|
Ukase Of 1821
The Ukase of 1821 (russian: Указ 1821 года) was a Russian Empire, Russian proclamation (a ''ukase'') of territorial sovereignty over northwestern North America, roughly present-day Alaska and most of the Pacific Northwest. The ''ukase'' was declared on September 4, 1821 (Julian calendar, O. S.). Jurisdiction The first section of the ukase stated that "the pursuits of commerce, whaling, fishing and other industry, on all islands, ports and gulfs, including the whole north-west coast of North America to the 45°50′ north latitude, are all included in this edict for the purpose of granting the same exclusivity to Russian subjects". The second section "prohibits all foreign vessels not only from landing on the coasts and islands belonging to Russia, but, also, does not permit them to approach these islands and coasts within less than one hundred Italian miles, without the vessels being subject to confiscation, along with the whole cargo" (one Italian mile was 2,025 yards/1, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. The rise of the Russian Empire coincided with the decline of neighbouring rival powers: the Swedish Empire, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, Qajar Iran, the Ottoman Empire, and Qing China. It also held colonies in North America between 1799 and 1867. Covering an area of approximately , it remains the third-largest empire in history, surpassed only by the British Empire and the Mongol Empire; it ruled over a population of 125.6 million people per the 1897 Russian census, which was the only census carried out during the entire imperial period. Owing to its geographic extent across three continents at its peak, it featured great ethnic, linguistic, religious, and economic diversity. From the 10th–17th centuries, the land ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Vancouver
Captain George Vancouver (22 June 1757 – 10 May 1798) was a British Royal Navy officer best known for his 1791–1795 expedition, which explored and charted North America's northwestern Pacific Coast regions, including the coasts of what are now the Canadian province of British Columbia as well as the US states of Alaska, Washington and Oregon. He also explored the Hawaiian Islands and the southwest coast of Australia. Vancouver Island, the city of Vancouver in British Columbia, Vancouver, Washington in the United States, Mount Vancouver on the Canadian–US border between Yukon and Alaska, and New Zealand's fourth-highest mountain, also Mount Vancouver, are all named after him. Early life George Vancouver was born in the seaport town of King's Lynn (Norfolk, England) on 22 June 1757 - the sixth and youngest child of John Jasper Vancouver, a Dutch-born deputy collector of customs, and Bridget Berners. He came from an old respected family. The surname Vancouver comes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Colonization Of The Americas
The Russian colonization of North America covers the period from 1732 to 1867, when the Russian Empire laid claim to northern Pacific Coast territories in the Americas. Russian colonial possessions in the Americas are collectively known as Russian America. Russian expansion eastward began in 1552, and in 1639 Russian explorers reached the Pacific Ocean. In 1725, Emperor Peter the Great ordered navigator Vitus Bering to explore the North Pacific for potential colonization. The Russians were primarily interested in the abundance of fur-bearing mammals on Alaska's coast, as stocks had been depleted by over hunting in Siberia. Bering's first voyage was foiled by thick fog and ice, but in 1741 a second voyage by Bering and Aleksei Chirikov made sight of the North American mainland. Russian ''promyshlenniki'' (trappers and hunters) quickly developed the maritime fur trade, which instigated several conflicts between the Aleuts and Russians in the 1760s. The fur trade proved to be a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monroe Doctrine
The Monroe Doctrine was a United States foreign policy position that opposed European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. It held that any intervention in the political affairs of the Americas by foreign powers was a potentially hostile act against the United States. The doctrine was central to American foreign policy for much of the 19th and early 20th centuries. President James Monroe first articulated the doctrine on December 2, 1823, during his seventh annual State of the Union Address to Congress (though it would not be named after him until 1850). At the time, nearly all Spanish colonies in the Americas had either achieved or were close to independence. Monroe asserted that the New World and the Old World were to remain distinctly separate spheres of influence, and thus further efforts by European powers to control or influence sovereign states in the region would be viewed as a threat to U.S. security. In turn, the United States would recognize and not interfere with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sitka, Alaska
russian: Ситка , native_name_lang = tli , settlement_type = Consolidated city-borough , image_skyline = File:Sitka 84 Elev 135.jpg , image_caption = Downtown Sitka in 1984 , image_size = 260 , image_flag = , image_seal = , nickname = , motto = , image_map = Map of Alaska highlighting Sitka City and Borough.svg , map_caption = , coordinates = , subdivision_type = , subdivision_name = , subdivision_type1 = State , subdivision_type2 = , subdivision_name1 = , subdivision_name2 = , established_title = Colonized Colonization, or colonisation, constitutes large-scale population movements wherein migrants maintain strong links with their, or their ancestors', former country – by such links, gain advantage over other inhabitants of the territo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the state capital and most populous city of the Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financial center of the New England region of the United States. It is the 24th- most populous city in the country. The city boundaries encompass an area of about and a population of 675,647 as of 2020. It is the seat of Suffolk County (although the county government was disbanded on July 1, 1999). The city is the economic and cultural anchor of a substantially larger metropolitan area known as Greater Boston, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) home to a census-estimated 4.8 million people in 2016 and ranking as the tenth-largest MSA in the country. A broader combined statistical area (CSA), generally corresponding to the commuting area and including Providence, Rhode Island, is home to approximately 8.2 million people, making it the sixth most populous in the United States. Boston is one of the oldest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
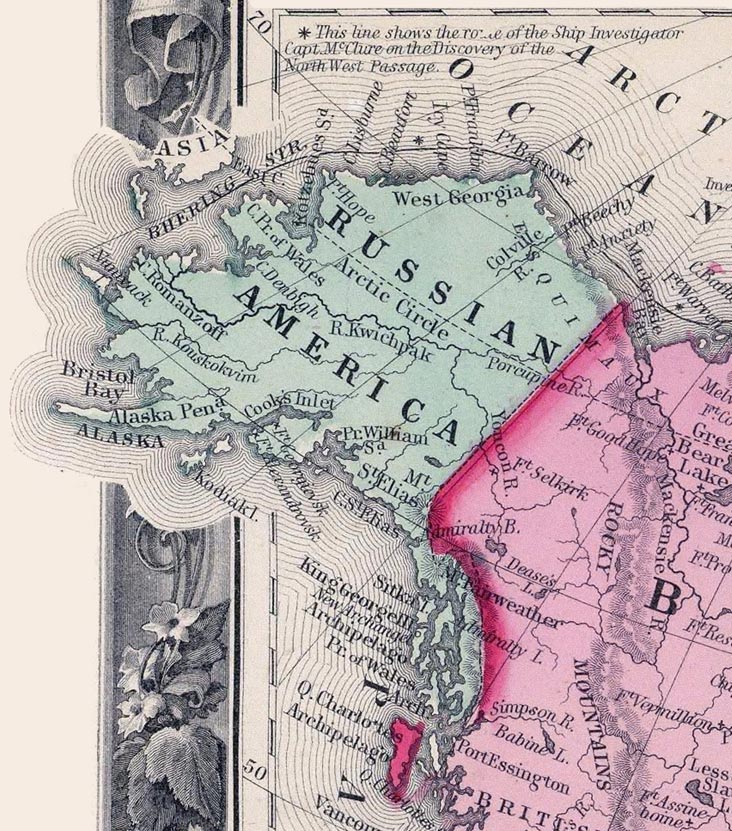
Alaska Boundary Dispute
The Alaska boundary dispute was a territorial dispute between the United States and the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, which then controlled Canada's foreign relations. It was resolved by arbitration in 1903. The dispute had existed between the Russian Empire and Britain since 1821, and was inherited by the United States as a consequence of the Alaska Purchase in 1867. The final resolution favored the American position, as Canada did not get an all-Canadian outlet from the Yukon gold fields to the sea. The disappointment and anger in Canada was directed less at the United States, and more at the British government for betraying Canadian interests in favor of healthier Anglo-American relations. Background 1825–1898 In 1825 Russia and the United Kingdom signed a treaty to define the borders of their respective colonial possessions, the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825. Part of the wording of the treaty was that: The vague phrase "the mountains parallel to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
League (unit)
A league is a unit of length. It was common in Europe and Latin America, but is no longer an official unit in any nation. Derived from an ancient Celtic unit and adopted by the Romans as the ''leuga'', the league became a common unit of measurement throughout western Europe. It may have originally represented, roughly, the distance a person could walk in an hour. Since the Middle Ages, many values have been specified in several countries. Different definitions Ancient Rome The league was used in Ancient Rome, defined as 1½ Roman miles (7,500 Roman feet, modern 2.2 km or 1.4 miles). The origin is the ''leuga Gallica'' ''(also: leuca Callica)'', the league of Gaul. Argentina The Argentine league (''legua'') is or 6,666 ''varas'': 1 ''vara'' is . English-speaking world On land, the league is most commonly defined as three miles (4.83km), though the length of a mile could vary from place to place and depending on the era. At sea, a league is . English usage also ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prince Of Wales Island (Alaska)
Prince of Wales Island (Tlingit: ''Taan'') is one of the islands of the Alexander Archipelago in the Alaska Panhandle. It is the fourth-largest island in the United States (after Hawaii, Kodiak Island, and Puerto Rico) and the 97th-largest island in the world. Geography and ecology The island is long, wide and has an area of , about one-tenth the size of Ireland and slightly larger than the state of Delaware. Approximately 6,000 people live on the island. Craig is the largest community; founded as a saltery in the early 20th century, it has a population of 1,500. Some 900 people live in Klawock, a long-established village that grew with the fishing industry. Hollis was a boom and bust mining town from 1900 to about 1915. Abandoned, it was re-established as a logging camp in the 1950s. It now has a population of 100 and is the location of the ferry terminal. Mountain peaks, all but the tallest of which were buried by Pleistocene glaciation, reach over . Fjords, steep-si ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
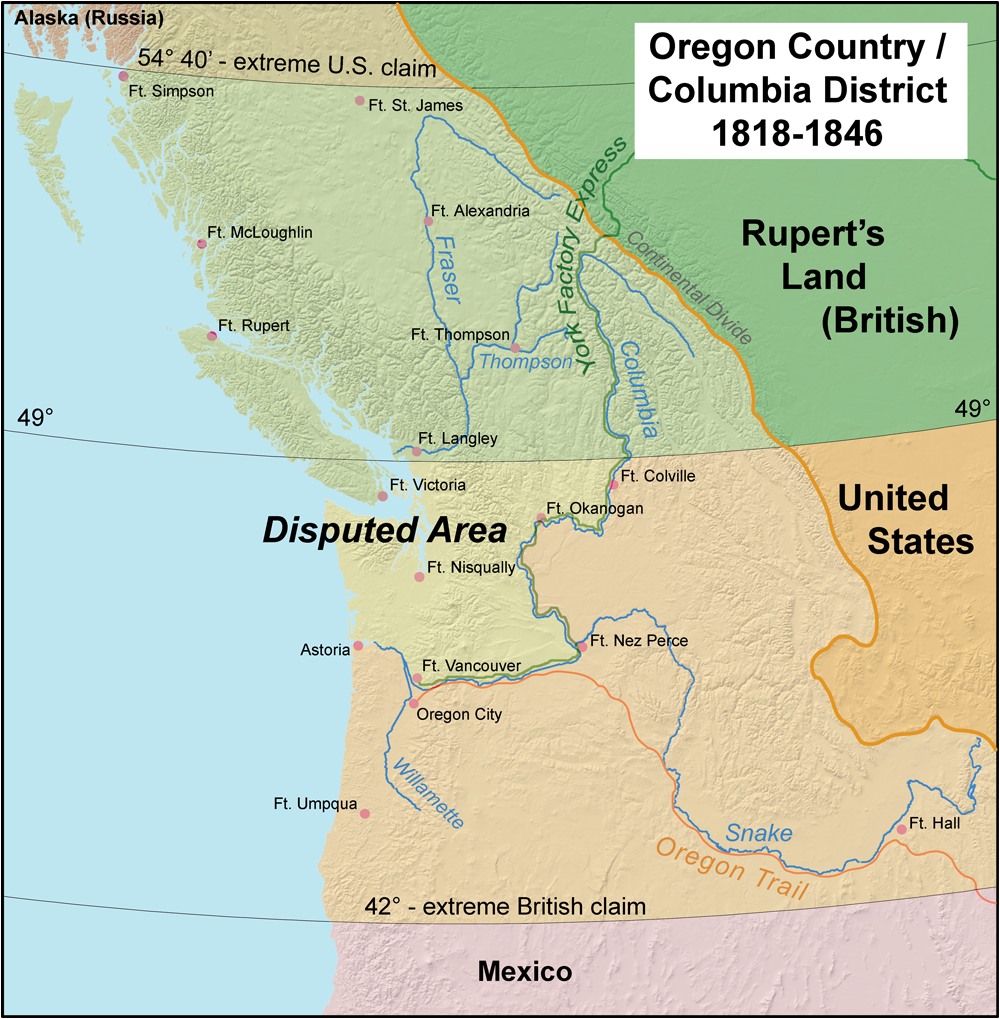
Parallel 54°40' North
The Oregon boundary dispute or the Oregon Question was a 19th-century territorial dispute over the political division of the Pacific Northwest of North America between several nations that had competing territorial and commercial aspirations in the region. Expansionist competition into the region began in the 18th century, with participants including the Russian Empire, Great Britain, Spain, and the United States. After the War of 1812, the Oregon dispute took on increased importance for diplomatic relations between the British Empire and the fledgling American republic. In the mid-1820s, the Russians signed the Russo-American Treaty of 1824 and the Russo-British Treaty of 1825, and the Spanish signed the Adams–Onís Treaty of 1819, by which Russia and Spain formally withdrew their respective territorial claims in the region, and the British and the Americans acquired residual territorial rights in the disputed area. But the question of sovereignty over a portion of the North Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Saint Petersburg (1825)
The Treaty of Saint Petersburg of 1825 or the Anglo-Russian Convention of 1825, officially the Convention Concerning the Limits of Their Respective Possessions on the Northwest Coast of America and the Navigation of the Pacific Ocean, defined the boundaries between Russian America and British claims and possessions of the Pacific Northwest, Pacific Coast, and the later Yukon and Arctic Ocean, Arctic regions of North America. It was agreed that along the coast at the southern tip of Prince of Wales Island (Alaska), Prince of Wales island (now known as parallel 54°40′ north) northward to the 56 parallel, with the island wholly belonging to Russia, then to 10 marine leagues () inland going north and west to the 141st meridian west and then north to the "Frozen Ocean", the current Alaska/Canadian Yukon boundary, would be the boundary. The coastal limit had, the year before, been established as the limit of overlapping American claims in the parallel Russo-American Treaty of 1824. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |