History Of White Americans In Baltimore on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of White Americans in Baltimore dates back to the 17th century when the first white European colonists came to what is now Maryland and established the
The history of White Americans in Baltimore dates back to the 17th century when the first white European colonists came to what is now Maryland and established the
 According to linguists, the "
According to linguists, the "
''Maryland Humanities Council''. May 11, 2019. White working-class families who migrated out of Baltimore city into
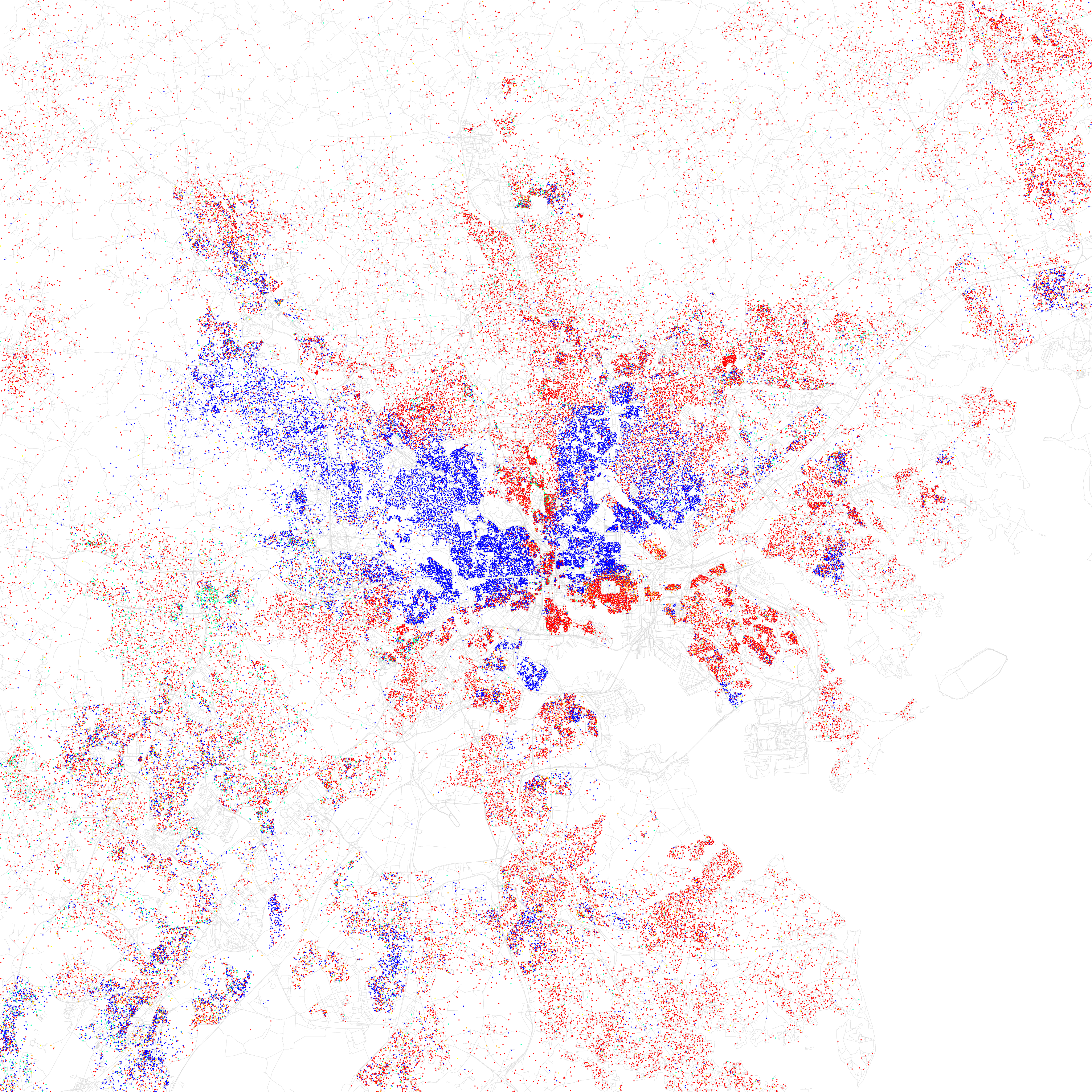
Percentage of Whites in Baltimore, MD by Zip CodeThe Stations of Whiteness in Baltimore
{{White people Central Asian American culture Ethnic groups in Baltimore European-American culture in Baltimore Middle Eastern-American culture in Maryland North African American culture
 The history of White Americans in Baltimore dates back to the 17th century when the first white European colonists came to what is now Maryland and established the
The history of White Americans in Baltimore dates back to the 17th century when the first white European colonists came to what is now Maryland and established the Province of Maryland
The Province of Maryland was an English and later British colony in North America that existed from 1632 until 1776, when it joined the other twelve of the Thirteen Colonies in rebellion against Great Britain and became the U.S. state of Maryland ...
on what was then Native American land. White Americans in Baltimore are Baltimoreans "having origins in any of the original peoples of Europe, the Middle East or North Africa." Majority white for most of its history, Baltimore no longer had a white majority by the 1970s. As of the 2010 Census, white Americans are a minority population of Baltimore at 29.6% of the population (Non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
were 28% of the population). White Americans have played a substantial impact on the culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups.Tyl ...
, dialect
The term dialect (from Latin , , from the Ancient Greek word , 'discourse', from , 'through' and , 'I speak') can refer to either of two distinctly different types of Linguistics, linguistic phenomena:
One usage refers to a variety (linguisti ...
, ethnic heritage
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
, history
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the History of writing#Inventions of writing, invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbr ...
, politics, and music
Music is generally defined as the art of arranging sound to create some combination of form, harmony, melody, rhythm or otherwise expressive content. Exact definitions of music vary considerably around the world, though it is an aspect ...
of the city. Since the earliest English settlers arrived on the shores of the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the ...
, Baltimore's white population has been sustained by substantial immigration from all over Europe, particularly Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area' ...
, Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the Europe, European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russ ...
, and Southern Europe
Southern Europe is the southern regions of Europe, region of Europe. It is also known as Mediterranean Europe, as its geography is essentially marked by the Mediterranean Sea. Definitions of Southern Europe include some or all of these countrie ...
, as well as a large out-migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (ex ...
of White Southerners
White Southerners, from the Southern United States, are considered an ethnic group by some historians, sociologists and journalists, although this categorization has proven controversial, and other academics have argued that Southern identity does ...
from Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
. Numerous white immigrants from Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
and the European diaspora
European emigration is the successive emigration waves from the European continent to other continents. The origins of the various European diasporas can be traced to the people who left the European nation states or stateless ethnic communitie ...
have immigrated to Baltimore from the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and North ...
, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical re ...
, the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
, France, Canada, and other countries, particularly during the late 19th century and early 20th century. Smaller numbers of white people have immigrated from Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
, the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean Se ...
(particularly Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
), the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
, North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
, and other non-European regions. Baltimore also has a prominent population of white Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
of European descent
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as " ...
, mostly with roots in Central and Eastern Europe. There is a smaller population of white Middle Easterners and white North Africans, most of whom are Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
, Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
, Israeli
Israeli may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the State of Israel
* Israelis, citizens or permanent residents of the State of Israel
* Modern Hebrew, a language
* ''Israeli'' (newspaper), published from 2006 to 2008
* Guni Israeli ...
, or Turkish
Turkish may refer to:
*a Turkic language spoken by the Turks
* of or about Turkey
** Turkish language
*** Turkish alphabet
** Turkish people, a Turkic ethnic group and nation
*** Turkish citizen, a citizen of Turkey
*** Turkish communities and mi ...
. The distribution of White Americans in Central and Southeast Baltimore is sometimes called "The White L", while the distribution of African Americans
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
in East and West Baltimore is called "The Black Butterfly."
Demographics
In the 1790 census, the first census in the history of the United States, white Americans constituted 88.3% of Baltimore's population. 11,925 lived in Baltimore in that year. In 1815, 36,000 white people lived in Baltimore. By 1829, Baltimore was home to 61,000 white people. From 1800 until 1840, white Americans were around 77–79% of Baltimore's population. The white population began to increase in the mid and late 1800s, boosted by large-scale European immigration, resulting in Baltimore's whites remaining between 80% to 87% of the population between the 1850s and the 1920s. During the time of theHillbilly Highway In the United States, the Hillbilly Highway is the out-migration of Appalachians from the Appalachian Highlands region to industrial cities in northern, midwestern, and western states, primarily in the years following World War II in search of bette ...
, between 1910 and 1970, thousands of white people from Appalachia
Appalachia () is a cultural region in the Eastern United States that stretches from the Southern Tier of New York State to northern Alabama and Georgia. While the Appalachian Mountains stretch from Belle Isle in Newfoundland and Labrador, Ca ...
and the Southern states moved to Baltimore in search of better socioeconomic
Socioeconomics (also known as social economics) is the social science that studies how economic activity affects and is shaped by social processes. In general it analyzes how modern societies progress, stagnate, or regress because of their local ...
conditions. Baltimore was a major destination for these white Southern and Appalachian economic migrants.
In the 1960 United States Census, Baltimore was home to 610,608 white residents, 65% of Baltimore's population. By 1970 white Americans were 53% of Baltimore's population, on the verge of becoming the minority for the first time due white flight
White flight or white exodus is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the United States. They refer ...
to the suburbs and an increasing African-American population.
In the 1980 United States Census
The United States census of 1980, conducted by the Census Bureau, determined the resident population of the United States to be 226,545,805, an increase of 11.4 percent over the 203,184,772 persons enumerated during the 1970 census. It was th ...
, there were 345,113 white people living in Baltimore, constituting 43.9% of the population. The 1980 census was the first census for which white people were a minority in Baltimore. By the 1990 United States Census, there were 287,753 white Americans, constituting 39.1% of the population.
In the 2010 United States Census
The United States census of 2010 was the twenty-third United States national census. National Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2010. The census was taken via mail-in citizen self-reporting, with enumerators servin ...
, 29.6% of the population of Baltimore was white, a total population of 183,830 people.
In 2018, 30.3% of Baltimore was white and 27.6% was non-Hispanic white.
Baltimore's white population has been increasing in numbers since the 2010s. This is largely due to gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more Wealth, affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and urban planning, planning. Gentrification ...
and an influx of white millennials.
History
Pre-history and early white European exploration
In the early 1600s, the immediate Baltimore vicinity was populated by Native Americans who had lived there since at least the10th millennium BC
The 10th millennium BC spanned the years 10,000 BC to 9001 BC (c. 12 ka to c. 11 ka). It marks the beginning of the transition from the Palaeolithic to the Neolithic via the interim Mesolithic ( Northern Europe and Western Europe) and Epip ...
, when Paleo-Indians first settled in the region. During the Late Woodland period, the archaeological culture
An archaeological culture is a recurring assemblage of types of artifacts, buildings and monuments from a specific period and region that may constitute the material culture remains of a particular past human society. The connection between thes ...
known as the "Potomac Creek complex" resided in an area from Baltimore to the Rappahannock River
The Rappahannock River is a river in eastern Virginia, in the United States, approximately in length.U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 1, 2011 It traverses the entir ...
in Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth ar ...
, primarily along the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augus ...
downstream from the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coa ...
. The Baltimore County area northward was used as hunting grounds by the Susquehannocks
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern pa ...
living in the lower Susquehanna River
The Susquehanna River (; Lenape: Siskëwahane) is a major river located in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, overlapping between the lower Northeast and the Upland South. At long, it is the longest river on the East Coast of the ...
valley who "controlled all of the upper tributaries of the Chesapeake" but "refrained from much contact with Powhatan
The Powhatan people (; also spelled Powatan) may refer to any of the indigenous Algonquian people that are traditionally from eastern Virginia. All of the Powhatan groups descend from the Powhatan Confederacy. In some instances, The Powhatan ...
in the Potomac region."
Pressured by the Susquehannocks, the Piscataway tribe
The Piscataway or Piscatawa , are Native Americans. They spoke Algonquian Piscataway, a dialect of Nanticoke. One of their neighboring tribes, with whom they merged after a massive decline of population following two centuries of interactions ...
of Algonquians
The Algonquian are one of the most populous and widespread North American native language groups. Historically, the peoples were prominent along the Atlantic Coast and into the interior along the Saint Lawrence River and around the Great Lakes. T ...
stayed well south of the Baltimore area and inhabited primarily the north bank of the Potomac River
The Potomac River () drains the Mid-Atlantic United States, flowing from the Potomac Highlands into Chesapeake Bay. It is long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map. Retrieved Augus ...
in what is now Charles
Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ...
and southern Prince George's south of the Fall Line
A fall line (or fall zone) is the area where an upland region and a coastal plain meet and is typically prominent where rivers cross it, with resulting rapids or waterfalls. The uplands are relatively hard crystalline basement rock, and the coa ...
as depicted on John Smith's 1608 map which faithfully mapped settlements, mapped none in the Baltimore vicinity, while noting a dozen Patuxent River
The Patuxent River is a tributary of the Chesapeake Bay in the state of Maryland. There are three main river drainages for central Maryland: the Potomac River to the west passing through Washington, D.C., the Patapsco River to the northeast ...
settlements that were under some degree of Piscataway suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is cal ...
.
In 1608, Captain John Smith traveled 210 miles from Jamestown to the uppermost Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the ...
, leading the first European expedition to the Patapsco River
The Patapsco River mainstem is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map , accessed April 1, 2011 river in central Maryland that flows into the Chesapeake Bay. The river's tidal port ...
, a word used by the Algonquin language natives who fished shellfish and hunted The name "Patapsco" is derived from ''pota-psk-ut'', which translates to "backwater" or "tide covered with froth" in Algonquian dialect. A quarter-century after John Smith's voyage, English colonists began to settle in Maryland. The English were initially frightened by the Piscataway in southern Maryland because of their body paint and war regalia, even though they were a peaceful tribe. The chief of the Piscataway tribe was quick to grant the English permission to settle within Piscataway territory and cordial relations were established between the English and the Piscataway.
17th century
18th century
19th century
20th century
During thecivil rights movement
The civil rights movement was a nonviolent social and political movement and campaign from 1954 to 1968 in the United States to abolish legalized institutional Racial segregation in the United States, racial segregation, Racial discrimination ...
between the 1930s and the 1960s, many white Americans in Baltimore reacted violently to African-Americans and were intransigent in their support for segregation Segregation may refer to:
Separation of people
* Geographical segregation, rates of two or more populations which are not homogenous throughout a defined space
* School segregation
* Housing segregation
* Racial segregation, separation of humans ...
. Some white residents of Baltimore engaged in acts of terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
against African-Americans, including the 1911 lynching of King Johnson in the neighborhood of Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
. White elected officials and citizens made life difficult for African-Americans by engaging in various forms of discrimination. However, some anti-racist
Anti-racism encompasses a range of ideas and political actions which are meant to counter racial prejudice, systemic racism, and the oppression of specific racial groups. Anti-racism is usually structured around conscious efforts and deliberate ...
white liberals and progressives joined with African-American activists. White Communists
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a so ...
were among the most vocal white supporters of the civil rights movement.
The largely white Baltimore Committee for Political Freedom was created due to fears that Baltimore police were planning to assassinate Black Panther Party
The Black Panther Party (BPP), originally the Black Panther Party for Self-Defense, was a Marxist-Leninist and black power political organization founded by college students Bobby Seale and Huey P. Newton in October 1966 in Oakland, Califo ...
leaders in Baltimore, with Reverend Chester Wickwire and the sociologist Peter H. Rossi
Peter Henry Rossi (December 27, 1921 – October 7, 2006) was a prominent sociologist best known for his research on the origin of homelessness, and documenting the changing face of American homelessness in the 1980s. Rossi was also known for his ...
playing a prominent role.
21st century
Due to demographic and socioeconomic changes, Baltimore's urban core is slowly becoming more white and more affluent. Young urban professionals have been attracted to the city, echoing patterns ofgentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more Wealth, affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and urban planning, planning. Gentrification ...
that have occurred across many major American cities in recent decades. As the city's white population has increased and the rate of poverty has dropped, income and property values have been rising. The effects of gentrification and a growing white population have been felt the most in the historically black working-class neighborhoods of East Baltimore and to a lesser extent in the neighborhoods of North Central Baltimore. The proximity of these neighborhoods to the Johns Hopkins Hospital
The Johns Hopkins Hospital (JHH) is the teaching hospital and biomedical research facility of the Johns Hopkins School of Medicine, located in Baltimore, Maryland, U.S. It was founded in 1889 using money from a bequest of over $7 million (1873 mo ...
has been a major factor in the gentrification and increasing white population of East Baltimore's neighborhoods. Because of these demographic changes, Baltimore has been called "the new Brooklyn" and has been compared to similarly gentrifying cities across the United States such as New York City and Washington, D.C.
Culture
Dialect
 According to linguists, the "
According to linguists, the "hon
Hon or HON may refer to:
People
* Han (surname) (Chinese: 韩/韓), also romanized Hon
* Louis Hon (1924–2008), French footballer
* Priscilla Hon (born 1998), Australian tennis player
Other uses
* Hon (Baltimore), a cultural stereotype of ...
" accent that is popularized in the media as being spoken by Baltimoreans is particular to Baltimore's white working-class."The Relevatory Power of Language"''Maryland Humanities Council''. May 11, 2019. White working-class families who migrated out of Baltimore city into
Baltimore County
Baltimore County ( , locally: or ) is the third-most populous county in the U.S. state of Maryland and is part of the Baltimore metropolitan area. Baltimore County (which partially surrounds, though does not include, the independent City of ...
and Carroll County along the Maryland Route 140
Maryland Route 140 (MD 140) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. The route runs from U.S. Route 1 (US 1) and US 40 Truck in Baltimore northwest to the Pennsylvania border, where the road continues into that state as Pennsylvania R ...
and Maryland Route 26
Maryland Route 26 (MD 26) is a state highway in the U.S. state of Maryland. Known for most of its length as Liberty Road, the state highway runs from U.S. Route 15 (US 15) in Frederick east to MD 140 in Baltimore. MD 26 connects Frederick and ...
corridors brought local pronunciations with them, creating colloquialisms that make up the Baltimore accent, cementing the image of "Bawlmerese" as the "Baltimore accent". This white working-class dialect is not the only "Baltimore accent", as Black Baltimoreans have their own unique accent. For example, among Black speakers, Baltimore is pronounced more like "Baldamore," as compared to "Bawlmer" among white speakers.
Literature
In 2003, Kenneth D. Durr published ''Behind the Backlash: White Working-Class Politics in Baltimore, 1940-1980'', an historical examination of white working-class life and politics in Baltimore during the mid to late 1900s.Religion
Most White Americans in Baltimore areChristians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
, generally either Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
or Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
. Smaller numbers of white Christians belong to denominations such as Mormonism
Mormonism is the religious tradition and theology of the Latter Day Saint movement of Restorationist Christianity started by Joseph Smith in Western New York in the 1820s and 1830s. As a label, Mormonism has been applied to various aspects of t ...
, the Jehovah's Witnesses
Jehovah's Witnesses is a millenarian restorationist Christian denomination with nontrinitarian beliefs distinct from mainstream Christianity. The group reports a worldwide membership of approximately 8.7 million adherents involved in ...
, Eastern Orthodoxy
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main Branches of Christianity, branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholic Church, Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first m ...
, and Oriental Orthodoxy
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent ...
. Minorities of White Americans belong to other religions such as Judaism
Judaism ( he, ''Yahăḏūṯ'') is an Abrahamic, monotheistic, and ethnic religion comprising the collective religious, cultural, and legal tradition and civilization of the Jewish people. It has its roots as an organized religion in the ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and gra ...
, Hinduism
Hinduism () is an Indian religion or '' dharma'', a religious and universal order or way of life by which followers abide. As a religion, it is the world's third-largest, with over 1.2–1.35 billion followers, or 15–16% of the global p ...
, and Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, while some are atheist
Atheism, in the broadest sense, is an absence of belief in the existence of deities. Less broadly, atheism is a rejection of the belief that any deities exist. In an even narrower sense, atheism is specifically the position that there no ...
or agnostic
Agnosticism is the view or belief that the existence of God, of the divine or the supernatural is unknown or unknowable. (page 56 in 1967 edition) Another definition provided is the view that "human reason is incapable of providing sufficient ...
.
Christianity
During the 1800s and 1900s, many neighborhoods of Baltimore were reserved exclusively for white Christians. One such neighborhood, Roland Park, was developed as a wealthy white Christian enclave for "discriminating" people that used racially restrictive covenants to exclude African-Americans. Some white Christian neighborhoods used restrictive covenants to exclude Jewish Americans as well. At that time, living in a white Christian neighborhood was a sign of social status. During this same time period, white Protestant-dominated banks would ignore or turn away customers who were Eastern European or Southern European immigrants; consequently "white ethnic" immigrants would establish their own banking institutions to serve the specific needs of their communities. These banks for white ethnic immigrants had hours and customs that seemed less alien to immigrants and often had translators on staff. Discrimination against non-WASP
A wasp is any insect of the narrow-waisted suborder Apocrita of the order Hymenoptera which is neither a bee nor an ant; this excludes the broad-waisted sawflies (Symphyta), which look somewhat like wasps, but are in a separate suborder. Th ...
immigrants persisted in banking until the 1930s. As late as the 1930s and 1940s it was not uncommon for Slavic Catholics, such as Poles and Czechs, to be called ethnic and religious slurs such as "bohunk
The following is a list of ethnic slurs or ethnophaulisms or ethnic epithets that are, or have been, used as insinuations or allegations about members of a given ethnicity or racial group or to refer to them in a derogatory, pejorative, or oth ...
s" and "fish eaters." Slavs were often stereotyped
In social psychology, a stereotype is a generalized belief about a particular category of people. It is an expectation that people might have about every person of a particular group. The type of expectation can vary; it can be, for example ...
as stupid and superstitious
A superstition is any belief or practice considered by non-practitioners to be irrational or supernatural, attributed to fate or magic, perceived supernatural influence, or fear of that which is unknown. It is commonly applied to beliefs and pr ...
. White Protestants coined the term "fish eater" to refer to Catholic immigrants because the Catholics did not eat meat on Fridays.
Baltimore, like many other major northeastern
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
cities, has a large population of white Catholics, many of whom are "white ethnic
White ethnic is a term used to refer to white Americans who are not Old Stock or White Anglo-Saxon Protestant. "Religion is the most critical factor in separating white ethnics in American society. As Catholics and secondarily Jews ... they were ...
" immigrants and descendants of immigrants from majority-Catholic countries of Europe such as Ireland, Italy, Germany, Poland, and the Czech Republic. Historically, the Catholic Church in Baltimore practiced segregation of its white and black worshippers. In the early 21st century, Roman Catholic authorities began to acknowledge the long legacy of racism from the majority-white leadership of the Church. The first Archbishop of Baltimore, John Carroll John Carroll may refer to:
People Academia and science
*Sir John Carroll (astronomer) (1899–1974), British astronomer
*John Alexander Carroll (died 2000), American history professor
*John Bissell Carroll (1916–2003), American cognitive sci ...
, was a white slave-owner. Many white Catholics in Baltimore moved to the suburbs during the period of white flight between the 1960s and 1980s, leaving most Roman Catholic churches in the city with an African-American majority while many Roman Catholic churches in the suburbs are majority white.
Judaism
A large minority of white Baltimoreans have been Jewish, predominantly Jews of European descent. Between the 1880s and the 1920s, Baltimore received tens of thousands of whiteAshkenazi Jewish
Ashkenazi Jews ( ; he, יְהוּדֵי אַשְׁכְּנַז, translit=Yehudei Ashkenaz, ; yi, אַשכּנזישע ייִדן, Ashkenazishe Yidn), also known as Ashkenazic Jews or ''Ashkenazim'',, Ashkenazi Hebrew pronunciation: , singu ...
immigrants arriving from Central and Eastern Europe. Due to the largely European origins of Baltimore's Jewish community, close to 90% of Baltimore area Jews are white. However, as of 2010, around 8% of Jewish households in the Greater Baltimore area were multiracial
Mixed race people are people of more than one race or ethnicity. A variety of terms have been used both historically and presently for mixed race people in a variety of contexts, including ''multiethnic'', ''polyethnic'', occasionally ''bi-ethn ...
. Following the 1968 riots 1968 riots may refer to:
* Orangeburg massacre, February 8, South Carolina State University, Orangeburg, South Carolina
* King assassination riots, April and May, across the United States, including:
** 1968 Washington, D.C., riots, April 4–8, ...
and the subsequent white flight, many white Jews in the city (along with many white gentile
Gentile () is a word that usually means "someone who is not a Jew". Other groups that claim Israelite heritage, notably Mormons, sometimes use the term ''gentile'' to describe outsiders. More rarely, the term is generally used as a synonym for ...
s), left the city for the suburbs. Today, thousands of descendants of these white Jews live in Baltimore County
Baltimore County ( , locally: or ) is the third-most populous county in the U.S. state of Maryland and is part of the Baltimore metropolitan area. Baltimore County (which partially surrounds, though does not include, the independent City of ...
, especially in Pikesville
Pikesville is a census-designated place (CDP) in Baltimore County, Maryland, United States. Pikesville is just northwest of the Baltimore city limits. It is the northwestern suburb closest to Baltimore.
The population was 30,764 at the 2010 cens ...
and Owings Mills
Owings Mills is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in Baltimore County, Maryland, United States. It is a suburb of Baltimore. Per the 2020 census, the population was 35,674. Owings Mills is home to the northern terminus of ...
, though many remain in the city in neighborhoods such as Park Heights, Mount Washington
Mount Washington is the highest peak in the Northeastern United States at and the most topographically prominent mountain east of the Mississippi River.
The mountain is notorious for its erratic weather. On the afternoon of April 12, 1934, ...
, and Roland Park
Roland Park is a community located in Baltimore, Maryland. It was developed between 1890 and 1920 as an upper-class streetcar suburb. The early phases of the neighborhood were designed by Edward Bouton and Frederick Law Olmsted, Jr.
History
J ...
. Historically, there were strong links between African-American and Jewish-American communities in Baltimore and many white Jewish Baltimoreans were strong supporters of the civil rights movement. However, there has been tension between the two communities, with instances of anti-black racism from white Jews such as the 2010 Park Heights beating of a black teenager by white members of an Orthodox Jewish
Orthodox Judaism is the collective term for the traditionalist and theologically conservative branches of contemporary Judaism. Theologically, it is chiefly defined by regarding the Torah, both Written and Oral, as revealed by God to Moses on M ...
community patrol group. White Jews in Baltimore have experienced a mixture of both religious
Religion is usually defined as a social system, social-cultural system of designated religious behaviour, behaviors and practices, morality, morals, beliefs, worldviews, religious text, texts, sacred site, sanctified places, prophecy, prophecie ...
and racial antisemitism
Racial antisemitism is prejudice against Jews based on a belief or assertion that Jews constitute a distinct race that has inherent traits or characteristics that appear in some way abhorrent or inherently inferior or otherwise different from t ...
as well as privilege due to their white skin. In majority-white Jewish spaces in Baltimore, white Jews are sometimes accepted while black Jews and other Jews of color may face skepticism and questioning of their identity. in 2010 the majority of white Americans in Baltimore city were of the Jewish religion in 2020 that number has only increased.
Islam
There are a small number of white Muslims in Baltimore, most of whom areconverts
Religious conversion is the adoption of a set of beliefs identified with one particular religious denomination to the exclusion of others. Thus "religious conversion" would describe the abandoning of adherence to one denomination and affiliatin ...
. Some white Muslims have earned leadership positions within their communities, with a few becoming teachers at children's schools for their local mosques.
Majority white neighborhoods in Baltimore
*Armistead Gardens
Armistead Gardens is a neighborhood in the Northeast District of Baltimore. It is located north of Pulaski Highway and east of Erdman Avenue, between Herring Run Park (northeast) and the East District neighborhood of Orangeville (southwest).
Ar ...
* Bayview
* Berverly Hills
* Butchers Hill
* Canton
*Cedarcroft
Cedarcroft, also known as Bayard Taylor House, is a historic house on Gatehouse Drive in Chester County, Pennsylvania near Kennett Square. It was built in 1859 for writer Bayard Taylor (1825–1878), and is a good local example of Italianate arc ...
*Charles Village
Charles Village is a neighborhood located in the north-central area of Baltimore, Maryland, USA. It is a diverse, eclectic, international, largely middle-class area with many single-family homes that is in proximity to many of Baltimore's cultural ...
*Fell's Point
Fell's Point is a historic waterfront neighborhood in southeastern Baltimore, Maryland. It was established around 1763 along the north shore of the Baltimore Harbor and the Northwest Branch of the Patapsco River. The area has many antique, musi ...
*Greektown
Greektown is a general name for an ethnic enclave populated primarily by Greeks or people of Greek ancestry, usually in an urban neighborhood.
History
The oldest Greek dominated neighborhood outside of Greece were probably the Fener in Istanbu ...
* Hampden
* Joseph Lee
* Kresson
* Mayfield
*Mount Vernon
Mount Vernon is an American landmark and former plantation of Founding Father, commander of the Continental Army in the Revolutionary War, and the first president of the United States George Washington and his wife, Martha. The estate is on ...
*Remington
Remington may refer to:
Organizations
* Remington Arms, American firearms manufacturer
* Remington Rand, American computer manufacturer
* Remington Products, American manufacturer of shavers and haircare products
* Remington College, American c ...
See also
* Ethnic groups in Baltimore *White Hispanic and Latino Americans
In the United States, a white Hispanic or Latino is an individual who is of full or partial Hispanic or Latino descent, the largest group being white Mexican Americans. Although not differentiated in the U.S. Census definition, White Latino Ame ...
*History of Baltimore
This article describes the history of the Baltimore and its surrounding area in central Maryland since the establishment of settlements by European colonists in 1661.
Native American settlement
The Baltimore area had been inhabited by Native ...
*History of the Hispanics and Latinos in Baltimore
The history of Hispanics and Latinos in Baltimore dates back to the mid-20th century. The Hispanic and Latino Americans, Hispanic and Latino community of Baltimore is the fastest growing ethnic group in the city. There is a significant Hispanic/L ...
*History of the Jews in Baltimore
Few Jews arrived in Baltimore, Maryland, in its early years. As an immigrant port of entry and border town between Northern United States, North and Southern United States, South and as a manufacturing center in its own right, Baltimore has ...
*Non-Hispanic whites
Non-Hispanic whites or Non-Latino whites are Americans who are classified as "white", and are not of Hispanic (also known as "Latino") heritage. The United States Census Bureau defines ''white'' to include European Americans, Middle Eastern Amer ...
*Old Stock Americans
Old Stock Americans, Pioneer Stock, or Colonial Stock are Americans who are descended from the original settlers of the Thirteen Colonies of mostly British ancestry who emigrated to British America in the 17th and the 18th centuries.
These Old ...
*White Americans in Maryland
White Marylanders are White Americans living in Maryland. As of 2019, they comprise 57.3% of the state's population. 49.8% of the population is non-Hispanic white, making Maryland a majority minority state. The regions of Western Maryland, Southern ...
*White flight
White flight or white exodus is the sudden or gradual large-scale migration of white people from areas becoming more racially or ethnoculturally diverse. Starting in the 1950s and 1960s, the terms became popular in the United States. They refer ...
* History of Italians in Baltimore
* History of Greeks in Baltimore
References
Further reading
*Durr, Kenneth D. ''Behind the Backlash: White Working-Class Politics in Baltimore, 1940-1980'', The University of North Carolina Press, 2003. *Pietila, Antero. ''Not in My Neighborhood: How Bigotry Shaped a Great American City'', Ivan R. Dee, 2010.External links
Percentage of Whites in Baltimore, MD by Zip Code
{{White people Central Asian American culture Ethnic groups in Baltimore European-American culture in Baltimore Middle Eastern-American culture in Maryland North African American culture
white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White on ...
baltimore
Baltimore ( , locally: or ) is the List of municipalities in Maryland, most populous city in the U.S. state of Maryland, fourth most populous city in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic, and List of United States cities by popula ...