Holy Chalice on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
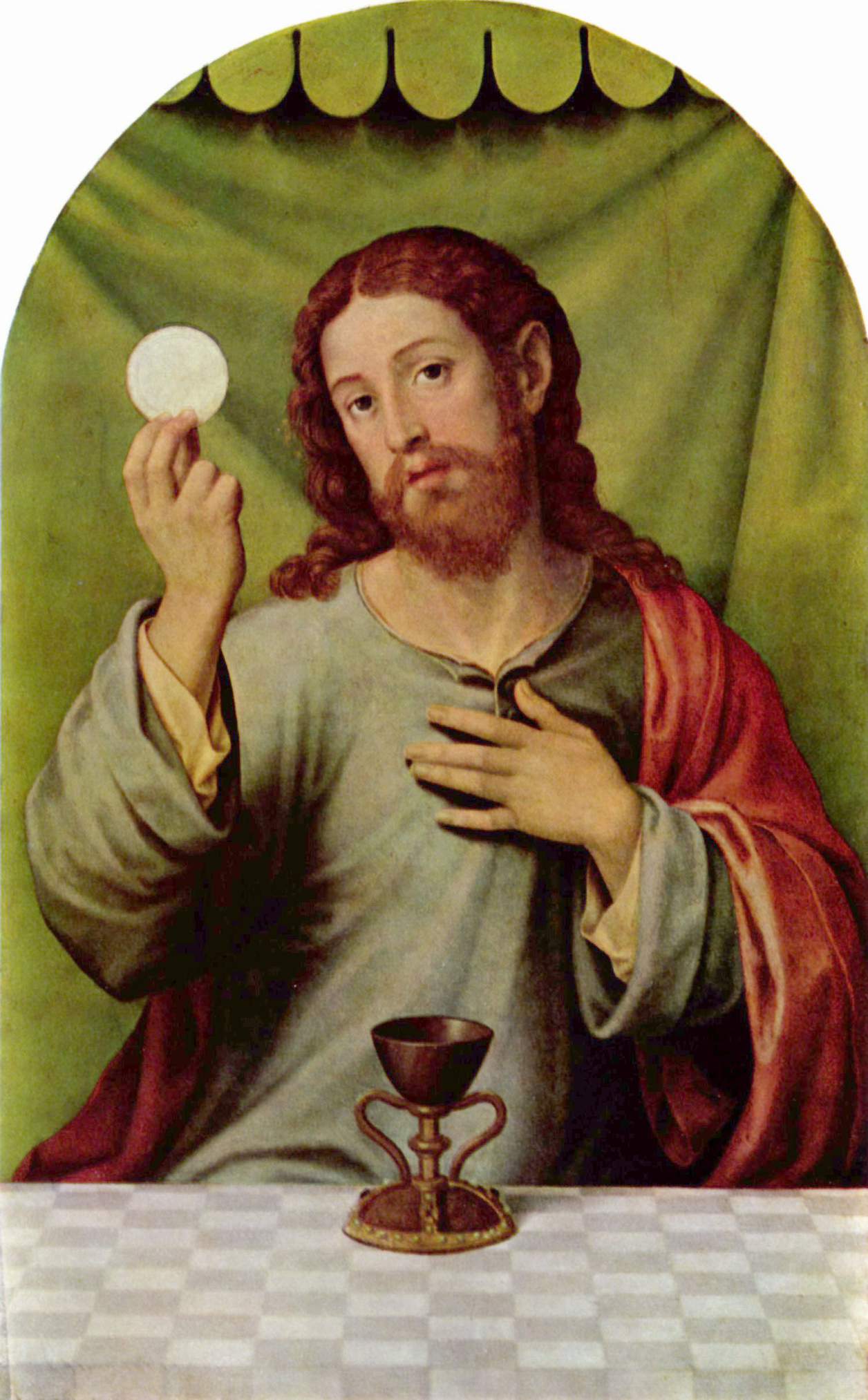 The Holy Chalice, also known as the Holy Grail, is in
The Holy Chalice, also known as the Holy Grail, is in
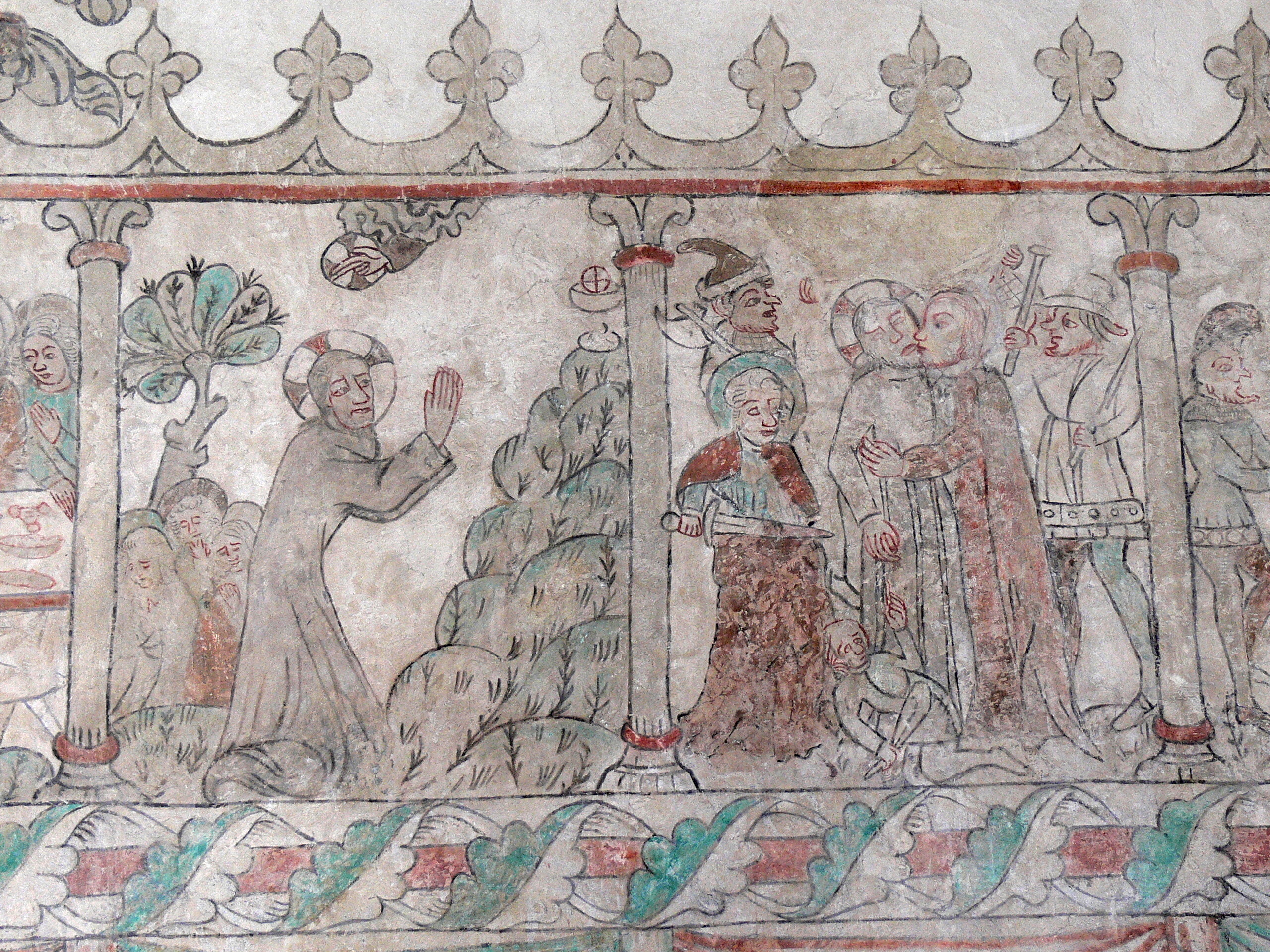 The iconic significance of the Chalice grew during the Early Middle Ages. Depictions of Jesus praying in the Garden of
The iconic significance of the Chalice grew during the Early Middle Ages. Depictions of Jesus praying in the Garden of
 The Holy Chalice vessel, or ''Santo Cáliz'', is an
The Holy Chalice vessel, or ''Santo Cáliz'', is an
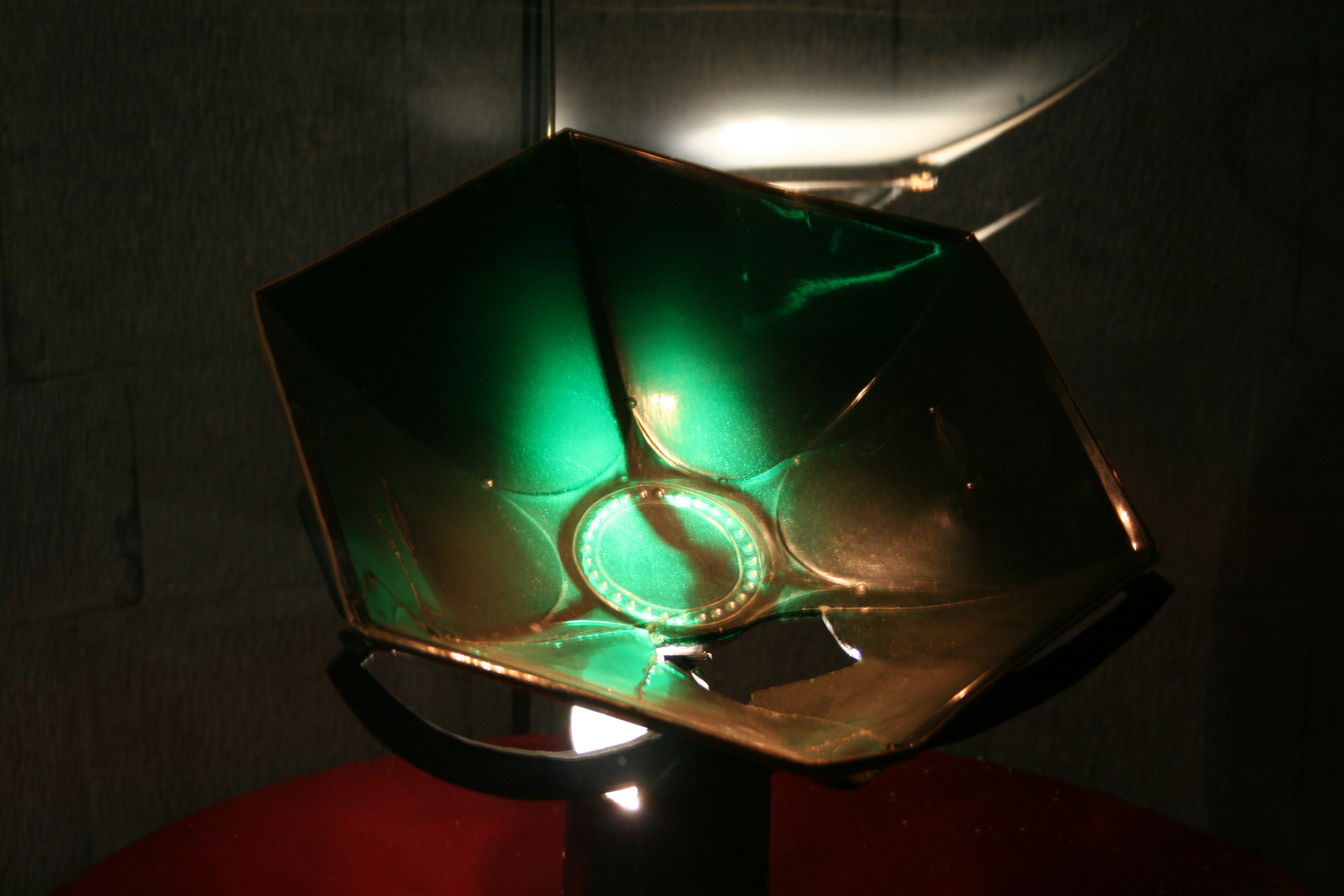 The ''Sacro Catino'', kept in
The ''Sacro Catino'', kept in
 The Chalice of Doña Urraca is an artifact kept in the
The Chalice of Doña Urraca is an artifact kept in the
by Bob Fredericks (
 The
The Metropolitan Museum
/ref>
''Catholic Encyclopedia'':
Chalice (illustration of the Holy Chalice of Valencia) * Weitzmann, Kurt, ed.,
Age of spirituality: late antique and early Christian art, third to seventh century
', no. 542, 1979,
 The Holy Chalice, also known as the Holy Grail, is in
The Holy Chalice, also known as the Holy Grail, is in Christian tradition
Christian tradition is a collection of traditions consisting of practices or beliefs associated with Christianity. These ecclesiastical traditions have more or less authority based on the nature of the practices or beliefs and on the group in que ...
the vessel that Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
used at the Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
to serve wine. The Synoptic Gospels
The gospels of Gospel of Matthew, Matthew, Gospel of Mark, Mark, and Gospel of Luke, Luke are referred to as the synoptic Gospels because they include many of the same stories, often in a similar sequence and in similar or sometimes identical ...
refer to Jesus sharing a cup of wine with the Apostles, saying it was the covenant
Covenant may refer to:
Religion
* Covenant (religion), a formal alliance or agreement made by God with a religious community or with humanity in general
** Covenant (biblical), in the Hebrew Bible
** Covenant in Mormonism, a sacred agreement b ...
in his blood. The use of wine and chalice
A chalice (from Latin 'mug', borrowed from Ancient Greek () 'cup') or goblet is a footed cup intended to hold a drink. In religious practice, a chalice is often used for drinking during a ceremony or may carry a certain symbolic meaning.
Re ...
in the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
in Christian church
In ecclesiology, the Christian Church is what different Christian denominations conceive of as being the true body of Christians or the original institution established by Jesus. "Christian Church" has also been used in academia as a synonym fo ...
es is based on the Last Supper story. In the late 12th century, the author Robert de Boron
Robert de Boron (also spelled in the manuscripts "Roberz", "Borron", "Bouron", "Beron") was a French poet of the late 12th and early 13th centuries, notable as the reputed author of the poems and ''Merlin''. Although little is known of him apart f ...
associated the pre-existing story of the Holy Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
, a magical item from Arthurian literature, with the Holy Chalice. This association was continued in many subsequent Arthurian works, including the Lancelot-Grail
The ''Lancelot-Grail'', also known as the Vulgate Cycle or the Pseudo-Map Cycle, is an early 13th-century French Arthurian literary cycle consisting of interconnected prose episodes of chivalric romance in Old French. The cycle of unknown authors ...
(Vulgate) cycle, the Post-Vulgate Cycle
The ''Post-Vulgate Cycle'', also known as the Post-Vulgate Arthuriad, the Post-Vulgate ''Roman du Graal'' (''Romance of the Grail'') or the Pseudo-Robert de Boron Cycle, is one of the major Old French prose cycles of Arthurian literature from th ...
, and Sir Thomas Malory
Sir Thomas Malory was an English writer, the author of '' Le Morte d'Arthur'', the classic English-language chronicle of the Arthurian legend, compiled and in most cases translated from French sources. The most popular version of '' Le Morte d' ...
's ''Le Morte d'Arthur
' (originally written as '; inaccurate Middle French for "The Death of Arthur") is a 15th-century Middle English prose reworking by Sir Thomas Malory of tales about the legendary King Arthur, Guinevere, Lancelot, Merlin and the Knights of the Rou ...
''. A cup kept in the Spanish Cathedral of Valencia
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan Cathedral–Basilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia ( es, Iglesia Catedral-Basílica Metropolitana de la Asunción de Nuestra Señora de Valencia, ca-valencia, Església Cated ...
has been identified since Medieval times as the purported Holy Chalice used at the Last Supper.
Last Supper
TheGospel of Matthew
The Gospel of Matthew), or simply Matthew. It is most commonly abbreviated as "Matt." is the first book of the New Testament of the Bible and one of the three synoptic Gospels. It tells how Israel's Messiah, Jesus, comes to his people and for ...
(26:27-29) says:
And He took a cup and when He had given thanks He gave it to them saying "Drink this, all of you; for this is My blood of the covenant, which is poured out for many for the forgiveness of sins. I tell you, I shall not drink again of the fruit of the vine until I drink it new with you in My Father's kingdom."This incident, traditionally known as the
Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
, is also described by the gospel writers, Mark
Mark may refer to:
Currency
* Bosnia and Herzegovina convertible mark, the currency of Bosnia and Herzegovina
* East German mark, the currency of the German Democratic Republic
* Estonian mark, the currency of Estonia between 1918 and 1927
* Fi ...
and Luke
People
*Luke (given name), a masculine given name (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Luke (surname) (including a list of people and characters with the name)
*Luke the Evangelist, author of the Gospel of Luke. Also known as ...
, and by the Apostle Paul
Paul; grc, Παῦλος, translit=Paulos; cop, ⲡⲁⲩⲗⲟⲥ; hbo, פאולוס השליח (previously called Saul of Tarsus;; ar, بولس الطرسوسي; grc, Σαῦλος Ταρσεύς, Saũlos Tarseús; tr, Tarsuslu Pavlus; ...
in I Corinthians. With the preceding description of the breaking of bread, it is the foundation for the Eucharist
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instit ...
or Holy Communion
The Eucharist (; from Greek , , ), also known as Holy Communion and the Lord's Supper, is a Christian rite that is considered a sacrament in most churches, and as an ordinance in others. According to the New Testament, the rite was instituted ...
, celebrated regularly in many Christian churches. The Bible
The Bible (from Koine Greek , , 'the books') is a collection of religious texts or scriptures that are held to be sacred in Christianity, Judaism, Samaritanism, and many other religions. The Bible is an anthologya compilation of texts of a ...
makes no mention of the cup except within the context of the Last Supper and gives no significance whatsoever to the object itself.
St. John Chrysostom
John Chrysostom (; gr, Ἰωάννης ὁ Χρυσόστομος; 14 September 407) was an important Early Church Father who served as archbishop of Constantinople. He is known for his homilies, preaching and public speaking, his denunciat ...
(347–407 AD) in his homily on ''Matthew
Matthew may refer to:
* Matthew (given name)
* Matthew (surname)
* ''Matthew'' (ship), the replica of the ship sailed by John Cabot in 1497
* ''Matthew'' (album), a 2000 album by rapper Kool Keith
* Matthew (elm cultivar), a cultivar of the Ch ...
'' asserted:
The table was not of silver, the chalice was not of gold in which Christ gave His blood to His disciples to drink, and yet everything there was precious and truly fit to inspire awe.The pilgrim
Antoninus of Piacenza
Saint Antoninus of Piacenza (or Placentia) (died 303 AD) is a patron saint of Piacenza in Italy. He is venerated as a saint and martyr in the Roman Catholic Church, with a feast day of 30 September.
The saint was said to have been martyred at ...
(AD 570) in his descriptions of the holy places of Jerusalem
Jerusalem (; he, יְרוּשָׁלַיִם ; ar, القُدس ) (combining the Biblical and common usage Arabic names); grc, Ἱερουσαλήμ/Ἰεροσόλυμα, Hierousalḗm/Hierosóluma; hy, Երուսաղեմ, Erusałēm. i ...
, said that he saw "the cup of onyx, which our Lord blessed at the last supper" among many relics displayed at the Basilica erected by Constantine near to Golgotha and the Tomb of Christ
The tomb of Jesus refers to any place where it is believed that Jesus was entombed or interred.
Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre is a church in the Christian Quarter of the Old City of Jerusalem. It contains, a ...
.
Herbert Thurston in the ''Catholic Encyclopedia
The ''Catholic Encyclopedia: An International Work of Reference on the Constitution, Doctrine, Discipline, and History of the Catholic Church'' (also referred to as the ''Old Catholic Encyclopedia'' and the ''Original Catholic Encyclopedia'') i ...
'' (1908) concluded that:
No reliable tradition has been preserved to us regarding the vessel used by Christ at the Last Supper. In the sixth and seventh centuries pilgrims to Jerusalem were led to believe that the actual chalice was still venerated in the church of the Holy Sepulchre, having within it the sponge which was presented to Our Saviour on Calvary.According to one tradition,
Saint Peter
Saint Peter; he, שמעון בר יונה, Šimʿōn bar Yōnāh; ar, سِمعَان بُطرُس, translit=Simʿa̅n Buṭrus; grc-gre, Πέτρος, Petros; cop, Ⲡⲉⲧⲣⲟⲥ, Petros; lat, Petrus; ar, شمعون الصفـا, Sham'un ...
brought it to Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, and passed it on to his successors (the Pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
s). In 258, when Christians were being persecuted by Emperor Valerian and the Romans demanded that relics be turned over to the government, Pope Sixtus II
Pope Sixtus II ( el, Πάπας Σίξτος Β΄), also written as Pope Xystus II, was bishop of Rome from 31 August 257 until his death on 6 August 258. He was martyred along with seven deacons, including Lawrence of Rome, during the persecutio ...
instead gave the cup to one of his deacon
A deacon is a member of the diaconate, an office in Christian churches that is generally associated with service of some kind, but which varies among theological and denominational traditions. Major Christian churches, such as the Catholic Churc ...
s, Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence ( la, Laurentius, lit. "Laurel wreath, laurelled"; 31 December AD 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, perse ...
, who passed it to a Spanish soldier, Proselius, with instructions to take it to safety in Lawrence's home country of Spain.
Medieval tradition
Iconography
 The iconic significance of the Chalice grew during the Early Middle Ages. Depictions of Jesus praying in the Garden of
The iconic significance of the Chalice grew during the Early Middle Ages. Depictions of Jesus praying in the Garden of Gethsemane
Gethsemane () is a garden at the foot of the Mount of Olives in Jerusalem where, according to the four Gospels of the New Testament, Jesus underwent the agony in the garden and was arrested before his crucifixion. It is a place of great resona ...
, such as that in the fourteenth-century frescoes of the church at Öja, Gotland
Gotland (, ; ''Gutland'' in Gutnish), also historically spelled Gottland or Gothland (), is Sweden's largest island. It is also a province, county, municipality, and diocese. The province includes the islands of Fårö and Gotska Sandön to the ...
(''illustration, right''), show a prefigured apparition of the Holy Chalice that stands at the top of the mountain, illustrating the words "Let this cup be taken from me". Together with the halo-enveloped Hand of God and the haloed figure of Jesus, the halo image atop the chalice, as if of a consecrated Host, completes the Trinity by embodying the Holy Spirit.
Holy Grail
TheHoly Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
appears as a miraculous artifact in Arthurian literature
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It was one of the three great Western ...
in the 12th century, and is soon associated with the Holy Chalice.
The "Grail" became interwoven with the legend of the Holy Chalice. The connection of the Holy Chalice with Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea was, according to all four canonical gospels, the man who assumed responsibility for the burial of Jesus after his crucifixion. The historical location of Arimathea is uncertain, although it has been identified with several t ...
dates from Robert de Boron
Robert de Boron (also spelled in the manuscripts "Roberz", "Borron", "Bouron", "Beron") was a French poet of the late 12th and early 13th centuries, notable as the reputed author of the poems and ''Merlin''. Although little is known of him apart f ...
's ''Joseph d'Arimathie'' (late 12th century). The fully developed "Grail legend" of the 13th century identifies the Holy Grail with the Holy Chalice used in the Last Supper and later used to collect
Christ's blood, brought to Hispania by Joseph of Arimathea
Joseph of Arimathea was, according to all four canonical gospels, the man who assumed responsibility for the burial of Jesus after his crucifixion. The historical location of Arimathea is uncertain, although it has been identified with several t ...
.
Medieval relics
In the account ofArculf
Arculf (later 7th century) was a Frankish bishop who toured the Levant in around 680. Bede claimed he was a bishop (). According to Bede's history of the Church in England (V, 15), Arculf was shipwrecked on the shore of Iona, Scotland on his return ...
, a 7th-century Anglo-Saxon pilgrim, mention is made of a chalice venerated as the one used in the Last Supper in a chapel near Jerusalem. This is the only mention of the veneration of such a relic in the Holy Land.
Two artifacts were claimed as the Holy Chalice in Western Christianity in the later medieval period. The first is the ''Santo Cáliz'', an agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancie ...
cup in the Cathedral of Valencia
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan Cathedral–Basilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia ( es, Iglesia Catedral-Basílica Metropolitana de la Asunción de Nuestra Señora de Valencia, ca-valencia, Església Cated ...
, purportedly from around the 1st century AD, and celebrated by Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereign ...
in 2006 as "this most famous chalice" (''hunc praeclarum Calicem''); Valencia's Holy Chalice is the object most commonly identified as a claimant to being the Holy Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
. The second is the ''Sacro Catino'' in Genoa Cathedral
Genoa Cathedral or Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Lawrence ( it, Duomo di Genova, ''Cattedrale di San Lorenzo'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the Italian city of Genoa. It is dedicated to Saint Lawrence (San Lorenzo), and is the seat of th ...
, a flat dish made of green glass; recovered from Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
in 1101, it was not identified as the Holy Chalice until much later, towards the end of the 13th century.
Valencia Chalice
agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancie ...
cup preserved in the Cathedral of Valencia
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan Cathedral–Basilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia ( es, Iglesia Catedral-Basílica Metropolitana de la Asunción de Nuestra Señora de Valencia, ca-valencia, Església Cated ...
. It is the object most commonly credited as being the actual Holy Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
used by Jesus
Jesus, likely from he, יֵשׁוּעַ, translit=Yēšūaʿ, label=Hebrew/Aramaic ( AD 30 or 33), also referred to as Jesus Christ or Jesus of Nazareth (among other names and titles), was a first-century Jewish preacher and religious ...
during the Last Supper
Image:The Last Supper - Leonardo Da Vinci - High Resolution 32x16.jpg, 400px, alt=''The Last Supper'' by Leonardo da Vinci - Clickable Image, Depictions of the Last Supper in Christian art have been undertaken by artistic masters for centuries, ...
. It is preserved in a chapel consecrated to it, where it still attracts the faithful on pilgrimage. The artifact has seemingly never been accredited with supernatural powers.
The cup is made of dark red agate
Agate () is a common rock formation, consisting of chalcedony and quartz as its primary components, with a wide variety of colors. Agates are primarily formed within volcanic and metamorphic rocks. The ornamental use of agate was common in Ancie ...
which is mounted by means of a knobbed stem and two curved handles onto a base made from an inverted cup of chalcedony
Chalcedony ( , or ) is a cryptocrystalline form of silica, composed of very fine intergrowths of quartz and moganite. These are both silica minerals, but they differ in that quartz has a trigonal crystal structure, while moganite is monoclinic. ...
. The agate cup is about 9 centimeters (3.5 inches) in diameter and the total height, including base, is about 17 centimetres (7 inches) high. The lower part has Arabic inscriptions. The base, stems and handles are posterior additions, but the red agate cup itself has been most likely produced in a Palestinian or Egyptian workshop between the 2nd century BC and the 1st century AD.
It is kept together with an inventory list on vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. Parchment is another term for this material, from which vellum is sometimes distinguished, when it is made from calfskin, as opposed to that made from other anima ...
, said to have accompanied a lost letter which detailed state-sponsored Roman persecution of Christians that forced the church to split up its treasury and hide it with members, specifically the deacon Saint Lawrence
Saint Lawrence or Laurence ( la, Laurentius, lit. "Laurel wreath, laurelled"; 31 December AD 225 – 10 August 258) was one of the seven deacons of the city of Rome under Pope Sixtus II who were martyred in the Persecution of Christians, perse ...
.
The first explicit inventory reference to the present ''Chalice of Valencia'' is found in an inventory of the treasury of the monastery of San Juan de la Peña drawn up by Don Carreras Ramírez, Canon of Zaragoza, on the 14th of December 1134. The Chalice is described as the vessel in which "Christ Our Lord consecrated his blood" (''En un arca de marfil está el Cáliz en que Cristo N. Señor consagró su sangre, el cual envió S. Lorenzo a su patria, Huesca
Huesca (; an, Uesca) is a city in north-eastern Spain, within the autonomous community of Aragon. It is also the capital of the Spanish province of the same name and of the comarca of Hoya de Huesca. In 2009 it had a population of 52,059, almo ...
'').
Reference to the chalice is made again in 1399, when it was given by the monastery of San Juan de la Peña to king Martin I of Aragon
Martin the Humane (29 July 1356 – 31 May 1410), also called the Elder and the Ecclesiastic, was King of Aragon, Valencia, Sardinia and Corsica and Count of Barcelona from 1396 and King of Sicily from 1409 (as Martin II). He failed to secure th ...
in exchange for a gold cup.
Pope John Paul II
Pope John Paul II ( la, Ioannes Paulus II; it, Giovanni Paolo II; pl, Jan Paweł II; born Karol Józef Wojtyła ; 18 May 19202 April 2005) was the head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 1978 until his ...
celebrated mass with the Holy Chalice in Valencia in November 1982, and in that occasion the Pope referred to it as "a witness to Christ's passage on earth". In July 2006, at the closing Mass of the 5th World Meeting of Families in Valencia, Pope Benedict XVI
Pope Benedict XVI ( la, Benedictus XVI; it, Benedetto XVI; german: link=no, Benedikt XVI.; born Joseph Aloisius Ratzinger, , on 16 April 1927) is a retired prelate of the Catholic church who served as the head of the Church and the sovereign ...
also celebrated mass with the Holy Chalice, on this occasion calling it "this most famous chalice" (''hunc praeclarum Calicem''), words in the Roman Canon The Canon of the Mass ( la, Canon Missæ), also known as the Canon of the Roman Mass and in the Mass of Paul VI as the Roman Canon or Eucharistic Prayer I, is the oldest anaphora used in the Roman Rite of Mass. The name ''Canon Missæ'' was used i ...
said to have been used for the first popes to refer to the Holy Grail until the 4th century in Rome.
Genoa Chalice
 The ''Sacro Catino'', kept in
The ''Sacro Catino'', kept in Genoa Cathedral
Genoa Cathedral or Metropolitan Cathedral of Saint Lawrence ( it, Duomo di Genova, ''Cattedrale di San Lorenzo'') is a Roman Catholic cathedral in the Italian city of Genoa. It is dedicated to Saint Lawrence (San Lorenzo), and is the seat of th ...
, is a hexagonal dish of the Roman era made of green Egyptian glass, some 9 cm high and 33 cm across. It was taken to Genoa by Guglielmo Embriaco
Guglielmo Embriaco (Latin ''Guillermus Embriacus'', Genoese ''Ghigærmo de ri Embrieghi'', English ''William the Drunkard''; born c. 1040), was a Genoese merchant and military leader who came to the assistance of the Crusader States in the afterm ...
as part of the spoils from the conquest of Caesarea
Caesarea () ( he, קֵיסָרְיָה, ), ''Keysariya'' or ''Qesarya'', often simplified to Keisarya, and Qaysaria, is an affluent town in north-central Israel, which inherits its name and much of its territory from the ancient city of Caesare ...
in 1101. William of Tyre
William of Tyre ( la, Willelmus Tyrensis; 113029 September 1186) was a medieval prelate and chronicler. As archbishop of Tyre, he is sometimes known as William II to distinguish him from his predecessor, William I, the Englishman, a former ...
(10.16) describes it as a "vessel of the most green colour, in the shape of a serving dish" (''vas coloris viridissimi, in modum parapsidis formatum'') which the Genoese thought to be made of emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p ...
, and accepted as their share of the spoils. William states that the Genoese were still exhibiting the bowl, insisting on its miraculous properties due to its being made of emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p ...
, in his own day (''Unde et usque hodie transeuntibus per eos magnatibus, vas idem quasi pro miraculo solent ostendere, persuadentes quod vere sit, id quod color esse indicat, smaragdus''), the implication being that emerald was thought to have miraculous properties of their own in medieval lore and not that the bowl was thought of as a holy relic. The ''Sacro Catino'' would later become identified as the Holy Grail. The first explicit claim to this effect is found in the ''Chronicon'' by Jacobus de Voragine
Jacobus de Voragine (c. 123013/16 July 1298) was an Italian chronicler and archbishop of Genoa. He was the author, or more accurately the compiler, of the ''Golden Legend'', a collection of the legendary lives of the greater saints of the medie ...
, written in the 1290s.
Pedro Tafur
Pedro Tafur (or Pero Tafur) (c. 1410 – c. 1484) was a traveller, historian and writer from Castile (modern day Spain). Born in Córdoba, to a branch of the noble house of Guzmán,He dedicated his manuscript to Don Fernando de Guzmán, Chief Co ...
, who visited Genoa in 1436, reported that the Holy Grail, "made of a single emerald" is kept in Genoa Cathedral.
The bowl was seized and taken to Paris by Napoleon in 1805, and it was damaged when it was returned to Genoa in 1816, in which occasion it was confirmed it is made of glass rather than emerald.
Modern candidates
Aside from the Holy Chalice of theCathedral of Valencia
Valencia Cathedral, at greater length the Metropolitan Cathedral–Basilica of the Assumption of Our Lady of Valencia ( es, Iglesia Catedral-Basílica Metropolitana de la Asunción de Nuestra Señora de Valencia, ca-valencia, Església Cated ...
, believed to be the Holy Grail since the first centuries AD, and which has been used by popes to celebrate mass until nowadays, and from the Sacro Catino, in Genoa, a number of other artifacts of greater or lesser notability have come to be identified with the "Holy Grail" or "Holy Chalice" in recent times with the rising popularity of the Grail legend in 19th-century Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
.
The Chalice of Doña Urraca, for example, had not traditionally been associated with the Holy Chalice, and was only proposed as such in a 2014 publication. The "Antioch Chalice", on the other hand, is an artifact discovered in Antioch in 1910 which was briefly marketed as the "Holy Chalice", but it is most likely a lamp in a style of the 6th century.
Chalice of Doña Urraca
 The Chalice of Doña Urraca is an artifact kept in the
The Chalice of Doña Urraca is an artifact kept in the Basilica of San Isidoro
In Ancient Roman architecture, a basilica is a large public building with multiple functions, typically built alongside the town's forum. The basilica was in the Latin West equivalent to a stoa in the Greek East. The building gave its name ...
in León, Spain
León (; ) is a city and Municipalities of Spain, municipality of Spain, capital of the province of León, part of the autonomous community of Castile and León, in the northwest of the Iberian Peninsula. It has a population of 124,303 (2019), ...
.''Historians claim Holy Grail is in church in Leon, northern Spain''by Bob Fredericks (
News.com.au
news.com.au is an Australian website owned by News Corp Australia. It had 9.6 million unique readers in April 2019 and covers national and international news, lifestyle, travel, entertainment, technology, finance, and sport.
Staff
The organiza ...
, 1 April 2014)
The connection of this artifact to the Holy Grail was made in the 2014 book ''Los Reyes del Grial'', which develops the hypothesis that this artifact had been taken by Egyptian troops following the invasion of Jerusalem and the looting of the Church of the Holy Sepulchre
The Church of the Holy Sepulchre, hy, Սուրբ Հարության տաճար, la, Ecclesia Sancti Sepulchri, am, የቅዱስ መቃብር ቤተክርስቲያን, he, כנסיית הקבר, ar, كنيسة القيامة is a church i ...
, then given by the Emir of Egypt to the Emir of Denia, who in the 11th century gave it to the Kings of Leon in order for them to spare his city in the Reconquista
The ' (Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the Nasrid ...
.
Antioch Chalice
 The
The silver-gilt
Silver-gilt or gilded/gilt silver, sometimes known in American English by the French term vermeil, is silver (either pure or sterling) which has been gilded with gold. Most large objects made in goldsmithing that appear to be gold are actually ...
object originally identified as an early Christian chalice is in the collection of the Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
in New York
New York most commonly refers to:
* New York City, the most populous city in the United States, located in the state of New York
* New York (state), a state in the northeastern United States
New York may also refer to:
Film and television
* '' ...
. It was apparently made at Antioch
Antioch on the Orontes (; grc-gre, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου, ''Antiókheia hē epì Oróntou'', Learned ; also Syrian Antioch) grc-koi, Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπὶ Ὀρόντου; or Ἀντιόχεια ἡ ἐπ� ...
in the early 6th century and is of double-cup construction, with an outer shell of cast-metal open work enclosing a plain silver inner cup. When it was first recovered in Antioch in 1910, it was touted as the Holy Chalice, an identification the Metropolitan Museum characterizes as "ambitious". It is no longer identified as a chalice, having been identified by experts at Walters Art Museum
The Walters Art Museum, located in Mount Vernon-Belvedere, Baltimore, Maryland, United States, is a public art museum founded and opened in 1934. It holds collections established during the mid-19th century. The museum's collection was amassed ...
in Baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...
, Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, believed to be a standing lamp, of a style of the 6th century./ref>
Nanteos Cup
TheNanteos Cup
The Nanteos Cup ( cy, Cwpan Nanteos) is a medieval wood mazer bowl, held for many years at Nanteos Mansion, near Aberystwyth in Wales.
Since at least the late 19th century, it has been attributed with a supernatural ability to heal those who dri ...
is a medieval wood mazer bowl, held for many years at Nanteos Mansion
Nanteos (Welsh: ''Plas Nanteos'', Nanteos Mansion) is an 18th-century former country house in Llanbadarn-y-Creuddyn, near Aberystwyth, Ceredigion, Wales. A Grade I listed building, it is now a country house hotel. The gardens and parkland surroundi ...
, Rhydyfelin
Rhydyfelin (, ''Mill Ford'') is a large village (originally known as Rhydfelen) and part of the community of Pontypridd Town, about two miles to its south east of Pontypridd, in the county borough of Rhondda Cynon Taf. It is on the eastern ban ...
, near Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth () is a university and seaside town as well as a community in Ceredigion, Wales. Located in the historic county of Cardiganshire, means "the mouth of the Ystwyth". Aberystwyth University has been a major educational location in ...
in Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the Wales–England border, east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the ...
.
It is recorded as having been attributed miraculous powers of healing in the late 19th century, and tradition apparently held it had been made from a piece of the True Cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, althoug ...
at the time, but it came to be identified as the Holy Chalice in the early 20th century.
See also
*Holy Grail
The Holy Grail (french: Saint Graal, br, Graal Santel, cy, Greal Sanctaidd, kw, Gral) is a treasure that serves as an important motif in Arthurian literature. Various traditions describe the Holy Grail as a cup, dish, or stone with miracul ...
* Holyrood (cross)
The Holyrood or Holy Rood is a Christian relic alleged to be part of the True Cross on which Jesus died. The word derives from the Old English ''rood'', meaning a pole and the cross, via Middle English, or the Scots ''haly ruid'' ("holy cross"). S ...
* Holy Prepuce
The Holy Prepuce, or Holy Foreskin (Latin or ), is one of several relics attributed to Jesus, a product of the circumcision of Jesus. At various points in history, a number of churches in Europe have claimed to possess Jesus's foreskin, sometim ...
* Holy Sponge
The Holy Sponge is one of the Instruments of the Passion of Jesus. It was dipped in vinegar (; in some translations sour wine), most likely posca, a regular beverage of Roman soldiers, and offered to Jesus to drink from during the Crucifixion, acc ...
* Nail (relic)
Relics that are claimed to be the Holy Nails with which Jesus was crucified are objects of veneration among some Christians, particularly Roman Catholics and the Eastern Orthodox. In Christian symbolism and art, they figure among the ''Arma ...
* Relics associated with Jesus
A number of alleged relics associated with Jesus have been displayed throughout the history of Christianity. While some individuals believe in the authenticity of Jesus relics, others doubt their validity. For instance, the sixteenth-century phil ...
* Sandals of Jesus Christ
The Sandals of Jesus Christ were among the most important relics of the Catholic Church in the Middle Ages. They were donated to Prüm Abbey by Pope Zachary (741–752) and Pope Stephen II (752–757).
Description
The sandals are the rema ...
* San Juan de la Peña
* Shroud of Turin
The Shroud of Turin ( it, Sindone di Torino), also known as the Holy Shroud ( it, Sacra Sindone, links=no or ), is a length of linen cloth bearing the negative image of a man. Some describe the image as depicting Jesus of Nazareth and bel ...
* Titulus Crucis
The Titulus Crucis (Latin for "Title of the Cross") is a piece of wood kept in the Church of Santa Croce in Gerusalemme in Rome which is claimed to be the (title panel) of the True Cross on which Jesus Christ was crucified. It is venerated by s ...
* Tree of Jesse
The Tree of Jesse is a depiction in art of the ancestors of Jesus Christ, shown in a branching tree which rises from Jesse of Bethlehem, the father of King David. It is the original use of the family tree as a schematic representation of a ge ...
* True cross
The True Cross is the cross upon which Jesus was said to have been crucified, particularly as an object of religious veneration. There are no early accounts that the apostles or early Christians preserved the physical cross themselves, althoug ...
References
Bibliography
* Salvador Antuñano Alea, ''Truth and Symbolism of Holy Grail: Revelations Surrounding Valencia's Sacred Chalice'' (in Spanish, with a prologue by Archbishop Agustin Garcia Gasco of Valencia), 1999 * Strzygowski, Josef, ''L'ancien art chrétien de Syrie'', Paris, E. de Boccard, 1936. * ''Relics of the Passion'', 2005,History Channel
History (formerly The History Channel from January 1, 1995 to February 15, 2008, stylized as HISTORY) is an American pay television network and flagship channel owned by A&E Networks, a joint venture between Hearst Communications and the Disney ...
video documentary
''Catholic Encyclopedia'':
Chalice (illustration of the Holy Chalice of Valencia) * Weitzmann, Kurt, ed.,
Age of spirituality: late antique and early Christian art, third to seventh century
', no. 542, 1979,
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
, New York, {{ISBN, 9780870991790; full text available online from The Metropolitan Museum of Art Libraries.
Chalices
Christian terminology
Holy Grail
Relics associated with Jesus