|
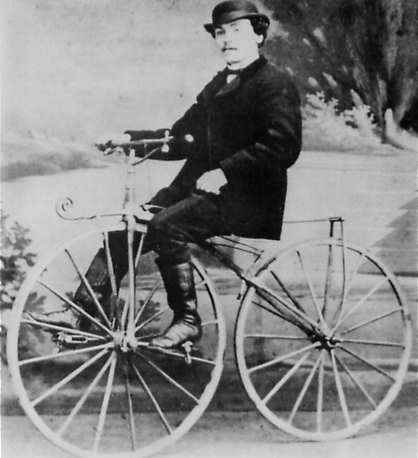
Boneshaker (bicycle)
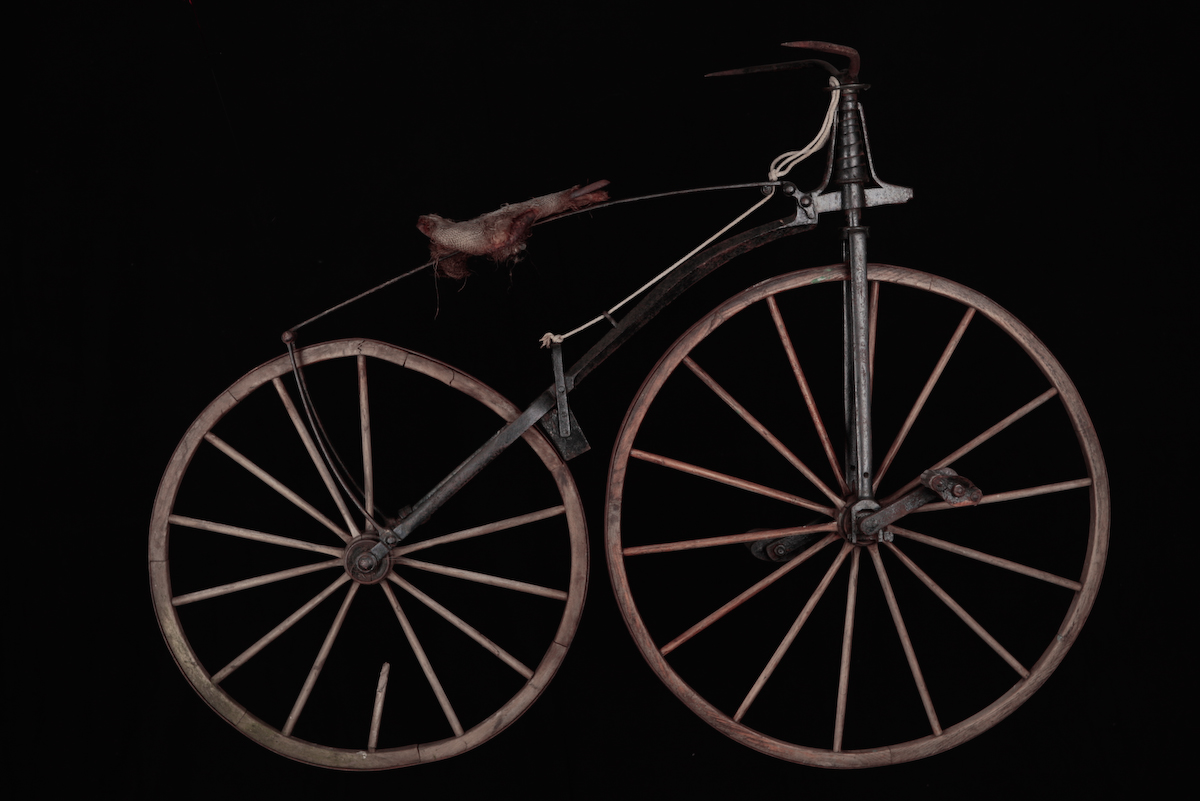
A velocipede () is a human-powered land vehicle with one or more wheels. The most common type of velocipede today is the bicycle. The term was probably first coined by Karl von Drais in French as ''vélocipède'' for the French translation of his advertising leaflet for his version of the '' Laufmaschine'', also now called a ' dandy horse', which he had developed in 1817. It is ultimately derived from the Latin ''velox'', ''veloc-'' 'swift' + ''pes'', ''ped-'' 'foot'.''Oxford Dictionary of English'', 'velocipede' The term 'velocipede' is today mainly used as a collective term for the different forerunners of the monowheel, the unicycle, the bicycle, the dicycle, the tricycle and the quadracycle developed between 1817 and 1880. It refers especially to the forerunner of the modern bicycle that was propelled, like a modern tricycle, by cranks, i.e. pedals, attached to the front axle before the invention of geared chains and belt and shaft drives powering the rear. History Am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Velocipedes
A velocipede () is a human-powered transport#Human-powered land vehicles, human-powered land vehicle with one or more wheels. The most common type of velocipede today is the bicycle. The term was probably first coined by Karl von Drais in French as ''vélocipède'' for the French translation of his advertising leaflet for his version of the ''Laufmaschine'', also now called a 'dandy horse', which he had developed in 1817. It is ultimately derived from the Latin ''velox'', ''veloc-'' 'swift' + ''pes'', ''ped-'' 'foot'.''Oxford Dictionary of English'', 'velocipede' The term 'velocipede' is today mainly used as a collective term for the different forerunners of the monowheel, the unicycle, the bicycle, the dicycle, the tricycle and the quadracycle developed between 1817 and 1880. It refers especially to the forerunner of the modern bicycle that was propelled, like a modern tricycle, by cranks, i.e. bicycle pedal, pedals, attached to the front axle before the invention of geared bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
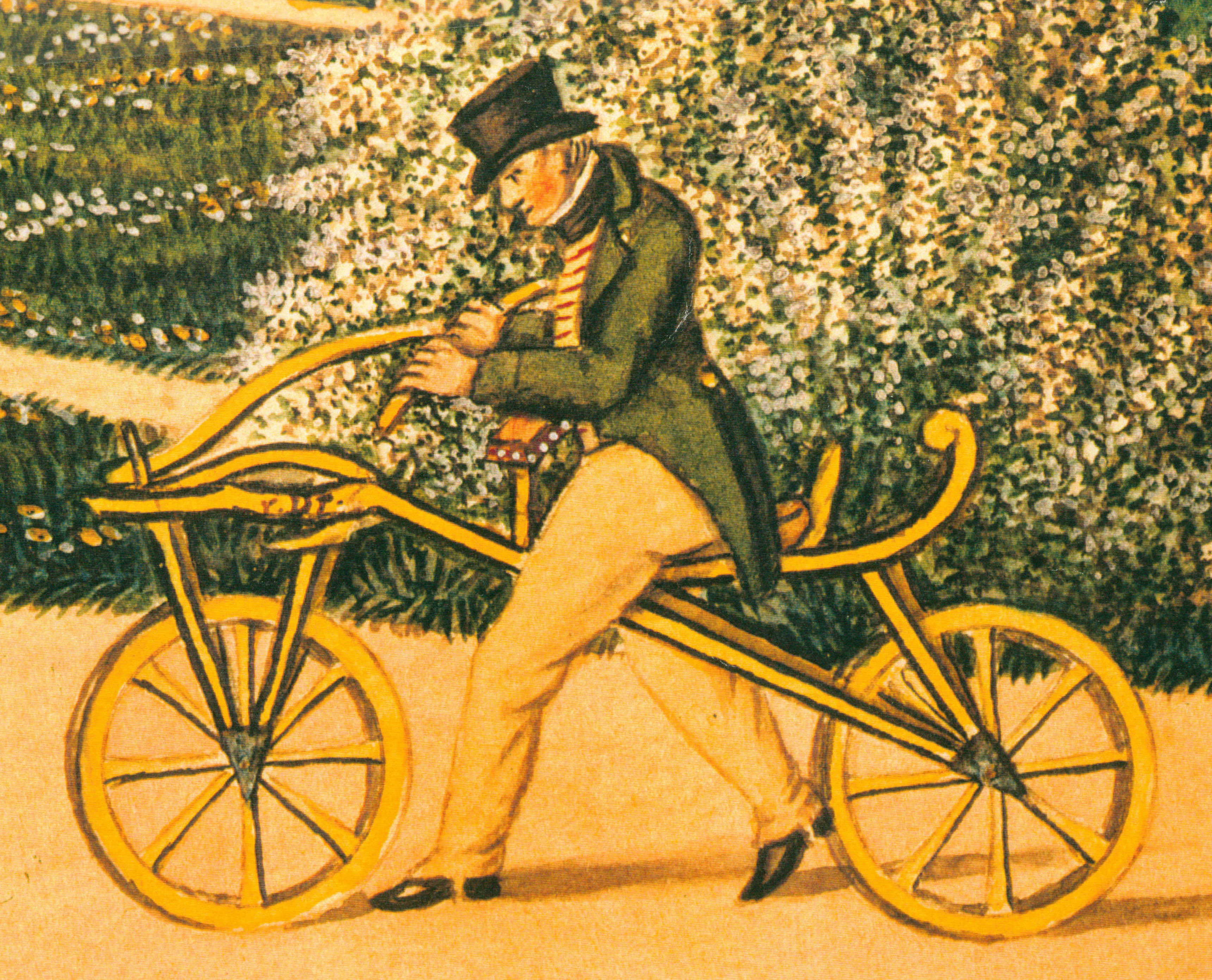
Karl Drais
Karl Freiherr von Drais (full name: Karl Friedrich Christian Ludwig Freiherr Drais von Sauerbronn) (29 April 1785 – 10 December 1851) was a noble German forest official and significant inventor in the Biedermeier period. He was born and died in Karlsruhe. He is seen as "the father of the bicycle". Bicycle Drais was a prolific inventor, who invented the Laufmaschine ("running machine"), also later called the velocipede, ''draisine'' (English) or ''Parisienne'' (French), also nicknamed the hobby horse or dandy horse. This was his most popular and widely recognized invention. It incorporated the two-wheeler principle that is basic to the bicycle and motorcycle and was the beginning of mechanized personal transport. This was the earliest form of a bicycle, without pedals. His first reported ride from Mannheim to the "Schwetzinger Relaishaus" (a coaching inn, located in "Rheinau", today a district of Mannheim) took place on 12 June 1817 using Baden's best road. Karl rode his bik ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exposition Universelle (1878)
The third Paris World's Fair, called an Exposition Universelle in French, was held from 1 May to 10 November 1878. It celebrated the recovery of France after the 1870–71 Franco-Prussian War. Construction The buildings and the fairgrounds were somewhat unfinished on opening day, as political complications had prevented the French government from paying much attention to the exhibition until six months before it was due to open. However, efforts made in April were prodigious, and by 1 June, a month after the formal opening, the exhibition was finally completed. This exposition was on a far larger scale than any previously held anywhere in the world. It covered over , the main building in the Champ de Mars and the hill of Chaillot, occupying . The Gare du Champ de Mars was rebuilt with four tracks to receive rail traffic occasioned by the exposition. The Pont d'Iéna linked the two exhibition sites along the central allée. The French exhibits filled one-half of the enti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Société Parisienne
Société Parisienne (''Maison Parisienne'') was a French manufacturer of velocipedes, bicycles and tricycles from 1876. They began limited automobile construction in 1894 and regular light car (voiturette) construction in 1898 or 1899, and they ceased operation in 1903. The vehicles, variously known as Parisienne, Victoria Combination, Eureka, l'Eclair, Duc-Spider and Duc-Tonneau, were manufactured by Société Parisienne E. Couturier et Cie of Paris. The first attempt at vehicle manufacture in 1894 was planned to be powered by an 'air compressor' but it did not work. The first successful motor vehicles were Benzes built under license by M. Laboure of La Maison Parisienne. In 1898 the company engineer, a M. Serex, designed a flat-twin car which ran in the Marseille-Nice Race of that year; this, too, was built along the lines of a Benz. The 'Victoria Combination' voiturette achieved front-wheel drive by mounting the engine directly on the front axle and then turning the whole a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
L'Industrie Vélocipédique
''L'Industrie Vélocipédique'' (''Bicycle Industry'') was a French periodical that was published bi-monthly from 1882. It covered cycling (velocipeding) and described itself as ''The organ of manufacturers, mechanics, depositors, agents, renters, amateurs, etc.'' It was published from offices at 33 rue Jean Jacques Rousseau, Paris. By 1910 it had changed its name to ''L' Industrie Vélocipédique et Automobile''. The last recorded publication was 27 December 1913 by which time the title had evolved to ''L' Industrie Vélocipédique et Automobile, Revue technique Hebdomadaire'' (Fortnightly) The Independent organ of the Cycle, Automobile and Aeronautical industries. Cycling Publication market By 1903 the French market for cycling publications was large, energetic and crowded. Thus ''L'Industrie Vélocipédique'' had to compete with ''La Revue des Sport''; ''La Revue du Sport Vélocipédique''; ''Le Veloce-Sport''; ''Le Cycle''; ''Le Monde Cycliste''; ''La France Cycliste''; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cobblestone
Cobblestone is a natural building material based on cobble-sized stones, and is used for pavement roads, streets, and buildings. Setts, also called Belgian blocks, are often casually referred to as "cobbles", although a sett is distinct from a cobblestone by being quarried or shaped to a regular form, whereas cobblestone is generally of a naturally occurring form and is less uniform in size. Use in roading Cobblestones are typically either set in sand or similar material, or are bound together with mortar. Paving with cobblestones allows a road to be heavily used all year long. It prevents the build-up of ruts often found in dirt roads. It has the additional advantage of immediately draining water, and not getting muddy in wet weather or dusty in dry weather. Shod horses are also able to get better traction on stone cobbles, pitches or setts than tarmac or asphalt. The fact that carriage wheels, horse hooves and even modern automobiles make a lot of noise when rolling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mass-production
Mass production, also known as flow production or continuous production, is the production of substantial amounts of standardized products in a constant flow, including and especially on assembly lines. Together with job production and batch production, it is one of the three main production methods. The term ''mass production'' was popularized by a 1926 article in the ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' supplement that was written based on correspondence with Ford Motor Company. ''The New York Times'' used the term in the title of an article that appeared before publication of the ''Britannica'' article. The concepts of mass production are applied to various kinds of products: from fluids and particulates handled in bulk (food, fuel, chemicals and mined minerals), to parts and assemblies of parts (household appliances and automobiles). Some mass production techniques, such as standardized sizes and production lines, predate the Industrial Revolution by many centuries; however ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Olivier Brothers
The Olivier brothers, Aimé, René, and Marius, were the first people responsible for recognizing the commercial potential of a new invention : the bicycle. The Olivier family was wealthy, owning a series of chemical plant in France based in Lyon. While students in Paris in 1864, they were among the first users of the new ''velocipede''. In 1868, the Oliviers formed a partnership with Pierre Michaux to mass-produce bicycles. All through the first bicycle craze The bike boom or bicycle craze is any of several specific historic periods marked by increased bicycle enthusiasm, popularity, and sales. Prominent examples include 1819 and 1868, as well as the decades of the 1890s and 1970sthe latter espec ..., from 1867 to 1869, it was René Olivier who led both the Michaux company and the industry as a whole. Then several major problems developed. The cast-iron frames would sometimes fail catastrophically. The relationship between the brothers and Michaud also broke down. In 186 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Lallement
Pierre Lallement (; October 25, 1843 – August 29, 1891) is considered by some''New York Times'' accessed July 18, 2010 to be the inventor of the pedal bicycle. Early years Lallement was born on October 25, 1843 in Pont-à-Mousson near Nancy, France. In 1862 while Lallement was employed building baby carriages in Nancy he saw someone riding a dandy horse, a forerunner of the bicycle that required the rider to propel the vehicle by walking. Lallement modified what he had seen by adding a transmission comprising a rotary crank mechanism and pedals attached to the front-wheel hub, thus creating the first true bicycle. He moved to Paris in 1863 and apparently interacted with the Olivier brothers who saw commercial potential in his invention. The Oliviers formed a partnership with Pierre Michaux to mass-produce a 2-wheeled velocipede. Whether these bicycles used Lallement's design of 1864 or another by Ernest Michaux is a matter of dispute. Lallement himself may have been an emp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pierre Michaux
Pierre Michaux (June 25, 1813 – 1883) was a blacksmith who furnished parts for the carriage trade in Paris during the 1850s and 1860s. He may have become the inventor of the bicycle when he added pedals to a draisine to form the Michaudine velocipede, the forerunner of the modern bicycle. However, historic sources reveal other possible claimants, such as his son Ernest Michaux and Pierre Lallement. History Pierre Michaux was born at Bar le Duc and worked as a blacksmith who furnished parts for the carriage trade in Paris during the 1850s and 1860s. He started building bicycles with pedals in the early 1860s. He, or his son Ernest, may have been the inventor of this machine, by adapting cranks and pedals on the front wheel of a draisine. In 1868, he formed a partnership with the Olivier brothers under his own name, Michaux et Cie ("Michaux and company"), which was the first company to mass produce pedal-powered velocipedes, known as the Michaudine. The design was bas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
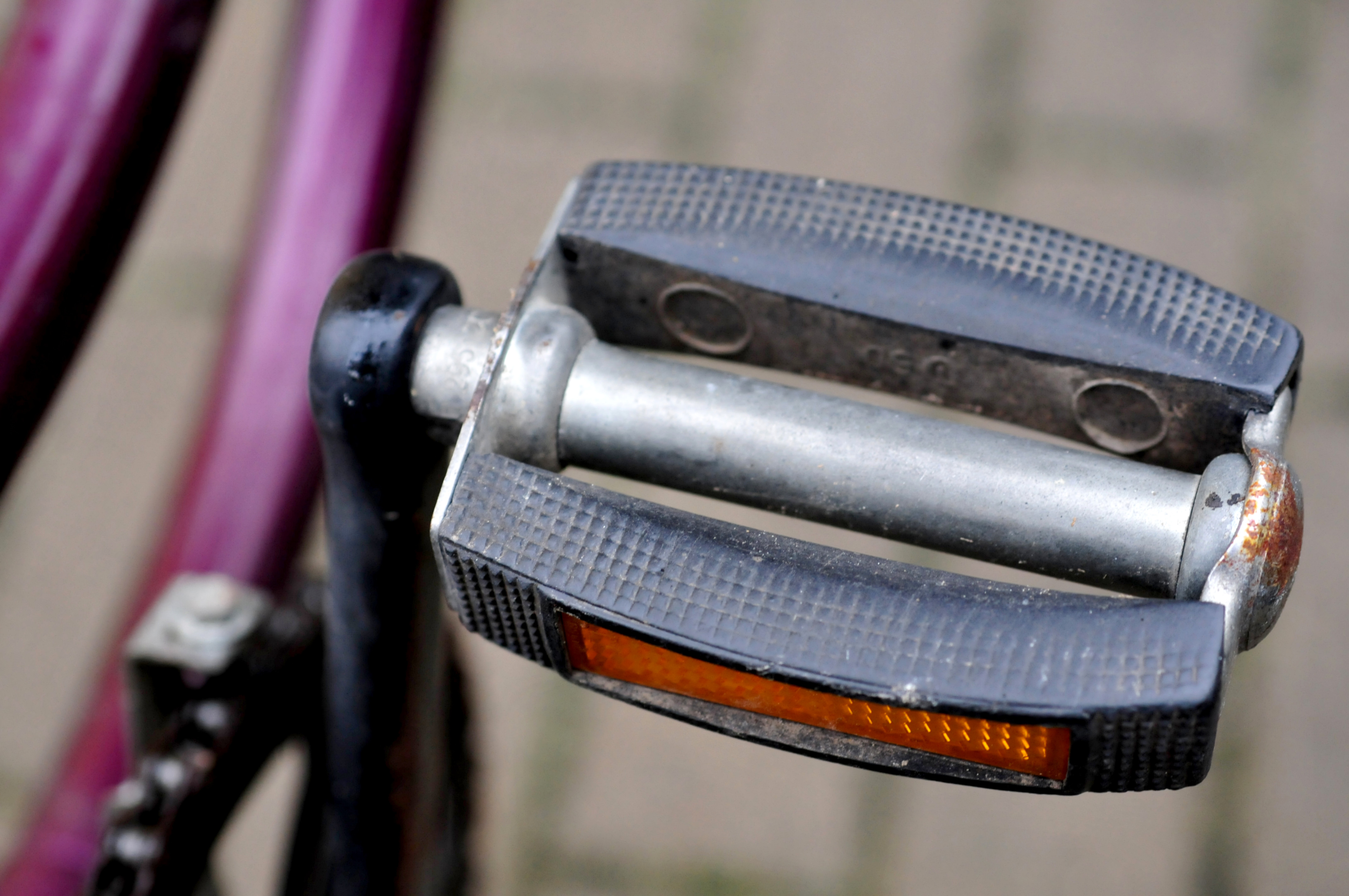
Bicycle Pedal
The pedal is the part of a bicycle that the rider pushes with their foot to propel the vehicle. It provides the connection between the cyclist's foot or shoe and the crank allowing the leg to turn the bottom bracket spindle and propel the bicycle's wheels. A pedal usually consists of a spindle that threads into the end of the crank, and a body on which the foot rest is attached, that is free to rotate on bearings with respect to the spindle. Pedals were initially attached to cranks connecting directly to the driven (usually front) wheel. The safety bicycle, as it is known today, came into being when the pedals were attached to a crank driving a sprocket that transmitted power to the driven wheel by means of a roller chain. Types Just as bicycles come in many varieties, there are different types of pedals to support different types of cycling. Flat and platform Traditionally, platform pedals were pedals with a relatively large flat area for the foot to rest on, in contrast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hobby Horse
The term "hobby horse" is used, principally by folklorists, to refer to the costumed characters that feature in some traditional seasonal customs, processions and similar observances around the world. They are particularly associated with May Day celebrations, mummers' plays and the Morris dance in England. Etymology The word ''hobby'' is glossed by the OED as "a small or middle-sized horse; an ambling or pacing horse; a pony." The word is attested in English from the 14th century, as Middle English ''hobyn''. Old French had ''hobin'' or ''haubby'', whence Modern French ''aubin'' and Italian ''ubino''. But the Old French term is apparently adopted from English rather than vice versa. OED connects it to "the by-name ''Hobin'', ''Hobby''", a variant of ''Robin''" (compare the abbreviation ''Hob'' for ''Robert''). This appears to have been a name customarily given to a cart-horse, as attested by White Kennett in his ''Parochial Antiquities '' (1695), who stated that "Our plough ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |