|
History Of U.S. Foreign Policy, 1829–1861
The history of U.S. foreign policy from 1829 to 1861 concerns the foreign policy of the United States during the presidential administrations of Andrew Jackson, Martin Van Buren, William Henry Harrison, John Tyler, James K. Polk, Zachary Taylor, Millard Fillmore, Franklin Pierce, and James Buchanan. During this era, the United States annexed the Republic of Texas, acquired the Mexican Cession by defeating Mexico in the Mexican–American War and partitioned Oregon Country with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland. The period began with the inauguration of Jackson in 1829, while the onset of the American Civil War in 1861 marked the start of the next period in U.S. foreign policy. Jackson's foreign policy focused on expanding trade and settling spoliation claims, and he reached an agreement with Britain to open Canadian and Caribbean ports to U.S. trade. After gaining independence from Mexico in 1835, the Republic of Texas sought annexation by the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
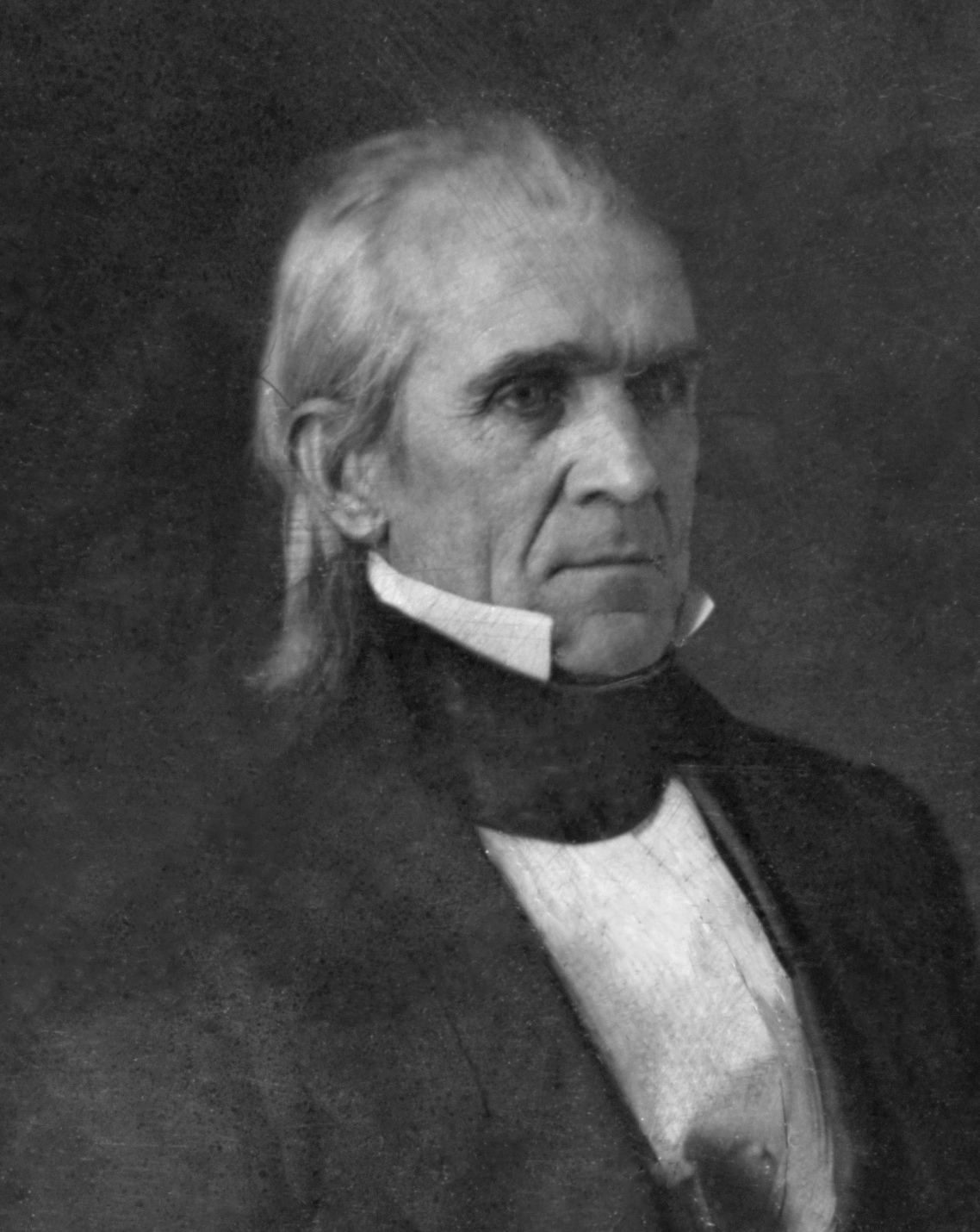
James Knox Polk By GPA Healy, 1858
James is a common English language surname and given name: * James (name), the typically masculine first name James * James (surname), various people with the last name James James or James City may also refer to: People * King James (other), various kings named James * Saint James (other) * James (musician) * James, brother of Jesus Places Canada * James Bay, a large body of water * James, Ontario United Kingdom * James College, a college of the University of York United States * James, Georgia, an unincorporated community * James, Iowa, an unincorporated community * James City, North Carolina * James City County, Virginia ** James City (Virginia Company) ** James City Shire * James City, Pennsylvania * St. James City, Florida Arts, entertainment, and media * ''James'' (2005 film), a Bollywood film * ''James'' (2008 film), an Irish short film * ''James'' (2022 film), an Indian Kannada-language film * James the Red Engine, a character in ''Tho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
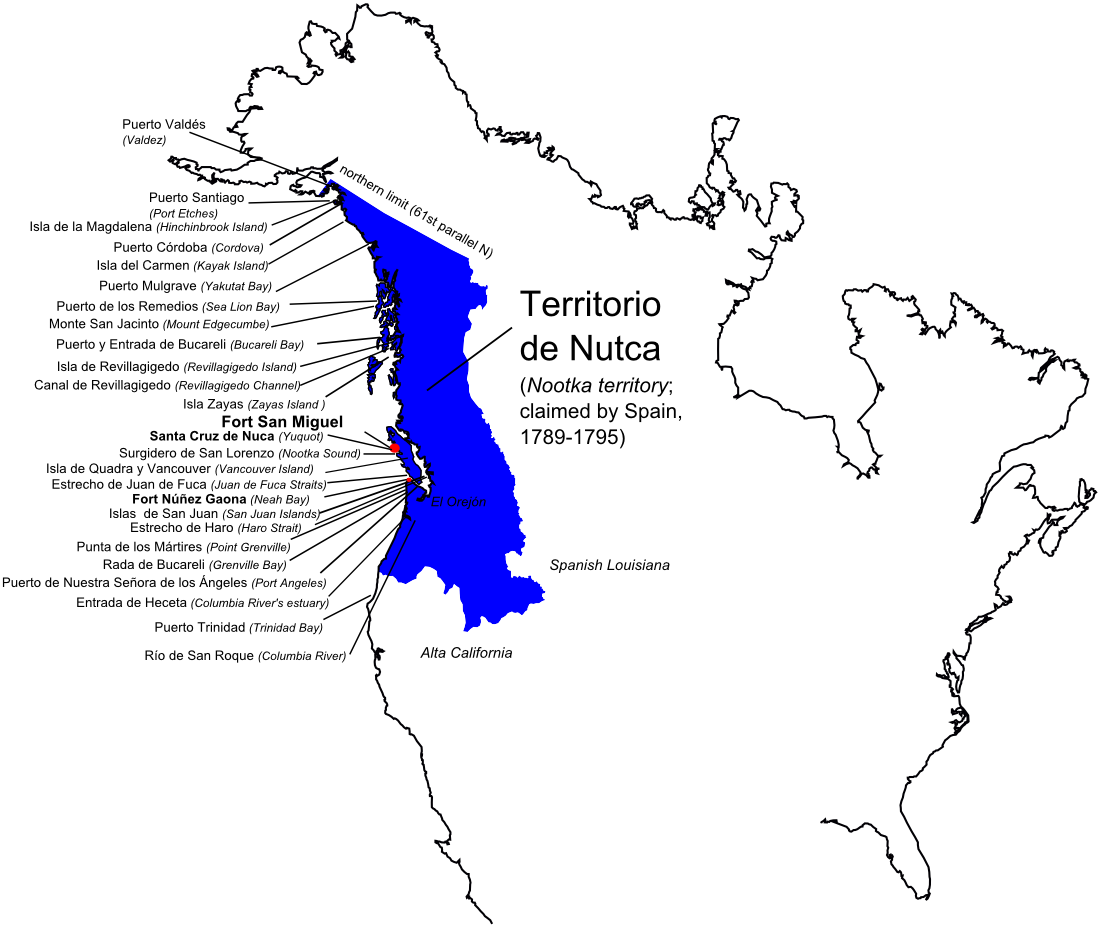
Oregon Country
Oregon Country was a large region of the Pacific Northwest of North America that was subject to a long dispute between the United Kingdom and the United States in the early 19th century. The area, which had been created by the Treaty of 1818, consisted of the land north of 42°N latitude, south of 54°40′N latitude, and west of the Rocky Mountains down to the Pacific Ocean and east to the Continental Divide. Article III of the 1818 treaty gave joint control to both nations for ten years, allowed land to be claimed, and guaranteed free navigation to all mercantile trade. However, both countries disputed the terms of the international treaty. Oregon Country was the American name while the British used Columbia District for the region. British and French Canadian fur traders had entered Oregon Country prior to 1810 before the arrival of American settlers from the mid-1830s onwards, which led to the foundation of the Provisional Government of Oregon. Its coastal areas north from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Winfield Scott
Winfield Scott (June 13, 1786May 29, 1866) was an American military commander and political candidate. He served as a general in the United States Army from 1814 to 1861, taking part in the War of 1812, the Mexican–American War, the early stages of the American Civil War and conflicts with Native Americans. Scott was the Whig Party's presidential nominee in the 1852 election, but was defeated by Democrat Franklin Pierce. He was known as Old Fuss and Feathers for his insistence on proper military etiquette, as well as the Grand Old Man of the Army for his many years of service. Scott was born near Petersburg, Virginia, in 1786. After training as a lawyer and brief militia service, he joined the army in 1808 as a captain of the light artillery. In the War of 1812, Scott served on the Canadian front, taking part in the Battle of Queenston Heights and the Battle of Fort George, and was promoted to brigadier general in early 1814. He served with distinction in the Battle o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rebellions Of 1837–1838
The Rebellions of 1837–1838 (french: Les rébellions de 1837), were two armed uprisings that took place in Lower and Upper Canada in 1837 and 1838. Both rebellions were motivated by frustrations with lack of political reform. A key shared goal was responsible government, which was eventually achieved in the incidents' aftermath. The rebellions led directly to Lord Durham's Report on the Affairs of British North America and to the Act of Union 1840 which partially reformed the British provinces into a unitary system and eventually led to the British North America Act, 1867, which created the contemporary Canadian federation and its government. Atlantic context Some historians contend that the rebellions in 1837 ought to be viewed in the wider context of the late-18th- and early-19th-century Atlantic revolutions. The American Revolutionary War of 1775–83, the French Revolution of 1789–99, the Haitian Revolution of 1791–1804, the Irish Rebellion of 1798 and the rebellio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Treaty Of Guadalupe Hidalgo
The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ( es, Tratado de Guadalupe Hidalgo), officially the Treaty of Peace, Friendship, Limits, and Settlement between the United States of America and the United Mexican States, is the peace treaty that was signed on 2 February 1848, in the Villa de Guadalupe Hidalgo (now a neighborhood of Mexico City) between the United States and Mexico that ended the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). The treaty was ratified by the United States on 10 March and by Mexico on 19 May. The ratifications were exchanged on 30 May, and the treaty was proclaimed on 4 July 1848. With the defeat of its army and the fall of its capital in September 1847, Mexico entered into negotiations with the U.S. peace envoy, Nicholas Trist, to end the war. On the Mexican side, there were factions that did not concede defeat or seek to engage in negotiations. The treaty called for the United States to pay US$15 million to Mexico and to pay off the claims of American citizens against Mex ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Santa Fe De Nuevo México
Santa Fe de Nuevo México ( en, Holy Faith of New Mexico; shortened as Nuevo México or Nuevo Méjico, and translated as New Mexico in English) was a Kingdom of the Spanish Empire and New Spain, and later a territory of independent Mexico. The first capital was San Juan de los Caballeros (at San Gabriel de Yungue-Ouinge) from 1598 until 1610, and from 1610 onward the capital was La Villa Real de la Santa Fe de San Francisco de Asís. The name of "New Mexico", the capital in Santa Fe, the gubernatorial office at the Palace of the Governors, ''vecino'' citizen-soldiers, and rule of law were retained as the New Mexico Territory and later state of New Mexico became part of the United States. The New Mexican citizenry, primarily consisting of Hispano, Pueblo, Navajo, Apache, and Comanche peoples, became citizens of the United States as a result of the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo (1848). ' is often incorrectly believed to have taken its name from the post-independent nation o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alta California
Alta California ('Upper California'), also known as ('New California') among other names, was a province of New Spain, formally established in 1804. Along with the Baja California peninsula, it had previously comprised the province of , but was split off into a separate province in 1804 (named ). Following the Mexican War of Independence, it became a territory of Mexico in April 1822 and was renamed in 1824. The territory included all of the modern U.S. states of California, Nevada, and Utah, and parts of Arizona, Wyoming, Colorado, and New Mexico. In the 1836 Siete Leyes government reorganization, the two Californias were once again combined (as a single ). That change was undone in 1846, but rendered moot by the U.S. military occupation of California in the Mexican-American War. Neither Spain nor Mexico ever colonized the area beyond the southern and central coastal areas of present-day California and small areas of present-day Arizona, so they exerted no effective cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1844 United States Presidential Election
The 1844 United States presidential election was the 15th quadrennial United States presidential election, presidential election, held from Friday, November 1 to Wednesday, December 4, 1844. History of the Democratic Party (United States), Democrat James K. Polk defeated Whig Party (United States), Whig Henry Clay in a close contest turning on the controversial issues of slavery in the United States, slavery and the Texas annexation, annexation of the Republic of Texas. This is the only election where both major party nominees served as Speaker of the House at one point. President John Tyler's pursuit of Texas annexation divided both major parties. Annexation would geographically expand American slavery. It also risked Mexican–American War, war with Mexico while the United States engaged in sensitive possession and boundary negotiations with the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, Great Britain, which controlled Canada, over Oregon Country, Oregon. Texas annexation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slavery In The United States
The legal institution of human chattel slavery, comprising the enslavement primarily of Africans and African Americans, was prevalent in the United States of America from its founding in 1776 until 1865, predominantly in the South. Slavery was established throughout European colonization in the Americas. From 1526, during early colonial days, it was practiced in what became Britain's colonies, including the Thirteen Colonies that formed the United States. Under the law, an enslaved person was treated as property that could be bought, sold, or given away. Slavery lasted in about half of U.S. states until abolition. In the decades after the end of Reconstruction, many of slavery's economic and social functions were continued through segregation, sharecropping, and convict leasing. By the time of the American Revolution (1775–1783), the status of enslaved people had been institutionalized as a racial caste associated with African ancestry. During and immediately ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
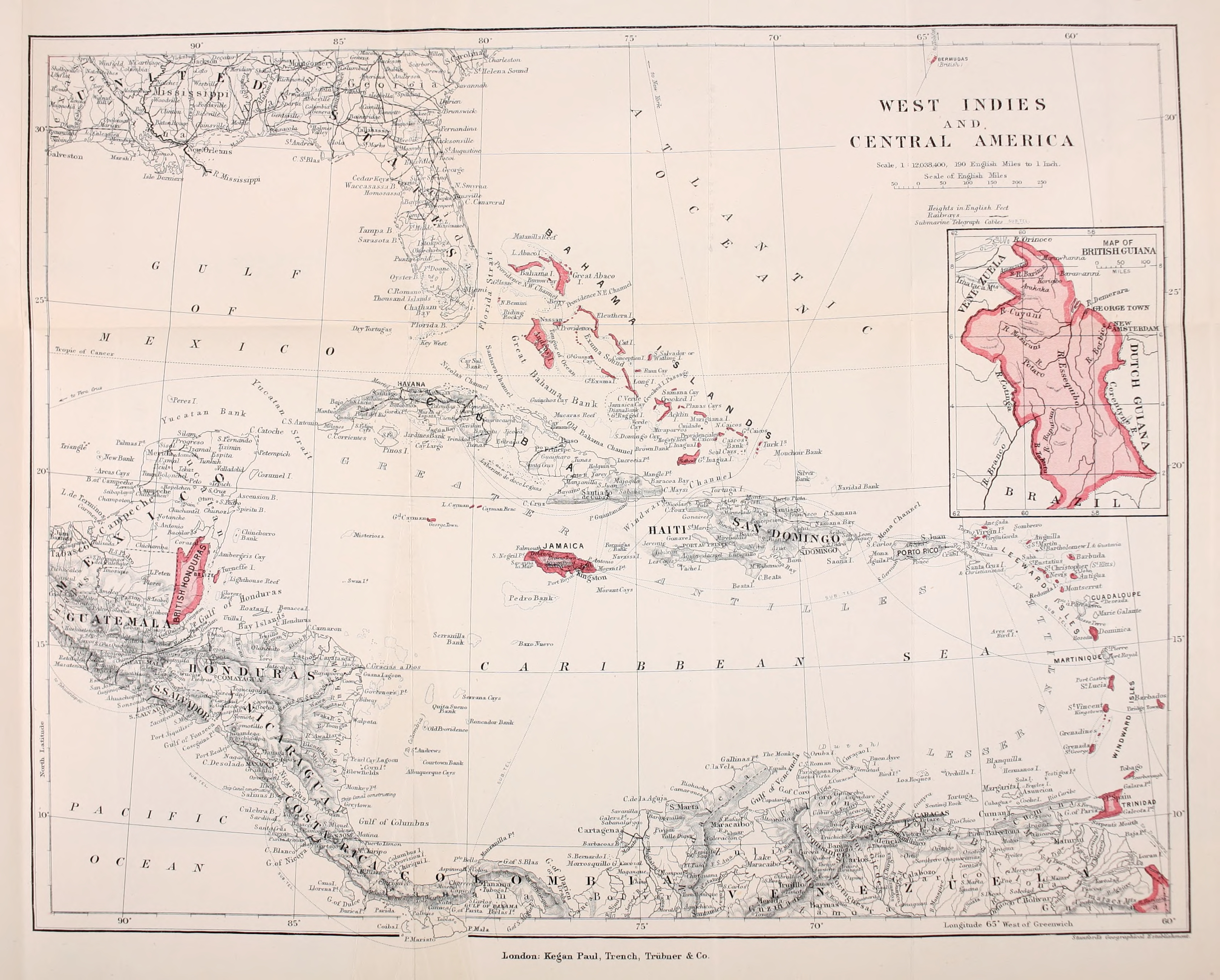
British West Indies
The British West Indies (BWI) were colonized British territories in the West Indies: Anguilla, the Cayman Islands, Turks and Caicos Islands, Montserrat, the British Virgin Islands, Antigua and Barbuda, The Bahamas, Barbados, Dominica, Grenada, Jamaica, Saint Kitts and Nevis, Saint Lucia, Saint Vincent and the Grenadines, British Guiana (now Guyana) and Trinidad and Tobago. Other territories include Bermuda, and the former British Honduras (now Belize). The colonies were also at the center of the transatlantic slave trade, around 2.3 million slaves were brought to the British Caribbean. Before the decolonisation period in the later 1950s and 1960s the term was used to include all British colonies in the region as part of the British Empire. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland. The United Kingdom includes the island of Great Britain, the north-eastern part of the island of Ireland, and many smaller islands within the British Isles. Northern Ireland shares a land border with the Republic of Ireland; otherwise, the United Kingdom is surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean, the North Sea, the English Channel, the Celtic Sea and the Irish Sea. The total area of the United Kingdom is , with an estimated 2020 population of more than 67 million people. The United Kingdom has evolved from a series of annexations, unions and separations of constituent countries over several hundred years. The Treaty of Union between the Kingdom of England (which included Wales, annexed in 1542) and the Kingdom of Scotland in 170 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)