Hot End on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or called ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or called ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a  The 3D printer head or 3D printer extruder is a part in material extrusion additive manufacturing responsible for raw material melting or softening and forming it into a continuous profile. A wide variety of filament materials are extruded, including thermoplastics such as ''acrylonitrile butadiene styrene'' (ABS), ''polylactic acid'' (PLA), ''polyethylene terephthalate glycol'' (PETG), ''polyethylene terephtathalate'' (PET), high-impact ''polystyrene'' (HIPS), ''thermoplastic polyurethane'' (TPU) and ''aliphatic polyamides'' (nylon).
The 3D printer head or 3D printer extruder is a part in material extrusion additive manufacturing responsible for raw material melting or softening and forming it into a continuous profile. A wide variety of filament materials are extruded, including thermoplastics such as ''acrylonitrile butadiene styrene'' (ABS), ''polylactic acid'' (PLA), ''polyethylene terephthalate glycol'' (PETG), ''polyethylene terephtathalate'' (PET), high-impact ''polystyrene'' (HIPS), ''thermoplastic polyurethane'' (TPU) and ''aliphatic polyamides'' (nylon).
 Fused deposition modeling was developed by S. Scott Crump, co-founder of
Fused deposition modeling was developed by S. Scott Crump, co-founder of

 Fused filament fabrication uses material
Fused filament fabrication uses material
 FFF begins with a software process which processes an STL file (STereoLithography file format), orienting the model for the build process and mathematically slicing the model according to the processing parameters selected. If required, support structures may be generated.
The nozzle can be moved in both horizontal and vertical directions, and is mounted to a mechanical stage, which can be moved in the xy plane.
FFF begins with a software process which processes an STL file (STereoLithography file format), orienting the model for the build process and mathematically slicing the model according to the processing parameters selected. If required, support structures may be generated.
The nozzle can be moved in both horizontal and vertical directions, and is mounted to a mechanical stage, which can be moved in the xy plane.
 As the nozzle is moved over the table in a prescribed geometry, it deposits a thin bead of extruded plastic, called a ‘‘road’’ which solidifies quickly upon contact with the substrate and/or roads deposited earlier. Solid layers are generated by following a rasterizing motion where the roads are deposited side by side within an enveloping domain boundary.
As the nozzle is moved over the table in a prescribed geometry, it deposits a thin bead of extruded plastic, called a ‘‘road’’ which solidifies quickly upon contact with the substrate and/or roads deposited earlier. Solid layers are generated by following a rasterizing motion where the roads are deposited side by side within an enveloping domain boundary.
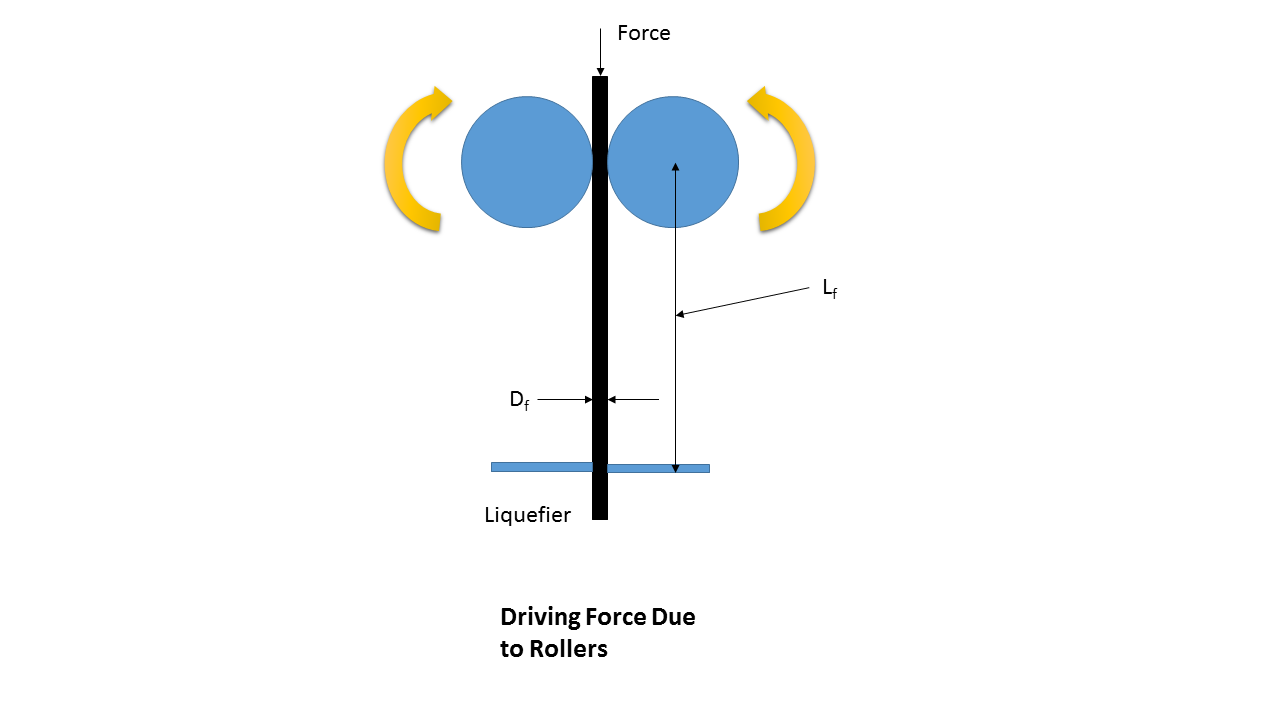 During extrusion the thermoplastic filament is introduced by mechanical pressure from rollers, into the liquefier, where it melts and is then extruded. Flow geometry of the extruder, heating method and the melt flow behavior of a non-Newtonian fluid are of main consideration in the part. The rollers are the only drive mechanism in the material delivery system, therefore filament is under tensile stress upstream to the roller and under compression at the downstream side acting as a plunger. Therefore, compressive stress is the driving force behind the extrusion process.
The force required to extrude the melt must be sufficient to overcome the pressure drop across the system, which strictly depends on the viscous properties of the melted material and the flow geometry of the liquefier and nozzle. The melted material is subjected to shear deformation during the flow.
During extrusion the thermoplastic filament is introduced by mechanical pressure from rollers, into the liquefier, where it melts and is then extruded. Flow geometry of the extruder, heating method and the melt flow behavior of a non-Newtonian fluid are of main consideration in the part. The rollers are the only drive mechanism in the material delivery system, therefore filament is under tensile stress upstream to the roller and under compression at the downstream side acting as a plunger. Therefore, compressive stress is the driving force behind the extrusion process.
The force required to extrude the melt must be sufficient to overcome the pressure drop across the system, which strictly depends on the viscous properties of the melted material and the flow geometry of the liquefier and nozzle. The melted material is subjected to shear deformation during the flow.

 There are multiple projects in the open-sourced community aimed at processing post-consumer plastic waste into filament. These involve machines used to shred and extrude the plastic material into filament such as recyclebots.
Several projects and companies are making efforts to develop affordable 3D printers for home desktop use. Much of this work has been driven by and targeted at
There are multiple projects in the open-sourced community aimed at processing post-consumer plastic waste into filament. These involve machines used to shred and extrude the plastic material into filament such as recyclebots.
Several projects and companies are making efforts to develop affordable 3D printers for home desktop use. Much of this work has been driven by and targeted at

 A different approach is taken with 'Rostock' or 'Kossel' pattern printers, based on a
A different approach is taken with 'Rostock' or 'Kossel' pattern printers, based on a
 Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or called ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a
Fused filament fabrication (FFF), also known as fused deposition modeling (with the trademarked acronym FDM), or called ''filament freeform fabrication'', is a 3D printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer co ...
process that uses a continuous filament of a thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
material. Filament is fed from a large spool through a moving, heated printer extruder head, and is deposited on the growing work. The print head is moved under computer control to define the printed shape. Usually the head moves in two dimensions to deposit one horizontal plane, or layer, at a time; the work or the print head is then moved vertically by a small amount to begin a new layer. The speed of the extruder head may also be controlled to stop and start deposition and form an interrupted plane without stringing or dribbling between sections. "Fused filament fabrication" was coined by the members of the RepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
project to give an acronym (FFF) that would be legally unconstrained in its use.
Fused filament printing is now the most popular process (by number of machines) for hobbyist-grade 3D printing. Other techniques such as photopolymerisation
In polymer chemistry, polymerization (American English), or polymerisation (British English), is a process of reacting monomer molecules together in a chemical reaction to form polymer chains or three-dimensional networks. There are many f ...
and powder sintering may offer better results, but they are much more costly.
History
 Fused deposition modeling was developed by S. Scott Crump, co-founder of
Fused deposition modeling was developed by S. Scott Crump, co-founder of Stratasys
Stratasys, Ltd. is an American-Israeli manufacturer of 3D printers, software, and materials for polymer additive manufacturing as well as 3D-printed parts on-demand. The company is incorporated in Israel. Engineers use Stratasys systems to model c ...
, in 1988. With the 2009 expiration of the patent on this technology, people could use this type of printing without paying Stratasys for the right to do so, opening up commercial, DIY
"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of professionals or certified experts. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals use raw and sem ...
, and open-source (RepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
) 3D printer applications. This has led to a two-orders-of-magnitude price drop since this technology's creation. Stratasys still owns the trademark on the term "FDM".
Process
3D printing, also referred to asadditive manufacturing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer co ...
(AM), involves manufacturing a part by depositing material layer by layer. There is a wide array of different AM technologies that can do this, including material extrusion, binder jetting, material jetting and directed energy deposition. These processes have varied types of extruders and extrude different materials to achieve the final product.
Material extrusion

 Fused filament fabrication uses material
Fused filament fabrication uses material extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex c ...
to print items, where a feedstock material is pushed through an extruder. In most fused filament fabrication 3D printing machines, the feedstock material comes in the form of a filament wound onto a spool.
The 3D printer liquefier is the component predominantly used in this type of printing. Extruders for these printers have a cold end and a hot end. The cold end pulls material from the spool, using gear- or roller-based torque to the material and controlling the feed rate by means of a stepper motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any posi ...
. The cold end pushes feedstock into the hot end. The hot end consists of a heating chamber and a nozzle. The heating chamber hosts the liquefier, which melts the feedstock to transform it into a liquid. It allows the molten material to exit from the small nozzle
A nozzle is a device designed to control the direction or characteristics of a fluid flow (specially to increase velocity) as it exits (or enters) an enclosed chamber or pipe.
A nozzle is often a pipe or tube of varying cross sectional area, ...
to form a thin, tacky bead of plastic that will adhere to the material it is laid on. The nozzle will usually have a diameter of between 0.3 mm and 1.0 mm. Different types of nozzles and heating methods are used depending upon the material to be printed.
Different types of nozzles have different ways of replacing them. The most common used nozzles are the V6 nozzles made popular by E3D and MK8 nozzles. Changing the nozzle must be done while hot, to avoid plastic leaks.
Variants of the process
* ''Hot extrusion of rods'' - In these types of 3d printing machines, the feedstock is in form of a rod instead of a filament. Since the rod is thicker than the filament, it can be pushed towards the hot end by means of a piston or rollers, applying a greater force and/or velocity compared to conventional FFF. *''Cold extrusion of slurries'' - In these types of 3D printing machines, the feedstock comes in form of aslurry
A slurry is a mixture of denser solids suspended in liquid, usually water. The most common use of slurry is as a means of transporting solids or separating minerals, the liquid being a carrier that is pumped on a device such as a centrifugal p ...
, a paste or a clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay pa ...
—all of which are viscous suspension of solid powder particles in a liquid medium, which is dried after deposition. In this case, the material is generally pushed towards the nozzle by the action of a piston, and the nozzle is not heated. Paste-like materials such as ceramics and chocolate can be extruded using the fused filament process and a specialized paste extruder.
*''Hot extrusion of pellets'' - In these types of 3d printing machines the feedstock comes in form of pellets, i.e. small granules of thermoplastic material or mixtures of thermoplastic binder with powder fillers. The material is pushed towards the nozzle by the action of a piston or a rotating screw, which are contained by an extrusion barrel. In this case the whole extrusion barrel is heated, along with the nozzle.
Printing
 FFF begins with a software process which processes an STL file (STereoLithography file format), orienting the model for the build process and mathematically slicing the model according to the processing parameters selected. If required, support structures may be generated.
The nozzle can be moved in both horizontal and vertical directions, and is mounted to a mechanical stage, which can be moved in the xy plane.
FFF begins with a software process which processes an STL file (STereoLithography file format), orienting the model for the build process and mathematically slicing the model according to the processing parameters selected. If required, support structures may be generated.
The nozzle can be moved in both horizontal and vertical directions, and is mounted to a mechanical stage, which can be moved in the xy plane.
Stepper motors
A stepper is a device used in the manufacture of integrated circuits (ICs) that is similar in operation to a slide projector or a photographic enlarger. ''Stepper'' is short for step-and-repeat camera. Steppers are an essential part of the comp ...
or servo motors
A servomotor (or servo motor) is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also ...
are typically employed to move the extrusion head. The mechanism used is often an X-Y-Z rectilinear design, although other mechanical designs such as deltabot
A delta robot is a type of parallel robot that consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. In contrast, ...
have been employed.
Once a layer is completed, the platform is lowered in the z direction in order to start the next layer. This process continues until the fabrication of the object is completed.
For successful bonding of the roads in the process, thermal control of the deposited material is necessary. The system can be kept inside a chamber, maintained at a temperature below the melting point of the material being deposited.
Although as a printing technology FFF is very flexible, and it is capable of dealing with small overhangs by the support from lower layers, FFF generally has some restrictions on the slope of the overhang, and cannot produce unsupported stalactite
A stalactite (, ; from the Greek 'stalaktos' ('dripping') via
''stalassein'' ('to drip') is a mineral formation that hangs from the ceiling of caves, hot springs, or man-made structures such as bridges and mines. Any material that is soluble ...
s.
Myriad materials are available, such as Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ( chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
...
(ABS), Polylactic acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula or , formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ri ...
(PLA), Polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily work ...
(PC), Polyamide
A polyamide is a polymer with repeating units linked by amide bonds.
Polyamides occur both naturally and artificially. Examples of naturally occurring polyamides are proteins, such as wool and silk. Artificially made polyamides can be made th ...
(PA), Polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the Aromatic hydrocarbon, aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin pe ...
(PS), lignin
Lignin is a class of complex organic polymers that form key structural materials in the support tissues of most plants. Lignins are particularly important in the formation of cell walls, especially in wood and bark, because they lend rigidity a ...
, rubber
Rubber, also called India rubber, latex, Amazonian rubber, ''caucho'', or ''caoutchouc'', as initially produced, consists of polymers of the organic compound isoprene, with minor impurities of other organic compounds. Thailand, Malaysia, and ...
, among many others, with different trade-offs between strength and temperature properties. In addition, even the color of a given thermoplastic
A thermoplastic, or thermosoft plastic, is any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or moldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling.
Most thermoplastics have a high molecular weight. The polymer chains associate ...
material may affect the strength of the printed object. Recently a German company demonstrated for the first time the technical possibility of processing granular PEEK
Polyether ether ketone (PEEK) is a colourless organic thermoplastic polymer in the polyaryletherketone (PAEK) family, used in engineering applications. The polymer was first developed in November 1978, later being introduced to the market by ...
into filament form and 3D printing parts from the filament material using FFF technology.
During FFF, the hot molten polymer is exposed to air. Operating the FFF process within an inert gas
An inert gas is a gas that does not readily undergo chemical reactions with other chemical substances and therefore does not readily form chemical compounds. The noble gases often do not react with many substances and were historically referred to ...
atmosphere such as nitrogen
Nitrogen is the chemical element with the symbol N and atomic number 7. Nitrogen is a nonmetal and the lightest member of group 15 of the periodic table, often called the pnictogens. It is a common element in the universe, estimated at se ...
or argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice a ...
can significantly increase the layer adhesion and leads to improved mechanical properties of the 3D printed objects. An inert gas is routinely used to prevent oxidation during selective laser sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined ...
.
Physics of the process
 During extrusion the thermoplastic filament is introduced by mechanical pressure from rollers, into the liquefier, where it melts and is then extruded. Flow geometry of the extruder, heating method and the melt flow behavior of a non-Newtonian fluid are of main consideration in the part. The rollers are the only drive mechanism in the material delivery system, therefore filament is under tensile stress upstream to the roller and under compression at the downstream side acting as a plunger. Therefore, compressive stress is the driving force behind the extrusion process.
The force required to extrude the melt must be sufficient to overcome the pressure drop across the system, which strictly depends on the viscous properties of the melted material and the flow geometry of the liquefier and nozzle. The melted material is subjected to shear deformation during the flow.
During extrusion the thermoplastic filament is introduced by mechanical pressure from rollers, into the liquefier, where it melts and is then extruded. Flow geometry of the extruder, heating method and the melt flow behavior of a non-Newtonian fluid are of main consideration in the part. The rollers are the only drive mechanism in the material delivery system, therefore filament is under tensile stress upstream to the roller and under compression at the downstream side acting as a plunger. Therefore, compressive stress is the driving force behind the extrusion process.
The force required to extrude the melt must be sufficient to overcome the pressure drop across the system, which strictly depends on the viscous properties of the melted material and the flow geometry of the liquefier and nozzle. The melted material is subjected to shear deformation during the flow. Shear thinning
In rheology, shear thinning is the non-Newtonian behavior of fluids whose viscosity decreases under shear strain. It is sometimes considered synonymous for pseudo-plastic behaviour, and is usually defined as excluding time-dependent effects, s ...
behavior is observed in most of the materials used in this type of 3-D printing. This is modeled using power law for generalized Newtonian fluids.
The temperature is regulated by heat input from electrical coil heaters. The system continuously adjusts the power supplied to the coils according to the temperature difference between the desired value and the value detected by the thermocouple, forming a negative feedback
Negative feedback (or balancing feedback) occurs when some function of the output of a system, process, or mechanism is fed back in a manner that tends to reduce the fluctuations in the output, whether caused by changes in the input or by othe ...
loop. This is similar to ambient heating of a room.
Applications
Commercial applications
FFF and the other technologies of additive manufacturing by material extrusion (EAM) techniques are commonly used for prototyping and rapid manufacturing. Rapid prototyping facilitates iterative testing, and for very short runs, rapid manufacturing can be a relatively inexpensive alternative. EAM is also used in prototyping scaffolds for medical tissue engineering applications. Moreover, EAM with multi extrusion have become very popular to fabricate biomimetic composites. FFF is also applied in manufacturing within other sectors, including aerospace, automotive, construction, electronics, energy, pharmaceuticals, sports, textiles, and toys.Free applications

 There are multiple projects in the open-sourced community aimed at processing post-consumer plastic waste into filament. These involve machines used to shred and extrude the plastic material into filament such as recyclebots.
Several projects and companies are making efforts to develop affordable 3D printers for home desktop use. Much of this work has been driven by and targeted at
There are multiple projects in the open-sourced community aimed at processing post-consumer plastic waste into filament. These involve machines used to shred and extrude the plastic material into filament such as recyclebots.
Several projects and companies are making efforts to develop affordable 3D printers for home desktop use. Much of this work has been driven by and targeted at DIY
"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of professionals or certified experts. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals use raw and sem ...
/enthusiast/ early adopter communities, with additional ties to the academic and hacker
A hacker is a person skilled in information technology who uses their technical knowledge to achieve a goal or overcome an obstacle, within a computerized system by non-standard means. Though the term ''hacker'' has become associated in popu ...
communities.
RepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
is one of the longest running projects in the desktop category. The RepRap project aims to produce a free and open source hardware (FOSH) 3D printer, whose full specifications are released under the GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general ...
, and which is capable of replicating itself by printing many of its own (plastic) parts to create more machines. RepRaps have already been shown to be able to print circuit board
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struc ...
s and metal parts. Fab@Home
Fab@Home is a multi-material 3D printer, launched in 2006. It was one of the first two open-source DIY 3D printers in the world, at a time when all other additive manufacturing machines were still proprietary. The Fab@Home and the RepRap are credi ...
is the other opensource hardware project for DIY
"Do it yourself" ("DIY") is the method of building, modifying, or repairing things by oneself without the direct aid of professionals or certified experts. Academic research has described DIY as behaviors where "individuals use raw and sem ...
3D printers.
Because of the FOSH aims of RepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
, many related projects have used their design for inspiration, creating an ecosystem of related or derivative 3D printers, most of which are also open source designs. The availability of these open source designs means that variants of 3D printers are easy to invent. The quality and complexity of printer designs, however, as well as the quality of kit or finished products, varies greatly from project to project. This rapid development of open source 3D printers is gaining interest in many spheres as it enables hyper-customization and the use of public domain
The public domain (PD) consists of all the creative work to which no exclusive intellectual property rights apply. Those rights may have expired, been forfeited, expressly waived, or may be inapplicable. Because those rights have expired ...
designs to fabricate open source appropriate technology
Open-source appropriate technology (OSAT) is appropriate technology developed through the principles of the open-design movement. Appropriate technology is technology designed with special consideration to the environmental, ethical, cultural, soc ...
. This technology can also assist initiatives in sustainable development
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The ...
since technologies are easily and economically made from resources available to local communities.
Development
Customer-driven product customization and demand for cost and time savings have increased interest in agility of manufacturing process. This has led to improvements in rapid prototyping technologies. The development of extruders is going rapidly because of the open source 3-D printer movement caused by products like RepRap. E3D and BondTech are the most known extruder manufacturers currently on the market. Consistent improvements are seen in the form of increased heating temperature of liquefiers, better control and precision of prints, and improved support for a wide variety of materials. Besides the improved hardware, the ability to calibrate the extruder according to the hardware setup has come a long way.Cost of 3D printer
The cost of 3D printers has decreased dramatically since about 2010, with machines that used to cost now costing less than . For instance, as of 2017, several companies and individuals are selling parts to build variousRepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
designs, with prices starting at about / .
The open source Fab@Home
Fab@Home is a multi-material 3D printer, launched in 2006. It was one of the first two open-source DIY 3D printers in the world, at a time when all other additive manufacturing machines were still proprietary. The Fab@Home and the RepRap are credi ...
project has developed printers for general use with anything that can be extruded through a nozzle, from chocolate to silicone sealant and chemical reactants. Printers following the project's designs have been available from suppliers in kits or in pre-assembled form since 2012 at prices in the range.
The LulzBot 3D printers manufactured by Aleph Objects are another example of an open-source application of fused deposition modeling technology. The flagship model in the LulzBot line, the TAZ printer takes inspiration for its design from the RepRap Mendel90 and Prusa i3 models. The LulzBot 3D printer is currently the only printer on the market to have received the "Respects Your Freedom" certification from the Free Software Foundation
The Free Software Foundation (FSF) is a 501(c)(3) non-profit organization founded by Richard Stallman on October 4, 1985, to support the free software movement, with the organization's preference for software being distributed under copyleft ( ...
.
As of September 2018 RepRap style printers are readily available in kit form through online retailers. These kits come complete with all parts needed to make a functioning printer, often including electronic files for test printing as well as a small quantity of PLA filament.
FIlaments used for printing with FDM printers are also substantially more cost-effective than their SLA resin counterparts. If we use 3DBenchy as a benchmark for comparing both technologies, it would cost roughly $0.20 to print such a model with an FDM machine, whereas the same object would cost almost $1.00 if created with resin.
Materials
Plastic is the most common material for 3d printing via FFF and other EAM variants. Various polymers may be used, includingacrylonitrile butadiene styrene
Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) ( chemical formula (C8H8)''x''·(C4H6)''y''·(C3H3N)''z'' is a common thermoplastic polymer. Its glass transition temperature is approximately . ABS is amorphous and therefore has no true melting point.
...
(ABS), polycarbonate
Polycarbonates (PC) are a group of thermoplastic polymers containing carbonate groups in their chemical structures. Polycarbonates used in engineering are strong, tough materials, and some grades are optically transparent. They are easily work ...
(PC), polylactic acid
Polylactic acid, also known as poly(lactic acid) or polylactide (PLA), is a thermoplastic polyester with backbone formula or , formally obtained by condensation of lactic acid with loss of water (hence its name). It can also be prepared by ri ...
(PLA), high-density polyethylene
High-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polyethylene high-density (PEHD) is a thermoplastic polymer produced from the monomer ethylene. It is sometimes called "alkathene" or "polythene" when used for HDPE pipes. With a high strength-to-density rat ...
(HDPE), PC/ABS, polyethylene terephthalate
Polyethylene terephthalate (or poly(ethylene terephthalate), PET, PETE, or the obsolete PETP or PET-P), is the most common thermoplastic polymer resin of the polyester family and is used in fibres for clothing, containers for liquids and food ...
(PETG), polyphenylsulfone Polyphenylsulfone (PPSF or PPSU) is a high performance polymer made of aromatic rings linked by sulfone (SO2) groups.
Production
Commercially important polysulfones are prepared by condensation of 4,4'-bis(chlorophenyl)sulfone with various bisph ...
(PPSU) and high impact polystyrene
Polystyrene (PS) is a synthetic polymer made from monomers of the aromatic hydrocarbon styrene. Polystyrene can be solid or foamed. General-purpose polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. It is an inexpensive resin per unit weight. It is ...
(HIPS). In general, the polymer is in the form of a filament fabricated from virgin resins. Additionally, fluoropolymers such as PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene that has numerous applications. It is one of the best-known and widely applied PFAS. The commonly known brand name of PTFE-based composition is Teflon by Chem ...
tubing are used in the process due to the material's ability to withstand high temperatures. This ability is especially useful in transferring filaments.
The many different variants of EAM, i.e. of material Extrusion based Additive Manufacturing allow dealing with many additional material types, summarised in the table below. Several material classes can be extruded and 3d printed:
* Thermoplastic polymers, it is the most typical application of FDM;
* Composite materials with polymeric matrix and short or long hard fibers;
* Ceramic slurries and clays, often used in combination with the robocasting Robocasting (also known as robotic material extrusion) is an additive manufacturing technique analogous to Direct Ink Writing and other extrusion-based 3D-printing techniques in which a filament of a paste-like material is extruded from a small nozz ...
technique;
* Green mixtures of ceramic or metal powders and polymeric binders, used in EAM of metals and ceramics;
* Food pastes;
* Biological pastes, used in bioprinting.

Print head kinematics
The majority of fused filament printers follow the same basic design. A flat bed is used as the starting point for the print workpiece. A gantry above this carries the moving print head. The gantry design is optimized for movement mostly in the horizontal X & Y directions, with a slow climb in the Z direction as the piece is printed.Stepper motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any posi ...
s drive the movement through either leadscrew
A leadscrew (or lead screw), also known as a power screw or translation screw,Bhandari, p. 202. is a screw used as a linkage in a machine, to translate turning motion into linear motion. Because of the large area of sliding contact between ...
s or toothed belt drives. It is common, owing to the differences in movement speed, to use toothed belts for the X,Y drives and a leadscrew for Z. Some machines also have X axis movement on the gantry, but move the bed (and print job) for Y. As, unlike laser cutter
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word "laser" is an acronym for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". The firs ...
s, head movement speeds are low, stepper motors are universally used and there is no need to use servomotor
A servomotor (or servo motor) is a rotary actuator or linear actuator that allows for precise control of angular or linear position, velocity and acceleration. It consists of a suitable motor coupled to a sensor for position feedback. It also ...
s instead.
Many printers, originally those influenced by the RepRap
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
project, make extensive use of 3D printed components in their own construction. These are typically printed connector blocks with a variety of angled holes, joined by cheap steel threaded rod. This makes a construction that is cheap and easy to assemble, easily allows non-perpendicular framing joints, but does require access to a 3D printer. The notion of 'bootstrapping
In general, bootstrapping usually refers to a self-starting process that is supposed to continue or grow without external input.
Etymology
Tall boots may have a tab, loop or handle at the top known as a bootstrap, allowing one to use fingers ...
' 3D printers like this has been something of a dogmatic theme within the RepRap designs. The lack of stiffness in the rod also requires either triangulation
In trigonometry and geometry, triangulation is the process of determining the location of a point by forming triangles to the point from known points.
Applications
In surveying
Specifically in surveying, triangulation involves only angle me ...
, or gives the risk of a gantry structure that flexes and vibrates in service, reducing print quality.
Many machines now use box-like semi-enclosed frames of either laser-cut plywood, plastic, pressed steel sheet and more recently aluminum extrusions. These are cheap, rigid and can also be used as the basis for an enclosed print volume, allowing temperature control within it to control warping of the print job.
A handful of machines use polar coordinates instead, usually machines optimized to print objects with circular symmetry. These have a radial gantry movement and a rotating bed. Although there are some potential mechanical advantages to this design for printing hollow cylinders, their different geometry and the resulting non-mainstream approach to print planning still keeps them from being popular as yet. Although it is an easy task for a robot's motion planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is use ...
to convert from Cartesian to polar coordinates, gaining any advantage from this design also requires the print slicing algorithms to be aware of the rotational symmetry from the outset.
Extruder mount to rest of machine
The ways extruders are mounted on the rest of the machine have evolved over time into informal mounting standards. Such factor standards allows new extruder designs to be tested on existing printer frames, and new printer frame designs to use existing extruders. These informal standards include: *Vertical X Axis Standard
Vertical is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
* Vertical direction, the direction aligned with the direction of the force of gravity, up or down
* Vertical (angles), a pair of angles opposite each other, formed by two intersecting ...
* Quick-fit extruder mount
* OpenX mount
Delta robot printers
 A different approach is taken with 'Rostock' or 'Kossel' pattern printers, based on a
A different approach is taken with 'Rostock' or 'Kossel' pattern printers, based on a delta robot
A delta robot is a type of parallel robot that consists of three arms connected to universal joints at the base. The key design feature is the use of parallelograms in the arms, which maintains the orientation of the end effector. In contrast ...
mechanism. These have a large open print volume with a three-armed delta robot mounted at the top. This design of robot is noted for its low inertia and ability for fast movement over a large volume. Stability and freedom from vibration when moving a heavy print head on the end of spindly arms is a technical challenge though. This design has mostly been favored as a means of gaining a large print volume without a large and heavy gantry.
As the print head moves the distance of its filament from storage coil to head also changes, the tension created on the filament is another technical challenge to overcome to avoid affecting the print quality.
See also
*3D printing
3D printing or additive manufacturing is the construction of a three-dimensional object from a CAD model or a digital 3D model. It can be done in a variety of processes in which material is deposited, joined or solidified under computer co ...
* 3D printer extruder
A 3D printer extruder is a filament feeding mechanism used in many fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers. There are several types of 3D printer extruders. A Bowden extruder is a type of extruder that pushes filament though a long and flex ...
* Ball bearing
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
The purpose of a ball bearing is to reduce rotational friction and support radial and axial loads. It achieves this ...
* Bowden extruder
A 3D printer extruder is a 3D printing filament, filament feeding mechanism used in many fused filament fabrication (FFF) 3D printers. There are several types of 3D printer extruders. A Bowden cable, Bowden extruder is a type of extruder that pus ...
* Direct metal laser sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined b ...
* Fab lab
A fab lab (''fabrication laboratory'') is a small-scale workshop offering (personal) digital fabrication.
A fab lab is typically equipped with an array of flexible computer-controlled tools that cover several different length scales and vari ...
* Fab@Home
Fab@Home is a multi-material 3D printer, launched in 2006. It was one of the first two open-source DIY 3D printers in the world, at a time when all other additive manufacturing machines were still proprietary. The Fab@Home and the RepRap are credi ...
* G-code
G-code (also RS-274) is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) programming language. It is used mainly in computer-aided manufacturing to control automated machine tools, and has many variants.
G-code instructions are provided to ...
* Hyrel 3D
Hyrel 3D is a company which manufactures 3D Printers for home, office and industrial settings, and is based in Atlanta, GA. Hyrel 3D makes modular manufacturing machines that are capable of additive and subtractive processes, including fused deposi ...
* MakerBot Industries
MakerBot Industries, LLC is an American desktop 3D printer manufacturer company headquartered in New York City. It was founded in January 2009 by Bre Pettis, Adam Mayer, and Zach "Hoeken" Smith to build on the early progress of the RepRap Proje ...
* Marlin (firmware)
* Methacrylate Methacrylates are derivatives of methacrylic acid.
* Methyl methacrylate
* Ethyl methacrylate
* Butyl methacrylate
* Hydroxyethyl methacrylate
Hydroxyethylmethacrylate (also known as glycol methyacrylate) is the organic compound with the chemic ...
* Plastics extrusion
Plastics extrusion is a high-volume manufacturing process in which raw plastic is melted and formed into a continuous profile. Extrusion produces items such as pipe/tubing, weatherstripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic fi ...
* Printrbot
* Prusa i3
* RAMPS
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
* Rapid prototyping
Rapid prototyping is a group of techniques used to quickly fabricate a scale model of a physical part or assembly using three-dimensional computer aided design (CAD) data.
Construction of the part or assembly is usually done using 3D printing ...
* RepRap Project
The RepRap project started in England in 2005 as a University of Bath initiative to develop a low-cost 3D printer that can print most of its own components, but it is now made up of hundreds of collaborators worldwide. RepRap is short for rep''li ...
* Robo 3D
* Selective laser sintering
Selective laser sintering (SLS) is an additive manufacturing (AM) technique that uses a laser as the power and heat source to sinter powdered material (typically nylon or polyamide), aiming the laser automatically at points in space defined ...
* Sindoh
* Spindle
* Stepper motor
A stepper motor, also known as step motor or stepping motor, is a brushless DC electric motor that divides a full rotation into a number of equal steps. The motor's position can be commanded to move and hold at one of these steps without any posi ...
* Stereolithography
Stereolithography (SLA or SL; also known as vat photopolymerisation, optical fabrication, photo-solidification, or resin printing) is a form of 3D printing technology used for creating models, prototypes, patterns, and production parts in a lay ...
* Thermistor
A thermistor is a type of resistor whose resistance is strongly dependent on temperature, more so than in standard resistors. The word thermistor is a portmanteau of ''thermal'' and ''resistor''.
Thermistors are divided based on their conduction ...
* Thermocouple
A thermocouple, also known as a "thermoelectrical thermometer", is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar electrical conductors forming an electrical junction. A thermocouple produces a temperature-dependent voltage as a result of th ...
* Ultimaker
* Von Neumann universal constructor
John von Neumann's universal constructor is a self-replicating machine in a cellular automaton (CA) environment. It was designed in the 1940s, without the use of a computer. The fundamental details of the machine were published in von Neumann's ...
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * {{cite web, title=FDM Technology Made Simple , url=https://www.chizel.io/blogs/fdm-technology-3d-printing/ , publisher=chizel.io , access-date=10 July 2019, date=2018-07-16 3D printing 3D printing processes