Huītzilōpōchtli on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Huitzilopochtli (, ) is the
 There are a handful of origin mythologies describing the deity's beginnings. One story tells of the cosmic creation and Huitzilopochtli's role in it. According to this legend, he was the smallest son of four — his parents being the creator couple of the
There are a handful of origin mythologies describing the deity's beginnings. One story tells of the cosmic creation and Huitzilopochtli's role in it. According to this legend, he was the smallest son of four — his parents being the creator couple of the
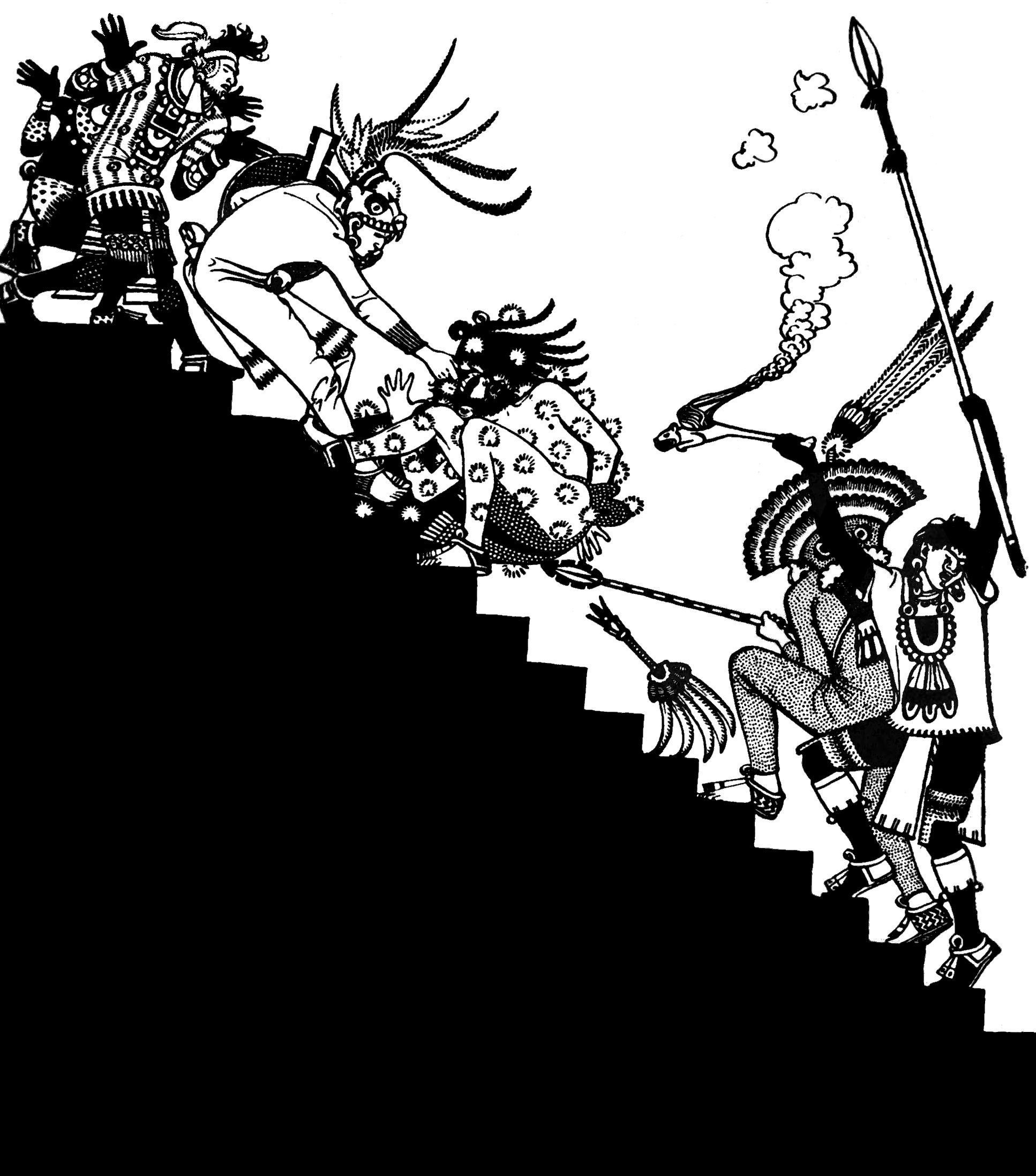 Warriors who died in battle or as sacrifices to Huitzilopochtli were called ''quauhteca'' (“the eagle’s people”). War was an important source of both human and material tribute. Human tribute was used for sacrificial purposes because human blood was believed to be extremely important, and thus powerful. According to Aztec mythology, Huitzilopochtli needed blood as sustenance in order to continue to keep his sister and many brothers at bay as he chased them through the sky.
Warriors who died in battle or as sacrifices to Huitzilopochtli were called ''quauhteca'' (“the eagle’s people”). War was an important source of both human and material tribute. Human tribute was used for sacrificial purposes because human blood was believed to be extremely important, and thus powerful. According to Aztec mythology, Huitzilopochtli needed blood as sustenance in order to continue to keep his sister and many brothers at bay as he chased them through the sky.
File:Codex Magliabechiano (141 cropped).jpg, Human sacrifice as shown in the
 There are several legends and myths of Huitzilopochtli. According to the ''
There are several legends and myths of Huitzilopochtli. According to the ''
The Gods and Goddesses of the Aztecs
{{DEFAULTSORT:Huitzilopochtli Avian humanoids Aztec gods Mesoamerican deities Solar gods War gods Tutelary gods
solar
Solar may refer to:
Astronomy
* Of or relating to the Sun
** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun
** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels")
** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate t ...
and war deity
A war god in mythology associated with war, combat, or bloodshed. They occur commonly in polytheistic religions.
Unlike most gods and goddesses in polytheistic religions, monotheistic deities have traditionally been portrayed in their mythologies ...
of sacrifice
Sacrifice is an act or offering made to a deity. A sacrifice can serve as propitiation, or a sacrifice can be an offering of praise and thanksgiving.
Evidence of ritual animal sacrifice has been seen at least since ancient Hebrews and Gree ...
in Aztec religion
The Aztec religion is a polytheistic and monistic pantheism in which the Nahua concept of '' teotl'' was construed as the supreme god Ometeotl, as well as a diverse pantheon of lesser gods and manifestations of nature. The popular religion te ...
. He was also the patron god
A tutelary (; also tutelar) is a deity or a spirit who is a guardian, patron, or protector of a particular place, geographic feature, person, lineage, nation, culture, or occupation. The etymology of "tutelary" expresses the concept of safety and ...
of the Aztec
The Aztecs ( ) were a Mesoamerican civilization that flourished in central Mexico in the Post-Classic stage, post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different Indigenous peoples of Mexico, ethnic groups of central ...
s and their capital city, Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th annivers ...
. He wielded Xiuhcoatl
In Aztec religion, Xiuhcōātl was a mythological serpent, regarded as the spirit form of Xiuhtecuhtli, the Aztec fire deity sometimes represented as an atlatl or a weapon wielded by Huitzilopochtli. Xiuhcoatl is a Classical Nahuatl word that t ...
, the fire serpent, as a weapon, thus also associating Huitzilopochtli with fire.
The Spaniards
Spaniards, or Spanish people, are a Romance-speaking ethnic group native to the Iberian Peninsula, primarily associated with the modern nation-state of Spain. Genetically and ethnolinguistically, Spaniards belong to the broader Southern a ...
recorded the deity's name as ''Huichilobos''. During their discovery and conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistad ...
, they wrote that human sacrifice
Human sacrifice is the act of killing one or more humans as part of a ritual, which is usually intended to please or appease deity, gods, a human ruler, public or jurisdictional demands for justice by capital punishment, an authoritative/prie ...
was common in worship ceremonies. These took place frequently throughout the region. When performed, typically multiple victims were sacrificed per day at any one of the numerous temples.
Etymology
There continues to be disagreement about the full significance of Huītzilōpōchtli's name. Generally it is agreed that there are two elements, "hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Cen ...
" and "left hand side." The name is often translated as "Left-Handed Hummingbird" or "Hummingbird of the South" on the basis that Aztec cosmology associated the south with the left hand side of the body.
However, Frances Karttunen
Frances Esther Karttunen (born 1942), also known as Frances Ruley Karttunen, is an American academic linguist, historian and author.
Education and career
She received her BA in 1964 from Harvard and her PhD in 1970 from Indiana University Bloom ...
points out that in Classical Nahuatl
Classical Nahuatl, also known simply as Aztec or Codical Nahuatl (if it refers to the variants employed in the Mesoamerican Codices through the medium of Aztec Hieroglyphs) and Colonial Nahuatl (if written in Post-conquest documents in the Lat ...
compounds are usually head final, implying that a more accurate translation may be "the left (or south) side of the hummingbird".
The hummingbird was spiritually important in Aztec culture. Diego Durán
Diego Durán (c. 1537 – 1588) was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, ''The History of the Indies of New Spain'', a book that was much criticised in ...
describes what appears to be the hummingbird hibernating in a tree, somewhat like the common poorwill
The common poorwill (''Phalaenoptilus nuttallii'') is a nocturnal bird of the family Caprimulgidae, the nightjars. It is found from British Columbia and southeastern Alberta, through the western United States to northern Mexico. The bird's habi ...
does. He writes, "It appears to be dead, but at the advent of spring, ... the little bird is reborn."
Origin stories
 There are a handful of origin mythologies describing the deity's beginnings. One story tells of the cosmic creation and Huitzilopochtli's role in it. According to this legend, he was the smallest son of four — his parents being the creator couple of the
There are a handful of origin mythologies describing the deity's beginnings. One story tells of the cosmic creation and Huitzilopochtli's role in it. According to this legend, he was the smallest son of four — his parents being the creator couple of the Ōmeteōtl
() ("Two-God") is a name used to refer to the pair of Aztec deities and , also known as and . translates as "two" or "dual" in Nahuatl and translates as "Divinity". Ometeotl was one as the first divinity, and Ometecuhtli and Omecihuatl ...
(Tōnacātēcuhtli
In Aztec mythology, Tonacatecuhtli was a creator and fertility god, worshipped for populating the earth and making it fruitful. Most Colonial-era manuscripts equate him with Ometeotl, Ōmetēcuhtli. His consort was Tonacacihuatl.
Tonacateuchtli i ...
and Tōnacācihuātl) while his brothers were Quetzalcōātl
Quetzalcoatl () (Nahuatl: "Feathered Serpent") is a deity in Aztecs, Aztec culture and Mesoamerican literature, literature. Among the Aztecs, he was related to wind, Venus, Sun, merchants, arts, crafts, knowledge, and learning. He was also the ...
("Precious Serpent" or "Quetzal-Feathered Serpent"), Xīpe Tōtec ("Our Lord Flayed"), and Tezcatlipōca ("Smoking Mirror"). His mother and father instructed him and Quetzalcoatl to bring order to the world. Together, Huitzilopochtli and Quetzalcoatl created fire, the first male and female humans, the Earth, and the Sun.
Another origin story tells of a fierce goddess, Coatlicue, being impregnated as she was sweeping by a ball of feathers on Mount Coatepec ("Serpent Hill"; near Tula, Hidalgo
Hidalgo may refer to:
People
* Hidalgo (nobility), members of the Spanish nobility
* Hidalgo (surname)
Places
Mexico
:''Most, if not all, named for Miguel Hidalgo y Costilla (1753–1811)''
* Hidalgo (state), in central Mexico
* Hidalgo, Coah ...
). Her other children, who were already fully grown, were the four hundred male Centzonuitznaua and the female deity Coyolxauhqui. These children, angered by the manner by which their mother became impregnated, conspired to kill her. Huitzilopochtli burst forth from his mother's womb in full armor and fully grown, or in other versions of the story, burst forth from the womb and immediately put on his gear. He attacked his older brothers and sister, defending his mother by beheading his sister and casting her body from the mountain top. He also chased after his brothers, who fled from him and became scattered all over the sky.
Huitzilopochtli is seen as the sun in mythology, while his many male siblings are perceived as the stars and his sister as the moon. In the Aztec worldview, this is the reason why the Sun is constantly chasing the Moon and stars. It is also why it was so important to provide tribute for Huitzilopochtli as sustenance for the Sun. If Huitzilopochtli did not have enough strength to battle his siblings, they would destroy their mother and thus the world.
History
Huitzilopochtli was the patron god of theMexica
The Mexica (Nahuatl: ; singular ) are a Nahuatl-speaking people of the Valley of Mexico who were the rulers of the Triple Alliance, more commonly referred to as the Aztec Empire. The Mexica established Tenochtitlan, a settlement on an island ...
tribe. Originally, he was of little importance to the Nahuas
The Nahuas ( ) are a Uto-Nahuan ethnicity and one of the Indigenous people of Mexico, with Nahua minorities also in El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Nicaragua, and Costa Rica. They comprise the largest Indigenous group in Mexico, as well as ...
, but after the rise of the Aztecs, Tlacaelel
Tlacaelel I (1397 – 1487) ( , "Man of Strong Emotions," from "tlācatl," person and "ēllelli," strong emotion) was the principal architect of the Aztec Triple Alliance and hence the Mexica (Aztec) empire. He was the son of Emperor Huitzil ...
reformed their religion and put Huitzilopochtli at the same level as Quetzalcoatl, Tlaloc, and Tezcatlipoca
Tezcatlipoca ( ) or Tezcatl Ipoca was a central deity in Aztec religion. He is associated with a variety of concepts, including the night sky, hurricanes, obsidian, and conflict. He was considered one of the four sons of Ometecuhtli and Omec ...
, making him a solar god. Through this, Huitzilopochtli replaced Nanahuatzin
In Aztec mythology, the god Nanahuatzin or Nanahuatl (or Nanauatzin, the suffix -tzin implies respect or familiarity; ), the most humble of the gods, sacrificed himself in fire so that he would continue to shine on Earth as the Sun, thus becoming ...
, the solar god from the Nahua legend. Huitzilopochtli was said to be in a constant struggle with the darkness and required nourishment in the form of sacrifices to ensure the sun would survive the cycle of 52 years, which was the basis of many Mesoamerican myths.
There were 18 especially holy festive days, and only one of them was dedicated to Huitzilopochtli. This celebration day, known as Toxcatl, falls within the fifteenth month of the Mexican calendar. During the festival, captives and slaves were brought forth and slain ceremoniously.
In the book ''El Calendario Mexica y la Cronografia'' by Rafael Tena and published by the National Institute of Anthropology and History of Mexico, the author gives the last day of the Nahuatl month Panquetzaliztli as the date of the celebration of the rebirth of the Lord Huitzilopochtli on top of Coatepec (Snake Hill); December 9 in the Julian calendar
The Julian calendar is a solar calendar of 365 days in every year with an additional leap day every fourth year (without exception). The Julian calendar is still used as a religious calendar in parts of the Eastern Orthodox Church and in parts ...
or December 19 in the Gregorian calendar
The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian cale ...
with the variant of December 18 in leap year
A leap year (also known as an intercalary year or bissextile year) is a calendar year that contains an additional day (or, in the case of a lunisolar calendar, a month) compared to a common year. The 366th day (or 13th month) is added to keep t ...
s.
Sacrifice
Ritual sacrifice and self bloodletting were key offerings to Huitzilopochtli. The Aztecs performed ritual self-sacrifice (also called autosacrifice or blood-letting) on a daily basis. The Aztecs believed that Huitzilopochtli needed daily nourishment (''tlaxcaltiliztli'') in the form of human blood and hearts and that they, as “people of the sun,” were required to provide Huitzilopochtli with his sustenance. When the Aztecs sacrificed people to Huitzilopochtli, the victim would be placed on a sacrificial stone. The priest would then cut through the abdomen with an obsidian or flint blade. The heart would be torn out still beating and held towards the sky in honor to the Sun-God. The body would then be pushed down the pyramid where the Coyolxauhqui stone could be found. The Coyolxauhqui Stone recreates the story of Coyolxauhqui, Huitzilopochtli's sister who was dismembered at the base of a mountain, just as the sacrificial victims were. The body would be carried away and either cremated or given to the warrior responsible for the capture of the victim. He would either cut the body in pieces and send them to important people as an offering, or use the pieces for ritualcannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is also well document ...
. The warrior would thus ascend one step in the hierarchy of the Aztec social classes, a system that rewarded successful warriors.
During the festival of Panquetzaliztli, of which Huitzilopochtli was the patron, sacrificial victims were adorned in the manner of Huitzilopochtli's costume and blue body paint, before their hearts would be sacrificially removed. Representations of Huitzilopochtli called teixiptla were also worshipped, the most significant being the one at the Templo Mayor which was made of dough mixed with sacrificial blood.
 Warriors who died in battle or as sacrifices to Huitzilopochtli were called ''quauhteca'' (“the eagle’s people”). War was an important source of both human and material tribute. Human tribute was used for sacrificial purposes because human blood was believed to be extremely important, and thus powerful. According to Aztec mythology, Huitzilopochtli needed blood as sustenance in order to continue to keep his sister and many brothers at bay as he chased them through the sky.
Warriors who died in battle or as sacrifices to Huitzilopochtli were called ''quauhteca'' (“the eagle’s people”). War was an important source of both human and material tribute. Human tribute was used for sacrificial purposes because human blood was believed to be extremely important, and thus powerful. According to Aztec mythology, Huitzilopochtli needed blood as sustenance in order to continue to keep his sister and many brothers at bay as he chased them through the sky.
Codex Magliabechiano
The Codex Magliabechiano is a pictorial Aztec codex created during the mid-16th century, in the early Spanish colonial period. It is representative of a set of codices known collectively as the ''Magliabechiano Group (others in the group include ...
File:Kodeks tudela 21.jpg, '' Codex Tudela''.
The Templo Mayor
The most important and powerful structure in Tenochtitlan is the Templo Mayor. Its importance as the sacred center is reflected in the fact that it was enlarged frontally eleven times during the two hundred years of its existence. The Great Temple of Tenochtitlan was dedicated to Huitzilopochtli and Tlaloc, the rain god. 16th century Dominican friarDiego Durán
Diego Durán (c. 1537 – 1588) was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, ''The History of the Indies of New Spain'', a book that was much criticised in ...
wrote, "These two gods were always meant to be together, since they were considered companions of equal power." The Templo Mayor consisted of a pyramidal platform, on top of which were twin temples, one painted with blue stripes and the other painted red. The red shrine, on the south side, was dedicated to Huitzilopochtli, while the blue shrine to the north was dedicated to Tlaloc. That these two deities were on opposite sides of the Great Temple is very representative of the Aztec dichotomy that the deities represent. Tlaloc, as the rain god, represented fertility and growth, while Huitzilopochtli, as the sun god, represented war and sacrifice.
The Coyolxauhqui stone
TheCoyolxauhqui stone
The Coyolxāuhqui Stone is a carved, circular Aztec stone, depicting the mythical being Coyolxāuhqui ("Bells-Her-Cheeks"), in a state of dismemberment and decapitation by her brother, the patron deity of the Aztecs, Huītzilōpōchtli, Huitzilopo ...
was found directly at the base of the stairway leading up to Huitzilopochtli's temple. On both sides of the stairway's base were two large grinning serpent heads. The image is clear. The Templo Mayor is the image of Coatepec or Serpent Mountain where the divine battle took place. Just as Huitzilopochtli triumphed at the top of the mountain, while his sister was dismembered and fell to pieces below, so Huitzilopochtli's temple and icon sat triumphantly at the top of the Templo Mayor while the carving of the dismembered goddess lay far below. This drama of sacrificial dismemberment was vividly repeated in some of the offerings found around the Coyolxauhqui stone in which the decapitated skulls of young women were placed. This would suggest that there was a ritual reenactment of the myth at the dedication of the stone sometime in the latter part of the fifteenth century.
Mythology
Many gods in the pantheon of deities of the Aztecs were inclined to have a fondness for a particular aspect of warfare. However, Huitzilopochtli was known as the primary god of war in ancient Mexico. Since he was the patron god of the Mexica, he was credited with both the victories and defeats that the Mexica people had on the battlefield. The people had to make sacrifices to him to protect the Aztec from infinite night. According toMiguel León-Portilla
Miguel León-Portilla (22 February 1926 – 1 October 2019) was a Mexican anthropologist and historian, specializing in Aztec culture and literature of the pre-Columbian and colonial eras. Many of his works were translated to English and he was ...
, in this new vision from Tlacaelel, the warriors that died in battle and women who died in childbirth would go to serve Huitzilopochtli in his palace (in the south, or left). From a description in the '' Florentine Codex'', Huitzilopochtli was so bright that the warrior souls had to use their shields to protect their eyes. They could only see the god through the arrow holes in their shields, so it was the bravest warrior who could see him best. Warriors and women who died during childbirth were transformed into hummingbirds upon death and went to join Huitzilopochtli.
As the precise studies of Johanna Broda have shown, the creation myth consisted of “several layers of symbolism, ranging from a purely historical explanation to one in terms of cosmovision and possible astronomical content.” At one level, Huitzilopochtli's birth and victorious battle against the four hundred children represent the character of the solar region of the Aztecs in that the daily sunrise was viewed as a celestial battle against the moon (Coyolxauhqui) and the stars (Centzon Huitznahua). Another version of the myth, found in the historical chronicles of Diego Duran and Alvarado Tezozomoc, tells the story with strong historical allusion and portrays two Aztec factions in ferocious battle. The leader of one group, Huitzilopochtli, defeats the warriors of a woman leader, Coyolxauh, and tears open their breasts and eats their hearts. Both versions tell of the origin of human sacrifice at the sacred place, Coatepec, during the rise of the Aztec nation and at the foundation of Tenochtitlan.
Origins of Tenochtitlan
 There are several legends and myths of Huitzilopochtli. According to the ''
There are several legends and myths of Huitzilopochtli. According to the ''Aubin Codex
The Aubin Codex is an 81-leaf Aztec codices, Aztec codex written in alphabetic Nahuatl on paper from Europe. Its textual and pictorial contents represent the history of the Aztec peoples who fled Aztlán, lived during the Spanish conquest of th ...
'', the Aztecs originally came from a place called Aztlán
Aztlán (from or romanized ''Aztlán'', ) is the ancestral home of the Aztec peoples. The word "Aztec" was derived from the Nahuatl a''ztecah'', meaning "people from Aztlán." Aztlán is mentioned in several ethnohistorical sources dating from t ...
. They lived under the ruling of a powerful elite called the " Azteca Chicomoztoca". Huitzilopochtli ordered them to abandon Aztlán and find a new home. He also ordered them never to call themselves Aztec; instead they should be called "Mexica." Huitzilopochtli guided them through the journey. For a time, Huitzilopochtli left them in the charge of his sister, Malinalxochitl, who, according to legend, founded Malinalco, but the Aztecs resented her ruling and called back Huitzilopochtli. He put his sister to sleep and ordered the Aztecs to leave the place. When she woke up and realized she was alone, she became angry and desired revenge. She gave birth to a son called Copil. When he grew up, he confronted Huitzilopochtli, who had to kill him. Huitzilopochtli then took his heart out and threw it in the middle of Lake Texcoco
Lake Texcoco (; ) was a natural saline lake within the ''Anahuac'' or Valley of Mexico. Lake Texcoco is best known for an island situated on the western side of the lake where the Mexica built the city of Mēxihco Tenōchtitlan, which would la ...
. Many years later, Huitzilopochtli ordered the Aztecs to search for Copil's heart and build their city over it. The sign would be an eagle perched on a cactus, eating a precious serpent, and the place would become their permanent home. After much traveling, they arrived at the area which would eventually be Tenochtitlan
, also known as Mexico-Tenochtitlan, was a large Mexican in what is now the historic center of Mexico City. The exact date of the founding of the city is unclear, but the date 13 March 1325 was chosen in 1925 to celebrate the 600th annivers ...
on an island in the Lago Texcoco of the Valley of Mexico.
Iconography
In art andiconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
, Huitzilopochtli could be represented either as a hummingbird
Hummingbirds are birds native to the Americas and comprise the Family (biology), biological family Trochilidae. With approximately 366 species and 113 genus, genera, they occur from Alaska to Tierra del Fuego, but most species are found in Cen ...
or as an anthropomorphic figure with just the feathers of such on his head and left leg, a black face, and holding a scepter shaped like a snake and a mirror. According to the Florentine Codex, Huitzilopochtli's body was painted blue. In the great temple his statue was decorated with cloth, feathers, gold, and jewels, and was hidden behind a curtain to give it more reverence and veneration. Another variation lists him having a face that was marked with yellow and blue stripes and he carries around the fire serpent Xiuhcoatl with him. According to legend, the statue was supposed to be destroyed by the soldier Gil González de Benavides, but it was rescued by a man called Tlatolatl. The statue appeared some years later during an investigation by Bishop Zummáraga in the 1530s, only to be lost again. There is speculation that the statue still exists in a cave somewhere in the Anahuac Valley
The Valley of Mexico (; ), sometimes also called Basin of Mexico, is a highlands plateau in central Mexico. Surrounded by mountains and volcanoes, the Valley of Mexico was a centre for several pre-Columbian civilizations including Teotihuacan, ...
.
He always had a blue-green hummingbird helmet in any of the depictions found. In fact, his hummingbird helmet was the one item that consistently defined him as Huitzilopochtli, the sun god, in artistic renderings. He is usually depicted as holding a shield adorned with balls of eagle feathers, a homage to his mother and the story of his birth. He also holds the blue snake, Xiuhcoatl
In Aztec religion, Xiuhcōātl was a mythological serpent, regarded as the spirit form of Xiuhtecuhtli, the Aztec fire deity sometimes represented as an atlatl or a weapon wielded by Huitzilopochtli. Xiuhcoatl is a Classical Nahuatl word that t ...
, in his hand in the form of an atlatl
A spear-thrower, spear-throwing lever, or ''atlatl'' (pronounced or ; Classical Nahuatl, Nahuatl ''ahtlatl'' ) is a tool that uses leverage to achieve greater velocity in Dart (missile), dart or javelin-throwing, and includes a Plain bearing, b ...
.
Calendar
Diego Durán
Diego Durán (c. 1537 – 1588) was a Dominican friar best known for his authorship of one of the earliest Western books on the history and culture of the Aztecs, ''The History of the Indies of New Spain'', a book that was much criticised in ...
described the festivities for Huitzilopochtli. Panquetzaliztli (November 9 to November 28) was the Aztec month dedicated to Huitzilopochtli. People decorated their homes and trees with paper flags; there were ritual races, processions, dances, songs, prayers, and finally human sacrifices. This was one of the more important Aztec festivals, and the people prepared for the whole month. They fasted or ate very little; a statue of the god was made with amaranth
''Amaranthus'' is a cosmopolitan distribution, cosmopolitan group of more than 50 species which make up the genus of annual plant, annual or short-lived perennial plants collectively known as amaranths. Some names include "prostrate pigweed" an ...
''(huautli)'' seeds and honey, and at the end of the month, it was cut into small pieces so everybody could eat a little piece of the god. After the Spanish conquest, cultivation of amaranth was outlawed, while some of the festivities were subsumed into the Christmas
Christmas is an annual festival commemorating Nativity of Jesus, the birth of Jesus Christ, observed primarily on December 25 as a Religion, religious and Culture, cultural celebration among billions of people Observance of Christmas by coun ...
celebration.
According to the '' Ramírez Codex'', in Tenochtitlan approximately sixty prisoners were sacrificed at the festivities. Sacrifices were reported to be made in other Aztec cities, including Tlatelolco, Xochimilco
Xochimilco (; ) is a borough () of Mexico City. The borough is centered on the formerly independent city of Xochimilco, which was established on what was the southern shore of Lake Xochimilco in the precolonial period.
Today, the borough cons ...
, and Texcoco, but the number is unknown, and no currently available archeological findings confirm this.
For the reconsecration of Great Pyramid of Tenochtitlan in 1487, dedicated to Tlaloc and Huitzilopochtli, the Aztecs reported that they sacrificed about 20,400 prisoners over the course of four days. While accepted by some scholars, this claim also has been considered Aztec propaganda. There were 19 altars in the city of Tenochtitlan.
See also
*History of Mexico City
The history of Mexico City stretches back to its founding ca. 1325 C.E as the Mexica city-state of Tenochtitlan, which evolved into the senior partner of the Aztec Empire, Aztec Triple Alliance that dominated central Mexico immediately prior to ...
* Human sacrifice in Aztec culture
Human sacrifice was a common practice in many parts of Mesoamerica. The rite was not new to the Aztecs when they arrived at the Valley of Mexico, nor was it something unique to pre-Columbian Mexico. Other Mesoamerican cultures, such as the Puré ...
* List of solar deities
A solar deity is a god or goddess who represents the Sun, or an aspect of it, usually by its perceived power and strength. Solar deities and Sun worship can be found throughout most of recorded history in various forms. The following is a list of ...
Citations
General and cited references
* * * * * * * * * * Elzey, Wayne (1991). "A Hill on a Land Surrounded by Water: An Aztec Story of Origin and Destiny". ''History of Religions'' 31(2): 105–149 * Klein, Cecelia, F. (2008). "A New Interpretation of the Aztec Statue Called Coatlicue, 'Snakes-Her-Skirt Ethnohistory 55(2) * * * * * * * *External links
The Gods and Goddesses of the Aztecs
{{DEFAULTSORT:Huitzilopochtli Avian humanoids Aztec gods Mesoamerican deities Solar gods War gods Tutelary gods