History Of U.S. Foreign Policy, 1801–1829 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1801 to 1829 concerns the
The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1801 to 1829 concerns the
 Jefferson believed that western expansion played an important role in furthering his vision of a republic of yeoman farmers. By the time Jefferson took office, Americans had settled as far west as the
Jefferson believed that western expansion played an important role in furthering his vision of a republic of yeoman farmers. By the time Jefferson took office, Americans had settled as far west as the
 After Jackson accused Madison of duplicity with Erskine, Madison had Jackson barred from the State Department and sent packing to Boston.Rutland (1990), pp. 44–45. In early 1810, Madison began asking Congress for more appropriations to increase the army and navy in preparation for war with Britain.Rutland (1990), pp. 46–47 Congress also passed an act known as
After Jackson accused Madison of duplicity with Erskine, Madison had Jackson barred from the State Department and sent packing to Boston.Rutland (1990), pp. 44–45. In early 1810, Madison began asking Congress for more appropriations to increase the army and navy in preparation for war with Britain.Rutland (1990), pp. 46–47 Congress also passed an act known as 
 After Napoleon's abdication following the March 1814 Battle of Paris, the British began to shift soldiers to North America. Under General
After Napoleon's abdication following the March 1814 Battle of Paris, the British began to shift soldiers to North America. Under General
 After his victory at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend, Jackson forced the defeated Muscogee to sign the
After his victory at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend, Jackson forced the defeated Muscogee to sign the
 For decades prior to Jefferson's accession to office, the Barbary Coast pirates of North Africa had been capturing American merchant ships, pillaging valuable cargoes and enslaving crew members, demanding huge ransoms for their release. Fremont-Barnes, 2006, p. 36. Before independence, American merchant ships were protected from the Barbary pirates by the naval and diplomatic influence of Great Britain, but that protection came to end after the colonies won their independence. In 1794, in reaction to the attacks, Congress had passed a law to authorize the payment of tribute to the Barbary States. At the same time, Congress passed the
For decades prior to Jefferson's accession to office, the Barbary Coast pirates of North Africa had been capturing American merchant ships, pillaging valuable cargoes and enslaving crew members, demanding huge ransoms for their release. Fremont-Barnes, 2006, p. 36. Before independence, American merchant ships were protected from the Barbary pirates by the naval and diplomatic influence of Great Britain, but that protection came to end after the colonies won their independence. In 1794, in reaction to the attacks, Congress had passed a law to authorize the payment of tribute to the Barbary States. At the same time, Congress passed the
 President Jefferson argued that the Louisiana Purchase had extended as far west as the
President Jefferson argued that the Louisiana Purchase had extended as far west as the
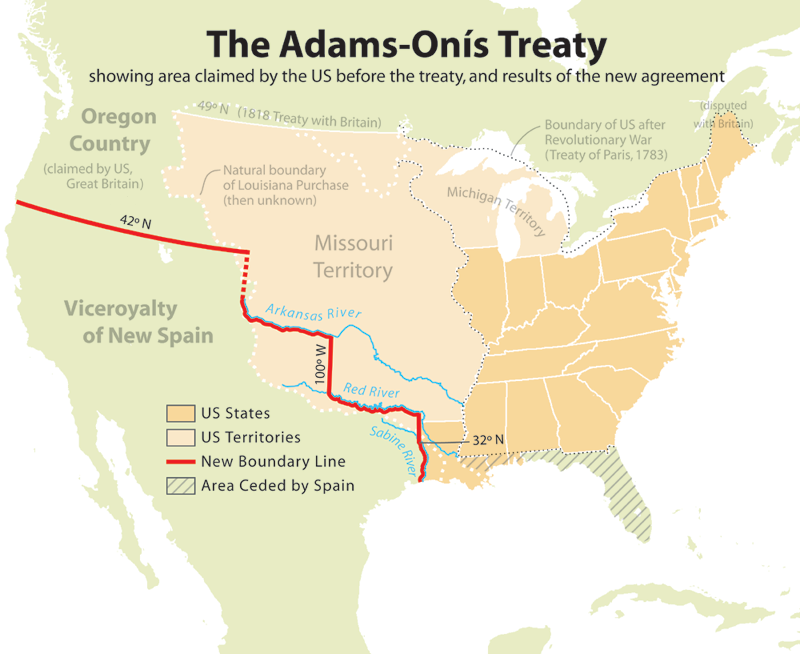 Negotiations over the purchase of the Floridas began in early 1818. Don
Negotiations over the purchase of the Floridas began in early 1818. Don
 Monroe was deeply sympathetic to the Latin American revolutionary movements against Spain. He was determined that the United States should never repeat the policies of the Washington administration during the French Revolution, when the nation had failed to demonstrate its sympathy for the aspirations of peoples seeking to establish republican governments. He did not envisage military involvement but only the provision of moral support, as he believed that a direct American intervention would provoke other European powers into assisting Spain. Despite his preferences, Monroe initially refused to recognize the Latin American governments due to ongoing negotiations with Spain over Florida.
In March 1822, Monroe officially recognized the countries of
Monroe was deeply sympathetic to the Latin American revolutionary movements against Spain. He was determined that the United States should never repeat the policies of the Washington administration during the French Revolution, when the nation had failed to demonstrate its sympathy for the aspirations of peoples seeking to establish republican governments. He did not envisage military involvement but only the provision of moral support, as he believed that a direct American intervention would provoke other European powers into assisting Spain. Despite his preferences, Monroe initially refused to recognize the Latin American governments due to ongoing negotiations with Spain over Florida.
In March 1822, Monroe officially recognized the countries of
 One of the major foreign policy goals of the Adams administration was the expansion of American trade. His administration reached
One of the major foreign policy goals of the Adams administration was the expansion of American trade. His administration reached
 After early 1802, when he learned that Napoleon intended to regain a foothold in Saint-Domingue and Louisiana, Jefferson proclaimed neutrality in relation to the
After early 1802, when he learned that Napoleon intended to regain a foothold in Saint-Domingue and Louisiana, Jefferson proclaimed neutrality in relation to the
''American Philosophical Society'' 140, no. 1 (March 1996), p. 22. They feared its success would encourage slave revolt in the
online free to borrow
* Pratt, Julius W. ''Expansionists of 1812'' (1957
online
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of U.S. foreign policy, 1801-1829 1801 establishments in the United States 1829 disestablishments in the United States History of the foreign relations of the United States Presidency of Thomas Jefferson Presidency of James Madison Presidency of James Monroe Presidency of John Quincy Adams
 The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1801 to 1829 concerns the
The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1801 to 1829 concerns the foreign policy of the United States
The officially stated goals of the foreign policy of the United States of America, including all the bureaus and offices in the United States Department of State, as mentioned in the ''Foreign Policy Agenda'' of the Department of State, are ...
during the presidential administrations of Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
, James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
, James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
, and John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
. International affairs in the first half of this period were dominated by the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, which the United States became involved with in various ways, including the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
. The period saw the United States double in size, gaining control of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and lands between the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
and the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
. The period began with the First inauguration of Thomas Jefferson
The first inauguration of Thomas Jefferson as the third president of the United States was held on Wednesday, March 4, 1801. The inauguration marked the commencement of the first four-year term of Thomas Jefferson as president and the only four-y ...
in 1801. The First inauguration of Andrew Jackson
The first inauguration of Andrew Jackson as the seventh president of the United States was held on Wednesday, March 4, 1829, at the United States Capitol in Washington, D.C. The inauguration marked the commencement of the first four-year term of ...
in 1829 marked the start of the next period in U.S. foreign policy.
Upon taking office, President Jefferson dispatched envoys to the French First Republic
In the history of France, the First Republic (french: Première République), sometimes referred to in historiography as Revolutionary France, and officially the French Republic (french: République française), was founded on 21 September 1792 ...
to purchase the city of New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
, which held a strategic position on the Mississippi River. French Emperor Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
instead offered to sell the entire territory of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
; the Jefferson administration accepted the offer, and the subsequent Louisiana Purchase
The Louisiana Purchase (french: Vente de la Louisiane, translation=Sale of Louisiana) was the acquisition of the territory of Louisiana by the United States from the French First Republic in 1803. In return for fifteen million dollars, or app ...
doubled the size of the United States. During Jefferson's second term, the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland was a sovereign state in the British Isles that existed between 1801 and 1922, when it included all of Ireland. It was established by the Acts of Union 1800, which merged the Kingdom of Great B ...
escalated attacks against American shipping as part of a blockade against France. These attacks continued under President Madison, and in 1812 the United States declared war against Britain, beginning the War of 1812. Defying Madison's hopes that the war would end with the quick capture of Canada under British rule
Canada is a country in North America. Its Provinces and territories of Canada, ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world ...
, the War of 1812 continued inconclusively until 1815. The Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
provided for a return to status quo ante bellum
The term ''status quo ante bellum'' is a Latin phrase meaning "the situation as it existed before the war".
The term was originally used in treaties to refer to the withdrawal of enemy troops and the restoration of prewar leadership. When used ...
borders, and the final defeat of Napoleon later in 1815 ended the issue of British and French attacks on American shipping.
Though the war with Britain was inconclusive, the U.S. defeated Native American allies of Britain at the Battle of the Thames
The Battle of the Thames , also known as the Battle of Moraviantown, was an American victory in the War of 1812 against Tecumseh's Confederacy and their British allies. It took place on October 5, 1813, in Upper Canada, near Chatham. The British ...
and the Battle of Horseshoe Bend
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as ''Tohopeka'', ''Cholocco Litabixbee'', or ''The Horseshoe''), was fought during the War of 1812 in the Mississippi Territory, now central Alabama. On March 27, 1814, United States forces and Indian a ...
, ensuring U.S. control of the Old Northwest
The Northwest Territory, also known as the Old Northwest and formally known as the Territory Northwest of the River Ohio, was formed from unorganized western territory of the United States after the American Revolutionary War. Established in 1 ...
and the Old Southwest
Old or OLD may refer to:
Places
* Old, Baranya, Hungary
* Old, Northamptonshire, England
*Old Street station, a railway and tube station in London (station code OLD)
*OLD, IATA code for Old Town Municipal Airport and Seaplane Base, Old Town, M ...
. In the aftermath of the war, the United States and Britain signed two treaties that eased tensions, settled border disputes, demilitarized the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
, and provided for the joint occupation of Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
. A separate treaty with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
established the southern border of Russian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
and opened Russian ports to U.S. trade. In 1819, the United States and the Kingdom of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = ''Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, i ...
agreed to the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined t ...
, through which Spain transferred control of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
to the United States. Numerous Latin American countries gained independence from Spain during Monroe's presidency. In 1823 he promulgated the Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile ac ...
, under which the U.S. pledged to oppose all future efforts to colonize the Western Hemisphere
The Western Hemisphere is the half of the planet Earth that lies west of the prime meridian (which crosses Greenwich, London, United Kingdom) and east of the antimeridian. The other half is called the Eastern Hemisphere. Politically, the term We ...
.
Leadership
Jefferson administration, 1801–1809
Thomas Jefferson
Thomas Jefferson (April 13, 1743 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, architect, philosopher, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the third president of the United States from 18 ...
took office in 1801 after defeating incumbent President John Adams
John Adams (October 30, 1735 – July 4, 1826) was an American statesman, attorney, diplomat, writer, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the second president of the United States from 1797 to 1801. Befor ...
in the 1800 presidential election. By July 1801, Jefferson had assembled his cabinet, which consisted of Secretary of State James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
, Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin
Abraham Alfonse Albert Gallatin (January 29, 1761 – August 12, 1849) was a Genevan– American politician, diplomat, ethnologist and linguist. Often described as "America's Swiss Founding Father", he was a leading figure in the early years ...
, Secretary of War Henry Dearborn
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American military officer and politician. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in his expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record ...
, Attorney General Levi Lincoln Sr.
Levi Lincoln Sr. (May 15, 1749 – April 14, 1820) was an American revolutionary, lawyer, and statesman from Massachusetts. A Democratic-Republican, he most notably served as Thomas Jefferson's first attorney general, and played a significant ro ...
, and Secretary of the Navy Robert Smith. Jefferson sought to make collective decisions with his cabinet, and each member's opinion was elicited before Jefferson made major decisions. Gallatin and Madison were particularly influential within Jefferson's cabinet; they held the two most important cabinet positions and served as Jefferson's key lieutenants.
Madison administration, 1809–1817
Jefferson's preferred successor,James Madison
James Madison Jr. (March 16, 1751June 28, 1836) was an American statesman, diplomat, and Founding Father. He served as the fourth president of the United States from 1809 to 1817. Madison is hailed as the "Father of the Constitution" for hi ...
, took office in 1809 after winning the 1808 presidential election. Upon his inauguration in 1809, Madison immediately faced opposition to his planned nomination of Albert Gallatin as Secretary of State; Madison chose not to fight Congress for the nomination but kept Gallatin in the Treasury Department. The talented Swiss-born Gallatin was Madison's primary advisor, confidant, and policy planner.Rutland (1990), pp. 32–33. Madison appointed Secretary of State Robert Smith only at the behest of Smith's brother, the powerful Senator Samuel Smith. With a cabinet full of those he distrusted, Madison rarely called cabinet meetings and instead frequently consulted with Gallatin alone. After feuding with Gallatin, Smith was dismissed in 1811 in favor of James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
, and Monroe became a major influence in the Madison administration.
Monroe administration, 1817–1825
James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
became president in 1817 after his victory in the 1816 presidential election. Monroe appointed a geographically-balanced cabinet, through which he led the executive branch. Monroe retained many of Madison's appointments, but, recognizing Northern discontent at the continuation of the Virginia dynasty, Monroe chose John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
of Massachusetts to fill the prestigious post of Secretary of State.
Adams administration, 1825–1829
John Quincy Adams
John Quincy Adams (; July 11, 1767 – February 23, 1848) was an American statesman, diplomat, lawyer, and diarist who served as the sixth president of the United States, from 1825 to 1829. He previously served as the eighth United States S ...
took office in 1825 after defeating Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
, William H. Crawford
William Harris Crawford (February 24, 1772 – September 15, 1834) was an American politician and judge during the early 19th century. He served as US Secretary of War and US Secretary of the Treasury before he ran for US president in the 1824 ...
, and Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
in the 1824 presidential election. As no one candidate won a majority of the electoral vote in the 1824 election, the election was decided by the House of Representatives in a contingent election
In the United States, a contingent election is used to elect the president or vice president if no candidate receives a majority of the whole number of Electors appointed. A presidential contingent election is decided by a special vote of th ...
that Adams won with the support of Clay.. Like Monroe, Adams sought a geographically-balanced cabinet that would represent the various party factions, and he asked the members of the Monroe cabinet to remain in place for his own administration. Adams chose Henry Clay as Secretary of State, angering those who believed that Clay had offered his support in the 1824 election for the most prestigious position in the cabinet. Adams presided over a harmonious and productive cabinet. He met with the cabinet as a group on a weekly basis to discuss major issues of policy, and he gave individual cabinet members a great deal of discretion in carrying out their duties.
Louisiana Purchase
 Jefferson believed that western expansion played an important role in furthering his vision of a republic of yeoman farmers. By the time Jefferson took office, Americans had settled as far west as the
Jefferson believed that western expansion played an important role in furthering his vision of a republic of yeoman farmers. By the time Jefferson took office, Americans had settled as far west as the Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it f ...
, though vast pockets of land remained vacant or inhabited only by Native Americans. Many in the United States, particularly those in the west, favored further territorial expansion, and especially hoped to annex the Spanish province of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-smallest by area and the 25th most populous of the 50 U.S. states. Louisiana is borde ...
. Given Spain's sparse presence in Louisiana, Jefferson believed that it was just a matter of time until Louisiana fell to either Britain or the United States.Wood, 2009, pp. 366–367. U.S. expansionary hopes were temporarily dashed when Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
convinced Spain to transfer the province to France in the 1801 Treaty of Aranjuez. Though French pressure played a role in the conclusion of the treaty, the Spanish also believed that French control of Louisiana would help protect New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Am ...
from American expansion.
Napoleon's dreams of a re-established French colonial empire in North America threatened to reignite the tensions of the recently concluded Quasi-War
The Quasi-War (french: Quasi-guerre) was an undeclared naval war fought from 1798 to 1800 between the United States and the French First Republic, primarily in the Caribbean and off the East Coast of the United States. The ability of Congres ...
.Appleby, 2003, pp. 63–64 He initially planned to re-establish a French empire in the Americas centered around New Orleans and Saint-Domingue
Saint-Domingue () was a French colony in the western portion of the Caribbean island of Hispaniola, in the area of modern-day Haiti, from 1659 to 1804. The name derives from the Spanish main city in the island, Santo Domingo, which came to refer ...
, a sugar-producing Caribbean island in the midst of a slave revolution. One army was sent to Saint-Domingue, and a second army began preparing to travel to New Orleans. After French forces in Saint-Domingue were defeated by the rebels, Napoleon gave up on his plans for an empire in the Western Hemisphere. In early 1803, Jefferson dispatched James Monroe
James Monroe ( ; April 28, 1758July 4, 1831) was an American statesman, lawyer, diplomat, and Founding Father who served as the fifth president of the United States from 1817 to 1825. A member of the Democratic-Republican Party, Monroe was ...
to France to join ambassador Robert Livingston in purchasing New Orleans, East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
, and West Florida
West Florida ( es, Florida Occidental) was a region on the northern coast of the Gulf of Mexico that underwent several boundary and sovereignty changes during its history. As its name suggests, it was formed out of the western part of former S ...
from France. To the surprise of the American delegation, Napoleon offered to sell the entire territory of Louisiana for $15 million. The Americans also pressed for the acquisition of the Floridas, but under the terms of the Treaty of Aranjuez, Spain retained control of both of those territories. On April 30, the two delegations agreed to the terms of the Louisiana Purchase, and Napoleon gave his approval the following day.
After Secretary of State James Madison gave his assurances that the purchase was well within even the strictest interpretation of the Constitution, the Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the el ...
quickly ratified the treaty, and the House immediately authorized funding. Rodriguez, 2002, p. 97. The purchase, concluded in December 1803, marked the end of French ambitions in North America and ensured American control of the Mississippi River. Ellis, 2008, p. 208. The Louisiana Purchase nearly doubled the size of the United States, and Treasury Secretary Gallatin was forced to borrow from foreign banks to finance the payment to France. Though the Louisiana Purchase was widely popular, some Federalists criticized it; Congressman Fisher Ames
Fisher Ames (; April 9, 1758 – July 4, 1808) was a Representative in the United States Congress from the 1st Congressional District of Massachusetts. He was an important leader of the Federalist Party in the House, and was noted for his o ...
argued that "we are to spend money of which he have too little for land of which we already have too much."
Burr conspiracy
After being dropped from Jefferson's 1804 Republican ticket, Burr was defeated for governor of New York in an April 1804 election. On July 11, 1804, Burr killed his political enemyAlexander Hamilton
Alexander Hamilton (January 11, 1755 or 1757July 12, 1804) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first United States secretary of the treasury from 1789 to 1795.
Born out of wedlock in Charlest ...
in a duel. Burr was indicted for murder in New York and New Jersey causing him to flee to Georgia. The British ambassador reported that Burr wanted to "effect a separation of the western part of the United States t the Appalachian Mountains
T, or t, is the twentieth Letter (alphabet), letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is English alphabe ...
. Jefferson believed that to be so by November 1806, because Burr had been rumored to be variously plotting with some western states to secede for an independent empire, or to raise a filibuster
A filibuster is a political procedure in which one or more members of a legislative body prolong debate on proposed legislation so as to delay or entirely prevent decision. It is sometimes referred to as "talking a bill to death" or "talking out ...
to conquer Mexico. At the very least, there were reports of Burr's recruiting men, stocking arms, and building boats. New Orleans seemed especially vulnerable, but at some point, the American general there, James Wilkinson
James Wilkinson (March 24, 1757 – December 28, 1825) was an American soldier, politician, and double agent who was associated with several scandals and controversies.
He served in the Continental Army during the American Revolutionary War, b ...
, a double agent for the Spanish, decided to turn on Burr. Jefferson issued a proclamation warning that there were U.S. citizens illegally plotting to take over Spanish holdings. Though Burr was nationally discredited, Jefferson feared for the very Union. By March 1807, Burr was arrested and placed on trial for treason; he was acquitted and went into exile in Europe.
War of 1812
Embargo Act
American trade boomed after the outbreak of theFrench Revolutionary Wars
The French Revolutionary Wars (french: Guerres de la Révolution française) were a series of sweeping military conflicts lasting from 1792 until 1802 and resulting from the French Revolution. They pitted French First Republic, France against Ki ...
in the early 1790s, in large part because American shipping was allowed to act as neutral carriers with European powers. Though the British sought to restrict trade with the French, they had largely tolerated U.S. trade with mainland France and French colonies after the signing of the Jay Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
in 1794. Jefferson favored a policy of neutrality in the European wars, and was strongly committed the principle of freedom of navigation
Freedom of navigation (FON) is a principle of law of the sea that ships flying the flag of any sovereign state shall not suffer interference from other states, apart from the exceptions provided for in international law. In the realm of internat ...
for neutral vessels, including American ships. Early in his tenure, Jefferson was able to maintain cordial relations with both France and Britain, but relations with Britain deteriorated after 1805. Needing sailors, the British Royal Navy seized hundreds of American ships and impressed 6,000 sailors from them, angering Americans. The British began to enforce a blockade of Europe, ending their policy of tolerance towards American shipping. Though the British returned many seized American goods that had not been intended for French ports, the British blockade badly affected American commerce and provoked immense anger throughout the nation. Aside from commercial concerns, Americans were outraged by what they saw an attack on national honor. In response to the attacks, Jefferson recommended an expansion of the navy, and Congress passed the Non-importation Act
The Non-Importation Act, passed by the United States Congress on April 18, 1806, forbid any kind of import of certain British goods in an attempt to coerce Britain to suspend its impressment of American sailors and to respect American sovereignty ...
, which restricted many, but not all, British imports.
To restore peaceful relations with Britain, Monroe negotiated the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty
The Monroe–Pinkney Treaty was a treaty drawn up in 1806 by diplomats of the United States and Great Britain to renew the 1795 Jay Treaty. As it was rejected by President Thomas Jefferson, it never took effect. The treaty was negotiated by the m ...
, which would have represented an extension of the Jay Treaty. Jefferson had never favored the Jay Treaty, which had prevented the United States from implementing economic sanctions on Britain, and he rejected the Monroe–Pinkney Treaty. Tensions with Britain heightened due to the Chesapeake–Leopard affair
The ''Chesapeake''–''Leopard'' affair was a naval engagement off the coast of Norfolk, Virginia, on June 22, 1807, between the British fourth-rate and the American frigate . The crew of ''Leopard'' pursued, attacked, and boarded the Americ ...
, a June 1807 naval confrontation between an American ship and a British ship that ended in the death or impressment of several American sailors. Beginning with Napoleon's December 1807 Milan Decree
The Milan Decree was issued on 17 December 1807 by Napoleon I of France to enforce the 1806 Berlin Decree, which had initiated the Continental System, the basis for his plan to defeat the British by waging economic warfare.
The Milan Decree st ...
, the French began to seize ships trading with the British, leaving American shipping vulnerable to attacks by both of the major naval powers. In response to attacks on American shipping, Congress passed the Embargo Act
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations that was enacted by the United States Congress. As a successor or replacement law for the 1806 Non-importation Act and passed as the Napoleonic Wars continued, it repr ...
in 1807, which was designed to force Britain and France into respecting U.S. neutrality by cutting off all American shipping to Britain or France. Almost immediately the Americans began to turn to smuggling in order to ship goods to Europe. Defying his own limited government principles, Jefferson used the military to enforce the embargo. Imports and exports fell immensely, and the embargo proved to be especially unpopular in New England.
Most historians consider Jefferson's embargo to have been ineffective and harmful to American interests. Even the top officials of the Jefferson administration viewed the embargo as a flawed policy, but they saw it as preferable to war. Appleby describes the strategy as Jefferson's "least effective policy", and Joseph Ellis calls it "an unadulterated calamity". Others, however, portray it as an innovative, nonviolent measure which aided France in its war with Britain while preserving American neutrality.
Prelude to war
In early 1809, Congress passed theNon-Intercourse Act
The Nonintercourse Act (also known as the Indian Intercourse Act or the Indian Nonintercourse Act) is the collective name given to six statutes passed by the Congress in 1790, 1793, 1796, 1799, 1802, and 1834 to set Amerindian boundaries of re ...
, which opened trade with foreign powers other than France and Britain. Aside from U.S. trade with France, the central dispute between the Great Britain and the United States was the impressment
Impressment, colloquially "the press" or the "press gang", is the taking of men into a military or naval force by compulsion, with or without notice. European navies of several nations used forced recruitment by various means. The large size of ...
of sailors by the British. During the long and expensive war against France, many British citizens were forced by their own government to join the navy, and many of these conscripts defected to U.S. merchant ships. Unable to tolerate this loss of manpower, the British seized several U.S. ships and forced captured crewmen, some of whom were not in fact not British subjects, to serve in the British navy. Though Americans were outraged by this impressment, they also refused to take steps to limit it, such as refusing to hire British subjects. For economic reasons, American merchants preferred impressment to giving up their right to hire British sailors.
Although initially promising, President Madison's diplomatic efforts to get the British to withdraw the Orders in Council were rejected by British Foreign Secretary George Canning
George Canning (11 April 17708 August 1827) was a British Tory statesman. He held various senior cabinet positions under numerous prime ministers, including two important terms as Foreign Secretary, finally becoming Prime Minister of the Unit ...
in April 1809. In August 1809, diplomatic relations with Britain deteriorated as minister David Erskine was withdrawn and replaced by "hatchet man" Francis James Jackson
Francis James Jackson (December 1770 – 5 August 1814) was a British diplomat, ambassador to the Ottoman Empire, Prussia and the United States.
Career
Francis Jackson entered the diplomatic service aged only 16 and served as a Foreign Office ...
.Rutland (1990), pp. 40–44. Madison resisted calls for war, as he was ideologically opposed to the debt and taxes necessary for a war effort. British historian Paul Langford sees the removal in 1809 of Erskine as a major British blunder, because Erskine:
brought affairs almost to an accommodation, and was ultimately disappointed not by American intransigence but by one of the outstanding diplomatic blunders made by a ritishForeign Secretary. It was Canning who, in his most irresponsible manner and apparently out of sheer dislike of everything American, recalled the ambassador Erskine and wrecked the negotiations, a piece of most gratuitous folly. As a result, the possibility of a new embarrassment for Napoleon turned into the certainty of a much more serious one for his enemy. Though the British cabinet eventually made the necessary concessions on the score of theOrders-in-Council An Order-in-Council is a type of legislation in many countries, especially the Commonwealth realms. In the United Kingdom this legislation is formally made in the name of the monarch by and with the advice and consent of the Privy Council ('' ..., in response to the pressures of industrial lobbying at home, its action came too late....The loss of the North American markets could have been a decisive blow. As it was by the time the United States declared war, theContinental System The Continental Blockade (), or Continental System, was a large-scale embargo against British trade by Napoleon Bonaparte against the British Empire from 21 November 1806 until 11 April 1814, during the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon issued the Berlin ...f Napoleon F, or f, is the sixth letter in the Latin alphabet, used in the modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its name in English is ''ef'' (pronounced ), and the plural is ''efs''. Hist ...was beginning to crack, and the danger correspondingly diminishing. Even so, the war, inconclusive though it proved in a military sense, was an irksome and expensive embarrassment which British statesman could have done much more to avert.
 After Jackson accused Madison of duplicity with Erskine, Madison had Jackson barred from the State Department and sent packing to Boston.Rutland (1990), pp. 44–45. In early 1810, Madison began asking Congress for more appropriations to increase the army and navy in preparation for war with Britain.Rutland (1990), pp. 46–47 Congress also passed an act known as
After Jackson accused Madison of duplicity with Erskine, Madison had Jackson barred from the State Department and sent packing to Boston.Rutland (1990), pp. 44–45. In early 1810, Madison began asking Congress for more appropriations to increase the army and navy in preparation for war with Britain.Rutland (1990), pp. 46–47 Congress also passed an act known as Macon's Bill Number 2
Macon's Bill Number 2, which became law in the United States on May 14, 1810, was intended to motivate Great Britain and France to stop seizing American ships, cargoes, and crews during the Napoleonic Wars. This was a revision of the original bill ...
, which reopened trade with France and Britain, but promised to reimpose the embargo on one country if the other country agreed to end its attacks on American shipping. Madison, who wished to simply continue the embargo, opposed the law, but he jumped at the chance to use the law's provision enabling a re-imposition of the embargo on one power. Seeking to split the Americans and British, Napoleon offered to end French attacks on American shipping so long as the United States punished any countries that did not similarly end restrictions on trade. Madison accepted Napoleon's proposal in the hope that it would convince the British to revoke the Orders-in-Council, but the British refused to change their policies. Despite assurances to the contrary, the French also continued to attack American shipping.
As the attacks on American shipping continued, both Madison and the broader American public were ready for war with Britain. Some observers believed that the United States might fight a three-way war with both Britain and France, but Democratic-Republicans, including Madison, considered Britain to be far more culpable for the attacks. Many Americans called for a "second war of independence" to restore honor and stature to the new nation, and an angry public elected a "war hawk" Congress, led by Henry Clay
Henry Clay Sr. (April 12, 1777June 29, 1852) was an American attorney and statesman who represented Kentucky in both the U.S. Senate and House of Representatives. He was the seventh House speaker as well as the ninth secretary of state, al ...
and John C. Calhoun
John Caldwell Calhoun (; March 18, 1782March 31, 1850) was an American statesman and political theorist from South Carolina who held many important positions including being the seventh vice president of the United States from 1825 to 1832. He ...
. With Britain in the midst of the Napoleonic Wars, many Americans, Madison included, believed that the United States could easily capture Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, at which point the U.S. could use Canada as a bargaining chip for all other disputes or simply retain control of it.. On June 1, 1812, Madison asked Congress for a declaration of war. The declaration was passed along sectional and party lines, with intense opposition from the Federalists and the Northeast, where the economy had suffered during Jefferson's trade embargo.Rutland, ''James Madison: The Founding Father'', pp. 217–24
Madison hurriedly called on Congress to put the country "into an armor and an attitude demanded by the crisis," specifically recommending enlarging the army, preparing the militia, finishing the military academy, stockpiling munitions, and expanding the navy. Madison faced formidable obstacles—a divided cabinet, a factious party, a recalcitrant Congress, obstructionist governors, and incompetent generals, together with militia who refused to fight outside their states. The most serious problem facing the war effort was lack of unified popular support. There were serious threats of disunion from New England, which engaged in extensive smuggling with Canada and refused to provide financial support or soldiers.Stagg, 1983. Events in Europe also went against the United States. Shortly after the United States declared war, Napoleon launched an invasion of Russia, and the failure of that campaign turned the tide against France and towards Britain and her allies. In the years prior to the war, Jefferson and Madison had reduced the size of the military, closed the Bank of the U.S., and lowered taxes. These decisions added to the challenges facing the United States, as by the time the war began, Madison's military force consisted mostly of poorly trained militia members.

Military action
Madison hoped that the war would end in a couple months after the capture of Canada, but his hopes were quickly dashed. Madison had believed the state militias would rally to the flag and invade Canada, but the governors in the Northeast failed to cooperate. Their militias either sat out the war or refused to leave their respective states for action. The senior command at the War Department and in the field proved incompetent or cowardly—the general at Detroit surrendered to a smaller British force without firing a shot. Gallatin discovered the war was almost impossible to fund, since the national bank had been closed, major financiers in the New England refused to help, and government revenue depended largely on tariffs. Though the Democratic-Republican Congress was willing to go against party principle to authorize an expanded military, they refused to levy direct taxes until June 1813. Lacking adequate revenue, and with its request for loans refused by New England bankers, the Madison administration relied heavily on high-interest loans furnished by bankers based in New York City and Philadelphia. The American campaign in Canada, led byHenry Dearborn
Henry Dearborn (February 23, 1751 – June 6, 1829) was an American military officer and politician. In the Revolutionary War, he served under Benedict Arnold in his expedition to Quebec, of which his journal provides an important record ...
, ended with defeat at the Battle of Stoney Creek
The Battle of Stoney Creek was a British victory over an American force fought on 6 June 1813, during the War of 1812 near present-day Stoney Creek, Ontario. British units made a night attack on the American encampment, and due in large part to ...
. Meanwhile, the British armed American Indians, most notably several tribes allied with the Shawnee
The Shawnee are an Algonquian-speaking indigenous people of the Northeastern Woodlands. In the 17th century they lived in Pennsylvania, and in the 18th century they were in Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana and Illinois, with some bands in Kentucky a ...
chief, Tecumseh
Tecumseh ( ; October 5, 1813) was a Shawnee chief and warrior who promoted resistance to the expansion of the United States onto Native American lands. A persuasive orator, Tecumseh traveled widely, forming a Native American confederacy and ...
, in an attempt to threaten American positions in the Northwest.Rutland (1990), pp. 133–134
After the disastrous start to the War of 1812, Madison accepted a Russian invitation to arbitrate the war and sent Gallatin, John Quincy Adams, and James Bayard to Europe in hopes of quickly ending the war. While Madison worked to end the war, the U.S. experienced some military success, particularly at sea. The United States had built up one of the largest merchant fleets in the world, though it had been partially dismantled under Jefferson and Madison. Madison authorized many of these ships to become privateer
A privateer is a private person or ship that engages in maritime warfare under a commission of war. Since robbery under arms was a common aspect of seaborne trade, until the early 19th century all merchant ships carried arms. A sovereign or deleg ...
s in the war, and they captured 1,800 British ships. As part of the war effort, an American naval shipyard was built up at Sackets Harbor, New York
Sackets Harbor (earlier spelled Sacketts Harbor) is a village in Jefferson County, New York, United States, on Lake Ontario. The population was 1,450 at the 2010 census. The village was named after land developer and owner Augustus Sackett, who ...
, where thousands of men produced twelve warships and had another nearly ready by the end of the war. The U.S. naval squadron on Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also has t ...
successfully defended itself and captured its opponents, crippling the supply and reinforcement of British military forces in the western theater of the war. In the aftermath of the Battle of Lake Erie, General William Henry Harrison
William Henry Harrison (February 9, 1773April 4, 1841) was an American military officer and politician who served as the ninth president of the United States. Harrison died just 31 days after his inauguration in 1841, and had the shortest pres ...
defeated the forces of the British and of Tecumseh's Confederacy
Tecumseh's confederacy was a confederation of native Americans in the Great Lakes region of the United States that began to form in the early 19th century around the teaching of Tenskwatawa (The Prophet).See , pg. 211. The confederation grew ove ...
at the Battle of the Thames
The Battle of the Thames , also known as the Battle of Moraviantown, was an American victory in the War of 1812 against Tecumseh's Confederacy and their British allies. It took place on October 5, 1813, in Upper Canada, near Chatham. The British ...
. The death of Tecumseh in that battle represented the permanent end of armed Native American resistance in the Old Northwest. In March 1814, General Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
broke the resistance of the British-allied Muscogee
The Muscogee, also known as the Mvskoke, Muscogee Creek, and the Muscogee Creek Confederacy ( in the Muscogee language), are a group of related indigenous (Native American) peoples of the Southeastern WoodlandsBattle of Horseshoe Bend
The Battle of Horseshoe Bend (also known as ''Tohopeka'', ''Cholocco Litabixbee'', or ''The Horseshoe''), was fought during the War of 1812 in the Mississippi Territory, now central Alabama. On March 27, 1814, United States forces and Indian a ...
. Despite those successes, the British continued to repel American attempts to invade Canada, and a British force captured Fort Niagara
Fort Niagara is a fortification originally built by New France to protect its interests in North America, specifically control of access between the Niagara River and Lake Ontario, the easternmost of the Great Lakes. The fort is on the river's e ...
and burned the American city of Buffalo in late 1813. In early 1814, the British agreed to begin peace negotiations in the town of Ghent
Ghent ( nl, Gent ; french: Gand ; traditional English: Gaunt) is a city and a municipality in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It is the capital and largest city of the East Flanders province, and the third largest in the country, exceeded in ...
, and the British pushed for the establishment of an Indian barrier state
The Indian barrier state or buffer state was a British proposal to establish a Native American state in the portion of the Great Lakes region of North America. It was never created. The idea was to create it west of the Appalachian Mountains, b ...
in the Old Northwest as part of any peace agreement.
 After Napoleon's abdication following the March 1814 Battle of Paris, the British began to shift soldiers to North America. Under General
After Napoleon's abdication following the March 1814 Battle of Paris, the British began to shift soldiers to North America. Under General George Izard
George Izard (October 21, 1776 – November 22, 1828) was a senior officer of the United States Army who served as the second governor of Arkansas Territory from 1825 to 1828. He was elected as a member to the American Philosophical Society in 18 ...
and General Jacob Brown
Jacob Jennings Brown (May 9, 1775 – February 24, 1828) was known for his victories as an American army officer in the War of 1812, where he reached the rank of general. His successes on the northern border during that war made him a national ...
, the U.S. launched another invasion of Canada in mid-1814. Despite an American victory at the Battle of Chippawa
The Battle of Chippawa, also known as the Battle of Chippewa, was a victory for the United States Army in the War of 1812, during its invasion on July 5, 1814, of the British Empire's colony of Upper Canada along the Niagara River. This battle a ...
, the invasion stalled once again. Meanwhile, the British increased the size and intensity of their raids against the Atlantic coast. General William H. Winder
William Henry Winder (February 18, 1775 – May 24, 1824) was an American soldier and a Maryland lawyer. He was a controversial general in the U.S. Army during the War of 1812. On August 24, 1814, as a brigadier general, he led American troops in ...
attempted to bring together a concentrated force to guard against a potential attack on Washington or Baltimore, but his orders were countermanded by Secretary of War Armstrong. The British landed a large force off the Chesapeake Bay
The Chesapeake Bay ( ) is the largest estuary in the United States. The Bay is located in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region and is primarily separated from the Atlantic Ocean by the Delmarva Peninsula (including the parts: the ...
in August 1814, and the British army approached Washington on August 24. An American force was routed at the Battle of Bladensburg
The Battle of Bladensburg was a battle of the Chesapeake campaign of the War of 1812, fought on 24 August 1814 at Bladensburg, Maryland, northeast of Washington, D.C.
Called "the greatest disgrace ever dealt to American arms," a British force ...
, and British forces set fire to the federal buildings of Washington. Dolley Madison rescued White House valuables and documents shortly before the British burned the White House. The British army next moved on Baltimore, but the British called off the raid after the U.S. repelled a naval attack on Fort McHenry
Fort McHenry is a historical American coastal pentagonal bastion fort on Locust Point, now a neighborhood of Baltimore, Maryland. It is best known for its role in the War of 1812, when it successfully defended Baltimore Harbor from an attack b ...
. Madison returned to Washington before the end of August, and the main British force departed from the region in September. The British attempted to launch an invasion from Canada, but the U.S. victory at the September 1814 Battle of Plattsburgh
The Battle of Plattsburgh, also known as the Battle of Lake Champlain, ended the final British invasion of the northern states of the United States during the War of 1812. An army under Lieutenant General Sir George Prévost and a naval squadro ...
ended British hopes of conquering New York.
Anticipating that the British would attack the city of New Orleans
New Orleans ( , ,New Orleans
Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
next, newly-installed Secretary of War James Monroe ordered General Jackson to prepare a defense of the city. Meanwhile, the British public began to turn against the war in North America, and British leaders began to look for a quick exit from the conflict. On January 8, 1815, Jackson's force defeated the British at the Merriam-Webster. ; french: La Nouvelle-Orléans , es, Nuev ...
Battle of New Orleans
The Battle of New Orleans was fought on January 8, 1815 between the British Army under Major General Sir Edward Pakenham and the United States Army under Brevet Major General Andrew Jackson, roughly 5 miles (8 km) southeast of the French ...
. Just over a month later, Madison learned that his negotiators had reached the Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
, ending the war without major concessions by either side. Additionally, both sides agreed to establish commissions to settle Anglo-American boundary disputes. Madison quickly sent the Treaty of Ghent to the Senate, and the Senate ratified the treaty on February 16, 1815. To most Americans, the quick succession of events at the end of the war, including the burning of the capital, the Battle of New Orleans, and the Treaty of Ghent, appeared as though American valor at New Orleans had forced the British to surrender. This view, while inaccurate, strongly contributed to the post-war euphoria that persisted for a decade. It also helps explain the significance of the war, even if it was strategically inconclusive. Madison's reputation as president improved and Americans finally believed the United States had established itself as a world power.Rutland (1988), p. 188 Napoleon's defeat at the June 1815 Battle of Waterloo
The Battle of Waterloo was fought on Sunday 18 June 1815, near Waterloo, Belgium, Waterloo (at that time in the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, now in Belgium). A French army under the command of Napoleon was defeated by two of the armie ...
brought a permanent end to the Napoleonic Wars.
Aftermath
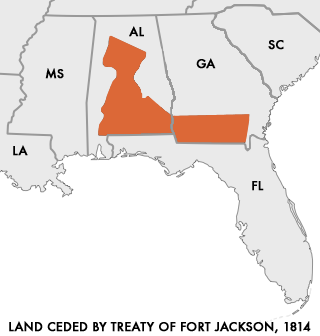
 After his victory at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend, Jackson forced the defeated Muscogee to sign the
After his victory at the Battle of Horseshoe Bend, Jackson forced the defeated Muscogee to sign the Treaty of Fort Jackson
The Treaty of Fort Jackson (also known as the Treaty with the Creeks, 1814) was signed on August 9, 1814 at Fort Jackson near Wetumpka, Alabama following the defeat of the Red Stick (Upper Creek) resistance by United States allied forces at t ...
, which forced the Muscogee and the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
(who had been allied with Jackson) to give up control of 22 million acres of land in Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
and Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
. Madison initially agreed to restore these lands in the Treaty of Ghent, but Madison backed down in the face of Jackson's resistance. The British abandoned their erstwhile allies, and the U.S. consolidated control of its southwest and northwest frontiers.
Near the beginning of Monroe's first term, the administration negotiated two important accords with Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
that resolved border disputes held over from the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
. The Rush-Bagot Treaty, signed in April 1817, regulated naval armaments on the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and Lake Champlain
, native_name_lang =
, image = Champlainmap.svg
, caption = Lake Champlain-River Richelieu watershed
, image_bathymetry =
, caption_bathymetry =
, location = New York/Vermont in the United States; and Quebec in Canada
, coords =
, type =
, ...
, demilitarizing the border between the U.S. and British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English overseas possessions, English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland (island), Newfound ...
. The Treaty of 1818
The Convention respecting fisheries, boundary and the restoration of slaves, also known as the London Convention, Anglo-American Convention of 1818, Convention of 1818, or simply the Treaty of 1818, is an international treaty signed in 1818 betw ...
, signed in October 1818, fixed the present Canada–United States border
The border between Canada and the United States is the longest international border in the world. The terrestrial boundary (including boundaries in the Great Lakes, Atlantic, and Pacific coasts) is long. The land border has two sections: Can ...
from Minnesota
Minnesota () is a state in the upper midwestern region of the United States. It is the 12th largest U.S. state in area and the 22nd most populous, with over 5.75 million residents. Minnesota is home to western prairies, now given over to ...
to the Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico in ...
at the 49th parallel. Britain ceded all of Rupert's Land
Rupert's Land (french: Terre de Rupert), or Prince Rupert's Land (french: Terre du Prince Rupert, link=no), was a territory in British North America which comprised the Hudson Bay drainage basin; this was further extended from Rupert's Land t ...
south of the 49th parallel and east of the Continental Divide
A continental divide is a drainage divide on a continent such that the drainage basin on one side of the divide feeds into one ocean or sea, and the basin on the other side either feeds into a different ocean or sea, or else is endorheic, not ...
, including all of the Red River Colony
The Red River Colony (or Selkirk Settlement), also known as Assiniboia, Assinboia, was a colonization project set up in 1811 by Thomas Douglas, 5th Earl of Selkirk, on of land in British North America. This land was granted to Douglas by the Hud ...
south of that latitude, while the U.S. ceded the northernmost edge of the Missouri Territory
The Territory of Missouri was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from June 4, 1812, until August 10, 1821. In 1819, the Territory of Arkansas was created from a portion of its southern area. In 1821, a southeas ...
above the 49th parallel. The treaty also established a joint U.S.–British occupation of Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
for the next ten years. Together, the Rush-Bagot Treaty and the Treaty of 1818 marked an important turning point in Anglo–American and American–Canadian relations, although they did not solve all outstanding issues. The easing of tensions contributed to expanded trade, particularly cotton
Cotton is a soft, fluffy staple fiber that grows in a boll, or protective case, around the seeds of the cotton plants of the genus ''Gossypium'' in the mallow family Malvaceae. The fiber is almost pure cellulose, and can contain minor perce ...
, and played a role in Britain's decision to refrain from becoming involved in the First Seminole War.
As president, Adams continued to pursue an agreement on territorial disputes with Britain, including the unsettled border between Maine and Canada. Gallatin favored partitioning Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
at the Columbia River
The Columbia River (Upper Chinook: ' or '; Sahaptin: ''Nch’i-Wàna'' or ''Nchi wana''; Sinixt dialect'' '') is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river rises in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, C ...
, but Adams and Clay were unwilling to concede territory below the 49th parallel north.
Barbary Wars
First Barbary War
 For decades prior to Jefferson's accession to office, the Barbary Coast pirates of North Africa had been capturing American merchant ships, pillaging valuable cargoes and enslaving crew members, demanding huge ransoms for their release. Fremont-Barnes, 2006, p. 36. Before independence, American merchant ships were protected from the Barbary pirates by the naval and diplomatic influence of Great Britain, but that protection came to end after the colonies won their independence. In 1794, in reaction to the attacks, Congress had passed a law to authorize the payment of tribute to the Barbary States. At the same time, Congress passed the
For decades prior to Jefferson's accession to office, the Barbary Coast pirates of North Africa had been capturing American merchant ships, pillaging valuable cargoes and enslaving crew members, demanding huge ransoms for their release. Fremont-Barnes, 2006, p. 36. Before independence, American merchant ships were protected from the Barbary pirates by the naval and diplomatic influence of Great Britain, but that protection came to end after the colonies won their independence. In 1794, in reaction to the attacks, Congress had passed a law to authorize the payment of tribute to the Barbary States. At the same time, Congress passed the Naval Act of 1794
The Act to Provide a Naval Armament (Sess. 1, ch. 12, ), also known as the Naval Act of 1794, or simply, the Naval Act, was passed by the 3rd United States Congress on March 27, 1794, and signed into law by President George Washington. The act a ...
, which initiated construction on six frigates that became the foundation of the United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
. By the end of the 1790s, the United States had concluded treaties with all of the Barbary States, but weeks before Jefferson took office Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
began attacking American merchant ships in an attempt to extract further tribute.
Jefferson was reluctant to become involved in any kind of international conflict, but he believed that force would best deter the Barbary States from demanding further tribute. He ordered the U.S. Navy into the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
to defend against the Barbary Pirates, beginning the First Barbary War
The First Barbary War (1801–1805), also known as the Tripolitan War and the Barbary Coast War, was a conflict during the Barbary Wars, in which the United States and Sweden fought against Tripolitania. Tripolitania had declared war against Sw ...
. The administration's initial efforts were largely ineffective, and in 1803 the frigate was captured by Tripoli. In February 1804, Lieutenant Stephen Decatur
Stephen Decatur Jr. (; January 5, 1779 – March 22, 1820) was an American naval officer and commodore. He was born on the eastern shore of Maryland in Worcester County. His father, Stephen Decatur Sr., was a commodore in the Unite ...
led a successful raid on Tripoli's harbor that burned the ''Philadelphia'', making Decatur a national hero. Jefferson and the young American navy forced Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
and Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
into breaking their alliance with Tripoli which ultimately moved it out of the war. Jefferson also ordered five separate naval bombardments of Tripoli, which restored peace in the Mediterranean for a while, although Jefferson continued to pay the remaining Barbary States until the end of his presidency.
Second Barbary War
During the War of 1812, the Barbary States had stepped up attacks on American shipping. These states, which were nominally vassals of theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
but were functionally independent, demanded tribute from countries that traded in the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ea ...
. With the end of the war, the United States could deploy the now-expanded U.S. Navy against the Barbary States. Congress declared war on Algiers
Algiers ( ; ar, الجزائر, al-Jazāʾir; ber, Dzayer, script=Latn; french: Alger, ) is the capital and largest city of Algeria. The city's population at the 2008 Census was 2,988,145Census 14 April 2008: Office National des Statistiques ...
in March 1815, beginning the Second Barbary War
The Second Barbary War (1815) or the U.S.–Algerian War was fought between the United States and the North African Barbary Coast states of Tripoli, Tunis, and Algiers. The war ended when the United States Senate ratified Commodore Stephen De ...
. Seventeen ships, the largest U.S. fleet that had been assembled up to that point in history, were sent to the Mediterranean Sea. After several defeats, Algiers agreed to sign a treaty, and Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
and Tripoli
Tripoli or Tripolis may refer to:
Cities and other geographic units Greece
*Tripoli, Greece, the capital of Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (region of Arcadia), a district in ancient Arcadia, Greece
* Tripolis (Larisaia), an ancient Greek city in ...
also subsequently signed treaties. The Barbary States agreed to release all of their prisoners and to stop demanding tributes.Wood, 2009, pp. 696–697.
Spanish Florida
West Florida controversy
 President Jefferson argued that the Louisiana Purchase had extended as far west as the
President Jefferson argued that the Louisiana Purchase had extended as far west as the Rio Grande River
The Rio Grande ( and ), known in Mexico as the Río Bravo del Norte or simply the Río Bravo, is one of the principal rivers (along with the Colorado River) in the southwestern United States and in northern Mexico.
The length of the Rio G ...
, and had included West Florida as far east as the Perdido River
Perdido River, historically Rio Perdido (1763), is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 15, 2011 river in the U.S. states of Alabama and Florida; the Perdido, a desig ...
. He hoped to use that claim, along with French pressure, to force Spain to sell both West Florida and East Florida. In 1806, he won congressional approval of a $2 million appropriation to obtain the Floridas; eager expansionists also contemplated authorizing the president to acquire Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, by force if necessary. In this case, unlike that of the Louisiana Territory, the dynamics of European politics worked against Jefferson. Napoleon had played Washington against Madrid to see what he could get, but by 1805 Spain was his ally. Spain had no desire to cede Florida, which was part of its leverage against an expanding United States. Revelations of the bribe which Jefferson offered to France over the matter provoked outrage and weakened Jefferson's hand with regards to Florida. President Madison continued to uphold the U.S. claim to Florida. Spanish control of its New World colonies had weakened due to the ongoing Peninsular War
The Peninsular War (1807–1814) was the military conflict fought in the Iberian Peninsula by Spain, Portugal, and the United Kingdom against the invading and occupying forces of the First French Empire during the Napoleonic Wars. In Spain ...
, and Spain exercised little effective control over West Florida and East Florida
East Florida ( es, Florida Oriental) was a colony of Great Britain from 1763 to 1783 and a province of Spanish Florida from 1783 to 1821. Great Britain gained control of the long-established Spanish colony of ''La Florida'' in 1763 as part of ...
. Madison was especially concerned about the possibility of the British taking control of the region, which, along with Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, would give the British Empire control of territories on the northern and southern borders of the United States. However, the United States was reluctant to go to war for the territory when France or Great Britain might intervene.
Madison sent William Wykoff into West Florida in the hopes of convincing the settlers of the region to request annexation by the United States. Partly due to Wykoff's prodding, the people of West Florida held the St. Johns Plains Convention in July 1810. Most of those who elected to the convention had been born in the United States, and they largely favored independence from Spain, but they feared that declaring independence would provoke a Spanish military response. In September 1810, after learning that the Spanish governor of West Florida had requested military assistance from Spain, a militia made up of West Floridians and led by Philemon Thomas
Philemon Thomas (February 9, 1763 – November 18, 1847) was a member of the United States House of Representatives representing the state of Louisiana. He served two terms as a Democrat (1831–1835).
Philemon was born in Orange County, Vir ...
captured the Spanish fort at Baton Rouge
Baton Rouge ( ; ) is a city in and the capital of the U.S. state of Louisiana
Louisiana , group=pronunciation (French: ''La Louisiane'') is a state in the Deep South and South Central regions of the United States. It is the 20th-sma ...
. The leaders of the St. Johns Plains Convention declared the establishment of the Republic of West Florida
The Republic of West Florida ( es, República de Florida Occidental, french: République de Floride occidentale), officially the State of Florida, was a short-lived republic in the western region of Spanish West Florida for just over months du ...
and requested that Madison send troops to prevent a Spanish reprisal. Acting on his own initiative, the governor of Mississippi Territory
The Territory of Mississippi was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from April 7, 1798, until December 10, 1817, when the western half of the territory was admitted to the Union as the State of Mississippi. T ...
. David Holmes, ordered U.S. Army soldiers into West Florida. In what became known as the October Proclamation, Madison announced that the United States had taken control of the Republic of West Florida, assigning it to the Territory of Orleans
The Territory of Orleans or Orleans Territory was an organized incorporated territory of the United States that existed from October 1, 1804, until April 30, 1812, when it was admitted to the Union as the State of Louisiana.
History
In 1804, ...
. Spain retained control of the portion of West Florida east of the Perdido River
Perdido River, historically Rio Perdido (1763), is a U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map accessed April 15, 2011 river in the U.S. states of Alabama and Florida; the Perdido, a desig ...
. Madison also employed George Mathews to stir up a rebellion against Spain in East Florida and the remaining Spanish portions of West Florida, but this effort proved unsuccessful.
Seminole Wars
With a minor military presence in the Floridas, Spain was unable to restrain theSeminole
The Seminole are a Native American people who developed in Florida in the 18th century. Today, they live in Oklahoma and Florida, and comprise three federally recognized tribes: the Seminole Nation of Oklahoma, the Seminole Tribe of Florida, an ...
Indians, who routinely conducted cross-border raids on American villages and farms and protected slave refugees from the United States. To stop the Seminole from raiding Georgia settlements and offering havens for runaway slaves, the U.S. Army led increasingly frequent incursions into Spanish territory. In early 1818, Monroe ordered General Andrew Jackson to the Georgia–Florida border to defend against Seminole attacks. Monroe authorized Jackson to attack Seminole encampments in Spanish Florida, but not Spanish settlements themselves. In what became known as the First Seminole War
The Seminole Wars (also known as the Florida Wars) were three related military conflicts in Florida between the United States and the Seminole, citizens of a Native American nation which formed in the region during the early 1700s. Hostilities ...
, Jackson crossed over into Spanish territory and attacked the Spanish fort at St. Marks. He also executed two British subjects whom he accused of having incited the Seminoles to raid American settlements. Jackson claimed that the attack on the fort was necessary as the Spanish were providing aid to the Seminoles. After taking the fort St. Marks, Jackson moved on the Spanish position at Pensacola
Pensacola () is the westernmost city in the Florida Panhandle, and the county seat and only incorporated city of Escambia County, Florida, United States. As of the 2020 United States census, the population was 54,312. Pensacola is the principal ci ...
, capturing it in May 1818.
In a letter to Jackson, Monroe reprimanded the general for exceeding his orders, but also acknowledged that Jackson may have been justified given the circumstances in the war against the Seminoles. Though he had not authorized Jackson's attacks on Spanish posts, Monroe recognized that Jackson's campaign left the United States with a stronger hand in ongoing negotiations over the purchase of the Floridas, as it showed that Spain was unable to defend its territories. The Monroe administration restored the Floridas to Spain, but requested that Spain increase efforts to prevent Seminole raids. Some in Monroe's cabinet, including Secretary of War John Calhoun, wanted the aggressive general court-martial
A court-martial or court martial (plural ''courts-martial'' or ''courts martial'', as "martial" is a postpositive adjective) is a military court or a trial conducted in such a court. A court-martial is empowered to determine the guilt of memb ...
ed, or at least reprimanded. Secretary of State Adams alone took the ground that Jackson's acts were justified by the incompetence of Spanish authority to police its own territory, arguing that Spain had allowed East Florida to become "a derelict open to the occupancy of every enemy, civilized or savage, of the United States, and serving no other earthly purpose than as a post of annoyance to them." His arguments, along with the restoration of the Floridas, convinced the British and Spanish not to retaliate against the United States for Jackson's conduct.
News of Jackson's exploits caused consternation in Washington and ignited a congressional investigation. Clay attacked Jackson's actions and proposed that his colleagues officially censure the general. Even many members of Congress who tended to support Jackson worried about the consequences of allowing a general to make war without the consent of Congress. In reference to popular generals who had taken power through military force, Speaker of the House Henry Clay urged his fellow congressmen to "remember that Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
had her Alexander
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
her Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, and ...
, England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
her Cromwell
Oliver Cromwell (25 April 15993 September 1658) was an English politician and military officer who is widely regarded as one of the most important statesmen in English history. He came to prominence during the 1639 to 1651 Wars of the Three Ki ...
, France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
her Bonaparte." Dominated by Democratic-Republicans, the 15th Congress was generally expansionist and supportive of the popular Jackson. After much debate, the House of Representatives voted down all resolutions that condemned Jackson, thus implicitly endorsing the military intervention. Jackson's actions in the First Seminole War would be the subject of ongoing controversy in subsequent years, as Jackson claimed that Monroe had secretly ordered him to attack the Spanish settlements, a claim that Monroe denied.
Acquisition of Florida
 Negotiations over the purchase of the Floridas began in early 1818. Don
Negotiations over the purchase of the Floridas began in early 1818. Don Luis de Onís
Luis is a given name. It is the Spanish form of the originally Germanic name or . Other Iberian Romance languages have comparable forms: (with an accent mark on the i) in Portuguese and Galician, in Aragonese and Catalan, while is archaic ...
, the Spanish Minister at Washington, suspended negotiations after Jackson attacked Spanish settlements, but he resumed his talks with Secretary of State Adams after the U.S. restored the territories. On February 22, 1819, Spain and the United States signed the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined t ...
, which ceded the Floridas
The Floridas ( es, Las Floridas) was a region of the southeastern United States comprising the historical colonies of East Florida and West Florida. The borders of East and West Florida varied. In 1783, when Spain acquired West Florida and re-ac ...
in return for the assumption by the United States of claims of American citizens against Spain to an amount not exceeding $5,000,000. The money was not actually a purchase price.
The treaty also contained a definition of the boundary between Spanish and American possessions on the North American continent. Beginning at the mouth of the Sabine River, the line ran along that river to the 32nd parallel, then due north to the Red River, which it followed to the 100th meridian, due north to the Arkansas River
The Arkansas River is a major tributary of the Mississippi River. It generally flows to the east and southeast as it traverses the U.S. states of Colorado, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Arkansas. The river's source basin lies in the western United Stat ...
, and along that river to its source
Source may refer to:
Research
* Historical document
* Historical source
* Source (intelligence) or sub source, typically a confidential provider of non open-source intelligence
* Source (journalism), a person, publication, publishing institute o ...
, then north to the 42nd parallel, which it followed to the Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continen ...
. The United States renounced all claims to the lands west and south of this boundary, while Spain surrendered its claim to Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, co ...
. Spanish delay in relinquishing control of the Floridas led some congressmen to call for war, but Spain peacefully transferred control in February 1821.
Latin America
Engagement
 Monroe was deeply sympathetic to the Latin American revolutionary movements against Spain. He was determined that the United States should never repeat the policies of the Washington administration during the French Revolution, when the nation had failed to demonstrate its sympathy for the aspirations of peoples seeking to establish republican governments. He did not envisage military involvement but only the provision of moral support, as he believed that a direct American intervention would provoke other European powers into assisting Spain. Despite his preferences, Monroe initially refused to recognize the Latin American governments due to ongoing negotiations with Spain over Florida.
In March 1822, Monroe officially recognized the countries of
Monroe was deeply sympathetic to the Latin American revolutionary movements against Spain. He was determined that the United States should never repeat the policies of the Washington administration during the French Revolution, when the nation had failed to demonstrate its sympathy for the aspirations of peoples seeking to establish republican governments. He did not envisage military involvement but only the provision of moral support, as he believed that a direct American intervention would provoke other European powers into assisting Spain. Despite his preferences, Monroe initially refused to recognize the Latin American governments due to ongoing negotiations with Spain over Florida.
In March 1822, Monroe officially recognized the countries of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th ...
, Peru
, image_flag = Flag of Peru.svg
, image_coat = Escudo nacional del Perú.svg
, other_symbol = Great Seal of the State
, other_symbol_type = Seal (emblem), National seal
, national_motto = "Fi ...
, Colombia
Colombia (, ; ), officially the Republic of Colombia, is a country in South America with insular regions in North America—near Nicaragua's Caribbean coast—as well as in the Pacific Ocean. The Colombian mainland is bordered by the Car ...
, Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
, and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
. Secretary of State Adams, under Monroe's supervision, wrote the instructions for the ambassadors to these new countries. They declared that the policy of the United States was to uphold republican institutions and to seek treaties of commerce on a most-favored-nation basis. The United States would support inter-American congresses dedicated to the development of economic and political institutions fundamentally differing from those prevailing in Europe. Monroe took pride as the United States was the first nation to extend recognition and to set an example to the rest of the world for its support of the "cause of liberty and humanity". In 1824, the U.S. and Gran Colombia
Gran Colombia (, "Great Colombia"), or Greater Colombia, officially the Republic of Colombia (Spanish: ''República de Colombia''), was a state that encompassed much of northern South America and part of southern Central America from 1819 to 18 ...
reached the Anderson–Gual Treaty
The Anderson–Gual Treaty (formally, the General Convention of Peace, Amity, Navigation, and Commerce) was an 1824 treaty between the United States and Gran Colombia. It is the first bilateral treaty that the United States concluded with another A ...
, a general convention of peace, amity, navigation, and commerce that represented the first treaty the United States entered into with another country in the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
. Between 1820 and 1830, the number of U.S. consuls assigned to foreign countries would double, with much of that growth coming in Latin America. These consuls would help merchants expand U.S. trade in the Western Hemisphere.
Monroe Doctrine
The British had a strong interest in ensuring the demise of Spanish colonialism, as the Spanish followed amercantilist
Mercantilism is an economic policy that is designed to maximize the exports and minimize the imports for an economy. It promotes imperialism, colonialism, tariffs and subsidies on traded goods to achieve that goal. The policy aims to reduce a ...
policy that imposed restrictions on trade between Spanish colonies and foreign powers. In October 1823, Ambassador Rush informed Secretary of State Adams that Foreign Secretary George Canning
George Canning (11 April 17708 August 1827) was a British Tory statesman. He held various senior cabinet positions under numerous prime ministers, including two important terms as Foreign Secretary, finally becoming Prime Minister of the Unit ...
desired a joint declaration to deter any other power from intervening in Central and South America. Canning was motivated in part by the restoration of King Ferdinand VII of Spain
, house = Bourbon-Anjou
, father = Charles IV of Spain
, mother = Maria Luisa of Parma
, birth_date = 14 October 1784
, birth_place = El Escorial, Spain
, death_date =
, death_place = Madrid, Spain
, burial_plac ...
by France. Britain feared that either France or the "Holy Alliance
The Holy Alliance (german: Heilige Allianz; russian: Священный союз, ''Svyashchennyy soyuz''; also called the Grand Alliance) was a coalition linking the monarchist great powers of Austria, Prussia, and Russia. It was created after ...
" of Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
would help Spain regain control of its colonies, and sought American cooperation in opposing such an intervention. Monroe and Adams deliberated the British proposal extensively, and Monroe conferred with former presidents Jefferson and Madison.
Monroe was at first inclined to accept Canning's proposal, and Madison and Jefferson both shared this preference. Adams, however, vigorously opposed cooperation with Great Britain, contending that a statement of bilateral nature could limit U.S. expansion in the future. Additionally, Adams and Monroe shared a reluctance to appear as a junior partner in any alliance. Rather than responding to Canning's alliance offer, Monroe decided to issue a statement regarding Latin America in his 1823 Annual Message to Congress. In series of meetings with the cabinet, Monroe formulated his administration's official policy regarding European intervention in Latin America. Adams in particular played a major role in these cabinet meetings, and the Secretary of State convinced Monroe to avoid antagonizing the members of the Holy Alliance with unduly belligerent language.
Monroe's annual message was read by both houses of Congress on December 2, 1823. In it, he articulated what became known as the Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile ac ...
. The doctrine reiterated the traditional U.S. policy of neutrality with regard to European wars and conflicts, but declared that the United States would not accept the recolonization of any country by its former European master. Monroe stated that European countries should no longer consider the Western Hemisphere open to new colonization, a jab aimed primarily at Russia, which was attempting to expand its colony on the northern Pacific Coast. At the same time, Monroe avowed non-interference with existing European colonies in the Americas.
The Monroe Doctrine was well received in the United States and Britain, while Russia, French, and Austrian leaders privately denounced it. The European powers knew that the U.S. had little ability to back up the Monroe Doctrine with force, but the United States was able to "free ride" on the strength of the British Royal Navy. Nonetheless, the issuance of the Monroe Doctrine displayed a new level of assertiveness by the United States in international relations, as it represented the country's first claim to a sphere of influence
In the field of international relations, a sphere of influence (SOI) is a spatial region or concept division over which a state or organization has a level of cultural, economic, military or political exclusivity.
While there may be a formal al ...
. It also marked the country's shift in psychological orientation away from Europe and towards the Americas. Debates over foreign policy would no longer center on relations with Britain and France, but would instead focus on western expansion and relations with Native Americans.
Adams
Adams and Clay sought engagement with Latin America in order to prevent it from falling under the British Empire's economic influence. As part of this goal, the administration favored sending a U.S. delegation to theCongress of Panama
The Congress of Panama (also referred to as the Amphictyonic Congress, in homage to the Amphictyonic League of Ancient Greece) was a congress organized by Simón Bolívar in 1826 with the goal of bringing together the new republics of Latin Americ ...
, an 1826 conference of New World republics organized by Simón Bolívar
Simón José Antonio de la Santísima Trinidad Bolívar y Palacios (24 July 1783 – 17 December 1830) was a Venezuelan military and political leader who led what are currently the countries of Colombia, Venezuela, Ecuador, Peru, Panama and B ...
.. Clay and Adams hoped that the conference would inaugurate a " Good Neighborhood Policy" among the independent states of the Americas.. However, the funding for a delegation and the confirmation of delegation nominees became entangled in a political battle over Adams's domestic policies, with opponents such as Senator Martin Van Buren impeding the process of confirming a delegation.. Though the delegation finally won confirmation from the Senate, it never reached the Congress of Panama due to the Senate's delay.
In 1825, Antonio José Cañas
Antonio José Cañas Quintanilla (26 October 1785 – 24 February 1844) was a Salvadoran military officer, diplomat, and politician. For two brief periods he was head of state of the State of El Salvador, within the Federal Republic of Central ...
, the Federal Republic of Central America's (FCRA) ambassador to the United States, proposed a treaty to provide for the construction of a canal across Nicaragua
Nicaragua (; ), officially the Republic of Nicaragua (), is the largest country in Central America, bordered by Honduras to the north, the Caribbean to the east, Costa Rica to the south, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Managua is the cou ...
. Impressed with the new Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
, Adams was intrigued by the possibility of the canal. The FCRA awarded a contract for the construction of the canal to a group of American businessmen, but the enterprise ultimately collapsed due to lack of funding. The failure of the canal contributed to the collapse of the FCRA, which was dissolved in 1839.
Mexico gained its independence shortly after the United States and Spain ratified the Adams–Onís Treaty
The Adams–Onís Treaty () of 1819, also known as the Transcontinental Treaty, the Florida Purchase Treaty, or the Florida Treaty,Weeks, p.168. was a treaty between the United States and Spain in 1819 that ceded Florida to the U.S. and defined t ...
, and the Adams administration approached Mexico about a renegotiation of the Mexico–United States border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border traver ...
. Joel Roberts Poinsett
Joel Roberts Poinsett (March 2, 1779December 12, 1851) was an American physician, diplomat and botanist. He was the first U.S. agent in South America, a member of the South Carolina legislature and the United States House of Representatives, the ...
, the ambassador to Mexico, unsuccessfully attempted to purchase Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
. In 1826, American settlers in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
launched the Fredonian Rebellion
The Fredonian Rebellion (December 21, 1826 – January 31, 1827) was the first attempt by Anglo settlers in Texas to secede from Mexico. The settlers, led by Empresario Haden Edwards, declared independence from Mexican Texas and created the R ...
, but Adams prevented the United States from becoming directly involved.
Adams, trade, and claims
 One of the major foreign policy goals of the Adams administration was the expansion of American trade. His administration reached
One of the major foreign policy goals of the Adams administration was the expansion of American trade. His administration reached reciprocity
Reciprocity may refer to:
Law and trade
* Reciprocity (Canadian politics), free trade with the United States of America
** Reciprocal trade agreement, entered into in order to reduce (or eliminate) tariffs, quotas and other trade restrictions on ...
treaties with a number of nations, including Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
, the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
, the Scandinavia
Scandinavia; Sámi languages: /. ( ) is a subregion#Europe, subregion in Northern Europe, with strong historical, cultural, and linguistic ties between its constituent peoples. In English usage, ''Scandinavia'' most commonly refers to Denmark, ...
n countries, Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
, and the Federal Republic of Central America
The Federal Republic of Central America ( es, República Federal de Centroamérica), originally named the United Provinces of Central America ( es, Provincias Unidas del Centro de América), and sometimes simply called Central America, in it ...
. The administration also reached commercial agreements with the Kingdom of Hawaii
The Hawaiian Kingdom, or Kingdom of Hawaiʻi ( Hawaiian: ''Ko Hawaiʻi Pae ʻĀina''), was a sovereign state located in the Hawaiian Islands. The country was formed in 1795, when the warrior chief Kamehameha the Great, of the independent island ...
and the Kingdom of Tahiti
The Kingdom of Tahiti was a monarchy founded by paramount chief Pōmare I, who, with the aid of British missionaries and traders, and European weaponry, unified the islands of Tahiti, Moʻorea, Teti‘aroa, and Mehetia. The kingdom eventually ...
. Adams also renewed existing treaties with Britain, France, and the Netherlands, and began negotiations with Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, and Mexico
Mexico (Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guatema ...
that would all lead to successful treaties after Adams left office. Collectively, these commercial treaties were designed to expand trade in peacetime and preserve neutral trading rights in wartime.
Adams sought to reinvigorate trade with the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greater A ...
, which had fallen dramatically since 1801. Agreements with Denmark and Sweden opened their colonies to American trade, but Adams was especially focused on opening trade with the British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grena ...
. The United States had reached a commercial agreement with Britain in 1815, but that agreement excluded British possessions in the Western Hemisphere. In response to U.S. pressure, the British had begun to allow a limited amount of American imports to the West Indies in 1823, but U.S. leaders continued to seek an end to Britain's protective Imperial Preference
Imperial Preference was a system of mutual tariff reduction enacted throughout the British Empire following the Ottawa Conference of 1932. As Commonwealth Preference, the proposal was later revived in regard to the members of the Commonwealth of N ...
system. In 1825, Britain banned U.S. trade with the British West Indies, dealing a blow to Adams's prestige.. The Adams administration negotiated extensively with the British to lift this ban, but the two sides were unable to come to an agreement. Despite the loss of trade with the British West Indies, the other commercial agreements secured by Adams helped expand overall volume of U.S. exports.
The Adams administration settled several outstanding American claims that arose from the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
, the War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States of America and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America, with limited participation by Spain in Florida. It bega ...
, and the Treaty of Ghent
The Treaty of Ghent () was the peace treaty that ended the War of 1812 between the United States and the United Kingdom. It took effect in February 1815. Both sides signed it on December 24, 1814, in the city of Ghent, United Netherlands (now in ...
. He viewed the pursuit of these claims as an important component in establishing U.S. freedom of trade. Gallatin, in his role as ambassador to Britain, convinced the British to agree to an indemnity of approximately $1 million. The U.S. also received smaller indemnities from Sweden, Denmark, and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
. The U.S. sought a large indemnity from France, but negotiations broke down after the government of Jean-Baptiste de Villèle
Jean-Baptiste is a male French name, originating with Saint John the Baptist, and sometimes shortened to Baptiste. The name may refer to any of the following:
Persons
* Charles XIV John of Sweden, born Jean-Baptiste Jules Bernadotte, was King ...
collapsed in 1828. Clay and Adams were also unsuccessful in their pursuit of several claims against Mexico.
Other issues and incidents
Haiti
 After early 1802, when he learned that Napoleon intended to regain a foothold in Saint-Domingue and Louisiana, Jefferson proclaimed neutrality in relation to the
After early 1802, when he learned that Napoleon intended to regain a foothold in Saint-Domingue and Louisiana, Jefferson proclaimed neutrality in relation to the Haitian Revolution
The Haitian Revolution (french: révolution haïtienne ; ht, revolisyon ayisyen) was a successful insurrection by slave revolt, self-liberated slaves against French colonial rule in Saint-Domingue, now the sovereign state of Haiti. The revolt ...
. The U.S. allowed war contraband to "continue to flow to the blacks through usual U.S. merchant channels and the administration would refuse all French requests for assistance, credits, or loans." The "geopolitical and commercial implications" of Napoleon's plans outweighed Jefferson's fears of a slave-led nation. After the rebels in Saint-Domingue proclaimed independence from France in the new republic of Haiti
Haiti (; ht, Ayiti ; French: ), officially the Republic of Haiti (); ) and formerly known as Hayti, is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean Sea, east of Cuba and Jamaica, and ...
in 1804, Jefferson refused to recognize Haiti as the second independent republic in the Americas. In part he hoped to win Napoleon's support over the acquisition of Florida. American slaveholders had been frightened and horrified by the slave massacres of the planter class during the rebellion and after, and a southern-dominated Congress was "hostile to Haiti."Matthewson, Tim. "Jefferson and the Non-recognition of Haiti"''American Philosophical Society'' 140, no. 1 (March 1996), p. 22. They feared its success would encourage slave revolt in the
American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
. Historian Tim Matthewson notes that Jefferson "acquiesced in southern policy, the embargo of trade and nonrecognition, the defense of slavery internally and the denigration of Haiti abroad." According to the historian George Herring, "the Florida diplomacy reveals him effersonat his worst. His lust for land trumped his concern for principle."Herring (2008), p. 108.
Slave trade
In the 1790s, many anti-slavery leaders had come to believe that the institution of slavery would become extinct in the United States in the foreseeable future. These hopes lay in part on the enthusiasm for the abolition of slavery in the North, and in the decline of the importation of slaves throughout the South. The Constitution had included a provision preventing Congress from enacting a law banning the importation of slaves until 1808. In the years before Jefferson took office, the growing fear of slave rebellions led to diminished enthusiasm in the South for the abolition of slavery, and many states began to enactBlack Codes
The Black Codes, sometimes called the Black Laws, were laws which governed the conduct of African Americans (free and freed blacks). In 1832, James Kent (jurist), James Kent wrote that "in most of the United States, there is a distinction in re ...
designed to restrict the behavior of free blacks. During his presidential term, Jefferson was disappointed that the younger generation was making no move to abolish slavery; he largely avoided the issue until 1806. He did succeed in convincing Congress to block the foreign importation of slaves into the newly purchased Louisiana Territory.
Seeing that in 1808 the twenty-year constitutional ban on ending the international slave trade would expire, in December 1806 in his presidential message to Congress, Jefferson called for a law to ban it. He denounced the trade as "violations of human rights which have been so long continued on the unoffending inhabitants of Africa, in which the morality, the reputation, and the best interests of our country have long been eager to proscribe." Jefferson signed the new law and the international trade became illegal in January 1808. Britain at the same time made the international trade illegal.
The legal trade had averaged 14,000 slaves a year; illegal smuggling at the rate of about 1000 slaves a year continued for decades. "The two major achievements of Jefferson's presidency were the Louisiana Purchase and the abolition of the slave trade," according to historian John Chester Miller. Miller, John Chester, ''The wolf by the ears: Thomas Jefferson and slavery'' (1980), p. 142.
Russo-American Treaty
In the 18th century, Russia had establishedRussian America
Russian America (russian: Русская Америка, Russkaya Amerika) was the name for the Russian Empire's colonial possessions in North America from 1799 to 1867. It consisted mostly of present-day Alaska in the United States, but a ...
on the Pacific coast. In 1821, Tsar Alexander I Alexander I may refer to:
* Alexander I of Macedon, king of Macedon 495–454 BC
* Alexander I of Epirus (370–331 BC), king of Epirus
* Pope Alexander I (died 115), early bishop of Rome
* Pope Alexander I of Alexandria (died 320s), patriarch of ...
issued an edict declaring Russia's sovereignty over the North American Pacific coast north of the 51st parallel north. The edict also forbade foreign ships to approach within 115 miles of the Russian claim. Adams strongly protested the edict, which potentially threatened both the commerce and expansionary ambitions of the United States. Seeking favorable relations with the U.S., Alexander agreed to the Russo-American Treaty of 1824
The Russo-American Treaty of 1824 (also known as the Convention of 1824) was signed in St. Petersburg between representatives of Russia and the United States on April 17, 1824, ratified by both nations on January 11, 1825 and went into effect on Ja ...
. In the treaty, Russia limited its claims to lands north of parallel 54°40′ north
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in t ...
, and also agreed to open Russian ports to U.S. ships.
References
Works cited
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Rutland, Robert A. ''The Presidency of James Madison'' (Univ. Press of Kansas, 1990). . * Stagg, John C. A. ''Mr. Madison's War: Politics, Diplomacy, and Warfare in the Early American Republic, 1783–1830'' (1983). * * *Further reading
* Dobson, John M. ''Belligerents, Brinkmanship, and the Big Stick: A Historical Encyclopedia of American Diplomatic Concepts: A Historical Encyclopedia of American Diplomatic Concepts'' (ABC-CLIO, 2009) pp 1–68. * Hill, Peter P. ''Napoleon's Troublesome Americans: Franco-American Relations, 1804-1815'' (2005)online free to borrow
* Pratt, Julius W. ''Expansionists of 1812'' (1957
online
{{DEFAULTSORT:History of U.S. foreign policy, 1801-1829 1801 establishments in the United States 1829 disestablishments in the United States History of the foreign relations of the United States Presidency of Thomas Jefferson Presidency of James Madison Presidency of James Monroe Presidency of John Quincy Adams