History Of Pomerania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The history of
Philipp Ther, Ana Siljak, ''Redrawing Nations: Ethnic Cleansing in East-Central Europe, 1944-1948'', 2001, p.114, , Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945", 2006, pp.363, , Buchholz (1999), p.515Dierk Hoffmann, Michael Schwartz, ''Geglückte Integration?'', p142
/ref>Karl Cordell, Andrzej Antoszewski, ''Poland and the European Union'', 2000, p.168, Piskorski (1999), p.406Selwyn Ilan Troen, Benjamin Pinkus, Merkaz le-moreshet Ben-Guryon, ''Organizing Rescue: National Jewish Solidarity in the Modern Period'', pp.283-284, 1992, , Most of
 After the glaciers of the Vistula Glacial Stage retreated from
After the glaciers of the Vistula Glacial Stage retreated from
 The southward movement of
The southward movement of

 *~650–~850:
*~650–~850:
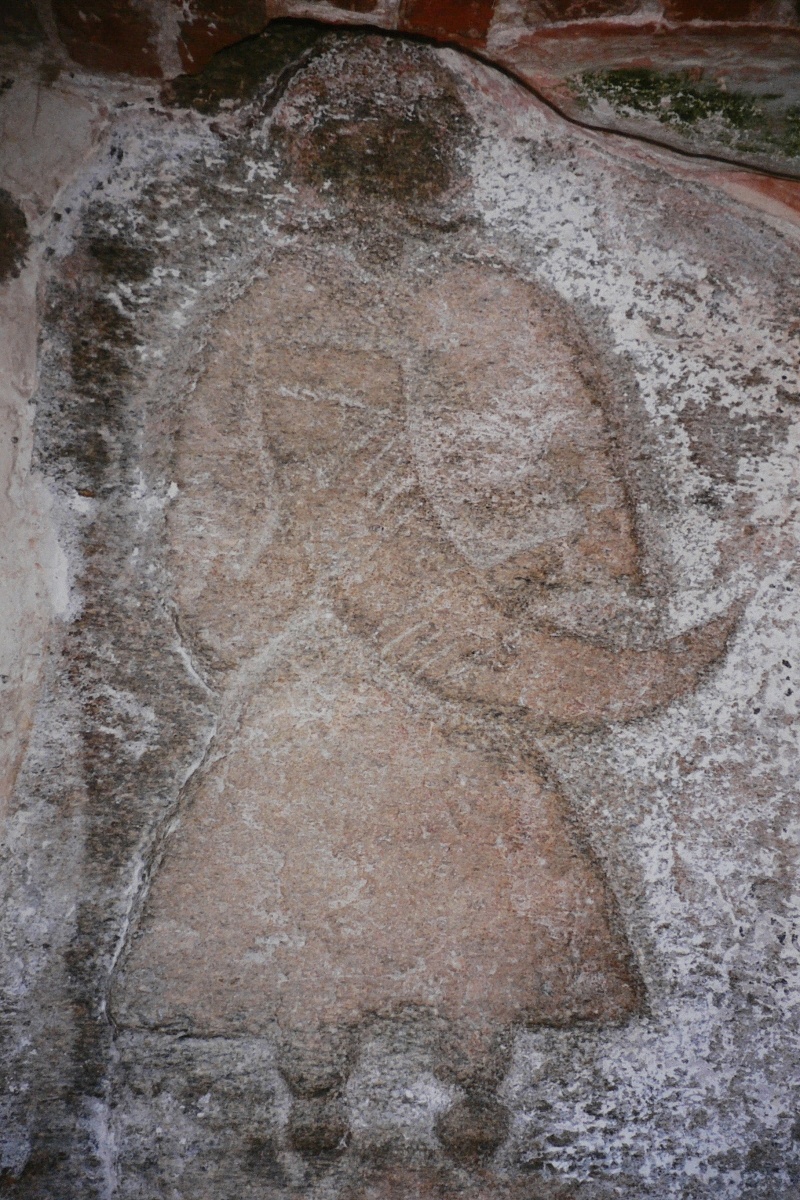
 In the early 12th century,
In the early 12th century,
 The towns of the
The towns of the
/ref>Buchholz (1999), p.189
 *1294–1308:
*1294–1308:

 Throughout this time,
Throughout this time,
 *1648: Peace of Westphalia – partition of the
*1648: Peace of Westphalia – partition of the
 From the
From the
 In 1933, the Province of Pomerania like all of Germany Enabling act of 1933, came under control of the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime. During the following years, the
In 1933, the Province of Pomerania like all of Germany Enabling act of 1933, came under control of the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime. During the following years, the
/ref> In 1939, the German Wehrmacht Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland. Inhabitants of the region from all ethnic backgrounds were subject to numerous atrocities by Nazi Germany forces, of which the most affected were Polish and Jewish civilians. Pomerelia was made part of



 In 1945, Pomerania was taken by the Red Army and Polish Armed Forces in the East during the East Pomeranian Offensive and the Battle of Berlin. After the Oder-Neisse line, post-war border changes, the Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II, German population that had not yet fled was expelled from what in Poland was propagatedTomasz Kamusella and Terry Sullivan in Karl Cordell, ''Ethnicity and Democratisation in the New Europe'', 1999, p.169: "[the term "recovered territories" was] christened so by the Polish communist-cum-nationalist propaganda", , to be Recovered Territories, recovered territory.Geoffrey Hosking, George Schopflin, ''Myths and Nationhood'', 1997, p.153, , The area east of the Oder and the Szczecin (former Stettin) area was resettled primarily with Poles, who themselves were expelled from Kresy, Eastern Poland that was re-attached to the USSR. Most of the German cultural heritage of the region was destroyed. Most of
In 1945, Pomerania was taken by the Red Army and Polish Armed Forces in the East during the East Pomeranian Offensive and the Battle of Berlin. After the Oder-Neisse line, post-war border changes, the Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II, German population that had not yet fled was expelled from what in Poland was propagatedTomasz Kamusella and Terry Sullivan in Karl Cordell, ''Ethnicity and Democratisation in the New Europe'', 1999, p.169: "[the term "recovered territories" was] christened so by the Polish communist-cum-nationalist propaganda", , to be Recovered Territories, recovered territory.Geoffrey Hosking, George Schopflin, ''Myths and Nationhood'', 1997, p.153, , The area east of the Oder and the Szczecin (former Stettin) area was resettled primarily with Poles, who themselves were expelled from Kresy, Eastern Poland that was re-attached to the USSR. Most of the German cultural heritage of the region was destroyed. Most of
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
starts shortly before 1000 AD with ongoing conquests by newly arrived Polans Polans may refer to two Slavic tribes:
* Polans (eastern)
The Polans (, ''Poliany'', ''Polyane'', pl, Polanie), also Polianians, were an East Slavic tribe between the 6th and the 9th century, which inhabited both sides of the Dnieper river ...
rulers. Before that, the area was recorded nearly 2000 years ago as Germania, and in modern-day times Pomerania is split between Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous ...
. Its name comes from the Slavic ''po more'', which means "land at the sea".
Settlement in the area started by the end of the Vistula Glacial Stage, about 13,000 years ago. Archeological traces have been found of various cultures during the Stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
and Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, of Veneti and Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
and, in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, Slavic tribes
This is a list of Slavic peoples and Slavic tribes reported in Late Antiquity and in the Middle Ages, that is, before the year AD 1500.
Ancestors
*Proto-Indo-Europeans (Proto-Indo-European speakers)
** Proto-Balto-Slavs (common ancestors of B ...
and Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and ...
. RGA 25 (2004), p.422From the First Humans to the Mesolithic Hunters in the Northern German Lowlands, Current Results and Trends - THOMAS TERBERGER. From: Across the western Baltic, edited by: Keld Møller Hansen & Kristoffer Buck Pedersen, 2006, , Sydsjællands Museums Publikationer Vol. 1 Piskorski (1999), pp.18ff 6Horst Wernicke, ''Greifswald, Geschichte der Stadt'', Helms, 2000, pp.16ff, A. W. R. Whittle, Europe in the Neolithic: The Creation of New Worlds, Cambridge University Press, 1996, p.198, Buchholz (1999), pp.22,23Herrmann (1985), pp.237ff,244ff Starting in the 10th century, Piast Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th ce ...
on several occasions acquired parts of the region from the south-east, while the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
reached the region in augmenting their territory to the west and north.Herrmann (1985), pp.261,345ffPiskorski (1999), p.32 :pagan reaction of 1005A. P. Vlasto, ''Entry of Slavs Christendom'', CUP Archive, 1970, p.129, : abandoned 1004 - 1005 in face of violent oppositionNora Berend, ''Christianization and the Rise of Christian Monarchy: Scandinavia, Central Europe and Rus' C. 900-1200'', Cambridge University Press, 2007, p.293, , David Warner, ''Ottonian Germany: The Chronicon of Thietmar of Merseburg'', Manchester University Press, 2001, p.358, , Michael Borgolte, Benjamin Scheller, ''Polen und Deutschland vor 1000 Jahren: Die Berliner Tagung über den "Akt von Gnesen"'', Akademie Verlag, 2002, p.282, ,
In the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, the area became Christian and was ruled by local dukes of the House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
and the Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
, at various times vassals of Denmark, the Holy Roman Empire and Poland.Addison (2003), pp.57ffPiskorski (1999), pp.35ffTheologische Realenzyklopädie (1997), pp.40ff From the late 12th century, the Griffin Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
stayed with the Holy Roman Empire and the Principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
with Denmark, while Denmark, Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
, Poland and the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
struggled for control in Samboride Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
. The Teutonic Knights succeeded in annexing Pomerelia to their monastic state in the early 14th century. Meanwhile, the Ostsiedlung started to turn Pomerania into a German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
-settled area; the remaining Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
, who became known as Slovincians Slovincians, also known as Łeba Kashubians, is a near-extinct ethnic subgroup of the Kashubian people, who originated from the north western Kashubia, located in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland, from the area around the lakes of Łebsko and G ...
and Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
, continued to settle within the rural East.Piskorski (1999), pp.77ffBuchholz (1999), pp.45ff In 1325, the line of the princes of Rügen died out, and the principality was inherited by the House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
, themselves involved in the Brandenburg-Pomeranian conflict about superiority in their often internally divided duchy. In 1466, with the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
's defeat, Pomerelia became subject to the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
as a part of Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
. While the Duchy of Pomerania adopted the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in 1534,Richard du Moulin Eckart, ''Geschichte der deutschen Universitäten'', Georg Olms Verlag, 1976, pp.111,112, Theologische Realenzyklopädie (1997), pp.43ff as part of the Empire by then termed the ''Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation'', Kashubia pl, Kaszuby
, native_name_lang = csb, de, csb
, settlement_type = Historical region
, anthem = Zemia Rodnô
, image_map = Kashubians in Poland.png
, image_flag ...
remained with the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. The Thirty Years' and subsequent wars severely ravaged and depopulated most of Pomerania. With the extinction of the Griffin house Griffin House may refer to:
People
*Griffin House (musician), American musician
Places
;in Canada
* Griffin House (Ancaster), a 19th-century house and museum, site along the Underground Railroad
The Underground Railroad was a network of clan ...
during the same period, the Duchy of Pomerania was divided between the Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
and Brandenburg-Prussia in 1648.
Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
gained the southern parts of Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania ( sv, Svenska Pommern; german: Schwedisch-Pommern) was a dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held ...
in 1720.Buchholz (1999), pp.341-343 It gained the remainder of Swedish Pomerania in 1815, when French occupation during the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
was lifted.Buchholz (1999), pp.363,364 The former Brandenburg-Prussian Pomerania and the former Swedish parts were reorganized into the Prussian Province of Pomerania,Buchholz (1999), p.366 while Pomerelia in the partitions of Poland was made part of the Province of West Prussia
The Province of West Prussia (german: Provinz Westpreußen; csb, Zôpadné Prësë; pl, Prusy Zachodnie) was a province of Prussia from 1773 to 1829 and 1878 to 1920. West Prussia was established as a province of the Kingdom of Prussia in 177 ...
. With Prussia, both provinces joined the newly constituted German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
in 1871. Following the empire's defeat in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Pomerelia became part of the Second Polish Republic (Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, easter ...
) and the Free City of Danzig was created. Germany's Province of Pomerania was expanded in 1938 to include northern parts of the former Province of Posen–West Prussia, and in 1939 the annexed Polish territories became the part of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
known as Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia (german: Reichsgau Danzig-Westpreußen) was an administrative division of Nazi Germany created on 8 October 1939 from annexed territory of the Free City of Danzig, the Greater Pomeranian Voivodship (Polish Corridor ...
. The Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
deported the Pomeranian Jews to a reservation near LublinLucie Adelsberger, Arthur Joseph Slavin, Susan H. Ray, Deborah E. Lipstadt, ''Auschwitz: A Doctor's Story'', Northeastern University Press, 1995, , p.138: February 12/13, 1940Isaiah Trunk, Jacob Robinson, ''Judenrat: The Jewish Councils in Eastern Europe Under Nazi Occupation'', U of Nebraska Press, 1996, , p.133: February 14, 1940; unheated wagons, elderly and sick suffered most, inhumane treatmentMartin Gilbert, Eilert Herms, Alexandra Riebe, ''Geistliche als Retter - auch eine Lehre aus dem Holocaust: Auch eine Lehre aus dem Holocaust'', Mohr Siebeck, 2003, , pp.14 (English) and 15 (German): February 15, 1940, 1000 Jews deportedYad Vashem Studies, Yad ṿa-shem, rashut ha-zikaron la-Shoʼah ṿela-gevurah, Yad Vashem Martyrs' and Heroes' Remembrance Authority, 1996
Notizen: v.12, p.69: 1,200 deported, 250 died during deportationNathan Stoltzfus, ''Resistance of the Heart: Intermarriage and the Rosenstrasse Protest in Nazi Germany'', Rutgers University Press, 2001, , p.130: February 11/12 from Stettin, soon thereafter from Schneidemühl, total of 1,260 Jews deported, among the deportees were intermarried non-Jewish women who had refused to divorce, eager Nazi Gauleiter Schwede-Coburg was the first to have his Gau "judenfrei", Eichmann's "RSHA" (Reich Security Main Office) ensured this was an isolated local incident to worried Eppstein of the Central Organization of Jews in Germany ( Reichsvereinigung der Juden in Deutschland)John Mendelsohn, ''Legalizing the Holocaust, the Later Phase, 1939-1943'', Garland Pub., 1982, , p.131: Stettin Jews' houses were sealed, belongings liquidated, funds to be held in blocked accountsBuchholz (1999), p.506: Only very few f the Pomeranian Jewssurvived the Nazi era. p.510: Nearly all Jews from Stettin and all the province, about a thousandAlicia Nitecki, Jack Terry, ''Jakub's World: A Boy's Story of Loss and Survival in the Holocaust'', SUNY Press, 2005, , pp.13ff: Stettin Jews to Belzyce in Lublin area, reservation purpose decline of Jews, terror command of Kurt Engels, shocking insights in life circumstances and mass-murdered Jews, Poles and Kashubians in Pomerania, planning to eventually exterminate Jews and Poles and Germanise the Kashubians.
After Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
's defeat in World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
, the German–Polish border was shifted west to the Oder–Neisse line
The Oder–Neisse line (german: Oder-Neiße-Grenze, pl, granica na Odrze i Nysie Łużyckiej) is the basis of most of the international border between Germany and Poland from 1990. It runs mainly along the Oder and Lusatian Neisse rivers a ...
and all of Pomerania was placed under Soviet military control.Piskorski (1999), pp.373ff The area west of the line became part of East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
, the other areas part of the People's Republic of Poland even though it did not have a sizeable Polish population. The German population of the areas east of the line was expelled, and the area was resettled primarily with Poles, some of whom were themselves expellees from former eastern Poland) and some Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavs, East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian language, Ukrainian. The majority ...
who were resettled under Operation Vistula
Operation Vistula ( pl, Akcja Wisła; uk, Опера́ція «Ві́сла») was a codename for the 1947 forced resettlement of 150,000 Ukrainians (Boykos and Lemkos) from the south-eastern provinces of post-war Poland, to the Recovered Te ...
) and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
.Piskorski (1999), pp.381ffTomasz Kamusella in Prauser and Reeds (eds), ''The Expulsion of the German communities from Eastern Europe'', p.28, EUI HEC 2004/Philipp Ther, Ana Siljak, ''Redrawing Nations: Ethnic Cleansing in East-Central Europe, 1944-1948'', 2001, p.114, , Gregor Thum, ''Die fremde Stadt. Breslau nach 1945", 2006, pp.363, , Buchholz (1999), p.515Dierk Hoffmann, Michael Schwartz, ''Geglückte Integration?'', p142
/ref>Karl Cordell, Andrzej Antoszewski, ''Poland and the European Union'', 2000, p.168, Piskorski (1999), p.406Selwyn Ilan Troen, Benjamin Pinkus, Merkaz le-moreshet Ben-Guryon, ''Organizing Rescue: National Jewish Solidarity in the Modern Period'', pp.283-284, 1992, , Most of
Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
(''Vorpommern'') today forms the eastern part of the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania
Mecklenburg-Vorpommern (MV; ; nds, Mäkelborg-Vörpommern), also known by its anglicized name Mecklenburg–Western Pomerania, is a state in the north-east of Germany. Of the country's sixteen states, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern ranks 14th in po ...
in Federal Republic of Germany, while the Polish part of the region is divided between West Pomeranian Voivodeship
The West Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as the West Pomerania Province, is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22 892.48 km² (8,838.84 sq mi), and in 2021, it was ...
and Pomeranian Voivodeship
Pomeranian Voivodeship, Pomorskie Region, or Pomerania Province (Polish: ''Województwo pomorskie'' ; ( Kashubian: ''Pòmòrsczé wòjewództwò'' ), is a voivodeship, or province, in northwestern Poland. The provincial capital is Gdańsk.
The ...
, with their capitals in Szczecin and Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
, respectively. During the late 1980s, the Solidarność
Solidarity ( pl, „Solidarność”, ), full name Independent Self-Governing Trade Union "Solidarity" (, abbreviated ''NSZZ „Solidarność”'' ), is a Polish trade union founded in August 1980 at the Lenin Shipyard in Gdańsk, Poland. Subseq ...
and Die Wende
The Peaceful Revolution (german: Friedliche Revolution), as a part of the Revolutions of 1989, was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders with the West, the end of the ruling of the Socialist Unity ...
movements overthrew the Communist regimes implemented during the post-war era . Since then, Pomerania has been democratically governed.
Prehistory and antiquity
Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
during the Allerød oscillation
The Allerød oscillation ( da, Allerødtiden) was a warm and moist global interstadial that occurred c.13,900 to 12,900 BP, nearly at the end of the Last Glacial Period. It raised temperatures in the northern Atlantic region to almost present-da ...
, a warming period that falls within the Early Stone Age
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in t ...
, they left a tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mou ...
. First humans appeared, hunting reindeer
Reindeer (in North American English, known as caribou if wild and ''reindeer'' if domesticated) are deer in the genus ''Rangifer''. For the last few decades, reindeer were assigned to one species, ''Rangifer tarandus'', with about 10 subspe ...
in the summer.Piskorski (1999), pp.16,17 A climate change in 8000 BCPiskorski (1999), p.17 allowed hunters and foragers of the Maglemosian culture, and from 6000 BC of the Ertebølle-Ellerbek culture, to continuously inhabit the area. These people became influenced by farmers of the Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
who settled in southern Pomerania. The hunters of the Ertebølle-Ellerbek culture became farmers of the Funnelbeaker culture
The Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK (german: Trichter(-rand-)becherkultur, nl, Trechterbekercultuur; da, Tragtbægerkultur; ) was an archaeological culture in north-central Europe.
It developed as a technological merger of lo ...
in 3000 BC. The Havelland culture dominated in the Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
from 2500 to 2000 BC. In 2400 BC, the Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a v ...
reached Pomerania and introduced the domestic horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million y ...
. Both Linear Pottery and Corded Ware culture have been associated with Indo-Europeans. Except for Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
, the Funnelbeaker culture was replaced by the Globular Amphora culture
The Globular Amphora culture (GAC, (KAK); ), c. 3400–2800 BC, is an archaeological culture in Central Europe. Marija Gimbutas assumed an Indo-European origin, though this is contradicted by newer genetic studies that show a connection to the ear ...
a thousand years later.Piskorski (1999), p.19
During the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
was part of the Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 2000/1750–500 BC.
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Battle Axe culture (th ...
cultures, while east of the Oder the Lusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1700 BC – 500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III (earl ...
dominated. Throughout the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
, the people of the western Pomeranian areas belonged to the Jastorf culture
The Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age and associating with Germanic peoples. The culture evo ...
, while the Lusatian culture of the East was succeeded by the Pomeranian culture
The Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age culture with origins in parts of the area south of the Baltic Sea (which later became Pomerania, part of northern Germany/Poland), from the 7th century BC to ...
, then in 150 BC by the Oxhöft (Oksywie) culture, and at the beginning of the first millennium by the Willenberg (Wielbark) Culture.
While the Jastorf culture
The Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age and associating with Germanic peoples. The culture evo ...
is usually associated with Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
, the ethnic category of the Lusatian culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1700 BC – 500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III (earl ...
and its successors is debated. Veneti, Germanic peoples (Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
, and Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
) and possibly Slavs are assumed to have been the bearers of these cultures or parts thereof.Piskorski (1999), pp.21ff 6
Beginning in the 3rd century, many settlements were abandoned, marking the beginning of the Migration Period in Pomerania. It is assumed that Burgundians, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
and Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
with parts of the Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
left Pomerania during that stage, while some Veneti, Vidivarii The Vidivarii are described by Jordanes in his Getica as a melting pot of tribes who in the mid-6th century lived at the lower Vistula:Mayke de Jong, Frans Theuws, Carine van Rhijn, ''Topographies of Power in the Early Middle Ages'', BRILL, 2001, p. ...
and other, Germanic groups remained, RGA 23 (2003), p.282 and formed the Gustow
Gustow is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Rügen district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe aft ...
, Debczyn and late Willenberg cultures, which existed in Pomerania until the 6th century. RGA 23 (2003), p.281
Timeline 10,000 BC–600 AD
*~10,000 BC (Early Stone Age
The Lower Paleolithic (or Lower Palaeolithic) is the earliest subdivision of the Paleolithic or Old Stone Age. It spans the time from around 3 million years ago when the first evidence for stone tool production and use by hominins appears in t ...
): first humans hunt in Pomerania after the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
glaciers left (Hamburg culture
The Hamburg culture or Hamburgian (15,500-13,100 BP) was a Late Upper Paleolithic culture of reindeer hunters in northwestern Europe during the last part of the Weichsel Glaciation beginning during the Bölling interstadial. Sites are found close ...
, a subgroup of the Ahrensburg culture)
*8000–3000 BC ( Middle Stone Age): Maglemosian culture, Ertebølle-Ellerbek culture (Lietzow subgroup)Horst Wernicke, ''Greifswald, Geschichte der Stadt'', Helms, 2000, p.16,
*3000–1900 BC ( Late Stone Age): Linear Pottery culture
The Linear Pottery culture (LBK) is a major archaeological horizon of the European Neolithic period, flourishing . Derived from the German ''Linearbandkeramik'', it is also known as the Linear Band Ware, Linear Ware, Linear Ceramics or Inci ...
,Piskorski (1999), pp.18,19 6 Funnelbeaker culture
The Funnel(-neck-)beaker culture, in short TRB or TBK (german: Trichter(-rand-)becherkultur, nl, Trechterbekercultuur; da, Tragtbægerkultur; ) was an archaeological culture in north-central Europe.
It developed as a technological merger of lo ...
,Piskorski (1999), p.19 6 Havelland culture,Horst Wernicke, ''Greifswald, Geschichte der Stadt'', Helms, 2000, pp.16,17, Corded Ware culture
The Corded Ware culture comprises a broad archaeological horizon of Europe between ca. 3000 BC – 2350 BC, thus from the late Neolithic, through the Copper Age, and ending in the early Bronze Age. Corded Ware culture encompassed a v ...
,Piskorski (1999), pp.19,20 6 Globular Amphora culture
The Globular Amphora culture (GAC, (KAK); ), c. 3400–2800 BC, is an archaeological culture in Central Europe. Marija Gimbutas assumed an Indo-European origin, though this is contradicted by newer genetic studies that show a connection to the ear ...
*1900–~550 BC (Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
): Nordic Bronze Age
The Nordic Bronze Age (also Northern Bronze Age, or Scandinavian Bronze Age) is a period of Scandinavian prehistory from c. 2000/1750–500 BC.
The Nordic Bronze Age culture emerged about 1750 BC as a continuation of the Battle Axe culture (th ...
(Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
), Lusatian Culture
The Lusatian culture existed in the later Bronze Age and early Iron Age (1700 BC – 500 BC) in most of what is now Poland and parts of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, eastern Germany and western Ukraine. It covers the Periods Montelius III (earl ...
( Eastern Pomerania)Piskorski (1999), pp.20,21 6
*~550 BC–~250 AD (Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
): Jastorf culture
The Jastorf culture was an Iron Age material culture in what is now northern Germany and southern Scandinavia spanning the 6th to 1st centuries BC, forming part of the Pre-Roman Iron Age and associating with Germanic peoples. The culture evo ...
(Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
, 550–50 BC),Piskorski (1999), p.23 6Horst Wernicke, ''Greifswald, Geschichte der Stadt'', Helms, 2000, pp.18,19, Pomeranian culture
The Pomeranian culture, also Pomeranian or Pomerelian Face Urn culture was an Iron Age culture with origins in parts of the area south of the Baltic Sea (which later became Pomerania, part of northern Germany/Poland), from the 7th century BC to ...
(Pomerelia, 650–150 BC), Oxhöft (Oksywie) culture (Pomerelia, 150 BC–1 AD), Willenberg (Wielbark) culture (Pomerelia, 1–250 AD). In part associated with Veneti and Germanic peoplesHorst Wernicke, ''Greifswald, Geschichte der Stadt'', Helms, 2000, p.19, like Suebi, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, and Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
.
*since 200: Migration Period: great parts of the population move south, associated with Burgundians, Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, Γήπαιδες) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
, and parts of the Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
*3rd–6th centuries: Gustow group The Gustow group (german: Gustow Gruppe or ''Gustower Gruppe'', pl, grupa gustowska) is an archaeological culture of the Roman Iron Age in Western Pomerania. The Gustow group is associated with the Germanic tribe of the Rugii.
Since the second h ...
in Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
, Dębczyn (Denzin) culture in most of Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
, late stage of the Willenberg (Wielbark) culture in Pomerelia and some areas west of it. Associated with Rugian remains and other Germanic tribes, Vistula Veneti
The Vistula Veneti (also called Baltic Veneti) were an Indo-European people that inhabited the region of central Europe east of the Vistula River and the areas around the Bay of Gdańsk. The name first appeared in the 1st century AD in the writin ...
, and Vidivarii The Vidivarii are described by Jordanes in his Getica as a melting pot of tribes who in the mid-6th century lived at the lower Vistula:Mayke de Jong, Frans Theuws, Carine van Rhijn, ''Topographies of Power in the Early Middle Ages'', BRILL, 2001, p. ...
.
Early Middle Ages

 The southward movement of
The southward movement of Germanic tribes
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and e ...
and Veneti during the Migration Period had left Pomerania largely depopulated by the 7th century.Piskorski (1999), p.26 Between 650 and 850 AD, West Slavic tribes
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some R ...
settled in Pomerania.Piskorski (1999), pp.29ff These tribes were collectively known as " Pomeranians" between the Oder and Vistula
The Vistula (; pl, Wisła, ) is the longest river in Poland and the ninth-longest river in Europe, at in length. The drainage basin, reaching into three other nations, covers , of which is in Poland.
The Vistula rises at Barania Góra in ...
rivers, or as "Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
" (later "Liuticians") west of the Oder. A distinct tribe, the Rani, was based on the island of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and the adjacent mainland.Piskorski (1999), p.30 In the 8th and 9th centuries, Slavic- Scandinavian emporia were set up along the coastline as powerful centres of craft and trade.Harck&Lübke (2001), pp.15ff
In 936, the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
set up the Billung
The House of Billung was a dynasty of Saxon noblemen in the 9th through 12th centuries.
The first known member of the house was Count Wichmann, mentioned as a Billung in 811. Oda, the wife of Count Liudolf, oldest known member of the Liudol ...
and Northern marches in Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
, divided by the Peene
The Peene () is a river in Germany.
Geography
The Westpeene, with the Ostpeene as its longer tributary, and the Kleine Peene/Teterower Peene (with a ''Peene '' without specification (or ''Nordpeene'') as its smaller and shorter affluent) flo ...
. The Liutician federation, in an uprising of 983, managed to regain independence, but broke apart in the course of the 11th century because of internal conflicts.Harck&Lübke (2001), p.27 Meanwhile, Polish Piasts
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
managed to acquire parts of eastern Pomerania during the late 960s, where the Diocese of Kołobrzeg
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
was installed in 1000 AD. The Pomeranians regained independence during the Pomeranian uprising of 1005.Buchholz (1999), p.25 : pagan uprising that also ended the Polish suzerainty in 1005Michael Müller-Wille, ''Rom und Byzanz im Norden: Mission und Glaubenswechsel im Ostseeraum während des 8.-14. Jahrhunderts: internationale Fachkonferenz der deutschen Forschungsgemeinschaft in Verbindung mit der Akademie der Wissenschaften und der Literatur, Mainz: Kiel, 18.-25. 9. 1994'', 1997, p.105, ,
During the first half of the 11th century, the Liuticians participated in the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
's wars against Piast Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in the early 12th ce ...
.Herrmann (1985), pp.356ff The alliance broke off when Poland was defeated,Herrmann (1985), p.359 and the Liutician federation broke apart in 1057 during a civil war.Herrmann (1985), p.365 The Liutician capital was destroyed by the Germans in 1068/69,Herrmann (1985), p.366 making way for the subsequent eastward expansion of their western neighbour, the Obodrite state. In 1093, the Luticians,Herrmann (1985), p.379 Pomeranians and Rani had to pay tribute to Obodrite prince Henry.Herrmann (1985), p.367
Timeline 600–1100
 *~650–~850:
*~650–~850: Slavic peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout ...
appear and differentiate into several tribes grouped as Polabian Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
(later ''Liuticians'', ''Lutizians'') in the West and Pomeranians in the East,Harck&Lübke (2001), p.15 resettling the regions left by the Germanic tribes
*since 800: various Scandinavian settlements and tradeposts, including Ralswiek
Ralswiek is a municipality in the Vorpommern-Rügen district, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe ...
, Altes Lager Menzlin
Altes Lager (German for "Old Camp") is a site south of the village of Menzlin near Anklam, Western Pomerania, Germany. The site, on the banks of the river Peene, was an important Viking trading-post during the Viking Age. At that time, Pomerania ...
, and Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
(then "Vineta
Vineta (sometimes ''Wineta'') is the name of a mythical city at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea. The myth evolved around the tradition about the medieval emporium called Jumne, Jomsborg (with which Vineta is sometimes identified), Julin or s ...
" or "Jomsborg
Jomsborg or Jómsborg (german: Jomsburg) was a semi-legendary Viking stronghold at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea (medieval Wendland, modern Pomerania), that existed between the 960s and 1043. Its inhabitants were known as Jomsvikings. Jom ...
" of the Jomsvikings
The Jomsvikings were purportedly a legendary order of Viking mercenaries or conquerors of the 10th and 11th centuries. Though reputed to be staunchly dedicated to the worship of the Old Norse gods, they would allegedly fight for any lord who ...
).
*918: western parts incorporated into Northern March and March of the Billungs (Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
, Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
)
*955: Battle of Recknitz
The Battle on the Raxa river (german: Schlacht an der Raxa) was fought on 16 October 955 over control of the Billung march (in present-day Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, northeast Germany) between the forces of Otto I of Germany allied with the Rani (Sla ...
("Raxa"): Germans and Rani suppress an Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
revolt in the Billung march
*In the 980s, a stronghold in Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
was built, probably by the Polish ruler Mieszko I, who thereby connected the future Polish state ruled by the Piast dynasty with the trade routes of the Baltic Sea.
*983: uprising in the marches, Lutici regain independence after forming the Lutici federation
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
*Mieszko I of Poland
Mieszko I (; – 25 May 992) was the first ruler of Poland and the founder of the first independent Polish state, the Duchy of Poland. His reign stretched from 960 to his death and he was a member of the Piast dynasty, a son of Siemomysł and ...
launches several campaigns since the 960s, acquiring KołobrzegPiskorski (1999), p.32
*1000: Congress of Gniezno constitutes Reinbern Reinbern (-1013/15) was the only bishop of the short-lived Diocese of Kołobrzeg (1000-~1007).
Reinbern was born in the Hassegau area of the medieval Duchy of Saxony.David Warner, ''Ottonian Germany: The Chronicon of Thietmar of Merseburg'', Manch ...
's Bishopric of Kołobrzeg
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associat ...
*1005: Pomerania regains independence, bishopric dissolved
*1046: A Siemomysł
Siemomysł or Ziemomysł (died ) was the third duke of Polans of the Piast dynasty, and the father of Poland's first Christian ruler, Mieszko I. He was listed by Gallus Anonymous in his ''Gesta principum Polonorum'' and was the son of Lestek, ...
, called to Merseburg
Merseburg () is a town in central Germany in southern Saxony-Anhalt, situated on the river Saale, and approximately 14 km south of Halle (Saale) and 30 km west of Leipzig. It is the capital of the Saalekreis district. It had a dioces ...
by king Henry III to conclude a peace settlement, is the first documented duke of Pomerania, though the extent and location of his realm is unknown.Piskorski (1999), p.33
*1056/57: The Lutici alliance breaks apart in a civil war, subsequent Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
eastward expansion.Herrmann (1985), p.365
*1067/68 and 1069: Saxon expeditions raid and destroy Rethra
Rethra (also known as ''Radagoszcz'', ''Radegost'', ''Radigast'', ''Redigast'', ''Radgosc'' and other forms like ''Ruthengost'') was, in the 10th to the 12th centuries, the main town and political center of the Slavic Redarians, one of the four m ...
, the main Liutician stronghold and temple.Herrmann (1985), p.366
*1093: Lutici,Herrmann (1985), p.379 Pomeranians and Rani had to pay tribute to Obodrite prince Henry.Herrmann (1985), p.367
High Middle Ages
Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
, Polish, Saxon, and Danish
Danish may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Denmark
People
* A national or citizen of Denmark, also called a "Dane," see Demographics of Denmark
* Culture of Denmark
* Danish people or Danes, people with a Danish a ...
conquests resulted in vassalage and Christianization
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of the formerly pagan and independent Pomeranian tribes.Theologische Realenzyklopädie (1997), p.40Herrmann (1985), pp.384ff Local dynasties ruled the Principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
(House of Wizlaw), the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
(House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
), the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp
The Schlawe and Stolp Land, also known as Słupsk and Sławno Land, is a historical region in Pomerania, centered on the towns of Sławno (''Schlawe'') and Słupsk (''Stolp'') in Farther Pomerania, in present-day Poland.
The area is of some his ...
(Ratiboride branch of the House of Pomerania), and the duchies in Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
(Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
). Monasteries were founded at Grobe, Kolbatz, Gramzow, and Belbuck which supported Pomerania's Christianization and advanced German settlements.
The dukes of Pomerania
This is a list of the duchies and dukes of Pomerania.
Dukes of the Slavic Pomeranian tribes (All Pomerania)
The lands of Pomerania were firstly ruled by local tribes, who settled in Pomerania around the 10th and 11th centuries.
Non-dynastic
...
expanded their realm into Circipania and Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
to the Southwest, and competed with the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
for territory and formal overlordship over their duchies. Pomerania-Demmin lost most of her territory and was integrated into Pomerania-Stettin in the mid-13th century. When the Ratiborides died out in 1223, competition arose for the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp,Buchholz (1999), p.87 which changed hands numerous times.
Throughout the High Middle Ages, a large influx of German settlers and the introduction of German law, custom, and Low German
:
:
:
:
:
(70,000)
(30,000)
(8,000)
, familycolor = Indo-European
, fam2 = Germanic
, fam3 = West Germanic
, fam4 = North Sea Germanic
, ancestor = Old Saxon
, ancestor2 = Middle L ...
language turned the area west of the Oder into a German one ( Ostsiedlung). The Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
, who during the Early Middle Ages had belonged to the Slavic Rani, Lutician and Pomeranian tribes, were assimilated by the German Pomeranians
The Pomeranians (german: Pommern) are a German people native to the historical region of Pomerania. In modern times, its population inhabits Germany, including the state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern.Paulus Gijsbertus Johannes Post, P. Post, G. Rouwh ...
. To the east of the Oder this development occurred later; in the area from Stettin eastward, the number of German settlers in the 12th century was still insignificant. The Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
descendants of Slavic Pomeranians, dominated many rural areas in Pomerelia.
The conversion of Pomerania
Medieval Pomerania was converted from Slavic paganism to Christianity by Otto von Bamberg in 1124 and 1128 (Duchy of Pomerania), and in 1168 by Absalon (Principality of Rügen).
Earlier attempts at Christianization, undertaken since the 10th ce ...
to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
was achieved primarily by the missionary efforts of Absalon
Absalon (21 March 1201) was a Danish statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church who served as the bishop of Roskilde from 1158 to 1192 and archbishop of Lund from 1178 until his death. He was the foremost politician and church father of Denm ...
and Otto von Bamberg
Otto of Bamberg (1060 or 1061 – 30 June 1139) was a German missionary and papal legate who converted much of medieval Pomerania to Christianity. He was the bishop of Bamberg from 1102 until his death. He was canonized in 1189.
Early life
Thr ...
, by the foundation of numerous monasteries, and by the assimilatory power of the Christian settlers. A Pomeranian diocese was set up in Wolin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
, the see was later moved to Cammin.
Timeline 1100–1300
*1100: Unsuccessful siege of theObodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
capital Liubice Liubice, also known by the German name Alt-Lübeck ("Old Lübeck"), was a medieval West Slavic settlement near the site of modern Lübeck, Germany. Liubice was located at the confluence of the Schwartau with the Trave across from Teerhof Island, a ...
by the RaniHerrmann (1985), p.268
*1102–1121/2: Bolesław III Wrymouth
Bolesław III Wrymouth ( pl, Bolesław III Krzywousty; 20 August 1086 – 28 October 1138), also known as Boleslaus the Wry-mouthed, was the duke of Lesser Poland, Silesia and Sandomierz between 1102 and 1107 and over the whole of Poland between ...
conquers Pomerania east of the Oder and the burghs of Szczecin (Stettin) and Wolin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
(Wollin, Jumne);Piskorski (1999), p.35 first known dukes of the House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
(West) and Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
(East)
*1120s: Wartislaw I
Wartislaw I (''Warcisław I'') (around 1092 – August 9, 1135) was the first historical ruler of the Duchy of Pomerania and the founder of the Griffin dynasty.
Most of the information about him comes from the writings on the life of Otto of ...
of the House of Pomerania expands his duchy westward and incorporates Liutician territory including the County of Gützkow
The County of Gützkow (german: Grafschaft Gützkow) was a county in the Duchy of Pomerania in the High Middle Ages. It was established in 1129 from the Castellany of Gützkow. Following the death of its last count in 1359, it was reestablished i ...
, Wolgast
Wolgast (; csb, Wòłogòszcz) is a town in the district of Vorpommern-Greifswald, in Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Germany. It is situated on the bank of the river (or strait) Peenestrom, vis-a-vis the island of Usedom on the Baltic coast that can b ...
, Circipania and Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
Piskorski (1999), pp.40,41
*1123–1125: Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
prince Henry
Henry may refer to:
People
*Henry (given name)
* Henry (surname)
* Henry Lau, Canadian singer and musician who performs under the mononym Henry
Royalty
* Portuguese royalty
** King-Cardinal Henry, King of Portugal
** Henry, Count of Portugal, ...
subdues the RaniHerrmann (1985), p.379 Wartislaw accepted the superiority of the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
and, with the exception of the newly won territories, also the superiority of the Polish duke.Inachin (2008), p.17
*1124/28: Otto of Bamberg's mission results in the Conversion of Pomerania
Medieval Pomerania was converted from Slavic paganism to Christianity by Otto von Bamberg in 1124 and 1128 (Duchy of Pomerania), and in 1168 by Absalon (Principality of Rügen).
Earlier attempts at Christianization, undertaken since the 10th ce ...
to Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
Buchholz (1999), p.25William Palmer, ''A Compendioius Ecclesiastical History from the Earliest Period to the Present Time'', Kessinger Publishing, 2005, pp.107ff, Herrmann (1985), pp.402ff
*1128: Rani forces assault and destroy Obodrite
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ( ...
Liubice Liubice, also known by the German name Alt-Lübeck ("Old Lübeck"), was a medieval West Slavic settlement near the site of modern Lübeck, Germany. Liubice was located at the confluence of the Schwartau with the Trave across from Teerhof Island, a ...
Herrmann (1985), p.381
*1135: Boleslaw accepts the superiority of Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
Lothair, who in turn grants him Pomerania as a fief, including the Oder area and the principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
which had not been subjugated yet.Piskorski (1999), p.43
*since 1138: Boleslaw dies, the Griffin duchy regains independence from the Piasts
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I (c. 930–992). The Piasts' royal rule in Poland ended in 1370 with the death of king Casimir III the Great.
Branche ...
Herrmann (1985), pp.386
*1140: Diocese of Cammin
The Bishopric of Cammin (also Kammin, Kamień Pomorski) was both a former Roman Catholic diocese in the Duchy of Pomerania from 1140 to 1544, and a secular territory of the Holy Roman Empire ( Prince-Bishopric) in the Kolberg (Kołobrzeg) area f ...
set up, centred at Wolin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
and subordinate directly to the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of Rome ...
*1147: Wendish Crusade
The Wendish Crusade (german: Wendenkreuzzug) was a military campaign in 1147, one of the Northern Crusades and a part of the Second Crusade, led primarily by the Kingdom of Germany within the Holy Roman Empire and directed against the Polabian Sl ...
mounted by dukes and bishops of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, Danish and Polish participation
*1155: Partition of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
into Pomerania-Demmin and Pomerania-Stettin
*1164: Battle of Verchen
The Battle of Verchen (german: Schlacht bei Verchen) was a battle between Saxons and West Slavic Obotrites on 6 July 1164.
The Obotrites were attacked by Saxons and Danes in 1160, resulting in the death of the Obotrite prince, Niklot, and the pa ...
, House of Pomerania becomes vassals of Henry the Lion
Henry the Lion (german: Heinrich der Löwe; 1129/1131 – 6 August 1195) was a member of the Welf dynasty who ruled as the duke of Saxony and Bavaria from 1142 and 1156, respectively, until 1180.
Henry was one of the most powerful German p ...
's Duchy of Saxony
The Duchy of Saxony ( nds, Hartogdom Sassen, german: Herzogtum Sachsen) was originally the area settled by the Saxons in the late Early Middle Ages, when they were subdued by Charlemagne during the Saxon Wars from 772 and incorporated into the C ...
Buchholz (1999), pp.30,34
*1168: Danish expedition led by Roskilde archbishop Absalon
Absalon (21 March 1201) was a Danish statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church who served as the bishop of Roskilde from 1158 to 1192 and archbishop of Lund from 1178 until his death. He was the foremost politician and church father of Denm ...
takes the Principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
, resulting in conversion of the Rani who became Danish vassals
*~1170: first German settlementsPiskorski (1999), p.77
*1170s and early 1180s: various encounters between Pomeranians and Danes. Danes raid Circipania and Wolin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from th ...
.
*1181 House of Pomerania becomes vassal of Barbarossa
Barbarossa, a name meaning "red beard" in Italian, primarily refers to:
* Frederick Barbarossa (1122–1190), Holy Roman Emperor
* Hayreddin Barbarossa (c. 1478–1546), Ottoman admiral
* Operation Barbarossa, the Axis invasion of the Soviet Un ...
's Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
Buchholz (1999), p.34Piskorski (1999), p.44
*1184: Pomeranian navy repelled and destroyed by the Danes in the Bay of GreifswaldPiskorski (1999), p.44
*1186: All Pomerania under Danish control, Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
temporarily renounces her claimsBuchholz (1999), pp.34,35
*since 1220: Ostsiedlung. Existing towns adopt German town law based on Lübeck law
The Lübeck law (german: Lübisches (Stadt)Recht) was the family of codified municipal law developed at Lübeck, which became a free imperial city in 1226 and is located in present day Schleswig-Holstein. It was the second most prevalent form of ...
, Magdeburg law
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within ...
or Kulm law Kulm law, Culm law or Chełmno Law (german: Kulmer Recht; lat, Jus Culmense vetus; pl, Prawo chełmińskie) was a legal constitution for a municipal form of government used in several Central European cities during the Middle Ages.
It was initia ...
), new ones are established with these laws, woods and swamps are cleared and settled, existing villages are expanded and reorganized, new villages are founded.
*1227: Denmark is defeated in the Battle of Bornhöved, Danish unable to keep Pomerania thereafter
*1231: Upon coming of age, the Margraves of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
Johann I and Otto III receive Pomerania from the Roman-German Emperor Frederick II at Ravenna
Ravenna ( , , also ; rgn, Ravèna) is the capital city of the Province of Ravenna, in the Emilia-Romagna region of Northern Italy. It was the capital city of the Western Roman Empire from 408 until its collapse in 476. It then served as the cap ...
.
*1236: Treaty of Kremmen
The Treaty of Kremmen was signed on 20 June 1236 by Duke Wartislaw III of Pomerania, recognizing the seigniory of the Brandenburg margraves over his Duchy of Pomerania-Demmin, and ceding the terrae Stargard, Wustrow and Beseritz to Brandenburg ...
: Pomerania-Demmin loses most of her territory to the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
*1250: Treaty of Landin
The Treaty of Landin was signed in Landin, Germany in 1250 between Barnim I of Pomerania-Stettin, the Ascanian margraves Johann I and Otto III of Brandenburg. Barnim I was accepted as co-ruler of Wartislaw III of Pomerania-Demmin by the Margravi ...
: Pomerania-Stettin able to incorporate remainder of Pomerania-Stettin, but loses Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
*since 1250: southern parts of Pomerania lost to Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
and become northern Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March ( pl, Nowa Marchia) or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945.
Call ...
Buchholz (1999), p.89
*1223–1283: House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
, the margraves of Brandenburg, the princes of Rügen and the Pomerelian Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
compete for the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp
The Schlawe and Stolp Land, also known as Słupsk and Sławno Land, is a historical region in Pomerania, centered on the towns of Sławno (''Schlawe'') and Słupsk (''Stolp'') in Farther Pomerania, in present-day Poland.
The area is of some his ...
after the Ratiborides branch of the House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
became extinctBuchholz (1999), p.87
*1283–1294: Lands of Schlawe and Stolp
The Schlawe and Stolp Land, also known as Słupsk and Sławno Land, is a historical region in Pomerania, centered on the towns of Sławno (''Schlawe'') and Słupsk (''Stolp'') in Farther Pomerania, in present-day Poland.
The area is of some his ...
part of Pomerelia
*1295: Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
partitioned in Pomerania-Wolgast and Pomerania-StettinBuchholz (1999), pp.104-105
Late Middle Ages
 The towns of the
The towns of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
were acting as quasi autonomous political and military entities.Craig J. Calhoun, Joseph Gerteis, James Moody, Steven Pfaff, Indermohan Virk, ''Contemporary Sociological Theory'', Blackwell Publishing, 2002, pp.157,158
, Buchholz (1999), pp.128-154,178-180 The Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
gained the Principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
after two wars with Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
,Buchholz (1999), pp. 115,116 the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp
The Schlawe and Stolp Land, also known as Słupsk and Sławno Land, is a historical region in Pomerania, centered on the towns of Sławno (''Schlawe'') and Słupsk (''Stolp'') in Farther Pomerania, in present-day Poland.
The area is of some his ...
Buchholz (1999), pp. 106 and the Lauenburg and Bütow Land
Lauenburg and Bütow Land (german: Länder or , csb, Lãbòrskò-bëtowskô Zemia, pl, Ziemia lęborsko-bytowska) formed a historical region in the western part of Pomerelia (Polish and papal historiography) or in the eastern part of Farther Po ...
.Buchholz (1999), p. 186 Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
was integrated into the Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Cen ...
after the Teutonic takeover of Danzig
Teutonic or Teuton(s) may refer to:
Peoples and cultures
* Teutons, a Germanic tribe or Celtic tribe mentioned by Greek and Roman authors
** ''Furor Teutonicus'', a Latin phrase referring to the proverbial ferocity of the Teutons
* Having qualit ...
in 1308, and became a part of Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
in 1466.
The Duchy of Pomerania was internally fragmented into Pomerania-Wolgast, -Stettin, -Barth, and -Stolp.Hartmut Boockmann, ''Die Anfänge der ständischen Vertretungen in Preussen und seinen Nachbarländern'', Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 1992, pp.131,132, Buchholz (1999), pp.143,146,147 The dukes were in continuous warfare with the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
due to Uckermark
The Uckermark () is a historical region in northeastern Germany, straddles the Uckermark District of Brandenburg and the Vorpommern-Greifswald District of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern. Its traditional capital is Prenzlau.
Geography
The region is nam ...
and Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March ( pl, Nowa Marchia) or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945.
Call ...
border disputes and disputes over formal overlordship of Pomerania.Buchholz (1999), pp. 160-166,180ff
In 1478, the duchy was reunited under the rule of Bogislaw X
Bogislaw X of Pomerania, ''the Great'', (3 June 1454 – 5 October 1523) was Duke of Pomerania from 1474 until his death in 1523.
Biography
Bogislaw was born in Rügenwalde (now Darłowo, Poland). His parents were Eric II, Duke of Pomerania ...
, when most of the other dukes had died of the plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
.''Bogislaw X'' in Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie/ref>Buchholz (1999), p.189
Timeline 1300–1500
 *1294–1308:
*1294–1308: Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
and Poland compete for Pomerelia after the Samborides
The Samborides () or House of Sobiesław () were a ruling dynasty in the historic region of Pomerelia. They were first documented about 1155 as governors (''princeps'') in the Eastern Pomeranian lands serving the royal Piast dynasty of Poland ...
died outBuchholz (1999), p.103
*1308: Teutonic take-over of Danzig (Gdańsk)
*1309: Treaty of Soldin (Myślibórz) - The Monastic state of the Teutonic Knights
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Cen ...
purchases the Margraviate of Brandenburg
The Margraviate of Brandenburg (german: link=no, Markgrafschaft Brandenburg) was a major principality of the Holy Roman Empire from 1157 to 1806 that played a pivotal role in the history of Germany and Central Europe.
Brandenburg developed out ...
's disputed claim to Pomerelia after conquering the territory
*1317–47: Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
takes the Lands of Schlawe and Stolp
The Schlawe and Stolp Land, also known as Słupsk and Sławno Land, is a historical region in Pomerania, centered on the towns of Sławno (''Schlawe'') and Słupsk (''Stolp'') in Farther Pomerania, in present-day Poland.
The area is of some his ...
as a Brandenburgian fief; in 1317, local Swenzones dynasty continues to rule; full incorporation into Pomerania-Wolgast in 1347.Buchholz (1999), p.105
*1325–1356: Rügen War of Succession
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
with Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
. Pomerania-Wolgast The Duchy of Pomerania-Wolgast, also known as the Duchy of Wolgast, and the Duchy of Wołogoszcz, was a feudal duchy in Western Pomerania within the Holy Roman Empire. Its capital was Wolgast. It was ruled by the Griffin dynasty.Edward Rymar, ''R ...
incorporates the Principality of Rügen
The Principality of Rügen; da, Fyrstendømmet Rygien; pl, Księstwo rugijskie; la, Rugia was a Danish principality, formerly a duchy, consisting of the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland from 1168 until 1325. It was governed by a loc ...
.
*1361–1368: Two wars of the Hanseatic League
The Hanseatic League (; gml, Hanse, , ; german: label=Modern German, Deutsche Hanse) was a medieval commercial and defensive confederation of merchant guilds and market towns in Central and Northern Europe. Growing from a few North German to ...
with Denmark result in the Treaty of Stralsund (1370)
The Treaty of Stralsund (24 May 1370) ended the war between the Hanseatic League and the kingdom of Denmark. The Hanseatic League reached the peak of its power by the conditions of this treaty.Phillip Pulsiano, Kirsten Wolf, ''Medieval Scandinavi ...
, the high-water mark of Hanseatic power.Phillip Pulsiano, Kirsten Wolf, ''Medieval Scandinavia: An Encyclopedia'', Taylor & Francis, 1993, p.265, Peter N. Stearns, William Leonard Langer, ''The Encyclopedia of World History: Ancient, Medieval, and Modern, Chronologically Arranged'', Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 2001, p.265, Angus MacKay, David Ditchburn, ''Atlas of Medieval Europe'', Routledge, 1997, p.171,
*1368/72: Pomerania-Wolgast partitioned into P.-Wolgast and P.-StolpHartmut Boockmann
Hartmut Boockmann (August 22, 1934 – June 15, 1998) was a German historian, specializing in medieval history.
Boockmann was born in Marienburg, East Prussia, Germany, after 1945 Malbork Poland. He received his Ph.D. in 1965. Boockmann was profes ...
, ''Die Anfänge der ständischen Vertretungen in Preussen und seinen Nachbarländern'', Oldenbourg Wissenschaftsverlag, 1992, pp.132,133,
*1376–1394: Pomerania-Wolgast partitioned into P.-Wolgast and P.-Barth
*1397: Eric of Pomerania
Eric of Pomerania (1381 or 1382 – 24 September 1459) was the ruler of the Kalmar Union from 1396 until 1439, succeeding his grandaunt, Queen Margaret I. He is known as Eric III as King of Norway (1389–1442), Eric VII as King of Denmark (1 ...
-Stolp becomes king of the Kalmar UnionBuchholz (1999), p.154-158
*1410: Gdańsk (Danzig) sides with Poland during the Polish war against the Teutonic Order
*1425: Pomerania-Wolgast again partitioned into P.-Wolgast and P.-BarthBuchholz (1999), p.154
*1448: First Peace of Prenzlau
Treaty of Prenzlau or Peace of Prenzlau (german: Vertrag von Prenzlau, Frieden vo Prenzlau, Vergleich von Prenzlau) may refer to several treaties during a series of wars between the Margraviate of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Pomerania fought for c ...
ends a war between Pomerania-Stettin and Brandenburg
*1455: Lauenburg and Bütow Land
Lauenburg and Bütow Land (german: Länder or , csb, Lãbòrskò-bëtowskô Zemia, pl, Ziemia lęborsko-bytowska) formed a historical region in the western part of Pomerelia (Polish and papal historiography) or in the eastern part of Farther Po ...
granted to the House of Pomerania
The House of Griffin or Griffin dynasty (german: Greifen; pl, Gryfici, da, Grif) was a dynasty ruling the Duchy of Pomerania from the 12th century until 1637. The name "Griffins" was used by the dynasty after the 15th century and had been tak ...
*1456: University of Greifswald
The University of Greifswald (; german: Universität Greifswald), formerly also known as “Ernst-Moritz-Arndt University of Greifswald“, is a public research university located in Greifswald, Germany, in the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pom ...
founded
*1464: Death of Otto III, Duke of Pomerania, Otto III of Pomerania-Stettin, causes war for succession between Pomerania-Wolgast and Brandenburg.
*1466: Treaty of Soldin (1466), Treaty of Soldin: Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
becomes a nominal fief of the Electorate of Brandenburg. Implementation failed, war flares up again.
*1466: Second Peace of Thorn: the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
cedes Pomerelia to the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
as part of what is later called Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
, Lauenburg and Bütow Land
Lauenburg and Bütow Land (german: Länder or , csb, Lãbòrskò-bëtowskô Zemia, pl, Ziemia lęborsko-bytowska) formed a historical region in the western part of Pomerelia (Polish and papal historiography) or in the eastern part of Farther Po ...
confirmed to the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
.
*1472/9: Second Peace of Prenzlau
Treaty of Prenzlau or Peace of Prenzlau (german: Vertrag von Prenzlau, Frieden vo Prenzlau, Vergleich von Prenzlau) may refer to several treaties during a series of wars between the Margraviate of Brandenburg and the Duchy of Pomerania fought for c ...
ends a war between Pomerania-Stettin and BrandenburgBuchholz (1999), p.190
*1478: Bogislaw X becomes sole ruler of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
since all other male Griffins deceased, most of a plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
epidemicBuchholz (1999), pp.181ff
*1493: Treaty of Pyritz ends the armed Brandenburg-Pomeranian conflicts
Early Modern Age

 Throughout this time,
Throughout this time, Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
was within Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
, a part of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth with considerable autonomy. In the late 18th century, it became a part of Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
.
The Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
was fragmented into Pomerania-Stettin (Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
) and Pomerania-Wolgast (Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
) in 1532,Buchholz (1999), pp.205-220 underwent Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
in 1534,Buchholz (1999), pp.205-212 and was even further fragmented in 1569.Buchholz (1999), pp.207 In 1627, the Thirty Years' War reached the duchy.Buchholz (1999), p.233 Since the Treaty of Stettin (1630), it was under Swedish control.Buchholz (1999), pp.235,236 In the midst of the war, the last duke Bogislaw XIV, Duke of Pomerania, Bogislaw XIV died without an issue. Garrison, plunder, numerous battles, famine and diseases left two thirds of the population dead and most of the country ravaged.Buchholz (1999), p.263Buchholz (1999), p.332 In the Peace of Westphalia of 1648, the Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
and Brandenburg-Prussia agreed on a partition of the duchy, which came into effect after the Treaty of Stettin (1653). Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
became Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania ( sv, Svenska Pommern; german: Schwedisch-Pommern) was a dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held ...
, a Dominions of Sweden, Swedish dominion, while Farther Pomerania became a Province of Pomerania (1653-1815), Brandenburg-Prussian province.
A series of wars affected Pomerania in the following centuries. As a consequence, most of the formerly free peasants became serfdom, serfs of the nobles.Buchholz (1999), p.264ff Brandenburg-Prussia was able to integrate southern Swedish Pomerania into her Pomeranian province during the Great Northern War, which was confirmed in the Treaty of Stockholm (Great Northern War), Treaty of Stockholm in 1720. In the 18th century, Prussia rebuild and colonised Province of Pomerania (1653-1815), her war-torn Pomeranian province.Buchholz (1999), pp.332,347,354
Timeline 1500–1806
*1520s:Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
*1529: Treaty of Grimnitz settles the Brandenburg-Pomeranian conflict between the houses of House of Pomerania, Pomerania and House of Hohenzollern, Hohenzollern
*1532: Partition of the Duchy of Pomerania into P.-Wolgast (Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
) and P.-Stettin (Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
)
*1534: Protestantism officially adopted in the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
by the Landtag
*1569: Pomerania-Barth split off Pomerania-Wolgast, Pomerania-Rügenwalde split off Pomerania-StettinBuchholz (1999), pp.207
*1627: Thirty Years' War reaches Pomerania, Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
surrendered to the Holy Roman Empire, imperial army in the Capitulation of FranzburgBuchholz (1999), p.233
*1628: Battle of Stralsund (1628), Battle of Wolgast
*1630: Treaty of Stettin (1630): Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
allied to and occupied by the Swedish Empire
The Swedish Empire was a European great power that exercised territorial control over much of the Baltic region during the 17th and early 18th centuries ( sv, Stormaktstiden, "the Era of Great Power"). The beginning of the empire is usually ta ...
*1635–1644: Holy Roman Empire, Imperial troops several times occupy Pomerania
*1637: last Duke of Pomerania deceased, districts of Lauenburg and Butow Land (Lebork and Bytow) had returned to Polish rule
*1644: Battle of Colberger Heide
 *1648: Peace of Westphalia – partition of the
*1648: Peace of Westphalia – partition of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
: Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
becomes Swedish Pomerania, Farther Pomerania granted to Brandenburg-Prussia. Two thirds of the population dead, most of the duchy ravaged.
*1653: Treaty of Stettin (1653): Swedes withdraw from Farther Pomerania, Brandenburg sets up Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), Province of Pomerania there
*1656–1660: Second Northern War – all of Pomerania affected by campaigns of Sweden, Brandenburg and Poland
*1656: Treaty of Labiau – Sweden allies with Prussia
*1657: Treaty of Wehlau, confirmed by subsequent Treaty of Bromberg – Prussian rights in Pomerania assured by the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
*1658: Sweden and Prussia break their alliance and battle each other in Swedish PomeraniaBuchholz (1999), p.318
*1660: Peace of Oliva restores the conditions before the war to Pomerania
*1675–1679: Scanian War between Sweden, Prussia and Denmark affects Swedish Pomerania and the Prussian Province of Pomerania (1653-1815), province of Pomerania.Buchholz (1999), pp.318,319 Battle of Stralsund (1678).
*1679: Treaty of Saint-Germain-en-Laye (1679), Peace of Saint-Germain-en-Laye restores pre-war conditions in Pomerania
*1700-1721: Great Northern War between Prussia, Sweden and Denmark; The plague during the Great Northern War, plague in Pomerania
*1715: Battle of Stralsund (1715), Denmark and Prussia conquer Swedish Pomerania
*1720: Treaty of Frederiksborg and Treaty of Stockholm (Great Northern War), Treaty of Stockholm – Southern Swedish Pomerania becomes part of the Kingdom of Prussia and is incorporated into the Province of Pomerania (1653-1815), Province of Pomerania
*1757–1762: Seven Years' War reaches the Swedish and Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), Prussian Pomerania, Swedish, Russian and Prussian forces ravage the duchy. Siege of Kolberg (Seven Years' War), Kolberg was the subject of sieges in 1759, 1760 and 1761.
*1772–1793: Partitions of Poland – Pomerelia is annexed into Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
's province of West Prussia, plans to Germanize the province and discrimination of Polish population.
Modern Age
Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
to World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, Pomerania was administered by the Kingdom of Prussia as the Province of Pomerania (Western Pomerania, Western and Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
) and West Prussia (Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
).
The Province of Pomerania was created from the Province of Pomerania (1653–1815) (Farther Pomerania and Altvorpommern, southern Vorpommern) and Swedish Pomerania
Swedish Pomerania ( sv, Svenska Pommern; german: Schwedisch-Pommern) was a dominion under the Swedish Crown from 1630 to 1815 on what is now the Baltic coast of Germany and Poland. Following the Polish War and the Thirty Years' War, Sweden held ...
(Neuvorpommern, northern Vorpommern), and the districts of Schivelbein and Dramburg, formerly belonging to the Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March ( pl, Nowa Marchia) or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945.
Call ...
.Buchholz (1999), p.366 While in the Kingdom of Prussia, the province was heavily influenced by the reforms of Karl August von Hardenberg and Otto von Bismarck.Buchholz (1999), pp.420ff The industrial revolution had an impact primarily on the Stettin area and the infrastructure, while most of the province retained a rural and agricultural character.Buchholz (1999), pp.412,413,464ff Since 1850, the net migration rate was negative, Pomeranians (German people), Pomeranians emigrated primarily to Berlin, the West German industrial regions and overseas. Also, more than 100,000 Kashubian Poles emigrated from Pomerania between 1855 and 1900, for economic and social reasons, in what is called the Kashubian diaspora. In areas where ethnically Polish population lived along with ethnic Germans a virtual apartheid existed (in Prussian Pomerania this was mostly the Lauenburg and Bütow Land
Lauenburg and Bütow Land (german: Länder or , csb, Lãbòrskò-bëtowskô Zemia, pl, Ziemia lęborsko-bytowska) formed a historical region in the western part of Pomerelia (Polish and papal historiography) or in the eastern part of Farther Po ...
), with bans on Kashubian or Polish language and religious discrimination, besides attempts to colonize areas of prevailingly ethnically Polish population with ethnic Germans the Prussian Settlement Commission, established in 1886 and restricted to act in Posen and West Prussia provinces only, parcelled acquired noble latifundium, latifundia into 21,727 homesteads of an average of 13 to 15 hectares, introducing 154,000 ethnic German colonists before World War I, which were all outside of Prussian Pomerania, but are also located in areas today denominated as Pomerania in Polish geography. This was surpassed after 1892 by efforts of new private initiatives by Poles in Germany#History, minority of ethnically Polish Germans, but a majority in wide parts of Posen and West Prussia province, who founded the Prussian banks ''Bank Ziemski'', ''Bank Społek Zarobkowych'' (cooperative central clearing bank) and land acquisition cooperatives (spółki ziemskie) which collected private funds and succeeded to buy more latifundia from defaulted owners and settle more ethnically Polish Germans as farmers on the parcelled land than their governmentally funded counter-party. A big success of the Prussian activists for the Polish nation.
After the First World War, the Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919–1939), Pomeranian Voivodeship of the Second Polish Republic was established from the bulk of West Prussia. Poland became a democracy and introduced women's right to vote already in 1918.
The German minority in Poland moved in large numbers to Germany, mostly of free will and due to their economic situation.Richard Blanke, Orphans of Versailles, p32ff, 1993 Poland built a large Baltic port at the site of the former village Gdynia. The Danzig (Gdańsk) area became the Free City of Danzig, a city-state.
In the Province of Pomerania that, after Kaiser's abdication became part of the Free State of Prussia within the Weimar Republic, democracy and Women's suffrage, women's right to vote were introduced.Buchholz (1999), pp.472ff The economic situation worsened due to the consequences of World War I and the worldwide recession.Buchholz (1999), pp.443ff,481ff As in the Kingdom of Prussia before, Pomerania was a stronghold of nationalistic and anti-SemiticAdolf Hitler: a biographical companion David Nicholls page 178 November 1, 2000 ''The main nationalist party the German National People's Party DNVP was divided between reactionary conservative monarchists, who wished to turn the clock back to the pre-1918 Kaisereich, and more radical volkisch and anti-semitic elements. It also inherited the support of old Pan-German League, whose nationalism rested on belief in the inherent superiority of the German people'' German National People's Party, DNVP.Buchholz (1999), pp.377ff,439ff,491ff The government of the state of Prussia, of which Pomerania was a province, was between 1920 and 1932 led by the Social Democratic Party of Germany, Social Democrats, Otto Braun being Prussian minister-president almost continuously during this time.
Timeline 1806–1933
*1806–1813:Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fren ...
in PomeraniaBuchholz (1999), pp.363,364
*1806: Gustavia, Rügen, Gustavia constructed
*1806/7: French forces take Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), Province of Pomerania except for Kolberg
*1807: Battle of Stralsund (1807), Battle of Stralsund and Siege of Kolberg (1807), Siege of Kolberg
*1807: Peace of Tilsit, Prussia surrenders
*1808: French troops withdraw from the Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), Province of Pomerania
*1809: Ferdinand von Schill killed in the Battle of Stralsund (1809)
*1812: French forces invade Swedish Pomerania and again occupy the Prussian Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), Province of Pomerania
*1812: Convention of Tauroggen, Pomeranian corps led by Ludwig Yorck von Wartenburg turns against France
*1813: Mobilization in the Prussian parts of Pomerania against France, Russian Empire, Russian forces occupy the Prussian Province of Pomerania (1653-1815), Province of Pomerania, French forces withdraw
*1815: Congress of Vienna: Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
gains Swedish Pomerania
*1815: reorganization of the Province of Pomerania: Swedish Pomerania and the Dramburg and Schivelbein counties merged into the Province of Pomerania (1653–1815), former province, administrative reforms implemented.Buchholz (1999), p.366
*1815: With the Kingdom of Prussia, the Province of Pomerania and West Prussia join the German Confederation (1815–1866)
*1829–1878: West Prussia merged with East Prussia into Province of Prussia
*since 1840: introduction of a railway system
*1839: Marcin Dunin archbishop of Poznań and Gniezno, primate of Poland is imprisoned by Prussian authorities in Kołobrzeg
*1846: 100 Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
led by Florian Ceynowa fail in an attempt to take the Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an em ...
n garrison Preußisch Stargard (Starograd Gdański) as part of anti-Prussian uprising
*1848: Poles stage an uprising in southern Pomerelia, engage in fights Tuchola Forest against Prussian soldiers.
*1862: Oder and Swine deepened, heavy industry settled in Stettin
*1867: With the Kingdom of Prussia, the Province of Pomerania and Pomerelia within the Province of Prussia join the North German Confederation (1867–1871)
*since 1870: considerable tourism at the Baltic Sea, Baltic coast, former fishing villages are turned into seaside resorts
*1871: With the Kingdom of Prussia, the Province of Pomerania (and Pomerelia within the Province of Prussia) join the German Empire
The German Empire (),Herbert Tuttle wrote in September 1881 that the term "Reich" does not literally connote an empire as has been commonly assumed by English-speaking people. The term literally denotes an empire – particularly a hereditary ...
(1871–1918)
*1872, 1875, 1891: administrative reforms
*1878: West Prussia reestablished
*1918: German Revolution of 1918–1919, November Revolution after World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, "soldiers' and workers' councils" take over most Pomeranian townsBuchholz (1999), p.471
*1919: Treaty of Versailles: West Prussia dissolved, Pomerelia becomes part of the Second Polish Republic as part of Pomeranian Voivodeship (1919–1939), Pomeranian Voivodeship, Danzig (Gdańsk) made Free City of Danzig
*1919: Counter-revolution, Freikorps active in German PomeraniaBuchholz (1999), p.472
*1920: new democratic constitution of the Free State of Prussia now within the Weimar Republic
*1920: Pomeranian Freikorps participate in the Kapp-Putsch
*since 1920: Poles construct Gdynia as their port city in Pomerelia (then the Pomeranian Voivodeship) and connect it to Upper Silesian industry by the Polish Coal Trunk-Line
*1920s: economic recession in the German parts of Pomerania
*1932: Regierungsbezirk Stralsund merged into Regierungsbezirk Stettin
Nazi era
 In 1933, the Province of Pomerania like all of Germany Enabling act of 1933, came under control of the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime. During the following years, the
In 1933, the Province of Pomerania like all of Germany Enabling act of 1933, came under control of the Nazi Germany, Nazi regime. During the following years, the Nazis
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) in N ...
led by Gauleiter Franz Schwede-Coburg manifested their power by Gleichschaltung and repression of their opponents.Buchholz (1999), pp.500ff,509ff Pomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
then formed the Polish Corridor
The Polish Corridor (german: Polnischer Korridor; pl, Pomorze, Polski Korytarz), also known as the Danzig Corridor, Corridor to the Sea or Gdańsk Corridor, was a territory located in the region of Pomerelia (Pomeranian Voivodeship, easter ...
of the Second Polish Republic. Concerning Pomerania, Nazi diplomacy aimed at incorporation of the Free City of Danzig and a transit route through the corridor, which was rejected by the Polish government.Joachim C. Fest, ''Hitler'', Harcourt Trade, 2002, pp.575-577,/ref> In 1939, the German Wehrmacht Invasion of Poland, invaded Poland. Inhabitants of the region from all ethnic backgrounds were subject to numerous atrocities by Nazi Germany forces, of which the most affected were Polish and Jewish civilians. Pomerelia was made part of
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia
Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia (german: Reichsgau Danzig-Westpreußen) was an administrative division of Nazi Germany created on 8 October 1939 from annexed territory of the Free City of Danzig, the Greater Pomeranian Voivodship (Polish Corridor ...
. The Nazis set up concentration camps, ethnically cleansed Poles and Jews, and systematically exterminated Poles, Roma and the Jews. In Pomerania Albert Forster was directly responsible for extermination of non-Germans in Danzig-West Prussia. He personally believed in the need to engage in genocide of Poles and stated that "We have to exterminate this nation, starting from the cradle" and declared that Poles and Jews were not human.
Around 70 camps were set up for Polish populations in Pomerania where they were subjected to murder, torture and in case of women and girls, rape before executions Between 10 and 15 September Forster organised a meeting of top Nazi officials in his region and ordered the immediate removal of all "dangerous" Poles, all Jews and Polish clergyDieter Schenk (2002): ''Albert Forster. Gdanski namiestnik Hitlera.'' Gdansk: Wydawnictwo Oskar. , pages 212-213. In some cases Forster ordered executions himself.Dieter Schenk (2002): ''Albert Forster. Gdanski namiestnik Hitlera.'' Gdansk: Wydawnictwo Oskar. , page 215. On 19 October he reprimanded Nazi officials in the city of Grudziadz for not "spilling enough Polish blood"
Timeline 1933–1945
*1933/1934: Enabling Act of 1933 established Nazi rule in the German Province of Pomerania. Gleichschaltung of the Province of Pomerania's administration, institutions and society. Repressions and internment of opponents. Establishment of an Sturmabteilung, SA-led "wild" concentration camp in Stettin. *1934: Nazi party headquarters cleansed the Pomeranian Nazi movement of inner-party opponents and exchanged many of the staff *1938: Grenzmark Posen-West Prussia and twoBrandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
ian counties merged into the German Province of Pomerania
*1938: Several counties from Mazovia and Greater Poland were joined to the Polish Pomeranian Voivodship, and her capital was moved from Toruń (Thorn) to Bydgoszcz (Bromberg).
*1938: Reichskristallnacht: Synagogues destroyed, all male Stettin Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
deported to Oranienburg concentration camp for several weeksBuchholz (1999), p.510
*1939: Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
Invasion of Poland, invades Poland and annexes Pomerelia and the Free City of Danzig, which were made part of the Reichsgau Danzig-West Prussia.
*since 1939: Atrocities by German Selbstschutz units and mass murder of the Polish, Kashubian and Jewish population of Danzig-West Prussia at Stutthof concentration camp and in the Mass murders in Piaśnica as part of the Intelligenzaktion in Pomerania
*1940: Deportation of all Jews from German Pomerania, including non-Jewish spouses living in Anti-miscegenation laws#Nazi Germany, mixed marriages, who had resisted pressure to divorce, to a reservation near Lublin in annexed Poland, where later they were murdered at the extermination camps of Bełżec extermination camp, Belzec, Majdanek and Sobibor, prepared according to the Nisko Plan; Province of Pomerania declared judenfrei.
*1945: Soviet Union, Soviet capture following the Red Army's East Pomeranian Offensive and the northern theater of the Battle of Berlin, all of Pomerania Soviet Military Administration in Germany, under Soviet military control.Buchholz (1999), pp.512-515 Mass suicide in Demmin, Mass suicides, Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II, evacuations, flight, expulsion
Communist era and recent history



Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
stayed with Germany and was merged into Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
.
With the consolidation of Communism in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
and Poland, Pomerania was part of the Eastern Bloc. In the 1980s, the Solidarność
Solidarity ( pl, „Solidarność”, ), full name Independent Self-Governing Trade Union "Solidarity" (, abbreviated ''NSZZ „Solidarność”'' ), is a Polish trade union founded in August 1980 at the Lenin Shipyard in Gdańsk, Poland. Subseq ...
movement in Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
(Danzig) and the Die Wende, Wende movement in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
forced the Communists out of power and led to the establishment of democracy in both the Polish and German part of Pomerania.
Timeline 1945–present
*1945: The Oder-Neisse line becomes the border between Poland and Germany *5July 1945: In addition, Stettin/Szczecin and the mouth of the Oder River were assigned to Poland by the Soviet Union *1945–1949: Soviet military officials east of the Oder-Neisse line subsequently hand over administration to Polish officials,Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
and the Stettin area reorganized in the Polish Szczecin Voivodeship (1946–1975), Szczecin Voivodeship
*1945–1950: Flight and expulsion of Germans from Poland during and after World War II, expulsion of nearly all Germans east of the line
*since 1945: Farther Pomerania
Farther Pomerania, Hinder Pomerania, Rear Pomerania or Eastern Pomerania (german: Hinterpommern, Ostpommern), is the part of Pomerania which comprised the eastern part of the Duchy and later Province of Pomerania. It stretched roughly from the Od ...
and other ethnically cleansed areas dubbed Recovered Territories and resettled primarily with Poles from Central Poland, but also with Poles from former eastern Poland, displaced Poles returning from forced labour in Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, Ukrainians displaced by Operation Vistula
Operation Vistula ( pl, Akcja Wisła; uk, Опера́ція «Ві́сла») was a codename for the 1947 forced resettlement of 150,000 Ukrainians (Boykos and Lemkos) from the south-eastern provinces of post-war Poland, to the Recovered Te ...
, and Jews.Piskorski (1999), p.406
*since 1945: population in Vorpommern nearly doubles due to influx of expellees
*1945/46: Land reform in German Pomerania (Junker#Bodenreform, Bodenreform)
*1950: Koszalin Voivodeship (1950–1975), Koszalin Voivodeship split off Szczecin Voivodeship (1946–1975), Szczecin Voivodeship
*1946–1952: Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
(Vorpommern) without the Stettin/Szczecin area and Wollin/Wolin was fused with Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
to form the East Germany, East German state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, later Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
*since 1948: Poland adopts Soviet style economy
*since 1949: East Germany adopts Soviet style economy
*since 1950: Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
n peasants forced to join Landwirtschaftliche Produktionsgenossenschaft, socialist LPG unitsBeatrice Vierneisel, ''Fremde im Land: Aspekte zur kulturellen Integration von Umsiedlern in Mecklenburg und Vorpommern 1945 bis 1953'', 2006, p.13, , Buchholz (1999), p.521
*1952: German Pomerania partitioned between Administrative divisions of East Germany, newly created administrative units ("Bezirk") Rostock (Bezirk), Rostock, Neubrandenburg (Bezirk), Neubrandenburg, and Frankfurt (Bezirk), Frankfurt.Buchholz (1999), p.519
*1970: Polish 1970 protests
*1975: administrative reform of the Szczecin Voivodeship (1975–1998), Szczecin Voivodeship
*1980: Solidarność
Solidarity ( pl, „Solidarność”, ), full name Independent Self-Governing Trade Union "Solidarity" (, abbreviated ''NSZZ „Solidarność”'' ), is a Polish trade union founded in August 1980 at the Lenin Shipyard in Gdańsk, Poland. Subseq ...
movement emerges in Gdańsk and Szczecin, Communist rule in Poland starts to collapse
*1986: new port built in Sassnitz-Neu Mukran for the railway ferry between East Germany and the Soviet Union
*1989: Die Wende
The Peaceful Revolution (german: Friedliche Revolution), as a part of the Revolutions of 1989, was the process of sociopolitical change that led to the opening of East Germany's borders with the West, the end of the ruling of the Socialist Unity ...
movement results in a collapse of Communist rule in East Germany
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
*1990: Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
becomes part of the newly re-established state of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern prior to German reunification
*1990: systematical decline of shipbuilding in Polish Pomerania
*1995: Pomerania euroregion established
*1999: Koszalin Voivodeship (1975–1998), Koszalin Voivodeship and Szczecin Voivodeship (1975–1998), Szczecin Voivodeship with some parts of neighboring voivodeships Słupsk Voivodeship, Piła Voivodeship and Gorzów Voivodeship merged into West Pomeranian Voivodeship
The West Pomeranian Voivodeship, also known as the West Pomerania Province, is a voivodeship (province) in northwestern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Szczecin. Its area equals 22 892.48 km² (8,838.84 sq mi), and in 2021, it was ...
*2007: the whole Pomerania in Schengen Area
*2011: new administrative division of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern
See also
* History of Denmark * History of Germany * History of Poland * History of SwedenSources
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * *Further reading
English: * Boehlke, LeRoy, ''Pomerania - Its People and Its History'', Pommerscher Verein Freistadt, Germantown, WI, U.S.A., 1983. German and Polish: *Jan Maria Piskorski et al. (Werner Buchholz (German historian), Werner Buchholz, Jörg Hackmann, Alina Hutnikiewicz, Norbert Kersken, Hans-Werner Rautenberg, Wlodzimierz Stepinski, Zygmunt Szultka, Bogdan Wachowiak, Edward Wlodarczyk), ''Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten'', Zamek Ksiazat Pomorskich, 1999, . This book is a co-edition of several German and Polish experts on Pomeranian history and covers the history of Pomerania, except forPomerelia
Pomerelia,, la, Pomerellia, Pomerania, pl, Pomerelia (rarely used) also known as Eastern Pomerania,, csb, Pòrénkòwô Pòmòrskô Vistula Pomerania, prior to World War II also known as Polish Pomerania, is a historical sub-region of Pome ...
, from the earliest appearance of humans in the area until the end of the second millennium. It is also available in a Polish version (''Pomorze poprzez wieki'').
Polish:
* Gerard Labuda (ed.), ''Historia Pomorza, vol. I (to 1466)'', parts 1–2, Poznań 1969
* Gerard Labuda (ed.), ''Historia Pomorza, vol. II (1466–1815)'', parts 1–2, Poznań 1976
* Gerard Labuda (ed.), ''Historia Pomorza, vol. III (1815–1850)'', parts 1–3, Poznań
* Gerard Labuda (ed.), ''Historia Pomorza, vol. IV (1850–1918)'', part 1, Toruń 2003
* B. Śliwiński, "Poczet książąt gdańskich", Gdańsk 1997
German:
* Werner Buchholz (German historian), Werner Buchholz et al., ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999/2002, , 576 pages; this book is part of the ''Deutsche Geschichte im Osten Europas'' series and covers the history of the Duchy of Pomerania
The Duchy of Pomerania (german: Herzogtum Pommern; pl, Księstwo Pomorskie; Latin: ''Ducatus Pomeraniae'') was a duchy in Pomerania on the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, ruled by dukes of the House of Pomerania (''Griffins''). The country ha ...
and Province of Pomerania from the 12th century to 1945, and Western Pomerania
Historical Western Pomerania, also called Cispomerania, Fore Pomerania, Front Pomerania or Hither Pomerania (german: Vorpommern), is the western extremity of the historic region of Pomerania forming the southern coast of the Baltic Sea, Weste ...
after 1945.
* Oskar Eggert, ''Geschichte Pommerns'', Hamburg 1974, ; this book treats the history of Pomerania from pre-historic times up to about 1500.
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Pomerania
History of Pomerania,
History of Prussia
Kashubians
Jomsvikings, Pomerania
History of Pomerania by period
Pomerania