History Of The Motorcycle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of the motorcycle begins in the second half of the 19th century.
 In the 1860s
In the 1860s
 The very first commercial design for a self-propelled bicycle was a three-wheel design called the ''Butler Petrol Cycle'', conceived of and built by Edward Butler in
The very first commercial design for a self-propelled bicycle was a three-wheel design called the ''Butler Petrol Cycle'', conceived of and built by Edward Butler in  Another early
Another early
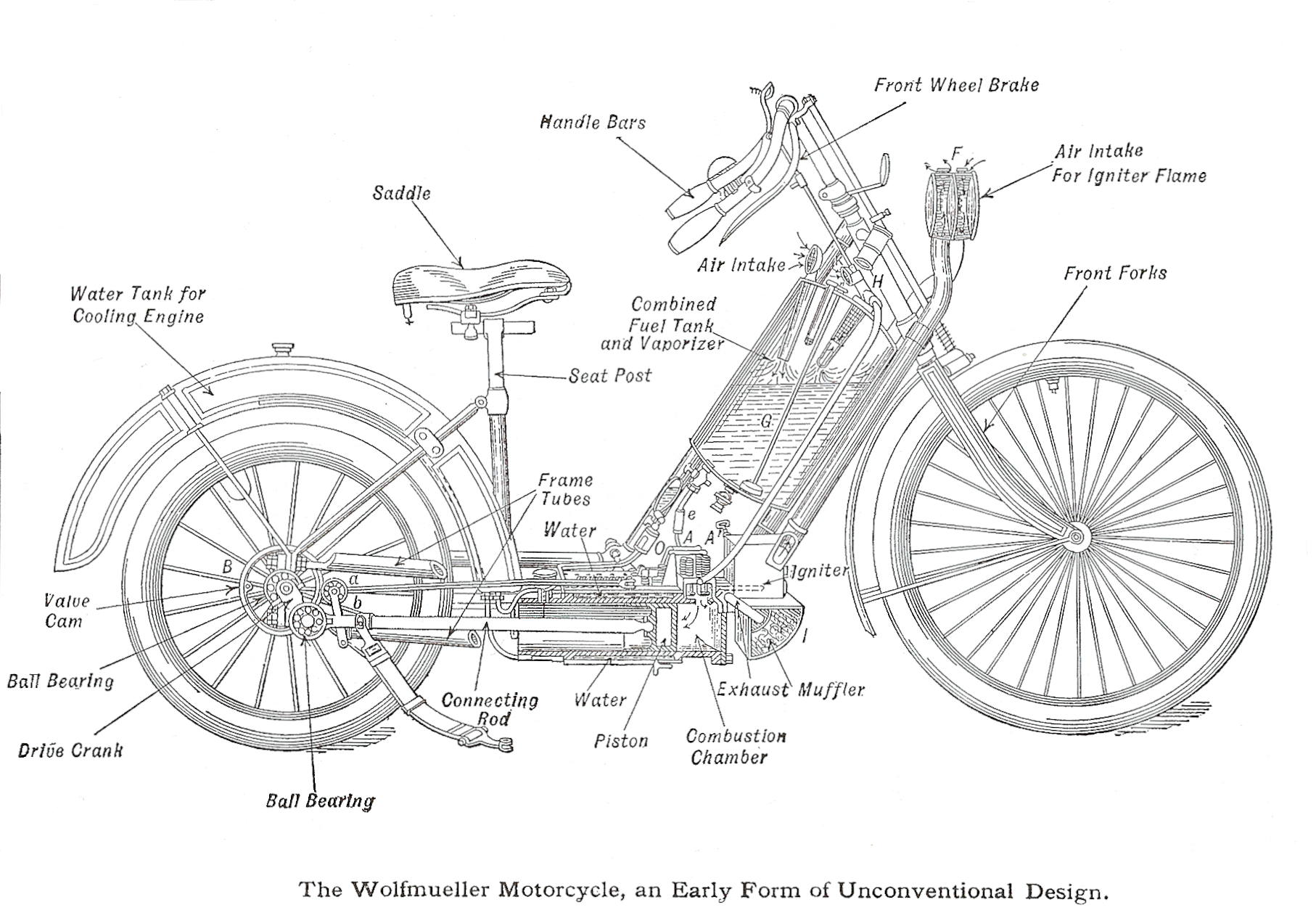 In 1894
In 1894  In 1901 English quadricycle- and bicycle-maker Royal Enfield introduced its first motorcycle, with a 239 cc engine mounted in the front and driving the rear wheel through a belt. In 1898 English bicycle-maker
In 1901 English quadricycle- and bicycle-maker Royal Enfield introduced its first motorcycle, with a 239 cc engine mounted in the front and driving the rear wheel through a belt. In 1898 English bicycle-maker
 During the
During the
 After the World War II, some American veterans found a replacement for the camaraderie, excitement, danger and speed of life at war in motorcycles. Grouped into loosely organized clubs, motorcycle riders in the US created a new social institution—the
After the World War II, some American veterans found a replacement for the camaraderie, excitement, danger and speed of life at war in motorcycles. Grouped into loosely organized clubs, motorcycle riders in the US created a new social institution—the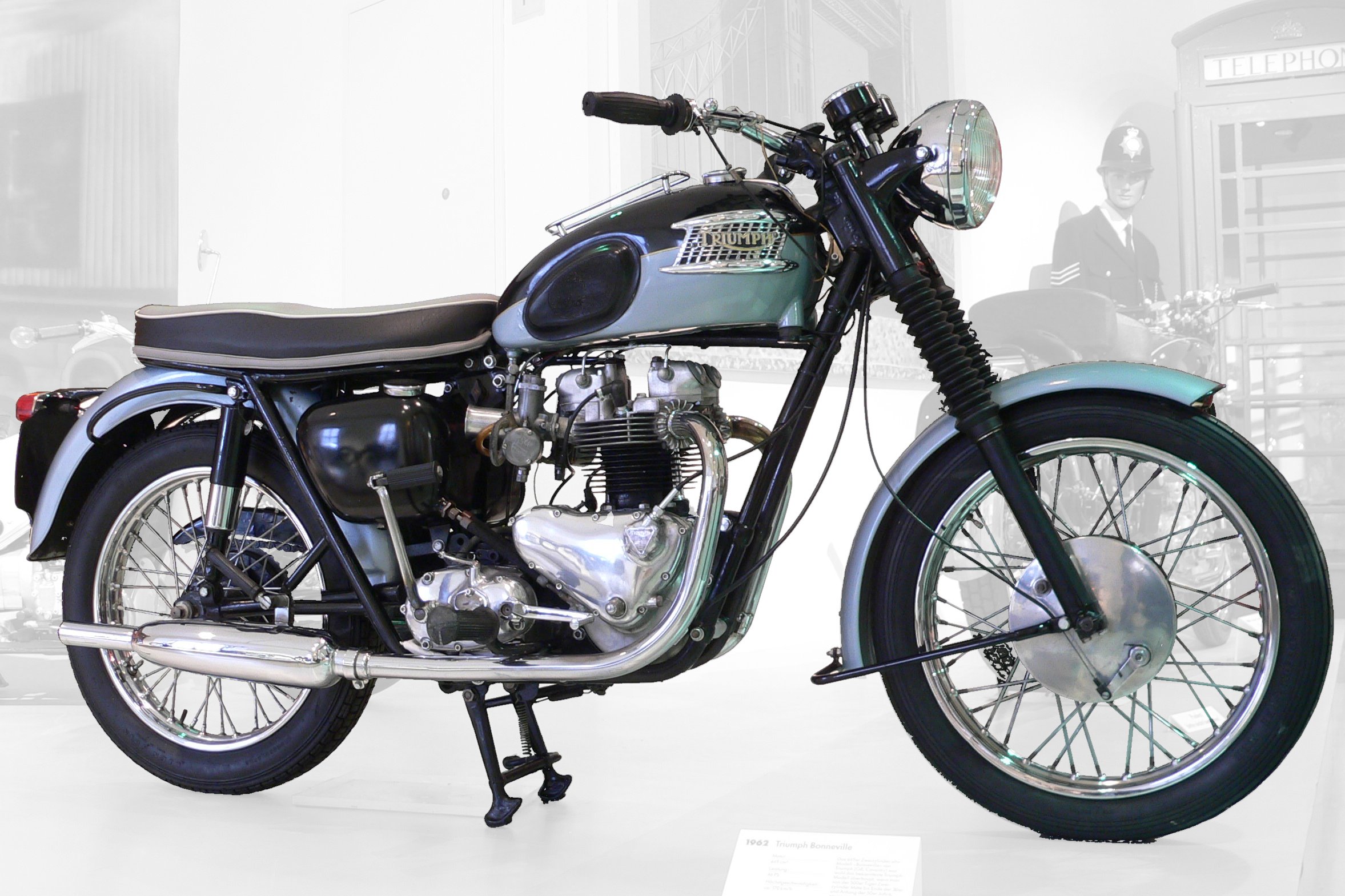  British manufacturers Triumph, BSA, and
British manufacturers Triumph, BSA, and
 The excellence of Japanese motorcycles caused similar effects in all Western markets: many Italian bike firms either went bust or only just managed to survive. As a result, BMW's worldwide sales sagged in the 1960s, but came back strongly with the introduction of a completely redesigned "slash-5" series for model year 1970.
From the 1960s through the 1990s, small two-stroke motorcycles were popular worldwide, partly as a result of the pioneering work of the
The excellence of Japanese motorcycles caused similar effects in all Western markets: many Italian bike firms either went bust or only just managed to survive. As a result, BMW's worldwide sales sagged in the 1960s, but came back strongly with the introduction of a completely redesigned "slash-5" series for model year 1970.
From the 1960s through the 1990s, small two-stroke motorcycles were popular worldwide, partly as a result of the pioneering work of the
 Today the Japanese manufacturers, Honda, Kawasaki, Suzuki, and Yamaha dominate the large motorcycle industry, although
Today the Japanese manufacturers, Honda, Kawasaki, Suzuki, and Yamaha dominate the large motorcycle industry, although
 There is a large demand for small, cheap motorcycles in the developing world, and many of the firms meeting that demand now also compete in mature markets, such as China's Hongdou which makes a version of Honda's venerable
There is a large demand for small, cheap motorcycles in the developing world, and many of the firms meeting that demand now also compete in mature markets, such as China's Hongdou which makes a version of Honda's venerable
CG 150 Titan Mix
During the first eight months after its market launch the CG 150 Titan Mix had captured a 10.6% market share, and ranking second in sales of new motorcycles in the Brazilian market in 2009. In September 2009, Honda launched a second flexible-fuel motorcycle, and by December 2010 both Honda flexible-fuel motorcycles had reached cumulative production of 515,726 units, representing an 18.1% market share of the Brazilian new motorcycle sales in that year. As of January 2011 there were four flex-fuel motorcycle models available in the market, and production reached the one million milestone in June 2011. ''Production through June 2011.''
Motorcycle
A motorcycle (motorbike, bike, or trike (if three-wheeled)) is a two or three-wheeled motor vehicle steered by a handlebar. Motorcycle design varies greatly to suit a range of different purposes: long-distance travel, commuting, cruising ...
s are descended from the "safety bicycle
A safety bicycle (or simply a safety) is a type of bicycle that became very popular beginning in the late 1880s as an alternative to the penny-farthing ("ordinary") and is now the most common type of bicycle. Early bicycles of this style were know ...
," a bicycle with front and rear wheels of the same size and a pedal crank mechanism to drive the rear wheel. Despite some early landmarks in its development, the motorcycle lacks a rigid pedigree that can be traced back to a single idea or machine. Instead, the idea seems to have occurred to numerous engineers and inventors around Europe at around the same time.
Early steam-powered cycles
 In the 1860s
In the 1860s Pierre Michaux
Pierre Michaux (June 25, 1813 – 1883) was a blacksmith who furnished parts for the carriage trade in Paris during the 1850s and 1860s. He may have become the inventor of the bicycle when he added pedals to a draisine to form the Michaud ...
, a blacksmith
A blacksmith is a metalsmith who creates objects primarily from wrought iron or steel, but sometimes from other metals, by forging the metal, using tools to hammer, bend, and cut (cf. tinsmith). Blacksmiths produce objects such as gates, gr ...
in Paris, founded 'Michaux et Cie' ("Michaux and company"), the first company to construct bicycles with pedals
A pedal (from the Latin '' pes'' ''pedis'', "foot") is a lever designed to be operated by foot and may refer to:
Computers and other equipment
* Footmouse, a foot-operated computer mouse
* In medical transcription, a pedal is used to control ...
called a velocipede
A velocipede () is a human-powered land vehicle with one or more wheels. The most common type of velocipede today is the bicycle.
The term was probably first coined by Karl von Drais in French as ''vélocipède'' for the French translation ...
at the time, or "Michauline". The first steam powered motorcycle, the Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede
The Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede was a steam powered velocipede made in France sometime from 1867 to 1871, when a small Louis-Guillaume Perreaux commercial steam engine was attached to a Pierre Michaux manufactured iron framed pedal bicycle ...
, can be traced to 1867, when Pierre's son Ernest Michaux fitted a small steam engine to one of the 'velocipedes'.
The design went to the United States when Pierre Lallement
Pierre Lallement (; October 25, 1843 – August 29, 1891) is considered by some''New York Times'' accessed July 18, 2010 to be the inventor of the pedal bicycle.
Early years
Lallement was born on October 25, 1843 in Pont-à-Mousson near Nancy, Fr ...
, a Michaux employee who also claimed to have developed the prototype in 1863, filed for the first bicycle patent with the US patent office in 1866. In 1868 an American, Sylvester H. Roper of Roxbury, Massachusetts
Roxbury () is a neighborhood within the City of Boston, Massachusetts.
Roxbury is a dissolved municipality and one of 23 official neighborhoods of Boston used by the city for neighborhood services coordination. The city states that Roxbury se ...
, developed a twin-cylinder steam velocipede, with a coal-fired boiler between the wheels. Roper's contribution to motorcycle development ended suddenly when he died demonstrating one of his machines in Cambridge, Massachusetts
Cambridge ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States. As part of the Boston metropolitan area, the cities population of the 2020 U.S. census was 118,403, making it the fourth most populous city in the state, behind Boston ...
on June 1, 1896.
Also in 1868, a French engineer Louis-Guillaume Perreaux
Louis-Guillaume Perreaux (19 February 1816 – 5 April 1889) was a French inventor and engineer who submitted one of the first patents for a working motorcycle in 1869.
Early life
Perreaux was born in the village of Almenêches, in Normandy, Fran ...
patented a similar steam powered single cylinder machine, the Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede
The Michaux-Perreaux steam velocipede was a steam powered velocipede made in France sometime from 1867 to 1871, when a small Louis-Guillaume Perreaux commercial steam engine was attached to a Pierre Michaux manufactured iron framed pedal bicycle ...
, with an alcohol burner and twin belt drives, which was possibly invented independently of Roper's. Although the patent is dated 1868, nothing indicates the invention had been operable before 1871.
In 1881, Lucius Copeland of Phoenix, Arizona
Phoenix ( ; nv, Hoozdo; es, Fénix or , yuf-x-wal, Banyà:nyuwá) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Arizona, with 1,608,139 residents as of 2020. It is the fifth-most populous city in the United States, and the on ...
designed a much smaller steam boiler which could drive the large rear wheel of an American Star high-wheeler at 12 mph. In 1887 Copeland formed the Northrop Manufacturing Co. to produce the first successful 'Moto-Cycle' (actually a three-wheeler).
Experimentation and invention
 The very first commercial design for a self-propelled bicycle was a three-wheel design called the ''Butler Petrol Cycle'', conceived of and built by Edward Butler in
The very first commercial design for a self-propelled bicycle was a three-wheel design called the ''Butler Petrol Cycle'', conceived of and built by Edward Butler in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
in 1884. He exhibited his plans for the vehicle at the Stanley Cycle Show in London in 1884, two years earlier than Karl Benz
Carl Friedrich Benz (; 25 November 1844 – 4 April 1929), sometimes also Karl Friedrich Benz, was a German engine designer and automotive engineer. His Benz Patent Motorcar from 1885 is considered the first practical modern automobile and fir ...
invented his first automobile who is generally recognized as the inventor of the modern automobile. Butler's vehicle was also the first design to be shown at the 1885 International Inventions Exhibition
The International Inventions Exhibition was a world's fair held in South Kensington in 1885. As with the earlier exhibitions in a series of fairs in South Kensington following the Great Exhibition, Queen Victoria was patron and her son Albert Edw ...
in London.
The vehicle was built by the Merryweather Fire Engine company in Greenwich
Greenwich ( , ,) is a town in south-east London, England, within the ceremonial county of Greater London. It is situated east-southeast of Charing Cross.
Greenwich is notable for its maritime history and for giving its name to the Greenwich ...
, in 1888. the Butler Petrol Cycle (first recorded use of the term) It was a three-wheeled vehicle, with the rear wheel directly driven by a 5/8hp (466W) 600 cc (40 in3; 2¼×5-inch ) flat twin four stroke
A four-stroke (also four-cycle) engine is an internal combustion (IC) engine in which the piston completes four separate strokes while turning the crankshaft. A stroke refers to the full travel of the piston along the cylinder, in either directi ...
engine (with magneto
A magneto is an electrical generator that uses permanent magnets to produce periodic pulses of alternating current. Unlike a dynamo, a magneto does not contain a commutator to produce direct current. It is categorized as a form of alternator, ...
ignition replaced by coil and battery), equipped with rotary valves
A rotary valve (also called rotary-motion valve) is a type of valve in which the rotation of a passage or passages in a transverse plug regulates the flow of liquid or gas through the attached pipes. The common stopcock is the simplest form of rot ...
and a float-fed carburettor (five years before Maybach
Maybach (, ) is a German luxury car brand that exists today as a part of Mercedes-Benz. The original company was founded in 1909 by Wilhelm Maybach and his son Karl Maybach, originally as a subsidiary of ''Luftschiffbau Zeppelin GmbH'', and ...
), and Ackermann steering, all of which were state of the art at the time. Starting was by compressed air. The engine was liquid-cooled, with a radiator over the rear driving wheel. Speed was controlled by means of a throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle'' ...
valve lever. No braking system was fitted; the vehicle was stopped by raising and lowering the rear driving wheel using a foot-operated lever; the weight of the machine was then borne by two small castor wheels. The driver was seated between the front wheels. It wasn't, however, a commercial success, as Butler failed to find sufficient financial backing.
 Another early
Another early internal combustion
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal combust ...
, petroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
fueled motorcycle was the Petroleum Reitwagen. It was designed and built by the German inventors Gottlieb Daimler
Gottlieb Wilhelm Daimler (; 17 March 1834 – 6 March 1900) was a German engineer, industrial designer and industrialist born in Schorndorf ( Kingdom of Württemberg, a federal state of the German Confederation), in what is now Germany. He w ...
and Wilhelm Maybach
Wilhelm Maybach (; 9 February 1846 – 29 December 1929) was an early German engine designer and industrialist. During the 1890s he was hailed in France, then the world centre for car production, as the "King of Designers".
From the late 19th ce ...
in Bad Cannstatt
Bad Cannstatt, also called Cannstatt (until July 23, 1933) or Kannstadt (until 1900), is one of the outer stadtbezirke, or city boroughs, of Stuttgart in Baden-Württemberg, Germany. Bad Cannstatt is the oldest and most populous of Stuttgart's bo ...
, Germany in 1885. This vehicle was unlike either the safety bicycle
A safety bicycle (or simply a safety) is a type of bicycle that became very popular beginning in the late 1880s as an alternative to the penny-farthing ("ordinary") and is now the most common type of bicycle. Early bicycles of this style were know ...
s or the boneshaker bicycles of the era in that it had zero degrees of steering axis angle and no fork offset, and thus did not use the principles of bicycle and motorcycle dynamics
Bicycle and motorcycle dynamics is the science of the motion of bicycles and motorcycles and their components, due to the forces acting on them. Dynamics falls under a branch of physics known as classical mechanics. Bike motions of interest ...
developed nearly 70 years earlier. Instead, it relied on two outrigger wheels to remain upright while turning.
The inventors called their invention the ''Reitwagen'' ("riding car"). It was designed as an expedient testbed for their new engine, rather than a true prototype vehicle.
First commercial products
In the decade from the late 1880s, dozens of designs and machines emerged, particularly in Germany and in England, and soon spread to America. During this early period of motorcycle history there were many manufacturers, since bicycle makers were adapting their designs for the newinternal combustion engine
An internal combustion engine (ICE or IC engine) is a heat engine in which the combustion of a fuel occurs with an oxidizer (usually air) in a combustion chamber that is an integral part of the working fluid flow circuit. In an internal c ...
.
 In 1894
In 1894 Hildebrand & Wolfmüller
The Hildebrand & Wolfmüller was the world's first production motorcycle. Heinrich and Wilhelm Hildebrand were steam-engine engineers before they teamed up with Alois Wolfmüller to produce their internal combustion ''Motorrad'' in Munich in 1894 ...
became the first series production motorcycle, and the first to be called a "motorcycle" (german: Motorrad). However, only a few hundred examples of this motorcycle were ever built. The first instance of the term "motor cycle" also appears in English the same year in materials promoting machines developed by E.J. Pennington, although Pennington's motorcycles never progressed past the prototype stage.
Excelsior Motor Company
Excelsior, based in Coventry, was a British bicycle, motorcycle and car maker. They were Britain’s first motorcycle manufacturer, starting production of their own ‘motor-bicycle’ in 1896. Initially they had premises at Lower Ford Street ...
, originally a bicycle-manufacturing company based in Coventry
Coventry ( or ) is a city in the West Midlands, England. It is on the River Sherbourne. Coventry has been a large settlement for centuries, although it was not founded and given its city status until the Middle Ages. The city is governed b ...
in Warwickshire (England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
), began production of their first motorcycle model in 1896, available for purchase by the public. The first production motorcycle in the US was the Orient-Aster, built by Charles Metz
Charles Gérard Emmanuel Metz (6 January 1799 – 24 April 1853) was a Luxembourgian politician, journalist, and lawyer. He was a prominent pro-Belgian in the Belgian Revolution, serving in the Belgian national legislature, before entering the ...
in 1898 at his factory in Waltham, Massachusetts
Waltham ( ) is a city in Middlesex County, Massachusetts, United States, and was an early center for the labor movement as well as a major contributor to the American Industrial Revolution. The original home of the Boston Manufacturing Company, ...
.
In 1898, Peugeot Motocycles
Peugeot is a French manufacturer of scooters and small motorcycles.
History
Peugeot built their first motorcycle in 1898 with a De Dion-Bouton engine mounted on the rear wheel. This model was shown at the 1898 Paris Exhibition but was not put ...
presents at the Paris Motorshow the first motorcycle equipped with a Dion-Bouton motor. Peugeot Motocycles remains the oldest motorcycle manufacturer in the world.
In the early period of motorcycle history, many producers of bicycles adapted their designs to accommodate the new internal-combustion engine. As the engines became more powerful and designs outgrew the bicycle origins, the number of motorcycle producers increased. Many of the nineteenth-century inventors who worked on early motorcycles often moved on to other inventions. Daimler and Roper, for example, both went on to develop automobiles.
At the turn of the 20th century the first major mass-production firms emerged.  In 1901 English quadricycle- and bicycle-maker Royal Enfield introduced its first motorcycle, with a 239 cc engine mounted in the front and driving the rear wheel through a belt. In 1898 English bicycle-maker
In 1901 English quadricycle- and bicycle-maker Royal Enfield introduced its first motorcycle, with a 239 cc engine mounted in the front and driving the rear wheel through a belt. In 1898 English bicycle-maker Triumph
The Roman triumph (Latin triumphus) was a celebration for a victorious military commander in ancient Rome. For later imitations, in life or in art, see Trionfo. Numerous later uses of the term, up to the present, are derived directly or indirectl ...
decided to extend its focus to include motorcycles, and by 1902 the company had produced its first motorcycle—a bicycle fitted with a Belgian-built engine. A year later it was the largest motorcycle-manufacturer, with an annual production of over 500 units. Other British firms included Norton Norton may refer to:
Places
Norton, meaning 'north settlement' in Old English, is a common place name. Places named Norton include: Canada
* Rural Municipality of Norton No. 69, Saskatchewan
*Norton Parish, New Brunswick
**Norton, New Brunswick, a ...
and Birmingham Small Arms Company who began motorbike production in 1902 and 1910, respectively.
In 1901 the Indian Manufacturing Company, which had been founded by two former bicycle-racers, designed the so-called "diamond framed" Indian Single, whose engine was built by the Aurora Firm in Illinois
Illinois ( ) is a state in the Midwestern United States. Its largest metropolitan areas include the Chicago metropolitan area, and the Metro East section, of Greater St. Louis. Other smaller metropolitan areas include, Peoria and Rockf ...
per Indian's specifications. The Single was made available in the deep blue. Indian's production was up to over 500 bikes by 1902, and would rise to 32,000, its best ever, in 1913.
Indian produced over 20,000 bikes per year.
The oldest surviving Russian-manufactured motorcycle, the Rossiya, dates from 1902.
The American company Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
started producing motorcycles in 1903.
During this period, experimentation and innovation were driven by the popular new sport of motorcycle racing, with its powerful incentive to produce tough, fast, reliable machines. These enhancements quickly found their way to the public's machines.
Chief August Vollmer
August "Gus" Vollmer (March 7, 1876 – November 4, 1955) was the first police chief of Berkeley, California, and a leading figure in the development of the field of criminal justice in the United States in the early 20th century. He has been de ...
of the Berkeley, California
Berkeley ( ) is a city on the eastern shore of San Francisco Bay in northern Alameda County, California, United States. It is named after the 18th-century Irish bishop and philosopher George Berkeley. It borders the cities of Oakland and E ...
Police Department is credited with organizing the first official police motorcycle
A police motorcycle is a motorcycle used by police and law enforcement. They may be custom designed to meet the requirements unique of a particular use. A police motorcycle is often called a "motor" by police officers in the United States. Units t ...
-patrol in the United States in 1911.
By 1914, motorcycles were no longer just bicycles with engines; they had their own technologies, although many still maintained bicycle elements, like the seats and suspension.
The First World War
 During the
During the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, motorbike production was greatly ramped up for the war effort to supply effective communications with front line troops. Messengers on horses were replaced with dispatch riders on motorcycles carrying messages, performing reconnaissance personnel and acting as a military police. American company Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
was devoting over 50% of its factory output toward military contract by the end of the war. The British company Triumph Motorcycles sold more than 30,000 of its Triumph Type H
The Triumph Model H (also known as the 'Type H' and 'the Trusty') is a British motorcycle made by Triumph Engineering Co Ltd in Coventry, England.
A total of 57,000 Triumph Model H motorcycles were made from 1915 until production ended in 1923.
...
model to allied forces during the war. With the rear wheel driven by a belt, the Model H was fitted with a 499 cc air-cooled four-stroke single-cylinder engine. It was also the first Triumph not to be fitted with pedals, so was a true motorcycle.
The Model H in particular, is regarded by many as having been the first "modern motorcycle". Introduced in 1915 it had a 550cc side-valve four-stroke engine with a three-speed gearbox and belt transmission. It was so popular with its users that it was nicknamed the "Trusty Triumph."
Postwar
Postwar
By 1920,Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
became the largest manufacturer, with their motorcycles being sold by dealers in 67 countries.
Amongst many British motorcycle manufacturers Chater-Lea with its twin-cylinder models followed by its large singles in the 1920s stood out. Initially, using converted a Woodmann-designed OHV Blackburne engine it became the first 350 cc to exceed 100 mph (160 km/h), recording 100.81 mph (162.24 km/h) over the flying kilometre during April 1924. Later, Chater-Lea set a world record for the flying kilometre for 350 cc and 500 cc motorcycles at 102.9 mph (165.6 km/h) for the firm. Chater-Lea produced variants of these world beating sports models and became popular among racers at the Isle of Man TT. Today, the firm is probably best remembered for its long-term contract to manufacture and supply AA Patrol motorcycles and sidecars.
By the late 1920s or early 1930s, DKW in Germany took over as the largest manufacturer.
BMW motorcycles
BMW Motorrad is the motorcycle brand of BMW, part of its Corporate and Brand Development division. It has produced motorcycles since 1923, and achieved record sales for the fifth year in succession in 2015. With a total of 136,963 vehicles sold ...
came on the scene in 1923 with a shaft drive and an opposed-twin or "boxer" engine enclosed with the transmission in a single aluminum housing.
By 1931, Indian and Harley-Davidson were the only two American manufacturers producing commercial motorcycles.
This two-company rivalry in the United States remained until 1953, when the Indian Motorcycle factory in Springfield, Massachusetts closed and Royal Enfield took over the Indian name.
There were over 80 different makes of motorcycle available in Britain in the 1930s, from the familiar marques like Norton Norton may refer to:
Places
Norton, meaning 'north settlement' in Old English, is a common place name. Places named Norton include: Canada
* Rural Municipality of Norton No. 69, Saskatchewan
*Norton Parish, New Brunswick
**Norton, New Brunswick, a ...
, Triumph and AJS to the obscure, with names like New Gerrard, NUT, SOS, Chell and Whitwood,
about twice as many motorcycle makes competing in the world market during the early 21st century.
In 1937, Joe Petrali set a new land speed record
The land speed record (or absolute land speed record) is the highest speed achieved by a person using a vehicle on land. There is no single body for validation and regulation; in practice the Category C ("Special Vehicles") flying start regula ...
of 136.183 mph (219.165 km/h) on a modified Harley-Davidson 61 cubic inch (1,000 cc) overhead valve-driven motorcycle.
The same day, Petrali also broke the speed record for 45 cubic inch (737 cc) engine motorcycles.
In Europe, production demands, driven by the buildup to World War II, included motorcycles for military use, and BSA supplied 126,000 BSA M20
The BSA M20 was a British motorcycle made by Birmingham Small Arms Company (BSA) at their factory in Small Heath, Birmingham. Although initially viewed as a near failure by the War Office in 1936, the M20 evolved into one of the longest servin ...
motorcycles to the British armed forces, starting in 1937 and continuing until 1950. Royal Enfield also produced motorcycles for the military, including a 125 cc lightweight motorcycle that could be dropped (in a parachute-fitted tube cage) from an aircraft.
After World War II
motorcyclist
Motorcycling is the act of riding a motorcycle. For some people, motorcycling may be the only affordable form of individual motorized transportation, and small- displacement motorcycles are the most common motor vehicle in the most populous c ...
s or "bikers"—which was later skewed by the "outlaw" persona Marlon Brando portrayed in the 1953 film ''The Wild One
''The Wild One'' is a 1953 American crime film directed by László Benedek and produced by Stanley Kramer. The picture is most noted for the character of Johnny Strabler, portrayed by Marlon Brando, whose persona became a cultural icon of the 1 ...
''.
In Europe, on the other hand, post-war motorcycle producers were more concerned with designing practical, economical transportation than the social aspects, or "biker" image.
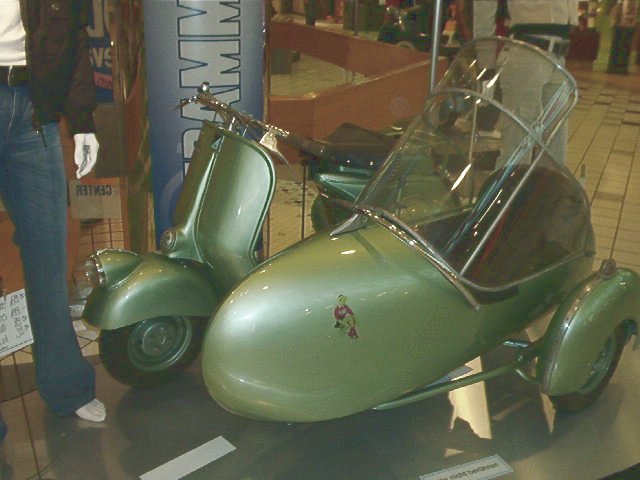
Italian designer Piaggio
Piaggio & C. SpA (Piaggio ) is an Italian motor vehicle manufacturer, which produces a range of two-wheeled motor vehicles and compact commercial vehicles under seven brands: Piaggio, Vespa, Gilera, Aprilia, Moto Guzzi, Derbi, and Scarabeo ...
introduced the Vespa
Vespa () is an Italian luxury brand of scooters and mopeds manufactured by Piaggio. The name means wasp in Italian. The Vespa has evolved from a single model motor scooter manufactured in 1946 by Piaggio & Co. S.p.A. of Pontedera, Italy to ...
in 1946, which experienced immediate and widespread popularity. Imports from the UK, Italy and Germany, thus found a niche in US markets that American bikes did not fill.
The BSA Group purchased Triumph Motorcycles in 1951 to become the largest producer of motorcycles in the world claiming "one in four". The German NSU was the largest manufacturer from 1955 until 1959 when Honda
is a Japanese public multinational conglomerate manufacturer of automobiles, motorcycles, and power equipment, headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan.
Honda has been the world's largest motorcycle manufacturer since 1959, reaching a producti ...
became the largest manufacturer.
Norton Norton may refer to:
Places
Norton, meaning 'north settlement' in Old English, is a common place name. Places named Norton include: Canada
* Rural Municipality of Norton No. 69, Saskatchewan
*Norton Parish, New Brunswick
**Norton, New Brunswick, a ...
retained a dominant position in some markets until the rise of the Japanese manufacturers, led by Honda, in the late 1960s and early 1970s. The role of the motorcycle shifted in the 1960s, from the tool of a life to a toy of a lifestyle. It became part of an image, of status, a cultural icon for individualism, a prop in Hollywood B-movies.
The motorcycle also became a recreational machine for sport and leisure, a vehicle for carefree youth, not essential transportation for the mature family man or woman, and the Japanese were able to produce modern designs more quickly, more cheaply, and of better quality than their competitors. Their motorbikes were more stylish and more reliable, so the British manufacturers fell behind as mass-market producers.
Honda, which was officially founded in Japan on September 24, 1948, introduced their SOHC inline-four engine
A straight-four engine (also called an inline-four) is a four-cylinder piston engine where cylinders are arranged in a line along a common crankshaft.
The vast majority of automotive four-cylinder engines use a straight-four layout (with the ...
CB750
The Honda CB750 is an air-cooled, transverse, in-line-four-cylinder-engine motorcycle made by Honda over several generations for year models 1969–2003, plus 2007, with an upright, or standard, riding posture. It is often called the original ...
in 1969, which was inexpensive and immediately successful. It established the across-the-frame-four engine configuration as a design with huge potential for power and performance. Shortly after the introduction of the SOHC, Kawasaki demonstrated the potential of the four-stroke four-cylinder engine with the introduction of the KZ900.
Suzuki, Kawasaki and the Yamaha Yamaha may refer to:
* Yamaha Corporation, a Japanese company with a wide range of products and services, established in 1887. The company is the largest shareholder of Yamaha Motor Company (below).
** Yamaha Music Foundation, an organization estab ...
each started producing motorcycles in the 1950s. Meanwhile, the sun was setting on British dominion over the big-displacement motorbike market.
Japanese dominance
East German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
Daniel Zimmermann (rotary disc valve) and MZ's Walter Kaaden who developed the two-stroke expansion chamber in the 1950s. These ideas were taken up by Suzuki when Ernst Degner
Ernst Degner (born Ernst Eugen Wotzlawek on 22 September 1931 in Gleiwitz, Upper Silesia, Germany - died 10 September 1983 in Arona, Tenerife, Spain) was a professional Grand Prix motorcycle road racer from Eastern Germany. Degner was noted f ...
, the MZ engineer and rider, defected to the West on 13 September 1961 after retiring from the 125cc Swedish Grand Prix at Kristianstad. Degner, an excellent engineer, immediately joined Suzuki and his knowledge became their technology springboard.
Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
in the US at the time suffered from the same problems as the European firms, but its unique product range, American tariff laws and nationalism-driven customer loyalty allowed it to survive. One alleged flaw, however, was retaining the characteristic Harley-Davidson 45° engine vee-angle, which causes excess vibration as well as the loping Harley-Davidson sound.
A factory full fairing was introduced by BMW motorcycle in the R100RS of 1977, the first factory fairing produced in quantity. In 1980, BMW stimulated the "adventure touring" category of motorcycling with its dual-sport
A dual-sport motorcycle is a type of street-legal motorcycle that is designed for both on and off-road use. The terms ''all-road,'' ''on/off road,'' and ''dual-purpose'' are also used for this class of motorcycles. Dual-sports are equipped with ...
model, the R80G/S. In 1988, BMW was the first motorcycle manufacturer to introduce anti-lock-brakes (ABS) on its sporting K100RS-SE and K1 models.
The present
 Today the Japanese manufacturers, Honda, Kawasaki, Suzuki, and Yamaha dominate the large motorcycle industry, although
Today the Japanese manufacturers, Honda, Kawasaki, Suzuki, and Yamaha dominate the large motorcycle industry, although Harley-Davidson
Harley-Davidson, Inc. (H-D, or simply Harley) is an American motorcycle manufacturer headquartered in Milwaukee, Wisconsin, United States. Founded in 1903, it is one of two major American motorcycle manufacturers to survive the Great Depressi ...
still maintains a high degree of popularity, particularly in the United States.
Recent years have seen a resurgence in the popularity around the world of many other motorcycle brands, including BMW, Triumph and Ducati, and the emergence of Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
as a second successful mass-builder of big-twin American cruisers.
In November 2006, the Dutch company E.V.A. Products BV Holland announced that the first commercially available diesel-powered motorcycle, its Track T-800CDI, achieved production status.
The Track T-800CDI uses an 800 cc three-cylinder Daimler Chrysler diesel engine. However, other manufacturers, including Royal Enfield, had been producing diesel-powered bikes since at least 1965.
In the developing world
 There is a large demand for small, cheap motorcycles in the developing world, and many of the firms meeting that demand now also compete in mature markets, such as China's Hongdou which makes a version of Honda's venerable
There is a large demand for small, cheap motorcycles in the developing world, and many of the firms meeting that demand now also compete in mature markets, such as China's Hongdou which makes a version of Honda's venerable CG125
The Honda CG125 or Honda CG is a commuter motorcycle made by Honda of Japan. It was in production from 1976 to 2008 in Japan and has been in production since 1992 in Pakistan. The CG was originally manufactured in Japan, but the source for the E ...
.
Motorcycle taxis are commonplace in the developing world. Scooters, mopeds and motorcycles offer a fast, cheap and risky way around snarled traffic and scarce mass transit, as they can easily squeeze through jams.
The first ethanol
Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound. It is an alcohol with the chemical formula . Its formula can be also written as or (an ethyl group linked to a ...
flex fuel motorcycle in the world was launched to the Brazilian market by Honda in March 2009, thCG 150 Titan Mix
During the first eight months after its market launch the CG 150 Titan Mix had captured a 10.6% market share, and ranking second in sales of new motorcycles in the Brazilian market in 2009. In September 2009, Honda launched a second flexible-fuel motorcycle, and by December 2010 both Honda flexible-fuel motorcycles had reached cumulative production of 515,726 units, representing an 18.1% market share of the Brazilian new motorcycle sales in that year. As of January 2011 there were four flex-fuel motorcycle models available in the market, and production reached the one million milestone in June 2011. ''Production through June 2011.''
See also
*List of motorcycle manufacturers
The following is a list of motorcycle manufacturers worldwide, sorted by extant/extinct status and by country. These are producers whose motorcycles are available to the public, including both street legal as well as racetrack-only or off-road-o ...
*Motorcycle land-speed record
The motorcycle land-speed record is the fastest speed achieved by a motorcycle on land. It is standardized as the speed over a course of fixed length, averaged over two runs in opposite directions. AMA National Land Speed Records requires 2 passes ...
* List of fastest production motorcycles
*Electric motorcycles and scooters
Electric motorcycles and scooters are plug-in electric vehicles with two or three wheels. Power is supplied by a rechargeable battery which drives one or more electric motors. Electric scooters are distinguished from motorcycles by having a st ...
*Outline of motorcycles and motorcycling
The following outline is provided as an overview of motorcycles and motorcycling:
Motorcycle — two-wheeled, single-track motor vehicle. Other names include: motorbike, bike, and cycle.
Motorcycling — act of riding a motorcycle, around wh ...
Further reading
Early history and use in the United Kingdom
* * * *Early history and use in the United States
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Motorcycle HistoryHistory
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
History
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
History of technology