Homunculi on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A homunculus ( , , ; "little person") is a representation of a small human being, originally depicted as small statues made out of clay. Popularized in sixteenth-century
 The homunculus first appears by name in
The homunculus first appears by name in
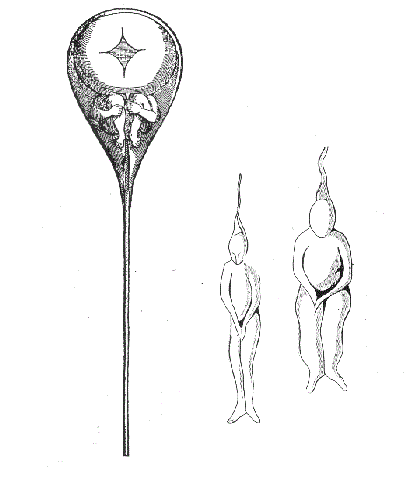 Preformationism is the formerly popular theory that animals developed from miniature versions of themselves. Sperm were believed to contain complete preformed individuals called "
Preformationism is the formerly popular theory that animals developed from miniature versions of themselves. Sperm were believed to contain complete preformed individuals called "
 Homunculi can be found in centuries worth of literature. These fictions are primarily centred around imaginative speculations on the quest for artificial life associated with
Homunculi can be found in centuries worth of literature. These fictions are primarily centred around imaginative speculations on the quest for artificial life associated with
Homunculus
article from The Mystica. {{Alchemy Alchemical concepts Paracelsus Literary motifs Narrative techniques Monsters
alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
and nineteenth-century fiction, it has historically referred to the creation of a miniature, fully formed human. The concept has roots in preformationism
In the history of biology, preformationism (or preformism) is a formerly popular theory that organisms develop from miniature versions of themselves. Instead of assembly from parts, preformationists believed that the form of living things exist, ...
as well as earlier folklore and alchemic traditions.
The term lends its name to the cortical homunculus
A cortical homunculus () is a distorted representation of the human body, based on a neurological "map" of the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor functions, or sensory functions, for different parts of the bo ...
, an image of a person with the size of the body parts distorted to represent how much area of the cerebral cortex of the brain is devoted to it.
History
Alchemy
 The homunculus first appears by name in
The homunculus first appears by name in alchemical
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
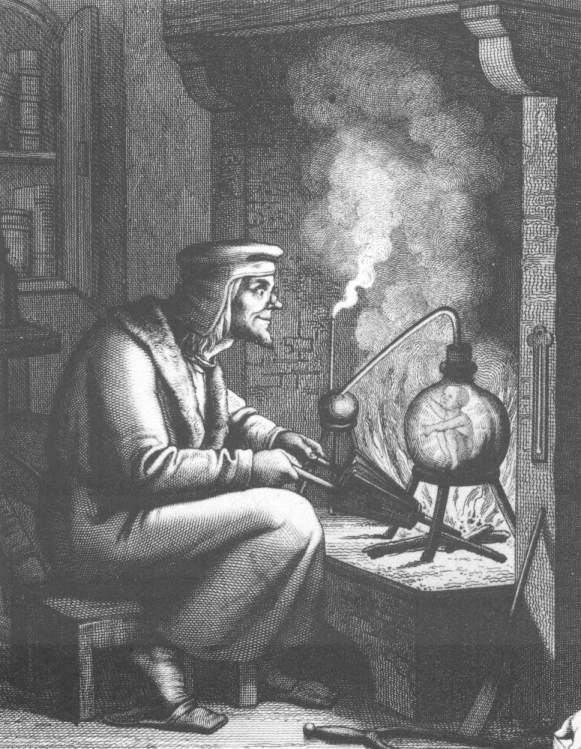
writings attributed to Paracelsus
Paracelsus (; ; 1493 – 24 September 1541), born Theophrastus von Hohenheim (full name Philippus Aureolus Theophrastus Bombastus von Hohenheim), was a Swiss physician, alchemist, lay theologian, and philosopher of the German Renaissance.
He w ...
(1493–1541). ''De natura rerum'' (1537) outlines his method for creating homunculi:
Comparisons have been made with several similar concepts in the writings of earlier alchemists. Although the actual word "homunculus" was never used, Carl Jung
Carl Gustav Jung ( ; ; 26 July 1875 – 6 June 1961) was a Swiss psychiatrist and psychoanalyst who founded analytical psychology. Jung's work has been influential in the fields of psychiatry, anthropology, archaeology, literature, philo ...
believed that the concept first appeared in the ''Visions of Zosimos'', written in the third century AD. In the visions, Zosimos encounters a priest who changes into "the opposite of himself, into a mutilated ''anthroparion''". The Greek word "anthroparion" is similar to "homunculus" – a diminutive form of "person". Zosimos subsequently encounters other anthroparia in his dream but there is no mention of the creation of artificial life. In his commentary, Jung equates the homunculus with the Philosopher's Stone
The philosopher's stone or more properly philosophers' stone (Arabic: حجر الفلاسفة, , la, lapis philosophorum), is a mythic alchemical substance capable of turning base metals such as mercury into gold (, from the Greek , "gold", ...
, and the "inner person" in parallel with Christ
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other Names and titles of Jesus in the New Testament, names and titles), was ...
.
In Islamic alchemy
Alchemy in the medieval Islamic world refers to both traditional alchemy and early practical chemistry (the early chemical investigation of nature in general) by Muslim scholars in the medieval Islamic world. The word ''alchemy'' was derive ...
, ''takwin
Takwin ( ar, تكوين) was a goal of certain Muslim alchemists, notably Jabir ibn Hayyan. In the alchemical context, takwin refers to the creation of synthetic life in the laboratory, up to and including human life. Whether Jabir meant this goa ...
'' ( ar, تكوين) was a goal of certain Muslim alchemists, and is frequently found in writings of the Jabirian corpus. In the alchemical context, ''takwin'' refers to the artificial creation of life, spanning the full range of the chain of being
The great chain of being is a hierarchical structure of all matter and life, thought by medieval Christianity to have been decreed by God. The chain begins with God and descends through angels, humans, animals and plants to minerals.
The great c ...
, from minerals to prophets, imitating the function of the demiurge
In the Platonic, Neopythagorean, Middle Platonic, and Neoplatonic schools of philosophy, the demiurge () is an artisan-like figure responsible for fashioning and maintaining the physical universe. The Gnostics adopted the term ''demiurge''. Al ...
. One set of instructions for creating animal life found within the Jabirian ''Kitab al-Tajmi'' involves finding a vessel shaped like the animal and combining the animal's bodily fluids within it, then placing the vessel at the center of a model of a celestial sphere
In astronomy and navigation, the celestial sphere is an abstract sphere that has an arbitrarily large radius and is concentric to Earth. All objects in the sky can be conceived as being projected upon the inner surface of the celestial sphere, ...
as heat is applied to it. Some of the alchemists believed that these methods originated somewhere in India or Southeast Asia.
The homunculus continued to appear in alchemical writings after Paracelsus' time. The ''Chymical Wedding of Christian Rosenkreutz
The ''Chymical Wedding of Christian Rosenkreutz'' (german: Chymische Hochzeit Christiani Rosencreutz anno 1459) is a German book edited in 1616 in Strasbourg. Its anonymous authorship is attributed to Johann Valentin Andreae. The ''Chymical Weddi ...
'' (1616) for example, concludes with the creation of a male and female form identified as ''Homunculi duo''. The allegorical text suggests to the reader that the ultimate goal of alchemy is not chrysopoeia, but it is instead the artificial generation of humans. Here, the creation of homunculi symbolically represents spiritual regeneration and Christian soteriology
In Christianity, salvation (also called deliverance or redemption) is the "saving fhuman beings from sin and its consequences, which include death and separation from God" by Christ's death and resurrection, and the justification following t ...
.
In 1775, Count Johann Ferdinand von Kufstein, together with Abbé Geloni, an Italian cleric, is reputed to have created ten homunculi with the ability to foresee the future, which von Kufstein kept in glass containers at his Masonic lodge
A Masonic lodge, often termed a private lodge or constituent lodge, is the basic organisational unit of Freemasonry. It is also commonly used as a term for a building in which such a unit meets. Every new lodge must be warranted or chartered ...
in Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
. Dr. Emil Besetzny's Masonic handbook, ''Die Sphinx'', devoted an entire chapter to the ''wahrsagenden Geister'' (scrying ghosts). These are reputed to have been seen by several people, including local dignitaries.
Folklore
References to the homunculus do not appear prior to sixteenth-century alchemical writings but alchemists may have been influenced by earlier folk traditions. The mandragora, known in German as ''Alreona'', ''Alraun'' or ''Alraune'' is one example;Jean-Baptiste Pitois
Jean-Baptiste Pitois, also known as Jean-Baptiste or Paul Christian (1811–1877), was a French author, known for ''The History and Practice of Magic'', first published in France in 1870.
Early life
Jean-Baptiste Pitois was born May 15, 1811, in ...
's ''The History and Practice of Magic'' makes a direct comparison to the mandragora in one excerpt:
The homunculus has also been compared to the golem
A golem ( ; he, , gōlem) is an animated, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is entirely created from inanimate matter (usually clay or mud). The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
of Jewish folklore. Though the specifics outlining the creation of the golem and homunculus are very different, the concepts both metaphorically relate man to the divine, in his construction of life in his own image.
Preformationism
animalcules
Animalcule ('little animal', from Latin ''animal'' + the diminutive suffix ''-culum'') is an old term for microscopic organisms that included bacteria, protozoans, and very small animals. The word was invented by 17th-century Dutch scientist A ...
". Development was therefore a matter of enlarging this into a fully formed being. The term homunculus was later used in the discussion of conception and birth.
Nicolas Hartsoeker
Nicolaas Hartsoeker (26 March 1656 – 10 December 1725) was a Dutch mathematician and physicist who invented the screw-barrel simple microscope .
Biography
He was the son of Anna van der Meij and Christiaan Hartsoeker (1626–1683), a Remonst ...
postulated the existence of animalcules in the semen of humans and other animals. This was the beginning of spermists' theory, which held that the sperm was in fact a "little man" that was placed inside a woman for growth into a child, a neat explanation for many of the mysteries of conception. It was later pointed out that if the sperm was a homunculus, identical in all but size to an adult, then the homunculus may have sperm of its own. This led to a ''reductio ad absurdum
In logic, (Latin for "reduction to absurdity"), also known as (Latin for "argument to absurdity") or ''apagogical arguments'', is the form of argument that attempts to establish a claim by showing that the opposite scenario would lead to absu ...
'' with a chain of homunculi " all the way down". This was not necessarily considered by spermists a fatal objection, however, as it neatly explained how it was that "in Adam" all had sinned: the whole of humanity was already contained in his loins. The spermists' theory also failed to explain why children tend to resemble their mothers as well as their fathers, though some spermists believed that the growing homunculus assimilated maternal characteristics from the womb.
Terminological use in modern science
The homunculus is commonly used today in scientific disciplines such aspsychology
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries betwe ...
as a teaching or memory tool to describe the distorted scale model
A scale model is a physical model which is geometrically similar to an object (known as the prototype). Scale models are generally smaller than large prototypes such as vehicles, buildings, or people; but may be larger than small prototypes ...
of a human drawn or sculpted to reflect the relative space human body parts occupy on the somatosensory cortex
In physiology, the somatosensory system is the network of neural structures in the brain and body that produce the perception of touch (haptic perception), as well as temperature (thermoception), body position (proprioception), and pain. It is ...
(the "sensory homunculus") and the motor cortex
The motor cortex is the region of the cerebral cortex believed to be involved in the planning, control, and execution of voluntary movements.
The motor cortex is an area of the frontal lobe located in the posterior precentral gyrus immediately ...
(the "motor homunculus"). Both the motor and sensory homunculi usually appear as small men superimposed over the top of precentral or postcentral gyri
In neuroanatomy, a gyrus (pl. gyri) is a ridge on the cerebral cortex. It is generally surrounded by one or more sulci (depressions or furrows; sg. ''sulcus''). Gyri and sulci create the folded appearance of the brain in humans and other ma ...
for motor and sensory cortices, respectively. The homunculus is oriented with feet medial and shoulders lateral on top of both the precentral and the postcentral gyrus (for both motor and sensory). The man's head is depicted upside down in relation to the rest of the body such that the forehead is closest to the shoulders. The lips, hands, feet and sex organs have more sensory neurons than other parts of the body, so the homunculus has correspondingly large lips, hands, feet, and genitals. The motor homunculus is very similar to the sensory homunculus, but differs in several ways. Specifically, the motor homunculus has a portion for the tongue most lateral while the sensory homunculus has an area for genitalia most medial and an area for visceral organs most lateral. Well known in the field of neurology, this is also commonly called "the little man inside the brain". This scientific model is known as the cortical homunculus
A cortical homunculus () is a distorted representation of the human body, based on a neurological "map" of the areas and proportions of the human brain dedicated to processing motor functions, or sensory functions, for different parts of the bo ...
.
In medical science, the term homunculus is sometimes applied to certain fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal deve ...
-like ovarian cystic teratoma
A teratoma is a tumor made up of several different types of tissue, such as hair, muscle, teeth, or bone. Teratomata typically form in the ovary, testicle, or coccyx.
Symptoms
Symptoms may be minimal if the tumor is small. A testicular ter ...
e. These will sometimes contain hair, sebaceous material and in some cases cartilagous or bony structures.
In a recent article published in the peer reviewed journal Leonardo "The Missing Female Homunculus” by Haven Wright and Preston Foerder revisits the history of the Homunculus, sheds light on current research in neuroscience on the female brain, and reveals what they believe to be the first sculpture of the female Homunculus, done by the artist and first author Haven Wright, based on the current research available.
In popular culture
Early literature
 Homunculi can be found in centuries worth of literature. These fictions are primarily centred around imaginative speculations on the quest for artificial life associated with
Homunculi can be found in centuries worth of literature. These fictions are primarily centred around imaginative speculations on the quest for artificial life associated with Paracelsian
Paracelsianism (also Paracelsism; German: ') was an early modern History of medicine, medical movement based on the theories and therapies of Paracelsus.
It developed in the second half of the 16th century, during the decades following Paracelsu ...
alchemy. One of the very earliest literary references occurs in Thomas Browne
Sir Thomas Browne (; 19 October 160519 October 1682) was an English polymath and author of varied works which reveal his wide learning in diverse fields including science and medicine, religion and the esoteric. His writings display a deep curi ...
's ''Religio Medici
''Religio Medici'' (''The Religion of a Doctor'') by Sir Thomas Browne is a spiritual testament and early psychological self-portrait. Published in 1643 after an unauthorized version was distributed the previous year, it became a European best-s ...
'' (1643), in which the author states:
The fable of the alchemically-created homunculus may have been central in Mary Shelley
Mary Wollstonecraft Shelley (; ; 30 August 1797 – 1 February 1851) was an English novelist who wrote the Gothic fiction, Gothic novel ''Frankenstein, Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' (1818), which is considered an History of scie ...
's novel ''Frankenstein
''Frankenstein; or, The Modern Prometheus'' is an 1818 novel written by English author Mary Shelley. ''Frankenstein'' tells the story of Victor Frankenstein, a young scientist who creates a sapient creature in an unorthodox scientific ex ...
'' (1818). Professor Radu Florescu
Radu Florescu (23 October 1925 – 18 May 2014) was a Romanian academic who held the position of Emeritus Professor of History at Boston College. His work on Vlad Dracula includes a series of bestselling books that he co-authored with his collea ...
suggests that Johann Konrad Dippel
Johann Konrad Dippel, also spelled Johann Conrad Dippel (10 August 1673 – 25 April 1734), was a German Pietist theologian, physician, alchemist and occultist.
Life
Dippel was born at Castle Frankenstein near Mühltal and Darmstadt, and theref ...
, an alchemist born in Castle Frankenstein, might have been the inspiration for Victor Frankenstein. German playwright Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as trea ...
's ''Faust, Part Two
''Faust: The Second Part of the Tragedy'' (german: Faust. Der Tragödie zweiter Teil in fünf Akten.) is the second part of the tragic play ''Faust'' by Johann Wolfgang von Goethe. It was published in 1832, the year of Goethe's death.
Only part o ...
'' (1832) famously features an alchemically-created homunculus. Here, the character of Homunculus embodies the quest of a pure spirit to be born into a mortal form, contrasting Faust's desire to shed his mortal body to become pure spirit. The alchemical idea that the soul is not imprisoned in the body, but instead may find its brightest state as it passes through the material plane, is central to the character.
William Makepeace Thackeray
William Makepeace Thackeray (; 18 July 1811 – 24 December 1863) was a British novelist, author and illustrator. He is known for his satirical works, particularly his 1848 novel '' Vanity Fair'', a panoramic portrait of British society, and t ...
wrote under the pen name of Homunculus.
Contemporary literature
The homunculus legend, ''Frankenstein'' and ''Faust'' have continued to influence works in the twentieth and twenty-first century. The theme has been used not only infantasy literature
Fantasy literature is literature set in an imaginary universe, often but not always without any locations, events, or people from the real world. Magic, the supernatural and magical creatures are common in many of these imaginary worlds. Fan ...
, but also to illuminate social topics. For instance, the British children's writers Mary Norton and Rumer Godden
Margaret Rumer Godden (10 December 1907 – 8 November 1998) was an English author of more than 60 fiction and non-fiction books. Nine of her works have been made into films, most notably ''Black Narcissus'' in 1947 and '' The River'' in ...
used homunculus motifs in their work, expressing various post-war anxieties about refugees, persecution of minorities in war, and the adaptation of these minorities to a "big" world. W. Somerset Maugham
William Somerset Maugham ( ; 25 January 1874 – 16 December 1965) was an English writer, known for his plays, novels and short stories. Born in Paris, where he spent his first ten years, Maugham was schooled in England and went to a German un ...
's 1908 novel ''The Magician'' utilises the concept of the homunculus as an important plot element. David H. Keller
David Henry Keller (December 23, 1880 – July 13, 1966) was an American writer who worked for pulp magazines in the mid-twentieth century, in the science fiction, fantasy, and horror genres. He was also a psychiatrist and physician to shell- ...
’s short story "A Twentieth-Century Homunculus" (1930) describes the creation of homunculi on an industrial scale by a pair of misogynists. Likewise, Sven Delblanc’s ''The Homunculus: A Magic Tale'' (1965) addresses alleged misogyny and the Cold War industrial-military complexes of the Soviet Union and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
. In German children's author Cornelia Funke
Cornelia Maria Funke () (born 10 December 1958) is a German author of children's fiction. Born in Dorsten, North Rhine-Westphalia, she began her career as a social worker before becoming a book illustrator. She began writing novels in the late 19 ...
's book, '' Dragon Rider'', the protagonists meet and are aided by a homunculus created by an alchemist. The homunculus, and alchemy
Alchemy (from Arabic: ''al-kīmiyā''; from Ancient Greek: χυμεία, ''khumeía'') is an ancient branch of natural philosophy, a philosophical and protoscientific tradition that was historically practiced in China, India, the Muslim world, ...
broadly, is seen as more of a magical phenomenon in the story, however, rather than necessarily having a symbolic meaning.
Other media
Homunculi appear in fantasy based television, film, and games in a manner consistent with literature. Examples can be found in numerous mediums, such as the podcast '' Hello From The Magic Tavern,'' the films ''Homunculus
A homunculus ( , , ; "little person") is a representation of a small human being, originally depicted as small statues made out of clay. Popularized in sixteenth-century alchemy and nineteenth-century fiction, it has historically referred to the ...
'' (1916), ''Bride of Frankenstein
''Bride of Frankenstein'' is a 1935 American science fiction horror film, and the first sequel to Universal Pictures' 1931 film ''Frankenstein''. As with the first film, ''Bride of Frankenstein'' was directed by James Whale starring Boris Karlo ...
'' (1935), ''The Golden Voyage of Sinbad
''The Golden Voyage of Sinbad'' is a 1973 fantasy film, fantasy adventure film directed by Gordon Hessler and featuring stop motion effects by Ray Harryhausen. Based on the ''Arabian Nights'' tales of Sinbad the Sailor, it is the second of thre ...
'' (1973), the made-for-television movie '' Don't Be Afraid of the Dark'' (1973) and its (2011) theatrical remake, ''Being John Malkovich
''Being John Malkovich'' is a 1999 American fantasy comedy film directed by Spike Jonze and written by Charlie Kaufman, both making their feature film debut. The film stars John Cusack, Cameron Diaz, and Catherine Keener, with John Malkovich as a ...
'' (1999), Guillermo del Toro's ''The Devil's Backbone
''The Devil's Backbone'' ( es, El espinazo del diablo) is a 2001 gothic horror film directed by Guillermo del Toro, and written by del Toro, David Muñoz, and Antonio Trashorras.
The film is set in Spain, 1939, during the final year of the ...
'' (2001), ''Fullmetal Alchemist
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Hiromu Arakawa. It was serialized in Square Enix's shōnen manga, ''shōnen'' manga anthology magazine ''Gangan Comics#Monthly Shōnen Gangan, Monthly Shōnen Gangan'' between July 20 ...
'' (2001), Shane Acker's '' 9'' (2009), Philipp Humm's ''The Last Faust
''The Last Faust'' is a 2019 feature art film written and directed by the German artist Philipp Humm. Set in 2059, it is a contemporary interpretation of Johann Wolfgang von Goethe's 1808 ''Faust'' and the first film directly based on both part ...
'' (2019), television shows (such as ''Bloodfeast'' and ''American Dad
''American Dad!'' is an American animated sitcom created by Seth MacFarlane, Mike Barker and Matt Weitzman for the Fox Broadcasting Company. Since 2014, the series has been airing new episodes on TBS. ''American Dad!'' is the first televisio ...
''), fantasy role-playing games (such as ''Dungeons & Dragons
''Dungeons & Dragons'' (commonly abbreviated as ''D&D'' or ''DnD'') is a fantasy tabletop role-playing game (RPG) originally designed by Gary Gygax and Dave Arneson. The game was first published in 1974 by TSR (company)#Tactical Studies Rules ...
''), video game
Video games, also known as computer games, are electronic games that involves interaction with a user interface or input device such as a joystick, controller, keyboard, or motion sensing device to generate visual feedback. This fee ...
s (such as ''Ragnarok Online
''Ragnarok Online'' ( ko, 라그나로크 온라인, marketed as ''Ragnarök'', and alternatively subtitled ''The Final Destiny of the Gods'') is a massively multiplayer online role-playing game (MMORPG) created by Gravity based on the manhwa '' ...
'', ''Valkyrie Profile
or is a series of role-playing video games created by Masaki Norimoto, primarily developed by tri-Ace and published by Square Enix (formerly Enix). The series is notable for featuring elements from Norse mythology.
Common elements
The ''Val ...
'', '' Shadow of Memories
(''Shadow of Destiny'' in North America) is a mystery adventure game developed by Konami Computer Entertainment Tokyo and published by Konami. Originally released for the PlayStation 2 in 2001, it was later ported to Xbox (which is only releas ...
'', '' The Legend of Heroes'' series, and '' Cabals: Magic & Battle Cards''), books (such as ''The Secret Series
''The Secret Series'' is a series of 'secret'-themed fantasy adventure novels written by Pseudonymous Bosch (Raphael Simon). The series centers on three middle school children: Cass, Max-Ernest, and Yo-Yoji; and their adventures as members of the ...
'' and '' Sword of Destiny'' or ''Seventy-Two Letters
“Seventy-Two Letters” is a science fiction novella by American writer Ted Chiang, published in June 2000 in the Ellen Datlow's anthology ''Vanishing Acts''. The novella can also be found in the anthologies ''Year's Best SF 6'' (2001), edited ...
'' by Ted Chiang), graphic novels (such as ''Bureau for Paranormal Research and Defense
The Bureau for Paranormal Research and Defense (the B.P.R.D. or BPRD) is a fictional organization in the comic book work of Mike Mignola, founded by the United States of America, United States and United Kingdom governments, charged with research ...
'') and manga (such as ''Homunculus
A homunculus ( , , ; "little person") is a representation of a small human being, originally depicted as small statues made out of clay. Popularized in sixteenth-century alchemy and nineteenth-century fiction, it has historically referred to the ...
, '' Stone Ocean, ''Fullmetal Alchemist
is a Japanese manga series written and illustrated by Hiromu Arakawa. It was serialized in Square Enix's shōnen manga, ''shōnen'' manga anthology magazine ''Gangan Comics#Monthly Shōnen Gangan, Monthly Shōnen Gangan'' between July 20 ...
'', '' Fullmetal Alchemist: Brotherhood'', ''Sorcerous Stabber Orphen
is a Japanese light novel series written by Yoshinobu Akita. It was adapted into manga, five anime television series (''Sorcerous Stabber Orphen'', ''Sorcerous Stabber Orphen 2: Revenge'', ''Sorcerous Stabber Orphen'' (2020), ...
'', '' Fate/Zero'', and ''Gosick
is a Japanese light novel series written by Kazuki Sakuraba, with illustrations by Hinata Takeda. The series includes 13 novels published by Fujimi Shobo between December 2003 and July 2011. Set in a fictional European country in 1924, a ...
'').
See also
*Cartesian theater
"Cartesian theater" is a derisive term coined by philosopher and cognitive scientist Daniel Dennett to refer pointedly to a defining aspect of what he calls Cartesian materialism, which he considers to be the often unacknowledged remnants of Carte ...
* Doppelgänger
A doppelgänger (), a compound noun formed by combining the two nouns (double) and (walker or goer) (), doppelgaenger or doppelganger is a biologically unrelated look-alike, or a double, of a living person.
In fiction and mythology, a doppelg ...
* Fastachee
* Galatea
Galatea is an ancient Greek name meaning "she who is milk-white".
Galatea, Galathea or Gallathea may refer to:
In mythology
* Galatea (Greek myth), three different mythological figures
In the arts
* ''Aci, Galatea e Polifemo'', cantata by H ...
, a mythical living sculpture made by Pygmalion
Pygmalion or Pigmalion may refer to:
Mythology
* Pygmalion (mythology), a sculptor who fell in love with his statue
Stage
* ''Pigmalion'' (opera), a 1745 opera by Jean-Philippe Rameau
* ''Pygmalion'' (Rousseau), a 1762 melodrama by Jean-Jacques ...
* Golem
A golem ( ; he, , gōlem) is an animated, anthropomorphic being in Jewish folklore, which is entirely created from inanimate matter (usually clay or mud). The most famous golem narrative involves Judah Loew ben Bezalel, the late 16th-century ...
* Homunculus argument
The homunculus argument is an informal fallacy whereby a concept is explained in terms of the concept itself, recursion, recursively, without first defining or explaining the original concept. This fallacy arises most commonly in the theory of ...
* Karzełek
The Karzełek (diminutive of ''karzeł'' – a small one, used for describing non-fantasy dwarfs) or Skarbnik, Kladenets (Russian: Скарбник, Кладенец) (the Treasurer) or Dzedka (Belarusian: Дзедка) in Slavic mythology ...
* Mind–body dichotomy
Mind–body may refer to:
* Mind–body dualism, a medical model
* Mind–body exercise, a form of exercise that combines body movement with mental focus
* Mind–body intervention, an alternative medicine
* Mind–body problem
The mind–bo ...
* Nuno
* Simulacrum
A simulacrum (plural: simulacra or simulacrums, from Latin '' simulacrum'', which means "likeness, semblance") is a representation or imitation of a person or thing. The word was first recorded in the English language in the late 16th century, u ...
* ''Snugglepot and Cuddlepie
''Snugglepot and Cuddlepie'' is a series of books written by Australian author May Gibbs. The books chronicle the adventures of the eponymous Snugglepot and Cuddlepie. The central story arc concerns Snugglepot and Cuddlepie (who are essentially ...
''
* Soul
In many religious and philosophical traditions, there is a belief that a soul is "the immaterial aspect or essence of a human being".
Etymology
The Modern English noun ''soul'' is derived from Old English ''sāwol, sāwel''. The earliest attes ...
* Telesphorus (mythology)
In ancient Greek religion, Telesphorus (Greek: Τελεσφόρος ''Telesphoros'') was a minor child-god of healing. He was a possible son of Asclepius and frequently accompanied his sister Hygieia. He was depicted as a dwarf whose head was a ...
* Tulpa
Tulpa is a concept in Theosophy, mysticism, and the paranormal, of an object or being that is created through spiritual or mental powers. Modern practitioners, who call themselves "tulpamancers", use the term to refer to a type of willed imaginary ...
* Human cloning
Human cloning is the creation of a genetically identical copy (or clone) of a human. The term is generally used to refer to artificial human cloning, which is the reproduction of human cells and tissue. It does not refer to the natural concepti ...
Notes
Further reading
* * * Watson JD, Berry A. ''DNA: The Secret of Life''. New York, New York: Random House; 2003. * * * * * * * *External links
*Homunculus
article from The Mystica. {{Alchemy Alchemical concepts Paracelsus Literary motifs Narrative techniques Monsters