|
Tlatelolco (altepetl)
Tlatelolco ( , ) (also called Mexico Tlatelolco) was a pre-Columbian altepetl, or city-state, in the Valley of Mexico. Its inhabitants, known as the ''Tlatelolca'', were part of the Mexica, a Nahuatl-speaking people who arrived in what is now central Mexico in the 13th century. The Mexica settled on an island in Lake Texcoco and founded the ''altepetl'' of Tenochtitlan, Mexico-Tenochtitlan on the southern portion of the island. In 1337, a group of dissident Mexica broke away from the Tenochca leadership in Tenochtitlan and founded Mexico-Tlatelolco on the northern portion of the island. Tenochtitlan was closely tied with its sister city, which was largely dependent on the market of Tlatelolco, the most important site of commerce in the area. History In 1337, thirteen years after the foundation of Tenochtitlan, the Tlatelolca declared themselves independent from the Tenochca and inaugurated their first independent ''tlatoani'' (dynastic ruler). Under the king Quaquapitzahuac (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quaquapitzahuac
Quaquapitzahuac (died 1417) was the first ruler of the Aztec city of Tlatelolco (altepetl), Tlatelolco. His name, which means "Slender Horn", was pronounced in Classical Nahuatl, and is also spelled Cuacuauhpitzahuac, Cuacuapitzahuac, and Quaquauhpitzahuac. His nephew was Tecollotzin. Reign Quaquapitzahuac was appointed by his father, Tezozomoc (Azcapotzalco), Tezozomoc, in 1376 to serve as the first tlatoani of Tlatelolco, thus beginning that city's royal house. Under his rule, Tlatelolcan armies participated in various conquests on behalf of the city of Azcapotzalco (altepetl), Azcapotzalco, winning the right to receive tribute from the conquered towns in the east of the valley of Mexico. Family He was a son of famous Tezozomoc (Azcapotzalco), Tezozomoc, the Tepanec ruler of Azcapotzalco. He was a brother of the kings Aculnahuacatl Tzaqualcatl, Tzihuactlayahuallohuatzin, Maxtla, Epcoatl and the queen Ayauhcihuatl. His wife was called Acxocueitl. Upon his death in 1417, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tlatoani
''Tlahtoāni'' ( , "ruler, sovereign"; plural ' ) is a historical title used by the dynastic rulers of (singular ''āltepētl'', often translated into English as "city-state"), autonomous political entities formed by many pre-Columbian Nahuatl-speaking peoples in the Valley of Mexico during the Postclassic Period. The title of ' (, "great ruler, emperor") was used by the rulers of the Aztec Empire, an alliance between the ''āltepēmeh'' of Tenochtitlan, Tetzcoco, and Tlacopan. Each ''āltepētl'' had its own ''tlahtoāni'' who would concurrently function as its ruler, high priest and commander-in-chief. The ''tlahtoāni'' wielded ultimate authority over all land within the ''āltepētl'', overseeing tribute collection, market activities, temple affairs, and the resolution of judicial disputes. Typically a dynastic ruler hailing from the royal lineage, the ''tlahtoāni'' served for life. However, in certain instances, a council of nobles, elders, and priests could elect a ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Conquest Of The Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire was a pivotal event in the history of the Americas, marked by the collision of the Aztec Triple Alliance and the Spanish Empire. Taking place between 1519 and 1521, this event saw the Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés, and his small army of European soldiers and numerous indigenous allies, overthrowing one of the most powerful empires in Mesoamerica. Led by the Aztec ruler Moctezuma II, the Aztec Empire had established dominance over central Mexico through military conquest and intricate alliances. Because the Aztec Empire ruled via hegemonic control by maintaining local leadership and relying on the psychological perception of Aztec power — backed by military force — the Aztecs normally kept subordinate rulers compliant. This was an inherently unstable system of governance, as this situation could change with any alteration in the status quo. A combination of factors including superior weaponry, strategic alliances with oppresse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire, sometimes referred to as the Hispanic Monarchy (political entity), Hispanic Monarchy or the Catholic Monarchy, was a colonial empire that existed between 1492 and 1976. In conjunction with the Portuguese Empire, it ushered in the European Age of Discovery. It achieved a global scale, controlling vast portions of the Americas, Africa, various islands in Asia and Oceania, as well as territory in other parts of Europe. It was one of the most powerful empires of the early modern period, becoming known as "the empire on which the sun never sets". At its greatest extent in the late 1700s and early 1800s, the Spanish Empire covered , making it one of the List of largest empires, largest empires in history. Beginning with the 1492 arrival of Christopher Columbus and continuing for over three centuries, the Spanish Empire would expand across the Caribbean Islands, half of South America, most of Central America and much of North America. In the beginning, Portugal was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Tenochtitlan
The fall of Tenochtitlan, the capital of the Aztec Empire, was an important event in the Spanish conquest of the empire. It occurred in 1521 following extensive negotiations between local factions and Spanish conquistador Hernán Cortés. He was aided by La Malinche, his interpreter and companion, and by thousands of indigenous allies, especially Tlaxcaltec warriors. Although numerous battles were fought between the Aztec Empire and the Spanish-led coalition, which was composed mainly of Tlaxcaltec men, it was the siege of Tenochtitlan that directly led to the fall of the Aztec civilization and the ensuing sacking and violence against the survivors. The indigenous population at the time was devastated due to a smallpox epidemic, which killed much of its leadership. Because smallpox had been endemic in Spain for centuries, the Spanish had developed an acquired immunity and were affected relatively little in the epidemic. The conquest of the Aztec Empire was a critical s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquis of the Valley of Oaxaca (December 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of what is now mainland Mexico under the rule of the King of Castile in the early 16th century. Cortés was part of the generation of Spanish explorers and conquistadors who began the first phase of the Spanish colonization of the Americas. Born in Medellín, Spain, to a family of lesser nobility, Cortés chose to pursue adventure and riches in the New World. He went to Hispaniola and later to Cuba, where he received an ''encomienda'' (the right to the labor of certain subjects). For a short time, he served as ''alcalde'' (magistrate) of the second Spanish town founded on the island. In 1519, he was elected captain of the third expedition to the mainland, which he partly funded. His enmity with the governor of Cuba, Diego Velázquez de Cué ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bernal Díaz Del Castillo
Bernal Díaz del Castillo ( 1492 – 3 February 1584) was a Spanish conquistador who participated as a soldier in the conquest of the Aztec Empire under Hernán Cortés and late in his life wrote an account of the events. As an experienced soldier of fortune, he had already participated in expeditions to Tierra Firme, Cuba, and to Yucatán before joining Cortés. In his later years, Castillo was an encomendero and governor in Guatemala where he wrote his memoirs called '' The True History of the Conquest of New Spain''. He began his account of the conquest almost thirty years after the events and later revised and expanded it in response to Cortés' letters to the king, which Castillo viewed as Cortés taking most of the credit for himself while minimizing the efforts and sacrifices of the other Spaniards and their Indigenous allies such as the Tlaxcaltec during the expedition. In addition to this, Castillo disputed the biography published by Cortés' chaplain Francisco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conquistador
Conquistadors (, ) or conquistadores (; ; ) were Spanish Empire, Spanish and Portuguese Empire, Portuguese colonizers who explored, traded with and colonized parts of the Americas, Africa, Oceania and Asia during the Age of Discovery. Sailing beyond the Iberian Peninsula, they established numerous Colony, colonies and trade routes, and brought much of the "New World" under the dominion of Spain and Portugal. After Christopher Columbus's arrival in the West Indies in 1492, the Spanish, usually led by Hidalgo (nobility), hidalgos from the west and south of Spain, began building a colonial empire in the Caribbean using colonies such as Captaincy General of Santo Domingo, Santo Domingo, Captaincy General of Cuba, Cuba, and Captaincy General of Puerto Rico, Puerto Rico as their main bases. From 1519 to 1521, Hernán Cortés led the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, ruled by Moctezuma II. From the territories of the Aztec Empire, conquistadors expanded Spanish rule to northern Ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historia Verdadera De La Conquista De La Nueva España
() is a first-person narrative written in 1568 by military adventurer, conquistador, and colonist settler Bernal Díaz del Castillo (1492–1584), who served in three Mexican expeditions: those of Francisco Hernández de Córdoba (1517) to the Yucatán peninsula; the expedition of Juan de Grijalva (1518); and the expedition of Hernán Cortés (1519) in the Valley of Mexico. The history relates his participation in the conquest of the Aztec Empire. Late in life, when Díaz del Castillo was in his 60s, he finished his first-person account of the Spanish conquest of the West Indies and the Aztec Empire. He wrote ''The True History of the Conquest of New Spain'' to defend the story of the common-soldier conquistador within the histories about the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. He presents his narrative as an alternative to the critical writings of Bartolomé de Las Casas, whose descriptions of Spanish treatment of native peoples emphasized the cruelty of the conquest. H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Broken Spears
''The Broken Spears: The Aztec Account of the Conquest of Mexico'' (Spanish title: ''Visión de los vencidos: Relaciones indígenas de la conquista''; lit. "Vision of the Defeated: Indigenous relations of the conquest") is a book by Mexican historian Miguel León-Portilla, translating selections of Nahuatl-language accounts of the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire. It was first published in Spanish in 1959, and in English in 1962. The most recent English edition was published in 2007 (). The English-language title, "The Broken Spears", comes from a phrase in one version ( BnF MS 22bis) of the Annals of Tlatelolco, ''xaxama oc omitl''. According to historian James Lockhart, this is a mistranslation resulting from confusion between the Nahuatl words ''mitl'' "arrow", "dart" or "spear", and ''omitl'' "bone"; an alternative translation is thus "broken bones". Synopsis The monograph ''Broken Spears'' is structured through three distinct sections: the first is the overall introdu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
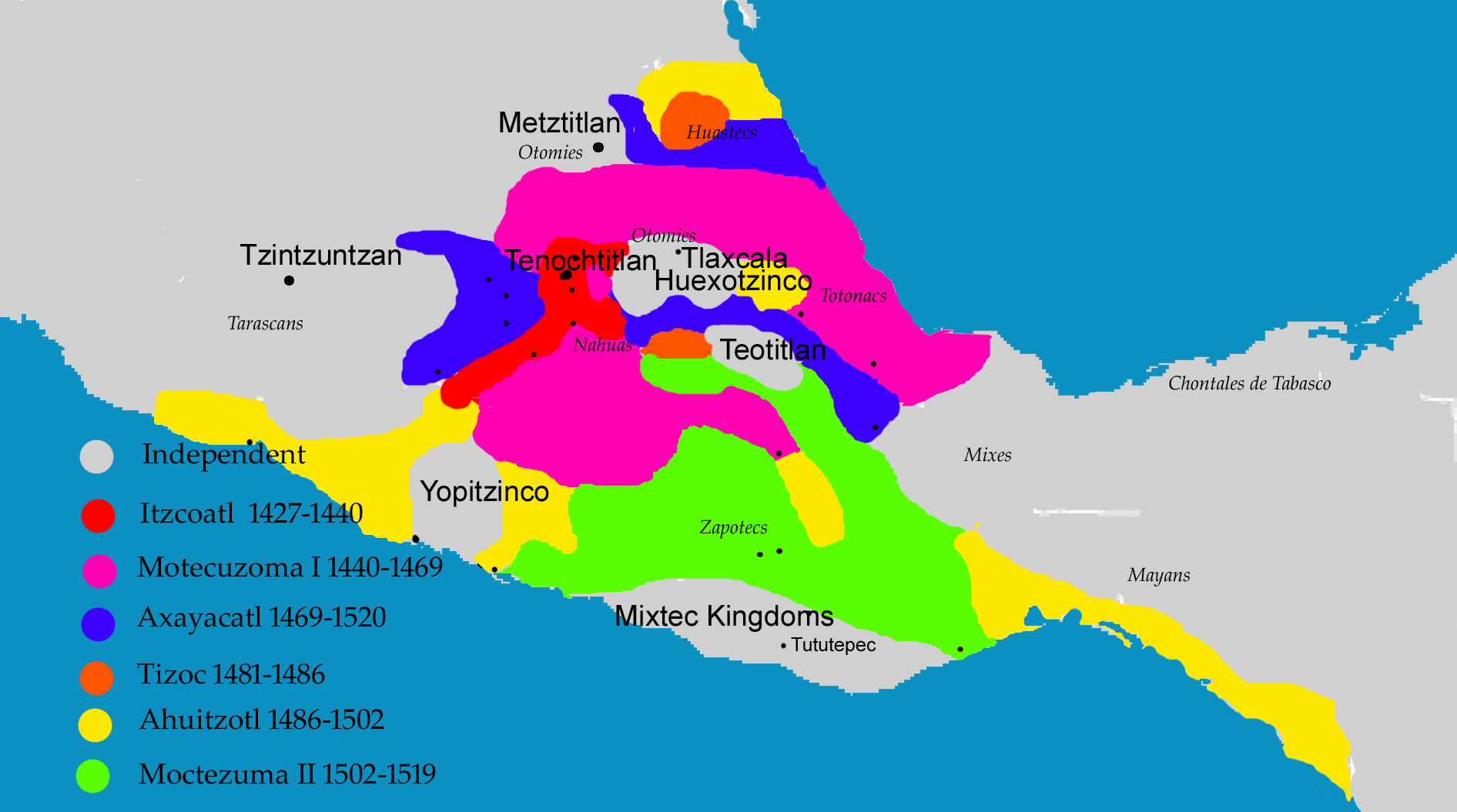
Axayacatl
Axayacatl (; ; ; meaning "face of water"; –1481) was the sixth of the of Tenochtitlan and Emperor of the Aztec Triple Alliance. Biography Early life and background Axayacatl was a son of the princess Atotoztli II and her cousin, prince Tezozomoc (son of Itzcoatl), Tezozomoc. He was a grandson of the Emperors Moctezuma I and Itzcoatl. He was a descendant of the king Cuauhtototzin. He was a successor of Moctezuma and his brothers were Emperors Tizoc and Ahuitzotl and his sister was the Queen Chalchiuhnenetzin. He was an uncle of the Emperor Cuauhtémoc and father of Emperors Moctezuma II and Cuitláhuac. Rise to power During his youth, his military prowess gained him the favor influential figures such as Nezahualcoyotl (tlatoani), Nezahualcoyotl and Tlacaelel I, and thus, upon the death of Moctezuma I in 1469, he was chosen to ascend to the throne, much to the displeasure of his two older brothers, Tizoc and Ahuitzotl. It is also important that the Aztec calendar stone, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chalco (altépetl)
Chālco was a complex pre-Columbian Nahua '' altepetl'' or confederacy in central Mexico. It was divided into the four sub-altepetl of Tlalmanalco/ Tlacochcalco, Amaquemecan, Tenanco Texopalco Tepopolla and Chimalhuacan-Chalco, which were themselves further subdivided into ''altepetl tlayacatl'', each with its own ''tlatoani'' (king). Its inhabitants were known as the ''Chālcatl'' (singular) or ''Chālcah'' (plural). In the 14th and early 15th centuries, flower wars were fought between the Chalca and the Aztecs. Serious war erupted in 1446. According to the Amaqueme historian Chimalpahin, this was because the Chalca refused a Mexica demand to contribute building materials for the temple of Huitzilopochtli. Chalco was finally conquered by the Aztecs under Moctezuma I in or around 1465, and the kings of Chalco were exiled to Huexotzinco. The rulerships were restored by Tizoc in 1486, who installed new ''tlatoque''. This was achieved, in part, by the diplomacy work car ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |