Hurricane Charley on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Hurricane Charley was the first of four separate hurricanes to impact or strike
 A strong
A strong 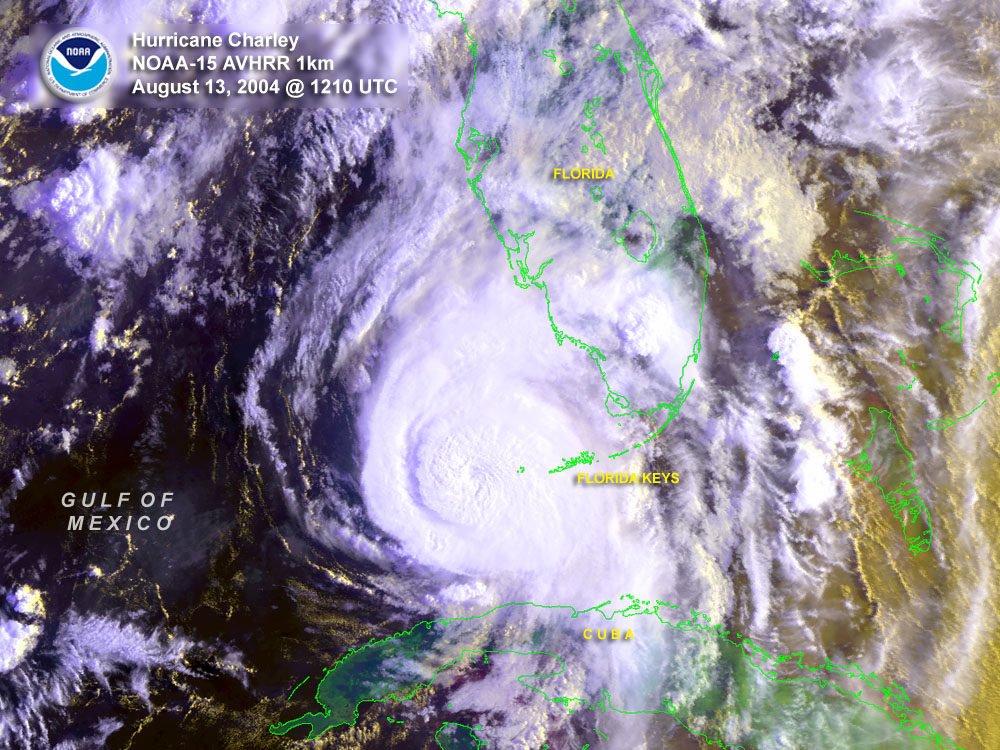 After crossing Cuba near Menelao Mora, Hurricane Charley accelerated to the north-northeast, toward the southwest coast of Florida in response to the approach of an unseasonal mid-tropospheric
After crossing Cuba near Menelao Mora, Hurricane Charley accelerated to the north-northeast, toward the southwest coast of Florida in response to the approach of an unseasonal mid-tropospheric
 On August 10, two days before the hurricane passed near the island,
On August 10, two days before the hurricane passed near the island,  The rapid strengthening of Charley in the eastern
The rapid strengthening of Charley in the eastern
 In
In
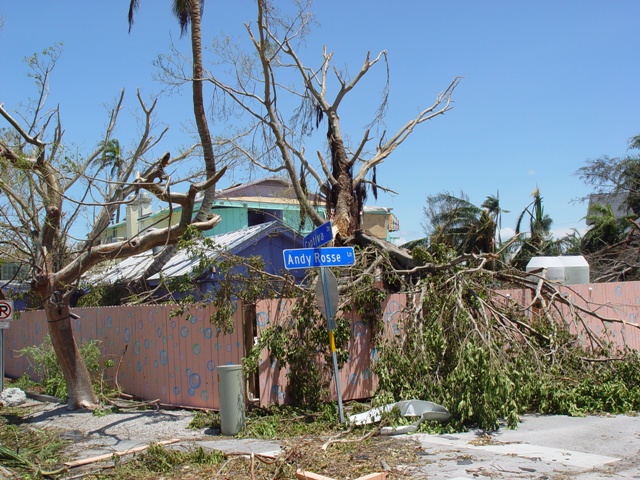 Hurricane Charley passed directly over
Hurricane Charley passed directly over 
 On mainland Florida, Charley produced a peak storm surge of at
On mainland Florida, Charley produced a peak storm surge of at  The most severe damage from Hurricane Charley occurred in Charlotte County. In Boca Grande, numerous houses sustained extensive roof damage, while thousands of trees and power lines were uprooted or snapped. In Port Charlotte and Punta Gorda, many buildings,
The most severe damage from Hurricane Charley occurred in Charlotte County. In Boca Grande, numerous houses sustained extensive roof damage, while thousands of trees and power lines were uprooted or snapped. In Port Charlotte and Punta Gorda, many buildings,  Public schools in some counties in the path of the hurricane were scheduled to be closed for two weeks. In some areas this was necessary because the school buildings were damaged or destroyed: all 59 of Osceola County's schools were damaged, and one-third of Charlotte County's were destroyed by Charley's impact. DeSoto County schools saw $6 million in damage, while
Public schools in some counties in the path of the hurricane were scheduled to be closed for two weeks. In some areas this was necessary because the school buildings were damaged or destroyed: all 59 of Osceola County's schools were damaged, and one-third of Charlotte County's were destroyed by Charley's impact. DeSoto County schools saw $6 million in damage, while
 Upon making landfall on northeastern
Upon making landfall on northeastern
 President
President
Hurricane Charley Advisory Archive
NHC August Monthly Tropical Weather Summary
Ćöincludes figures for damages and fatalities
Lack of a standard places Charley's deaths in question
Air Photos of Charley's Damage From FloridaDisaster.org
Wildlife and Habitat Damage Assessment from Hurricane Charley: Recommendations for Recovery of the J. N. "Ding" Darling National Wildlife Refuge Complex
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charley (2004) 2004 Atlantic hurricane season 2004 in Cuba 2004 in Florida 2004 in Jamaica 2004 in North Carolina 2004 in South Carolina 2004 in the Cayman Islands August 2004 events in North America Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes Charlotte County, Florida Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Retired Atlantic hurricanes Tropical cyclones in 2004
Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
during 2004, along with Frances
Frances is a French and English given name of Latin origin. In Latin the meaning of the name Frances is 'from France' or 'free one.' The male version of the name in English is Francis. The original Franciscus, meaning "Frenchman", comes from the F ...
, Ivan
Ivan () is a Slavic languages, Slavic male given name, connected with the variant of the Greek name (English: John (given name), John) from Hebrew language, Hebrew meaning 'God is gracious'. It is associated worldwide with Slavic countries. T ...
and Jeanne, as well as one of the strongest hurricanes ever to strike the United States. It was the third named storm, the second hurricane
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Depend ...
, and the second major hurricane of the 2004 Atlantic hurricane season. Charley lasted from August 9 to 15, and at its peak intensity it attained winds, making it a strong Category 4 hurricane on the SaffirŌĆōSimpson scale
The SaffirŌĆōSimpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanesŌĆöwhich in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical stormsŌĆöinto five categories distinguished by ...
. It made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
in Southwest Florida
Southwest Florida is the region along the southwest Gulf coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The area is known for its beaches, subtropical landscape, and winter resort economy.
Definitions of the region vary, though its boundaries are generally ...
at maximum strength, making it the strongest hurricane to hit the United States since Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a very powerful and destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It is the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures damaged ...
struck Florida in 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: 1992 Los Angeles riots, Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the Police brutality, police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment buildi ...
and at the time the strongest hurricane to hit southwest Florida in recorded history until Hurricane Ian
Hurricane Ian was a large and destructive Category 4 Atlantic hurricane that was the deadliest hurricane to strike the state of Florida since the 1935 Labor Day hurricane. Ian caused widespread damage across western Cuba and the southeast Unit ...
in 2022.
After moving slowly through the Caribbean, Charley crossed Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, Rep├║blica de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
on Friday, August 13 as a Category 3 hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
Philosophy and general uses
*Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally
*Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
*Category (Kant)
*Categories (Peirce)
*C ...
, causing heavy damage and four deaths. That same day, it crossed over the Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's c ...
, just 22 hours after Tropical Storm Bonnie The name Bonnie has been used for ten tropical cyclones worldwide, eight in the Atlantic Ocean (one of which crossed over into the eastern Pacific Ocean) and one each in the Western Pacific and the Australian region of the Southern Hemisphere.
In t ...
had struck northwestern Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. It was the first time in history that two tropical cyclones struck the same state in a 24-hour period.
At its peak intensity of , Hurricane Charley struck the northern tip of Captiva Island
Captiva is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Lee County, Florida, United States. It is located on Captiva Island. As of the 2020 census the population was 318, down from 583 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Ca ...
and the southern tip of North Captiva Island, before crossing over Bokeelia causing severe damage. Charley then continued to produce severe damage as it made landfall on the peninsula
A peninsula (; ) is a landform that extends from a mainland and is surrounded by water on most, but not all of its borders. A peninsula is also sometimes defined as a piece of land bordered by water on three of its sides. Peninsulas exist on all ...
in Punta Gorda. It continued to the north-northeast along the Peace River corridor, devastating Punta Gorda, Port Charlotte, Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U.S. ...
, Fort Ogden, Nocatee, Arcadia
Arcadia may refer to:
Places Australia
* Arcadia, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney
* Arcadia, Queensland
* Arcadia, Victoria
Greece
* Arcadia (region), a region in the central Peloponnese
* Arcadia (regional unit), a modern administrative un ...
, Zolfo Springs, Sebring, and Wauchula. Zolfo Springs was isolated for nearly two days as masses of large trees, power poles, power lines, transformers, and debris filled the streets. Wauchula sustained gusts to ; buildings in the downtown areas caved onto Main Street. Ultimately, the storm passed through the central and eastern parts of the Orlando
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures rele ...
metropolitan area, still carrying winds gusting up to . The city of Winter Park, north of Orlando, also sustained considerable damage since its many old, large oak trees had not experienced high winds. Falling trees tore down power utilities and smashed cars, and their huge roots lifted underground water and sewer utilities. The storm slowed as it exited the state over Ormond Beach just north of Daytona Beach. The storm was ultimately absorbed by a front in the Atlantic Ocean shortly after sunrise on August 15, near southeastern Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, m╔Öhswat╩ā╔Öwi╦És╔Öt'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
.
Charley was initially expected to hit further north in Tampa
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
, and caught many Floridians off-guard due to a sudden change in the storm's track as it approached the state. Along its path, Charley caused 10 deaths and $16.9 billion in damage to insured residential property, making it the second costliest hurricane in United States history at the time. Charley was a compact, fast-moving storm, which limited the scope and severity of the damage.
Meteorological history
Charley began as a tropical wave that moved off the west coast of Africa on August 4. It moved quickly westward and steadily organized over the open Atlantic Ocean, withconvection
Convection is single or multiphase fluid flow that occurs spontaneously due to the combined effects of material property heterogeneity and body forces on a fluid, most commonly density and gravity (see buoyancy). When the cause of the convec ...
developing in curved bands. The wave continued to develop as it approached the Lesser Antilles
The Lesser Antilles ( es, link=no, Antillas Menores; french: link=no, Petites Antilles; pap, Antias Menor; nl, Kleine Antillen) are a group of islands in the Caribbean Sea. Most of them are part of a long, partially volcanic island arc betwe ...
, and became Tropical Depression Three on August 9 while 115 mi (185 km) south-southeast of Barbados
Barbados is an island country in the Lesser Antilles of the West Indies, in the Caribbean region of the Americas, and the most easterly of the Caribbean Islands. It occupies an area of and has a population of about 287,000 (2019 estimate). ...
, near the island of Grenada
Grenada ( ; Grenadian Creole French: ) is an island country in the West Indies in the Caribbean Sea at the southern end of the Grenadines island chain. Grenada consists of the island of Grenada itself, two smaller islands, Carriacou and Pe ...
, however, the threat to Barbados was short-lived. Low upper-level wind shear
Wind shear (or windshear), sometimes referred to as wind gradient, is a difference in wind speed and/or direction over a relatively short distance in the atmosphere. Atmospheric wind shear is normally described as either vertical or horizontal ...
and well-defined outflow contributed to further intensification, and the depression strengthened on August 10, despite being located in the eastern Caribbean, which is an area not particularly suited to tropical cyclogenesis
Tropical cyclogenesis is the development and strengthening of a tropical cyclone in the atmosphere. The mechanisms through which tropical cyclogenesis occurs are distinctly different from those through which temperate cyclogenesis occurs. Tropi ...
. At this time, the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
in Miami
Miami ( ), officially the City of Miami, known as "the 305", "The Magic City", and "Gateway to the Americas", is a East Coast of the United States, coastal metropolis and the County seat, county seat of Miami-Dade County, Florida, Miami-Dade C ...
designated the name "Charley".
 A strong
A strong ridge
A ridge or a mountain ridge is a geographical feature consisting of a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for an extended distance. The sides of the ridge slope away from the narrow top on either side. The line ...
of high pressure to the system's north forced Charley to change track quickly to the west-northwest. It continued to strengthen and became a Category 1 hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
Philosophy and general uses
*Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally
*Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
*Category (Kant)
*Categories (Peirce)
*C ...
on August 11, while south of Kingston, Jamaica
Kingston is the capital and largest city of Jamaica, located on the southeastern coast of the island. It faces a natural harbour protected by the Palisadoes, a long sand spit which connects the town of Port Royal and the Norman Manley Inter ...
. The storm was being steered around the periphery of the high pressure area, and as a result, Charley changed direction toward the northwest. The following day, the core passed southwest of Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, affecting the island on August 11 and 12. The storm then passed northeast of Grand Cayman
Grand Cayman is the largest of the three Cayman Islands and the location of the territory's capital, George Town. In relation to the other two Cayman Islands, it is approximately 75 miles (121 km) southwest of Little Cayman and 90 miles ( ...
, reaching Category 2 status just after passing the island. The hurricane continued to strengthen as it turned to the northwest and rounded the southwest portion of the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
, becoming a major hurricane
Major (commandant in certain jurisdictions) is a military rank of commissioned officer status, with corresponding ranks existing in many military forces throughout the world. When used unhyphenated and in conjunction with no other indicators ...
ŌĆöa storm classified as a Category 3 hurricane
Category, plural categories, may refer to:
Philosophy and general uses
*Categorization, categories in cognitive science, information science and generally
*Category of being
* ''Categories'' (Aristotle)
*Category (Kant)
*Categories (Peirce)
*C ...
or higherŌĆöjust before making landfall on southern Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, Rep├║blica de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
. Charley came ashore near Punta Cayamas with maximum sustained winds of and gusts of up to , at about 0430 UTC on August 13. It crossed the island, passing about west of downtown Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
before weakening to .
 After crossing Cuba near Menelao Mora, Hurricane Charley accelerated to the north-northeast, toward the southwest coast of Florida in response to the approach of an unseasonal mid-tropospheric
After crossing Cuba near Menelao Mora, Hurricane Charley accelerated to the north-northeast, toward the southwest coast of Florida in response to the approach of an unseasonal mid-tropospheric trough
Trough may refer to:
In science
* Trough (geology), a long depression less steep than a trench
* Trough (meteorology), an elongated region of low atmospheric pressure
* Trough (physics), the lowest point on a wave
* Trough level (medicine), the l ...
. Charley passed over the Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's c ...
at 1200 UTC on August 13, with maximum winds of about . The strike occurred only 22 hours after Tropical Storm Bonnie The name Bonnie has been used for ten tropical cyclones worldwide, eight in the Atlantic Ocean (one of which crossed over into the eastern Pacific Ocean) and one each in the Western Pacific and the Australian region of the Southern Hemisphere.
In t ...
made landfall on St. Vincent Island, marking the first time two tropical cyclones hit the same state within a 24-hour period. Then Charley rapidly intensified
In meteorology, rapid intensification is a situation where a tropical cyclone intensifies dramatically in a short period of time. The United States National Hurricane Center defines rapid intensification as an increase in the maximum sustained wi ...
, strengthening from a hurricane with a minimum central barometric pressure of to a hurricane with a pressure of in just three hours. It continued to strengthen as it turned more to the northeast, and made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
near the island of Cayo Costa, Florida as a Category 4 hurricane with a pressure of at approximately 1945 UTC on August 13. An hour later, the hurricane struck Punta Gorda as a storm and then passed up through Port Charlotte and the Charlotte Harbor. However, the eye had shrunk before landfall, limiting the most powerful winds to an area within of the center.
Charley weakened considerably due to its passage over land, but still retained sustained winds of about as it passed directly over Orlando
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures rele ...
between 0020 and 0140 UTC August 14; gusts of up to were recorded at Orlando International Airport
Orlando International Airport is a major public airport located 6 miles (10 km) southeast of Downtown Orlando, Florida. In 2021, it handled 19,618,838 passengers, making it the busiest airport in the state and seventh busiest airport i ...
. It cut a swath of destruction across Florida, also passing near Kissimmee
Kissimmee ( ) is the largest city and county seat of Osceola County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 census, the population was 79,226. It is a Principal City of the Orlando-Kissimmee-Sanford, Florida, Metropolitan Statistical Area, wh ...
. The hurricane reemerged into the Atlantic Ocean after crossing directly over New Smyrna Beach
New Smyrna Beach is a city in Volusia County, Florida, United States, located on the central east coast of the state, with the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Its population is 30,142 in 2020 by the United States Census Bureau.
The downtown section o ...
as a Category 1 hurricane, but restrengthened slightly over open waters. Continuing to move rapidly to the north-northeast, Charley struck near Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge
The Cape Romain National Wildlife Refuge is a 66,287 acre (267 km┬▓) National Wildlife Refuge in southeastern South Carolina near Awendaw, South Carolina. The refuge lands and waters encompass water impoundments, creeks and bays, eme ...
, South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
as an hurricane, moved offshore briefly, and made its final landfall near North Myrtle Beach
North Myrtle Beach is a city in Horry County, South Carolina, United States. It was created in 1968 from four existing municipalities, and is located about northeast of Myrtle Beach. It serves as one of the primary tourist destinations along ...
as a minimal hurricane, with winds of . Charley then began interacting with an approaching frontal boundary, becoming a tropical storm over southeastern North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
. After moving back into the Atlantic Ocean near Virginia Beach
Virginia Beach is an independent city located on the southeastern coast of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The population was 459,470 at the 2020 census. Although mostly suburban in character, it is the most populous city ...
on August 15, the storm became extratropical
Extratropical cyclones, sometimes called mid-latitude cyclones or wave cyclones, are low-pressure areas which, along with the anticyclones of high-pressure areas, drive the weather over much of the Earth. Extratropical cyclones are capable of p ...
and became embedded in the frontal zone. The extratropical storm continued to move rapidly to the northeast, and was completely absorbed by the front shortly after sunrise on August 15, near southeastern Massachusetts
Massachusetts (Massachusett language, Massachusett: ''Muhsachuweesut assachusett writing systems, m╔Öhswat╩ā╔Öwi╦És╔Öt'' English: , ), officially the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, is the most populous U.S. state, state in the New England ...
.
Preparations
 On August 10, two days before the hurricane passed near the island,
On August 10, two days before the hurricane passed near the island, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
n officials issued a tropical storm warning
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
, which was upgraded to a hurricane warning
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
a day later. In Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, the threat of the storm forced the country's two airports to close, and also forced two cruise ships to reroute. The Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas TerritoryŌĆöthe largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
issued a hurricane warning on August 11, a day before the hurricane passed near the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Archi ...
.
Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, Rep├║blica de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
n government officials issued a hurricane watch
Tropical cyclone warnings and watches are alerts issued by national weather forecasting bodies to coastal areas threatened by the imminent approach of a tropical cyclone of tropical storm or hurricane intensity. They are notices to the local popul ...
for the southern coastline on August 11, two days before the hurricane struck the island. This was upgraded to a hurricane warning on the 12th, 13 ┬Į hours before Charley made landfall. Because of the threat, the government issued a mandatory evacuation for 235,000 citizens and 159,000 animals in the area of the expected impact. An additional 3,800 residents were evacuated from offshore islands, while 47,000 in Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
were transported from old, unsafe buildings to safer areas. The people were transported to shelters provisioned with supplies. In addition, the power grid in southern Cuba was turned off to avoid accidents.
On August 11, Florida governor
The governor of Florida is the head of government of the state of Florida and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor has a duty to enforce state laws and the power to either approve or veto bills passed by the Florida ...
Jeb Bush
John Ellis "Jeb" Bush (born February 11, 1953) is an American politician and businessman who served as the 43rd governor of Florida from 1999 to 2007. Bush, who grew up in Houston, was the second son of former President George H. W. Bush a ...
issued a state of emergency
A state of emergency is a situation in which a government is empowered to be able to put through policies that it would normally not be permitted to do, for the safety and protection of its citizens. A government can declare such a state du ...
declaration due to the impending threat Charley presented to the state while the storm was still located south of Jamaica. The National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
issued hurricane warnings for the Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago located off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and e ...
and from Cape Sable
Cape Sable is the southernmost point of the United States mainland and mainland Florida. It is located in southwestern Florida, in Monroe County, and is part of the Everglades National Park.
The cape is a peninsula issuing from the southeast ...
to the mouth of the Suwannee River
The Suwannee River (also spelled Suwanee River) is a river that runs through south Georgia southward into Florida in the southern United States. It is a wild blackwater river, about long.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset hig ...
a day prior to Charley's passage through the state, while tropical storm warnings were issued elsewhere throughout Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
. Because of the threat, 1.9 million people along the Florida west coast were urged to evacuate, including 380,000 residents in the Tampa Bay
Tampa Bay is a large natural harbor and shallow estuary connected to the Gulf of Mexico on the west-central coast of Florida, comprising Hillsborough Bay, McKay Bay, Old Tampa Bay, Middle Tampa Bay, and Lower Tampa Bay. The largest freshwater in ...
area, and 11,000 in the Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago located off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and e ...
. It was the largest evacuation order for Pinellas County
Pinellas County (, ) is a county located on the west central coast of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 959,107. The county is part of the TampaŌĆōSt. PetersburgŌĆō Clearwater, Florida Metropolitan Statistical ...
history, and the largest evacuation request in Florida since Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful Cape Verde hurricane which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Floyd tr ...
five years before. Many Floridians remained despite the evacuation order, as authorities estimated that up to a million people would not go to shelters; instead, these residents boarded up their homes and bought supplies to ride out the storm. However, about 1.42 million people evacuated their homes in Florida, and approximately 50,000 residents were placed in shelters throughout the state. Power companies mobilized workers to prepare for the expected widespread power outages. MacDill Air Force Base
MacDill Air Force Base (MacDill AFB) is an active United States Air Force installation located 4 miles (6.4 km) south-southwest of downtown Tampa, Florida.
The "host wing" for MacDill AFB is the 6th Air Refueling Wing (6 ARW), assig ...
, home of U.S. Central Command
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Tas ...
(USCENTCOM
The United States Central Command (USCENTCOM or CENTCOM) is one of the eleven unified combatant commands of the U.S. Department of Defense. It was established in 1983, taking over the previous responsibilities of the Rapid Deployment Joint Tas ...
) and the U.S. military center for the Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, žŁž▒ž© ž¦┘äž╣ž▒ž¦┘é (Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, ž┤█Ģ┌Ģ█ī ž╣█Äž▒ž¦┘é (Kurdish languages, Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict (2003ŌĆōpresent), I ...
, severely limited its staff on base, shifting most of its operations to its forward headquarters in Doha, Qatar
Doha ( ar, ž¦┘äž»┘łžŁž®, ad-DawßĖźa or ''ad-D┼ŹßĖźa'') is the capital city and main financial hub of Qatar. Located on the Persian Gulf coast in the east of the country, north of Al Wakrah and south of Al Khor, it is home to most of the coun ...
. Similarly, Kennedy Space Center
The John F. Kennedy Space Center (KSC, originally known as the NASA Launch Operations Center), located on Merritt Island, Florida, is one of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's (NASA) ten field centers. Since December 1968 ...
, which usually counts with 13,000 on-site personnel, reduced its staff to only 200 people in preparation for the hurricane, and secured all Space Shuttle
The Space Shuttle is a retired, partially reusable low Earth orbital spacecraft system operated from 1981 to 2011 by the U.S. National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) as part of the Space Shuttle program. Its official program na ...
s by sealing them in their hangars. Many amusement parks in the Orlando
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures rele ...
area closed early, and Walt Disney World
The Walt Disney World Resort, also called Walt Disney World or Disney World, is an entertainment resort complex in Bay Lake and Lake Buena Vista, Florida, United States, near the cities of Orlando and Kissimmee. Opened on October 1, 1971, th ...
's Animal Kingdom remained closed. This was only the second time in history that a Disney park was closed due to a hurricane, with the other occurrence being after Hurricane Floyd
Hurricane Floyd was a very powerful Cape Verde hurricane which struck the Bahamas and the East Coast of the United States. It was the sixth named storm, fourth hurricane, and third major hurricane in the 1999 Atlantic hurricane season. Floyd tr ...
. The approaching hurricane also forced several cruise ships to reroute their paths, and forced rail service between Miami and New York to shut down.
 The rapid strengthening of Charley in the eastern
The rapid strengthening of Charley in the eastern Gulf of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de M├®xico) is an oceanic basin, ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of ...
caught many by surprise. Around five hours before its Florida landfall, Charley was a strong Category 2 hurricane predicted to strengthen its strongest winds to upon its landfall in the Tampa
Tampa () is a city on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The city's borders include the north shore of Tampa Bay and the east shore of Old Tampa Bay. Tampa is the largest city in the Tampa Bay area and the seat of Hillsborough County ...
ŌĆōSaint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, ąĪą░ąĮą║čé-ą¤ąĄč鹥čĆą▒čāčĆą│, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=╦łsankt p╩▓╔¬t╩▓╔¬r╦łburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914ŌĆō1924) and later Leningrad (1924ŌĆō1991), i ...
area. About two hours before landfall, the National Hurricane Center
The National Hurricane Center (NHC) is the division of the United States' NOAA/National Weather Service responsible for tracking and predicting tropical weather systems between the Prime Meridian and the 140th meridian west poleward to the 3 ...
issued a special advisory, notifying the public that Charley had become a Category 4 hurricane, with a predicted landfall location in the Port Charlotte area. As a result of this change in forecast, numerous people in the Charlotte County area were unprepared for the hurricane, although the new track prediction was well within the previous forecast's margin of error. National Hurricane Center forecasting intern Robbie Berg publicly blamed the media for misleading residents into believing that a Tampa landfall was inevitable. He also stated that residents of Port Charlotte had ample warning, as a hurricane warning had been issued for the landfall area 23 hours before, and a hurricane watch had existed for 35 hours.
Several local meteorologists, however, did depart from the official predictions of a Tampa Bay landfall as early as the morning of August 13. Jim Farrell of WINK
A wink is a facial expression made by briefly closing one eye. A wink is an informal mode of non-verbal communication usually signaling shared hidden knowledge or intent. However, it is ambiguous by itself and highly dependent upon additional c ...
, Robert Van Winkle WBBH, Steve Jerve of WFLA in Tampa, Jim Reif of WZVN in Fort Myers
Fort Myers (or Ft. Myers) is a city in southwestern Florida and the county seat and commercial center of Lee County, Florida, United States. The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 92,245 in 20 ...
, and Tom Terry of WFTV
WFTV (channel 9) is a television station in Orlando, Florida, United States, affiliated with ABC. It is owned by Cox Media Group alongside independent station WRDQ (channel 27). Both stations share studios on East South Street (SR 15) in do ...
in Orlando
Orlando () is a city in the U.S. state of Florida and is the county seat of Orange County. In Central Florida, it is the center of the Orlando metropolitan area, which had a population of 2,509,831, according to U.S. Census Bureau figures rele ...
all broke with their national news forecasts and stated at around 1500 UTC that Charley was going to turn early, striking around Charlotte Harbor and traveling over Orlando, as would prove to be the case.
Following the Florida landfall, Georgia Governor
The governor of Georgia is the head of government of Georgia and the commander-in-chief of the state's military forces. The governor also has a duty to enforce state laws, the power to either veto or approve bills passed by the Georgia Legisl ...
Sonny Perdue
George Ervin "Sonny" Perdue III (born December 20, 1946) is an American veterinarian, businessman, politician, and university administrator who served as the 31st United States Secretary of Agriculture from 2017 to 2021. He previously served as t ...
declared a state of emergency as a precaution against a storm surge and price gouging
Price gouging is a pejorative term used to describe the situation when a seller increases the prices of goods, services, or commodities to a level much higher than is considered reasonable or fair. Usually, this event occurs after a demand or ...
. In South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, Governor
A governor is an administrative leader and head of a polity or political region, ranking under the head of state and in some cases, such as governors-general, as the head of state's official representative. Depending on the type of political ...
Mark Sanford
Marshall Clement "Mark" Sanford Jr. (born May 28, 1960) is an American politician and author who served as the U.S. Representative for South Carolina's 1st congressional district from 1995 to 2001 and again from 2013 to 2019, and also as the ...
declared a state of emergency as Charley approached its final landfall. Two coastal counties were forced to evacuate, with state troopers redirecting traffic further inland from Myrtle Beach
Myrtle Beach is a resort city on the east coast of the United States in Horry County, South Carolina. It is located in the center of a long and continuous stretch of beach known as "The Grand Strand" in the northeastern part of the state. Its ...
. In all, 180,000 evacuated from the Grand Strand
The Grand Strand is an arc of beach land on the Atlantic Ocean in South Carolina, United States, extending more than from Little River to Winyah Bay. It is located in Horry and Georgetown Counties on the NE South Carolina coast.
The term G ...
area.
Impact
One death in Jamaica, four deaths in Cuba, and ten deaths in the United States were directly attributed to Charley. Numerous injuries were reported, as well as 25 indirect deaths in the U.S. Property damage from Charley in the United States was estimated by the NHC to be $16billion
Billion is a word for a large number, and it has two distinct definitions:
*1,000,000,000, i.e. one thousand million, or (ten to the ninth power), as defined on the short scale. This is its only current meaning in English.
* 1,000,000,000,000, i.e ...
. At the time, this figure made Charley the second costliest hurricane in United States history, behind 1992
File:1992 Events Collage V1.png, From left, clockwise: 1992 Los Angeles riots, Riots break out across Los Angeles, California after the Police brutality, police beating of Rodney King; El Al Flight 1862 crashes into a residential apartment buildi ...
's Hurricane Andrew
Hurricane Andrew was a very powerful and destructive Category 5 Atlantic hurricane that struck the Bahamas, Florida, and Louisiana in August 1992. It is the most destructive hurricane to ever hit Florida in terms of structures damaged ...
's $27.3 billion.
Caribbean Sea
Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of His ...
, strong winds caused moderate damage to the agricultural sector, with crop and livestock damage totaling to $1.44 million. As the storm traveled along the southwest coast of Jamaica, it caused heavy wind and rain damage. Damage was heaviest in Saint Elizabeth Parish
Saint Elizabeth, one of Jamaica's largest parishes, is located in the southwest of the island, in the county of Cornwall. Its capital, Black River, is located at the mouth of the Black River, the widest on the island.
History
Saint Elizabe ...
, where 100 people had to be housed in six shelters. Strong winds downed trees and power lines, causing power outages and blocking roads. Throughout the country, Charley caused $4.1 million in damage and one fatality. In spite of the close approach that Charley made on the Cayman Islands
The Cayman Islands () is a self-governing British Overseas TerritoryŌĆöthe largest by population in the western Caribbean Sea. The territory comprises the three islands of Grand Cayman, Cayman Brac and Little Cayman, which are located to the ...
, the islands were mostly spared, and were subjected to little damage. Rainfall was light, peaking at in Grand Cayman
Grand Cayman is the largest of the three Cayman Islands and the location of the territory's capital, George Town. In relation to the other two Cayman Islands, it is approximately 75 miles (121 km) southwest of Little Cayman and 90 miles ( ...
, while Cayman Brac
Cayman Brac is an island that is part of the Cayman Islands. It lies in the Caribbean Sea about north-east of Grand Cayman and east of Little Cayman. It is about long, with an average width of . Its terrain is the most prominent of the thre ...
reported tropical storm force winds.
Operationally, forecasters estimated that Charley struck southern Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, Rep├║blica de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribbea ...
as a Category 2 hurricane on the SaffirŌĆōSimpson scale
The SaffirŌĆōSimpson hurricane wind scale (SSHWS) classifies hurricanesŌĆöwhich in the Western Hemisphere are tropical cyclones that exceed the intensities of tropical depressions and tropical stormsŌĆöinto five categories distinguished by ...
. In post-hurricane-season analysis, Charley was determined to have struck southern Cuba as a hurricane; the original estimate was revised based on a report of a sustained wind measurement in Playa Baracoa
Playa Baracoa, sometimes shortened as ''Baracoa'', is a Cuban village and ''consejo popular'' ("people's council", i.e. hamlet) of the municipality of Bauta, in Artemisa Province. In 2011 it had a population of about 7,000.
History
The village ...
, and meant that Charley was a major hurricane at landfall. The hurricane produced a storm surge of up to in Playa Cajio; on the other hand, Charley's quick passage caused precipitation
In meteorology, precipitation is any product of the condensation of atmospheric water vapor that falls under gravitational pull from clouds. The main forms of precipitation include drizzle, rain, sleet, snow, ice pellets, graupel and hail. ...
amounts to be small, with the largest total, occurring in Mariel.
Strong wind gusts downed nearly 1,500 power lines and knocked over 28 large high tension wire towers at a power plant in Mariel. As a result, more than half of the electricity customers in Havana Province
La Habana Province , formerly known as Ciudad de La Habana Province, is a province of Cuba that includes the territory of the city of Havana, the Republic's capital. Between 1878 and 2010, the name referred to another province that covered a m ...
were left without power for 12 days after the storm, and all of Pinar del R├Ło Province
Pinar del R├Ło is one of the provinces of Cuba. It is at the western end of the island of Cuba.
Geography
The Pinar del R├Ło province is Cuba's westernmost province and contains one of Cuba's three main mountain ranges, the Cordillera de Guanig ...
was without power for over 11 days. Blackouts continued in areas where power returned. The power outages resulted in lack of drinking water for numerous people, including no potable water in the city of Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
for four days. As a result, the Cuban government sent water tanks to satisfy the short term need. Similarly, there was a lack of gas for cooking for over a week. However, one Cuban government official stated that it could take up to two months for basic utilities to be returned to many isolated villages.
Near its landfall location, Charley destroyed 290 of the 300 houses in the village, while over 70,000 homes in Havana
Havana (; Spanish: ''La Habana'' ) is the capital and largest city of Cuba. The heart of the La Habana Province, Havana is the country's main port and commercial center.
were either damaged or destroyed. Numerous hotels reported damage, potentially impacting the important tourism industry in the country. Agricultural damage was heavy, with the hurricane damaging more than 3,000 agricultural institutions. Citrus officials estimated a loss of 15,000 metric ton
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton (United States c ...
s of grapefruit
The grapefruit (''Citrus'' ├Ś ''paradisi'') is a subtropical citrus tree known for its relatively large, sour to semi-sweet, somewhat bitter fruit. The interior flesh is segmented and varies in color from pale yellow to dark pink.
Grapefruit is ...
on the Isle of Youth
Isla de la Juventud (; en, Isle of Youth) is the second-largest Cuban island (after Cuba's mainland) and the seventh-largest island in the West Indies (after mainland Cuba itself, Hispaniola, Jamaica, Puerto Rico, Trinidad, and Andros Isla ...
, while strong winds ruined 66,000 metric tons of citrus trees in the Havana area. Charley also destroyed around 57,000 acres (230 km2) of fruit trees in the Havana area. Approximately 95% of the sugar cane, bean, and banana crops were affected in Cuban territory. In all, Charley was directly responsible for four deaths in Cuba, and was responsible for $923 million in property damage, primarily from agricultural losses.
Florida
Hurricane Charley severely affected the state of Florida. There were nine direct fatalities, 20 indirect fatalities, and numerous injuries attributed to the storm. Property damage was estimated at $5.4 billion, and approximately $285 million in agricultural damage. However, due to Charley's speed (it crossed the Florida peninsula in approximately seven hours) and small size, rainfall along theeyewall
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
was mostly limited to .
While moving northward to the west of the Florida Keys
The Florida Keys are a coral cay archipelago located off the southern coast of Florida, forming the southernmost part of the continental United States. They begin at the southeastern coast of the Florida peninsula, about south of Miami, and e ...
, Charley produced moderate winds of with gusts to in Key West
Key West ( es, Cayo Hueso) is an island in the Straits of Florida, within the U.S. state of Florida. Together with all or parts of the separate islands of Dredgers Key, Fleming Key, Sunset Key, and the northern part of Stock Island, it cons ...
. The winds toppled a few trees, power lines, and unreinforced signs. A boat, knocked loose by strong waves, struck a power transmission line, causing widespread power outages from Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
to Key West. On Fort Jefferson in the Dry Tortugas
Dry Tortugas National Park is a national park located about west of Key West in the Gulf of Mexico. The park preserves Fort Jefferson and the seven Dry Tortugas islands, the westernmost and most isolated of the Florida Keys. The archipelago's c ...
, the hurricane produced an estimated storm surge of up to . The surge, combined with incoming waves, caused extensive flooding in the park and damaged numerous docks. In spite of this, property damage was minimal in the area, totaling $160,000.
 Hurricane Charley passed directly over
Hurricane Charley passed directly over Captiva Island
Captiva is an unincorporated community and census-designated place (CDP) in Lee County, Florida, United States. It is located on Captiva Island. As of the 2020 census the population was 318, down from 583 at the 2010 census. It is part of the Ca ...
near Cayo Costa with peak winds of . The Category 4 hurricane produced an estimated storm surge of up to on the island, which is lower than expected for a storm of its intensity. The decrease in the height of the surge was due to the hurricane's small size and its rapid intensification just prior to landfall. Furthermore, the storm surge, combined with the strong pressure gradient, produced a inlet on North Captiva Island
North Captiva Island is an island in Lee County in Southwest Florida, located just offshore in the Gulf of Mexico. It lies just north of Captiva Island, separated by a channel called Redfish Pass which was created in a 1921 hurricane. It lies j ...
, known as Charley's Cut. Strong waves and storm surge caused severe beach erosion and dune damage at various locations. The storm severely damaged five houses, lightly damaged many others, and downed many trees on Gasparilla Island
Gasparilla Island is a barrier island in southwest Florida, United States, straddling the border of Charlotte and Lee counties. Its largest town is Boca Grande, and it is the location of the Gasparilla Island State Park. The island has been an ...
. At least half of the 300 homes on North Captiva Island were substantially damaged, including ten that were destroyed. On Captiva Island, the strong winds severely damaged most houses, as well as several recreational buildings.
The city of Arcadia
Arcadia may refer to:
Places Australia
* Arcadia, New South Wales, a suburb of Sydney
* Arcadia, Queensland
* Arcadia, Victoria
Greece
* Arcadia (region), a region in the central Peloponnese
* Arcadia (regional unit), a modern administrative un ...
in DeSoto County saw extreme damage, in spite of being relatively further inland. About 95% of the buildings in the downtown area saw some sort of damage. The only shelter in the town had its roof torn open by the wind, leaving 3,500 evacuees inside unprotected from the onslaught of the storm.

Hardee County
Hardee County is a county located in the Florida Heartland, Central Florida region U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 25,327. Its county seat is Wauchula.
Hardee County comprises the Wauchula, FL Micropolitan St ...
saw property damage estimated at $750 million, along with six injuries, but no deaths were reported. Charley caused blackouts in the entire county, as well as damage to 3,600 homes and the destruction of 1,400. A radio tower near Sebring was toppled, along with numerous trees and power poles along the north and east side of Highlands County
Highlands County is a county located in the Florida Heartland region of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 census, the population was 101,235. Its county seat is Sebring.
Highlands County comprises the Sebring-Avon Park, FL Metropolita ...
. Additionally, there were several reports of severely damaged homes in Polk County near Babson Park and Avon Park. In Lake Wales, Florida, a sand mine lake encroached into State Road 60 due to wave action and swallowed a car. Additionally, Lake Wales saw 23,000 buildings damaged, as well as the destruction of 739 structures. Seven deaths were reported in the county, one of them determined to be direct.
Throughout the rest of the islands in Sarasota
Sarasota () is a city in Sarasota County on the Gulf Coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The area is renowned for its cultural and environmental amenities, beaches, resorts, and the Sarasota School of Architecture. The city is located in the sout ...
, Charlotte
Charlotte ( ) is the List of municipalities in North Carolina, most populous city in the U.S. state of North Carolina. Located in the Piedmont (United States), Piedmont region, it is the county seat of Mecklenburg County, North Carolina, Meckl ...
, Lee, and Collier counties, strong winds from Hurricane Charley caused severe damage to hundreds of buildings and trees. Lee County also endured an storm surge
A storm surge, storm flood, tidal surge, or storm tide is a coastal flood or tsunami-like phenomenon of rising water commonly associated with low-pressure weather systems, such as cyclones. It is measured as the rise in water level above the n ...
. These counties were exposed to Charley's eyewall
The eye is a region of mostly calm weather at the center of tropical cyclones. The eye of a storm is a roughly circular area, typically in diameter. It is surrounded by the ''eyewall'', a ring of towering thunderstorms where the most severe weat ...
, so they saw the most damage. Due to its small size, the area of most intense damage was located within a 10-mi (16-km) band centered on Charley's track, with additional heavy damage forming an outer band extending to each side of the inner swath of damage. In Charlotte County, 80% of buildings were damaged.
 On mainland Florida, Charley produced a peak storm surge of at
On mainland Florida, Charley produced a peak storm surge of at Vanderbilt Beach
Vanderbilt Beach is an unincorporated community in Collier County, Florida, United States. It is located north of the Pelican Bay census-designated place and west of Naples Park, along the Gulf of Mexico. Vanderbilt Beach is north of the cente ...
near Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, ╬Ø╬Ą╬¼ŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣Žé, Ne├Īpolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, along with a much lower surge at its Punta Gorda landfall. The hurricane dropped generally light rainfall across Florida, with the maximum amount of occurring in Bud Slough in Manatee County
Manatee County is a county in the Central Florida portion of the U.S. state of Florida. As of the 2020 US Census, the population was 399,710. Manatee County is part of the North Port-Sarasota-Bradenton Metropolitan Statistical Area. Its county s ...
, east of Myakka River State Park
Myakka River State Park is a Florida State Park, that is located east of Interstate 75 in Sarasota County and a portion of southeastern Manatee County on the Atlantic coastal plain. This state park consists of , making it one of the state's ...
. In Punta Gorda's airport, where the hurricane made landfall, wind speeds of up to were measured, alongside gusts of up to , before the instrument was blown apart, along with most of the planes and the airport itself. The Charlotte Regional Medical Center
ShorePoint Health Punta Gorda, is a for-profit hospital in Punta Gorda, Florida, owned by Community Health Systems.
History
On August 17, 1947, Charlotte Hospital opened in Charlotte County becoming the first hospital in the county. It had 12 h ...
recorded an unofficial peak wind gust of . Port Charlotte's Saint Joseph's Hospital had its roof blown away by Charley's strong winds. Due to the compact nature of the hurricane, the storm's radius of maximum sustained winds only extended a short distance from its center. In comparison, Fort Myers
Fort Myers (or Ft. Myers) is a city in southwestern Florida and the county seat and commercial center of Lee County, Florida, United States. The Census Bureau's Population Estimates Program calculated that the city's population was 92,245 in 20 ...
, which is only from where Charley made landfall, experienced sustained winds of only with gusts of . In South Florida, Charley spawned several tornadoes, including a long-lived F2 that struck Clewiston
Clewiston is a city in Hendry County, Florida, United States. Its location is northwest of Fort Lauderdale on the Atlantic coastal plain. The population was 7,327 at the 2020 census, up from 7,155 at the 2010 census. The estimated population in 2 ...
, and five weak tornadoes near the point where the hurricane made landfall.
 The most severe damage from Hurricane Charley occurred in Charlotte County. In Boca Grande, numerous houses sustained extensive roof damage, while thousands of trees and power lines were uprooted or snapped. In Port Charlotte and Punta Gorda, many buildings,
The most severe damage from Hurricane Charley occurred in Charlotte County. In Boca Grande, numerous houses sustained extensive roof damage, while thousands of trees and power lines were uprooted or snapped. In Port Charlotte and Punta Gorda, many buildings, RVs
A recreational vehicle, often abbreviated as RV, is a motor vehicle or trailer that includes living quarters designed for accommodation. Types of RVs include motorhomes, campervans, coaches, caravans (also known as travel trailers and camper ...
, and mobile homes were completely destroyed, while other buildings suffered roofing damage due to the powerful winds.
Charley devastated Southwest Florida
Southwest Florida is the region along the southwest Gulf coast of the U.S. state of Florida. The area is known for its beaches, subtropical landscape, and winter resort economy.
Definitions of the region vary, though its boundaries are generally ...
, causing $14.6 billion in property damage on the peninsula of Florida alone. Many towns such as Punta Gorda and Port Charlotte were leveled by the hurricane. Trees were downed and trailer parks were obliterated as far as Ormond Beach
Ormond Beach is a city in central Florida in Volusia County. The population was 43,080 at the 2020 census. Ormond Beach lies directly north of Daytona Beach and is a principal city of the DeltonaŌĆōDaytona BeachŌĆōOrmond Beach, FL Metropolitan ...
.
Charley also caused considerable damage in the central and eastern parts of the state. Several possible tornadoes occurred, with severe thunderstorms during the duration of the storm. Winds were estimated to be at sustained near, and to the north of Okeechobee, while winds at Orlando International Airport topped out around in a gust. At Orlando International Airport
Orlando International Airport is a major public airport located 6 miles (10 km) southeast of Downtown Orlando, Florida. In 2021, it handled 19,618,838 passengers, making it the busiest airport in the state and seventh busiest airport i ...
, debris littered two runways and lashing winds tore the roofs off three terminals and shattered two giant glass panels in the main terminal. The winds also ripped the roof right off of Brookside Elementary in Winter Park, leaving damage to the school, as well as the schoolŌĆÖs cafeteria. The storm caused 2 million customers to lose electricity in Florida. In some areas, power was not restored for weeks: 136,000 residents had no electricity a week after Charley's landfall, and 22,000 customers, primarily from cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-control ...
s, were still waiting for their service to be restored on August 26. Citizens in Daytona Beach
Daytona Beach, or simply Daytona, is a coastal resort-city in east-central Florida. Located on the eastern edge of Volusia County near the Atlantic coastline, its population was 72,647 at the 2020 census. Daytona Beach is approximately nort ...
, New Smyrna Beach
New Smyrna Beach is a city in Volusia County, Florida, United States, located on the central east coast of the state, with the Atlantic Ocean to the east. Its population is 30,142 in 2020 by the United States Census Bureau.
The downtown section o ...
, and Port Orange
Port Orange is a city in Volusia County, Florida. The city's population was estimated at 64,842 in 2019 by the U.S. Census Bureau.
The city is part of the DeltonaŌĆōDaytona BeachŌĆōOrmond Beach metropolitan area; the metropolitan area's populati ...
in Southeastern Volusia County
Volusia County (, ) is located in the east-central part of the U.S. state of Florida, stretching between the St. Johns River and the Atlantic Ocean. As of the 2020 United States Census, 2020 census, the county was home to 553,543 people, an incr ...
also dealt with storm surge from the St. Johns River
The St. Johns River ( es, R├Ło San Juan) is the longest river in the U.S. state of Florida and its most significant one for commercial and recreational use. At long, it flows north and winds through or borders twelve counties. The drop in eleva ...
and Halifax River
The Halifax River is part of the Atlantic Intracoastal Waterway, located in northeast Volusia County, Florida. The waterway was originally known as the North Mosquito River, but was renamed after George Montagu-Dunk, 2nd Earl of Halifax (for whom ...
, and Intracoastal Waterway
The Intracoastal Waterway (ICW) is a inland waterway along the Atlantic and Gulf of Mexico coasts of the United States, running from Massachusetts southward along the Atlantic Seaboard and around the southern tip of Florida, then following th ...
as Charley passed over before re-emerging into the Atlantic Ocean. Further inland, Seminole County experienced some of the highest winds ever recorded from a hurricane in the area, with a gust of in Longwood at 0407 UTC on August 14 and in Altamonte Springs
Altamonte Springs is a suburban city in central Florida in Seminole County, Florida, United States, which had a population of 46,231 at the 2020 United States Census. The city is in the northern suburbs of the OrlandoŌĆōKissimmeeŌĆōSanford Metr ...
. Power was out in these areas for up to 12 days after the storm in some locations.
 Public schools in some counties in the path of the hurricane were scheduled to be closed for two weeks. In some areas this was necessary because the school buildings were damaged or destroyed: all 59 of Osceola County's schools were damaged, and one-third of Charlotte County's were destroyed by Charley's impact. DeSoto County schools saw $6 million in damage, while
Public schools in some counties in the path of the hurricane were scheduled to be closed for two weeks. In some areas this was necessary because the school buildings were damaged or destroyed: all 59 of Osceola County's schools were damaged, and one-third of Charlotte County's were destroyed by Charley's impact. DeSoto County schools saw $6 million in damage, while Orange County Public Schools
Orange County Public Schools (OCPS) is the public school district for Orange County, Florida. It is based in the Ronald Blocker Educational Leadership Center in downtown Orlando. As of the 2021-22 school year, OCPS has an enrollment of 206,246 st ...
saw $9 million in damage to their educational infrastructure.
Agricultural losses were heavy. In Florida, the second-largest producer of oranges
An orange is a fruit of various citrus species in the family Rutaceae (see list of plants known as orange); it primarily refers to ''Citrus'' ├Ś ''sinensis'', which is also called sweet orange, to distinguish it from the related ''Citrus ├Ś ...
in the world, damage to the citrus crop was estimated at $200 million, and caused a 50% increase in the price of grapefruit juice. Charley, along with the other storms that hit Florida during 2004, caused a total agricultural loss of $2.2 billion. Other crops, nurseries, buildings, and agricultural equipment also suffered.
Due to its track being directly over Interstate 4, Charley is sometimes referred to as the I-4 hurricane.
Rest of United States
South Carolina
)''Animis opibusque parati'' ( for, , Latin, Prepared in mind and resources, links=no)
, anthem = " Carolina";" South Carolina On My Mind"
, Former = Province of South Carolina
, seat = Columbia
, LargestCity = Charleston
, LargestMetro = ...
, Charley produced a storm tide that was unofficially measured to up to in Myrtle Beach
Myrtle Beach is a resort city on the east coast of the United States in Horry County, South Carolina. It is located in the center of a long and continuous stretch of beach known as "The Grand Strand" in the northeastern part of the state. Its ...
. Wind gusts were moderate, peaking at in North Myrtle Beach
North Myrtle Beach is a city in Horry County, South Carolina, United States. It was created in 1968 from four existing municipalities, and is located about northeast of Myrtle Beach. It serves as one of the primary tourist destinations along ...
, though there were several unofficial records of hurricane-force gusts. Charley produced moderate rainfall along its path, peaking at over 7 in (178 mm). Moderate winds knocked down numerous trees. Flash flooding occurred in Charleston County
Charleston County is located in the U.S. state of South Carolina along the Atlantic coast. As of the 2020 census, its population was 408,235, making it the third most populous county in South Carolina (behind Greenville and Richland counties). ...
, causing drainage problems. Damage in South Carolina totaled to $20 million.
In North Carolina
North Carolina () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the 28th largest and 9th-most populous of the United States. It is bordered by Virginia to the north, the Atlantic Ocean to the east, Georgia and So ...
, Charley produced an estimated storm surge of , along with waves of up to in height. This produced minor beach erosion along the coastline. Winds gusted from , causing minor wind damage. Rainfall amounts in the state were moderate, ranging from , but still caused flooding across seven North Carolina counties. The hurricane spawned five weak tornadoes across the state, including an F1 tornado in Nags Head Nag's Head or Nags Head may refer to:
;In London
* Nag's Head, London, a locality in Holloway
** Nag's Head Market, a street market
* Nag's Head, Covent Garden, a pub
;Elsewhere in the United Kingdom
* Nag's Head Island, Abingdon-on-Thames
* ...
that damaged twenty structures. Charley destroyed 40 houses and damaged 2,231, 231 severely, including 221 damaged beach homes in Sunset Beach. Damage was the greatest in Brunswick County, where wind gusts peaked at . Crop damage was also heavy in Brunswick County, with 50% of the tobacco crop lost and 30% of the corn and vegetable fields destroyed. Strong winds downed trees and power lines, leaving 65,000 without power. Damage in North Carolina totaled to $25 million.
Tropical Storm Charley produced wind gusts of up to at Chesapeake Light in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, causing scattered power outages. Rainfall was light, ranging from . Charley produced one tornado in Chesapeake Chesapeake often refers to:
*Chesapeake people, a Native American tribe also known as the Chesepian
* The Chesapeake, a.k.a. Chesapeake Bay
*Delmarva Peninsula, also known as the Chesapeake Peninsula
Chesapeake may also refer to:
Populated plac ...
and one in Virginia Beach
Virginia Beach is an independent city located on the southeastern coast of the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. The population was 459,470 at the 2020 census. Although mostly suburban in character, it is the most populous city ...
. In Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
, one man drowned in a rip current.
Aftermath
 President
President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
declared Florida a federal disaster area. He later reflected on the government response to Charley:
U.S. Health and Human Services Secretary Tommy Thompson
Tommy George Thompson (born November 19, 1941) is an American Republican politician who most recently served as interim president of the University of Wisconsin System from 2020 to 2022. A member of the Republican Party, he previously served ...
released $11 million in additional aid and other assistance to Florida, with $10 million to be earmarked to Head Start facilities that need repair or new supplies, another $1 million was provided to the DeSoto Memorial Hospital in Arcadia and Osceola Regional Medical Center in Kissimmee, and $200,000 would be spent to provide services to senior citizens. Across Florida, 114 food service operations and eight comfort stations were set up. FEMA opened four disaster recovery centers.
Retirement
Because of its effects in the United States, the name Charley was retired from the rotating lists of tropical cyclone names in the spring of 2005 by theWorld Meteorological Organization
The World Meteorological Organization (WMO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations responsible for promoting international cooperation on atmospheric science, climatology, hydrology and geophysics.
The WMO originated from the Internati ...
. As a result, the name will never again be used for an Atlantic hurricane. The name was replaced with Colin for the 2010 Atlantic hurricane season.
See also
* List of Florida hurricanes (2000ŌĆōpresent) *List of retired Atlantic hurricane names
This is a cumulative list of previously used tropical cyclone (tropical storm and hurricane) names which have been permanently removed from reuse in the North Atlantic region. As of April 2022, 94 storm names have been retired.
The naming of N ...
* List of Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes
Category 4 hurricanes are tropical cyclones that reach Category 4 intensity on the SaffirŌĆōSimpson scale. Category 4 hurricanes that later attained Category 5 strength are not included in this list. The Atlantic basin inclu ...
* Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, ...
(1960) ŌĆō Another Category 4 hurricane that crossed Florida from southwest to northeast
* Hurricane Irma
Hurricane Irma was an extremely powerful Cape Verde hurricane that caused widespread destruction across its path in September 2017. Irma was the first Category 5 hurricane to strike the Leeward Islands on record, followed by Maria two ...
(2017) ŌĆō A Category 5 hurricane that also made landfall as a major hurricane on the southwest side of Florida
* Hurricane Ian
Hurricane Ian was a large and destructive Category 4 Atlantic hurricane that was the deadliest hurricane to strike the state of Florida since the 1935 Labor Day hurricane. Ian caused widespread damage across western Cuba and the southeast Unit ...
(2022) ŌĆō Another Category 4 hurricane that hit at the same location, but was much larger in size
References
External links
*Hurricane Charley Advisory Archive
NHC August Monthly Tropical Weather Summary
Ćöincludes figures for damages and fatalities
Lack of a standard places Charley's deaths in question
Air Photos of Charley's Damage From FloridaDisaster.org
Wildlife and Habitat Damage Assessment from Hurricane Charley: Recommendations for Recovery of the J. N. "Ding" Darling National Wildlife Refuge Complex
{{DEFAULTSORT:Charley (2004) 2004 Atlantic hurricane season 2004 in Cuba 2004 in Florida 2004 in Jamaica 2004 in North Carolina 2004 in South Carolina 2004 in the Cayman Islands August 2004 events in North America Category 4 Atlantic hurricanes Charlotte County, Florida Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Charley 2004 Retired Atlantic hurricanes Tropical cyclones in 2004