Historic Columbia River Highway on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Historic Columbia River Highway is an approximately
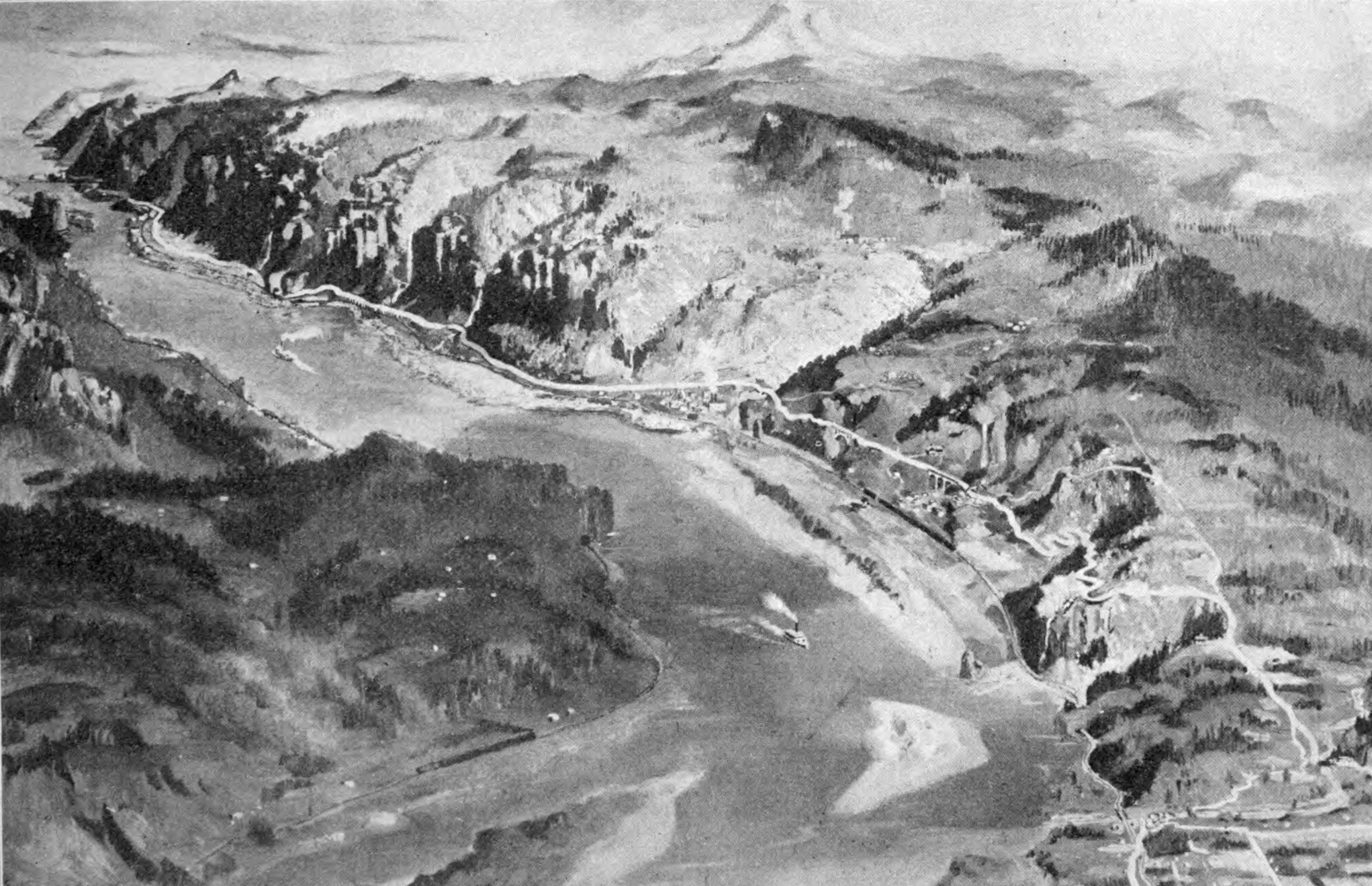
 The
The  The eventual highway was primarily designed by
The eventual highway was primarily designed by  In laying out the highway, Lancaster sought not only to create a transportation artery, but to make the gorge's "beautiful waterfalls, canyons, cliffs and mountain domes" accessible to "men from all climes". According to
In laying out the highway, Lancaster sought not only to create a transportation artery, but to make the gorge's "beautiful waterfalls, canyons, cliffs and mountain domes" accessible to "men from all climes". According to
scenic highway
A scenic route, tourist road, tourist route, tourist drive, holiday route, theme route, or scenic byway is a specially designated road or waterway that travels through an area of natural or cultural beauty. It often passes by scenic viewpoints ...
in the U.S. state of Oregon
Oregon () is a U.S. state, state in the Pacific Northwest region of the Western United States. The Columbia River delineates much of Oregon's northern boundary with Washington (state), Washington, while the Snake River delineates much of it ...
between Troutdale and The Dalles
The Dalles is the largest city of Wasco County, Oregon, United States. The population was 16,010 at the 2020 census, and it is the largest city on the Oregon side of the Columbia River between the Portland Metropolitan Area, and Hermiston ...
, built through the Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range, forming the boundary between the st ...
between 1913 and 1922. As the first planned scenic roadway in the United States, it has been recognized in numerous ways, including being listed on the National Register of Historic Places
The National Register of Historic Places (NRHP) is the United States federal government's official list of districts, sites, buildings, structures and objects deemed worthy of preservation for their historical significance or "great artistic ...
, being designated as a National Historic Landmark
A National Historic Landmark (NHL) is a building, district, object, site, or structure that is officially recognized by the United States government for its outstanding historical significance. Only some 2,500 (~3%) of over 90,000 places liste ...
by the U.S. Secretary of the Interior
The United States secretary of the interior is the head of the United States Department of the Interior. The secretary and the Department of the Interior are responsible for the management and conservation of most federal land along with natura ...
, being designated as a National Historic Civil Engineering Landmark by the American Society of Civil Engineers
American(s) may refer to:
* American, something of, from, or related to the United States of America, commonly known as the "United States" or "America"
** Americans, citizens and nationals of the United States of America
** American ancestry, p ...
, and being considered a "destination unto itself" as an All-American Road
A National Scenic Byway is a road recognized by the United States Department of Transportation for one or more of six "intrinsic qualities": archeological, cultural, historic, natural, recreational, and scenic. The program was established by Co ...
by the U.S. Secretary of Transportation
The United States secretary of transportation is the head of the United States Department of Transportation. The secretary serves as the principal advisor to the president of the United States on all matters relating to transportation. The sec ...
. The historic roadway was bypassed by the present Columbia River Highway No. 2 ( Interstate 84) from the 1930s to the 1950s, leaving behind the old two-lane road. The road is now mostly owned and maintained by the state through the Oregon Department of Transportation
The Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT) is a department of the state government of the U.S. state of Oregon responsible for systems of transportation. It was first established in 1969. It had been preceded by the Oregon State Highway Depart ...
as the Historic Columbia River Highway No. 100 (still partially marked as U.S. Route 30
U.S. Route 30 or U.S. Highway 30 (US 30) is an east–west main route in the system of the United States Numbered Highways, with the highway traveling across the northern tier of the country. With a length of , it is the third longest ...
; see Oregon highways and routes
The state highway system of the U.S. state of Oregon is a network of highways that are owned and maintained by the Highway Division of the Oregon Department of Transportation (ODOT).
Highways and routes
The state highway system consists of abo ...
) or the Oregon Parks and Recreation Department
The Oregon Parks and Recreation Department (OPRD), officially known (in state law) as the State Parks and Recreation Department, is the government agency of the U.S. state of Oregon which operates its system of state parks. In addition, it has pro ...
as the Historic Columbia River Highway State Trail.
The original highway was promoted by lawyer and entrepreneur Sam Hill and engineer Samuel C. Lancaster, to be modeled after the great scenic roads of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. From the very beginning, the roadway was envisioned not just as means of traveling by the then popular Model T
The Ford Model T is an automobile that was produced by Ford Motor Company from October 1, 1908, to May 26, 1927. It is generally regarded as the first affordable automobile, which made car travel available to middle-class Americans. The relati ...
, but designed with an elegance that took full advantage of all the natural beauty along the route.
When the United States highway
The United States Numbered Highway System (often called U.S. Routes or U.S. Highways) is an integrated network of roads and highways numbered within a nationwide grid in the contiguous United States. As the designation and numbering of these hi ...
system was officially established in 1926, the highway became the part of U.S. Route 30
U.S. Route 30 or U.S. Highway 30 (US 30) is an east–west main route in the system of the United States Numbered Highways, with the highway traveling across the northern tier of the country. With a length of , it is the third longest ...
. Since then, modern Interstate 84 has been built parallel to the highway between Portland and The Dalles, replacing it as the main travel route and resulting in the loss of some of the original sections of road.
History
Planning and construction

 The
The Columbia River Gorge
The Columbia River Gorge is a canyon of the Columbia River in the Pacific Northwest of the United States. Up to deep, the canyon stretches for over as the river winds westward through the Cascade Range, forming the boundary between the st ...
is the lowest crossing of the Cascade Mountains
The Cascade Range or Cascades is a major mountain range of western North America, extending from southern British Columbia through Washington and Oregon to Northern California. It includes both non-volcanic mountains, such as the North Cascades, a ...
, carved by the Columbia River
The Columbia River ( Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia ...
during the Cascades' uplift
Uplift may refer to: Science
* Geologic uplift, a geological process
** Tectonic uplift, a geological process
* Stellar uplift, the theoretical prospect of moving a stellar mass
* Uplift mountains
* Llano Uplift
* Nemaha Uplift
Business
* Upli ...
. Rafting down the gorge from The Dalles
The Dalles is the largest city of Wasco County, Oregon, United States. The population was 16,010 at the 2020 census, and it is the largest city on the Oregon side of the Columbia River between the Portland Metropolitan Area, and Hermiston ...
was one of the most expensive and dangerous parts of the Oregon Trail
The Oregon Trail was a east–west, large-wheeled wagon route and emigrant trail in the United States that connected the Missouri River to valleys in Oregon. The eastern part of the Oregon Trail spanned part of what is now the state of Kans ...
, traveled by thousands of emigrant
Emigration is the act of leaving a resident country or place of residence with the intent to settle elsewhere (to permanently leave a country). Conversely, immigration describes the movement of people into one country from another (to permanentl ...
s to the Oregon Territory
The Territory of Oregon was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from August 14, 1848, until February 14, 1859, when the southwestern portion of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Oregon. O ...
, until the Barlow Road
The Barlow Road (at inception, Mount Hood Road) is a historic road in what is now the U.S. state of Oregon. It was built in 1846 by Sam Barlow and Philip Foster, with authorization of the Provisional Legislature of Oregon, and served as the la ...
opened in 1846 around the south side of Mount Hood
Mount Hood is a potentially active stratovolcano in the Cascade Volcanic Arc. It was formed by a subduction zone on the Pacific coast and rests in the Pacific Northwest region of the United States. It is located about east-southeast of Portl ...
. A wagon road was finally built through the gorge in the 1870s, when The Dalles and Sandy Wagon Road was constructed along the south shore from The Dalles to the Sandy River east of Portland. However, this road had steep (20%) grades and a crooked and narrow alignment, and it was not until 1882 that the Oregon Railway and Navigation Company
The Oregon Railroad and Navigation Company (OR&N) was a railroad that operated a rail network of running east from Portland, Oregon, United States, to northeastern Oregon, northeastern Washington, and northern Idaho. It operated from 1896 as a ...
finally opened a water-level route, partially destroying the wagon road. With the onset of the automobile and the good roads movement of the early 20th century, a road was once again needed, and Multnomah County
Multnomah County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 815,428. Multnomah County is part of the Portland–Vancouver– Hillsboro, OR–WA Metropolitan Statistical Area. Th ...
began constructing a 20-foot (6 m) roadway with 9% grades, but ran into difficulties relating to the railroad's location. At Shellrock Mountain to the east, long believed to be an impassable barrier, Governor Oswald West
Oswald West (May 20, 1873 – August 22, 1960) was an American politician, a Democrat, who served most notably as the 14th Governor of Oregon.
He was called "Os West" by Oregon writer Stewart Holbrook, who described him as "by all odds the m ...
used prison labor in 1912 to prove that it was possible to build a road, at least temporarily.
 The eventual highway was primarily designed by
The eventual highway was primarily designed by engineer
Engineers, as practitioners of engineering, are professionals who Invention, invent, design, analyze, build and test machines, complex systems, structures, gadgets and materials to fulfill functional objectives and requirements while considerin ...
and landscape architect
A landscape architect is a person who is educated in the field of landscape architecture. The practice of landscape architecture includes: site analysis, site inventory, site planning, land planning, planting design, grading, storm water manage ...
Samuel C. Lancaster, a lifelong friend of good roads promoter Samuel Hill
Samuel Hill (13 May 1857 – 26 February 1931), usually known as Sam Hill, was an American businessman, lawyer, railroad executive, and advocate of good roads. He substantially influenced the Pacific Northwest region's economic dev ...
. His first contribution to the Pacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
was as a consultant for Seattle
Seattle ( ) is a seaport city on the West Coast of the United States. It is the seat of King County, Washington. With a 2020 population of 737,015, it is the largest city in both the state of Washington and the Pacific Northwest region o ...
's Olmsted boulevard system, part of its preparations for the 1909 Alaska-Yukon-Pacific Exposition. In 1908, the two traveled to Europe for the First International Road Congress, where Hill represented the state of Washington. Hill was especially impressed by Switzerland
). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Luzern, Neuchâtel ...
's Axenstrasse
The Axenstrasse is an two-lane middle section with ongoing traffic between the A4 motorway and the A2 motorway, and part of European route E41 between the resort of Brunnen in the canton of Schwyz to the village of Flüelen in the canton of Uri ...
, a road built along Lake Lucerne
__NOTOC__
Lake Lucerne (german: Vierwaldstättersee, literally "Lake of the four forested settlements" (in English usually translated as ''forest cantons''), french: lac des Quatre-Cantons, it, lago dei Quattro Cantoni) is a lake in central S ...
in 1865 that included a windowed tunnel, and wanted to build a similar scenic highway through the Columbia River Gorge. With Lancaster's help, Hill built the experimental Maryhill Loops Road
The Maryhill Loops Road was an experimental road in south central Washington, United States, built by Good Roads promoter Samuel Hill with the help of engineer and landscape architect Samuel C. Lancaster. Laid in 1911 as the first asphalt road in ...
from the river east of the gorge up the Columbia Hills to his planned Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belief in each human's abili ...
utopian community
An intentional community is a voluntary residential community which is designed to have a high degree of social cohesion and teamwork from the start. The members of an intentional community typically hold a common social, political, relig ...
at Maryhill
Maryhill ( gd, Cnoc Màiri) is an area of the City of Glasgow in Scotland. Maryhill is a former burgh. Maryhill stretches over along Maryhill Road.
The far north west of the area is served by Maryhill railway station.
History
Hew Hill, ...
. The road was the first asphalt
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term ...
road in the state, designed with gradual horseshoe curve
A horseshoe curve is a class of climbing curve in a roadbed which reverses turn direction (inflection) twice on either side of a single tight curve that varies through an angle of about 180 degrees or more.
Such curves are more commonly found ...
s to avoid steep grades. However, Washington's lawmakers denied his request for a cross-state trunk route on the river's north bank, and Hill crossed the river to Oregon, the last of the states in the far Western U.S.
The Western United States (also called the American West, the Far West, and the West) is the region comprising the westernmost states of the United States. As American settlement in the U.S. expanded westward, the meaning of the term ''the Wes ...
to create a highway department. With the help of his life-size model at Maryhill, he convinced the state legislature to create the State Highway Commission in 1913, which would work with the counties
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
to build roads. The Multnomah County
Multnomah County is one of the 36 counties in the U.S. state of Oregon. As of the 2020 census, the county's population was 815,428. Multnomah County is part of the Portland–Vancouver– Hillsboro, OR–WA Metropolitan Statistical Area. Th ...
commissioners agreed later that year that the state should design the route to distance it from county politics
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studies ...
, and set aside an initial $75,000.
 In laying out the highway, Lancaster sought not only to create a transportation artery, but to make the gorge's "beautiful waterfalls, canyons, cliffs and mountain domes" accessible to "men from all climes". According to
In laying out the highway, Lancaster sought not only to create a transportation artery, but to make the gorge's "beautiful waterfalls, canyons, cliffs and mountain domes" accessible to "men from all climes". According to locating engineer
{{Short pages monitor
{{Authority control
Auto trails in the United States
Historic trails and roads in Oregon
All-American Roads
Columbia River Gorge
U.S. Route 30
National Historic Landmarks in Oregon
Named state highways in Oregon
Interstate 84 (Oregon–Utah)
Scenic highways in Oregon
State parks of Oregon
Roads on the National Register of Historic Places in Oregon
National Register of Historic Places in Multnomah County, Oregon
National Forest Scenic Byways
Transportation in Multnomah County, Oregon
Historic Civil Engineering Landmarks
Transportation in Wasco County, Oregon
Transportation in Hood River County, Oregon
National Register of Historic Places in Wasco County, Oregon
Tourist attractions in Multnomah County, Oregon
Tourist attractions in Wasco County, Oregon
Tourist attractions in Hood River County, Oregon
National Register of Historic Places in Hood River County, Oregon
Historic American Engineering Record in Oregon