History Of Geophysics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The historical development of geophysics has been motivated by two factors. One of these is the research curiosity of humankind related to planet Earth and its several components, its events and its problems. The second is economical usage of Earth's resources (ore deposits, petroleum, water resources, etc.) and Earth-related hazards such as earthquakes, volcanoes, tsunamis, tides, and floods.
 Arguably the first modern experimental treatise was William Gilbert's ''
Arguably the first modern experimental treatise was William Gilbert's ''
 Determining the physics of Earth's interior was enabled by the development of the first seismographs in the 1880s. Based on the behavior of the waves reflected off the internal layers of the Earth, several theories developed as to what would cause variances in wave speed or loss of certain frequencies. This led to scientists like Inge Lehmann discovering the presence of the Earth's core in 1936. Beno Gutenberg and Harold Jeffreys worked at explaining the difference in Earth's density due to compression and the shear velocity of waves. Since seismology is based on elastic waves, the speed of waves could help determine density and therefore the behavior of the layers within the Earth.
Nomenclature for the behavior of seismic waves was produced based on these findings.
Determining the physics of Earth's interior was enabled by the development of the first seismographs in the 1880s. Based on the behavior of the waves reflected off the internal layers of the Earth, several theories developed as to what would cause variances in wave speed or loss of certain frequencies. This led to scientists like Inge Lehmann discovering the presence of the Earth's core in 1936. Beno Gutenberg and Harold Jeffreys worked at explaining the difference in Earth's density due to compression and the shear velocity of waves. Since seismology is based on elastic waves, the speed of waves could help determine density and therefore the behavior of the layers within the Earth.
Nomenclature for the behavior of seismic waves was produced based on these findings.
 The motion of the conductive molten metal beneath the Earth's crust, or the Earth's
The motion of the conductive molten metal beneath the Earth's crust, or the Earth's
AGU History of Geophysics Committee
* :* :* * {{History of physics Geophysics History of Earth science
Classical and observational period
In circa 240 BC,Eratosthenes
Eratosthenes of Cyrene (; grc-gre, Ἐρατοσθένης ; – ) was a Greek polymath: a mathematician, geographer, poet, astronomer, and music theorist. He was a man of learning, becoming the chief librarian at the Library of Alexandria ...
of Cyrene measured the circumference of Earth using geometry and the angle of the Sun at more than one latitude in Egypt.
There is some information about earthquakes in Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of phil ...
's ''Meteorology'', in ''Naturalis Historia
The ''Natural History'' ( la, Naturalis historia) is a work by Pliny the Elder. The largest single work to have survived from the Roman Empire to the modern day, the ''Natural History'' compiles information gleaned from other ancient authors. ...
'' by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
, and in Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
's ''Geographica
The ''Geographica'' (Ancient Greek: Γεωγραφικά ''Geōgraphiká''), or ''Geography'', is an encyclopedia of geographical knowledge, consisting of 17 'books', written in Ancient Greek, Greek and attributed to Strabo, an educated citizen ...
''. Aristotle and Strabo recorded observations on tide
Tides are the rise and fall of sea levels caused by the combined effects of the gravity, gravitational forces exerted by the Moon (and to a much lesser extent, the Sun) and are also caused by the Earth and Moon orbiting one another.
Tide t ...
s.
A natural explanation of volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
es was first undertaken by the Greek philosopher Empedocles
Empedocles (; grc-gre, Ἐμπεδοκλῆς; , 444–443 BC) was a Greek pre-Socratic philosopher and a native citizen of Akragas, a Greek city in Sicily. Empedocles' philosophy is best known for originating the cosmogonic theory of the fo ...
(c. 490-430 B.C.), who considered the world to be divided into four elemental forces: earth, air, fire and water. He maintained that volcanoes were manifestation of elemental fire. Winds and earthquake
An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ...
s would play a key role in explanations of volcanoes. Lucretius
Titus Lucretius Carus ( , ; – ) was a Roman poet and philosopher. His only known work is the philosophical poem ''De rerum natura'', a didactic work about the tenets and philosophy of Epicureanism, and which usually is translated into E ...
claimed Mount Etna
Mount Etna, or simply Etna ( it, Etna or ; scn, Muncibbeḍḍu or ; la, Aetna; grc, Αἴτνα and ), is an active stratovolcano on the east coast of Sicily, Italy, in the Metropolitan City of Catania, between the cities of Messina a ...
was completely hollow and the fires of the underground driven by a fierce wind circulating near sea level. Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
noted that the presence of earthquakes preceded an eruption. Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath
A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans ...
(1602–1680) witnessed eruptions of Mount Etna and Stromboli, then visited the crater of Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma-stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples
The Gulf of Naples (), also called the Bay of Naples, is a roughly 15-kilometer-wide (9 ...
and published his view of an Earth with a central fire connected to numerous others caused by the burning of sulfur
Sulfur (or sulphur in British English) is a chemical element with the symbol S and atomic number 16. It is abundant, multivalent and nonmetallic. Under normal conditions, sulfur atoms form cyclic octatomic molecules with a chemical formula ...
, bitumen
Asphalt, also known as bitumen (, ), is a sticky, black, highly viscous liquid or semi-solid form of petroleum. It may be found in natural deposits or may be a refined product, and is classed as a pitch. Before the 20th century, the term a ...
and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when dea ...
.
Instrumental and analytical period
 Arguably the first modern experimental treatise was William Gilbert's ''
Arguably the first modern experimental treatise was William Gilbert's ''De Magnete
''De Magnete, Magneticisque Corporibus, et de Magno Magnete Tellure'' (''On the Magnet and Magnetic Bodies, and on That Great Magnet the Earth'') is a scientific work published in 1600 by the English physician and scientist William Gilbert. A h ...
'' (1600), in which he deduced that compasses point north because the Earth itself is magnetic. In 1687 Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton (25 December 1642 – 20 March 1726/27) was an English mathematician, physicist, astronomer, alchemist, theologian, and author (described in his time as a "natural philosopher"), widely recognised as one of the grea ...
published his '' Principia'', which not only laid the foundations for classical mechanics
Classical mechanics is a physical theory describing the motion of macroscopic objects, from projectiles to parts of machinery, and astronomical objects, such as spacecraft, planets, stars, and galaxies. For objects governed by classical ...
and gravitation
In physics, gravity () is a fundamental interaction which causes mutual attraction between all things with mass or energy. Gravity is, by far, the weakest of the four fundamental interactions, approximately 1038 times weaker than the stron ...
but also explained a variety of geophysical phenomena such as tides and the precession of the equinox
In astronomy, axial precession is a gravity-induced, slow, and continuous change in the orientation of an astronomical body's rotational axis. In the absence of precession, the astronomical body's orbit would show axial parallelism. In partic ...
.
These experimental and mathematical analyses were applied to several areas of geophysics: Earth's shape, density, and gravity field (Pierre Bouguer
Pierre Bouguer () (16 February 1698, Croisic – 15 August 1758, Paris) was a French mathematician, geophysicist, geodesist, and astronomer. He is also known as "the father of naval architecture".
Career
Bouguer's father, Jean Bouguer, one ...
, Alexis Clairaut
Alexis Claude Clairaut (; 13 May 1713 – 17 May 1765) was a French mathematician, astronomer, and geophysicist. He was a prominent Newtonian whose work helped to establish the validity of the principles and results that Sir Isaac Newton had out ...
and Henry Cavendish
Henry Cavendish ( ; 10 October 1731 – 24 February 1810) was an English natural philosopher and scientist who was an important experimental and theoretical chemist and physicist. He is noted for his discovery of hydrogen, which he termed "infl ...
), Earth's magnetic field (Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
, Edmund Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Ha ...
and Carl Friedrich Gauss
Johann Carl Friedrich Gauss (; german: Gauß ; la, Carolus Fridericus Gauss; 30 April 177723 February 1855) was a German mathematician and physicist who made significant contributions to many fields in mathematics and science. Sometimes refer ...
), seismology (John Milne
John Milne (30 December 1850 – 31 July 1913) was a British geologist and mining engineer who worked on a horizontal seismograph.
Biography
Milne was born in Liverpool, England, the only child of John Milne of Milnrow, and at first raised in ...
and Robert Mallet
Robert Mallet (3 June 1810 – 5 November 1881) was an Irish geophysicist, civil engineer, and inventor who distinguished himself in research on earthquakes and is sometimes called the father of seismology. His son, Frederick Richard Mallet was ...
), and the Earth's age, heat and radioactivity (Arthur Holmes
Arthur Holmes (14 January 1890 – 20 September 1965) was an English geologist who made two major contributions to the understanding of geology. He pioneered the use of radiometric dating of minerals, and was the first earth scientist to grasp ...
and William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
).
There are several descriptions and discussions about a philosophical theory of the water cycle
The water cycle, also known as the hydrologic cycle or the hydrological cycle, is a biogeochemical cycle that describes the continuous movement of water on, above and below the surface of the Earth. The mass of water on Earth remains fairly cons ...
by Marcus Vitruvius, Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
and Bernard Palissy
Bernard Palissy (c. 1510c. 1589) was a French Huguenot potter, hydraulics engineer and craftsman, famous for having struggled for sixteen years to imitate Chinese porcelain. He is best known for his so-called "rusticware", typically highly decor ...
. Pioneers in hydrology
Hydrology () is the scientific study of the movement, distribution, and management of water on Earth and other planets, including the water cycle, water resources, and environmental watershed sustainability. A practitioner of hydrology is calle ...
include Pierre Perrault
Pierre Perrault (29 June 1927 – 24 June 1999) was a Québécois documentary film director. He directed 20 films between 1963 and 1996. He was one of the most important filmmakers in Canada, although largely unknown outside of Québec. In ...
, Edme Mariotte
Edme Mariotte (; ; c. 162012 May 1684) was a French physicist and priest ( abbé). He is particularly well known for formulating Boyle's law independently of Robert Boyle. Mariotte is also credited with designing the first Newton's cradle.
Biogr ...
and Edmund Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, Ha ...
in studies of such things as rainfall, runoff, drainage area, velocity, river cross-section measurements and discharge. Advances in the 18th century included Daniel Bernoulli
Daniel Bernoulli FRS (; – 27 March 1782) was a Swiss mathematician and physicist and was one of the many prominent mathematicians in the Bernoulli family from Basel. He is particularly remembered for his applications of mathematics to mechan ...
's piezometer
A piezometer is either a device used to measure liquid pressure in a system by measuring the height to which a column of the liquid rises against gravity, or a device which measures the pressure (more precisely, the piezometric head) of groundwa ...
and Bernoulli's equation
In fluid dynamics, Bernoulli's principle states that an increase in the speed of a fluid occurs simultaneously with a decrease in static pressure or a decrease in the fluid's potential energy. The principle is named after the Swiss mathematic ...
as well as the Pitot tube
A pitot ( ) tube (pitot probe) measures fluid flow velocity. It was invented by a French engineer, Henri Pitot, in the early 18th century, and was modified to its modern form in the mid-19th century by a French scientist, Henry Darcy. It is ...
by Henri Pitot. In the 19th century, groundwater hydrology was furthered by Darcy's law
Darcy's law is an equation that describes the flow of a fluid through a porous medium. The law was formulated by Henry Darcy based on results of experiments on the flow of water through beds of sand, forming the basis of hydrogeology, a branch of e ...
, the Dupuit-Thiem well formula, and the Hagen-Poiseuille equation for flows through pipes. ''Physical Geography of the Sea'', the first textbook of oceanography, was written by Matthew Fontaine Maury
Matthew Fontaine Maury (January 14, 1806February 1, 1873) was an American oceanographer and naval officer, serving the United States and then joining the Confederacy during the American Civil War.
He was nicknamed "Pathfinder of the Seas" and i ...
in 1855.
The thermoscope, or Galileo thermometer
A Galileo thermometer (or Galilean thermometer) is a thermometer made of a sealed glass cylinder containing a clear liquid and several glass vessels of varying density. The individual floats rise or fall in proportion to their respective density ...
, was constructed by Galileo Galilei
Galileo di Vincenzo Bonaiuti de' Galilei (15 February 1564 – 8 January 1642) was an Italian astronomer, physicist and engineer, sometimes described as a polymath. Commonly referred to as Galileo, his name was pronounced (, ). He was ...
in 1607. In 1643, Evangelista Torricelli
Evangelista Torricelli ( , also , ; 15 October 160825 October 1647) was an Italian physicist and mathematician, and a student of Galileo. He is best known for his invention of the barometer, but is also known for his advances in optics and work o ...
invented the mercury barometer
A barometer is a scientific instrument that is used to measure air pressure in a certain environment. Pressure tendency can forecast short term changes in the weather. Many measurements of air pressure are used within surface weather analysis ...
. Blaise Pascal
Blaise Pascal ( , , ; ; 19 June 1623 – 19 August 1662) was a French mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher, and Catholic Church, Catholic writer.
He was a child prodigy who was educated by his father, a tax collector in Rouen. Pa ...
(in 1648) rediscovered that atmospheric pressure decreases with height, and deduced that there is a vacuum above the atmosphere.
Emergence as a discipline
The first known use of the word ''geophysics'' was byJulius Fröbel
Carl Ferdinand Julius Fröbel (16 July 1805 – 7 November 1893) was a German geologist and mineralogist, journalist, and democratic revolutionary already during the ''Vormärz'' era. He was active in Germany, Switzerland, the United States and S ...
in 1834 (in German). It was used occasionally in the next few decades, but did not catch on until journals devoted to the subject began to appear, beginning with ''Beiträge zur Geophysik'' in 1887. The future ''Journal of Geophysical Research
The ''Journal of Geophysical Research'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal. It is the flagship journal of the American Geophysical Union. It contains original research on the physical, chemical, and biological processes that contribute to the un ...
'' was founded in 1896 with the title ''Terrestrial Magnetism''. In 1898, a Geophysical Institute was founded at the University of Göttingen
The University of Göttingen, officially the Georg August University of Göttingen, (german: Georg-August-Universität Göttingen, known informally as Georgia Augusta) is a public research university in the city of Göttingen, Germany. Founded ...
, and Emil Wiechert
Emil Johann Wiechert (26 December 1861 – 19 March 1928) was a German physicist and geophysicist who made many contributions to both fields, including presenting the first verifiable model of a layered structure of the Earth and being among the ...
became the world's first Chair of Geophysics. An international framework for geophysics was provided by the founding of the International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics
The International Union of Geodesy and Geophysics (IUGG; french: Union géodésique et géophysique internationale, UGGI) is an international non-governmental organization dedicated to the scientific study of Earth and its space environment us ...
in 1919.
20th century
The 20th century was a revolutionary age for geophysics. As an international scientific effort between 1957 and 1958, theInternational Geophysical Year
The International Geophysical Year (IGY; french: Année géophysique internationale) was an international scientific project that lasted from 1 July 1957 to 31 December 1958. It marked the end of a long period during the Cold War when scientific ...
or IGY was one of the most important for scientific activity of all disciplines of geophysics: aurora
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of bri ...
and airglow
Airglow (also called nightglow) is a faint emission of light by a planetary atmosphere. In the case of Earth's atmosphere, this optical phenomenon causes the night sky never to be completely dark, even after the effects of starlight and diff ...
, cosmic rays
Cosmic rays are high-energy particles or clusters of particles (primarily represented by protons or atomic nuclei) that move through space at nearly the speed of light. They originate from the Sun, from outside of the Solar System in our own ...
, geomagnetism, gravity, ionospheric physics, longitude and latitude determinations (precision mapping), meteorology, oceanography, seismology and solar activity.
Earth's interior and seismology
 Determining the physics of Earth's interior was enabled by the development of the first seismographs in the 1880s. Based on the behavior of the waves reflected off the internal layers of the Earth, several theories developed as to what would cause variances in wave speed or loss of certain frequencies. This led to scientists like Inge Lehmann discovering the presence of the Earth's core in 1936. Beno Gutenberg and Harold Jeffreys worked at explaining the difference in Earth's density due to compression and the shear velocity of waves. Since seismology is based on elastic waves, the speed of waves could help determine density and therefore the behavior of the layers within the Earth.
Nomenclature for the behavior of seismic waves was produced based on these findings.
Determining the physics of Earth's interior was enabled by the development of the first seismographs in the 1880s. Based on the behavior of the waves reflected off the internal layers of the Earth, several theories developed as to what would cause variances in wave speed or loss of certain frequencies. This led to scientists like Inge Lehmann discovering the presence of the Earth's core in 1936. Beno Gutenberg and Harold Jeffreys worked at explaining the difference in Earth's density due to compression and the shear velocity of waves. Since seismology is based on elastic waves, the speed of waves could help determine density and therefore the behavior of the layers within the Earth.
Nomenclature for the behavior of seismic waves was produced based on these findings. P-wave
A P wave (primary wave or pressure wave) is one of the two main types of elastic body waves, called seismic waves in seismology. P waves travel faster than other seismic waves and hence are the first signal from an earthquake to arrive at any ...
s and S-wave
__NOTOC__
In seismology and other areas involving elastic waves, S waves, secondary waves, or shear waves (sometimes called elastic S waves) are a type of elastic wave and are one of the two main types of elastic body waves, so named because th ...
s were used to describe two types of elastic body waves possible. Love wave
In elastodynamics, Love waves, named after Augustus Edward Hough Love, are horizontally polarized surface waves. The Love wave is a result of the interference of many shear waves (S-waves) guided by an elastic layer, which is ''welded'' to an e ...
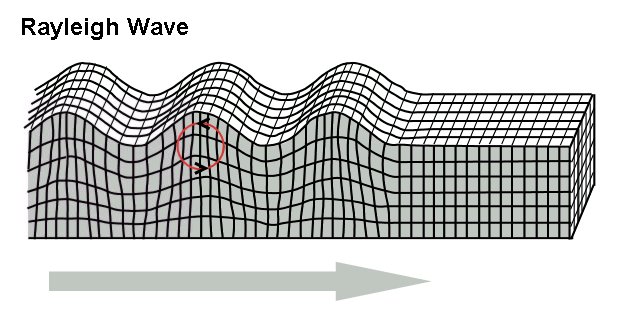
s and Rayleigh wave
Rayleigh waves are a type of surface acoustic wave that travel along the surface of solids. They can be produced in materials in many ways, such as by a localized impact or by piezo-electric transduction, and are frequently used in non-destructiv ...
s were used to describe two types of surface waves possible.
Scientists who have contributed to advances in knowledge about the Earth's interior and seismology
Seismology (; from Ancient Greek σεισμός (''seismós'') meaning "earthquake" and -λογία (''-logía'') meaning "study of") is the scientific study of earthquakes and the propagation of elastic waves through the Earth or through other ...
include Emil Wiechert
Emil Johann Wiechert (26 December 1861 – 19 March 1928) was a German physicist and geophysicist who made many contributions to both fields, including presenting the first verifiable model of a layered structure of the Earth and being among the ...
, Beno Gutenberg
Beno Gutenberg (; June 4, 1889 – January 25, 1960) was a German-American seismologist who made several important contributions to the science. He was a colleague and mentor of Charles Francis Richter at the California Institute of Technolog ...
, Andrija Mohorovičić
Andrija Mohorovičić (23 January 1857 – 18 December 1936) was a Croatian geophysicist. He is best known for the eponymous Mohorovičić discontinuity and is considered one of the founders of modern seismology.
Early years
Mohorovičić wa ...
, Harold Jeffreys
Sir Harold Jeffreys, FRS (22 April 1891 – 18 March 1989) was a British mathematician, statistician, geophysicist, and astronomer. His book, ''Theory of Probability'', which was first published in 1939, played an important role in the revival ...
, Inge Lehmann
Inge Lehmann (13 May 1888 – 21 February 1993) was a Danish seismologist and geophysicist. In 1936, she discovered that the Earth has a solid inner core inside a molten outer core. Before that, seismologists believed Earth's core to be a sin ...
, Edward Bullard
Sir Edward Crisp Bullard FRS (21 September 1907 – 3 April 1980) was a British geophysicist who is considered, along with Maurice Ewing, to have founded the discipline of marine geophysics. He developed the theory of the geodynamo, pioneere ...
, Charles Francis Richter, Francis Birch, Frank Press
Frank Press (December 4, 1924 – January 29, 2020) was an American geophysicist. He was an advisor to four U.S. presidents, and later served two consecutive terms as president of the U.S. National Academy of Sciences (1981–1993). He was the au ...
, Hiroo Kanamori
is a Japanese seismologist who has made fundamental contributions to understanding the physics of earthquakes and the tectonic processes that cause them.
Career
Kanamori and American seismologist Thomas C. Hanks developed the moment magnitud ...
and Walter Elsasser
Walter Maurice Elsasser (March 20, 1904 – October 14, 1991) was a German-born American physicist, a developer of the presently accepted dynamo theory as an explanation of the Earth's magnetism. He proposed that this magnetic field resulted ...
.
One highly debated topic about Earth's interior is mantle plumes. These are theorized to be rising magma, which is responsible for the hotspots in the world, like Hawaii. Originally the theory was that mantle plumes rose up in a direct path, but now there is evidence that the plumes may deflect by small degrees as they rise. It was also found that the proposed hotspot underneath Yellowstone may not be related to a rising mantle plume. This theory has not been fully researched.
Plate tectonics
In the second half of the 20th century,plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
theory was developed by several contributors including Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
, Maurice Ewing
William Maurice "Doc" Ewing (May 12, 1906 – May 4, 1974) was an American geophysicist and oceanographer.
Ewing has been described as a pioneering geophysicist who worked on the research of seismic reflection and refraction in ocean basi ...
, Robert S. Dietz
Robert Sinclair Dietz (September 14, 1914 – May 19, 1995) was a scientist with the US Coast and Geodetic Survey. Dietz, born in Westfield, New Jersey, was a marine geologist, geophysicist and oceanographer who conducted pioneering research along ...
, Harry Hammond Hess, Hugo Benioff
Victor Hugo Benioff (September 14, 1899 – February 29, 1968) was an American seismologist and a professor at the California Institute of Technology. He is best remembered for his work in charting the location of deep earthquakes in the Pacific ...
, Walter C. Pitman, III
Walter Clarkson Pitman III (21 October 1931 – 1 October 2019) was an American geophysicist and a professor emeritus at Columbia University. His measurements of magnetic anomalies on the ocean floor supported the Morley–Vine–Matthews hypothe ...
, Frederick Vine
Frederick John Vine FRS (born 17 June 1939) is an English marine geologist and geophysicist. He made key contributions to the theory of plate tectonics, helping to show that the seafloor spreads from mid-ocean ridges with a symmetrical patter ...
, Drummond Matthews
Drummond Hoyle Matthews FRS (5 February 1931 – 20 July 1997), known as "Drum", was a British marine geologist and geophysicist and a key contributor to the theory of plate tectonics. His work, along with that of fellow Briton Fred Vine a ...
, Keith Runcorn
(Stanley) Keith Runcorn (19 November 1922 – 5 December 1995) was a British physicist whose paleomagnetic reconstruction of the relative motions of Europe and America revived the theory of continental drift and was a major contribution to plat ...
, Bryan L. Isacks, Edward Bullard
Sir Edward Crisp Bullard FRS (21 September 1907 – 3 April 1980) was a British geophysicist who is considered, along with Maurice Ewing, to have founded the discipline of marine geophysics. He developed the theory of the geodynamo, pioneere ...
, Xavier Le Pichon
Xavier Le Pichon (born 18 June 1937 in Qui Nhơn, French protectorate of Annam (after South Vietnam and today Vietnam) is a French geophysicist. Among many other contributions, he is known for his comprehensive model of plate tectonics (1968), ...
, Dan McKenzie, W. Jason Morgan
William Jason Morgan (born October 10, 1935) is an American geophysicist who has made seminal contributions to the theory of plate tectonics and geodynamics. He retired as the Knox Taylor Professor emeritus of geology and professor of geoscienc ...
and John Tuzo Wilson
John Tuzo Wilson (October 24, 1908 – April 15, 1993) was a Canadian geophysicist and geologist who achieved worldwide acclaim for his contributions to the theory of plate tectonics.
''Plate tectonics'' is the scientific theory that the rigi ...
. Prior to this, people had ideas of continental drift, but no real evidence came until the late 20th century. Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, p ...
observed in the early 19th century the geometry and geology of the shores of continents of the Atlantic Ocean. James Hutton
James Hutton (; 3 June O.S.172614 June 1726 New Style. – 26 March 1797) was a Scottish geologist, agriculturalist, chemical manufacturer, naturalist and physician. Often referred to as the father of modern geology, he played a key role i ...
and Charles Lyell
Sir Charles Lyell, 1st Baronet, (14 November 1797 – 22 February 1875) was a Scottish geologist who demonstrated the power of known natural causes in explaining the earth's history. He is best known as the author of ''Principles of Geolo ...
brought about the idea of gradual change, uniformitarianism, which helped people cope with the slow drift of the continents. Alfred Wegener
Alfred Lothar Wegener (; ; 1 November 1880 – November 1930) was a German climatologist, geologist, geophysicist, meteorologist, and polar researcher.
During his lifetime he was primarily known for his achievements in meteorology and ...
spearheaded the original theory of continental drift and spent much of his life devoted to this theory. He proposed "Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
", one unified giant continent.
During the development of continental drift theory, there was not much exploration of the oceanic part of the world, only continental. Once people began to pay attention to the ocean, geologists found that the floor was spreading, and in different rates at different spots. There are three different main ways in which plates can move: transform
Transform may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* Transform (scratch), a type of scratch used by turntablists
* ''Transform'' (Alva Noto album), 2001
* ''Transform'' (Howard Jones album) or the title song, 2019
* ''Transform'' (Powerman 5000 album ...
, divergent, and Convergent. As well, there can be Rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
s, areas where the land is beginning to spread apart.
Oceanography
Advances inphysical oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters.
Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divi ...
occurred in the 20th century. Sea depth by acoustic measurements was first made in 1914. The German "Meteor" expedition gathered 70,000 ocean depth measurements using an echo sounder
Echo sounding or depth sounding is the use of sonar for ranging, normally to determine the depth of water (bathymetry). It involves transmitting acoustic waves into water and recording the time interval between emission and return of a pulse; ...
, surveying the Mid-Atlantic Ridge
The Mid-Atlantic Ridge is a mid-ocean ridge (a divergent or constructive plate boundary) located along the floor of the Atlantic Ocean, and part of the longest mountain range in the world. In the North Atlantic, the ridge separates the North Ame ...
between 1925 and 1927. The Great Global Rift
A mid-ocean ridge (MOR) is a seafloor mountain system formed by plate tectonics. It typically has a depth of about and rises about above the deepest portion of an ocean basin. This feature is where seafloor spreading takes place along a diver ...
was discovered by Maurice Ewing
William Maurice "Doc" Ewing (May 12, 1906 – May 4, 1974) was an American geophysicist and oceanographer.
Ewing has been described as a pioneering geophysicist who worked on the research of seismic reflection and refraction in ocean basi ...
and Bruce Heezen
Bruce Charles Heezen (; April 11, 1924 – June 21, 1977) was an American geologist. He worked with oceanographic cartographer Marie Tharp at Columbia University to map the Mid-Atlantic Ridge in the 1950s.
Biography
Heezen was born in Vinton, Io ...
in 1953, and the mountain range under the Arctic was found in 1954 by the Arctic Institute of the USSR. The theory of seafloor spreading was developed in 1960 by Harry Hammond Hess. The Ocean Drilling Program
The Ocean Drilling Program (ODP) was a multinational effort to explore and study the composition and structure of the Earth's oceanic basins. ODP, which began in 1985, was the successor to the Deep Sea Drilling Project initiated in 1968 by th ...
started in 1966. There has been much emphasis on the application of large scale computers to oceanography to allow numerical predictions of ocean conditions and as a part of overall environmental change prediction.
Geomagnetism
dynamo
file:DynamoElectricMachinesEndViewPartlySection USP284110.png, "Dynamo Electric Machine" (end view, partly section, )
A dynamo is an electrical generator that creates direct current using a commutator (electric), commutator. Dynamos were the f ...
, is responsible for the existence of the magnetic field. The interaction of the magnetic field and solar radiation has an impact on how much radiation reaches the surface of Earth and the integrity of the atmosphere. It has been found that the magnetic poles of the Earth have reversed several times, allowing researchers to get an idea of the surface conditions of the planet at that time. The cause of the magnetic poles being reversed is unknown, and the intervals of change vary and do not show a consistent interval. It is believed that the reversal is correlated to the Earth's mantle, although exactly how is still debated.
Distortions to the Earth's magnetic field cause the phenomenon Aurora Borealis
An aurora (plural: auroras or aurorae), also commonly known as the polar lights, is a natural light display in Earth's sky, predominantly seen in high-latitude regions (around the Arctic and Antarctic). Auroras display dynamic patterns of br ...
, commonly called the Northern Lights. The magnetic field stores energy given by cosmic particles known as solar wind, which causes the magnetic field lines to expand. When the lines contract, they release this energy, which can be seen as the Northern Lights.
Atmospheric influences
The Earth's climate changes over time due to the planet's atmospheric composition, the sun's luminosity, and the occurrence of catastrophic events. Atmospheric composition affects and is affected by the biological mechanisms active on the Earth's surface. Organisms effect the amount of oxygen vs. carbon dioxide throughrespiration
Respiration may refer to:
Biology
* Cellular respiration, the process in which nutrients are converted into useful energy in a cell
** Anaerobic respiration, cellular respiration without oxygen
** Maintenance respiration, the amount of cellul ...
and photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored i ...
. They also affect the levels of nitrogen through fixation, nitrification
''Nitrification'' is the biological oxidation of ammonia to nitrite followed by the oxidation of the nitrite to nitrate occurring through separate organisms or direct ammonia oxidation to nitrate in comammox bacteria. The transformation of amm ...
, and denitrification
Denitrification is a microbially facilitated process where nitrate (NO3−) is reduced and ultimately produces molecular nitrogen (N2) through a series of intermediate gaseous nitrogen oxide products. Facultative anaerobic bacteria perform denitr ...
. The ocean is capable of absorbing carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, but this varies based on the levels of nitrogen and phosphorus present in the water. Humans have also played a role in changing the atmospheric composition of the Earth through industrial byproducts, deforestation
Deforestation or forest clearance is the removal of a forest or stand of trees from land that is then converted to non-forest use. Deforestation can involve conversion of forest land to farms, ranches, or urban use. The most concentrated d ...
, and motor vehicles.
The luminosity of the Sun increases as it progresses through its life cycle and are visible over the course of millions of years. Sunspots can form on the Sun's surface, which can cause greater variability in the emissions that Earth receives.
Volcano
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface.
On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are ...
es form when two plates meet and one subducts underneath the other. They thus form along most plate boundaries; the Ring of Fire
The Ring of Fire (also known as the Pacific Ring of Fire, the Rim of Fire, the Girdle of Fire or the Circum-Pacific belt) is a region around much of the rim of the Pacific Ocean where many volcanic eruptions and earthquakes occur. The Ring o ...
is an example of this. The study of volcanoes along plate boundaries has shown a correlation between eruptions and climate. Alan Robock
Alan may refer to:
People
* Alan (surname), an English and Turkish surname
* Alan (given name), an English given name
** List of people with given name Alan
''Following are people commonly referred to solely by "Alan" or by a homonymous name.''
...
theorizes that volcanic activity can influence climate and can lead to global cooling for years. The leading idea, based on volcanic eruptions, is that sulfur dioxide
Sulfur dioxide (IUPAC-recommended spelling) or sulphur dioxide (traditional Commonwealth English) is the chemical compound with the formula . It is a toxic gas responsible for the odor of burnt matches. It is released naturally by volcanic activ ...
released from volcanoes has a major effect on the cooling of the atmosphere following the eruption.
Impacts from large celestial bodies, commonly asteroid
An asteroid is a minor planet of the inner Solar System. Sizes and shapes of asteroids vary significantly, ranging from 1-meter rocks to a dwarf planet almost 1000 km in diameter; they are rocky, metallic or icy bodies with no atmosphere.
...
s, create shock waves that push air and distribute dust into the atmosphere, blocking sunlight. This causes global cooling, which can lead to the death and possible extinction of many species.
Industrial application
Industrial applications of geophysics were developed by demand ofpetroleum
Petroleum, also known as crude oil, or simply oil, is a naturally occurring yellowish-black liquid mixture of mainly hydrocarbons, and is found in geological formations. The name ''petroleum'' covers both naturally occurring unprocessed crud ...
exploration and recovery in the 1920s. Later, petroleum, mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic via ...
and groundwater
Groundwater is the water present beneath Earth's surface in rock and soil pore spaces and in the fractures of rock formations. About 30 percent of all readily available freshwater in the world is groundwater. A unit of rock or an unconsolidate ...
geophysics were improved. Earthquake hazard minimization and soil/site investigations for earthquake-prone areas were new applications of geophysical engineering in the 1990s.
Seismology is used in the mining industry to read and build models of events that may have been caused or contributed to by the process of mining. This allows scientists to predict the hazards associated with mining in the area.
Much like mining, seismic waves are used to create models of the Earth's subsurface. Geological features, called traps, that commonly indicate the presence of oil, can be identified from the model and used to determine suitable sites to drill.
Groundwater is highly vulnerable to the pollution produced from industry and waste disposal. In order to preserve the quality of fresh water sources, maps of groundwater depth are created and compared to the locations of pollutant sources.
See also
*History of geology
The history of geology is concerned with the development of the natural science of geology. Geology is the scientific study of the origin, history, and structure of Earth.
Antiquity
Some of the first geological thoughts were about the ori ...
* History of geomagnetism
The history of geomagnetism is concerned with the history of the study of Earth's magnetic field. It encompasses the history of navigation using compasses, studies of the prehistoric magnetic field (archeomagnetism and paleomagnetism), and applica ...
* Timeline of the development of tectonophysics
References
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
AGU History of Geophysics Committee
* :* :* * {{History of physics Geophysics History of Earth science