Ice Hockey Clubs Established In 1994 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ice is
 As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a
As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a


 The low coefficient of friction ("
The low coefficient of friction ("
 The term that collectively describes all of the parts of the Earth's surface where water is in frozen form is the ''
The term that collectively describes all of the parts of the Earth's surface where water is in frozen form is the ''
Multi-language
) ''World Meteorological Organization'' / ''
 Ice on land ranges from the largest type called an "
Ice on land ranges from the largest type called an "
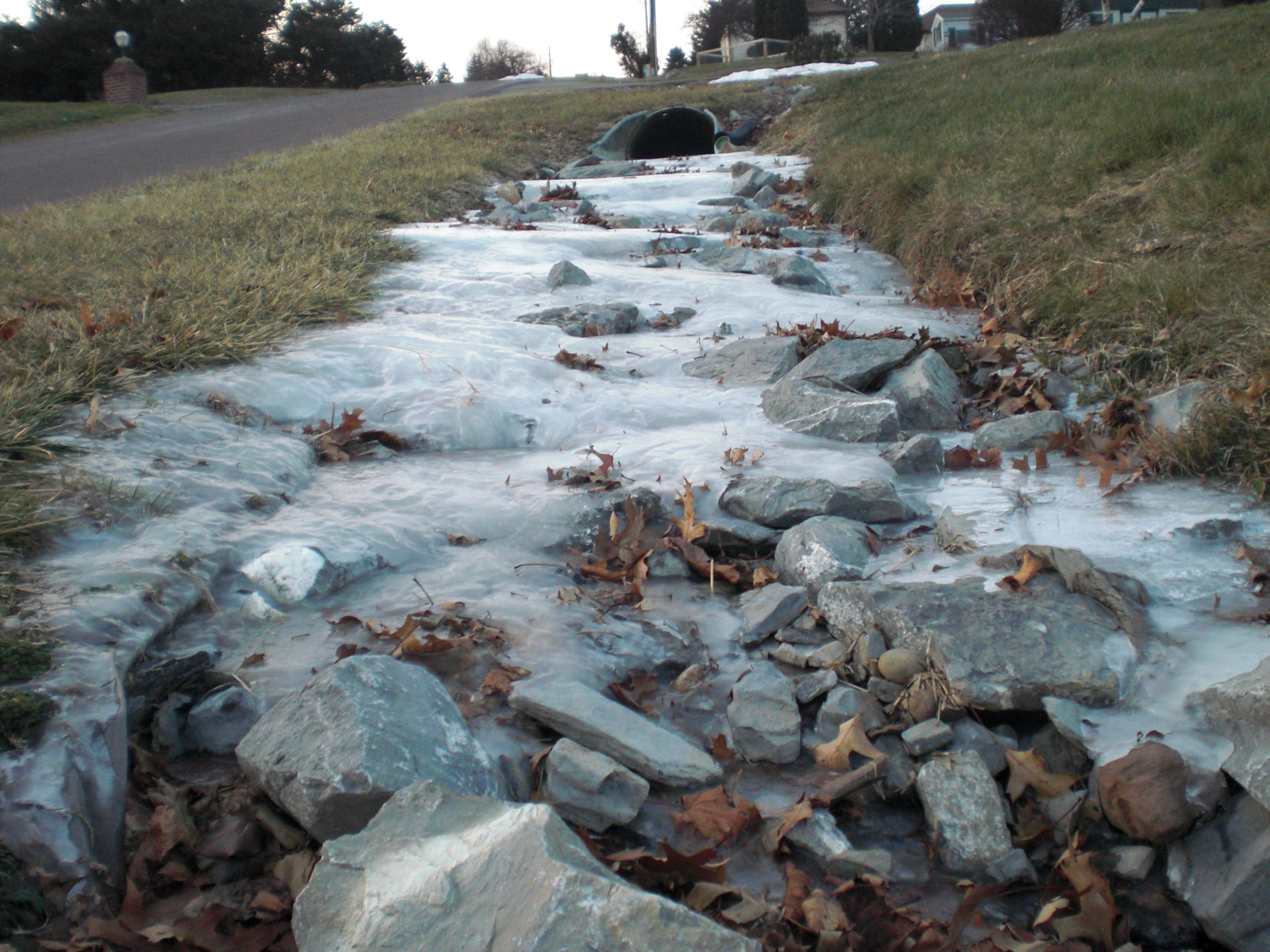 Ice which forms on moving water tends to be less uniform and stable than ice which forms on calm water.
Ice which forms on moving water tends to be less uniform and stable than ice which forms on calm water.

 Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm
Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm
 Snow crystals form when tiny
Snow crystals form when tiny
 There were thriving industries in 16th–17th century England whereby low-lying areas along the
There were thriving industries in 16th–17th century England whereby low-lying areas along the
 Ice is now produced on an industrial scale, for uses including food storage and processing, chemical manufacturing, concrete mixing and curing, and consumer or packaged ice.
Ice is now produced on an industrial scale, for uses including food storage and processing, chemical manufacturing, concrete mixing and curing, and consumer or packaged ice.
 Ice forming on
Ice forming on
 For ships, ice presents two distinct hazards. First, spray and freezing rain can produce an ice build-up on the superstructure of a vessel sufficient to make it unstable, and to require it to be hacked off or melted with steam hoses. Second,
For ships, ice presents two distinct hazards. First, spray and freezing rain can produce an ice build-up on the superstructure of a vessel sufficient to make it unstable, and to require it to be hacked off or melted with steam hoses. Second,
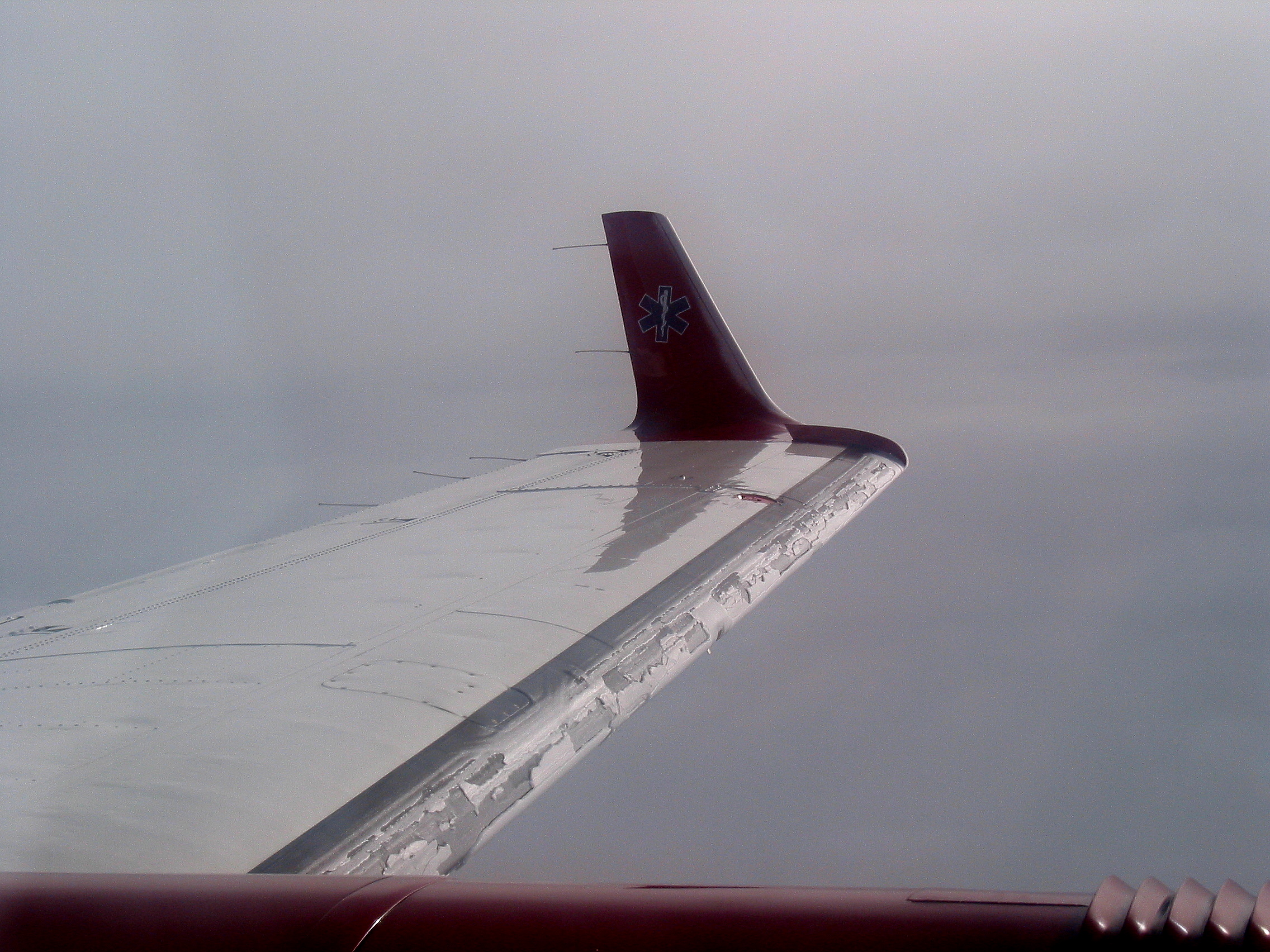 For aircraft, ice can cause a number of dangers. As an aircraft climbs, it passes through air layers of different temperature and humidity, some of which may be conducive to ice formation. If ice forms on the wings or control surfaces, this may adversely affect the flying qualities of the aircraft. During the first non-stop flight across the Atlantic, the British aviators Captain John Alcock and Lieutenant
For aircraft, ice can cause a number of dangers. As an aircraft climbs, it passes through air layers of different temperature and humidity, some of which may be conducive to ice formation. If ice forms on the wings or control surfaces, this may adversely affect the flying qualities of the aircraft. During the first non-stop flight across the Atlantic, the British aviators Captain John Alcock and Lieutenant
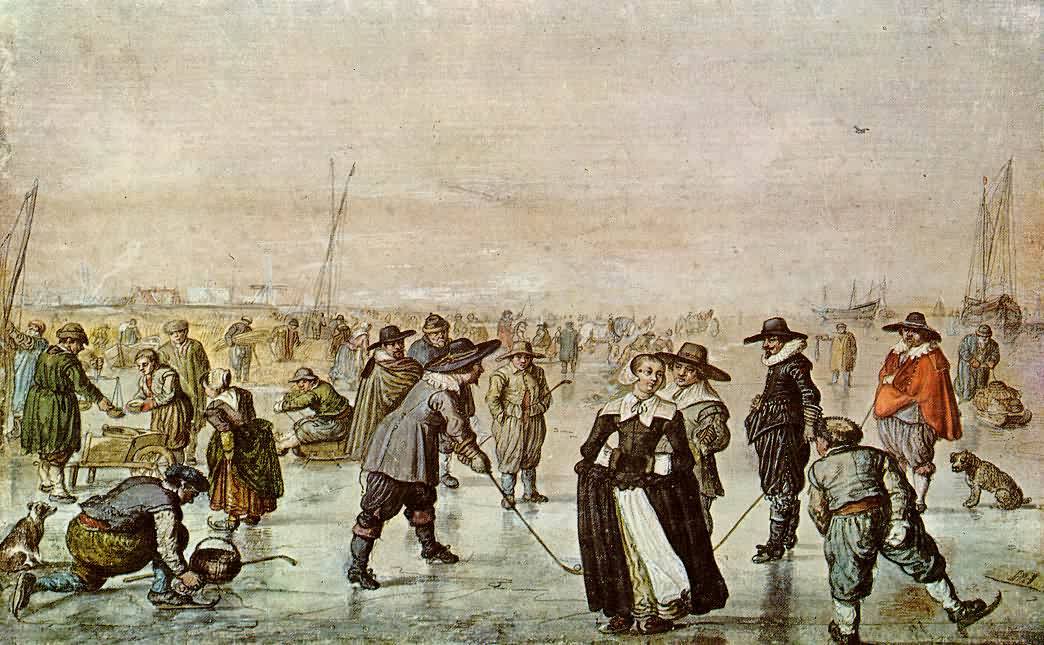 Ice also plays a central role in winter recreation and in many sports such as
Ice also plays a central role in winter recreation and in many sports such as
 * Engineers used the substantial strength of pack ice when they constructed Antarctica's first floating
* Engineers used the substantial strength of pack ice when they constructed Antarctica's first floating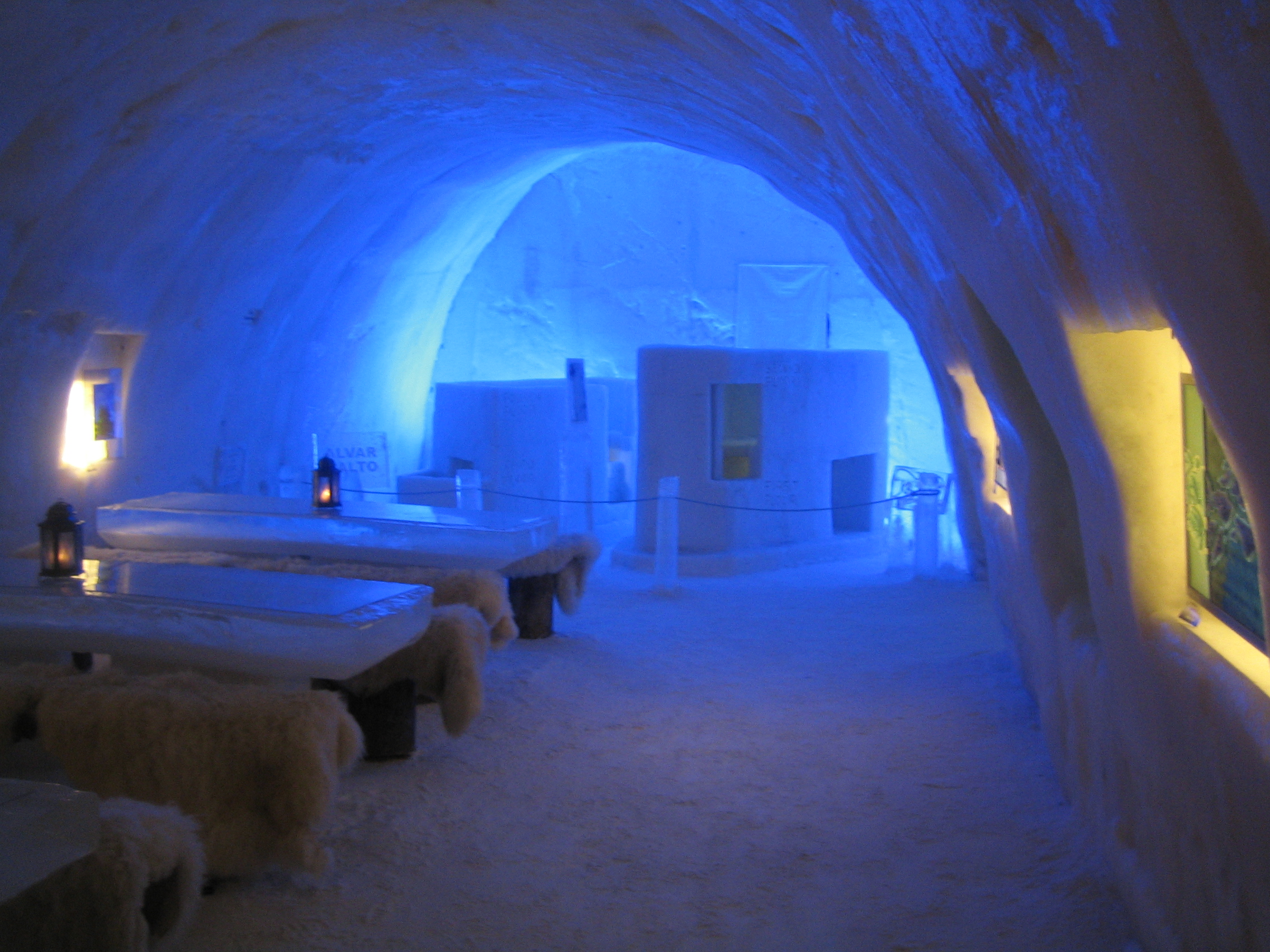  * Structures and ice sculptures are built out of large chunks of ice or by spraying waterMakkonen, L. (1994) "Ice and Construction". E & FN Spon, London. . The structures are mostly ornamental (as in the case with ice castles), and not practical for long-term habitation.
* Structures and ice sculptures are built out of large chunks of ice or by spraying waterMakkonen, L. (1994) "Ice and Construction". E & FN Spon, London. . The structures are mostly ornamental (as in the case with ice castles), and not practical for long-term habitation.
Webmineral listing for Ice
Estimating the bearing capacity of ice
{{Authority control Glaciology Minerals Transparent materials Articles containing video clips Limnology Oceanography Cryosphere
water
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
frozen into a solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structura ...
state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities
In chemistry and materials science, impurities are chemical substances inside a confined amount of liquid, gas, or solid, which differ from the chemical composition of the material or compound. Firstly, a pure chemical should appear thermodyn ...
such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaque
Opacity or opaque may refer to:
* Impediments to (especially, visible) light:
** Opacities, absorption coefficients
** Opacity (optics), property or degree of blocking the transmission of light
* Metaphors derived from literal optics:
** In lingui ...
bluish-white color.
In the Solar System
The Solar System Capitalization of the name varies. The International Astronomical Union, the authoritative body regarding astronomical nomenclature, specifies capitalizing the names of all individual astronomical objects but uses mixed "Solar ...
, ice is abundant and occurs naturally from as close to the Sun as Mercury to as far away as the Oort cloud
The Oort cloud (), sometimes called the Öpik–Oort cloud, first described in 1950 by the Dutch astronomer Jan Oort, is a theoretical concept of a cloud of predominantly icy planetesimals proposed to surround the Sun at distances ranging f ...
objects. Beyond the Solar System, it occurs as interstellar ice Interstellar ice consists of grains of volatiles in the ice phase that form in the interstellar medium. Ice and dust grains form the primary material out of which the Solar System was formed. Grains of ice are found in the dense regions of molecular ...
. It is abundant on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surf ...
's surfaceparticularly in the polar regions and above the snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
and, as a common form of precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hai ...
and deposition
Deposition may refer to:
* Deposition (law), taking testimony outside of court
* Deposition (politics), the removal of a person of authority from political power
* Deposition (university), a widespread initiation ritual for new students practiced ...
, plays a key role in Earth's water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
and climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologica ...
. It falls as snowflakes and hail or occurs as frost, icicles or ice spike
An ice spike is an ice formation, often in the shape of an inverted icicle, that projects upwards from the surface of a body of frozen water. Ice spikes created by natural processes on the surface of small bodies of frozen water have been repor ...
s and aggregates from snow as glaciers
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
and ice sheets.
Ice exhibits at least eighteen phases ( packing geometries), depending on temperature and pressure. When water is cooled rapidly (quenching
In materials science, quenching is the rapid cooling of a workpiece in water, oil, polymer, air, or other fluids to obtain certain material properties. A type of heat treating, quenching prevents undesired low-temperature processes, such as ...
), up to three types of amorphous ice
Amorphous ice (non-crystalline or "vitreous" ice) is an amorphous solid form of water. Common ice is a crystalline material wherein the molecules are regularly arranged in a hexagonal lattice, whereas amorphous ice has a lack of long-range ord ...
can form depending on its history of pressure and temperature. When cooled slowly, correlated proton tunneling occurs below (, ) giving rise to macroscopic quantum phenomena
Macroscopic quantum phenomena are processes showing quantum behavior at the macroscopic scale, rather than at the atomic scale where quantum effects are prevalent. The best-known examples of macroscopic quantum phenomena are superfluidity and s ...
. Virtually all ice on Earth's surface and in its atmosphere is of a hexagonal
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A ''regular hexagon'' has ...
crystalline structure
In crystallography, crystal structure is a description of the ordered arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline material. Ordered structures occur from the intrinsic nature of the constituent particles to form symmetric patterns t ...
denoted as ice Ih (spoken as "ice one h") with minute traces of cubic ice, denoted as ice Ic and, more recently found, Ice VII
Ice VII is a cubic crystalline form of ice. It can be formed from liquid water above 3 Pascal (unit), GPa (30,000 atmospheres) by lowering its temperature to room temperature, or by decompressing heavy water (D2O) Ice#Phases, ice VI below 95 K. ( ...
inclusions in diamonds. The most common phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ...
to ice Ih occurs when liquid water is cooled below (, ) at standard atmospheric pressure
The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as Pa. It is sometimes used as a ''reference pressure'' or ''standard pressure''. It is approximately equal to Earth's average atmospheric pressure at sea level.
History
The s ...
. It may also be deposited directly by water vapor
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous p ...
, as happens in the formation of frost. The transition from ice to water is melting and from ice directly to water vapor is sublimation
Sublimation or sublimate may refer to:
* ''Sublimation'' (album), by Canvas Solaris, 2004
* Sublimation (phase transition), directly from the solid to the gas phase
* Sublimation (psychology), a mature type of defense mechanism
* Sublimate of mer ...
.
Ice is used in a variety of ways, including for cooling, for winter sport
Winter sports or winter activities are competitive sports or non-competitive recreational activities which are played on snow or ice. Most are variations of skiing, ice skating and sledding. Traditionally, such games were only played in cold ...
s, and ice sculpting
Ice sculpture is a form of sculpture that uses ice as the raw material. Sculptures from ice can be abstract or realistic and can be functional or purely decorative. Ice sculptures are generally associated with special or extravagant events because ...
.
Physical properties
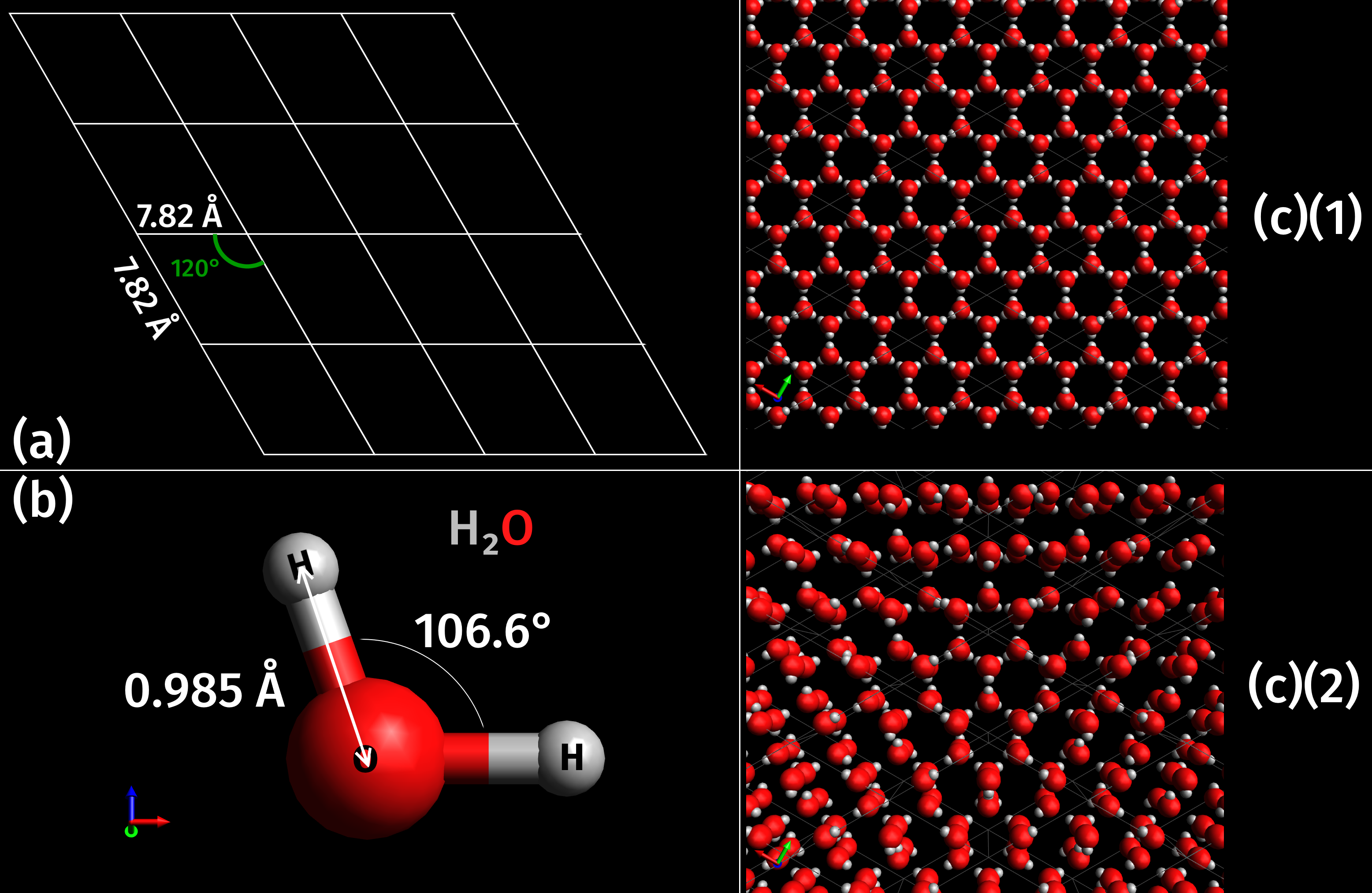
 As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a
As a naturally occurring crystalline inorganic solid with an ordered structure, ice is considered to be a mineral
In geology and mineralogy, a mineral or mineral species is, broadly speaking, a solid chemical compound with a fairly well-defined chemical composition and a specific crystal structure that occurs naturally in pure form.John P. Rafferty, ed. ...
. It possesses a regular crystalline
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macros ...
structure based on the molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bio ...
of water, which consists of a single oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as we ...
atom covalently
A covalent bond is a chemical bond that involves the sharing of electrons to form electron pairs between atoms. These electron pairs are known as shared pairs or bonding pairs. The stable balance of attractive and repulsive forces between atom ...
bonded to two hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen cons ...
s, or H–O–H. However, many of the physical properties of water and ice are controlled by the formation of hydrogen bond
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing ...
s between adjacent oxygen and hydrogen atoms; while it is a weak bond, it is nonetheless critical in controlling the structure of both water and ice.
An unusual property of water is that its solid form—ice frozen at atmospheric pressure
Atmospheric pressure, also known as barometric pressure (after the barometer), is the pressure within the atmosphere of Earth. The standard atmosphere (symbol: atm) is a unit of pressure defined as , which is equivalent to 1013.25 millibar ...
—is approximately 8.3% less dense than its liquid form; this is equivalent to a volumetric expansion of 9%. The density
Density (volumetric mass density or specific mass) is the substance's mass per unit of volume. The symbol most often used for density is ''ρ'' (the lower case Greek letter rho), although the Latin letter ''D'' can also be used. Mathematicall ...
of ice is 0.9167–0.9168 g/cm3 at 0 °C and standard atmospheric pressure (101,325 Pa), whereas water has a density of 0.9998–0.999863 g/cm3 at the same temperature and pressure. Liquid water is densest, essentially 1.00 g/cm3, at 4 °C and begins to lose its density as the water molecules begin to form the hexagonal
In geometry, a hexagon (from Greek , , meaning "six", and , , meaning "corner, angle") is a six-sided polygon. The total of the internal angles of any simple (non-self-intersecting) hexagon is 720°.
Regular hexagon
A ''regular hexagon'' has ...
crystal
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macr ...
s of ice
Ice is water frozen into a solid state, typically forming at or below temperatures of 0 degrees Celsius or Depending on the presence of impurities such as particles of soil or bubbles of air, it can appear transparent or a more or less opaq ...
as the freezing point is reached. This is due to hydrogen bonding dominating the intermolecular forces, which results in a packing of molecules less compact in the solid. Density of ice increases slightly with decreasing temperature and has a value of 0.9340 g/cm3 at −180 °C (93 K).
When water freezes, it increases in volume (about 9% for fresh water). The effect of expansion during freezing can be dramatic, and ice expansion is a basic cause of freeze-thaw
Frost weathering is a collective term for several mechanical weathering processes induced by stresses created by the freezing of water into ice. The term serves as an umbrella term for a variety of processes such as frost shattering, frost wedgi ...
weathering of rock in nature and damage to building foundations and roadways from frost heaving
Frost heaving (or a frost heave) is an upwards swelling of soil during freezing conditions caused by an increasing presence of ice as it grows towards the surface, upwards from the depth in the soil where freezing temperatures have penetrated in ...
. It is also a common cause of the flooding of houses when water pipes burst due to the pressure of expanding water when it freezes.
The result of this process is that ice (in its most common form) floats on liquid water, which is an important feature in Earth's biosphere
The biosphere (from Greek βίος ''bíos'' "life" and σφαῖρα ''sphaira'' "sphere"), also known as the ecosphere (from Greek οἶκος ''oîkos'' "environment" and σφαῖρα), is the worldwide sum of all ecosystems. It can also be ...
. It has been argued that without this property, natural bodies of water would freeze, in some cases permanently, from the bottom up, resulting in a loss of bottom-dependent animal and plant life in fresh and sea water. Sufficiently thin ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at ...
s allow light to pass through while protecting the underside from short-term weather extremes such as wind chill
Wind chill or windchill (popularly wind chill factor) is the lowering of body temperature due to the passing-flow of lower-temperature air.
Wind chill numbers are always lower than the air temperature for values where the formula is valid. When ...
. This creates a sheltered environment for bacterial and algal colonies. When sea water freezes, the ice is riddled with brine-filled channels which sustain sympagic organisms such as bacteria, algae, copepods and annelids, which in turn provide food for animals such as krill and specialised fish like the bald notothen
The bald notothen (''Pagothenia borchgrevinki''), also known as the bald rockcod, is a species of marine ray-finned fish belonging to the family Nototheniidae, the notothens or cod icefishes. It is native to the Southern Ocean.
Taxonomy
The bald ...
, fed upon in turn by larger animals such as emperor penguins and minke whales
The minke whale (), or lesser rorqual, is a species complex of baleen whale. The two species of minke whale are the common (or northern) minke whale and the Antarctic (or southern) minke whale. The minke whale was first described by the Danish na ...
.
When ice melts, it absorbs as much energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
as it would take to heat an equivalent mass of water by 80 °C. During the melting process, the temperature remains constant at 0 °C. While melting, any energy added breaks the hydrogen bonds between ice (water) molecules. Energy becomes available to increase the thermal energy (temperature) only after enough hydrogen bonds are broken that the ice can be considered liquid water. The amount of energy consumed in breaking hydrogen bonds in the transition from ice to water is known as the ''heat of fusion
In thermodynamics, the enthalpy of fusion of a substance, also known as (latent) heat of fusion, is the change in its enthalpy resulting from providing energy, typically heat, to a specific quantity of the substance to change its state from a so ...
''.
As with water, ice absorbs light at the red end of the spectrum preferentially as the result of an overtone of an oxygen–hydrogen (O–H) bond stretch. Compared with water, this absorption is shifted toward slightly lower energies. Thus, ice appears blue, with a slightly greener tint than liquid water. Since absorption is cumulative, the color effect intensifies with increasing thickness or if internal reflections cause the light to take a longer path through the ice.
Other colors can appear in the presence of light absorbing impurities, where the impurity is dictating the color rather than the ice itself. For instance, iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". Th ...
s containing impurities (e.g., sediments, algae, air bubbles) can appear brown, grey or green.
Because ice in natural environments is usually close to its melting temperature, its hardness shows pronounced temperature variations. At its melting point, ice has a Mohs hardness
The Mohs scale of mineral hardness () is a qualitative ordinal scale, from 1 to 10, characterizing scratch resistance of various minerals through the ability of harder material to scratch softer material.
The scale was introduced in 1812 by the ...
of 2 or less, but the hardness increases to about 4 at a temperature of and to 6 at a temperature of , the vaporization point of solid carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
(dry ice).
Phases
Ice may be any one of the 19 known solid crystalline phases ofwater
Water (chemical formula ) is an inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living organisms (in which it acts as ...
, or in an amorphous solid state at various densities.
Most liquids under increased pressure freeze at ''higher'' temperatures because the pressure helps to hold the molecules together. However, the strong hydrogen bonds in water make it different: for some pressures higher than , water freezes at a temperature ''below'' 0 °C, as shown in the phase diagram below. The melting of ice under high pressures is thought to contribute to the movement of glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s.
Ice, water, and water vapour
(99.9839 °C)
, -
, Boiling point
,
, -
, specific gas constant
, 461.5 J/( kg·K)
, -
, Heat of vaporization
, 2.27 MJ/kg
, -
, Heat capacity
, 1.864 kJ/(kg·K)
Water vapor, water vapour or aqueous vapor is the gaseous ph ...
can coexist at the triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases ( gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the subli ...
, which is exactly at a pressure of 611.657 Pa. The kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ph ...
was in fact defined as of the difference between this triple point and absolute zero
Absolute zero is the lowest limit of the thermodynamic temperature scale, a state at which the enthalpy and entropy of a cooled ideal gas reach their minimum value, taken as zero kelvin. The fundamental particles of nature have minimum vibrati ...
, though this definition changed in May 2019. Unlike most other solids, ice is difficult to superheat. In an experiment, ice at −3 °C was superheated to about 17 °C for about 250 picosecond
A picosecond (abbreviated as ps) is a unit of time in the International System of Units (SI) equal to 10−12 or (one trillionth) of a second. That is one trillionth, or one millionth of one millionth of a second, or 0.000 000 000&nbs ...
s.
Subjected to higher pressures and varying temperatures, ice can form in 19 separate known crystalline phases. With care, at least 15 of these phases (one of the known exceptions being ice X) can be recovered at ambient pressure and low temperature in metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
form. The types are differentiated by their crystalline structure, proton ordering, and density. There are also two metastable
In chemistry and physics, metastability denotes an intermediate energetic state within a dynamical system other than the system's state of least energy.
A ball resting in a hollow on a slope is a simple example of metastability. If the ball i ...
phases of ice under pressure, both fully hydrogen-disordered; these are IV and XII. Ice XII was discovered in 1996. In 2006, XIII
XIII may refer to:
* 13 (number) or XIII in Roman numerals
* 13th century in Roman numerals
* ''XIII'' (comics), a Belgian comic book series by Jean Van Hamme and William Vance
** ''XIII'' (2003 video game), a 2003 video game based on the comic ...
and XIV were discovered. Ices XI, XIII, and XIV are hydrogen-ordered forms of ices I, V, and XII respectively. In 2009, ice XV was found at extremely high pressures and −143 °C. At even higher pressures, ice is predicted to become a metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typi ...
; this has been variously estimated to occur at 1.55 TPa or 5.62 TPa.
As well as crystalline forms, solid water can exist in amorphous states as amorphous ice
Amorphous ice (non-crystalline or "vitreous" ice) is an amorphous solid form of water. Common ice is a crystalline material wherein the molecules are regularly arranged in a hexagonal lattice, whereas amorphous ice has a lack of long-range ord ...
(ASW) of varying densities. Water in the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
is dominated by amorphous ice, making it likely the most common form of water in the universe. Low-density ASW (LDA), also known as hyperquenched glassy water, may be responsible for noctilucent clouds
Noctilucent clouds, or night shining clouds, are tenuous cloud-like phenomena in the upper atmosphere of Earth. When viewed from space, they are called polar mesospheric clouds (PMCs), detectable as a diffuse scattering layer of water ice crysta ...
on Earth and is usually formed by deposition
Deposition may refer to:
* Deposition (law), taking testimony outside of court
* Deposition (politics), the removal of a person of authority from political power
* Deposition (university), a widespread initiation ritual for new students practiced ...
of water vapor in cold or vacuum conditions. High-density ASW (HDA) is formed by compression of ordinary ice I or LDA at GPa pressures. Very-high-density ASW (VHDA) is HDA slightly warmed to 160 K under 1–2 GPa pressures.
In outer space, hexagonal crystalline ice (the predominant form found on Earth) is extremely rare. Amorphous ice is more common; however, hexagonal crystalline ice can be formed by volcanic action.
Ice from a theorized superionic water
Superionic water, also called superionic ice or ice XVIII is a phase of water that exists at extremely high temperatures and pressures. In superionic water, water molecules break apart and the oxygen ions crystallize into an evenly spaced la ...
may possess two crystalline structures. At pressures in excess of such ''superionic ice'' would take on a body-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties of ...
structure. However, at pressures in excess of the structure may shift to a more stable face-centered cubic
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals.
There are three main varieties o ...
lattice. It is speculated that superionic ice could compose the interior of ice giants such as Uranus and Neptune.

Friction properties
slipperiness
Slipperiness is when a surface has a low coefficient of friction, allowing objects to glide across the surface. People walking on slippery surfaces are likely to slip or fall. A surface can for example be slippery due to it being wet, or due to ...
") of ice has been attributed to the pressure of an object coming into contact with the ice, melting a thin layer of the ice and allowing the object to glide across the surface. For example, the blade of an ice skate, upon exerting pressure on the ice, would melt a thin layer, providing lubrication between the ice and the blade. This explanation, called " pressure melting", originated in the 19th century. However, it does not account for skating on ice temperatures lower than , which is often skated upon. Also, the effect of pressure melting is too small to account for the reduced friction as commonly experienced.
A second theory describing the coefficient of friction of ice suggested that ice molecules at the interface cannot properly bond with the molecules of the mass of ice beneath (and thus are free to move like molecules of liquid water). These molecules remain in a semi-liquid state, providing lubrication regardless of pressure against the ice exerted by any object. However, the significance of this hypothesis is disputed by experiments showing a high coefficient of friction
Friction is the force resisting the relative motion of solid surfaces, fluid layers, and material elements sliding against each other. There are several types of friction:
*Dry friction is a force that opposes the relative lateral motion of tw ...
for ice using atomic force microscopy
Atomic force microscopy (AFM) or scanning force microscopy (SFM) is a very-high-resolution type of scanning probe microscopy (SPM), with demonstrated resolution on the order of fractions of a nanometer, more than 1000 times better than the opt ...
.
A third theory is "friction heating", which suggests that friction of the material is the cause of the ice layer melting. However, this theory does not sufficiently explain why ice is slippery when standing still even at below-zero temperatures.
A comprehensive theory of ice friction takes into account all the above-mentioned friction mechanisms. This model allows quantitative estimation of the friction coefficient of ice against various materials as a function of temperature and sliding speed. In typical conditions related to winter sports and tires of a vehicle on ice, melting of a thin ice layer due to the frictional heating is the primary reason for the slipperiness. The mechanism controlling the frictional properties of ice is still an active area of scientific study.
Natural formation
 The term that collectively describes all of the parts of the Earth's surface where water is in frozen form is the ''
The term that collectively describes all of the parts of the Earth's surface where water is in frozen form is the ''cryosphere
]
The cryosphere (from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''kryos'', "cold", "frost" or "ice" and ''sphaira'', "globe, ball") is an all-encompassing term for those portions of Earth's surface where water is in solid form, including sea ice, lake ice, ri ...
.'' Ice is an important component of the global climate, particularly in regard to the water cycle. Glaciers and snowpack
Snowpack forms from layers of snow that accumulate in geographic regions and high elevations where the climate includes cold weather for extended periods during the year. Snowpacks are an important water resource that feed streams and rivers as th ...
s are an important storage mechanism for fresh water; over time, they may sublimate or melt. Snowmelt
In hydrology, snowmelt is surface runoff produced from melting snow. It can also be used to describe the period or season during which such runoff is produced. Water produced by snowmelt is an important part of the annual water cycle in many part ...
is an important source of seasonal fresh water. The World Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Intern ...
defines several kinds of ice depending on origin, size, shape, influence and so on."WMO SEA-ICE NOMENCLATURE"Multi-language
) ''World Meteorological Organization'' / ''
Arctic and Antarctic Research Institute
, image =
, image_upright =
, alt =
, caption =
, latin_name =
, motto =
, founder =
, established =
, mission =
, focus = Researc ...
''. Retrieved 8 April 2012. Clathrate hydrate
Clathrate hydrates, or gas hydrates, clathrates, hydrates, etc., are crystalline water-based solids physically resembling ice, in which small non-polar molecules (typically gases) or polar molecules with large hydrophobic moieties are trapped i ...
s are forms of ice that contain gas molecules trapped within its crystal lattice.
On the oceans
Ice that is found at sea may be in the form ofdrift ice
Drift ice, also called brash ice, is sea ice that is not attached to the shoreline or any other fixed object (shoals, grounded icebergs, etc.).Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. Unlike fast ice, which is "fasten ...
floating in the water, fast ice
Fast ice (also called ''land-fast ice'', ''landfast ice'', and ''shore-fast ice'') is sea ice that is "fastened" to the coastline, to the sea floor along shoals or to grounded icebergs.Leppäranta, M. 2011. The Drift of Sea Ice. Berlin: Springe ...
fixed to a shoreline or anchor ice
Anchor ice is defined by the World Meteorological Organization as "submerged ice attached or anchored to the bottom, irrespective of the nature of its formation". It may also be called bottom-fast ice. Anchor ice is most commonly observed in fast ...
if attached to the sea bottom. Ice which calves (breaks off) from an ice shelf
An ice shelf is a large floating platform of ice that forms where a glacier or ice sheet flows down to a coastline and onto the ocean surface. Ice shelves are only found in Antarctica, Greenland, Northern Canada, and the Russian Arctic. Th ...
or glacier may become an iceberg. Sea ice can be forced together by currents and winds to form pressure ridges up to tall. Navigation through areas of sea ice occurs in openings called "polynya
A polynya () is an area of open water surrounded by sea ice. It is now used as a geographical term for an area of unfrozen seawater within otherwise contiguous pack ice or fast ice. It is a loanword from the Russian полынья (), which r ...
s" or "leads
Lead is a chemical element with symbol Pb and atomic number 82.
Lead or The Lead may also refer to:
Animal handling
* Leash, or lead
* Lead (leg), the leg that advances most in a quadruped's cantering or galloping stride
* Lead (tack), a li ...
" or requires the use of a special ship called an "icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to sma ...
".
On land and structures
 Ice on land ranges from the largest type called an "
Ice on land ranges from the largest type called an "ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at ...
" to smaller ice cap
In glaciology, an ice cap is a mass of ice that covers less than of land area (usually covering a highland area). Larger ice masses covering more than are termed ice sheets.
Description
Ice caps are not constrained by topographical featu ...
s and ice field
An ice field (also spelled icefield) is a mass of interconnected valley glaciers (also called mountain glaciers or alpine glaciers) on a mountain mass with protruding rock ridges or summits. They are often found in the colder climates and highe ...
s to glaciers and ice stream
An ice stream is a region of fast-moving ice within an ice sheet. It is a type of glacier, a body of ice that moves under its own weight. They can move upwards of a year, and can be up to in width, and hundreds of kilometers in length. They ...
s to the snow line
The climatic snow line is the boundary between a snow-covered and snow-free surface. The actual snow line may adjust seasonally, and be either significantly higher in elevation, or lower. The permanent snow line is the level above which snow wil ...
and snow field
A snow field, snowfield or neve is an accumulation of permanent snow and ice, typically found above the snow line, normally in mountainous and glacial terrain.
Glaciers originate in snowfields. The lower end of a glacier is usually free from sn ...
s.
Aufeis
Aufeis, ( ), (German for "ice on top") is a sheet-like mass of layered ice that forms from successive flows of ground or river water during freezing temperatures. This form of ice is also called overflow, icings, or the Russian term, naled. The ...
is layered ice that forms in Arctic and subarctic stream valleys. Ice, frozen in the stream bed, blocks normal groundwater discharge, and causes the local water table to rise, resulting in water discharge on top of the frozen layer. This water then freezes, causing the water table to rise further and repeat the cycle. The result is a stratified ice deposit, often several meters thick.
Freezing rain
Freezing rain is rain maintained at temperatures below freezing by the ambient air mass that causes freezing on contact with surfaces. Unlike a mixture of rain and snow or ice pellets, freezing rain is made entirely of liquid droplets. The rai ...
is a type of winter storm called an ice storm
An ice storm, also known as a glaze event or a silver storm is a type of winter storm characterized by freezing rain. The U.S. National Weather Service defines an ice storm as a storm which results in the accumulation of at least of ice on ...
where rain falls and then freezes producing a glaze of ice. Ice can also form icicles, similar to stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via
''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble an ...
s in appearance, or stalagmite
A stalagmite (, ; from the Greek , from , "dropping, trickling")
is a type of rock formation that rises from the floor of a cave due to the accumulation of material deposited on the floor from ceiling drippings. Stalagmites are typically ...
-like forms as water drips and re-freezes.
The term "ice dam" has three meanings (others discussed below). On structures, an ice dam is the buildup of ice on a sloped roof which stops melt water from draining properly and can cause damage from water leaks in buildings.
On rivers and streams
Ice jam
Ice jams occur when a topographic feature of the river causes floating river ice to accumulate and impede further progress downstream with the river current. Ice jams can significantly reduce the flow of a river and cause upstream flooding—som ...
s (sometimes called "ice dams"), when broken chunks of ice pile up, are the greatest ice hazard on rivers. Ice jams can cause flooding, damage structures in or near the river, and damage vessels on the river. Ice jams can cause some hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ὕδωρ, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of ...
industrial facilities to completely shut down. An ice dam is a blockage from the movement of a glacier which may produce a proglacial lake
In geology, a proglacial lake is a lake formed either by the damming action of a moraine during the retreat of a melting glacier, a glacial ice dam, or by meltwater trapped against an ice sheet due to isostatic depression of the crust around th ...
. Heavy ice flows in rivers can also damage vessels and require the use of an icebreaker to keep navigation possible.
Ice disc
Ice discs, ice circles, ice pans, ice pancakes or ice crepes are a very rare natural phenomenon that occurs in slow moving water in cold climates. They are thin circular slabs of ice that rotate slowly on a body of water's surface.
Types
Ice ...
s are circular formations of ice surrounded by water in a river.
Pancake ice
Pancake ice is a form of sea ice that consists of round pieces of ice with diameters ranging from 30 centimetres (12 in) to 3 metres (9.8 ft) and thicknesses up to 10 centimetres (3.9 inches), depending on the local conditions. It forms as a resu ...
is a formation of ice generally created in areas with less calm conditions.
On lakes
Ice forms on calm water from the shores, a thin layer spreading across the surface, and then downward. Ice on lakes is generally four types: primary, secondary, superimposed and agglomerate. Primary ice forms first. Secondary ice forms below the primary ice in a direction parallel to the direction of the heat flow. Superimposed ice forms on top of the ice surface from rain or water which seeps up through cracks in the ice which often settles when loaded with snow.Shelf ice
Shelf ice is ice that forms when a portion of a lake surface freezes. It is often then washed upon the shore. The phenomenon is common within the Great Lakes.
Formation
Shelf ice forms from float ice. Float ice is like drift ice, but seldo ...
occurs when floating pieces of ice are driven by the wind piling up on the windward shore.
Candle ice
Rotten ice is a loose term for ice that is melting or structurally disintegrating due to being honeycombed by liquid water, air, or contaminants trapped between the initial growth of ice crystals. It may appear transparent or splotchy grey, and it ...
is a form of rotten ice that develops in columns perpendicular to the surface of a lake.
An ice shove
An ice shove (also known as an ice surge, ice push, ice heave, shoreline ice pileup, ice piling, ice thrust, ice tsunami, ice ride-up, or ''ivu'' in Inupiat) is a surge of ice from an ocean or large lake onto the shore.
Ice shoves are caused b ...
occurs when ice movement, caused by ice expansion and/or wind action, occurs to the extent that ice pushes onto the shores of lakes, often displacing sediment that makes up the shoreline.
In the air
Rime
Rime is a type of ice formed on cold objects when drops of water crystallize on them. This can be observed infog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily inf ...
gy weather, when the temperature drops during the night. Soft rime
Rime ice forms when supercooled water liquid droplets freeze onto surfaces. Meteorologists distinguish between three basic types of ice forming on vertical and horizontal surfaces by deposition of supercooled water droplets. There are also interm ...
contains a high proportion of trapped air, making it appear white rather than transparent, and giving it a density about one quarter of that of pure ice. Hard rime
Rime ice forms when supercooled water liquid droplets freeze onto surfaces. Meteorologists distinguish between three basic types of ice forming on vertical and horizontal surfaces by deposition of supercooled water droplets. There are also inter ...
is comparatively dense.
Pellets

Ice pellets
Ice pellets are a form of precipitation consisting of small, hard, translucent balls of ice. Ice pellets are different from graupel ("soft hail") which is made of frosty white opaque rime, and from a mixture of rain and snow which is a slus ...
are a form of precipitation consisting of small, translucent
In the field of optics, transparency (also called pellucidity or diaphaneity) is the physical property of allowing light to pass through the material without appreciable scattering of light. On a macroscopic scale (one in which the dimensions ...
balls of ice. This form of precipitation is also referred to as "sleet" by the United States National Weather Service
The National Weather Service (NWS) is an agency of the United States federal government that is tasked with providing weather forecasts, warnings of hazardous weather, and other weather-related products to organizations and the public for the ...
. (In British English
British English (BrE, en-GB, or BE) is, according to Lexico, Oxford Dictionaries, "English language, English as used in Great Britain, as distinct from that used elsewhere". More narrowly, it can refer specifically to the English language in ...
"sleet" refers to a mixture of rain and snow.) Ice pellets are usually smaller than hailstones. They often bounce when they hit the ground, and generally do not freeze into a solid mass unless mixed with freezing rain
Freezing rain is rain maintained at temperatures below freezing by the ambient air mass that causes freezing on contact with surfaces. Unlike a mixture of rain and snow or ice pellets, freezing rain is made entirely of liquid droplets. The rai ...
. The METAR
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.
Raw METAR is the most common form ...
code for ice pellets is ''PL''.
Ice pellets form when a layer of above-freezing air is located between above the ground, with sub-freezing air both above and below it. This causes the partial or complete melting of any snowflakes falling through the warm layer. As they fall back into the sub-freezing layer closer to the surface, they re-freeze into ice pellets. However, if the sub-freezing layer beneath the warm layer is too small, the precipitation will not have time to re-freeze, and freezing rain will be the result at the surface. A temperature profile showing a warm layer above the ground is most likely to be found in advance of a warm front
A warm front is a density discontinuity located at the leading edge of a homogeneous warm air mass, and is typically located on the equator-facing edge of an isotherm gradient. Warm fronts lie within broader troughs of low pressure than cold fr ...
during the cold season, but can occasionally be found behind a passing cold front
A cold front is the leading edge of a cooler mass of air at ground level that replaces a warmer mass of air and lies within a pronounced surface trough of low pressure. It often forms behind an extratropical cyclone (to the west in the Northern ...
.
Hail
 Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm
Like other precipitation, hail forms in storm cloud
In meteorology, a cloud is an aerosol consisting of a visible mass of miniature liquid droplets, frozen crystals, or other particles suspended in the atmosphere of a planetary body or similar space. Water or various other chemicals may ...
s when supercooled
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a seed crystal or nucleus around which a crystal ...
water droplets freeze on contact with condensation nuclei
Cloud condensation nuclei (CCNs), also known as cloud seeds, are small particles typically 0.2 µm, or one hundredth the size of a cloud droplet. CCNs are a unique subset of aerosols in the atmosphere on which water vapour condenses. This c ...
, such as dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
or dirt
Dirt is an unclean matter, especially when in contact with a person's clothes, skin, or possessions. In such cases, they are said to become dirty.
Common types of dirt include:
* Debris: scattered pieces of waste or remains
* Dust: a genera ...
. The storm's updraft
In meteorology, an updraft is a small-scale current of rising air, often within a cloud.
Overview
Localized regions of warm or cool air will exhibit vertical movement. A mass of warm air will typically be less dense than the surrounding region ...
blows the hailstones to the upper part of the cloud. The updraft dissipates and the hailstones fall down, back into the updraft, and are lifted up again. Hail has a diameter of or more. Within METAR
METAR is a format for reporting weather information. A METAR weather report is predominantly used by aircraft pilots, and by meteorologists, who use aggregated METAR information to assist in weather forecasting.
Raw METAR is the most common form ...
code, GR is used to indicate larger hail, of a diameter of at least and GS for smaller. Stones just larger than golf ball
A golf ball is a special ball designed to be used in the game of golf.
Under the rules of golf, a golf ball has a mass no more than , has a diameter not less than , and performs within specified velocity, distance, and symmetry limits. Like ...
-sized are one of the most frequently reported hail sizes. Hailstones can grow to and weigh more than . In large hailstones, latent heat
Latent heat (also known as latent energy or heat of transformation) is energy released or absorbed, by a body or a thermodynamic system, during a constant-temperature process — usually a first-order phase transition.
Latent heat can be underst ...
released by further freezing may melt the outer shell of the hailstone. The hailstone then may undergo 'wet growth', where the liquid outer shell collects other smaller hailstones. The hailstone gains an ice layer and grows increasingly larger with each ascent. Once a hailstone becomes too heavy to be supported by the storm's updraft, it falls from the cloud.
Hail forms in strong thunderstorm
A thunderstorm, also known as an electrical storm or a lightning storm, is a storm characterized by the presence of lightning and its acoustic effect on the Earth's atmosphere, known as thunder. Relatively weak thunderstorms are somet ...
clouds, particularly those with intense updrafts, high liquid water content, great vertical extent, large water droplets, and where a good portion of the cloud layer is below freezing . Hail-producing clouds are often identifiable by their green coloration. The growth rate is maximized at about , and becomes vanishingly small much below as supercooled water droplets become rare. For this reason, hail is most common within continental interiors of the mid-latitudes, as hail formation is considerably more likely when the freezing level is below the altitude of . Entrainment
Entrainment may refer to:
* Air entrainment, the intentional creation of tiny air bubbles in concrete
* Brainwave entrainment, the practice of entraining one's brainwaves to a desired frequency
* Entrainment (biomusicology), the synchronization of ...
of dry air into strong thunderstorms over continents can increase the frequency of hail by promoting evaporational cooling which lowers the freezing level of thunderstorm clouds giving hail a larger volume to grow in. Accordingly, hail is actually less common in the tropics despite a much higher frequency of thunderstorms than in the mid-latitudes because the atmosphere
An atmosphere () is a layer of gas or layers of gases that envelop a planet, and is held in place by the gravity of the planetary body. A planet retains an atmosphere when the gravity is great and the temperature of the atmosphere is low. ...
over the tropics tends to be warmer over a much greater depth. Hail in the tropics occurs mainly at higher elevations.
Snow
 Snow crystals form when tiny
Snow crystals form when tiny supercool
Supercooling, also known as undercooling, is the process of lowering the temperature of a liquid or a gas below its melting point without it becoming a solid. It achieves this in the absence of a nucleation, seed crystal or nucleus around which ...
ed cloud droplets (about 10 μm
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Uni ...
in diameter) freeze. These droplets are able to remain liquid at temperatures lower than , because to freeze, a few molecules in the droplet need to get together by chance to form an arrangement similar to that in an ice lattice; then the droplet freezes around this "nucleus". Experiments show that this "homogeneous" nucleation of cloud droplets only occurs at temperatures lower than . In warmer clouds an aerosol particle or "ice nucleus" must be present in (or in contact with) the droplet to act as a nucleus. Our understanding of what particles make efficient ice nuclei is poor – what we do know is they are very rare compared to that cloud condensation nuclei on which liquid droplets form. Clays, desert dust and biological particles may be effective, although to what extent is unclear. Artificial nuclei are used in cloud seeding
Cloud seeding is a type of weather modification that aims to change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds by dispersing substances into the air that serve as cloud condensation or ice nuclei, which alter the microphysical ...
. The droplet then grows by condensation of water vapor onto the ice surfaces.
Diamond dust
So-called "diamond dust", also known as ice needles or ice crystals, forms at temperatures approaching due to air with slightly higher moisture from aloft mixing with colder, surface-based air. The METAR identifier for diamond dust within international hourly weather reports is ''IC''.Ablation
Ablation of ice refers to both itsmelting
Melting, or fusion, is a physical process that results in the phase transition of a substance from a solid to a liquid. This occurs when the internal energy of the solid increases, typically by the application of heat or pressure, which inc ...
and its dissolution
Dissolution may refer to:
Arts and entertainment Books
* ''Dissolution'' (''Forgotten Realms'' novel), a 2002 fantasy novel by Richard Lee Byers
* ''Dissolution'' (Sansom novel), a 2003 historical novel by C. J. Sansom Music
* Dissolution, in mu ...
.
The melting of ice means entails the breaking of hydrogen bonds
In chemistry, a hydrogen bond (or H-bond) is a primarily electrostatic force of attraction between a hydrogen (H) atom which is covalently bound to a more electronegative "donor" atom or group (Dn), and another electronegative atom bearing a ...
between the water molecules. The ordering of the molecules in the solid breaks down to a less ordered state and the solid melts to become a liquid. This is achieved by increasing the internal energy of the ice beyond the melting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depends ...
. When ice melts it absorbs as much energy as would be required to heat an equivalent amount of water by 80 °C. While melting, the temperature of the ice surface remains constant at 0 °C. The rate of the melting process depends on the efficiency of the energy exchange process. An ice surface in fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does incl ...
melts solely by free convection with a rate that depends linearly on the water temperature, ''T''∞, when ''T''∞ is less than 3.98 °C, and superlinearly when ''T''∞ is equal to or greater than 3.98 °C, with the rate being proportional to (T∞ − 3.98 °C)''α'', with ''α'' = for ''T''∞ much greater than 8 °C, and α = for in between temperatures ''T''∞.
In salty ambient conditions, dissolution rather than melting often causes the ablation of ice. For example, the temperature of the Arctic Ocean
The Arctic Ocean is the smallest and shallowest of the world's five major oceans. It spans an area of approximately and is known as the coldest of all the oceans. The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) recognizes it as an ocean, ...
is generally below the melting point of ablating sea ice. The phase transition from solid to liquid is achieved by mixing salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quanti ...
and water molecules, similar to the dissolution of sugar in water, even though the water temperature is far below the melting point of the sugar. Thus the dissolution rate is limited by salt transport whereas melting can occur at much higher rates that are characteristic for heat transport.
Role in human activities
Humans have used ice for cooling andfood preservation
Food preservation includes processes that make food more resistant to microorganism growth and slow the oxidation of fats. This slows down the decomposition and rancidification process. Food preservation may also include processes that inhi ...
for centuries, relying on harvesting natural ice in various forms and then transitioning to the mechanical production of the material. Ice also presents a challenge to transportation in various forms and a setting for winter sports.
Cooling
Ice has long been valued as a means of cooling. In 400 BC Iran,Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
engineers had already mastered the technique of storing ice in the middle of summer in the desert. The ice was brought in during the winters from nearby mountains in bulk amounts, and stored in specially designed, naturally cooled ''refrigerators'', called yakhchal (meaning ''ice storage''). This was a large underground space (up to 5000 m3) that had thick walls (at least two meters at the base) made of a special mortar called ''sarooj
Sarooj is a traditional water-resistant mortar used in Iranian architecture, used in the construction of bridges, and yakhchal.
'', composed of sand, clay, egg whites, lime, goat hair, and ash in specific proportions, and which was known to be resistant to heat transfer. This mixture was thought to be completely water impenetrable. The space often had access to a qanat
A qanat or kārīz is a system for transporting water from an aquifer or water well to the surface, through an underground aqueduct; the system originated approximately 3,000 BC in what is now Iran. The function is essentially the same acro ...
, and often contained a system of windcatcher
A windcatcher, wind tower, or wind scoop ( ar, برجيل ; fa, بادگیر) is a traditional architectural element used to create cross ventilation and passive cooling in buildings. Windcatchers come in various designs: unidirectional, b ...
s which could easily bring temperatures inside the space down to frigid levels on summer days. The ice was used to chill treats for royalty.
Harvesting
 There were thriving industries in 16th–17th century England whereby low-lying areas along the
There were thriving industries in 16th–17th century England whereby low-lying areas along the Thames Estuary
The Thames Estuary is where the River Thames meets the waters of the North Sea, in the south-east of Great Britain.
Limits
An estuary can be defined according to different criteria (e.g. tidal, geographical, navigational or in terms of salini ...
were flooded during the winter, and ice harvested in carts and stored inter-seasonally in insulated wooden houses as a provision to an icehouse often located in large country houses, and widely used to keep fish fresh when caught in distant waters. This was allegedly copied by an Englishman who had seen the same activity in China. Ice was imported into England from Norway on a considerable scale as early as 1823.
In the United States, the first cargo of ice was sent from New York City to Charleston, South Carolina, in 1799, and by the first half of the 19th century, ice harvesting had become a big business. Frederic Tudor
Frederic Tudor (September 4, 1783 – February 6, 1864) was an American businessman and merchant. Known as Boston's "Ice King", he was the founder of the Tudor Ice Company and a pioneer of the international ice trade in the early 19th century. ...
, who became known as the "Ice King", worked on developing better insulation products for long distance shipments of ice, especially to the tropics; this became known as the ice trade
The ice trade, also known as the frozen water trade, was a 19th-century and early-20th-century industry, centering on the east coast of the United States and Norway, involving the large-scale harvesting, transport and sale of natural ice, and ...
.
Trieste
Trieste ( , ; sl, Trst ; german: Triest ) is a city and seaport in northeastern Italy. It is the capital city, and largest city, of the autonomous region of Friuli Venezia Giulia, one of two autonomous regions which are not subdivided into pr ...
sent ice to Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, Corfu, and Zante
Zakynthos (also spelled Zakinthos; el, Ζάκυνθος, Zákynthos ; it, Zacinto ) or Zante (, , ; el, Τζάντε, Tzánte ; from the Venetian form) is a Greek island in the Ionian Sea. It is the third largest of the Ionian Islands. Za ...
; Switzerland, to France; and Germany sometimes was supplied from Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
n lakes. The Hungarian Parliament
The National Assembly ( hu, Országgyűlés, lit=Country Assembly) is the parliament of Hungary. The unicameral body consists of 199 (386 between 1990 and 2014) members elected to 4-year terms. Election of members is done using a semi-propo ...
building used ice harvested in the winter from Lake Balaton
Lake Balaton () is a freshwater lake in the Transdanubian region of Hungary. It is the largest lake in Central Europe, and one of the region's foremost tourist destinations. The Zala River provides the largest inflow of water to the lake, and ...
for air conditioning.
Ice houses were used to store ice formed in the winter, to make ice available all year long, and an early type of refrigerator known as an icebox
An icebox (also called a cold closet) is a compact non-mechanical refrigerator which was a common early-twentieth-century kitchen appliance before the development of safely powered refrigeration devices. Before the development of electric refri ...
was cooled using a block of ice placed inside it. In many cities, it was not unusual to have a regular ice delivery service during the summer. The advent of artificial refrigeration technology has since made delivery of ice obsolete.
Ice is still harvested for ice and snow sculpture events. For example, a swing saw
Swing or swinging may refer to:
Apparatus
* Swing (seat), a hanging seat that swings back and forth
* Pendulum, an object that swings
* Russian swing, a swing-like circus apparatus
* Sex swing, a type of harness for sexual intercourse
* Swing rid ...
is used to get ice for the Harbin International Ice and Snow Sculpture Festival
The Harbin International Ice and Snow festival () is an annual winter festival that takes place with a theme in Harbin, Heilongjiang, China, and now is the largest ice and snow festival in the world. At first participants in the festival were ...
each year from the frozen surface of the Songhua River
The Songhua or Sunghwa River (also Haixi or Xingal, russian: Сунгари ''Sungari'') is one of the primary rivers of China, and the longest tributary of the Amur. It flows about from the Changbai Mountains on the China–North Korea bord ...
.
Mechanical production
 Ice is now produced on an industrial scale, for uses including food storage and processing, chemical manufacturing, concrete mixing and curing, and consumer or packaged ice.
Ice is now produced on an industrial scale, for uses including food storage and processing, chemical manufacturing, concrete mixing and curing, and consumer or packaged ice.ASHRAE
The American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers (ASHRAE ) is an American professional association seeking to advance heating, ventilation, air conditioning and refrigeration (HVAC&R) systems design and constructio ...
. "Ice Manufacture". ''2006 ASHRAE Handbook
The ASHRAE Handbook is the four-volume flagship publication of the nonprofit technical organization ASHRAE (American Society of Heating, Refrigerating and Air-Conditioning Engineers). This Handbook is considered the most comprehensive and auth ...
: Refrigeration.'' Inch-Pound Edition. . Most commercial icemaker
An icemaker, ice generator, or ice machine may refer to either a consumer device for making ice, found inside a home freezer; a stand-alone appliance for making ice, or an industrial machine for making ice on a large scale. The term "ice machi ...
s produce three basic types of fragmentary ice: flake, tubular and plate, using a variety of techniques. Large batch ice makers can produce up to 75 tons of ice per day. In 2002, there were 426 commercial ice-making companies in the United States, with a combined value of shipments of $595,487,000. Home refrigerators can also make ice with a built in icemaker
An icemaker, ice generator, or ice machine may refer to either a consumer device for making ice, found inside a home freezer; a stand-alone appliance for making ice, or an industrial machine for making ice on a large scale. The term "ice machi ...
, which will typically make ice cube
An ice cube is a small piece of ice, which is typically rectangular as viewed from above and trapezoidal as viewed from the side. Ice cubes are products of mechanical refrigeration and are usually produced to cool beverages. They may be p ...
s or crushed ice. Stand-alone icemaker units that make ice cubes are often called ice machines.
Transportation
Ice can present challenges to safe transportation on land, sea and in the air.Land travel
 Ice forming on
Ice forming on road
A road is a linear way for the conveyance of traffic that mostly has an improved surface for use by vehicles (motorized and non-motorized) and pedestrians. Unlike streets, the main function of roads is transportation.
There are many types of ...
s is a dangerous winter hazard. Black ice
Black ice, sometimes called clear ice, is a thin coating of glaze ice on a surface, especially on streets. The ice itself is not black, but visually transparent, allowing the often black road below to be seen through it. The typically low leve ...
is very difficult to see, because it lacks the expected frosty surface. Whenever there is freezing rain or snow which occurs at a temperature near the melting point, it is common for ice to build up on the window
A window is an opening in a wall, door, roof, or vehicle that allows the exchange of light and may also allow the passage of sound and sometimes air. Modern windows are usually glazed or covered in some other transparent or translucent mate ...
s of vehicles. Driving safely requires the removal of the ice build-up. Ice scraper
An ice scraper is a handheld tool for removing frost, ice, and snow from windows, usually on automobiles. Basic scrapers have a plastic blade and handle, though some have blades made out of metal. More complex models often include brus ...
s are tools designed to break the ice free and clear the windows, though removing the ice can be a long and laborious process.
Far enough below the freezing point, a thin layer of ice crystals can form on the inside surface of windows. This usually happens when a vehicle has been left alone after being driven for a while, but can happen while driving, if the outside temperature is low enough. Moisture from the driver's breath is the source of water for the crystals. It is troublesome to remove this form of ice, so people often open their windows slightly when the vehicle is parked in order to let the moisture dissipate, and it is now common for cars to have rear-window defroster
A defogger, demister, or defroster is a system to clear condensation and thaw frost from the windshield, backglass, or side windows of a motor vehicle. The rear window defroster was invented by German automobile engineer Heinz Kunert.
Types
P ...
s to solve the problem. A similar problem can happen in homes, which is one reason why many colder regions require double-pane windows for insulation.
When the outdoor temperature stays below freezing for extended periods, very thick layers of ice can form on lake
A lake is an area filled with water, localized in a basin, surrounded by land, and distinct from any river or other outlet that serves to feed or drain the lake. Lakes lie on land and are not part of the ocean, although, like the much lar ...
s and other bodies of water, although places with flowing water require much colder temperatures. The ice can become thick enough to drive onto with automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarded ...
s and truck
A truck or lorry is a motor vehicle designed to transport cargo, carry specialized payloads, or perform other utilitarian work. Trucks vary greatly in size, power, and configuration, but the vast majority feature body-on-frame constructi ...
s. Doing this safely requires a thickness of at least 30 cm (one foot).
Water-borne travel
 For ships, ice presents two distinct hazards. First, spray and freezing rain can produce an ice build-up on the superstructure of a vessel sufficient to make it unstable, and to require it to be hacked off or melted with steam hoses. Second,
For ships, ice presents two distinct hazards. First, spray and freezing rain can produce an ice build-up on the superstructure of a vessel sufficient to make it unstable, and to require it to be hacked off or melted with steam hoses. Second, iceberg
An iceberg is a piece of freshwater ice more than 15 m long that has broken off a glacier or an ice shelf and is floating freely in open (salt) water. Smaller chunks of floating glacially-derived ice are called "growlers" or "bergy bits". Th ...
s – large masses of ice floating in water (typically created when glaciers reach the sea) – can be dangerous if struck by a ship when underway. Icebergs have been responsible for the sinking of many ships, the most famous being the ''Titanic''. For harbor
A harbor (American English), harbour (British English; see spelling differences), or haven is a sheltered body of water where ships, boats, and barges can be docked. The term ''harbor'' is often used interchangeably with ''port'', which is a ...
s near the pole
Pole may refer to:
Astronomy
*Celestial pole, the projection of the planet Earth's axis of rotation onto the celestial sphere; also applies to the axis of rotation of other planets
* Pole star, a visible star that is approximately aligned with th ...
s, being ice-free, ideally all year long, is an important advantage. Examples are Murmansk
Murmansk ( Russian: ''Мурманск'' lit. " Norwegian coast"; Finnish: ''Murmansk'', sometimes ''Muurmanski'', previously ''Muurmanni''; Norwegian: ''Norskekysten;'' Northern Sámi: ''Murmánska;'' Kildin Sámi: ''Мурман ланнҍ ...
(Russia), Petsamo Petsamo may refer to:
* Petsamo Province, a province of Finland from 1921 to 1922
* Petsamo, Tampere, a district in Tampere, Finland
* Pechengsky District, Russia, formerly known as Petsamo
* Pechenga (urban-type settlement), Murmansk Oblast
...
(Russia, formerly Finland), and Vardø
( fi, Vuoreija, fkv, Vuorea, se, Várggát) is a municipality in Troms og Finnmark county in the extreme northeastern part of Norway. Vardø is the easternmost town in Norway, more to the east than Saint Petersburg or Istanbul. The administra ...
(Norway). Harbors which are not ice-free are opened up using icebreaker
An icebreaker is a special-purpose ship or boat designed to move and navigate through ice-covered waters, and provide safe waterways for other boats and ships. Although the term usually refers to ice-breaking ships, it may also refer to sma ...
s.
Air travel
 For aircraft, ice can cause a number of dangers. As an aircraft climbs, it passes through air layers of different temperature and humidity, some of which may be conducive to ice formation. If ice forms on the wings or control surfaces, this may adversely affect the flying qualities of the aircraft. During the first non-stop flight across the Atlantic, the British aviators Captain John Alcock and Lieutenant
For aircraft, ice can cause a number of dangers. As an aircraft climbs, it passes through air layers of different temperature and humidity, some of which may be conducive to ice formation. If ice forms on the wings or control surfaces, this may adversely affect the flying qualities of the aircraft. During the first non-stop flight across the Atlantic, the British aviators Captain John Alcock and Lieutenant Arthur Whitten Brown
Lieutenant colonel (United Kingdom), Lieutenant-Colonel Sir Arthur Whitten Brown, (23 July 1886 – 4 October 1948) was a British military officer and aviator who flew as navigator of the Transatlantic flight of Alcock and Brown, first success ...
encountered such icing conditions – Brown left the cockpit and climbed onto the wing several times to remove ice which was covering the engine air intakes of the Vickers Vimy
The Vickers Vimy was a British heavy bomber aircraft developed and manufactured by Vickers Limited. Developed during the latter stages of the First World War to equip the Royal Flying Corps (RFC), the Vimy was designed by Reginald Kirshaw "Rex ...
aircraft they were flying.
One vulnerability effected by icing that is associated with reciprocating internal combustion engines is the carburetor
A carburetor (also spelled carburettor) is a device used by an internal combustion engine to control and mix air and fuel entering the engine. The primary method of adding fuel to the intake air is through the venturi tube in the main meter ...
. As air is sucked through the carburetor into the engine, the local air pressure is lowered, which causes adiabatic cooling. Thus, in humid near-freezing conditions, the carburetor will be colder, and tend to ice up. This will block the supply of air to the engine, and cause it to fail. For this reason, aircraft reciprocating engines with carburetors are provided with carburetor air intake heaters. The increasing use of fuel injection
Fuel injection is the introduction of fuel in an internal combustion engine, most commonly automotive engines, by the means of an injector. This article focuses on fuel injection in reciprocating piston and Wankel rotary engines.
All com ...
—which does not require carburetors—has made "carb icing" less of an issue for reciprocating engines.
Jet engines do not experience carb icing, but recent evidence indicates that they can be slowed, stopped, or damaged by internal icing in certain types of atmospheric conditions much more easily than previously believed. In most cases, the engines can be quickly restarted and flights are not endangered, but research continues to determine the exact conditions which produce this type of icing, and find the best methods to prevent, or reverse it, in flight.
Recreation and sports
 Ice also plays a central role in winter recreation and in many sports such as
Ice also plays a central role in winter recreation and in many sports such as ice skating
Ice skating is the self-propulsion and gliding of a person across an ice surface, using metal-bladed ice skates. People skate for various reasons, including recreation (fun), exercise, competitive sports, and commuting. Ice skating may be per ...
, tour skating
Tour skating is recreational long distance ice skating on natural ice. It is particularly popular in the Netherlands and the Nordic countries. It is becoming more popular in areas of North America such as New England,
Southcentral Alaska, and N ...
, ice hockey
Ice hockey (or simply hockey) is a team sport played on ice skates, usually on an Ice rink, ice skating rink with Ice hockey rink, lines and markings specific to the sport. It belongs to a family of sports called hockey. In ice hockey, two o ...
, bandy
Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two teams wearing ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The international governing body for bandy is ...
, ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
Lo ...
, ice climbing, curling
Curling is a sport in which players slide stones on a sheet of ice toward a target area which is segmented into four concentric circles. It is related to bowls, boules, and shuffleboard. Two teams, each with four players, take turns sliding ...
, broomball
Broomball is a both a recreational and organized competitive winter team sport played on ice or snow and is played either indoors or outdoors, depending on climate and location. It is a ball sport and is most popularly played in Canada and the ...
and sled racing on bobsled
Bobsleigh or bobsled is a team winter sport that involves making timed runs down narrow, twisting, banked, iced tracks in a gravity-powered sleigh. International bobsleigh competitions are governed by the International Bobsleigh and Skeleton Fede ...
, luge and skeleton
A skeleton is the structural frame that supports the body of an animal. There are several types of skeletons, including the exoskeleton, which is the stable outer shell of an organism, the endoskeleton, which forms the support structure inside ...
. Many of the different sports played on ice get international attention every four years during the Winter Olympic Games
The Winter Olympic Games (french: link=no, Jeux olympiques d'hiver) is a major international multi-sport event held once every four years for sports practiced on snow and ice. The first Winter Olympic Games, the 1924 Winter Olympics, were he ...
.
A sort of sailboat on blades gives rise to ice yachting
An iceboat (occasionally spelled ice boat or traditionally called an ice yacht) is a recreational or competition sailing craft supported on metal runners for traveling over ice. One of the runners is steerable. Originally, such craft were boats ...
. Another sport is ice racing
Ice racing is a form of racing that uses cars, motorcycles, snowmobiles, all-terrain vehicles, or other motorized vehicles. Ice racing takes place on frozen lakes or rivers, or on groomed frozen lots. As cold weather is a requirement for natural ...
, where drivers must speed on lake ice, while also controlling the skid of their vehicle (similar in some ways to dirt track racing). The sport has even been modified for ice rink
An ice rink (or ice skating rink) is a frozen body of water and/or an artificial sheet of ice created using hardened chemicals where people can ice skate or play winter sports. Ice rinks are also used for exhibitions, contests and ice shows. The ...
s.
Other uses
As thermal ballast
* Ice is used to cool and preserve food inicebox
An icebox (also called a cold closet) is a compact non-mechanical refrigerator which was a common early-twentieth-century kitchen appliance before the development of safely powered refrigeration devices. Before the development of electric refri ...
es.
*Ice cube
An ice cube is a small piece of ice, which is typically rectangular as viewed from above and trapezoidal as viewed from the side. Ice cubes are products of mechanical refrigeration and are usually produced to cool beverages. They may be p ...
s or crushed ice
An ice cube is a small piece of ice, which is typically rectangular as viewed from above and trapezoidal as viewed from the side. Ice cubes are products of mechanical refrigeration and are usually produced to cool beverages. They may be produc ...
can be used to cool drinks. As the ice melts, it absorbs heat and keeps the drink near .
* Ice can be used as part of an air conditioning system, using battery- or solar-powered
Solar power is the conversion of energy from sunlight into electricity, either directly using photovoltaics (PV) or indirectly using concentrated solar power. Photovoltaic cells convert light into an electric current using the photovoltaic ef ...
fans to blow hot air over the ice. This is especially useful during heat wave
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
s when power is out and standard (electrically powered) air conditioners do not work.
* Ice can be used (like other cold packs) to reduce swelling (by decreasing blood flow) and pain by pressing it against an area of the body.
As structural material
 * Engineers used the substantial strength of pack ice when they constructed Antarctica's first floating
* Engineers used the substantial strength of pack ice when they constructed Antarctica's first floating ice pier
An ice pier or ice wharf is a man-made structure used to assist the unloading of ships in Antarctica. It is constructed by pumping seawater into a contained area and allowing the water to freeze. By repeating this procedure several times, additio ...
in 1973. Such ice piers are used during cargo operations to load and offload ships. Fleet operations personnel make the floating pier during the winter. They build upon naturally occurring frozen seawater in McMurdo Sound
McMurdo Sound is a sound in Antarctica. It is the southernmost navigable body of water in the world, and is about from the South Pole.
Captain James Clark Ross discovered the sound in February 1841, and named it after Lt. Archibald McMurdo of ...
until the dock reaches a depth of about . Ice piers have a lifespan of three to five years. * Structures and ice sculptures are built out of large chunks of ice or by spraying waterMakkonen, L. (1994) "Ice and Construction". E & FN Spon, London. . The structures are mostly ornamental (as in the case with ice castles), and not practical for long-term habitation.
* Structures and ice sculptures are built out of large chunks of ice or by spraying waterMakkonen, L. (1994) "Ice and Construction". E & FN Spon, London. . The structures are mostly ornamental (as in the case with ice castles), and not practical for long-term habitation. Ice hotel
An ice hotel is a temporary hotel made up of snow and sculpted blocks of ice. Ice hotels, dependent on sub-freezing temperatures, are constructed from ice and snow and typically have to be rebuilt every year. Ice hotels exist in several countri ...
s exist on a seasonal basis in a few cold areas. Igloo
An igloo (Inuit languages: , Inuktitut syllabics (plural: )), also known as a snow house or snow hut, is a type of shelter built of suitable snow.
Although igloos are often associated with all Inuit, they were traditionally used only ...
s are another example of a temporary structure, made primarily from snow.
* In cold climates, roads are regularly prepared on iced-over lakes and archipelago areas. Temporarily, even a railroad has been built on ice.
* During World War II, Project Habbakuk
Project Habakkuk or Habbakuk (spelling varies) was a plan by the British during the Second World War to construct an aircraft carrier out of pykrete (a mixture of wood pulp and ice) for use against German U-boats in the mid-Atlantic, which wer ...
was an Allied programme which investigated the use of pykrete
Pykrete is a frozen ice composite, originally made of approximately 14% sawdust or some other form of wood pulp (such as paper) and 86% ice by weight (6 to 1 by weight). During World War II, Geoffrey Pyke proposed it as a candidate material fo ...
(wood fibers mixed with ice) as a possible material for warships, especially aircraft carriers, due to the ease with which a vessel immune to torpedoes, and a large deck, could be constructed by ice. A small-scale prototype was built, but the need for such a vessel in the war was removed prior to building it in full-scale.
* Ice has even been used as the material for a variety of musical instruments, for example by percussionist Terje Isungset.
Non-water
The solid phases of several other volatile substances are also referred to as ''ices''; generally a volatile is classed as an ice if its melting point lies above or around 100 K. The best known example isdry ice
Dry ice is the solid form of carbon dioxide. It is commonly used for temporary refrigeration as CO2 does not have a liquid state at normal atmospheric pressure and sublimates directly from the solid state to the gas state. It is used primarily ...
, the solid form of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
.
A "magnetic analogue" of ice is also realized in some insulating magnetic materials in which the magnetic moments mimic the position of protons in water ice and obey energetic constraints similar to the Bernal-Fowler ice rules In chemistry, ice rules are basic principles that govern arrangement of atoms in water ice. They are also known as Bernal–Fowler rules, after British physicists John Desmond Bernal and Ralph H. Fowler who first described them in 1933.
The rules ...
arising from the geometrical frustration In condensed matter physics, the term geometrical frustration (or in short: frustration) refers to a phenomenon where atoms tend to stick to non-trivial positions or where, on a regular crystal lattice, conflicting inter-atomic forces (each one fav ...
of the proton configuration in water ice. These materials are called spin ice
A spin ice is a magnetic substance that does not have a single minimal-energy state. It has magnetic moments (i.e. "spin") as elementary degrees of freedom which are subject to frustrated interactions. By their nature, these interactions preven ...
.
See also
* * * * * * *References
External links
Webmineral listing for Ice
Estimating the bearing capacity of ice
{{Authority control Glaciology Minerals Transparent materials Articles containing video clips Limnology Oceanography Cryosphere