Feu d'artifice'' attracted the attention of Diaghilev, he commissioned Stravinsky to orchestrate Chopin's Nocturne in A-flat major and Grande valse brillante in E-flat major for the new ballet ''Les Sylphides
''Les Sylphides'' () is a short, non-narrative ''ballet blanc'' to piano music by Frédéric Chopin, selected and orchestrated by Alexander Glazunov.
The ballet, described as a "romantic reverie","Ballet Theater", until 1955. A compact disk ...
'', and commissioned Stravinsky's first ballet, ''The Firebird'', a few months after''.''
''The Firebird
''The Firebird'' (french: L'Oiseau de feu, link=no; russian: Жар-птица, Zhar-ptitsa, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral concert work by the Russian composer Igor Stravinsky. It was written for the 1910 Paris season of Sergei Diaghilev's ...
'' used a harmonic structure
In music, harmony is the process by which individual sounds are joined together or composed into whole units or compositions. Often, the term harmony refers to simultaneously occurring frequencies, pitches ( tones, notes), or chords. However, ...
that Stravinsky called "leit-harmony", a portmanteau
A portmanteau word, or portmanteau (, ) is a blend of wordsleitmotif
A leitmotif or leitmotiv () is a "short, recurring musical phrase" associated with a particular person, place, or idea. It is closely related to the musical concepts of ''idée fixe'' or ''motto-theme''. The spelling ''leitmotif'' is an anglici ...
and harmony used by Rimsky-Korsakov in his opera ''The Golden Cockerel
''The Golden Cockerel'' ( rus, Золотой петушок, Zolotoy petushok ) is an opera in three acts, with short prologue and even shorter epilogue, composed by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, his last opera he completed before his death in 1908. ...
''. The "leit-harmony" was used to juxtapose
Juxtaposition is an act or instance of placing two elements close together or side by side. This is often done in order to compare/contrast the two, to show similarities or differences, etc.
Speech
Juxtaposition in literary terms is the showin ...
the protagonist, the Firebird
Firebird and fire bird may refer to:
Mythical birds
* Phoenix (mythology), sacred firebird found in the mythologies of many cultures
* Bennu, Egyptian firebird
* Huma bird, Persian firebird
* Firebird (Slavic folklore)
Bird species
''Various spe ...
, and the antagonist
An antagonist is a character in a story who is presented as the chief foe of the protagonist.
Etymology
The English word antagonist comes from the Greek ἀνταγωνιστής – ''antagonistēs'', "opponent, competitor, villain, enemy, riv ...
, Koschei the Deathless
Koschei ( rus, Коще́й, r=Koshchey, p=kɐˈɕːej), often given the epithet "the Immortal", or "the Deathless" (russian: Коще́й Бессме́ртный), is an archetypal male antagonist in Russian folklore.
The most common feature of ...
, the Firebird being associated with whole-tone
In Western music theory, a major second (sometimes also called whole tone or a whole step) is a second spanning two semitones (). A second is a musical interval encompassing two adjacent staff positions (see Interval number for more det ...
phrases and Koschei being associated with octatonic
An octatonic scale is any eight-Musical note, note musical scale. However, the term most often refers to the symmetric scale composed of alternating major second, whole and semitone, half steps, as shown at right. In classical theory (in contras ...
music. Stravinsky later wrote how he composed ''The Firebird'' in a state of "revolt against Rimsky", and that he "tried to surpass him with ''ponticello
A variety of musical terms are likely to be encountered in printed scores, music reviews, and program notes. Most of the terms Italian musical terms used in English, are Italian, in accordance with the Italian origins of many European musical co ...
'', ''col legno
In music for bowed string instruments, , or more precisely (, ), is an instruction to strike the string with the stick of the bow across the strings.
History
The earliest known use of in Western music is to be found in a piece entitled "Har ...
'', ''flautando
String instruments, stringed instruments, or chordophones are musical instruments that produce sound from vibrating strings when a performer plays or sounds the strings in some manner.
Musicians play some string instruments by plucking the Str ...
'', ''glissando
In music, a glissando (; plural: ''glissandi'', abbreviated ''gliss.'') is a glide from one pitch to another (). It is an Italianized musical term derived from the French ''glisser'', "to glide". In some contexts, it is distinguished from the co ...
'', and fluttertongue
Flutter-tonguing is a wind instrument tonguing technique in which performers flutter their tongue to make a characteristic "FrrrrrFrrrrr" sound. The effect varies according to the instrument and at what volume it is played, ranging from cooing soun ...
effects". quoting .
Stravinsky's second ballet for the Ballets Russes, ''Petrushka
Petrushka ( rus, Петру́шка, p=pʲɪtˈruʂkə, a=Ru-петрушка.ogg) is a stock character of Russian folk puppetry. Italian puppeteers introduced it in the first third of the 19th century. While most core characters came from Italy ...
'', is where Stravinsky defined his musical character. Originally meant to be a ''konzertstück
A concert piece (German: Konzertstück; French: pièce de concert, also morceau de concert) is a musical composition, in most cases in one movement, intended for performance in a concert. Usually it is written for one or more virtuoso instrumenta ...
'' for piano and orchestra, Diaghilev convinced Stravinsky that he should instead compose it as a ballet instead for the 1911 season. The Russian influence can be seen in the use of a number of Russian folk tunes in addition to two waltzes by Viennese composer Joseph Lanner
Joseph Franz Karl Lanner (12 April 1801 – 14 April 1843) was an Austrian dance music composer and dance orchestra conductor. He is best remembered as one of the earliest Viennese composers to reform the waltz from a simple peasant dance to s ...
and a French music hall tune (''La Jambe en bois'' or ''The Wooden Leg''). Stravinsky also used a folk tune from Rimsky-Korsakov's opera ''The Snow Maiden
''The Snow Maiden'' (subtitle: A Spring Fairy Tale) ( rus, Снегурочка–весенняя сказка, Snegúrochka–vesénnyaya skázka, italic=yes ) is an opera in four acts with a prologue by Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov, composed ...
'', showing his continued influence on the music of Stravinsky.
Stravinsky's third ballet, ''The Rite of Spring
''The Rite of Spring''. Full name: ''The Rite of Spring: Pictures from Pagan Russia in Two Parts'' (french: Le Sacre du printemps: tableaux de la Russie païenne en deux parties) (french: Le Sacre du printemps, link=no) is a ballet and orchestral ...
'', caused a sensation at the premiere due to the avant-garde nature of the work. Stravinsky had begun to experiment with polytonality Polytonality (also polyharmony) is the musical use of more than one key simultaneously. Bitonality is the use of only two different keys at the same time. Polyvalence or polyvalency is the use of more than one harmonic function, from the same key, a ...
in ''The Firebird'' and ''Petrushka'', but for ''The Rite of Spring'', he "pushed tto its logical conclusion," as Eric Walter White describes it. In addition, the complex metre
The metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its pref ...
in the music consists of phrases combining conflicting time signature
The time signature (also known as meter signature, metre signature, or measure signature) is a notational convention used in Western musical notation to specify how many beats (pulses) are contained in each measure (bar), and which note value ...
s and odd accents Accent may refer to:
Speech and language
* Accent (sociolinguistics), way of pronunciation particular to a speaker or group of speakers
* Accent (phonetics), prominence given to a particular syllable in a word, or a word in a phrase
** Pitch acce ...
, such as the "jagged slashes" in the "Sacrificial Dance". Both polytonality and unusual rhythms can be heard in the chords that open the second episode, "Augurs of Spring", consisting of an E dominant 7 superimposed on an F major triad
Triad or triade may refer to:
* a group of three
Businesses and organisations
* Triad (American fraternities), certain historic groupings of seminal college fraternities in North America
* Triad (organized crime), a Chinese transnational orga ...
written in an uneven rhythm, Stravinsky shifting the accents seemingly at random to create asymmetry. ''The Rite of Spring'' is one of the most famous and influential works of the 20th century; the musicologist Donald Jay Grout
Donald Jay Grout (September 28, 1902 – March 9, 1987) was an American musicologist. He is best known as the author of ''A Short History of Opera,'' first published in 1947. The fourth edition was published by Columbia University Press in 2003.
...
described it as having "the effect of an explosion that so scattered the elements of musical language that they could never again be put together as before."
Russian period, 1913–1920
The musicologist Jeremy Noble says that Stravinsky's "intensive researches into Russian folk material" took place during his time in Switzerland from 1914 to 1920. The composer Béla Bartók considered Stravinsky's Russian period to have begun in 1913 with ''The Rite of Spring'' due to the works' use of Russian folk songs, themes, and techniques. The use of duple or triplemetres
The metre (British spelling) or meter (American spelling; see spelling differences) (from the French unit , from the Greek noun , "measure"), symbol m, is the primary unit of length in the International System of Units (SI), though its prefi ...
was especially prevalent in Stravinsky's Russian period music; while the pulse may have remained constant, the time signature would often change to constantly shift the accents.
Stravinsky did not use as many folk melodies as he had in his first three ballets, but his works were with Russian style. Stravinsky used folk poetry often; his next opera, ''Les noces
''Les Noces'' (French for The Wedding; russian: Свадебка, ''Svadebka'') is a ballet and orchestral concert work composed by Igor Stravinsky for percussion, pianists, chorus, and vocal soloists. The composer gave it the descriptive title " ...
'', was based on texts from a collection of Russian folk poetry by Pyotr Kireevsky
Pyotr Vasilievich Kireevsky (russian: Пётр Васи́льевич Кире́евский, 23 February 1808 in Dolbino, Likhvinsky Uyezd, Kaluga Governorate – 6 November 1856) was a Russian folklorist and philologist many of whose mate ...
, and his opera-ballet '' Renard'' was based on a folktale collected by Alexander Afanasyev
Alexander Nikolayevich Afanasyev (Afanasief, Afanasiev or Afanas'ev, russian: link=no, Александр Николаевич Афанасьев) ( — ) was a Russian Slavist and ethnographer who published nearly 600 Russian fairy and folk ta ...
. Many of Stravinsky's Russian period works featured animal characters and themes, likely due to exposure to nursery rhyme
A nursery rhyme is a traditional poem or song for children in Britain and many other countries, but usage of the term dates only from the late 18th/early 19th century. The term Mother Goose rhymes is interchangeable with nursery rhymes.
From t ...
s he read with his four children. Stravinsky also used unique theatrical styles. ''Les noces'' blended the ballet and cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir.
The meaning of ...
, a unique production described on the score as "Russian Choreographic Scenes". In ''Renard'', the voices were placed in the orchestra, as they were meant to accompany the action on stage. ''L'Histoire du soldat
' (''The Soldier's Tale'') is a theatrical work "to be read, played, and danced" () by three actors and one or several dancers, accompanied by a septet of instruments. Conceived by Igor Stravinsky and Swiss writer C. F. Ramuz, the piece was bas ...
'' was composed in 1918 with the Swiss novelist Charles F. Ramuz as a "quirky musical-theatre work" for dancers, a narrator, and a septet
A septet is a formation containing exactly seven members. It is commonly associated with musical groups but can be applied to any situation where seven similar or related objects are considered a single unit, such as a seven-line stanza of poetry. ...
. The work mixed the Russian folktales in the narrative with common musical structures of the time, like the tango
Tango is a partner dance and social dance that originated in the 1880s along the Río de la Plata, the natural border between Argentina and Uruguay. The tango was born in the impoverished port areas of these countries as the result of a combina ...
, waltz
The waltz ( ), meaning "to roll or revolve") is a ballroom and folk dance, normally in triple ( time), performed primarily in closed position.
History
There are many references to a sliding or gliding dance that would evolve into the wa ...
, rag
Rag, rags, RAG or The Rag may refer to:
Common uses
* Rag, a piece of old cloth
* Rags, tattered clothes
* Rag (newspaper), a publication engaging in tabloid journalism
* Rag paper, or cotton paper
Arts and entertainment Film
* ''Rags'' (1915 ...
, and chorale
Chorale is the name of several related musical forms originating in the music genre of the Lutheran chorale:
* Hymn tune of a Lutheran hymn (e.g. the melody of "Wachet auf, ruft uns die Stimme"), or a tune in a similar format (e.g. one of the t ...
. According to Walsh, Stravinsky's music was always influenced by his Russian roots, and despite their decreased use in his later output, he maintained continuous musical innovation.
Neoclassical period, 1920–1951
In Naples, Italy, Stravinsky saw a ''commedia dell'arte
(; ; ) was an early form of professional theatre, originating from Italian theatre, that was popular throughout Europe between the 16th and 18th centuries. It was formerly called Italian comedy in English and is also known as , , and . Charact ...
'' featuring the "great drunken lout" of a character Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
, who would later become the subject of his ballet ''Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
''. Officially begun in 1919, ''Pulcinella
Pulcinella (; nap, Pulecenella) is a classical character that originated in of the 17th century and became a stock character in Neapolitan puppetry. Pulcinella's versatility in status and attitude has captivated audiences worldwide and kept t ...
'' was commissioned by Diaghilev after he proposed the idea of a ballet based on music by Giovanni Battista Pergolesi
Giovanni Battista Draghi (; 4 January 1710 – 16 or 17 March 1736), often referred to as Giovanni Battista Pergolesi (), was an Italian Baroque composer, violinist, and organist. His best-known works include his Stabat Mater and the opera ''L ...
, Domenico Gallo
Domenico Gallo (1730 – c. 1768) was an Italian composer and violinist. Born in Venice in 1730, Gallo composed mostly church music, including a Stabat Mater. Gallo also composed violin sonatas, symphonies and possibly violin concertos.
Some ...
, and others whose music was published under Pergolesi's name. Composing a work based on harmonic and rhythmic systems by a late-Baroque era composer was the beginning of Stravinsky's turn towards 18th-century music that would "serve him for some 30 productive years."
Although White and Jeremy Noble consider Stravinsky's neoclassical period to have begun in 1920 with his ''Symphonies for Wind Instruments'', Bartók argues that the period "really starts with his Octet for Wind Instruments, followed by his Concerto for Piano ..." During this period, Stravinsky used techniques and themes from the Classical period of music
The Classical period was an era of classical music between roughly 1750 and 1820.
The Classical period falls between the Baroque and the Romantic periods. Classical music has a lighter, clearer texture than Baroque music, but a more sophistic ...
.

Greek mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical co ...
was a common theme in Stravinsky's neoclassical works. His first Greek mythology-based work was the ballet ''Apollon musagète
''Apollo'' (originally ''Apollon musagète'' and variously known as ''Apollo musagetes'', ''Apolo Musageta'', and ''Apollo, Leader of the Muses'') is a neoclassical ballet in two ''tableaux'' composed between 1927 and 1928 by Igor Stravinsky. ...
'' (1927), choosing the leader of the Muses
In ancient Greek religion and mythology, the Muses ( grc, Μοῦσαι, Moûsai, el, Μούσες, Múses) are the inspirational goddesses of literature, science, and the arts. They were considered the source of the knowledge embodied in the p ...
and god of art Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label=Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label= ...
as the subject. Stravinsky would use themes from Greek mythology in future works like ''Oedipus rex
''Oedipus Rex'', also known by its Greek title, ''Oedipus Tyrannus'' ( grc, Οἰδίπους Τύραννος, ), or ''Oedipus the King'', is an Athenian tragedy by Sophocles that was first performed around 429 BC. Originally, to the ancient Gr ...
'' (1927), ''Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
'' (1935), and ''Orpheus
Orpheus (; Ancient Greek: Ὀρφεύς, classical pronunciation: ; french: Orphée) is a Thracian bard, legendary musician and prophet in ancient Greek religion. He was also a renowned poet and, according to the legend, travelled with Jaso ...
'' (1947). Taruskin writes that ''Oedipus rex'' was "the product of Stravinsky's neo-classical manner at its most extreme," and that musical techniques "thought outdated" were juxtaposed against "a deliberately offputting '' hauteur''." In addition, Stravinsky turned towards older musical structures and techniques during this period and modernised them. His Octet
Octet may refer to:
Music
* Octet (music), ensemble consisting of eight instruments or voices, or composition written for such an ensemble
** String octet, a piece of music written for eight string instruments
*** Octet (Mendelssohn), 1825 compos ...
(1923) uses the sonata form
Sonata form (also ''sonata-allegro form'' or ''first movement form'') is a musical form, musical structure generally consisting of three main sections: an exposition, a development, and a recapitulation. It has been used widely since the middle ...
, modernising it by disregarding the standard ordering of themes and traditional tonal relationships for different sections. The idea of musical counterpoint
In music, counterpoint is the relationship between two or more musical lines (or voices) which are harmonically interdependent yet independent in rhythm and melodic contour. It has been most commonly identified in the European classical tradi ...
, commonly used in the Baroque era, was used throughout the choral ''Symphony of Psalms
The ''Symphony of Psalms'' is a choral symphony in three movements composed by Igor Stravinsky in 1930 during his neoclassical period. The work was commissioned by Serge Koussevitzky to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the Boston Symphony Orch ...
''.
Stravinsky's neoclassical period ended in 1951 with the opera ''The Rake's Progress
''The Rake's Progress'' is an English-language opera from 1951 in three acts and an epilogue by Igor Stravinsky. The libretto, written by W. H. Auden and Chester Kallman, is based loosely on the eight paintings and engravings ''A Rake's Progres ...
''. Taruskin described the opera as "the hub and essence of 'neo-classicism'." He points out how the opera contains numerous references to Greek mythology and other operas like ''Don Giovanni
''Don Giovanni'' (; K. 527; Vienna (1788) title: , literally ''The Rake Punished, or Don Giovanni'') is an opera in two acts with music by Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart to an Italian libretto by Lorenzo Da Ponte. Its subject is a centuries-old Spanis ...
'' and ''Carmen
''Carmen'' () is an opera in four acts by the French composer Georges Bizet. The libretto was written by Henri Meilhac and Ludovic Halévy, based on the Carmen (novella), novella of the same title by Prosper Mérimée. The opera was first perfo ...
'', but still "embody the distinctive structure of a fairy tale." Stravinsky was inspired by the operas of Mozart in composing the music, but other scholars also point out influence from Handel
George Frideric (or Frederick) Handel (; baptised , ; 23 February 1685 – 14 April 1759) was a German-British Baroque composer well known for his operas, oratorios, anthems, concerti grossi, and organ concertos. Handel received his training i ...
, Gluck
Christoph Willibald (Ritter von) Gluck (; 2 July 1714 – 15 November 1787) was a composer of Italian and French opera in the early classical period (music), classical period. Born in the Upper Palatinate and raised in Bohemia, both part of the ...
, Beethoven
Ludwig van Beethoven (baptised 17 December 177026 March 1827) was a German composer and pianist. Beethoven remains one of the most admired composers in the history of Western music; his works rank amongst the most performed of the classical ...
, Schubert
Franz Peter Schubert (; 31 January 179719 November 1828) was an Austrian composer of the late Classical and early Romantic eras. Despite his short lifetime, Schubert left behind a vast ''oeuvre'', including more than 600 secular vocal wor ...
, Weber
Weber (, or ; German: ) is a surname of German origin, derived from the noun meaning " weaver". In some cases, following migration to English-speaking countries, it has been anglicised to the English surname 'Webber' or even 'Weaver'.
Notable pe ...
, Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards f ...
, Donizetti
Domenico Gaetano Maria Donizetti (29 November 1797 – 8 April 1848) was an Italian composer, best known for his almost 70 operas. Along with Gioachino Rossini and Vincenzo Bellini, he was a leading composer of the '' bel canto'' opera style dur ...
, and Verdi
Giuseppe Fortunino Francesco Verdi (; 9 or 10 October 1813 – 27 January 1901) was an Italian composer best known for his operas. He was born near Busseto to a provincial family of moderate means, receiving a musical education with the h ...
. ''The Rake's Progress'' has become an important work in opera repertoire, being " ore performedthan any other opera written after the death of Puccini
Giacomo Puccini (Lucca, 22 December 1858Bruxelles, 29 November 1924) was an Italian composer known primarily for his operas. Regarded as the greatest and most successful proponent of Italian opera after Verdi, he was descended from a long lin ...
."
Serial period, 1954–1968
In the 1950s, Stravinsky began using serial compositional techniques such as thetwelve-tone technique
The twelve-tone technique—also known as dodecaphony, twelve-tone serialism, and (in British usage) twelve-note composition—is a method of musical composition first devised by Austrian composer Josef Matthias Hauer, who published his "law o ...
originally devised by Arnold Schoenberg
Arnold Schoenberg or Schönberg (, ; ; 13 September 187413 July 1951) was an Austrian-American composer, music theorist, teacher, writer, and painter. He is widely considered one of the most influential composers of the 20th century. He was as ...
. Noble writes that this time was "the most profound change in Stravinsky's musical vocabulary," partly due to Stravinsky's newfound interest in the music of the Second Viennese School
The Second Viennese School (german: Zweite Wiener Schule, Neue Wiener Schule) was the group of composers that comprised Arnold Schoenberg and his pupils, particularly Alban Berg and Anton Webern, and close associates in early 20th-century Vienna. ...
after meeting Robert Craft.
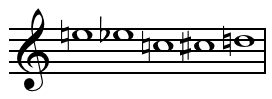 Stravinsky first experimented with non-twelve-tone serial techniques in vocal and chamber works such as the
Stravinsky first experimented with non-twelve-tone serial techniques in vocal and chamber works such as the Cantata
A cantata (; ; literally "sung", past participle feminine singular of the Italian verb ''cantare'', "to sing") is a vocal composition with an instrumental accompaniment, typically in several movements, often involving a choir.
The meaning of ...
(1952), the Septet
A septet is a formation containing exactly seven members. It is commonly associated with musical groups but can be applied to any situation where seven similar or related objects are considered a single unit, such as a seven-line stanza of poetry. ...
(1953) and ''Three Songs from Shakespeare'' (1953). The first of his compositions fully based on such techniques was ''In Memoriam Dylan Thomas'' (1954). ''Agon
Agon (Greek ) is a Greek term for a conflict, struggle or contest. This could be a contest in athletics, in chariot or horse racing, or in music or literature at a public festival in ancient Greece. Agon is the word-forming element in 'agony', ...
'' (1954–57) was the first of his works to include a twelve-tone series and the second movement from ''Canticum Sacrum
''Canticum Sacrum ad Honorem Sancti Marci Nominis'' is a 17-minute choral-orchestral piece composed in 1955 by Igor Stravinsky (1882–1971) in tribute "To the City of Venice, in praise of its Patron Saint, the Blessed Mark, Apostle." The piec ...
'' (1956) was the first piece to contain a movement entirely based on a tone row
In music, a tone row or note row (german: Reihe or '), also series or set, is a non-repetitive ordering of a set of pitch-classes, typically of the twelve notes in musical set theory of the chromatic scale, though both larger and smaller sets ar ...
. ''Agon''diatonic
Diatonic and chromatic are terms in music theory that are most often used to characterize Scale (music), scales, and are also applied to musical instruments, Interval (music), intervals, Chord (music), chords, Musical note, notes, musical sty ...
, moves towards full 12-tone serialism in the middle, and returns to diatonicism in the end. Stravinsky returned to sacred themes in works such as ''Canticum Sacrum,'' '' Threni'' (1958), ''A Sermon, a Narrative and a Prayer
''A Sermon, a Narrative and a Prayer'' is a cantata for alto and tenor singers, a narrator, chorus, and orchestra by Igor Stravinsky, composed in 1960–61. It belongs to the composer’s Serialism, serial period, and lasts a little over a quarte ...
'' (1961), and ''The Flood'' (1962). Stravinsky used a number of concepts from earlier works in his serial pieces; for example, the voice of God
In monotheism, monotheistic thought, God is usually viewed as the supreme being, creator deity, creator, and principal object of Faith#Religious views, faith.Richard Swinburne, Swinburne, R.G. "God" in Ted Honderich, Honderich, Ted. (ed)''The Ox ...
being two bass voices in homophony
In music, homophony (;, Greek: ὁμόφωνος, ''homóphōnos'', from ὁμός, ''homós'', "same" and φωνή, ''phōnē'', "sound, tone") is a texture in which a primary part is supported by one or more additional strands that flesh ou ...
seen in ''The Flood'' was previously used in ''Les noces''. Stravinsky's final work, the ''Requiem Canticles
''Requiem Canticles'' is a 15-minute composition by Igor Stravinsky, for contralto and bass soli, chorus, and orchestra. Stravinsky completed the work in 1966, and it received its first performance that same year.
The work is a partial setting o ...
'' (1966), made use of a complex four-part array of tone rows throughout, showing the evolution of Stravinsky's serialist music. Noble describes the ''Requiem Canticles'' as "a distillation both of the liturgical text and of his own musical means of setting it, evolved and refined through a career of more than 60 years."
 Influence from other composers can be seen throughout this period. Stravinsky was heavily influenced by Schoenberg, not only in his use of the twelve-tone technique, but also in the distinctly "Schoenbergian" instrumentation of the Septet and the "Stravinskian interpretation of Schoenberg's ''
Influence from other composers can be seen throughout this period. Stravinsky was heavily influenced by Schoenberg, not only in his use of the twelve-tone technique, but also in the distinctly "Schoenbergian" instrumentation of the Septet and the "Stravinskian interpretation of Schoenberg's ''Klangfarbenmelodie
''Klangfarbenmelodie'' (German for "sound-color melody") is a musical technique that involves splitting a musical line or melody between several instruments, rather than assigning it to just one instrument (or set of instruments), thereby adding c ...
''" found in Stravinsky's ''Variations
Variation or Variations may refer to:
Science and mathematics
* Variation (astronomy), any perturbation of the mean motion or orbit of a planet or satellite, particularly of the moon
* Genetic variation, the difference in DNA among individuals ...
.'' Stravinsky also used a number of themes found in works by Benjamin Britten
Edward Benjamin Britten, Baron Britten (22 November 1913 – 4 December 1976, aged 63) was an English composer, conductor, and pianist. He was a central figure of 20th-century British music, with a range of works including opera, other ...
, commenting in ''Themes and Conclusions'' about the "many titles and subjects have sharedwith Mr. Britten already." In addition, Stravinsky was very familiar with the works of Anton Webern
Anton Friedrich Wilhelm von Webern (3 December 188315 September 1945), better known as Anton Webern (), was an Austrian composer and conductor whose music was among the most radical of its milieu in its sheer concision, even aphorism, and stea ...
, being one of the figures who inspired Stravinsky to consider serialism a possible form of composition.
Influences
Literary
Stravinsky displayed a taste in literature that was wide and reflected his constant desire for new discoveries. The texts and literary sources for his work began with interest inRussian folklore
Folklore of Russia is folklore of Russians and other ethnic groups of Russia.
Russian folklore takes its roots in the pagan beliefs of ancient Slavs and now is represented in the Russian fairy tales. Epic Russian bylinas are also an important ...
. After moving to Switzerland in 1914, Stravinsky began gathering folk stories from numerous collections, which were later used in works like ''Les noces'', ''Renard'', ''Pribaoutki
''Pribaoutki'' () is a cycle of four songs composed by Igor Stravinsky in 1914 to Russian texts by Alexander Afanasyev. Its Russian title has no direct English equivalent, although Richard Taruskin suggests "nonsense rhymes" or "jingles." (The Fr ...
'', and various songs. Many of Stravinsky's works, including ''The Firebird'', ''Renard'', and ''L'Histoire du soldat'' were inspired by Alexander Afanasyev
Alexander Nikolayevich Afanasyev (Afanasief, Afanasiev or Afanas'ev, russian: link=no, Александр Николаевич Афанасьев) ( — ) was a Russian Slavist and ethnographer who published nearly 600 Russian fairy and folk ta ...
's famous collection ''Russian Folk Tales''. Collections of folk music influenced Stravinsky's music; numerous melodies from ''The Rite of Spring'' were found in an anthology of Lithuanian folk songs.
An interest in the Latin liturgy
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
began shortly after Stravinsky rejoined the church in 1926, beginning with the composition of his first religious work in 1926 ''Pater Noster'', written in Old Church Slavonic
Old Church Slavonic or Old Slavonic () was the first Slavic languages, Slavic literary language.
Historians credit the 9th-century Byzantine Empire, Byzantine missionaries Saints Cyril and Methodius with Standard language, standardizing the lan ...
. He later used three psalms
The Book of Psalms ( or ; he, תְּהִלִּים, , lit. "praises"), also known as the Psalms, or the Psalter, is the first book of the ("Writings"), the third section of the Tanakh, and a book of the Old Testament. The title is derived ...
from the Latin Vulgate
The Vulgate (; also called (Bible in common tongue), ) is a late-4th-century Latin translation of the Bible.
The Vulgate is largely the work of Jerome who, in 382, had been commissioned by Pope Damasus I to revise the Gospels us ...
in his ''Symphony of Psalms'' for orchestra and mixed choir. Many works in the composer's neoclassical and serial periods used (or were based on) liturgical texts.
Stravinsky worked with many authors throughout his career. He first worked with the Swiss novelist Charles F. Ramuz on ''L'Histoire du soldat'' in 1918, who wrote the text and helped form the idea. In 1933, Ida Rubinstein
Ida Lvovna Rubinstein (russian: И́да Льво́вна Рубинште́йн; – 20 September 1960) was a Russian dancer, actress, art patron and Belle Époque figure. She performed with Diaghilev's Ballets Russes from 1909 to 1911 and ...
commissioned Stravinsky to set music to a poem by André Gide
André Paul Guillaume Gide (; 22 November 1869 – 19 February 1951) was a French author and winner of the Nobel Prize in Literature (in 1947). Gide's career ranged from its beginnings in the Symbolism (arts), symbolist movement, to the advent o ...
, later becoming the melodrama ''Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
''. The two collaborated well at first, but disagreements over the text caused Gide to leave the project. The story of ''The Rake's Progress'' was first conceived by Stravinsky and W. H. Auden
Wystan Hugh Auden (; 21 February 1907 – 29 September 1973) was a British-American poet. Auden's poetry was noted for its stylistic and technical achievement, its engagement with politics, morals, love, and religion, and its variety in ...
, the latter of whom wrote the libretto with Chester Kallman
Chester Simon Kallman (January 7, 1921 – January 18, 1975) was an American poet, librettist, and translator, best known for collaborating with W. H. Auden on opera librettos for Igor Stravinsky and other composers.
Life
Kallman was born in ...
. Stravinsky befriended many other authors as well, including T.S. Eliot, Aldous Huxley, Christopher Isherwood, and Dylan Thomas
Dylan Marlais Thomas (27 October 1914 – 9 November 1953) was a Welsh poet and writer whose works include the poems "Do not go gentle into that good night" and "And death shall have no dominion", as well as the "play for voices" ''Under ...
, the last of whom Stravinsky began working with on an opera in 1953 but stopped due to Thomas's death.
Artistic
Stravinsky worked with some of the most famous artists of his time, many of whom he met after the premiere of ''The Firebird''. Diaghilev was one of the composer's most prominent artistic influences, having introduced him to composing for the stage and bringing him international fame with his first three ballets. Through the Ballets Russes and Diaghilev, Stravinsky worked with figures likeVaslav Nijinsky
Vaslav (or Vatslav) Nijinsky (; rus, Вацлав Фомич Нижинский, Vatslav Fomich Nizhinsky, p=ˈvatsləf fɐˈmʲitɕ nʲɪˈʐɨnskʲɪj; pl, Wacław Niżyński, ; 12 March 1889/18908 April 1950) was a ballet dancer and choreog ...
, Léonide Massine
Leonid Fyodorovich Myasin (russian: Леони́д Фёдорович Мя́син), better known in the West by the French transliteration as Léonide Massine (15 March 1979), was a Russian choreographer and ballet dancer. Massine created the wo ...
, Alexandre Benois
Alexandre Nikolayevich Benois (russian: Алекса́ндр Никола́евич Бенуа́, also spelled Alexander Benois; ,Salmina-Haskell, Larissa. ''Russian Paintings and Drawings in the Ashmolean Museum''. pp. 15, 23-24. Published by ...
, Michel Fokine
Michael Fokine, ''Mikhail Mikhaylovich Fokin'', group=lower-alpha ( – 22 August 1942) was a groundbreaking Imperial Russian choreographer and dancer.
Career Early years
Fokine was born in Saint Petersburg to a prosperous merchant and a ...
, and Léon Bakst
Léon Bakst (russian: Леон (Лев) Николаевич Бакст, Leon (Lev) Nikolaevich Bakst) – born as Leyb-Khaim Izrailevich (later Samoylovich) Rosenberg, Лейб-Хаим Израилевич (Самойлович) Розенбе ...
. The composer's interest in art propelled him to develop a strong relationship with Picasso, whom he met in 1917. From 1917 to 1920, the two engaged in an artistic dialogue in which they exchanged small-scale works of art to each other as a sign of intimacy, which included the famous portrait of Stravinsky by Picasso, and a short sketch of clarinet music by Stravinsky. This exchange was essential to establish how the artists would approach their collaborative space in ''Ragtime'' and ''Pulcinella''.
Legacy
Stravinsky is widely regarded as one of the greatest composers of the 20th century. In 1998, ''Time'' magazine named him one of the100 most influential people
''Time'' 100 (often stylized as ''TIME'' 100) is an annual listicle of the 100 most influential people in the world, assembled by the American news magazine ''Time''. First published in 1999 as the result of a debate among American academics, po ...
of the century. Stravinsky was not only recognised for his composing; he also achieved fame as a pianist and as a conductor; Philip Glass
Philip Glass (born January 31, 1937) is an American composer and pianist. He is widely regarded as one of the most influential composers of the late 20th century. Glass's work has been associated with minimal music, minimalism, being built up fr ...
wrote in 1998, "He conducted with an energy and vividness that completely conveyed his every musical intention. Here was Stravinsky, a musical revolutionary whose own evolution never stopped. There is not a composer who lived during his time or is alive today who was not touched, and sometimes transformed, by his work."
 Stravinsky had a number of dissenters throughout his career, particularly regarding his later works. In 1935, the American composer
Stravinsky had a number of dissenters throughout his career, particularly regarding his later works. In 1935, the American composer Marc Blitzstein
Marcus Samuel Blitzstein (March 2, 1905January 22, 1964), was an American composer, lyricist, and librettist. He won national attention in 1937 when his pro-union musical ''The Cradle Will Rock'', directed by Orson Welles, was shut down by the Wo ...
compared Stravinsky to Jacopo Peri
Jacopo Peri (20 August 156112 August 1633), known under the pseudonym Il Zazzerino, was an Italian composer and singer of the transitional period between the Renaissance and Baroque styles, and is often called the inventor of opera. He wrote the ...
and C. P. E. Bach
Carl Philipp Emanuel Bach (8 March 1714 – 14 December 1788), also formerly spelled Karl Philipp Emmanuel Bach, and commonly abbreviated C. P. E. Bach, was a German Classical period musician and composer, the fifth child and sec ...
, conceding that, "There is no denying the greatness of Stravinsky. It is just that he is not great enough." In 1934, the composer Constant Lambert
Leonard Constant Lambert (23 August 190521 August 1951) was a British composer, conductor, and author. He was the founder and music director of the Royal Ballet, and (alongside Ninette de Valois and Frederick Ashton) he was a major figure in th ...
described pieces such as ''L'Histoire du soldat'' as containing "essentially cold-blooded abstraction ... melodic fragments in are completely meaningless themselves. They are merely successions of notes that can conveniently be divided into groups of three, five, and seven and set against other mathematical groups." On the contrary, Erik Satie
Eric Alfred Leslie Satie (, ; ; 17 May 18661 July 1925), who signed his name Erik Satie after 1884, was a French composer and pianist. He was the son of a French father and a British mother. He studied at the Paris Conservatoire, but was an und ...
argued that measuring the "greatness" of an artist by comparing him to other artists is illusory, and that every piece of music should be judged on its own merits and not by comparing it to the standards of other composers.
Stravinsky's reputation in Russia and the USSR varied. Performances of his music were banned from around 1933 until 1962, the year Khrushchev invited him to the USSR for an official visit. In 1972, an official proclamation by the Soviet Minister of Culture, Yekaterina Furtseva
Yekaterina Alexeyevna Furtseva (russian: Екатерина Алексеевна Фурцева; 7 December 1910 – 24 October 1974) was a Soviet politician and the second woman to be admitted as secretary of the Central Committee of the Comm ...
, ordered Soviet musicians to "study and admire" Stravinsky's music, and she made hostility toward it a potential offence.
White writes that the attention given to the composer's first three ballets undermined the importance of his later works, and that works like ''Les noces
''Les Noces'' (French for The Wedding; russian: Свадебка, ''Svadebka'') is a ballet and orchestral concert work composed by Igor Stravinsky for percussion, pianists, chorus, and vocal soloists. The composer gave it the descriptive title " ...
'', the ''Symphony of Psalms
The ''Symphony of Psalms'' is a choral symphony in three movements composed by Igor Stravinsky in 1930 during his neoclassical period. The work was commissioned by Serge Koussevitzky to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the Boston Symphony Orch ...
'', and ''Persephone
In ancient Greek mythology and religion, Persephone ( ; gr, Περσεφόνη, Persephónē), also called Kore or Cora ( ; gr, Κόρη, Kórē, the maiden), is the daughter of Zeus and Demeter. She became the queen of the underworld after ...
'' "represent the high-water mark of his invention and form one of the most precious contributions to the musical treasury of the twentieth century." The conductor Michael Tilson Thomas
Michael Tilson Thomas (born December 21, 1944) is an American conductor, pianist and composer. He is Artistic Director Laureate of the New World Symphony, an American orchestral academy based in Miami Beach, Florida, Music Director Laureate of ...
said in a 2013 interview for NPR
National Public Radio (NPR, stylized in all lowercase) is an American privately and state funded nonprofit media organization headquartered in Washington, D.C., with its NPR West headquarters in Culver City, California. It differs from other ...
, " travinskyhad insatiable curiosity about words, about geography, about just things that he encountered in his day-to-day life ... he was never going to stay still, he was always going to move forward." Georg Predota's profile of Stravinsky for ''Interlude'' says regarding Stravinsky's vast styles, "he might well have represented the face of an entire century as his works touch almost every important trend and tendency the century had on offer."
Stravinsky was noted for his distinctive use of rhythm, especially in ''The'' ''Rite of Spring''. According to Glass, "the idea of pushing the rhythms across the bar lines ... led the way ... orthe rhythmic structure of music o become
O, or o, is the fifteenth letter and the fourth vowel letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''o'' (pronounced ), plu ...
much more fluid and in a certain way spontaneous." Glass also noted Stravinsky's "primitive, offbeat rhythmic drive". Andrew J. Browne wrote, "Stravinsky is perhaps the only composer who has raised rhythm in itself to the dignity of art." Over the course of his career, Stravinsky called for a wide variety of orchestral, instrumental, and vocal forces, ranging from single instruments in such works as ''Three Pieces for Solo Clarinet'' (1918) or ''Elegy for Solo Viola'' (1944) to the enormous orchestra of ''The'' ''Rite of Spring'' (1913), which Copland characterised as "the foremost orchestral achievement of the 20th century".
Stravinsky influenced many composers and musicians. George Benjamin wrote in ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers ''The Observer'' and ''The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the Gu ...
'' that, "Since 1913 generation after generation of composers – from Varèse to Boulez, Bartók to Ligeti — has felt impelled to face the challenges set by 'The Rite of Spring''" while Walsh wrote, "For younger composers of almost every persuasion, his work has continued to offer inspiration and a source of method." Stravinsky's rhythm and vitality greatly influenced Aaron Copland
Aaron Copland (, ; November 14, 1900December 2, 1990) was an American composer, composition teacher, writer, and later a conductor of his own and other American music. Copland was referred to by his peers and critics as "the Dean of American Com ...
and Pierre Boulez
Pierre Louis Joseph Boulez (; 26 March 1925 – 5 January 2016) was a French composer, conductor and writer, and the founder of several musical institutions. He was one of the dominant figures of post-war Western classical music.
Born in Mont ...
, the latter who Stravinsky had worked with on ''Threni''. Stravinsky's combination of folklore and modernism influenced the works and style of Béla Bartók as well. Stravinsky also influenced composers like Elliott Carter
Elliott Cook Carter Jr. (December 11, 1908 – November 5, 2012) was an American modernist composer. One of the most respected composers of the second half of the 20th century, he combined elements of European modernism and American "ultra- ...
, Harrison Birtwistle
Sir Harrison Birtwistle (15 July 1934 – 18 April 2022) was an English composer of contemporary classical music best known for his operas, often based on mythological subjects. Among his many compositions, his better known works include ''Th ...
, and John Tavener
Sir John Kenneth Tavener (28 January 1944 – 12 November 2013) was an English composer, known for his extensive output of choral religious works. Among his best known works are '' The Lamb'' (1982), '' The Protecting Veil'' (1988), and ''Song ...
. Included among his students are Robert Craft
Robert Lawson Craft (October 20, 1923 – November 10, 2015) was an American conductor and writer. He is best known for his intimate professional relationship with Igor Stravinsky, on which Craft drew in producing numerous recordings and books.
...
, Robert Strassburg
Robert Strassburg (August 30, 1915 – October 25, 2003) was a
leading American conductor, composer, musicologist and music educator of the twentieth century. His studies in music were completed under the supervision of such leading composers a ...
, and Warren Zevon
Warren William Zevon (; January 24, 1947 – September 7, 2003) was an American rock singer, songwriter, and musician.
Zevon's most famous compositions include "Werewolves of London", "Lawyers, Guns and Money", and " Roland the Headless Tho ...
.
Honours
Stravinsky received theRoyal Philharmonic Society
The Royal Philharmonic Society (RPS) is a British music society, formed in 1813. Its original purpose was to promote performances of instrumental music in London. Many composers and performers have taken part in its concerts. It is now a memb ...
's gold medal in 1954, the Léonie Sonning Music Prize
The Léonie Sonning Music Prize, or Sonning Award, which is recognized as Denmark's highest musical honor, is given annually to an international composer or musician. It was first awarded in 1959 to composer Igor Stravinsky. Laureates are no ...
in 1959, and the Wihuri Sibelius Prize
The Wihuri Sibelius Prize is a music prize awarded by the Wihuri Foundation for International Prizes to prominent composers who have become internationally known and acknowledged. The Wihuri Sibelius Prize is one of the biggest and most prestig ...
in 1963. On 25 July 1966, he was awarded the Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
Military Order of Saint James of the Sword
The Military Order of Saint James of the Sword ( pt, Ordem Militar de Sant'Iago da Espada) is a Portuguese order of chivalry. Its full name is the Ancient, Most Noble and Enlightened Military Order of Saint James of the Sword, of the Scientifi ...
. In 1977, the "Sacrificial Dance" from ''The Rite of Spring'' was included among many tracks around the world on the Voyager Golden Record
The Voyager Golden Records are two phonograph records that were included aboard both Voyager spacecraft launched in 1977. The records contain sounds and images selected to portray the diversity of life and culture on Earth, and are intended for ...
. In 1982, the composer was featured on a 2¢ postage stamp by the United States Postal Service
The United States Postal Service (USPS), also known as the Post Office, U.S. Mail, or Postal Service, is an independent agency of the executive branch of the United States federal government responsible for providing postal service in the U ...
as part of its Great Americans stamp series. He received a star on the Hollywood Walk of Fame
The Hollywood Walk of Fame is a historic landmark which consists of more than 2,700 five-pointed terrazzo and brass stars embedded in the sidewalks along 15 blocks of Hollywood Boulevard and three blocks of Vine Street in Hollywood, Californ ...
in 1960 and was posthumously inducted into the National Museum of Dance and Hall of Fame
The National Museum of Dance and Hall of Fame, in the Saratoga Spa State Park, Saratoga Springs, New York, was established in 1986. It contains photographs, videos, artifacts, costumes, and biographies. The museum is located in the former Washi ...
in 2004.
A number of major works were dedicated to Stravinsky, including ''En blanc et noir
''En blanc et noir'' (; en, "In White and Black"), L. 134, CD. 142, is a suite in three movements for two pianos by Claude Debussy, written in June 1915. He composed the work on the Normandy coast, suffering from cancer and concerned about the i ...
'' by Claude Debussy, ''Trois poèmes de Mallarmé
''Trois poèmes de Mallarmé'' is a sequence of three art songs by Maurice Ravel, based on poems by Stéphane Mallarmé for soprano, two flutes, two clarinets, piano, and string quartet. Composed in 1913, it was premiered on 14 January 1914, perf ...
'' by Maurice Ravel, and the revised version of '' La tragédie de Salomé'' by Florent Schmitt
Florent Schmitt (; 28 September 187017 August 1958) was a French composer. He was part of the group known as Les Apaches. His most famous pieces are ''La tragédie de Salome'' and ''Psaume XLVII'' (Psalm 47). He has been described as "one of the ...
. The composer received five Grammy Awards
The Grammy Awards (stylized as GRAMMY), or simply known as the Grammys, are awards presented by the Recording Academy of the United States to recognize "outstanding" achievements in the music industry. They are regarded by many as the most pres ...
and eleven total nominations. Three records of his works were inducted into the Grammy Hall of Fame
The Grammy Hall of Fame is a hall of fame to honor musical recordings of lasting qualitative or historical significance. Inductees are selected annually by a special member committee of eminent and knowledgeable professionals from all branches of ...
in 1993, 1999, and 2000, and he was posthumously awarded
A posthumous award is granted after the recipient has died. Many prizes, medals, and awards can be granted posthumously. Australian actor Heath Ledger, for example, won many awards after his death in 2008. Military decorations, such as Hero of ...
the Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award
The Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award is a special Grammy Award that is awarded by The Recording Academy to "performers who, during their lifetimes, have made creative contributions of outstanding artistic significance to the field of recording."
...
in 1987.
Recordings
Stravinsky found recordings a practical and useful tool in preserving his thoughts on the interpretation of his music. As a conductor of his own music, he recorded primarily forColumbia Records
Columbia Records is an American record label owned by Sony Music, Sony Music Entertainment, a subsidiary of Sony Corporation of America, the North American division of Japanese Conglomerate (company), conglomerate Sony. It was founded on Janua ...
, beginning in 1928 with a performance of the original suite from ''The Firebird'' and concluding in 1967 with the 1945 suite from the same ballet. In the late 1940s he made several recordings for RCA Victor
RCA Records is an American record label currently owned by Sony Music Entertainment, a subsidiary of Sony Corporation of America. It is one of Sony Music's four flagship labels, alongside RCA's former long-time rival Columbia Records; also Aris ...
at the Republic Studios
Republic Pictures Corporation (currently held under Melange Pictures, LLC) was an American motion picture production-distribution corporation in operation from 1935 to 1967, that was based in Los Angeles. It had studio facilities in Studio City an ...
in Los Angeles. Although most of his recordings were made with studio musicians, he also worked with the Chicago Symphony Orchestra, the Cleveland Orchestra
The Cleveland Orchestra, based in Cleveland, is one of the five American orchestras informally referred to as the " Big Five". Founded in 1918 by the pianist and impresario Adella Prentiss Hughes, the orchestra plays most of its concerts at Sev ...
, the CBC Symphony Orchestra
The CBC Symphony Orchestra (french: Orchestre symphonique de la SRC; CBCSO/OSSRC) was a radio orchestra based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was operated by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation during the 1950s and 1960s.
History
The CBCSO was f ...
, the New York Philharmonic
The New York Philharmonic, officially the Philharmonic-Symphony Society of New York, Inc., globally known as New York Philharmonic Orchestra (NYPO) or New York Philharmonic-Symphony Orchestra, is a symphony orchestra based in New York City. It is ...
, the Royal Philharmonic Orchestra
The Royal Philharmonic Orchestra (RPO) is a British symphony orchestra based in London, that performs and produces primarily classic works.
The RPO was established by Thomas Beecham in 1946. In its early days, the orchestra secured profitable ...
, and the Bavarian Radio Symphony Orchestra
The Bavarian Radio Symphony Orchestra (german: Symphonieorchester des Bayerischen Rundfunks, BRSO) is a German radio orchestra. Based in Munich, Germany, it is one of the city's four orchestras. The BRSO is one of two full-size symphony orchestr ...
.
During his lifetime, Stravinsky appeared on several telecasts, including the 1962 world premiere of ''The Flood'' on CBS Television
CBS Broadcasting Inc., commonly shortened to CBS, the abbreviation of its former legal name Columbia Broadcasting System, is an American commercial broadcast television and radio network serving as the flagship property of the CBS Entertainmen ...
. Although he made an appearance, the actual performance was conducted by Craft. Numerous films and videos of the composer have been preserved, including the 1966 award-winning National Film Board of Canada
The National Film Board of Canada (NFB; french: Office national du film du Canada (ONF)) is Canada's public film and digital media producer and distributor. An agency of the Government of Canada, the NFB produces and distributes documentary f ...
documentary ''Stravinsky'', directed by Roman Kroitor
Roman Kroitor (December 12, 1926 – September 17, 2012) was a Canadian filmmaker who was known as an early practitioner of ''cinéma vérité'', as co-founder of IMAX, and as creator of the Sandde hand-drawn stereoscopic animation system. H ...
and Wolf Koenig
Wolf Koenig (October 17, 1927 – June 26, 2014) was a Canadian film director, Film producer, producer, animator, cinematographer, and a pioneer in Direct Cinema at the National Film Board of Canada.
Early life
Born in Dresden, Germany, Koenig em ...
, in which he conducts the CBC Symphony Orchestra
The CBC Symphony Orchestra (french: Orchestre symphonique de la SRC; CBCSO/OSSRC) was a radio orchestra based in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It was operated by the Canadian Broadcasting Corporation during the 1950s and 1960s.
History
The CBCSO was f ...
in a recording of the ''Symphony of Psalms
The ''Symphony of Psalms'' is a choral symphony in three movements composed by Igor Stravinsky in 1930 during his neoclassical period. The work was commissioned by Serge Koussevitzky to celebrate the 50th anniversary of the Boston Symphony Orch ...
''.
Writings
Stravinsky published a number of books throughout his career, almost always with the aid of a (sometimes uncredited) collaborator. In his 1936 autobiography, ''Chronicle of My Life'', which was written with the help ofWalter Nouvel
Walter Feodorovich Nouvel (russian: Вальтер Федорович Нувель) (1871–1949) was a Russian émigré art-lover and writer. He co-wrote with Arnold Haskell a biography of Sergei Pavlovitch Diaghilev (''Diaghileff. His Artisti ...
, Stravinsky included his well-known statement that "music is, by its very nature, essentially powerless to express anything at all". With Alexis Roland-Manuel
Alexis Roland-Manuel (22 March 18911 November 1966) was a French composer and critic, remembered mainly for his criticism.
Biography
He was born Roland Alexis Manuel Lévy in Paris, to a family of Belgian and Jewish origins. He studied composi ...
and Pierre Souvtchinsky
Pyotr Petrovich Suvchinsky ( pl, Piotr Suwczyński, russian: Пётр Петро́вич Сувчи́нский), later known as Pierre Souvtchinsky (October 5, 1892, St-Petersburg – January 24, 1985, Paris), was a Russian artistic patron and wri ...
, he wrote his 1939–40 Harvard University Charles Eliot Norton Lectures, which were delivered in French and first collected under the title in 1942 and then translated in 1947 as ''Poetics of Music''. In 1959, several interviews between the composer and Craft were published as ''Conversations with Igor Stravinsky'', which was followed by a further five volumes over the following decade. A collection of Stravinsky's writings and interviews appears under the title ''Confidences sur la musique''.
Books and articles are selected from Appendix E of Eric Walter White's ''Stravinsky: The Composer and His Works'' and Stephen Walsh's profile of Stravinsky on ''Oxford Music Online
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theo ...
''.
Books
* Originally published in French as ''Chroniques de ma vie'', 2 vols. (Paris: Denoël et Steele, 1935), subsequently translated (anonymously) as ''Chronicle of My Life''. This edition reprinted as ''Igor Stravinsky – An Autobiography'', with a preface by Eric Walter White (London: Calder and Boyars, 1975) . Reprinted again as ''An Autobiography (1903–1934)'' (London: Boyars, 1990) . Also published as ''Igor Stravinsky – An Autobiography'' (New York: M. & J. Steuer, 1958), and * * Reprinted Berkeley: University of California Press, 1980. . * Reprinted 1981, Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press. The 2002 reprinted "One-Volume Edition" varies from the 1960 original, London: Faber and Faber. . * Reprinted, Berkeley and Los Angeles: University of California Press, 1981. * The 1968 reprinted ''Dialogues'' varies from the 1963 original, London: Faber and Faber. . * * * A one-volume edition of ''Themes and Episodes'' (1966) and ''Retrospectives and Conclusions'' (1969) as revised by Igor Stravinsky in 1971. .Articles
* ADICTECO
* A
DICTECO
* * A
DICTECO
* A
SCRIBD
* * A
DICTECO
* A
DICTECO
* Translated in English, 1936, as ''An Autobiography''. * * *
References
Notes
Citations
Sources
*Facsimile
Shortened at * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
*The Stravinsky Foundation
website * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Stravinsky, Igor 1882 births 1971 deaths 20th-century American composers 20th-century American conductors (music) 20th-century American male musicians 20th-century American pianists 20th-century classical composers 20th-century classical pianists 20th-century French composers 20th-century French conductors (music) 20th-century French male classical pianists 20th-century French male musicians Academic staff of the École Normale de Musique de Paris American classical composers American classical pianists American male classical composers American male classical pianists American male conductors (music) American opera composers American people of Polish descent American people of Russian descent Ballets Russes composers Burials at Isola di San Michele Composers for piano Naturalized citizens of France French classical composers French classical pianists French male classical composers French male classical pianists French people of Polish descent French people of Russian descent Grammy Award winners Grammy Lifetime Achievement Award winners Honorary Members of the Royal Philharmonic Society Emigrants from the Russian Empire to France Emigrants from the Russian Empire to Switzerland Emigrants from the Russian Empire to the United States Jazz-influenced classical composers Male opera composers Modernist composers Neoclassical composers People from Lomonosov People from Petergofsky Uyezd Pupils of Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov Ragtime composers Recipients of the Léonie Sonning Music Prize Royal Philharmonic Society Gold Medallists Russian anti-communists Russian classical pianists Russian male conductors (music) Russian male classical composers Russian opera composers Russian Orthodox Christians from the United States Russian people of Polish descent Twelve-tone and serial composers