|
Altes Lager Menzlin
Altes Lager (German for "Old Camp") is a site south of the village of Menzlin near Anklam, Western Pomerania, Germany. The site, on the banks of the river Peene, was an important Viking trading-post during the Viking Age. At that time, Pomerania was inhabited by Slavic Wends, yet several Viking trading-posts were set up along the coast (the nearest were Ralswiek to the West and Jomsborg/Wollin to the east). The settlement covered an area of approximately 18 hectares in the 9th century. Remnants of a bridge and a cemetery have been excavated. Some artifacts found in the graves originated in Ireland and in the lands east of the Baltic. Following Scandinavian customs, the dead were buried either in stone ships, i.e. ship-like graves, or within stone circles. The graves excavated so far have been found to be the tombs of women. Most findings date back to the 9th and 10th centuries. Name The ancient name of the site is unknown. ''Altes Lager'', the current name, dates back to Frie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Ship
The stone ship or ship setting was an early burial custom in Scandinavia, Northern Germany, and the Baltic states. The grave or cremation burial was surrounded by slabs or stones in the shape of a boat or ship. The ships vary in size and were erected from c. 1000BCE to 1000CE. History Stone ships were an early burial custom, characteristically Scandinavian but also found in Northern Germany and the Baltic states. The grave or cremation burial was surrounded by tightly or loosely fit slabs or stones in the outline of a ship. They are often found in grave fields, but are sometimes far from any other archaeological remains. Ship settings are of varying sizes, some of monumental proportions. The largest known is the mostly destroyed Jelling stone ship in Denmark, which was at least long. In Sweden, the size varies from (Ale's Stones) to only a few metres. The orientation also varies. Inside, they can be cobbled or filled with stones, or have raised stones in the positions of mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sunset, Sun sets on the Earth. Etymology The word "west" is a Germanic languages, Germanic word passed into some Romance languages (''ouest'' in French, ''oest'' in Catalan, ''ovest'' in Italian, ''oeste'' in Spanish and Portuguese). As in other languages, the word formation stems from the fact that west is the direction of the setting sun in the evening: 'west' derives from the Indo-European root ''*wes'' reduced from ''*wes-pero'' 'evening, night', cognate with Ancient Greek ἕσπερος Hesperus, hesperos 'evening; evening star; western' and Latin vesper 'evening; west'. Examples of the same formation in other languages include Latin Occident, occidens 'west' from occidō 'to go down, to set' and Hebrew מַעֲרָב maarav 'west' from עֶרֶב erev 'evening'. Navigation To go west using a compass for navigation (in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Populated Places In Germany
A former is an object, such as a template, gauge or cutting die, which is used to form something such as a boat's hull. Typically, a former gives shape to a structure that may have complex curvature. A former may become an integral part of the finished structure, as in an aircraft fuselage, or it may be removable, being using in the construction process and then discarded or re-used. Aircraft formers Formers are used in the construction of aircraft fuselage, of which a typical fuselage has a series from the nose to the empennage, typically perpendicular to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft. The primary purpose of formers is to establish the shape of the fuselage and reduce the column length of stringers to prevent instability. Formers are typically attached to longerons, which support the skin of the aircraft. The "former-and-longeron" technique (also called stations and stringers) was adopted from boat construction, and was typical of light aircraft built until the ad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pomerania During The Early Middle Ages
Pomerania during the Early Middle Ages covers the History of Pomerania from the 7th to the 11th centuries. The southward movement of Germanic tribes during the migration period had left territory later called Pomerania largely depopulated by the 7th century.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, p.26, Between 650 and 850 AD, West Slavic tribes settled in Pomerania.Jan M Piskorski, Pommern im Wandel der Zeiten, 1999, pp.29ff The tribes between the Oder and the Vistula were collectively known as Pomeranians, and those west of the Oder as Veleti and later Lutici. A distinct Slavic tribe, the Rani, was based on the island of Rügen and the adjacent mainland.Werner Buchholz, ''Pommern'', Siedler, 1999, pp.22,23, In the 8th and 9th centuries, Slavic- Scandinavian emporia were set up along the coastline as powerful centers of craft and trade.Ole Harck, Christian Lübke, Zwischen Reric und Bornhöved: Die Beziehungen zwischen den Dänen und ihren slawischen Nachbarn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm I Of Brandenburg
Frederick William (german: Friedrich Wilhelm; 16 February 1620 – 29 April 1688) was Elector of Brandenburg and Duke of Prussia, thus ruler of Brandenburg-Prussia, from 1640 until his death in 1688. A member of the House of Hohenzollern, he is popularly known as "the Great Elector" (') because of his military and political achievements. Frederick William was a staunch pillar of the Calvinist faith, associated with the rising commercial class. He saw the importance of trade and promoted it vigorously. His shrewd domestic reforms gave Prussia a strong position in the post-Westphalian political order of north-central Europe, setting Prussia up for elevation from duchy to kingdom, achieved under his son and successor. Biography Elector Frederick William was born in Berlin to George William, Elector of Brandenburg, and Elisabeth Charlotte of the Palatinate. His inheritance consisted of the Margraviate of Brandenburg, the Duchy of Cleves, the County of Mark, and the Duchy of Prussi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
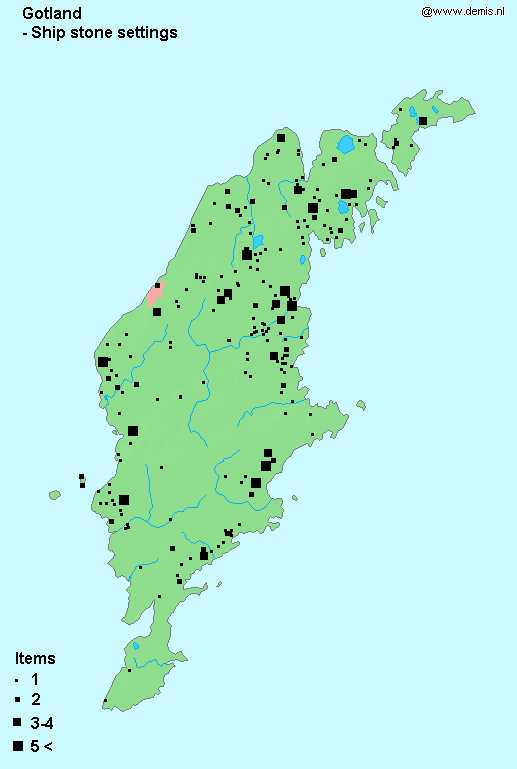
Stone Circle (Iron Age)
The stone circles of the Iron Age (c. 500 BC – c. 400 AD) were a characteristic burial custom of southern Scandinavia and Southwestern Finland, especially on Gotland and in Götaland Finland court stones are found in Eura, Ulvila and Kokemäki. They date typically during the Pre-Roman Iron Age and the Roman Iron Age. In Sweden, they are called Domarringar (judge circles), Domkretsar (judge circles) or Domarsäten (judge seats). In Finland they are called Käräjäkivet (court stones). In some places in Nordic countries they were used until 17th century They should not be confused with the Stone circles of the Bronze Age and Britain. History A tradition of making stone circles existed on the European continent in Wielbark culture near the mouth of the Vistula River in the first century. The practice suggests Norse influence but may have been established in the area before the arrival of the Goths. The stone circles were sometimes used as burial grounds. Shapes Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stone Ship
The stone ship or ship setting was an early burial custom in Scandinavia, Northern Germany, and the Baltic states. The grave or cremation burial was surrounded by slabs or stones in the shape of a boat or ship. The ships vary in size and were erected from c. 1000BCE to 1000CE. History Stone ships were an early burial custom, characteristically Scandinavian but also found in Northern Germany and the Baltic states. The grave or cremation burial was surrounded by tightly or loosely fit slabs or stones in the outline of a ship. They are often found in grave fields, but are sometimes far from any other archaeological remains. Ship settings are of varying sizes, some of monumental proportions. The largest known is the mostly destroyed Jelling stone ship in Denmark, which was at least long. In Sweden, the size varies from (Ale's Stones) to only a few metres. The orientation also varies. Inside, they can be cobbled or filled with stones, or have raised stones in the positions of mast ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baltic States
The Baltic states, et, Balti riigid or the Baltic countries is a geopolitical term, which currently is used to group three countries: Estonia, Latvia, and Lithuania. All three countries are members of NATO, the European Union, the Eurozone, and the OECD. The three sovereign states on the eastern coast of the Baltic Sea are sometimes referred to as the "Baltic nations", less often and in historical circumstances also as the "Baltic republics", the "Baltic lands", or simply the Baltics. All three Baltic countries are classified as high-income economies by the World Bank and maintain a very high Human Development Index. The three governments engage in intergovernmental and parliamentary cooperation. There is also frequent cooperation in foreign and security policy, defence, energy, and transportation. The term "Baltic states" ("countries", "nations", or similar) cannot be used unambiguously in the context of cultural areas, national identity, or language. While the majority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Great Britain and Ireland), North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the List of islands of the British Isles, second-largest island of the British Isles, the List of European islands by area, third-largest in Europe, and the List of islands by area, twentieth-largest on Earth. Geopolitically, Ireland is divided between the Republic of Ireland (officially Names of the Irish state, named Ireland), which covers five-sixths of the island, and Northern Ireland, which is part of the United Kingdom. As of 2022, the Irish population analysis, population of the entire island is just over 7 million, with 5.1 million living in the Republic of Ireland and 1.9 million in Northern Ireland, ranking it the List of European islan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wollin
Wolin (; formerly german: Wollin ) is the name both of a Polish island in the Baltic Sea, just off the Polish coast, and a town on that island. Administratively, the island belongs to the West Pomeranian Voivodeship. Wolin is separated from the island of Usedom (Uznam) by the Strait of Świna, and from mainland Pomerania by the Strait of Dziwna. The island has an area of and its highest point is Mount Grzywacz at 116 m above sea level. The number of inhabitants is 30,000. Water from the river Oder flows into the Szczecin Lagoon and from there through the Peene west of Usedom, Świna and Dziwna into the Bay of Pomerania in the Baltic Sea. Most of the island consists of forests and postglacial hills. In the middle is the Wolin National Park. The island is the main tourist attraction of northwestern Poland, and it is crossed by several specially marked tourist trails, such as a trail from Międzyzdroje to Dziwnówek. There is a main, electrified rail line, which connects S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jomsborg
Jomsborg or Jómsborg (german: Jomsburg) was a semi-legendary Viking stronghold at the southern coast of the Baltic Sea (medieval Wendland, modern Pomerania), that existed between the 960s and 1043. Its inhabitants were known as Jomsvikings. Jomsborg's exact location, or its existence, has not yet been established, though it is often maintained that Jomsborg was located on the eastern outlet of the Oder river. Historian Lauritz Weibull dismissed Jomsborg as a legend. The only source that mentions a precise location of Jomsborg () is the controversial '' Gesta Wulinensis ecclesiae pontificum'' that was discovered in the autumn of 2019.Sven Rosborn (2021)''The Viking King’s Golden Treasure: About the discovery of a lost manuscript, Harald Bluetooth´s grave and the location of the fortress of Jomsborg'' Rivengate AB, ISBN 9198678116 Location Jomsborg is often thought to be identical with the present-day town of Wolin (also Wollin) on the southeastern tip of the isle of Wolin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |