The history of art focuses on objects made by humans for any number of spiritual, narrative, philosophical, symbolic, conceptual, documentary, decorative, and even functional and other purposes, but with a primary emphasis on its
aesthetic visual form.
Visual art
The visual arts are art forms such as painting, drawing, printmaking, sculpture, ceramics, photography, video, filmmaking, design, crafts and architecture. Many artistic disciplines such as performing arts, conceptual art, and textile ar ...
can be classified in
diverse ways, such as separating
fine arts from
applied arts; inclusively focusing on human creativity; or focusing on different media such as
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
,
sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
,
painting
Painting is the practice of applying paint, pigment, color or other medium to a solid surface (called the "matrix" or "support"). The medium is commonly applied to the base with a brush, but other implements, such as knives, sponges, and ai ...
,
film,
photography
Photography is the visual art, art, application, and practice of creating durable images by recording light, either electronically by means of an image sensor, or chemically by means of a light-sensitive material such as photographic film. It i ...
, and
graphic arts. In recent years, technological advances have led to
video art,
computer art,
performance art
Performance art is an artwork or art exhibition created through actions executed by the artist or other participants. It may be witnessed live or through documentation, spontaneously developed or written, and is traditionally presented to a pu ...
,
animation,
television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication Media (communication), medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of Transmission (telecommunications), television tra ...
, and
videogames.
The history of art is often told as a chronology of
masterpieces created during each
civilization
A civilization (or civilisation) is any complex society characterized by the development of a state, social stratification, urbanization, and symbolic systems of communication beyond natural spoken language (namely, a writing system).
C ...
. It can thus be framed as a story of
high culture, epitomized by the
Wonders of the World
Various lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, in order to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural features and human-built structures.
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World is the o ...
. On the other hand,
vernacular
A vernacular or vernacular language is in contrast with a "standard language". It refers to the language or dialect that is spoken by people that are inhabiting a particular country or region. The vernacular is typically the native language, n ...
art expressions can also be integrated into art historical narratives, referred to as
folk arts or
craft. The more closely that an art historian engages with these latter forms of
low culture, the more likely it is that they will identify their work as examining
visual culture or
material culture
Material culture is the aspect of social reality grounded in the objects and architecture that surround people. It includes the usage, consumption, creation, and trade of objects as well as the behaviors, norms, and rituals that the objects crea ...
, or as contributing to fields related to art history, such as
anthropology
Anthropology is the scientific study of humanity, concerned with human behavior, human biology, cultures, societies, and linguistics, in both the present and past, including past human species. Social anthropology studies patterns of be ...
or
archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
. In the latter cases, art objects may be referred to as
archeological artifacts.
Prehistory
Prehistoric art includes a broad range of art made by painters and sculptors from illiterate cultures, including some of the earliest human artifacts. Among the first art objects are decorative artifacts from
Middle Stone Age Africa.
Containers from that period have also been discovered in South Africa that may have been used to hold paints dating as far back as 100,000 years ago.
A form of prehistoric art found all over the world, especially in Europe, small prehistoric statuettes known as
Venus figurines with exaggerated breasts and bellies were made, the most famous ones being the
Venus of Hohle Fels and the
Venus of Willendorf, found in
Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
and
Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
. Most have small heads, wide hips, and legs that taper to a point. Arms and feet are often absent, and the head is usually small and faceless.
The Venus of Hohle Fels is one of the numerous objects found at the
Caves and Ice Age Art in the Swabian Jura UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. I ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, where the oldest non-stationary works of human art yet discovered were found, in the form of carved animal and humanoid figurines, in addition to the oldest musical instruments unearthed so far, with the artifacts dating between 43.000 and 35.000 BC.
The best-known Prehistoric artworks are the large
Paleolithic
The Paleolithic or Palaeolithic (), also called the Old Stone Age (from Greek: παλαιός '' palaios'', "old" and λίθος ''lithos'', "stone"), is a period in human prehistory that is distinguished by the original development of stone to ...
cave painting
In archaeology, Cave paintings are a type of parietal art (which category also includes petroglyphs, or engravings), found on the wall or ceilings of caves. The term usually implies prehistoric origin, and the oldest known are more than 40,00 ...
s that depict animals in continental Europe, particularly the ones at
Lascaux in the
Dordogne
Dordogne ( , or ; ; oc, Dordonha ) is a large rural department in Southwestern France, with its prefecture in Périgueux. Located in the Nouvelle-Aquitaine region roughly half-way between the Loire Valley and the Pyrenees, it is named ...
region of France. Several hundred decorated caves are known, spanning the
Upper Paleolithic period ( 38,000–12,000 BC). There are examples in
Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian invas ...
,
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and
Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It is ...
, but most of them are in
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
and
Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
. Many theories have been suggested about the art's purpose, the most accepted being that it was part of religious rituals, possibly to evoke hunting success.
Riesenhirsch Fussknochen Einhornhöhle Gravur.jpg, '' Riesenhirschknochen der Einhornhöhle'' 49,000 BC; Megaloceros bone; Einhornhöhle, Germany
Loewenmensch1.jpg, ''Löwenmensch
The figurine, also called the Lion-man of , is a prehistoric ivory sculpture discovered in Hohlenstein-Stadel, a German cave in 1939. The German name, , meaning "lion-person" or "lion-human", is used most frequently because it was discovered a ...
''; 40,000-35,000 BC; Hohlenstein-Stadel caves Swabian Jura, Germany
MUT127024.jpg, ''Wild horse''; 32,000 BC; Vogelherd Cave Swabian Jura, Germany
16 PanneauDesLions(CentreGauche)RhinocérosEnFuite.jpg, Painting of rhinoceroses; 32,000-14,000 BC; charcoal on rock; length: 2 m; Chauvet Cave ( Ardèche, France)
Venus of Willendorf frontview retouched 2.jpg, Venus of Willendorf; 25,000 BC; limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
with ochre colouring; height: 11 cm; Natural History Museum (Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
)
Venus de Brassempouy.jpg, Venus of Brassempouy; 23,000 BC; mammoth ivory; height: 3.5 cm; National Archaeological Museum of France ( Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye)
Antiquity
Ancient Near East
Ancient
Near East stretched from
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
and the Mediterranean seaboard in the west to
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
and the
Arabian peninsula in the east. Over time, multiple civilizations appeared, lived and disappeared here. One of the key regions was
Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
, which witnessed during the 4th millennium BC the emergence of the first cities and the earliest form of writing. Ancient Mesopotamia covers present-day Iraq, and parts of
Syria and
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
. Its northern half forms part of the so-called
Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, State of Palestine, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, sou ...
, where important
Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several part ...
developments such as early farming and the establishment of permanent village settlements first appeared. Because the region is situated within the
Tigris–Euphrates river delta, numerous civilizations lived here, notably
Sumer,
Akkad,
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the As ...
and
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state ...
.
Mesopotamian architecture was characterized by the use of
bricks,
lintels, and
cone mosaic. Notable examples are the
ziggurat
A ziggurat (; Cuneiform: 𒅆𒂍𒉪, Akkadian: ', D-stem of ' 'to protrude, to build high', cognate with other Semitic languages like Hebrew ''zaqar'' (זָקַר) 'protrude') is a type of massive structure built in ancient Mesopotamia. It has ...
s, large
temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called church (building), churches), Hindui ...
s in the form of
step pyramids.
The political, economic, artistic and architectural traditions of the Sumerians lead to the foundation of
Western civilization. Multiple things appeared for the first time in Sumer: the first
city-state (
Uruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.H ...
), ruled by king
Gilgamesh; the first organized religion, based on a hierarchical structure of gods, people and rituals; the first known writing, the
cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo- syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedg ...
s; the first irrigation system and the first vehicles with wheels.
Cylinder seals appeared here as well, engraved with little inscriptions and illustrations. Another civilization that developed here was the
Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one rul ...
, the world's first great empire.
During the early 1st millennium BC, after the Akkadians, an empire called
Assyria
Assyria (Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the As ...
came to dominate the whole of Middle East, stretching from the
Persian Gulf
The Persian Gulf ( fa, خلیج فارس, translit=xalij-e fârs, lit=Gulf of Fars, ), sometimes called the ( ar, اَلْخَلِيْجُ ٱلْعَرَبِيُّ, Al-Khalīj al-ˁArabī), is a mediterranean sea in Western Asia. The bo ...
to the
Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
. Its cities were filled with impressive buildings and art. Assyrian art is best known for its detailed stone reliefs, depicting scenes of court life, religious practice, hunting and epic battles. These reliefs were initially painted in bright colours and placed in palaces. Besides their beauty, they also show us Assyrian life and views of the world, including Assyrian clothing and furniture.
Later, the
Babylonia
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state ...
ns conquered the Assyrian Empire. During the 6th century BC,
Babylon became the largest city in the world. Upon entering Babylon, visitors were greeted with the impressive
Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate was the eighth gate to the inner city of Babylon (in the area of present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq). It was constructed circa 575 BCE by order of King Nebuchadnezzar II on the north side of the city. It was part ...
, with its walls covered in vivid blue glazed bricks and reliefs showing dragons, bulls and lions. This gate is named after
Ishtar, the goddess of war and love.
In the mid-6th century BC, after a series of military campaigns, the Babylonian Empire fell to the
Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
, ruled by King
Cyrus II, stretching across the Middle East and
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, from Egypt to the
Indus Valley. Its art incorporates elements from across the empire, celebrating its wealth and power.
Persepolis (
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
) was the capital of the empire, and it is full of impressive sculptures showing religious images and people of the empire. There are also the ruins of a palace here, with a big audience hall for receiving guests.
Besides Mesopotamia and Iran, there were Ancient civilizations who produced art and architecture in other regions as well. In
Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The r ...
(present-day
Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a list of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolia, Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with ...
), the
Hittite Empire
The Hittites () were an Anatolian people who played an important role in establishing first a kingdom in Kussara (before 1750 BC), then the Kanesh or Nesha kingdom (c. 1750–1650 BC), and next an empire centered on Hattusa in north-cent ...
appeared. During Antiquity,
South Arabia was important in the production and trade of aromatics, bringing wealth to the kingdoms that were in this region. Before circa 4000 BC, the climate of Arabia was wetter than today. In south-west, several kingdoms appeared, like
Saba’. The south Arabian human figure is usually stylized, based on rectangular shapes, but with fine details.
Sumerian Status from Tell Asmar, part of the Tell Asmar Hoard.jpg, Votive statuettes (Sumerian
Sumerian or Sumerians may refer to:
*Sumer, an ancient civilization
**Sumerian language
**Sumerian art
**Sumerian architecture
**Sumerian literature
**Cuneiform script, used in Sumerian writing
*Sumerian Records, an American record label based in ...
); 2600 BC; gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and dr ...
, inlaid shell, black limestone and bitumen paint; heights: 73 cm (right) and 59 cm (left); Iraq Museum (Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesipho ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
)
Denis Bourez - British Museum, London (8747049029) (2).jpg, Standard of Ur (Sumerian); 2600-2400 BC; shell, red limestone and lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
on wood; length: 49.5 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Bronze head of an Akkadian ruler, discovered in Nineveh in 1931, presumably depicting either Sargon or Sargon's grandson Naram-Sin (Rijksmuseum van Oudheden).jpg, King of Akkad (Akkadian Akkadian or Accadian may refer to:
* Akkadians, inhabitants of the Akkadian Empire
* Akkadian language, an extinct Eastern Semitic language
* Akkadian literature, literature in this language
* Akkadian cuneiform, early writing system
* Akkadian myt ...
); 2250 BC; copper alloy; height: 30 cm; Iraq Museum
Sumerian Cylinder Seal of King Ur-Nammu.jpg, Cylinder seal of Hash-hamer, showing enthroned king Ur-Nammu, with modern impression (Sumerian); 2100 BC; greenstone; height: 5.3 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Vessel terminating in the forepart of a stag MET DT871.jpg, Stag rhyton ( Hittite); 1400-1200 BC; silver with gold inlay; height: 13 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Ashurnasirpal II, 2 royal attendants, and 2 apkallus, wall relief from Nimrud, Iraq. 9th century BCE. British Museum.jpg, King Ashurnasirpal II
Ashur-nasir-pal II ( transliteration: ''Aššur-nāṣir-apli'', meaning "Ashur is guardian of the heir") was king of Assyria from 883 to 859 BC.
Ashurnasirpal II succeeded his father, Tukulti-Ninurta II, in 883 BC. During his reign he embarke ...
( Assyrian); 883-859 BC; gypsum; 2.4 x 6 m; British Museum
Assyrian monumental bas-relief -(30626865213).jpg, Winged bulls ( Neo-Assyrian); 710 BC; alabaster; height (max): 4.2 m; Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
File:Ishtar gate in Pergamon museum in Berlin..jpg, Reconstruction of the Ishtar Gate
The Ishtar Gate was the eighth gate to the inner city of Babylon (in the area of present-day Hillah, Babil Governorate, Iraq). It was constructed circa 575 BCE by order of King Nebuchadnezzar II on the north side of the city. It was part ...
(Babylonian Babylonian may refer to:
* Babylon, a Semitic Akkadian city/state of ancient Mesopotamia founded in 1894 BC
* Babylonia, an ancient Akkadian-speaking Semitic nation-state and cultural region based in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq)
...
); 605-539 BC; glazed bricks; Pergamon Museum (Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany)
Incense burner MET DT893.jpg, Incense burner ( Pre-Islamic South Arabian); mid-1st millennium BC; bronze; height: 27.6 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Persépolis, Irán, 2016-09-24, DD 50 (cropped section).jpg, Delegation bearing gifts ( Persian Achaemenid
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
); 490 BC; limestone; 260 x 150 cm; in situ, Persepolis (Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkm ...
)
Egypt
One of the first great civilizations arose in
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
, which had elaborate and complex works of art produced by professional artists and craftspeople. Egypt's art was religious and symbolic. Given that the culture had a highly centralized power structure and hierarchy, a great deal of art was created to honour the
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
, including great monuments. Egyptian art and culture emphasized the religious concept of immortality. Later Egyptian art includes
Coptic and
Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
art.
The
architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
is characterized by monumental structures, built with large stone blocks, lintels, and solid
columns. Funerary monuments included
mastaba, tombs of rectangular form;
pyramids, which included step pyramids (
Saqqarah) or smooth-sided pyramids (
Giza); and the
hypogeum, underground tombs (
Valley of the Kings). Other great buildings were the
temple
A temple (from the Latin ) is a building reserved for spiritual rituals and activities such as prayer and sacrifice. Religions which erect temples include Christianity (whose temples are typically called church (building), churches), Hindui ...
, which tended to be monumental complexes preceded by an avenue of
sphinxes and
obelisk
An obelisk (; from grc, ὀβελίσκος ; diminutive of ''obelos'', " spit, nail, pointed pillar") is a tall, four-sided, narrow tapering monument which ends in a pyramid-like shape or pyramidion at the top. Originally constructed by An ...
s. Temples used
pylons and
trapezoid walls with
hypaethros and
hypostyle halls and
shrines. The temples of
Karnak,
Luxor
Luxor ( ar, الأقصر, al-ʾuqṣur, lit=the palaces) is a modern city in Upper (southern) Egypt which includes the site of the Ancient Egyptian city of ''Thebes''.
Luxor has frequently been characterized as the "world's greatest open-ai ...
,
Philae
; ar, فيلة; cop, ⲡⲓⲗⲁⲕ
, alternate_name =
, image = File:File, Asuán, Egipto, 2022-04-01, DD 93.jpg
, alt =
, caption = The temple of Isis from Philae at its current location on Agilkia Island in Lake Nas ...
and
Edfu are good examples. Another type of temple is the
rock temple, in the form of a
hypogeum, found in
Abu Simbel
Abu Simbel is a historic site comprising two massive rock-cut temples in the village of Abu Simbel ( ar, أبو سمبل), Aswan Governorate, Upper Egypt, near the border with Sudan. It is situated on the western bank of Lake Nasser, about ...
and
Deir el-Bahari.
Painting of the Egyptian era used a juxtaposition of overlapping planes. The images were represented hierarchically, i.e., the Pharaoh is larger than the common subjects or enemies depicted at his side. Egyptians painted the outline of the head and limbs in profile, while the torso, hands, and eyes were painted from the front.
Applied arts were developed in Egypt, in particular
woodwork
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinet making ( cabinetry and furniture), wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first mate ...
and
metalwork. There are superb examples such as
cedar furniture
inlaid
Inlay covers a range of techniques in sculpture and the decorative arts for inserting pieces of contrasting, often colored materials into depressions in a base object to form Ornament (art), ornament or pictures that normally are flush with th ...
with
ebony
Ebony is a dense black/brown hardwood, coming from several species in the genus '' Diospyros'', which also contains the persimmons. Unlike most woods, ebony is dense enough to sink in water. It is finely textured and has a mirror finish when ...
and
ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
which can be seen in the tombs at the
Egyptian Museum. Other examples include the pieces found in
Tutankhamun
Tutankhamun (, egy, twt-ꜥnḫ-jmn), Egyptological pronunciation Tutankhamen () (), sometimes referred to as King Tut, was an Egyptian pharaoh who was the last of his royal family to rule during the end of the Eighteenth Dynasty (ruled ...
's tomb, which are of great artistic value.
Tomb of Nebamun.jpg, Nebamun Hunting in the Marshes; 1380 BC; paint on plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "r ...
; 98 × 83 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Relief depicting Akhenaton and Nefertiti with three of their daughters under the rays of Aton 01 (cropped).jpg, Akhenaten
Akhenaten (pronounced ), also spelled Echnaton, Akhenaton, ( egy, ꜣḫ-n-jtn ''ʾŪḫə-nə-yātəy'', , meaning "Effective for the Aten"), was an ancient Egyptian pharaoh reigning or 1351–1334 BC, the tenth ruler of the Eighteenth ...
and Nefertiti
Neferneferuaten Nefertiti () ( – c. 1330 BC) was a queen of the 18th Dynasty of Ancient Egypt, the great royal wife of Pharaoh Akhenaten. Nefertiti and her husband were known for a radical change in national religious policy, in whic ...
with Daughters; 1345 BC; painted limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
; 32.5 x 39 cm; Egyptian Museum of Berlin (Germany)
CairoEgMuseumTaaMaskMostlyPhotographed.jpg, Mask of Tutankhamun; ; gold, glass and semi-precious stones; height: 54 cm; Egyptian Museum (Cairo
Cairo ( ; ar, القاهرة, al-Qāhirah, ) is the capital of Egypt and its largest city, home to 10 million people. It is also part of the largest urban agglomeration in Africa, the Arab world and the Middle East: The Greater Cairo met ...
)
Nofretete Neues Museum.jpg, Nefertiti Bust; 1352–1336 BC; painted limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
; height: 50 cm; Neues Museum (Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany)
Philae temple at night.jpg, Temple of Philae
; ar, فيلة; cop, ⲡⲓⲗⲁⲕ
, alternate_name =
, image = File:File, Asuán, Egipto, 2022-04-01, DD 93.jpg
, alt =
, caption = The temple of Isis from Philae at its current location on Agilkia Island in Lake Nas ...
(Egypt), 380 BC-117 AD
Indus Valley Civilization
Discovered in 1922, long after the contemporary cultures of Mesopotamia and Egypt, the Indus Valley Civilization, aka the Harappan Civilization ( 2400–1900 BC) is now recognized as extraordinarily advanced, comparable in some ways with those cultures. Its sites span an area stretching from today's northeast
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
, through much of
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, and into western and northwestern
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
. Major cities of the culture include
Harappa and
Mohenjo-daro, located respectively in
Punjab
Punjab (; Punjabi: پنجاب ; ਪੰਜਾਬ ; ; also romanised as ''Panjāb'' or ''Panj-Āb'') is a geopolitical, cultural, and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the northern part of the Indian subcontinent, comprising ...
and in
Sindh
Sindh (; ; ur, , ; historically romanized as Sind) is one of the four provinces of Pakistan. Located in the southeastern region of the country, Sindh is the third-largest province of Pakistan by land area and the second-largest province ...
province in northern Pakistan, and the port city
Lothal, in the state of
Gujarat
Gujarat (, ) is a state along the western coast of India. Its coastline of about is the longest in the country, most of which lies on the Kathiawar peninsula. Gujarat is the fifth-largest Indian state by area, covering some ; and the nin ...
(
India
India, officially the Republic of India ( Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the ...
). The most numerous artefacts are square and rectangular
stamp seals and seal impressions, featuring animals, usually bulls, very short
Harappan texts. Many stylized terracotta figurines have also been found in Harappan sites, and a few stone and bronze sculptures, more naturalistic than the ceramic ones.
IndusValleySeals.JPG, Seals with Indus script and impressions; 2500-2000 BC; steatite; various sizes, mostly 3 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Dancing girl of Mohenjo-daro.jpg, ''Dancing Girl
Dance is a performing art form consisting of sequences of movement, either improvised or purposefully selected. This movement has aesthetic and often symbolic value. Dance can be categorized and described by its choreography, by its repertoire ...
''; 2400–1900 BC; bronze; height: 10.8 cm; National Museum (New Delhi
New Delhi (, , ''Naī Dillī'') is the Capital city, capital of India and a part of the NCT Delhi, National Capital Territory of Delhi (NCT). New Delhi is the seat of all three branches of the government of India, hosting the Rashtrapati B ...
, India)
Shiva Pashupati.jpg, Proto-Shiva Stamp Seal; 2400-1900 BC; steatite; height: 3.6 cm; National Museum (New Delhi)
Mohenjo-daro Priesterkönig.jpeg, '' Priest-King''; 2400–1900 BC; steatite; height: 17.5 cm; National Museum of Pakistan (Karachi
Karachi (; ur, ; ; ) is the most populous city in Pakistan and 12th most populous city in the world, with a population of over 20 million. It is situated at the southern tip of the country along the Arabian Sea coast. It is the former ...
)
Clevelandart 1973.160.jpg, Seal with two-horned bull and inscription; 2010 BC; steatite; overall: 3.2 × 3.2 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, located in the Wade Park District, in the University Circle neighborhood on the city's east side. Internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian and Egypt ...
(Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, US)
China

Th first metal objects produced in China were made almost 4000 years ago, during the
Xia dynasty
The Xia dynasty () is the first dynasty in traditional Chinese historiography. According to tradition, the Xia dynasty was established by the legendary Yu the Great, after Shun, the last of the Five Emperors, gave the throne to him. In tradi ...
(2100–1700 BC). During the
Chinese Bronze Age (the
Shang
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally succeeding the Xia dynasty and f ...
and
Zhou dynasties) court intercessions and communication with the spirit world were conducted by a shaman (possibly the king himself). In the
Shang dynasty
The Shang dynasty (), also known as the Yin dynasty (), was a Dynasties in Chinese history, Chinese royal dynasty founded by Tang of Shang (Cheng Tang) that ruled in the Yellow River valley in the second millennium BC, traditionally suc ...
(1600–1050 BC), the supreme deity was
Shangdi, but aristocratic families preferred to contact the spirits of their ancestors. They prepared elaborate banquets of food and drink for them, heated and served in
bronze ritual vessels. These bronze vessels had many shapes, depending on their purpose: for wine, water, cereals or meat, and some of them were marked with readable characters, which shows the development of writing. This kind of vessels, of a very high quality and complexity, were discovered on the Valley of the
Yellow River
The Yellow River or Huang He (Chinese: , Mandarin: ''Huáng hé'' ) is the second-longest river in China, after the Yangtze River, and the sixth-longest river system in the world at the estimated length of . Originating in the Bayan ...
in the
Henan
Henan (; or ; ; alternatively Honan) is a landlocked province of China, in the central part of the country. Henan is often referred to as Zhongyuan or Zhongzhou (), which literally means "central plain" or "midland", although the name is al ...
province, in sites like
Erlitou,
Anyang or
Zhengzhou
Zhengzhou (; ), also spelt Zheng Zhou and alternatively romanized as Chengchow, is the capital and largest city of Henan Province in the central part of the People's Republic of China. Located in north-central Henan, it is one of the Nationa ...
. They were used in religious rituals to cement the Dhang authority, and when the Shang capital fell, around 1050 BC, its conquerors, the Zhou (1050–156 BC), continued to use these containers in religious rituals, but principally for food rather than drink. The Shang court had been accused of excessive drunkenness, and the Zhou, promoting the imperial
Tian ("Heaven") as the prime spiritual force, rather than ancestors, limited wine in religious rites, in favour of food. The use of ritual bronzes continued into the early
Han dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(206 BC–220 AD).
One of the most commonly used motifs was the ''
taotie'', a stylized face divided centrally into two almost mirror-image halves, with nostrils, eyes, eyebrows, jaws, cheeks and horns, surrounded by incised patterns. Whether ''taotie'' represented real, mythological or wholly imaginary creatures cannot be determined.
The enigmatic bronzes of
Sanxingdui, near
Guanghan (in
Sichuan province), are evidence for a mysterious sacrificial religious system unlike anything elsewhere in
ancient China and quite different from the art of the contemporaneous Shang at
Anyang. Excavations at Sanxingdui since 1986 have revealed four pits containing artefacts of
bronze,
jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
and
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
. There was found a great bronze statue of a human figure which stands on a plinth decorated with abstract elephant heads. Besides the standing figure, the first two pits contained over 50 bronze heads, some wearing headgear and three with a frontal covering of
gold leaf. Tubular bronze fragments with little branches were discovered here as well, probably representing trees, and also bronze leaves, fruits and birds. Over 4000 objects were found at Sanxingdui in 1986.
Succeeding the Shang Dynasty
Zhou (1050–221 BC) ruled more than any other one from Chinese history. Its last centuries were characterized by violence, the era being known as the
Warring States period
The Warring States period () was an era in ancient Chinese history characterized by warfare, as well as bureaucratic and military reforms and consolidation. It followed the Spring and Autumn period and concluded with the Qin wars of conquest ...
. During this troubling time, some philosophical movements appeared:
Confucianism
Confucianism, also known as Ruism or Ru classicism, is a system of thought and behavior originating in ancient China. Variously described as tradition, a philosophy, a religion, a humanistic or rationalistic religion, a way of governing, or ...
,
Daoism and
Legalism.
The Warring States period was ended by
Qinshi Huangdi, who united China in 221 BC. He ordered a huge tomb, guarded by the
Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting the emperor i ...
. Another huge project was a predecessor of the
Great Wall, erected for rejecting pillaging tribes from the north. After the death of the emperor, his dynasty, the
Qin (221–206 BC), lasted only three years. Qinshi Huangdi was followed by the
Han Dynasty
The Han dynasty (, ; ) was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China (202 BC – 9 AD, 25–220 AD), established by Emperor Gaozu of Han, Liu Bang (Emperor Gao) and ruled by the House of Liu. The dynasty was preceded by th ...
(202 BC-220 AD), during which the
Silk Road developed considerably, bringing new cultural influences in China.
Liu Ding.jpg, Ding; ; bronze; height: 22.9 cm; Shanghai Museum (Shanghai
Shanghai (; , , Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is one of the four direct-administered municipalities of the People's Republic of China (PRC). The city is located on the southern estuary of the Yangtze River, with the Huangpu River flowin ...
, China)
Bronze Standing Figure.jpg, Lifesize figure; ; bronze; height: 2.62 m; Sanxingdui Museum ( Guanghan, Sichuan
Sichuan (; zh, c=, labels=no, ; zh, p=Sìchuān; alternatively romanized as Szechuan or Szechwan; formerly also referred to as "West China" or "Western China" by Protestant missions) is a province in Southwest China occupying most of th ...
, China)
File:Middle Western Zhou Bronze "Yi" Fangyi.jpg, Fang Lei; ; bronze; height: 22.8 cm; National Museum of China (Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the capital of the People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's most populous national capital city, with over 21 ...
, China)
Mawangdui silk banner from tomb no1.jpg, Funerary banner; 180 BC; silk; 205 x 92 cm (upper part); Hunan Museum
The Hunan Museum () is the provincial museum of Hunan, China. It was built in 1951 and opened to the public in July 1956. It is located in the provincial capital Changsha at No. 50, Dongfeng Lu next to the Revolutionary Martyr's Park.
It spans ...
(Changsha
Changsha (; ; ; Changshanese pronunciation: (), Standard Mandarin pronunciation: ) is the capital and the largest city of Hunan Province of China. Changsha is the 17th most populous city in China with a population of over 10 million, and th ...
, Hunan
Hunan (, ; ) is a landlocked province of the People's Republic of China, part of the South Central China region. Located in the middle reaches of the Yangtze watershed, it borders the province-level divisions of Hubei to the north, Jiangxi ...
, China)jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
; 18 x 14 cm; Museum of the Mausoleum of the Nanyue King (Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong ...
, Guangdong
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020 ...
, China)
Greek
Through harmonious proportion and a focus on aesthetics, ancient Greek and Roman art became the foundation and inspiration of all Western art, being the standard to which most European artists aspired, until the 19th century. The Latin poet
Horace, writing in the age of
Roman emperor
Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
(1st century BC to 1st century AD), famously remarked that although conquered on the battlefield, "captive Greece overcame its savage conqueror and brought the arts to rustic Rome." The power of Greek art lies in its representation of the human figure and its focus on human beings and the anthropomorphic gods as chief subjects. The artworks of the Greeks were meant to decorate temples and public buildings, to celebrate battle victories and remarkable personalities, and to commemorate the dead. They were also given as offerings to the gods.
Although there was no definitive transition, the art is usually divided stylistically into the four periods of Geometric, Archaic, Classical and Hellenistic. During the
Classical period (5th and 4th centuries BC), realism and idealism were delicately balanced. In comparison, the works of the earlier Geometric (9th to 8th centuries BC) and Archaic (7th to 6th centuries BC) ages can seem appear primitive, but these artists had different goals: naturalistic representation was not necessarily their aim.
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
and artists built on the artistic foundations of Egypt, further developing the arts of sculpture, painting, architecture, and ceramics. Among the techniques they perfected include methods of carving and casting sculptures, fresco painting and building magnificent buildings.
Roman art lovers collected ancient Greek originals, Roman replicas of Greek art, or newly created paintings and sculptures fashioned in a variety of Greek styles, thus preserving for posterity works of art otherwise lost. Wall and panel paintings, sculptures and mosaics decorated public spaces and private homes. Greek imagery also appeared on Roman jewellery, vessels of gold, silver, bronze and terracotta, and even on weapons and commercial weights. Rediscovered during the early
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
, the arts of ancient Greece, transmitted through the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
, have served as the foundation of Western art until the 19th century.
Since the advent of the
Classical Age in
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
, in the 5th century BC, the Classical way of building has been deeply woven into Western understanding of architecture and, indeed, of civilization itself. From circa circa 850 BC to circa 300 AD,
ancient Greek culture flourished on the
Greek mainland, on the
Peloponnese
The Peloponnese (), Peloponnesus (; el, Πελοπόννησος, Pelopónnēsos,(), or Morea is a peninsula and geographic region in southern Greece. It is connected to the central part of the country by the Isthmus of Corinth land bridge whi ...
, and on the
Aegean islands. Five of the
Wonders of the World
Various lists of the Wonders of the World have been compiled from antiquity to the present day, in order to catalogue the world's most spectacular natural features and human-built structures.
The Seven Wonders of the Ancient World is the o ...
were Greek: the
Temple of Artemis
The Temple of Artemis or Artemision ( gr, Ἀρτεμίσιον; tr, Artemis Tapınağı), also known as the Temple of Diana, was a Greek temple dedicated to an ancient, local form of the goddess Artemis (identified with Diana
Diana most ...
at
Ephesus
Ephesus (; grc-gre, Ἔφεσος, Éphesos; tr, Efes; may ultimately derive from hit, 𒀀𒉺𒊭, Apaša) was a city in ancient Greece on the coast of Ionia, southwest of present-day Selçuk in İzmir Province, Turkey. It was built i ...
, the
Statue of Zeus at Olympia, the
Mausoleum at Halicarnassus, the
Colossus of Rhodes, and the
Lighthouse of Alexandria. However, Ancient Greek architecture is best known for
its temples, many of which are found throughout the region, and the
Parthenon
The Parthenon (; grc, Παρθενών, , ; ell, Παρθενώνας, , ) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are conside ...
is a prime example of this. Later, they will serve as inspiration for
Neoclassical architects during the late 18th and the 19th century. The most well-known temples are the
Parthenon
The Parthenon (; grc, Παρθενών, , ; ell, Παρθενώνας, , ) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are conside ...
and the
Erechtheion, both on the
Acropolis of Athens
The Acropolis of Athens is an ancient citadel located on a rocky outcrop above the city of Athens and contains the remains of several ancient buildings of great architectural and historical significance, the most famous being the Parthenon. ...
. Another type of important Ancient Greek buildings were the theatres. Both temples and theatres used a complex mix of optical illusions and balanced ratios.
Looking at the archaeological remains of ancient buildings it is easy to perceive them as limestone and concrete in a grey taupe tone and to make the assumption that ancient buildings were monochromatic. However, architecture was
polychromed in much of the Ancient world. One of the most iconic Ancient buildings, the
Parthenon
The Parthenon (; grc, Παρθενών, , ; ell, Παρθενώνας, , ) is a former temple on the Athenian Acropolis, Greece, that was dedicated to the goddess Athena during the fifth century BC. Its decorative sculptures are conside ...
( 447–432 BC) in
Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
, had details painted with vibrant reds, blues and greens. Besides ancient temples, Medieval cathedrals were never completely white. Most had colored highlights on
capitals
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used f ...
and
columns. This practice of coloring buildings and artworks was abandoned during the early Renaissance. This is because
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
and other Renaissance artists, including
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was in ...
, promoted a color palette inspired by the ancient Greco-Roman ruins, which because of neglect and constant decay during the Middle Ages, became white despite being initially colorful. The pigments used in the ancient world were delicate and especially susceptible to weathering. Without necessary care, the colors exposed to rain, snow, dirt, and other factors, vanished over time, and this way Ancient buildings and artworks became white, like they are today and were during the Renaissance.
Bronze horse MET DT11722.jpg, Horse figurine ( Geometric); ; bronze; height: 17.6 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Terracotta krater MET DT258.jpg, Pedestalled krater (Geometric); ; terracotta; height: 108.3 cm, diameter: 72.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Marble statue of a kouros (youth) MET DT263.jpg, New York Kouros (Archaic
Archaic is a period of time preceding a designated classical period, or something from an older period of time that is also not found or used currently:
*List of archaeological periods
**Archaic Sumerian language, spoken between 31st - 26th cent ...
); ; marble and pigment; height: 1.95 m; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Terracotta Panathenaic prize amphora MET DT5492.jpg, Panathenaic amphora (Archaic); ; ceramic; height: 62.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Red-figure cup showing the death of Pentheus and a Maenad by Douris, Kimbell Art Museum (bottom).jpg, Red-figure kylix ( Classical); ; ceramic; height: 12.7 cm, diameter: 27.2 cm; Kimbell Art Museum ( Fort Worth, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, USA)
Bronze statue of Zeus or Poseidon from Artemision, Euboea. ca. 460 BC.jpg, Zeus of Artemision (Classical); ; bronze; height: 209 cm; National Archaeological Museum (Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital city, capital and List of cities and towns in Greece, largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh List ...
, Greece)
Segesta AncientGreekTemple 0932.jpg, Temple of Segesta ( Calatafimi-Segesta, present-day Italy), 5th century BC
File:Erechtheum Acropolis Athens.jpg, Erechtheion (Athens), with its Ionic columns and caryatid porch, 421-405 BC
Terracotta vase MET DT1069 (cropped).jpg, Centuripe vase (Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium i ...
); 300-100 BC; ceramic; height: 9.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Rome
No civilization has had an impact as enduring and powerful on Western art as the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
. The legacy of ancient Rome is evident through the
medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and
early modern periods, and Roman art continue to be reused in the modern era in both traditionalist and
Postmodern
Postmodernism is an intellectual stance or mode of discourseNuyen, A.T., 1992. The Role of Rhetorical Devices in Postmodernist Discourse. Philosophy & Rhetoric, pp.183–194. characterized by skepticism toward the " grand narratives" of modern ...
artworks. Sometimes it is viewed as derived from Greek precedents, but also has its own distinguishing features, some of them inherited from
Etruscan art. Roman sculpture is often less idealized than its Greek precedents, being very realistic. Roman architecture often used
concrete
Concrete is a composite material composed of fine and coarse aggregate bonded together with a fluid cement (cement paste) that hardens (cures) over time. Concrete is the second-most-used substance in the world after water, and is the most ...
, and features such as the round
arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vau ...
and
dome were invented. Luxury objects in
metal-work
Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale ...
,
gem engraving
An engraved gem, frequently referred to as an intaglio, is a small and usually semi-precious gemstone that has been carved, in the Western tradition normally with images or inscriptions only on one face. The engraving of gemstones was a major lu ...
,
ivory carvings, and
glass
Glass is a non-Crystallinity, crystalline, often transparency and translucency, transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most ...
are sometimes considered in modern terms to be minor forms of Roman art, although this would not necessarily have been the case for contemporaries. An innovation made possible by the Roman development of glass-blowing was
cameo glass. A white 'shell' was first created, into which coloured glass was then blown so as to produce an interior lining. The white shell was then cut down to create relief patterns of white against a darker background. They also made
mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
s, this way producing durable pictorial art with cut-stone cubes (''tesserae'') and/or chips of coloured terracotta and glass. Some villas of wealthy Romans had their walls covered with
frescos, aimed at dazziling and entertaining guests. Much of Roman wall painting that survives comes from sites around the Bay of
Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adminis ...
, in particular
Pompeii and
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the ...
, thriving towns that were preserved under metres of volcanic debris when Mount
Vesuvius erupted in 79 AD. As a result, Roman wall painting is often discussed in terms of four 'Pompeian styles'.
The Romans were deeply influenced by all aspects of
Hellenistic culture. In architecture, just like in other
art media
Arts media is the material and tools used by an artist, composer or designer to create a work of art, for example, "pen and ink" where the pen is the tool and the ink is the material. Here is a list of types of art and the media used within tho ...
, they essentially adopted the Classical language and adapted it to new situations and uses. The Romans also have their own innovations brought to Classical architecture. They used the
Doric,
Ionic and
Corinthian orders
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of ...
in a far freer manner than the Greeks had, creating their own version of the Doric and using the Corinthian far more frequently. They also added two new orders to the repertoire: the
Tuscan, a simpler, more massive version of the Doric derived from
Etruscan architecture; and the
Composite, a combination of the scroll-like
volute
A volute is a spiral, scroll-like ornament that forms the basis of the Ionic order, found in the capital of the Ionic column. It was later incorporated into Corinthian order and Composite column capitals. Four are normally to be found on an ...
s of the Ionic with the Corinthian's
acanthus leaves. Other important innovations include the
arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vau ...
, and the
dome. Using arches, they built
aqueducts and monumental
triumphal arches. Roman emperors were proud of their conquests, and commemorated them at home and in the conquered territories through triumphal arches, a good example of this being the
Arch of Constantine
The Arch of Constantine ( it, Arco di Costantino) is a triumphal arch in Rome dedicated to the emperor Constantine the Great. The arch was commissioned by the Roman Senate to commemorate Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of Milvi ...
in Rome. Between 30 and 15 BC, the architect and civil and military engineer
Marcus Vitruvius Pollio published a majore treatise, ''
De Architectura'', which influenced architects around the world for centuries.
After the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, with the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
that started in
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
(
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
), a growing interest for ancient Rome started. During it, for the first time since
Classical Antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations ...
, art became convincingly lifelike. The Renaissance also sparked interest for ancient Greek and Roman literature, not just for art and architecture.
File:Roman fresco Villa dei Misteri Pompeii 005.jpg, Mysteries Fresco; mid-1st century BC; fresco; height: 1.62 m; Villa of the Mysteries
The Villa of the Mysteries ( it, Villa dei Misteri) is a well-preserved suburban ancient Roman villa on the outskirts of Pompeii, southern Italy. It is famous for the series of exquisite frescos in Room 5, which are usually interpreted as show ...
( Pompeii, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
)
Portland Vase BM Gem4036 n5.jpg, Portland Vase; late 1st century BC; glass; height: 24 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
)
Maison Carree in Nimes (16).jpg, The Maison Carrée ( Nîmes, France), one of the best-preserved Roman temples,
Marine mosaic (central panel of three panels from a floor) - Google Art Project.jpg, Marine mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
(central panel of three panels from a floor); 200–230; mosaic (stone and glass tesserae); 2,915 mm x 2,870 mm; Museum of Fine Arts (Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, US)
500px photo (217110515).jpeg, Arch of Constantine
The Arch of Constantine ( it, Arco di Costantino) is a triumphal arch in Rome dedicated to the emperor Constantine the Great. The arch was commissioned by the Roman Senate to commemorate Constantine's victory over Maxentius at the Battle of Milvi ...
(Rome), that commemorates the triumph of Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to convert to Christianity. Born in Naissus, Dacia Mediterran ...
after his victory over Maxentius in the Battle of the Milvian Bridge, 316
Islamic
Islamic art is well-known since the Middle Ages for the use of elaborate
geometric patterns
A pattern is a regularity in the world, in human-made design, or in abstract ideas. As such, the elements of a pattern repeat in a predictable manner. A geometric pattern is a kind of pattern formed of geometric shapes and typically repeated li ...
, colourful tiles, stylized natural motifs and detailed calligraphy. Rarely has lettering had such a profound impact on applied arts and architecture. Islam appeared in western
Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
in the 7th century AD through revelations delivered to the prophet
Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monot ...
in
Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow val ...
. Within a century of Muhammad's death the Islamic empires controlled the
Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europ ...
, Spain and parts of Asia and Africa. Because of this, similarly with
Roman art, Islamic art and architecture had regional versions. As the Islamic world extended into centres of late antique culture, it was enriched by philosophical and intellectual movements. The translation of Greek works into Arabic and advances in mathematics and science were encouraged by early caliphates. This is in contrast with the modern perception that Islamic art is dogmatic and unchanging. Human and animal representation wasn't rare. Only certain periods restricted it (similar with the Byzantine
Iconoclasm).
Pyxis MET DT4840.jpg, Perfume box; 950–975; ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
; height: 11.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Mezquita de Cordoba Mihrab.jpg, Mihrab; 961–976; stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
and glass mosaic; diameter (internal arch): ; Mosque–Cathedral of Córdoba (Córdoba Córdoba most commonly refers to:
* Córdoba, Spain, a major city in southern Spain and formerly the imperial capital of Islamic Spain
* Córdoba, Argentina, 2nd largest city in the country and capital of Córdoba Province
Córdoba or Cordoba may ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
)
Mosque Lamp for the Mausoleum of Amir Aydakin al-'Ala'i al-Bunduqdar MET 17.190.985.jpg, Mosque lamp; ; glass, enamels and gold; height: 26.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Alhambra Löwenhof mit Löwenbrunnen 2014.jpg, Court of the Lions ( Alhambra, Granada
Granada (,, DIN: ; grc, Ἐλιβύργη, Elibýrgē; la, Illiberis or . ) is the capital city of the province of Granada, in the autonomous community of Andalusia, Spain. Granada is located at the foot of the Sierra Nevada mountains, at the c ...
, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
), 1362-1391
Ardabil Carpet.jpg, Ardabil Carpet; 1539–1540; wool pile on silk; length: 10.51 m; Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and ...
(London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
)
Americas
Mesoamerica
Some of the first great civilizations in the Americas developed in
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
(meaning 'middle Americas'), the most well known being the
Mayans and the
Aztecs.
The
Olmecs
The Olmecs () were the earliest known major Mesoamerican civilization. Following a progressive development in Soconusco, they occupied the tropical lowlands of the modern-day Mexican states of Veracruz and Tabasco. It has been speculated tha ...
(1400–400 BC) were the first major civilization in modern-day Mexico. Many elements of Mesoamerican civilizations, like the practice of building of pyramids, the complex calendar, the pantheon of gods and hieroglyphic writing have origins in Olmec culture. They produced jade and ceramic figurines,
colossal heads and pyramids with temples at the top, all without the advantage of metal tools. For them, jadeite was a stone more precious than gold and symbolized divine powers and fertility. 17
Olmec colossal heads have been discovered, each weighing a few tons. Each head, with the flattened nose and thick lips, wears a helmet, similar with the ones worn during official ball games, possibly representing kings of officials.
The
Maya civilization
The Maya civilization () of the Mesoamerican people is known by its ancient temples and glyphs. Its Maya script is the most sophisticated and highly developed writing system in the pre-Columbian Americas. It is also noted for its art, ar ...
began around 1800 BC and grew until the arrival of Spanish colonizers in the 1500s. They occupied southeast Mexico,
Guatemala,
Belize
Belize (; bzj, Bileez) is a Caribbean and Central American country on the northeastern coast of Central America. It is bordered by Mexico to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and Guatemala to the west and south. It also shares a wa ...
, and parts of
Honduras and
El Salvador
El Salvador (; , meaning " The Saviour"), officially the Republic of El Salvador ( es, República de El Salvador), is a country in Central America. It is bordered on the northeast by Honduras, on the northwest by Guatemala, and on the south by ...
. The Mayans were trading with cities, like
Teotihuacán
Teotihuacan ( Spanish: ''Teotihuacán'') (; ) is an ancient Mesoamerican city located in a sub-valley of the Valley of Mexico, which is located in the State of Mexico, northeast of modern-day Mexico City. Teotihuacan is known today as ...
, but also with many Mesoamerican civilizations, like the
Zapotecs or the other groups from central or coast areas of Mexico, and also with populations that didn't inhabit Mesoamerican territories, like the
Taíno from the
Caribbean. They produced impressive king portraits,
polychrome ceramic vessels, earthenware figures, wooden sculptures,
stelas, and built complex cities with pyramids. Most of the well preserved polychrome ceramic vessels were discovered in the tombs of nobles.
Arising from humble beginnings as a nomadic group, the Aztecs created the largest empire in Mesoamerican history, lasting from 1427 to 1521. They didn't call themselves 'Aztecs', but Mexica. The term Aztecs was assigned by historians. They transformed the capital of their empire,
Tenochtitlan, into a place where artists of Mesoamerica created impressive artworks for their new masters. The present-day
Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
was built over the Aztec capital, Tenochtitlan.
Cabeza Colosal 8.jpg, Colossal head; 1050 BC; steatite; height: 2.2 m; Museo de Antropología de Xalapa ( Xalapa, Mexico
Mexico ( Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a country in the southern portion of North America. It is bordered to the north by the United States; to the south and west by the Pacific Ocean; to the southeast by Guate ...
)
Seated ruler in ritual pose, Highland Olmec culture, San Martin Texmelucan, Puebla state, Middle Formative period, c. 900-500 BC, serpentine, cinnabar - Dallas Museum of Art - DSC04572.jpg, Seated shaman in ritual pose-shaped pendant ( Olmec); 9th-5th century BC; serpentine
Serpentine may refer to:
Shapes
* Serpentine shape, a shape resembling a serpent
* Serpentine curve, a mathematical curve
* Serpentine, a type of riding figure
Science and nature
* Serpentine subgroup, a group of minerals
* Serpentinite, a ...
and cinnabar
Cinnabar (), or cinnabarite (), from the grc, κιννάβαρι (), is the bright scarlet to brick-red form of mercury(II) sulfide (HgS). It is the most common source ore for refining elemental mercury and is the historic source for the bri ...
; height: 18.5 cm; Dallas Museum of Art (Dallas
Dallas () is the List of municipalities in Texas, third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of metropolitan statistical areas, fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, USA)
Mascara Dios Murcielago.jpg, Bat effigy ( Zapotec); 50 BC; jadeite and shell; height: 28 cm; National Museum of Anthropology
The National Museum of Anthropology ( es, Museo Nacional de Antropología, MNA) is a national museum of Mexico. It is the largest and most visited museum in Mexico. Located in the area between Paseo de la Reforma and Mahatma Gandhi Street wit ...
(Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
)
K'inich Janaab Pakal I v2.jpg, Portrait of K'inich Janaab Pakal I (Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a popu ...
; 615–683; stucco
Stucco or render is a construction material made of aggregates, a binder, and water. Stucco is applied wet and hardens to a very dense solid. It is used as a decorative coating for walls and ceilings, exterior walls, and as a sculptural and a ...
; height 43 cm; National Museum of Anthropology
Vessel, Throne Scene MET DT4514.jpg, Vessel with a throne scene (Maya); late 7th–8th century; ceramic; 21.59 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Yaxchilan Lintel 24.jpg, Yaxchilán Lintel
A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. In the case o ...
24 (Maya); 702; limestone; 109 x 74 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Telamones Tula.jpg, Warrior columns ( Toltec); 1000; basalt; height: 460 cm; Tula de Allende (Mexico)
Double headed turquoise serpentAztecbritish museum.jpg, Double-headed serpent (Aztecs#Art and cultural production, Aztec); 1450–1521; cedar, turquoise, shell and traces of gilding; length: 43.3 cm; British Museum
File:Mexico-3980 - Coyolxauhqui Stone (2508259597).jpg, Coyolxauhqui Stone (Aztec); 1469–1481; stone; diameter: 3 m; Templo Mayor Museum (Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital and largest city of Mexico, and the most populous city in North America. One of the world's alpha cities, it is located in the Valley of ...
)
Tlaloc Vasija.jpg, Tlāloc effigy vessel (Aztec); 1440–1469; painted earthenware; height: 35 cm; Templo Mayor Museum
Colombia
Similarly with Mesoamerica, the present-day territory of Colombia is an area where multiple cultures developed before the arrival of Spanish colonizers. Here, gold body accessories were produced, many golden ones, but also many other ones made of tumbaga, a non-specific alloy of
gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
and copper given by Spanish Conquistadors to metals composed of these elements found in widespread use in pre-Columbian
Mesoamerica
Mesoamerica is a historical region and cultural area in southern North America and most of Central America. It extends from approximately central Mexico through Belize, Guatemala, El Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, and northern Costa Rica. W ...
in North America and South America.
Calima Animal-Headed Figure Pendant MET DT11629 (cropped).jpg, Animal-headed figure pendant (Calima culture#Yotoco culture, Yotoco); 1st–7th century; gold; height: 6.35 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Lime Container (Poporo) MET DT1262.jpg, Lime container (Quimbaya civilization, Quimbaya); 5th–9th century; gold; height: 23 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Male Figure (tunjo) MET DP215691.jpg, Male figure/''tunjo'' (Muisca art, Muisca); 10th–mid-16th century; gold; height: 14.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Figure Pendant MET DT4860.jpg, Pendant (Tairona); 10th–16th century; gold; height: 14 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Andean regions

The ancient civilizations of Peru and Bolivia nurtured unique artistic traditions, including one of the world's most aesthetically impressive fibre art traditions. Two of the first important cultures from this land are the Chavín culture, Chavín and the Paracas culture.
The Paracas culture of the south coast of Peru is best known for its complex patterned textiles, particularly mantels. The Moche culture, Moche controlled the river valleys of the north coast, while the Nazca culture, Nazca of southern Peru held sway along the coastal deserts and contiguous mountains. The Nazca are best known for the famous Nazca Lines, a group of geoglyphs in a desert in southern Peru. They also produced polychrome ceramics and textiles influenced by the Paracas, and used a palette of at least 10 colours for their pottery. Both cultures flourished around 100–800 AD. Moche pottery is some of the most varied in the world. In the north, the Huari culture, Wari (or Huari) Empire are noted for their stone architecture and sculpture accomplishments.
The Chimú were preceded by a simple ceramic style known as Sican culture#Early Sican, Sicán (700–900 AD). The Chimú produced excellent portrait and decorative works in metal, notably gold but especially silver. Later, the Inca Empire (1100–1533) stretched across the Andes Mountains. They crafted precious metal figurines, and like other civilizations from the same area, complex textiles. Llamas were important animals, because of their wool and for carrying loads.
Líneas de Nazca, Nazca, Perú, 2015-07-29, DD 52.JPG, The Hummingbird, one of the Nazca Lines (Nazca culture, Nazca); 200 BC-600 AD; rocks, gravel and dirt; length: 50 m; Nasca Province, Nasca and Palpa Province, Palpa Provinces (Peru)
Portrait Head Bottle MET 82.1.28.jpeg, Moche portrait vessel, Portrait head bottle (Moche culture, Moche); 3rd–6th century; painted ceramic; overall: 26.35 x 16.21 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Peru Huari Standing Dignitary 1 Kimbell.jpg, Mosaic figurine of a noble man (Wari culture, Wari); 7th-9th century; wood, shell, stone and silver; height: 10.2 cm; Kimbell Art Museum ( Fort Worth, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, USA)
Ceremonial Knife (Tumi) MET DP215693.jpg, Ceremonial knife/''tumi'' (Sican culture, Sican); 10th–13th century; gold, turquoise, greenstone and shell; height: 33 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Tupa-inca-tunic.png, Royal tunic (Inca Empire, Inca); 1476–1534; camelid fibre and cotton; height: 91 cm; Dumbarton Oaks (Washington, D.C., USA)
Asian
Eastern world, Eastern civilization broadly includes Asia, and it also includes a complex tradition of art making. One approach to Eastern art history divides the field by nation, with foci on Indian art, Chinese art, and Japanese art. Due to the size of the continent, the distinction between Eastern Asia and Southern Asia in the context of arts can be clearly seen. In most of Asia, pottery was a prevalent form of art. The pottery is often decorated with geometric patterns or abstract representations of animals, people or plants. Other very widespread forms of art were, and are, sculpture and painting.
Central Asia
Central Asian art developed in
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the former ...
, in areas corresponding to modern Kyrgyzstan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Turkmenistan, Azerbaijan, Tajikistan,
Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bord ...
,
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
, and parts of modern Mongolia, China and Russia.
The art of ancient and medieval Central Asia reflects the rich history of this vast area, home to a huge variety of peoples, religions and ways of life. The artistic remains of the region show a remarkable combinations of influences that exemplify the multicultural nature of Central Asian society. The Silk Road transmission of art, Scythian art, Greco-Buddhist art, Serindian art and more recently Persianate culture, are all part of this complicated history. Central Asia has always been a crossroads of cultural exchange, the hub of the so-called
Silk Road – that complex system of trade routes stretching from China to the Mediterranean. Already in the Bronze Age (3rd and 2nd millennium BC), growing settlements formed part of an extensive network of trade linking Central Asia to the Indus Valley, Mesopotamia and Egypt.
Seated female MET DT867.jpg, Seated figurine (Bactria–Margiana Archaeological Complex, Bactrian); 3rd-2nd millennia BC; chlorite and limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms wh ...
; height: 9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Belt buckle with paired felines attacking ibexes MET DT5088.jpg, Belt buckle; 3rd-1st centuries BC; gold; height: 7.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Bagram Guimet 12.JPG, Goblet showing The Rape of Europa (consort of Zeus), Europa and of Ganymede (mythology), Ganymede, part of the Bagram Treasure; 1st century AD; painted glass; height: 16 cm, diameter: 10 cm; Guimet Museum (Paris)
God and Female Musician, Kizil, Cave 171, 417-435 AD, wall painting - Ethnological Museum, Berlin - DSC01720.JPG, Goddess and celestial musician (Buddhist art, Buddhist); 7th century; pigments on plaster; height: 2.03 m; Museum of Asian Art (Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany)
Samarcanda, Gur-e Amir 19.jpg, Gur-e-Amir, Gur-i Amir Mausoleum (Samarkand, Uzbekistan), 15th century
Indian
Early Buddhists in India developed symbols related to Buddha. The major survivals of Buddhist art begin in the period after the Mauryan Empire, Mauryans, within North India Kushan Empire, Kushan art, the Greco-Buddhist art of Gandhara and finally the "classic" period of Gupta art. Additionally, there was the Andhra school which appeared before the Gandhara school and which was based in South India. Good quantities of sculpture survives from some key sites such as Sanchi, Bharhut and Amaravati Stupa, Amaravati, some of which remain ''in situ'', with others in museums in India or around the world. Stupas were surrounded by ceremonial fences with four profusely carved toranas or ornamental gateways facing the cardinal directions. These are in stone, though clearly adopting forms developed in wood. They and the walls of the stupa itself can be heavily decorated with reliefs, mostly illustrating the lives of the Buddha. Gradually life-size figures were sculpted, initially in deep relief, but then free-standing. Mathura art was the most important centre in this development, which applied to Hindu and Jain art as well as Buddhist. The facades and interiors of rock-cut ''chaitya'' prayer halls and monastic ''viharas'' have survived better than similar free-standing structures elsewhere, which were for long mostly in wood. The caves at Ajanta Caves, Ajanta, Karla Caves, Karle, Bhaja Caves, Bhaja and elsewhere contain early sculpture, often outnumbered by later works such as iconic figures of the Buddha and bodhisattvas, which are not found before 100 AD at the least.
Sanchi1 N-MP-220.jpg, The Great Stupa of Sanchi (Madhya Pradesh, India), 3rd century- 100 BC
Sarnath_capital.jpg, Lion Capital of Ashoka; 250 BC; polished sandstone; height: 2.2 m; Sarnath Museum (India)
Buddha in Sarnath Museum (Dhammajak Mutra).jpg, Buddha Preaching his First Sermon (Sarnath), Seated Buddha; 475; sandstone; height: 1.6 m; Sarnath Museum
022 Cave 1, Padmapani (33896247830).jpg, ''Bodhisattva Padmapani''; 450–490; pigments on rock; height: 1.2 m; Ajanta Caves (India)
Shiva Nataraja Musée Guimet 25971.jpg, Shiva as lord of the dance; 11th century; bronze; height: 96 cm; Musée Guimet (Paris)
Beauty of khajuraho temple.jpg, Kandariya Mahadeva Temple (Khajuraho, India), 1030
MET DT238.jpg, Durga killing the buffalo demon; 1150; argilite; height: 13.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
MET DP22193.jpg, Ganesha; 14th-15th century; ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
; height: 18.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Basawan. Akbar Taming Mad Elephant Hawai. Composition by Basawan, coloring by Chitra. (left part) Akbarnama, ca. 1590, Victoria and Albert Museum, London.jpg, Basawan Akbarnama; 1590; watercolor on paper; 33 x 20 cm; Victoria and Albert Museum
The Victoria and Albert Museum (often abbreviated as the V&A) in London is the world's largest museum of applied arts, decorative arts and design, housing a permanent collection of over 2.27 million objects. It was founded in 1852 and ...
(London)
Taj Mahal, Agra, India.jpg, Taj Mahal (Agra, India), an iconic example of Mughal architecture, 1632-1648
Chinese
In Eastern Asia, painting was derived from the practice of calligraphy, and portraits and landscapes were painted on silk cloth. Most of the paintings represent landscapes or portraits. The most spectacular sculptures are the Chinese ritual bronzes, ritual bronzes and the bronze sculptures from
Sanxingdui. A very well-known example of Chinese art is the ''
Terracotta Army
The Terracotta Army is a collection of terracotta sculptures depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BCE with the purpose of protecting the emperor i ...
'', depicting the armies of Qin Shi Huang, the first Emperor of China. It is a form of funerary art buried with the emperor in 210–209 BC whose purpose was to protect the emperor in his afterlife.
Chinese art is one of the oldest continuous traditional arts in the world, and is marked by an unusual degree of continuity within, and consciousness of, that tradition, lacking an equivalent to the Western collapse and gradual recovery of classical styles. The media that have usually been classified in the West since the
Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass id ...
as the decorative arts are extremely important in Chinese art, and much of the finest work was produced in large workshops or factories by essentially unknown artists, especially in Chinese ceramics. The range and quality of goods that decorated Chinese palaces and households, and their inhabitants, is dazzling. Materials came from across China and far beyond: gold and silver, mother of pearl, ivory and rhinoceros horn, wood and lacquer,
jade
Jade is a mineral used as jewellery or for ornaments. It is typically green, although may be yellow or white. Jade can refer to either of two different silicate minerals: nephrite (a silicate of calcium and magnesium in the amphibole gro ...
and soap stone, silk and paper.
Pagodaoffogongtemple2019.jpg, Pagoda of Fogong Temple, Buddha Pagoda (Fogong Monastery, Yingxian, China), 1056
Guo Xi - Early Spring (large).jpg, Early Spring; by Guo Xi; 1072; hanging scroll, ink on silk; 1.58 x 1.08 m; National Palace Museum (Taipei, Taiwan)
Liao Dynasty Avalokitesvara Statue Clear.jpeg, Guanyin of the Southern Seas; 11th-12th century; painted and gilded wood; height: 2.41 m; Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art (Kansas City, Missouri, USA)
Court Ladies Preparing Newly Woven Silk (捣练图) by Emperor Huizong (1082–1135).jpg, Ladies Preparing Silk; after Zhang Xuan; early 12th century; ink and colours on silk; 0.37 x 1.47 m; Museum of Fine Arts (Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, USA)
Chao Meng-fu Couleurs d'automne sur les monts Qiao et Hua.jpg, Autumn Colours on the Qiao and Hua Mountains; by Zhao Mengfu; 1296; handscroll (detail), ink and colours on paper; 28.4 x 93.2 cm; National Palace Museum (Taipei, Taiwan)
明初 剔紅庭園高士圖漆盤-Dish with garden scene MET DP256068.jpg, Lacquer dish with garden scene; late 14th century; carved red lacquer; diameter: 19.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
The David Vases.jpg, David Vases; 1351; glazed porcelain; height: 63.5 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
SFEC BritMus Asia 023.JPG, Assistant to a judge of hell; 1522–1620; stoneware; height: 137 cm; British Museum
File:11 Temple of Heaven.jpg, Hall of Prayer for Good Harvests, Temple of Heaven (Beijing), 1545, rebuilt in 1890
Chinese - Covered Box - Walters 44543.jpg, Cloisonné box; 18th century; cloisonné enamels on copper with gilt bronze; 20.5 × 19.8 cm; Walters Art Museum (Baltimore, Maryland, USA)
Japanese
Japanese art covers a wide range of art styles and media, including Jōmon pottery, ancient pottery, Japanese sculpture, sculpture, Ink wash painting, ink painting and Japanese calligraphy, calligraphy on silk and paper, ''ukiyo-e'' paintings and woodblock printing, woodblock prints, ceramics, origami, and more recently manga—modern Japanese cartooning and comics—along with a myriad of other types.
The first settlers of Japan, the Jōmon people (c. 11,000–300 BC). They crafted Jomon pottery, lavishly decorated pottery storage vessels, clay figurines called ''dogū''. Japan has been subject to sudden invasions of new ideas followed by long periods of minimal contact with the outside world. Over time the Japanese developed the ability to absorb, imitate, and finally assimilate those elements of foreign culture that complemented their aesthetic preferences. The earliest complex art in Japan was produced in the 7th and 8th centuries in connection with Buddhism. In the 9th century, as the Japanese began to turn away from China and develop indigenous forms of expression, the secular arts became increasingly important; until the late 15th century, both religious and secular arts flourished. After the Ōnin War (1467–1477), Japan entered a period of political, social, and economic disruption that lasted for over a century. In the state that emerged under the leadership of the Tokugawa shogunate, organized religion played a much less important role in people's lives, and the arts that survived were primarily secular.
Kinkaku-ji the Golden Temple in Kyoto overlooking the lake - high rez.JPG, Kinkaku-ji, Temple of the Golden Pavilion (Kitayama, Kyoto), a Zen Buddhist temples in Japan, Buddhist temple in Kyoto, 1398
色絵婦人立像-Figure of a Standing Beauty MET DP220704.jpg, Female figure; 1670–1690; porcelain with overglaze polychrome enamels; height: 39.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
胴箔地南天冊子模様縫箔-Noh Costume (Nuihaku) with Books and Nandina Branches MET DT289471.jpg, Noh robe; 1750–1800; silk embroidery and gold leaf on silk satin; length: 1.66 m; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Tsunami by hokusai 19th century.jpg, ''The Great Wave off Kanagawa'', by Katsushika Hokusai; 1830–1832; full-colour Woodblock printing, woodblock print; 25.7 x 37.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
De pruimenboomgaard te Kameido-Rijksmuseum RP-P-1956-743.jpeg, ''Plum Park in Kameido''; by Hiroshige; 1857; full-colour woodblock print; 36.4 x 24.4 cm; Rijksmuseum (Amsterdam, the Netherlands)
Sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan African art includes both African sculpture, sculpture, typified by the brass castings of the Benin art, Benin people, Archaeology of Igbo-Ukwu, Igbo Ukwu and the Kingdom of Ifẹ, and terracottas of Djenne-Jeno, Ife, and the more ancient Nok culture, as well as African folk art, folk art. Concurrent with the European Middle Ages, in the eleventh century AD a nation that made grand architecture, gold sculpture, and intricate jewelry was founded in Great Zimbabwe. Impressive sculpture was concurrently being cast from brass by the Yoruba art, Yoruba people of what is now Nigeria. In the Benin art, Benin Kingdom, also of southern Nigeria, which began around the same time, elegant altar tusks, brass heads, plaques of brass, and palatial architecture were created. The Benin Kingdom was ended by the British in 1897, and little of the culture's art now remains in Nigeria. Today, the most significant arts venue in Africa is the Johannesburg Biennale.
Sub-Saharan Africa is characterized by a high density of cultures. Notable are the, Dogon people from Mali; Edo people, Edo, yoruba people, Yoruba, Igbo people, Igbo people and the Nok civilization from Nigeria; Kuba Kingdom, Kuba and Luba people from Central Africa; Ashanti people from Ghana; Zulu people from Southern Africa; and Fang people from Equatorial Guinea (85%), Cameroon and Gabon; the Sao civilization people from Chad; Kwele people from eastern Gabon, Republic of the Congo and Cameroon.
The myriad forms of African art are components of some of the most vibrant and responsive artistic traditions in the world and are integral to the lives of African people. Created for specific purposes, artworks can reveal their ongoing importance through physical transformations that enhance both their appearance and their potency. Many traditional African art forms are created as conduits to the spirit world and change appearance as materials are added to enhance their beauty and potency. The more a work is used and blessed, the more abstract it becomes with the accretion of sacrificial matter and the wearing down of original details.
Nok sculpture Louvre 70-1998-11-1.jpg, Seated figure; by Nok culture; 5th century BC-5th century AD; earthenware (central Nigeria); height: 38 cm; Musée du Quai Branly (Paris)
Bronze pot, 9th century, Igbo-Ukwu, Nigeria.jpg, Pot; from Archaeology of Igbo-Ukwu, Igbo-Ukwu (Nigeria); 9th century; bronze; unknown dimensions; Nigerian National Museum (Lagos)
Afrikaabteilung in Ethnological Museum Berlin 02.JPG, Head of a king or dignitary; by Yoruba people; 12th-15th century; terracotta; 19 cm; discovered at Ife (Nigeria); Ethnological Museum of Berlin (Germany)
Seated Figure MET DT1213.jpg, Seated figure; by Djenné-Djenno#Terra-cotta figurines from the Inner Niger Delta region, Djenné-Djenno culture (Mali); 13th century; earthenware; width: 29.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
British Museum - Room 25 (18020107461).jpg, Benin ivory mask, Pendant mask; by Edo people (Nigeria); 16th century (?); ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals ...
and iron; height: 24.5 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
Plaque- Warrior and Attendants MET DT1231.jpg, Plaque with warriors and attendants; by Edo people; 16th-17th century (Nigeria); brass; height: 47.6 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Brooklyn Museum 61.33 Ndop Portrait of King Mishe miShyaang maMbul (5).jpg, Ndop (Kuba), N'dop, king Mishe miShyaang maMbul; from the Kuba Kingdom (Democratic Republic of the Congo); 18th century; wood; 49.5 cm; Brooklyn Museum (New York City)
Helmet Mask MET DT1234.jpg, Royal mask; by Bamum people (Cameroon); before 1880; wood, copper, glass beads, raffia and shells; height: 66 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Rep. dem. del congo, kuba, maschera ngaady-a-mwaash, xx secolo.jpg, Ngaad-A-Mwash mask; by the Kuba people; late 19th-early 20th centuries; wood, shells, glass beads, raffia and pigment; height: 82 cm; Detroit Institute of Arts (Detroit, Michigan, USA)
Appuie-tête Luba-RDC.jpg, Headrest; by Luba people; 19th century; wood; height: 18.5 cm; Musée du quai Branly (Paris)
Oceania
The Art of Oceania includes the geographic areas of Micronesia, Polynesia, Australia, New Zealand, and Melanesia. One approach treats the area thematically, with foci on ancestry, warfare, the body, gender, trade, religion, and tourism. Unfortunately, little ancient art survives from Oceania. Scholars believe that this is likely because artists used perishable materials, such as wood and feathers, which did not survive in the tropical climate, and there are no historical records to refer to most of this material. The understanding of Oceania's artistic cultures thus begins with the documentation of it by Westerners, such as Captain James Cook, in the 18th century. At the turn of the 20th century the French artist Paul Gauguin spent significant amounts of time in Tahiti, living with local people and making modern art — a fact that has become intertwined with Tahitian visual culture to the present day. The indigenous Australian art, art of Australia often looks like abstract modern art, but it has deep roots in local culture.
The art of Oceania is the last great tradition of art to be appreciated by the world at large. Despite being one of the longest continuous traditions of art in the world, dating back at least fifty millennia, it remained relatively unknown until the second half of the 20th century.
The often ephemeral materials of Aboriginal art of Australia makes it difficult to determine the antiquity of the majority of the forms of art practised today. The most durable forms are the multitudes of rock engravings and rock paintings which are found across the continent. In the Arnhem Land escarpment, evidence suggests that paintings were being made fifty thousand years ago, antedating the Palaeolithic rock paintings of Cave of Altamira, Altamira &
Lascaux in Europe.
British Museum (6424973639).jpg, Hoa Hakananai'a, an example of a moai; 1200 AD; flow lava; height: 242 cm; British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docume ...
(London)
British Museum (2082156178).jpg, Statue of A'a from Rurutu; probably 18th century; wood; height: 117 cm; British Museum
Nuova zelanda, isola del nord, maori, prua di piroga taurapa, 1800-20 ca.jpg, ''Taurapa'' (māori people, māori canoe sternpost); late 18th-early 19th century; wood and sheel; height: 148 cm; Musée du Quai Branly (Paris)
Australie Aborigene ancetre totemique kangourou.jpg, Australian painting of a kangaroo totemic ancestor; 1915; painting on bark; 92.5 × 35.5 cm; Musée du Quai Branly
European
Medieval
With the decline of the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
in 300 AD, the Medieval art, Medieval era began, lasting for about a millennium, until the beginning of the Renaissance art, Renaissance in 1400. Early Christian art begins the period, followed by Byzantine art, Anglo-Saxon art, Viking art, Ottonian art, Romanesque art and Gothic art, with Islamic art dominating the eastern Mediterranean. Medieval art grew out of the artistic heritage of the Roman Empire and Byzantium, mixed with the 'barbarian' artistic culture of northern Europe.
In Byzantine and Gothic art, Gothic art of the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
, the dominance of the church resulted in a large amount of religious art. There was extensive use of gold in paintings, which presented figures in simplified forms.
Byzantine
Byzantine art refers to the body of Christian Greek artistic products of the Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman (Byzantine) Empire, as well as the nations and states that inherited culturally from the empire. Though the empire itself emerged from Rome's decline and lasted until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453, the start date of the Byzantine period is rather clearer in art history than in political history, if still imprecise. Many Eastern Orthodox Church, Eastern Orthodox states in Eastern Europe, as well as to some degree the Muslim world, Muslim states of the eastern Mediterranean, preserved many aspects of the empire's culture and art for centuries afterward.
Surviving Byzantine art is mostly religious and with exceptions at certain periods is highly conventionalised, following traditional models that translate carefully controlled church theology into artistic terms. Painting in
fresco, illuminated manuscripts and on wood panel and, especially in earlier periods,
mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
were the main media, and figurative
sculpture
Sculpture is the branch of the visual arts that operates in three dimensions. Sculpture is the three-dimensional art work which is physically presented in the dimensions of height, width and depth. It is one of the plastic arts. Durable sc ...
very rare except for small ivory carving, carved ivories. Manuscript painting preserved to the end some of the classical realist tradition that was missing in larger works. Byzantine art was highly prestigious and sought-after in Western Europe, where it maintained a continuous influence on medieval art until near the end of the period. This was especially so in Italy, where Byzantine styles persisted in modified form through the 12th century, and became formative influences on Italian Renaissance art. But few incoming influences affected the Byzantine style. With the expansion of the Eastern Orthodox church, Byzantine forms and styles spread throughout the Orthodox world and beyond. Influences from Byzantine architecture, particularly in religious buildings, can be found in diverse regions from Egypt and Arabia to Russia and Romania.
Byzantine architecture is notorious for the use of domes. It also often featured marble columns, coffered ceilings and sumptuous decoration, including the extensive use of
mosaic
A mosaic is a pattern or image made of small regular or irregular pieces of colored stone, glass or ceramic, held in place by plaster/mortar, and covering a surface. Mosaics are often used as floor and wall decoration, and were particularly pop ...
s with golden backgrounds. The building material used by Byzantine architects was no longer marble, which was very appreciated by the Ancient Greeks. They used mostly stone and brick, and also thin
alabaster sheets for windows. Mosaics were used to cover brick walls, and any other surface where
fresco wouldn't resist. Good examples of mosaics from the proto-Byzantine era are in Hagios Demetrios in Thessaloniki (Greece), the Basilica of Sant'Apollinare Nuovo and the Basilica of San Vitale, both in Ravenna (Italy), and Hagia Sophia in Istanbul. Greco-Roman temples and Byzantine churches differ substantially in terms of their exterior and interior aspect. In Antiquity, the exterior was the most important part of the temple, because in the interior, where the cult statue of the deity to whom the temple was built was kept, only the priest had access. The ceremonies here held outside, and what the worshipers view was the facade of the temple, consisting of columns, with an entablature and two pediments. Meanwhile, Christian liturgies were held in the interior of the churches, the exterior usually having little to no ornamentation.
"The good Shepherd" mosaic - Mausoleum of Galla Placidia.jpg, Christ as the Good Shepherd; 425–430; mosaic; width: 3 m; Mausoleum of Galla Placidia (Ravenna, Italy)
KHM Wien Kaiserin Ariadne X 39.jpg, Diptych Leaf with a Byzantine Empress; 6th century; ivory with traces of gilding and leaf; height: 26.5 cm; Kunsthistorisches Museum (Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
)
Officina costantinopolitana, tesoro di asyut (egitto), V-VI sec ca. 01 collier.JPG, Collier; late 6th–7th century; gold, an emerald, a sapphire, amethysts and pearls; diameter: 23 cm; from a Constantinopolitan workshop; Antikensammlung Berlin (Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany)
Byzantium, Constantinople, 11th century - Gospel Book with Commentaries - 1942.152 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, Page of the Gospel Book with Commentaries: Portrait of Mark; 1000–1100; ink, tempera, gold, vellum and leather binding; sheet: 28 × 23 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, located in the Wade Park District, in the University Circle neighborhood on the city's east side. Internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian and Egypt ...
(Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, US)
The Ladder of Divine Ascent Monastery of St Catherine Sinai 12th century.jpg, ''Ladder of Divine Ascent (icon), Ladder of Divine Ascent''; late 12th century; tempera and gold leaf on panel; 41 x 29.5 cm; Saint Catherine's Monastery (Sinai Peninsula, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Med ...
)
Ottonian
Ottonian art is a style (visual arts), style in Pre-Romanesque art, pre-romanesque German art, covering also some works from the Low Countries, northern Italy and eastern France. It was named by the art historian Hubert Janitschek after the Ottonian dynasty which ruled Germany and northern Italy between 919 and 1024 under the kings Henry the Fowler, Henry I, Otto I, Otto II, Otto III and Emperor Henry II, Henry II. With Ottonian architecture, it is a key component of the Ottonian Renaissance (circa 951–1024). However, the style neither began nor ended to neatly coincide with the rule of the dynasty. It emerged some decades into their rule and persisted past the Ottonian emperors into the reigns of the early Salian dynasty, which lacks an artistic "style label" of its own.
[Suckale-Redlefsen, 524] In the traditional scheme of art history, Ottonian art follows Carolingian art and precedes Romanesque art, though the transitions at both ends of the period are gradual rather than sudden. Like the former and unlike the latter, it was very largely a style restricted to a few of the small cities of the period, and important monastery, monasteries, as well as the court circles of the emperor and his leading vassals.
After the decline of the Carolingian Empire, the Holy Roman Empire was re-established under the Duchy of Saxony, Saxon Ottonian dynasty. From this emerged a renewed faith in the idea of Empire and a reformed Church, creating a period of heightened cultural and artistic fervour. It was in this atmosphere that masterpieces were created that fused the traditions from which Ottonian artists derived their inspiration: models of Late Antique, Carolingian, and Byzantine origin. Surviving Ottonian art is very largely religious, in the form of illuminated manuscripts and metalwork, and was produced in a small number of centres for a narrow range of patrons in the circle of the Imperial court, as well as important figures in the church. However much of it was designed for display to a wider public, especially of pilgrims.
The style is generally grand and heavy, sometimes to excess, and initially less sophisticated than the Carolingian equivalents, with less direct influence from Byzantine art and less understanding of its classical models, but around 1000 a striking intensity and expressiveness emerge in many works, as "a solemn monumentality is combined with a vibrant inwardness, an unworldly, visionary quality with sharp attention to actuality, surface patterns of flowing lines and rich bright colours with passionate emotionalism".
[Honour and Fleming, 277]
Romanesque
The Romanesque art, Romanesque was the first pan-European style to emerge after the
Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Medite ...
, spanning the mid-tenth century to the thirteenth. The period saw a resurgence of monumental stone structures with complex structural programmes.
Romanesque architecture, Romanesque churches are characterized by rigid articulation and geometric clarity, incorporated into a unified volumetric whole. The architecture is austere but enlivened by decorative sculpting of capitals and portals, as well as frescoed interiors. Geometric and foliate patterning gives way to increasingly three-dimensional figurative sculpture.
From the mid-eleventh to the early thirteenth centuries, Romanesque paintings were two-dimensional, defined by bold, linear outlines and geometry, particularly in the handling of drapery; symmetry and frontality were emphasised. Virtually all Western churches were painted, but probably only a few wall painters were monks; instead, itinerant artists carried out most of this work. Basic blocking out was done on wet
plaster
Plaster is a building material used for the protective or decorative coating of walls and ceilings and for moulding and casting decorative elements. In English, "plaster" usually means a material used for the interiors of buildings, while "r ...
with earth colours. A limited palette, dominated by white, red, yellow ochres and azure, was employed for maximum visual effect, with dense colouring forming a backdrop of bands, a practice that originated in late Classical art as an attempt to distinguish earth and sky.
During the later eleventh and twelfth centuries, the great age of Western monasticism, Europe experienced unprecedented economic, social and political change, leading to burgeoning wealth among landowners, including monasteries. There was increasing demand for books, and economic wealth allowed many manuscripts to be richly Illuminated manuscript, illuminated.
One of the outstanding artefacts of the age is the 70 m long Bayeux Tapestry. It depicts the events leading up to the Norman conquest of England with protagonists William the Conqueror, William, Duke of Normandy, and Harold Godwinson, Harold, Earl of Wessex, later King of England, and culminating in the Battle of Hastings. It is thought to date from the 11th century. It tells the story from the point of view of the conquering Normans, but is now agreed to have been made in England most likely by women, although the designer is unknown. It is housed in
France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan ar ...
.
Arte carolingia, volto santo di sansepolcro, VIII-IX secolo circa con policromia del XII secolo.JPG, 'Holy Face'; 904–1018; wood with polychromy; height: 2.9 m; Sansepolcro Cathedral (Sansepolcro, Italy)
File:Glees Germany Maria-Laach-Abbey-01.jpg, Maria Laach Abbey (Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany), 1093-1230
Pope Alexander head reliquary, from Abbey Saint-Remacle de Stavelot, Mosan workshop, c. 1145 AD, silver partially gilt, brass, enamel, precious stones - Cinquantenaire Museum - Brussels, Belgium - DSC08823.jpg, Head of pope Alexander; 1145; wood, silver, gilt bronze, gems, pearls and champlevé enamel; height: 45 cm; Art & History Museum (Brussels, Belgium)
Klosterkirche Müstair Freske Steinigung Stephanus.jpg, The stoning of Saint Stephen; 1160s; fresco; height: 1.3 m; Saint John Abbey, Müstair, Saint John Abbey (Val Müstair, Canton of Grisons, Switzerland)
Manuscript Illumination with Initial V, from a Bible MET DP102859.jpg, Manuscript Illuminated manuscript, Illumination with Initial V, from a Bible; 1175–1195; tempera on parchment; 27.5 x 15.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
Gothic
Gothic art developed in Northern France out of Romanesque in the 12th century AD, and led by the concurrent development of Gothic architecture. It spread to all of Western Europe, and much of Southern Europe, Southern and Central Europe, never quite effacing more classical styles in Italy. In the late 14th century, the sophisticated court style of International Gothic developed, which continued to evolve until the late 15th century.
The imposing Gothic cathedrals, with their sculptural programmes and stained glass windows, epitomize the Gothic style. It differs from Romanesque through its rib-shaped Vault (architecture), vaults, and the use of ogives. Instead of the thick Romanesque walls, Gothic buildings are thin and tall. Spiral stairs in towers are specific to Gothic architecture.
Gothic painting, much of it executed in tempera and, later, oils on panel, as well as fresco, and with an increasingly broad palette of secondary colours, is generally seen as more 'naturalistic' than Romanesque. The humanity of religious narrative was highlighted, and the emotional state of the characters individualized. The increased urbanity of the medieval economy and the rise of the clerical and lay patron saw a change in the nature of the art market, which can be seen in developments in Gothic Illuminated manuscript, manuscript illumination. Workshops employed specialists for different elements of the page, such as figures or marginal vine motifs.
Chartres RosetteNord 121 DSC08241.jpg, North transept windows; 1230–1235; stained glass; diameter (rose window): 10.2 m; Chartres Cathedral (Chartres, France)
Sainte Chapelle Interior Stained Glass.jpg, The Sainte-Chapelle (Paris), 1243–1248, by Pierre de Montreuil
Naumburg Dom Stifterfiguren Uta und Ekkehard 2012-04-29-17-31-47.jpg, Ekkehard and Uta; attributed to the Master of Namburg; 1245–1260; limestone and polychrome, polychromy; height: 1.9 m; Naumburg Cathedral (Naumburg, Germany)
4 Jean Pucelle. Hours of Jeanne d'Evreux. 1325-28, Metropolitan Museum, New-York.jpg, Arrest of Christ and Annunciation of the Virgin; by Jean Pucelle; 1324–1328; grisaille and temprea on vellum; 8.9 x 12.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Anonimo inglese o francese, dittico wilton, 1395-99 ca. 01.jpg, The ''Wilton Diptych''; 1395–1459; tempera and gold on panel; 53 × 37 cm; National Gallery (London)
Renaissance
Encompassing Early, Northern and High Renaissance, the term Renaissance describes the 'rebirth' in Europe of a new interest for Classical antiquity. For the first time since antiquity, art became convincingly lifelike. Besides the ancient past, Renaissance artists also studied nature, understanding the human body, animals, plants, space, perspective and the qualities of light. The most common theme were religious subjects, but depictions of mythological stories were produced as well. Also, there was no uniform Renaissance style. Each artist developed their own distinct visual language, influenced by their predecessors and contemporaries.
The Early Renaissance was a period of great creative and intellectual activity when artists broke away completely from the parameters of Byzantine art. It is generally accepted that it started in
Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
in present-day
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in the early 15th century. It is characterized by a surge of interest in classical literature, philosophy and art, the growth of commerce, the discovery of new continents, and new inventions. There was a revival of interest in the art and literature of ancient Rome, and the study of Ancient Greek literature, ancient Greek and Latin literature, Latin texts instigated concepts of individualism and reason, which became known as humanism. Humanists considered life in the present and emphasized the importance of individual thought, which affected artists' approaches.
Despite being highly associated with Italy, particularly with Florence, Rome, and Venice, the rest of Western Europe participated to the Renaissance as well. The Northern Renaissance occurred in Europe north of the Alps from the early 15th century, following a period of artistic cross-fertilization between north and south known as 'International Gothic'. There was a big difference between the Northern and Italian Renaissance. The North artists did not seek to revive the values of ancient Greece and Rome like the Italians, while in the south Italian artists and patrons were amazed by the empirical study of nature and the human society, and by the deep colors that northern artists could achieve in the newly developed medium of oil paint. The Protestant Reformation increased the northern interest in secular painting, like portraits or landscapes. Two key northern artists are Hieronymus Bosch, known for his surreal paintings filled with hybrid creatures like The Garden of Earthly Delights, and Albrecht Dürer, who brought the new art of printmaking to a new level.
The High Renaissance took place in the late 15th-early 16th centuries and was influenced by the fact that as papal power stabilized in Rome, several popes commissioned art and architecture, determined to recreate the city's former glory. Raphael and
Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was in ...
produced vast and grandiose projects for the popes. The most famous artwork of this part of the Renaissance is probably the ceiling of the Sistine Chapel ceiling, Sistine Chapel.
Mannerism broke away from High Renaissance ideals of harmony and a rational approach to art, to embrace exaggerated forms, elongated proportions, and more vibrant colors. It developed in Italy between 1510 and 1520, among artists who prized originality above all. The name of this movement comes from the Italian ''maniera'', meaning 'style or 'manner'. The word was meant to describe the standard of excellence achieved during the High Renaissance, to which all art should now adhere, but in practice it led to stylization and art 'to show art', sometimes with great success, an example being Raphael's pupil Giulio Romano. Mannerism has also been used more generally to describe a period following the Renaissance and preceding the Baroque.
Florence Duomo (167859687).jpeg, The Florence Cathedral (Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
, Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
), 1294–1436, by Arnolfo di Cambio, Filippo Brunelleschi and Emilio De Fabris
File:Giotto. the-crucifix-1290-1300 Florence, Santa Maria Novella.jpg, Crucifix; by Giotto; 1300; tempera on panel; 5.78 x 4.06 m; Santa Maria Novella (Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
, Italy)
Van Eyck - Arnolfini Portrait.jpg, ''Arnolfini Portrait''; by Jan van Eyck; 1434; oil on panel; 82.2 x 60 cm; National Gallery (London)
File:Florence - David by Donatello.jpg, ''David (Donatello), David''; by Donatello; 1460s; bronze; height: 1.6 m; Bargello (Florence)
Paolo Uccello 047b.jpg, ''Saint George and the Dragon (Uccello), Saint George and the Dragon''; by Paolo Uccello; 1470; oil on canvas; 55.6 x 74.2 cm; National Gallery (London)
Botticelli-primavera.jpg, ''Primavera (Botticelli), Primavera''; by Sandro Botticelli; 1478; tempera on panel; 2 x 3.1 m; Uffizi, Uffizi Gallery (Florence)
Tempietto del Bramante Vorderseite.jpg, San Pietro in Montorio#The Tempietto, The Tempietto (San Pietro in Montorio, Rome), 1502, by Donato Bramante
Mona Lisa, by Leonardo da Vinci, from C2RMF retouched.jpg, ''Mona Lisa''; by Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially re ...
; 1503-1519; Oil painting, oil on Populus, poplar panel; 77 × 53 cm; Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
The Garden of earthly delights.jpg, ''The Garden of Earthly Delights''; by Hieronymus Bosch; 1504; oil on panel; 2.2 x 1.95 m; Museo del Prado (Madrid, Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' ( Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
)
File:Sistine ceiling.jpg, Sistine Chapel ceiling; by Michelangelo
Michelangelo di Lodovico Buonarroti Simoni (; 6 March 1475 – 18 February 1564), known as Michelangelo (), was an Italian sculptor, painter, architect, and poet of the High Renaissance. Born in the Republic of Florence, his work was in ...
; 1508–1512; fresco; 13.7 x 39 m; Sistine Chapel (Vatican City)
"The School of Athens" by Raffaello Sanzio da Urbino.jpg, ''The School of Athens''; by Raphael; 1509–1510; fresco; 5.8 x 8.2 m; Apostolic Palace (Vatican City)
The Rhinoceros (NGA 1964.8.697) enhanced.png, ''Dürer's Rhinoceros, The Rhinoceros''; by Albrecht Dürer; 1515; woodcut; 23.5 × 29.8 cm; National Gallery of Art (Washington, D.C., USA)
Chateau-Azay-le-Rudeau-1.jpg, Château d'Azay-le-Rideau (Loire, France), 1518-1527
Pieter Bruegel the Elder - The Tower of Babel (Vienna) - Google Art Project - edited.jpg, ''The Tower of Babel (Bruegel), The Tower of Babel''; by Pieter Bruegel the Elder; 1563; oil on panel; 1.14 x 1.55 m; Kunsthistorisches Museum (Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
)
Armoire Louvre OA 6968.jpg, Cupboard; 1580; walnut and oak, partially gilded and painted; height: 2.06 m, width: 1.50 m; Louvre
Baroque
The 17th century was a period of volatile change, both in science, through inventions and developments, such as the telescope or the microscope, and in religion, as the Catholic Counter-Reformation contested the growing popularity of Protestant faith. After the Protestant Reformation the Catholic Church reacted with the Counter-Reformation, decreeing that art should inspire viewers with passionate religious themes.
Succeeding Mannerism, and developing as a result of religious tensions across Europe, Baroque art emerged in the late 16th century. The name may derive from 'barocco', the Portuguese language, Portuguese word for misshaped pearl, and it describes art that combined emotion, dynamism and dramawith powerful color, realism and strong tonal contrasts. Between 1545 and 1563 at the Council of Trent, it was decided that religious art must encourage piety, realism and accuracy, and, by attracting viewers' attention and empathy, glorify the Catholic Church and strengthen the image of Catholicism. In the next century the radical new styles of Baroque art both embraced and developed High Renaissance models, and broke new ground both in religious art and in new varieties of secular art – above all landscape. The Baroque and its late variant the Rococo were the first truly global styles in the arts, dominating more than two centuries of art and architecture in Europe, Latin America and beyond from circa 1580 to circa 1750. Born in the painting studios of Bologna and Rome in the 1580s and 1590s, and in Roman sculptural and architectural ateliers in the second and third decades of the 17th century, the Baroque spread swiftly throughout Italian Baroque architecture, Italy, Spanish Baroque architecture, Spain and Baroque architecture in Portugal, Portugal, Flanders, French Baroque architecture, France, the Netherlands, England, Scandinavia, and Russia, as well as to central and eastern European centres from Munich (Germany) to Vilnius (Lithuania). The Portuguese Empire, Portuguese, Spanish Empire, Spanish and French colonial empire, French empires and the Dutch treading network had a leading role in spreading the two styles into the Americas and colonial Africa and Asia, to places such as Lima, Mozambique, Goa and the Philippines.
Just like paintings and sculptures, Baroque cathedrals and palaces are characterised by the use of illusion and drama as well. They also frequently use dramatic effects of light and shade, and have sumptuous, highly decorated interiors that blurred the boundaries between architecture, painting and sculpture. Another important characteristic of Baroque architecture was the presence of dynamism, done through curves, Solomonic columns and ovals. In France, Baroque is synonymous with the reign of Louis XIV between 1643 and 1715, since multiple monumental buildings were built in Paris, Versailles and other parts of France during his rule, such as the Palace of Versailles, the Château de Maisons, the Vaux-le-Vicomte, Château de Vaux-le-Vicomte, the Louvre Colonnade or The Dôme Les Invalides, des Invalides. Besides the building itself, the space where it was placed has a role too. Baroque buildings try to seize viewers' attention and to dominate their surroundings, whether on a small scale such as the San Carlo alle Quattro Fontane in Rome, or on a massive one, like the new facade of the Santiago de Compostela Cathedral, designed to tower over the city. Applied arts prospered during this period as well. Baroque furniture could be as bombastic as the rooms they were meant to adorn, and their motifs and techniques were carefully calibrated to coordinate with the architect's overall decorative programme. One of the most prestigious furniture makers was André Charles Boulle, known for his marquetry technique, made by gluing sheets of tortoiseshell and brass together and cut to form the design. His works were also adorned with gilded bronze mounts. Complex Gobelins Manufactory, Gobelins tapestries featured scenes inspired by classical antiquity, and the Savonnerie manufactory produced big highly detailed carpets for the Louvre. These carpets with black or yellow backgrounds had a central motif or a Medallion (architecture), medallion. Chinese porcelain, Delftware and mirrors fabricated at Saint-Gobain#1665-1789: Manufacture royale, Saint-Gobain (France) spread rapidly in all princely palaces and aristocratic residences in France. During the reign of Louis XIV, big mirrors are put above fireplace mantels, and this trend will last long after the Baroque period.
Peter Paul Rubens - The Four Continents.jpg, ''The Four Continents''; by Peter Paul Rubens; 1615; oil on canvas; 209 x 284 cm; Kunsthistorisches Museum (Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Austria)
Château de Maisons-Laffitte 001.jpg, Château de Maisons (France), by François Mansart, 1630-1651
Nicolas Poussin - L'Enlèvement des Sabines (1634-5).jpg, ''The Rape of the Sabine Women''; by Nicolas Poussin; 1634–1635; oil on canvas; 1.55 × 2.1 m; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
La ronda de noche, por Rembrandt van Rijn.jpg, ''The Night Watch''; by Rembrandt; 1642; oil on canvas; 3.63 × 4.37 m; Rijksmuseum (Amsterdam, the Netherlands)
Ecstasy of St. Teresa HDR.jpg, ''Ecstasy of Saint Teresa''; by Gian Lorenzo Bernini; 1647–1652; marble; height: 3.5 m; Santa Maria della Vittoria, Rome, Santa Maria della Vittoria (Rome)
Las Meninas, by Diego Velázquez, from Prado in Google Earth.jpg, ''Las Meninas''; by Diego Velázquez; 1656; oil on canvas; 3.18 cm × 2.76 m; Museo del Prado (Madrid, Spain)
Maria van Oosterwijck, Kunsthistorisches Museum Wien, Gemäldegalerie - Vanitas-Stilleben - GG 5714.jpg, ''Vanitas Still Life''; by Maria van Oosterwijck; 1668; oil on canvas; 73 x 88.5 cm; Kunsthistorisches Museum
Carpet with Fame and Fortitude MET DP212204.jpg, Carpet with fame and fortitude; by the Savonnerie manufactory; 1668–1685; knotted and cut wool pile, woven with about 90 knots per square inch; 909.3 x 459.7 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Cathédrale Saint-Louis-des-Invalides, 140309 2.jpg, Dôme Les Invalides, des Invalides (Paris), 1677–1706, by Jules Hardouin-Mansart
Commode MET DP108742.jpg, Commode; by André Charles Boulle; 1710–1732; walnut veneered with ebony and marquetry of engraved brass and tortoiseshell, gilt-bronze mounts, antique marble top; 87.6 x 128.3 x 62.9 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Rococo
Originating in 1720 Paris, Rococo is characterized by natural motifs, soft colours, curving lines, asymmetry and themes including love, nature and light-hearted entertainment. Its ideals were delicacy, gaiety, youthfulness and sensuality.
Beginning in France as a reaction against the heavy Baroque grandeur of Louis XIV's court at the Palace of Versailles, the rococo movement became associated particularly with the powerful Madame de Pompadour (1721–1764), the mistress of the new king Louis XV (1710–1774). Because of this, the style was also known as 'Pompadour'. The name of the movement derives from the French 'rocaille', or pebble, and refers to stones and shells that decorate the interiors of caves, as similar shell forms became a common feature in Rococo design. It began as a design and decorative arts style, and was characterized by elegant flowing shapes. Architecture followed and then painting and sculpture. The French painted with whom the term Rococo is most often associated is Jean-Antoine Watteau, whose pastoral scenes, or ''fêtes galantes'', dominate the early part of the 18th century.
Although there are some important Bavarian churches in this style, such as the Pilgrimage Church of Wies, Wieskirche, Rococo is most often associated with secular buildings, principally great palaces and salons where educated elites would meet to discuss literary and philosophical ideas. In Paris, its popularity coincided with the emergence of the salon as a new type of social gathering, the venues for which were often decorated in the Rococo style. Among the most characteristically elegant and refined examples is the Salon Oval de la Princesse of the Hôtel de Soubise, one of the most beautiful 18th century hôtel particulier, mansions in Paris. The Rococo introduced dramatic changes to elite furniture, as it favoured smaller pieces with narrow, sinewy frames and more delicate, often asymmetrical decoration, often including elements of chinoiserie. The taste for Far Eastern objects (mainly Chinese) lead to the use of Chinese painted and lacquered panels for furniture.
The movement spread quickly throughout Europe and as far as Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turkey and China thanks to ornament books featuring cartouche (design), cartouches, arabesques and shell work, as well as designs for wall panels and fireplaces. The most popular were made by Juste-Aurèle Meissonnier (1695–1750), Jacques-François Blondel (1705–1774), Pierre-Edmé Babel (1720–1775) and François de Cuvilliés (1695–1768).
L'Embarquement pour Cythere, by Antoine Watteau, from C2RMF retouched.jpg, ''The Embarkation for Cythera''; by Jean-Antoine Watteau; 1718; oil on canvas; 1.29 x 1.94 m; Schloss Charlottenburg
Salon ovale de la princesse in the Hôtel de Soubise (11).jpg, The Salon Oval de la Princesse of the Hôtel de Soubise (Paris), 1737–1739, by Germain Boffrand, Charles-Joseph Natoire and Jean-Baptiste Lemoyne
Jean Joseph de Saint-Germain - Candelabrum - 1946.81 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, Candelabrum; by Jean Joseph de Saint-Germain; 1750; gilt bronze; overall: 72.4 x 49.3 x 39.7 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art
The Cleveland Museum of Art (CMA) is an art museum in Cleveland, Ohio, located in the Wade Park District, in the University Circle neighborhood on the city's east side. Internationally renowned for its substantial holdings of Asian and Egypt ...
(Cleveland
Cleveland ( ), officially the City of Cleveland, is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Cuyahoga County. Located in the northeastern part of the state, it is situated along the southern shore of Lake Erie, across the U ...
, Ohio
Ohio () is a U.S. state, state in the Midwestern United States, Midwestern region of the United States. Of the List of states and territories of the United States, fifty U.S. states, it is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 34th-l ...
, USA)
Fire MET DP104979.jpg, ''Fire''; by Jean-Pierre Defrance; 1750-1760; limestone; height: 223 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Side table (commode en console) MET DP105703.jpg, Side table (commode en console); by Bernard II van Risamburgh; 1755-1760; Japanese lacquer, gilt-bronze mounts and Sarrancolin marble top; height: 90.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Madame de Pompadour.jpg, ''Madame de Pompadour''; by François Boucher; 1756; oil on canvas; 2.01 x 1.57 m; Alte Pinakothek (Munich, Germany)
Coffeepot MET DP103144 (cropped),.jpg, Coffeepot; 1757; silver; height: 29.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Sèvres Porcelain Manufactory - Covered Tureen (Terrine du roi) - 1949.15 - Cleveland Museum of Art.tif, Covered tureen (terrine du roi); by the Manufacture nationale de Sèvres 1756; soft-paste porcelain with enamel and gilt decoration; overall: 24.2 cm; Cleveland Museum of Art
Fragonard - swing.jpg, ''The Swing (Fragonard), The Swing''; by Jean-Honoré Fragonard; 1767; oil on canvas; 81 x 64 cm; Wallace Collection (London)
Louise Elisabeth Vigée-Lebrun - Marie-Antoinette dit « à la Rose » - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Marie-Antoinette with the Rose''; by Élisabeth Vigée Le Brun; 1783; oil on canvas; 130 x 87 cm; Palace of Versailles (Versailles, France)
Neoclassicism

Inspired by the excavations of the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman cities of
Pompeii and
Herculaneum
Herculaneum (; Neapolitan and it, Ercolano) was an ancient town, located in the modern-day ''comune'' of Ercolano, Campania, Italy. Herculaneum was buried under volcanic ash and pumice in the eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79.
Like the ...
from 1748, a renewed interest in the arts of antiquity occurred. Neoclassicism dominates Western art from the mid to late 18th century until the 1830s. Embracing order and restraint, it developed in reaction to the perceived frivolity, hedonism and decadence of Rococo and exemplifying the rational thinking of the 'Age of Enlightenment' (aka the 'Age of Reason'). Initially, the movement was developed not by artists, but by Enlightenment philosophers. They requested replacing Rococo with a style of rational art, moral and dedicated to the soul. This fitted well with a perception of Classical art as the embodiment of realism, restraint and order. Inspired by Ancient Greek art, ancient Greek and
Roman art, the classical history paintings of the French artist Nicolas Poussin (1594–1665) and the ideas of the German writer Anton Raphael Mengs (1728–1779) and the archaeologist and art historian Johann Joachim Winckelmann (1717–1768), Neoclassicism began in Rome, but soon spread throughout Europe. Rome had become the main focus of the Grand Tour by the mid-18th century, and aristocratic travellers went there in search of Classical visions to recreate on their country estates, thus spreading the style across Europe, particularly in England and France. The tour was also an opportunity for collecting Classical antiquities. Neoclassical paintings tended to be populated with figures posed like Classical statues or reliefs, set in a locations filled with archaeological details. The style favoured Greek art over Roman, considering it purer and more authentically classical in its aesthetic goal.
In 1789, France was on the brink of French Revolution, its first revolution and Neoclassicism sought to express their patriotic feelings. Politics and art were closely entwined during this period. They believed that art should be serious, and valued drawings above painting; smooth contours and paint with no discernible brushstrokes were the ultimate aim. Both painting and sculpture exerted calmness and restraint and focused on heroic themes, expressing such noble notions as self-sacrifice and nationalism.
This movement paved the way for Romanticism, that appeared when the idealism of the revolution faded away and after the Napoleonic period came to an end in the early 19th century. Neoclassicism should not be seen as the opposite of Romanticism, however, but in some ways an early manifestation of it.
Giovanni Paolo Panini - Fantasy View with the Pantheon and other Monuments of Ancient Rome - 61.62 - Museum of Fine Arts.jpg, ''Fantasy View with the Pantheon and other Monuments of Ancient Rome''; by Giovanni Paolo Panini; 1737; oil on canvas; 98.9 x 137.49 cm; Museum of Fine Arts, Houston, Museum of Fine Arts (Houston, USA)
The ancient Capitol ascended by approximately one hundred steps . . . (Campidoglio antico a cui si ascendeva per circa cento gradini . . .) MET DP827987.jpg, ''The ancient Capitol ascended by approximately one hundred steps . . .''; by Giovanni Battista Piranesi; 1750; etching; size of the entire sheet: 33.5 × 49.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
L'Hôtel de la Marine (Paris) (51346237676).jpg, Hôtel de la Marine (Paris), 1761–1770, by Ange-Jacques Gabriel
West facade of Petit Trianon 002.JPG, The Petit Trianon (Versailles, France), 1764, by Ange-Jacques Gabriel
Wright of Derby, The Orrery.jpg, ''A Philosopher Lecturing on the Orrery''; by Joseph Wright of Derby; 1766; oil on canvas; 1.47 x 2.03 m; Derby Museum and Art Gallery (Derby, England)
Osterley House, entrance hall.jpg, The Hall (Osterley Park, London), 1767, by Robert Adam
Washstand (athénienne or lavabo) MET DP106594.jpg, Washstand (athénienne or lavabo); 1800–1814; legs, base and shelf of yew wood, gilt-bronze mounts, iron plate beneath shelf; height: 92.4 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Villers Young Woman Drawing.jpg, ''Portrait of Charlotte du Val d'Ognes (Marie-Denise Villers), Portrait of Charlotte du Val d'Ognes''; by Marie-Denise Villers; 1801; oil on canvas; 161.3 x 128.6 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ingres, Napoleon on his Imperial throne.jpg, ''Napoleon I on His Imperial Throne''; by Jean-Auguste-Dominique Ingres; 1806; oil on canvas; 2.62 x 1.62 m; Army Museum (Paris), Army Museum (Paris)
Canova - The Three Graces, between 1813 and 1816, Н.ск-506.jpg, ''The Three Graces (sculpture), The Three Graces''; by Antonio Canova; 1813–1816; marble; height: 1.82 m; Hermitage Museum (Saint Petersburg, Russia)
Western art after 1770

Many art historians place the origins of modern art in the late 18th century, others in the mid 19th century. Art historian H. Harvard Arnason stated "a gradual metamorphosis took place in the course of a hundred years." Events such as the age of enlightenment, revolutions and democracies in American Revolution, America and French Revolution, France, and the Industrial Revolution had far reaching affects in western culture. People, commodities, ideas, and information could travel between countries and continents with unprecedented speed and these changes were reflected in the arts. The invention of photography in the 1830s further altered certain aspects of art, particularly painting. By the dawn of the 19th century, a long and gradual paradigm shift was complete, from the Gothic when artists were viewed as craftsmen in the service of the church and monarchies, to the idea of art for art's sake, where the ideas and visions of the individual artist were held in the high regard, with patronage from an increasingly literate, affluent, and urban middle and upper class population that had been emerging for 200 years (particularly in Paris and London). A dichotomy began in the late 18th century between neoclassicism and romanticism that subdivided and continued to run through virtually every new movement in modern art: "Spreading like waves, these "isms" defy national, ethnic, and chronological boundaries; never dominant anywhere for long, they compete or merge with each other in endlessly shifting patterns."
Modern art has consistently moved toward international influences and exchanges, from the exotic curiosity of Orientalism, the deeper influence of Japonisme, to the arts of Oceania, Africa, and the Americas. Conversely modern art has increasingly extended beyond western Europe. In Russia and the USA the arts were developing to a degree that rivaled the leading European countries by the end of the 19th century. Many of the major movements appeared in Latin America, Australia, and Asia too and geography and nationality became increasingly insignificant with each passing decade. By the 20th century important and influential artists were emerging around the world: e.g. Foujita (Japan), Arshile Gorky (Armenia), Diego Rivera and Frida Kahlo (Mexico), Wifredo Lam (Cuba), Edvard Munch (Norwegian), Roberto Matta (Chilean), Mark Rothko (Lithuanian-American), Fernando Botero Angulo (Colombia), Constantin Brâncuși and Victor Brauner (Romania).
Étienne-Louis Boullée Memorial Newton Night.jpg, ''Newton's Cenotaph, exterior by night''; by Étienne-Louis Boullée; 1784; ink and wash, 40.2 × 63.3 cm.; Bibliothèque Nationale
Goya Dog.jpg, ''The Dog (Goya), The Dog''; Francisco de Goya; ca. 1819–1823; mural transferred to canvas, 131.5 × 79.3 cm.; Museo del Prado
Joseph Mallord William Turner - Death on a pale horse - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Death on a Pale Horse''; J. M. W. Turner; c. 1830; oil on canvas, 60 × 76 cm.; Tate Britain
Honoré daumier, le celebrità dell'Aurea mediocritas, terracotta, 1832-35, charles philipon.JPG, ''Toothless Man Laughing, Charles Philipon form Célébrités du Juste milieu''; Honoré Daumier; 1832–33; painted clay, 6.12 high; Musée d'Orsay
Daguerre kynzvart.jpg, ''Kynžvart Daguerreotype, Still life with statue of Jupiter Tonans''; by Louis Jacques Daguerre; c. 1839; daguerreotype
19th century
Romanticism (c. 1790–1880)

Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century and flourished in the first half of the 19th century with significant and international manifestations in music, literature, and architecture, as well as the visual arts. It grew from a disillusionment with the rationalism of 18th century Enlightenment. Despite being often viewed as the opposite of Neoclassicism, there were some stylistic overlapping with both movements, and many Romantic artists were excited by classicism. The movement focused on intense emotions, imagination, and on the impressive power of nature, a bigger and more powerful force than the one of men, with its potential for disaster. "Neoclassicism is a new revival of classical antiquity... while Romanticism refers not to a specific style but to an attitude of mind that may reveal itself in any number of ways."
One of the earliest expressions of romanticism was in the English landscape garden, carefully designed to appear natural and standing in dramatic contrast to the formal gardens of the time. The concept of the "natural" English garden was adopted throughout Europe and America in the following decades. In architecture, the romantics frequently turned to alternative sources other than the Greek and Roman examples admired by the neo-classicist. Romantic architecture often revived Gothic architecture, Gothic forms and other styles such as exotic eastern models. The Palace of Westminster (Houses of Parliament), London is an example of romantic architecture that is also referred to as Gothic Revival. In painting romanticism is exemplified by the paintings of Francisco Goya in Spain, Eugène Delacroix and Théodore Géricault in France, William Blake, Henry Fuseli, Samuel Palmer, and J. M. W. Turner, William Turner in England, Caspar David Friedrich and Philipp Otto Runge in Germany, Francesco Hayez in Italy, Johan Christian Claussen Dahl in Norway, and Thomas Cole in America. Examples of sculptors of the romantic period include Antoine-Louis Barye, Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux, Auguste Préault, and François Rude. As romanticism ran its course, some aspects of the movement evolved into symbolism.
William Blake 008.jpg, ''Elohim Creating Adam''; by William Blake; 1795; color print finished in ink and watercolour on paper; 43.1 × 53.6 cm; Tate Britain (London)
El Tres de Mayo, by Francisco de Goya, from Prado in Google Earth.jpg, ''The Third of May 1808''; by Francisco Goya; 1814; oil on canvas; 2.68 × 3.47 m; Museo del Prado (Madrid, Spain)
JEAN LOUIS THÉODORE GÉRICAULT - La Balsa de la Medusa (Museo del Louvre, 1818-19).jpg, ''The Raft of the Medusa''; by Théodore Géricault; 1819; oil on canvas; 4.91 × 7.16 m; Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
Delacroix - La Mort de Sardanapale (1827).jpg, ''The Death of Sardanapalus''; by Eugène Delacroix; 1827; oil on canvas; 3.92 × 4.96 m; Louvre
Parliament at Sunset.JPG, Palace of Westminster (London), 1840–1870, by Sir Charles Barry and Pugin, A. Welby Pugin
Academism
Academism is the codification of art into rules that can be learned in art academies. It promotes the Classical ideals of beauty and artistic perfection. There was also a very strict hierarchy of subjects. At the top, there were paintings that depicted historic events, including the biblical and Classical antiquity, Classical ones, followed by the portrait and by the landscape. At the bottom of the hierarchy were still life and genre painting. Nicolas Poussin was the artist whose works and theories played the most significant role in the development of academism. The vales of academism were situated in the centre of the Age of Enlightenment, Enlightenment project of discovering the basic principles and ideals of art.
During the 18th century, across all Europe, many academies were founded, that will later dominate the art of the 19th century. In order to study at an art academy, young artist had to take an admission exam, and after being admitted, they would study there for multiple years. Most of the 19th century French art movements were exterior or even opposing the values of academism.
Some of the most important artists of the French academy were William Bouguereau (1825–1905), Jean-Léon Gérôme (1824–1904), Alexandre Cabanel (1823–1889) and Thomas Couture (1815–1879). Academic art is closely related to Beaux-Arts architecture, which developed in the same place and holds to a similar classicizing ideal. The Beaux-Arts style takes its name from the École des Beaux-Arts in Paris, where it developed and where many of the main exponents of the style studied.
Paris Palais Garnier 2010-04-06 16.55.07.jpg, Palais Garnier (Paris), 1860–1875, by Charles Garnier (architect), Charles Garnier
Jean-Leon Gerome Pollice Verso.jpg, ''Pollice Verso'' (Thumbs Down); by Jean-Léon Gérôme; 1872; oil on canvas; height: 96.5 cm; Phoenix Art Museum (Phoenix, Arizona, Phoenix, Arizona, USA)
The Birth of Venus by William-Adolphe Bouguereau (1879).jpg, ''The Birth of Venus (Bouguereau), The Birth of Venus''; by William-Adolphe Bouguereau; 1879; oil on canvas; 300 x 215 cm; Musée d'Orsay (Paris)
Alexandre Cabanel Phèdre.jpg, ''Phaedra''; by Alexandre Cabanel; 1880; oil on canvas; 194 x 286 cm; Musée Fabre (Montpellier, France)
The Roses of Heliogabalus.jpg, ''The Roses of Heliogabalus''; by Lawrence Alma-Tadema; 1888; oil on canvas; 1.3 x 2.1 m; private collection of Juan Antonio Pérez Simón
= Revivalism and Eclecticism
=
When it comes to architecture and applied arts, the 19th century is best known as the century of Revivalism (architecture), revivals. One of the most well-known revivalist styles is the Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival or Neo-Gothic, which first appeared in the mid-18th century in a few houses in England, like the Strawberry Hill House in London. However, these houses were isolated cases, since the beginning of the 19th century was dominated by Neoclassicism. Later, between 1830 and 1840, a taste and nostalgia for the rediscovery of past styles, ranging from the Middle Ages to the 18th century, developed under the influence of romanticism. Approximatively until World War I, rehashes of the past dominated the world of architecture and applied arts. Associations between styles and building types appeared, for example: Egyptian Revival architecture, Egyptian for prisons, Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic for churches, or Renaissance Revival architecture, Renaissance Revival for banks and exchanges. These choices were the result of other associations: the
pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: '' pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until th ...
s with death and eternity, the
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
with Christianity, or the House of Medici, Medici family with the rise of banking and modern commerce. Sometimes, these styles were also seen in a nationalistic way, on the idea that architecture might represent the glory of a nation. Some of them were seen as 'national styles', like the Gothic Revival in the UK and the German states or the Romanian Revival architecture, Romanian Revival in Romania. Augustus Pugin called the Gothic style the 'absolute duty' of the English architect, despite the fact that the style is of French origin. This way, architecture and the applied arts were used to grant the aura of a highly idealized glorious past. Some architects and designers associated historic styles, especially the medieval ones, with an idealized fantasy organic life, which they put in comparison with the reality of their time.
Despite revivalism being so prevalent, this doesn't mean that there was no originality in these works. Architects, ébénistes and other craftsmen, especially during the second half of the 19th century, created mixes of styles, by extracting and interpreting elements specific to certain eras and areas. This practice is known as ''eclecticism''. This stylistic development occurred during a period when the competition of World's Fairs motivated many countries to invent new industrial methods of creation.
File:Coin cabinet MET DP103176.jpg, Egyptian revival decorative arts, Egyptian Revival - Coin cabinet; 1809–1819; mahogany (probably Swietenia mahagoni), with applied and inlaid silver; 90.2 x 50.2 x 37.5 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
File:Vase (vase gothique Fragonard) (one of a pair) MET DP169251.jpg, Gothic Revival architecture, Gothic Revival - Pair of vases; manufactured in 1832, decorated in 1844; hard-paste porcelain; 36.4 x 32.7 x 20 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
Saint Augustin Church Paris.jpg, Eclecticism in architecture, Eclectic - Saint-Augustin, Paris, Église Saint-Augustin de Paris, 1860–1868, by Victor Baltard
Musée des arts décoratifs Gründerzeit-Büffet (1).jpg, Renaissance Revival architecture, Renaissance Revival - Buffet; by Henri-Auguste Fourdinois, Nivillier, Party, Hugues Protat, Primo and Maigret; 1867; walnut, jasper and lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mine ...
marquetry, and ivory and silver-inlayed interior; unknown dimensions; Musée des Arts décoratifs, Paris, Musée des Arts Décoratifs (Paris)
Immeuble rue La Boétie, rue de Miromesnil, Paris 8e.jpg, Rococo Revival - Apartment building no. 8 on Rue de Miromesnil (Paris), 1900, by P. Lobrot
Realism (c. 1830–1890)
Realism (art movement), Realism emerged in the mid-nineteenth century, c. 1840, and had counterparts in sculpture, literature, and drama, often referred to as Naturalism (literature), Naturalism in literature. In nineteenth-century painting, the term Realism refers more to the subject matter depicted than to the style or technique. Realist paintings typically represent ordinary places and people engaged in everyday activities, as opposed to grand, idealized landscapes, mythological gods, biblical subjects, and historical figures and events that had often dominated painting in western culture. Courbet said "I cannot paint an angel because I have never seen one".
Realism was also in part a reaction to the often dramatic, exotic, and emotionally charged work of romanticism. The term realism is applied relative to the idealized imagery of neo-classicism and the romanticized imagery of romanticism. Artists such as Jean-Baptiste-Camille Corot and Honoré Daumier had loose associations with realism, as did members of the Barbizon School, particularly Jean-François Millet, but it was perhaps Gustave Courbet who was the central figure in the movement, self identifying as a realist, advocating realism, and influencing younger artists such as Édouard Manet. One significant aspect of realism was the practice of painting landscapes en plein air and its subsequent influence on impressionism.
Beyond France, realism is exemplified by artists such as Wilhelm Leibl in Germany, Ford Madox Brown in England, and Winslow Homer in the United States. Art historian H. Harvard Arnason, H. H. Arnason wrote, "The chronological sequence of neo-classicism, romanticism, and realism is, of course, only a convenient stratification of movements or tendencies so inextricably bound up with one another and with the preceding movements that it is impossible to tell where one ended and another began", and this becomes even more pertinent and complex as one follows all of the movements and "isms" into the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
Courbet LAtelier du peintre.jpg, ''The Painter's Studio''; by Gustave Courbet; 1854–1855; oil on canvas; 3.59 x 5.98 m; Musée d'Orsay (Paris)
Jean-François Millet - Gleaners - Google Art Project 2.jpg, ''The Gleaners''; by Jean-François Millet; 1857; oil on canvas; 0.84 x 1.12 m; Musée d'Orsay
Honoré Daumier, The Third-Class Carriage - The Metropolitan Museum of Art.jpg, ''The Third-Class Carriage''; by Honoré Daumier; 1862–1864; oil on canvas; 65.4 x 90.2 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
Adolph Menzel - Eisenwalzwerk - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Iron Rolling Mill''; by Adolph von Menzel; 1875; oil on canvas; 153 x 253 cm; Alte Nationalgalerie (Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany
Germany, officially the Federal Republic of Germany (FRG),, is a country in Central Europe. It is the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany lies between the Baltic and North Sea to the north and the Alps to the sou ...
)
Impressionism (c. 1865–1885)

Impressionism emerged in France, under the influences of Realism (art movement), Realism, the Barbizon School, and en plein air painters like Eugène Boudin, Camille Corot, Charles-François Daubigny, Charles- Francois Daubigny, and Johan Barthold Jongkind. Starting in the late 1850s, several of the impressionists had made acquaintances and friendships as students in Paris, notably at the free Académie Suisse and Charles Gleyre's studio. Their progressive work was frequently rejected by the conservative juries of the prestigious Académie des Beaux-Arts, Académie des Beaux Arts salons, a forum where many artist turned to establish their reputations, and many of the young artist were included in a highly publicized, but much ridiculed Salon des Refusés in 1863. In 1874 they formed the Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, Graveurs, independent of the academy, and mounted the first of several impressionist exhibitions in Paris, through to 1886 when their eighth and final exhibition was held. Important figures in the movement included Frédéric Bazille, Gustave Caillebotte, Mary Cassatt, Paul Cézanne, Edgar Degas, Armand Guillaumin, Édouard Manet, Claude Monet, Berthe Morisot, Camille Pissarro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley. Although impressionism was primarily a movement of painters, Degas and Renoir also produced sculptures and others like Auguste Rodin and Medardo Rosso are sometimes linked to impressionism. By 1885 impressionism had achieved some prominence, and yet a younger generation were already pushing the limits beyond impressionism. Artist from Museum of Russian impressionism, Russia, Heidelberg School, Australia, American Impressionism, America and Latin America soon adopted impressionist styles. A few of the original impressionist continued producing significant work into the 1910s and 1920s.
Although not unprecedented, many of the techniques used were in contrast to traditional methods. Paintings were often completed in hours or days with wet paint applied to wet paint (opposed to wet on dry paint, completed in weeks and months). Rather than applying glazes and mixed colors, pure colors were often applied side by side, in thick, opaque, impasto strokes; blending in the eye of the viewer when observed from a distance. Black was used very sparingly, or not at all, and defining lines replaced with nuanced strokes of color forming the subjects, contours, and shapes. Art historian H. W. Janson said "instead of adding to the illusion of real space, it strengthens the unity of the actual painted surface." Impressionist paintings typically depict landscapes, portraits, still lifes, domestic scenes, daily leisure and nightlife, all treated in a realist manner. Compositions were often based on unusual perspectives, appearing spontaneous and candid. The paintings were usually void of didactic, symbolic, or metaphoric meanings, and rarely addressed the biblical, mythological, and historical subjects that were so highly regarded by the academies or the darker and psychological interest explored by the symbolist. The nuances of light, shadow, atmosphere, and reflections of colors from surfaces were examined, sometimes emphasizing changes of these elements in time. The painting itself was the subject of the painting. It was art for art's sake, an idea that had been floating around for a few of decades but it perhaps reached a new high and consistency in impressionism.
Edgar Degas - At the Races in the Countryside - Google Art Project.jpg, ''At the Races in the Countryside''; by Edgar Degas; 1869; oil on canvas; 36.5 x 56 cm; Museum of Fine Arts (Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, USA)
Claude Monet, 1873-74, Boulevard des Capucines, oil on canvas, 80.3 x 60.3 cm, Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art, Kansas City.jpg, ''Boulevard des Capucines (Monet), Boulevard des Capucines''; by Claude Monet; 1873; oil on canvas; 80.5 x 60.2 cm; Nelson-Atkins Museum of Art (Kansas City, Missouri, Kansas City, Missouri, USA)
Camille Pissarro - Gelée blanche, ancienne route d´Ennery, Pontoise - 1873.jpg, ''Hoarfrost: Old Road to Ennery, Pontoise''; by Camille Pissarro; 1873; oil on canvas; 64.7 x 92.6 cm; Musée d'Orsay (Paris)
Alfred Sisley, L'automne - Bords de la Seine pres Bougival (Autumn - Banks of the Seine near Bougival), 1873.jpg, ''Banks of the Seine near Bougival''; by Alfred Sisley; 1873; oil on canvas; 46.2 x 62.1 cm; Montreal Museum of Fine Arts (Montreal, Canada)
Pierre-Auguste Renoir 023.jpg, ''La Loge''; Pierre-Auguste Renoir; 1874; oil on canvas; 80 x 63.4 cm; Courtauld Gallery (London)
Gustave Caillebotte - The Floor Planers - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Les raboteurs de parquet, The Floor Scrapers''; by Gustave Caillebotte; 1875; oil on canvas; 1 x 1.54 m; Musée d'Orsay
Gustave Caillebotte - Paris Street; Rainy Day - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Paris Street; Rainy Day''; by Gustave Caillebotte; 1877; oil on canvas; 2.12 x 2.76 cm; Art Institute of Chicago
Berthe Morisot - Sommertag - 1879.jpeg, ''Summer's Day''; by Berthe Morisot; 1879; oil on canvas; 45.7 cm × 75.2 cm; National Portrait Gallery, London, National Portrait Gallery (London)
Edouard Manet, A Bar at the Folies-Bergère.jpg, ''A Bar at the Folies-Bergère''; by Édouard Manet; 1881–1882; oil on canvas; 0.96 × 1.30 cm.; Courtauld Institute of Art (London)
Nicolae Grigorescu - Car cu boi (8).jpg, ''Ox-Drawn Cart''; by Nicolae Grigorescu; 1899; oil on canvas; 66 x 81 cm; National Museum of Art of Romania (Bucharest, Romania)
Symbolism (c. 1860–1915)
Symbolism emerged in France and Belgium in the 3rd quarter of the nineteenth century and spread throughout Europe in the 1870s, and later to America to a lesser extent. It evolved from romanticism without a clear or defining demarcation point, although poetry, literature, and specifically the publication of Charles Baudelaire's ''Les Fleurs du mal'' (''The Flowers of Evil'') in 1857 were significant in the development of symbolism. It had international expression in poetry, literature, drama, and music. In architecture, the applied arts, and decorative arts symbolism closely paralleled and overlapped into Art Nouveau. Symbolism is often inextricably linked to other contemporary art movements, surfacing and finding expression within other styles like Post-Impressionism, Les Nabis, the Decadent Movement, the Fin de siècle, Fin-de Siecle, Art Nouveau, The Munich Secession, The Vienna Secession, Expressionism, and even the Pre-Raphaelites, which had formed before and influenced symbolism as well. Artist as diverse as James McNeill Whistler, Eugène Carrière, Ferdinand Hodler, Fernand Khnopff, Giovanni Segantini, Lucien Lévy-Dhurmer, Jean Delville, and James Ensor all had varying degrees of association with symbolism. Art historian Robert L. Delevoy wrote "Symbolism was less a school than the atmosphere of a period." It quickly began to fade with the onset of Fauvism, Cubism, Futurism and had largely dissipated by the outbreak of the First World War, however it did find some sustained development and relevance in the Metaphysical art, metaphysical school, which in turn had a profound influence on surrealism.
The subjects, themes, and meanings of symbolist art are frequently veiled and obscure, but at its best still manage to resonate deeply on psychological or emotional levels. The subjects are often presented as metaphors or allegories, aiming to evoke highly subjective, personal, introspective emotions and ideas in the viewer, without clearly defining or addressing the subject directly. The poet Stéphane Mallarmé wrote "depict not the thing but the effect it produces"
and "To name an object is to suppress three quarters of the pleasure of the poem which is made to be understood little by little". The English painter George Frederic Watts stated "I paint ideas, not things."
Head of Orpheus.jpg, ''Thracian Girl with Head of Orpheus on his Lyre''; by Gustave Moreau; 1865; oil; 154 × 99.5 cm; Musée d'Orsay (Paris)
La vision après le sermon (Paul Gauguin).jpg, ''Vision After the Sermon'' (Jacob Wrestling with the Angel); 1888; oil on canvas; 73 x 92 cm; Scottish National Gallery (Edinburgh, Scotland)
Edvard Munch, 1893, The Scream, oil, tempera and pastel on cardboard, 91 x 73 cm, National Gallery of Norway.jpg, ''The Scream''; by Edvard Munch; 1893; tempera and crayon on cardboard; 91 x 73.5 cm; National Gallery (Norway), National Gallery (Oslo, Norway)
Redon - Green Death c. 1905.jpg, ''Green Death''; by Odilon Redon; 1905; oil on canvas; 54.9 x 46.3 cm; Museum of Modern Art
Odilon Redon - The Cyclops, c. 1914.jpg, ''The Cyclops (Redon), The Cyclops''; by Odilon Redon; 1914; oil on cardboard on panel; 64 x 51 cm; Kröller-Müller Museum (Otterlo, the Netherlands)
Post-Impressionism (c. 1885–1910)
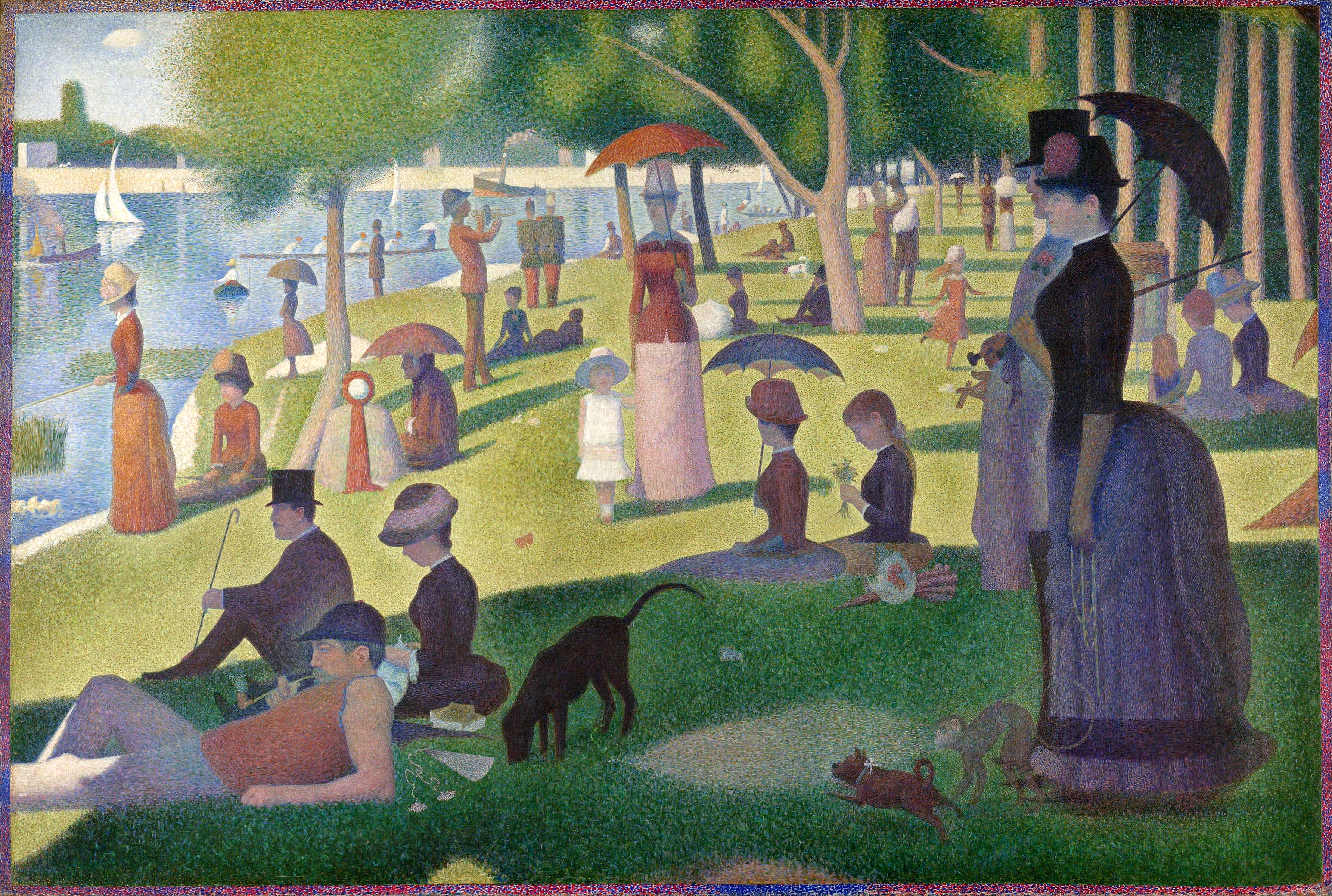
Post-Impressionism is a rather imprecise term applied to a diverse generation of artists. In its strictest sense, it pertains to four highly influential artists: Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat, and Vincent van Gogh. Each passed through an impressionist phase, but ultimately emerged with four very original but different styles. Collectively, their work anticipated, and often directly influenced, much of the avant-garde art that appear before the First World War including fauvism, cubism, expressionism, and early abstraction. Cézanne (particularly influential on cubism) and Van Gogh worked in relative isolation, away from Paris, at critical points in their careers, while Seurat and Gauguin worked in groups, more collaboratively, at key points in their development. Another important artist of the period is Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Toulouse-Lautrec, an influential painter as well as graphic artist. In a broader sense, post-impressionism includes a generation of predominantly French and Belgian artist who worked in a range of styles and groups. Most had come under the sway of impressionism at some point, but pushed their work beyond it into a number of factions as early as the mid-1880s, sometimes as a logical development of impressionism, other times as a reaction against it. Post-Impressionists typically depicted impressionist subjects, but the work, particularly synthetism, often contained symbolism, spiritualism, and moody atmospheres that rarely appeared in impressionism. Unnatural colors, patterns, flat plains, odd perspectives and viewpoints pushed to extremes, all moved the center of modernism a step closer to abstraction with a standard for experimentation.
Neo-Impressionism (Divisionism or Pointillism, c. 1884–1894) explored light and color based on scientific color theories, creating mosaics of brush strokes in pure colors, sometimes laid out in rhythmic patterns with lines influenced by Art Nouveau. The leading artists were Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, others include Henri-Edmond Cross, Maximilien Luce, Albert Dubois-Pillet, and for a period Pissarro and Van Gogh. It was influential on fauvism, and elements of the style appeared in expressionism, cubism, and early abstraction. Synthetism (Cloisonnism c. 1888–1903) Cloisonnism was conceived by Émile Bernard and immediately taken up and developed by Paul Gauguin and others while at an artists' colony in Pont-Aven (Brittany, France). The style resembled cloisonné enamel or stained glass, with flat, bold colors outlined in black or dark colors. Synthetism, exemplified in the work of Gauguin and Paul Sérusier, is slightly a broader term with less emphasis on dark outlines and cloisonné qualities. Other artist include Cuno Amiet, Louis Anquetin, Charles Filiger, Meyer de Haan, Jacob Meyer de Haan, Charles Laval, and Armand Séguin (painter), Armand Seguin. Their work greatly influenced fauvism and expressionism. Les Nabis (c. 1890–1905: Hebrew for prophets or illuminati) was a larger movement in France and Belgium that eclectically drew on progressive elements in synthetism, neo-impressionism, symbolism, and Art Nouveau. Perhaps more influential than the art, were the numerous theories, manifestoes, and infectious enthusiasm for the avant-garde, setting the tone for the proliferation of movements and "isms" in the first quarter of the 20th century. La Revue Blanche often published Les Nabis and symbolist content. The work of Édouard Vuillard, and Pierre Bonnard, ca. 1890–1910 is exemplary of Les Nabis, though both evolved in their styles and produced significant work into the 1940s. Other artist include Maurice Denis, Maxime Dethomas, Meyer de Haan, Henri-Gabriel Ibels, Georges Lacombe (painter), Georges Lacombe, Aristide Maillol, Paul Ranson, Ker-Xavier Roussel, Armand Séguin, Paul Sérusier, Félix Vallotton, Jan Verkade, and others.
Van Gogh - Starry Night - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Starry Night''; by Vincent van Gogh; 1889; oil on canvas; height: 73.7 cm; Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
Signac - Portrait de Félix Fénéon.jpg, ''Opus 217. Against the Enamel of a Background Rhythmic with Beats and Angles, Tones, and Tints, Portrait of M. Félix Fénéon in 1890, Félix Fénéon''; by Paul Signac; 1890; oil on canvas; 73.5 x 92.5 cm; Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
Eh quoi! Tu es jaloux? by Paul Gauguin.jpg, ''Aha Oe Feii?'' (Are You Jealous?); by Paul Gauguin; 1892; oil on canvas; 68 x 92 cm; Pushkin Museum (Moscow, Russia)
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, At the Moulin Rouge.jpg, ''At the Moulin Rouge''; by Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec; 1892/1895; oil on canvas, 1.23 × 1.41 m; Art Institute of Chicago
Paul Cézanne, French - The Large Bathers - Google Art Project.jpg, ''The Bathers (Cézanne), The Bathers''; by Paul Cézanne; 1898–1905; oil on canvas; 210.5 cm × 250.8 cm; Philadelphia Museum of Art (Philadelphia, USA)
Early 20th century
The history of 20th-century art is a narrative of endless possibilities and the search for new standards, each being torn down in succession by the next. The art movements of Fauvism, Expressionism, Cubism, abstract art, Dadaism and Surrealism led to further explorations of new creative styles and manners of expression. Increasing globalization, global interaction during this time saw an equivalent influence of other cultures into Western art, such as Pablo Picasso being influenced by Iberian sculpture, African art, African sculpture and Primitivism. Japonism, and Japanese woodcuts (which had themselves been influenced by Western Renaissance draftsmanship) had an immense influence on Impressionism and subsequent artistic developments. The influential example set by Paul Gauguin's interest in Oceanic art and the sudden popularity among the Connoisseur, cognoscenti in early 20th century Paris of newly discovered African fetish sculptures and other works from non-European cultures were taken up by Picasso, Henri Matisse, and many of their colleagues. Later in the 20th century, Pop Art and Abstract Expressionism came to prominence.
Art Nouveau (c. 1890–1914)

Art Nouveau (french: new art) was an international and widespread art and design movement that emerged in the final decades of the 19th century until the First World War in 1914. It was catapulted into international prominence with the Exposition Universelle (1900), 1900 Exposition Universelle in Paris. Developing almost simultaneously in parts of Europe and the US, it was an attempt to create a unique and modern form of expression that evoked the spirit of the new century. It manifested in painting, illustration, sculpture, jewellery, metalwork, glass, ceramics, textiles, graphic design, furniture, architecture, costume design and fashion. Art Nouveau artists aimed to raise the status of craft and design to the level of
fine art.
The movement is highly associated with sinuous organic forms, such as flowers, vines and leaves, but also insects and animals, through the works of artists like Alphonse Mucha, Victor Horta, Hector Guimard, Antoni Gaudí, René Lalique or Émile Gallé. Art Nouveau designs and buildings can often be asymmetrical. Although there are identifying characteristics, the style also displayed many regional and national interpretations.
Despite being a short-lived fashion, it paved the way for the modern architecture and design of the 20th century. It was the first architectural style without historic precedent, the 19th century being notorious for a practice known as Historicism (art), Historicism, which is the use of visual styles that consciously echo the style of a previous artistic era. Between 1870 and 1900, a crisis of historicism occurred, during which the historicist culture was critiqued, one of the voices being Friedrich Nietzsche in 1874, who diagnosed 'a malignant historical fervour' as one of the crippling symptoms of a modern culture burdened by archaeological study and faith in the laws of historical progression. Despite this, Art Nouveau was also heavily influenced by styles from the past such as Celtic art, Celtic, Gothic art, Gothic and Rococo art, and also by the Arts and Crafts movement, Aestheticism, Symbolism (arts), Symbolism and especially by Japanese art.
Aubrey Beardsley - The Climax.jpg, ''The Climax (illustration), The Climax'', illustration for Oscar Wilde's ''Salome (play), Salome''; by Aubrey Vincent Beardsley; 1893; line block print; 34 × 27 cm; private collection
Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec - Divan Japonais - Google Art Project.jpg, ''Divan Japonais (lithograph), Divan Japonais''; by Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec; 1893–1894; lithograph; 81 × 62.3 cm; Museum of Fine Arts (Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
, USA)
Le Printemps - Eugène Grasset - 8003.jpg, ''Le Printemps''; by Eugène Grasset (designer) and Félix Gaudin (glazier); 1894; glass and lead; 298 x 136 cm; Musée des Arts décoratifs, Paris, Musée des Arts Décoratifs (Paris)Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
)
Alfons Mucha - 1896 - Biscuits Lefèvre-Utile.jpg, ''Biscuits Lefèvre-Utile'', advertisement; by Alfons Mucha; 1897; lithograph; 62 × 43.5 cm; private collection
René lailique, pettorale libellula, in oro, smalti, crisoprazio, calcedonio, pietre lunari e diamanti, 1897-98 ca. 01.jpg, The ''Dragonfly brooch''; by René Lalique; 1897–1898; gold, vitreous enamel, chrysoprase, chalcedony, moonstone (gemstone), moonstone and diamond; height: 23 cm, width: 26.5 cm; Calouste Gulbenkian Museum (Lisboa, Portugal)
Émile gallé, bureau 'foresta lorenese', 1900.JPG, Desk (Art Nouveau), presented at the Exposition Universelle (1900), 1900 Paris Exposition; by Émile Gallé; 1900; molded and carved oak, with chiseled and patinated bronze; height: 108.5 cm; Musée d'Orsay (Paris)
Fauvism (c. 1898–1909)
Fauvism emerged from post-impressionism, gradually developing into the first major movement of the 20th century. Its genesis was in 1895 when Henri Matisse, the oldest and central figure, entered the studio of Gustave Moreau at the Ecole des Beaux Arts (Paris), Ecole des Beaux-Arts. There he met Georges Rouault, Charles Camoin, Henri Manguin, and Albert Marquet. Marquet said "As early as 1898 Matisse and I were working in what was later to be called the Fauve manner. The first exhibitions at the Indepéndants in which we were, I believe, the only ones to paint in pure tones, go back to 1901." By 1902–03 the circle of like-minded artist had grown to include Georges Braque, André Derain, Raoul Dufy, Othon Friesz, Jean Metzinger, Jean Puy, Louis Valtat, Kees van Dongen, and Maurice de Vlaminck. During this period a number of influential retrospective exhibitions were held in Paris: Seurat (1900, 1905), Van Gogh (1901, 1905), Toulouse-Lautrec (1902), Gauguin (1906), Cézanne (1907), all relatively unknown to the public at that time. Matisse and Derain collected African carvings, a novel but growing curiosity of the time. Matisse spent the summer of 1904 in Saint-Tropez painting with the neo-impressionist Paul Signac and Henri-Edmond Cross, followed in 1905 by Camoin, Manguin, and Marquet. The artist exhibited regularity at the Salon Des Independants, Salon des Indepéndants and the Salon d'Automne 1903–1908 and in 1905 their work created a sensation and a scandal. Matisse stated "We were exhibiting at the Salon d'Automne, Derain, Manguin, Marquet, Puy, and a few others were hung together in one of the larger galleries. In the center of this room the sculptor Albert Marque, Marque exhibited a bust of a child very much in the Italian style. Louis Vauxcelles, Vauxcelles [art critic for Gil Blas (periodical), Gil Blas] entered the room and said, Well! well! Donatello in the mist of wild beasts! [Donatello chez les fauves]." The movement had not been perceived as an entity by the public, but once published the name stuck. Unlike the impressionist and their long struggle for acceptance, the avant-garde had an eager audience by 1906–1907 and the fauvist were attracting collectors from America to Russia. However fauvism largely dissolved in 1908, as cubism appeared, most of the artist began exploring other styles and moving in different directions. Only Matisse and Dufy continued to explore fauvism into the 1950s.
[Diehl, Gaston (1972) The Fauves: Library of Great Art Movements. Harry N. Abrams, Inc., Publishers, New York. 168 pp. ][Jacobus, J. (1973) Matisse: Library of Great Painters. Harry N. Abrams, Inc., Publishers, New York, 184 pp.]
The fauvist painted landscapes en plein air, interiors, figures, and still lifes, following examples of realism, impressionism, and post-impressionism. They applied paint with loose brushstrokes, in thick, unnatural, often contrasting, vibrant colors, at times straight from the tube. Gauguin's influence, with his exploration of the expressive values and spatial aspects of patterning with flat, pure colors, as well as his interest in primitivism were significant, as was neo-impressionism. Matisse explained – for a long time color served as a complement of design, the painters of the Renaissance constructed the picture by line, adding local color afterwards – writing: "From Eugène Delacroix, Delacroix to Van Gogh and chiefly to Gauguin, by way of the Impressionist, who cleared the ground, and Cézanne, who gave the final impulse and introduced colored volumes, we can follow this rehabilitation of color's function, this restoration of its emotive power" Fauvism was the culmination in a shift, from drawing and line as the fundamental foundations of design in painting to color, and they depicted their subjects on the verge of abstraction.
Expressionism (c. 1905–1930)
Expressionism was an international movement in painting, sculpture, the graphic arts, poetry, literature, theater, film, and architecture. Some associate the Second Viennese School and other music of the period with the movement. Most historians place the beginning of expressionism in 1905 with the founding of the Die Brücke. However, several artist were producing influential work that was in the spirit of expressionism c. 1885–1905 including Lovis Corinth, James Ensor, Käthe Kollwitz, Paula Modersohn-Becker, Edvard Munch, Emil Nolde, and Christian Rohlfs among others. Many of these artist later exhibited and associated with various expressionist groups. Expressionist painting is characterized by loose, spontaneous, frequently thick, impasto brushwork. It often conveyed how the artist felt about their subject, opposed to what it looked like, putting intuition and gut feelings over realistic representations or art theories. Expressionism was frequently infused with an angst or joy, and an overall engagement with contemporary life and social issues that was often absent from fauvism's focus on design and color applied to neutral subjects. Woodcut prints are particularly noteworthy in expressionism. Expressionism can sometimes overlap and integrate with other styles and movements, such as Symbolism (arts), symbolism, fauvism, cubism, futurism, abstraction, and dada. Several groups and factions of expressionist appeared at various times and places.
Die Brücke (The Bridge: 1905 -1913) aspired to connect "all revolutionary and surging elements." It was founded by four architectural students Ernst Ludwig Kirchner, Erich Heckel, Karl Schmidt-Rottluff, and Fritz Bleyl. Sharing a studio in Dresden they produced paintings, carvings, prints, and organized exhibitions, separating in the summer to work independently. Their first exhibit was in 1905, later joined by Emil Nolde and Max Pechstein in 1906, and Otto Mueller in 1910 among others. Influences included Gothic art, primitivism, Art Nouveau, and developments in Paris, particularly Van Gogh and fauvism. The group shifted to Berlin in 1911 and later dissolved in 1913. Der Blaue Reiter (The Blue Rider: 1911–1914), founded by Wassily Kandinsky and Franz Marc, was a relatively informal group that organized exhibitions of art from Paris and Europe, as well their own. It was one in a series of increasingly progressive groups splitting from the Art Academy in Munich including The Munich Secession in 1892 (realist and impressionist), Phalanx in 1901 (postimpressionist), Neue Künstlervereinigung München, Neue Kunstler Vereiningung in 1909, and The Blue Rider in 1911. Artist associated with the latter two groups included the David Burliuk, Burliuk brothers, Heinrich Campendonk, Alexej von Jawlensky, Paul Klee, August Macke, Gabriele Münter, and Marianne von Werefkin. The euphonious almanac ''Der Blaue Reiter'', a collection of influential essays, and Kandinsky's ''Concerning the Spiritual in Art'' with his ideas on non-objective art were both published in 1912. The Blue Rider ended with the outbreak of World War I in which Macke and Marc both died.
Other artists such as Oskar Kokoschka, Egon Schiele, and Richard Gerstl emerged in Austria. French artist Georges Rouault and Chaïm Soutine had affinities with the movement. Sculptors include Ernst Barlach, Wilhelm Lehmbruck, Gerhard Marcks, and William Wauer. Architects associated with expressionism include Max Berg, Hermann Finsterlin, Johann Friedrich Höger, Michel de Klerk, Erich Mendelsohn, Hans Poelzig, Hans Scharoun, Rudolf Steiner, and Bruno Taut. Der Sturm (The Storm 1910–1932) was a magazine with much expressionist content founded by Herwarth Walden, with an associated gallery in Berlin opened in 1912 and a theater company and school in opened 1918. Films regarded as expressionistic, some considered as classics, include ''The Cabinet of Dr. Caligari'' (Robert Wiene, 1920), ''Nosferatu'' (F. W. Murnau,1922), and ''Metropolis (1927 film), Metropolis'' (Fritz Lang, 1927).
After World War I a tendency to withdraw from the avant-garde by many artist occurred, seen in the work of the original fauvists during the 1920s, Picasso and Igor Stravinsky, Stravinsky's neoclassical periods, and Giorgio de Chirico, De Chirico's late work. This tendency was called New Objectivity (ca. 1919–1933) in Germany, and in contrast to the nostalgic nature of this work elsewhere, it was characterized by disillusionment and ruthless social criticisms. New objectivity artists mostly emerged from expressionist and dada milieus including Otto Dix, Christian Schad, Rudolf Schlichter, Georg Scholz, and Jeanne Mammen. Max Beckmann and George Grosz also had some association with new objectivity for a period. Although not intrinsically expressionistic, the Staatliches Bauhaus (School of Building: 1919–1933) was an influential German school merging crafts, decorative, and fine arts. Moving from Weimar, to Dessau, to Berlin, it changed and evolved in focus with time. Directors included architects Walter Gropius (1919–1928), Hannes Meyer (1928–1930), and Ludwig Mies van der Rohe (1930–1933). At various points the faculty included Josef Albers, Theo van Doesburg, Lyonel Feininger, Johannes Itten, Paul Klee, Wassily Kandinsky, El Lissitzky, Gerhard Marcks, László Moholy-Nagy, Oskar Schlemmer. Bauhaus architects greatly influenced the International Style (architecture), International Style, which was characterized by simplified forms, a lack of ornamentation, a union of design and function, and the idea that mass production could be compatible with personal artistic vision. As the Nazi Party rose to power, modern art was dubbed "degenerate art" and the Bauhaus was closed in 1933, subduing modernism in Germany for several years.
Edvard Munch, 1893, The Scream, oil, tempera and pastel on cardboard, 91 x 73 cm, National Gallery of Norway.jpg, ''The Scream''; by Edvard Munch; 1893; tempera and crayon on cardboard; 91 x 73.5 cm; National Gallery of Norway (Oslo)
Franz Marc 028.jpg, ''Tower of Blue Horses''; by Franz Marc; 1912; ink and guache on card; 14.3 x 9.4 cm; Bavarian State Painting Collections (Munich, Germany)
Wassily Kandinsky Composition VII.jpg, ''Composition VII''; by Wassily Kandinsky; 1913; oil on canvas; 2 x 3 m; Tretyakov Gallery (Moscow, Russia)
Einsteinturm 7443a.jpg, The Einstein Tower (Potsdam, near Berlin
Berlin is Capital of Germany, the capital and largest city of Germany, both by area and List of cities in Germany by population, by population. Its more than 3.85 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European U ...
, Germany), 1920–1924, by Erich Mendelsohn
Paul klee actors mask 1924.jpg, ''Actor's Mask''; by Paul Klee; 1924; oil on canvas mounted on board; 36.7 x 33.8 cm; Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
Cubism (c. 1907–1914)
Cubism consisted in the rejection of perspective, which leads to a new organisation of space where viewpoints multiply producing a fragmentation of the object that renders the predilection for form over the content of the representation obvious. Pablo Picasso, Georges Braque and other Cubist artists were inspired by the sculptures of Iberian sculpture, Iberia, African art, Africa and Oceanic art, Oceania exhibited in the
Louvre
The Louvre ( ), or the Louvre Museum ( ), is the world's most-visited museum, and an historic landmark in Paris, France. It is the home of some of the best-known works of art, including the ''Mona Lisa'' and the ''Venus de Milo''. A central l ...
and the ethnographic museum in the Trocadéro, and which were being offered at flee markets and in sale rooms.
'A Picasso studies an object the way a surgeon dissects a corpse,' wrote the critic and poet Guillaume Apollinaire in 1913. Five years earlier, Pablo Picasso and Georges Braque – friends, colleagues and rivals – had begun to reject perspectival Realism (arts), realism for a form of artistic autopsy: an utterly revolutionary painting style that looked inside and around objects, presenting them analytically, objectively and completely impersonally.
Les Demoiselles d'Avignon.jpg, ''Les Demoiselles d'Avignon''; by Pablo Picasso; 1907; oil on canvas; 2.43 × 2.3 m; Museum of Modern Art
Georges Braque, 1909-10, Pitcher and Violin, oil on canvas, 116.8 x 73.2 cm, Kunstmuseum Basel.jpg, ''Violin and Pitcher''; by Georges Braque; 1909–1910; oil on canvas; 1.17 x 0.73 cm; Kunstmuseum Basel (Basel, Switzerland)
Robert Delaunay - Eiffel Tower - 1911 - Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum.jpg, ''Eiffel Tower (Delaunay series), The Eiffel Tower''; by Robert Delaunay; 1911; oil on canvas; 2.02 x 1.38 m; Solomon R. Guggenheim Museum (New York City)
1914 Gris Le Petit Déjeuner.jpg, ''Breakfast''; by Juan Gris; 1914; gouache, oil and crayon on cut-and-pasted printed paper on canvas; 80.9 x 59.7 cm; Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
Art Deco (c. 1920–1940)
Art Deco appeared in France as a style of luxury and modernity. Soon, it spread quickly throughout the world, most dramatically in America, becoming more Streamline Moderne, streamlined though the 1930s. The style was named after the International Exhibition of Modern Decorative and Industrial Arts held in Paris in 1925. Its exuberance and fantasy captured the spirit of the 'roaring 20s' and provided an escape from the realities of the Great Depression during the 1930s. It had ancient Greek art, ancient Greek, Roman art, Roman, African art, African, Aztec and Japanese art, Japanese influences, but also Futurism, Futurist, Cubism, Cubist and Bauhaus ones. It sometimes blended with the Egyptian Revival architecture, Egyptian Revival style, due to the discovery in 1922 of the Tomb of Tutankhamun and the Egyptomania that it caused. Two examples of this are Le Louxor Cinema in Paris, 1919–1921, by Henri Zipcy, and the Egyptian Theatre (DeKalb, Illinois), Egyptian Theatre in DeKalb, Illinois, DeKalb (Illinois, USA), 1929–1930, by Elmer F. Behrns. In decorative arts, including architecture, low-relief designs, and angular patterns and shapes were used. Predominant materials include chrome plating, chrome, brass, polished steel and aluminum, inlaid wood, stone and stained glass.
Some of the most important Art Deco artists are the Paris-based Polish painter Tamara de Lempicka, the Ukrainian-born French poster artist Adolphe Jean-Marie Mouron, known as Cassandre, and the French furniture designer and interior decorator Émile-Jacques Ruhlmann.
Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann (French, 1879-1933). Corner Cabinet, ca. 1923..jpg, Corner Cabinet; by Emile-Jacques Ruhlmann; 1923; kingwood (amaranth) veneer on mahogany, and ivory inlay; 126.7 x 80.6 x 59.7 cm; Brooklyn Museum (New York City)
"Fortissimo" MET DP292823.jpg, ''Fortissimo''; by Séraphin Soudbinine; 1925–1926; lacquered wood, eggshell, mother-of-pearl, and gold; 248.9 x 88.9 x 3.8 cm; Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
(New York City)
La samaritaine as seen from the Pont Neuf.jpg, La Samaritaine (Paris), 1926–1928, by Henri Sauvage
Chrysler Building spire, Manhattan, by Carol Highsmith (LOC highsm.04444).png, Chrysler Building (New York City), 1930, by William Van Allen
Biarritz - Musée de la mer.jpg, Biarritz Aquarium, Musée de la Mer (Biarritz, France), 1933, by Joseph Hiriart
Surrealism (c. 1924–1966)
Surrealism emerged as a faction of Dada, formally announcing its inception in 1924 with André Breton's ''Manifesto of Surrealism''. Originally a literary group of poets and writers in Paris, it soon developed into an international movement that included painters, sculptors, photographers, and filmmakers. A ''Second Manifeste du Surréalisme'' was published in 1929. Surrealism did not have significant expression in applied or decorative arts, architecture, or music, although a few isolated examples could be identified (e.g. chess sets, furniture, and Las Pozas). The small and short lived Metaphysical art, Metaphysical School (c. 1910–1921), with Giorgio de Chirico as its principal figure, was highly influential on surrealism. The surrealist explored a myriad of innovative techniques, some had recently been developed in Cubism and Dada, others were new, including collage, found objects, assemblage, random chance, rayographs (photograms), painting on sand, dripping and flinging paint, decalcomania, Frottage (art), frottage, fumage, and raclage. Two fundamental approaches predominate surrealist art. Surrealist automatism, Automatism dominated in the early years which can be seen in the work of artist like André Masson and Joan Miró. Other artist, swayed by work of Giorgio de Chirico, used more traditional methods and mediums to illustrate unfiltered thoughts and incongruous juxtapositions, including Salvador Dalí and René Magritte. Significant artist include Jean Arp, Hans Bellmer, Victor Brauner, Luis Buñuel, Joseph Cornell, Óscar Domínguez, Max Ernst, Wifredo Lam, Yves Tanguy, Man Ray, Alberto Giacometti, Méret Oppenheim, and Roberto Matta. Other important artist informally accosted with surrealism include Marcel Duchamp, Pablo Picasso, and Frida Kahlo. Surrealist ideas and theories were discussed in a successive series of journals, ''La Révolution Surréaliste'' (1924–1929), ''Le Surrealisme au service de la revolution'' (1930–1933), ''Minotaure'' (1933–1939), ''VVV (magazine), VVV'' (1942–1944). The automatic paintings produced by André Masson and Joan Miró, as well as latecomers to surrealism like Roberto Matta and Arshile Gorky had a considerable influenced on the abstract expressionist in the late 1940s.
With a measure of Dada's irreverence and contempt for the traditional political, religious, and bourgeois values of western culture that they believed had led the world into the First World War (Breton and other founding members were veterans); the surrealist explored the possibilities that had been opened up by Sigmund Freud regarding the subconscious mind: "Pure psychic automatism, by which one intends to express verbally, in writing or by any other method, the real functioning of the mind. Dictation by thought, in the absence of any control exercised by reason, and beyond any aesthetic or moral preoccupation." Surrealism sought to express pure thought, unfiltered and uncensored by political, religious, moral, or rational principles.
File:De Chirico's Love Song.jpg, ''The Song of Love''; by Giorgio de Chirico; 1914; oil on canvas; 73 x 59.1 cm; Museum of Modern Art (New York City)
The Elephant Celebes.jpg, ''The Elephant Celebes''; by Max Ernst; 1921; oil on canvas; 125.4 × 107.9 cm; Tate Modern (London)
Time Transfixed.jpg, ''Time Transfixed''; by René Magritte; 1938; oil on canvas; 1.47 × 0.99 cm.; Art Institute of Chicago
Mid and late 20th century
As Europe struggled to recover from World War II, America moved into a position of political, economic and cultural strength. During the 1940s and 1950s, Abstract Expressionism emerged as the first specifically American art movement to have an international impact. In consequence, the art world's focus shifted from Europe to New York. Abstract Expressionists were a small group of loosely associated artists who had similar outlooks but different approaches. They were influenced by Surrealism, and believed in spontaneity, freedom of expression and abandonment of the themes of American life that had characterized national art of recent decades. One of the most famous representative of this movement was Jackson Pollock, known for his painting made by pouring, flicking and dripping paint on to huge canvases on the ground. Other artists include Willem de Kooning, Franz Kline, Robert Motherwell, Barnett Newman, Mark Rothko and Clyfford Still.
After World War II, consumerism and the mass media surged, and as a result, Pop art developed in both London and New York. In a London exhibition in 1956, the word 'Pop' was used in a collage created by Richard Hamilton (artist), Richard Hamilton (1922–2011) made of American magazines. Pop art was a reaction against Abstract Expressionism, and interpreted ideas of pop culture. In celebrating and commenting on consumerism, pop artists, as they became known, produced colorful images based on advertising, the media and shopping, featuring film stars, comic strips, flags, packaging and food – things that everyone, rather than just a highbrow few, could relate to.
The term Minimalism (visual arts), Minimalism was not new, but it gained momentum in the 1960s, specifically describing a style of art characterized by detached restraint. Originating in New York, it was a reaction against Abstract Expressionism, but it also embraced Constructivism (art), Constructivist ideas that art should be made of modern materials. Thus, Minimalist artists, primarily sculptors, often used non-traditional materials and production methods, often employing industrial or specialist fabricators to produce works to their specifications. The term was chiefly used to describe a group of American sculptors who re-evaluated the space around them, aiming to challenge assumptions and present familiar objects in new ways. Their artworks don't have any symbolism or hidden meaning, as they try to enable viewers to re-evaluate art and space around forms. Unlike a figural sculpture on which the viewer focuses to the exclusion of the room in which it stands, Minimalist art becomes one with its space. By focusing on the effects of context and the theatricality of the viewing experience, Minimalism exerted an indirect but powerful influence on later developments in Conceptual art, Conceptual and Performance art, as well as providing a foil for the rise of Postmodernism.
Despite developing almost 50 years after Marcel Duchamp's ideas, Conceptual art showed that art does not always have to be judged aesthetically. It was never a single, cohesive movement, but an umbrella term that now covers several types of art and emerged more or less concurrently in America and Europe, first defined in New York. Conceptual artists promote the art of ideas, or concepts, suggesting that they can be more valid in the modern world than technical skill or aesthetics. No matter the art media of an artwork, it is considered as no more than a vehicle for presenting the concept. At its most extreme, Conceptual art foregoes the physical object completely, using verbal or written message to convey the idea.
Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, USA)
See also
* Art of Europe
* Art market
* Art movement
* Art periods
* Ancient art
* History of animation
* History of Asian art
* History of film
* History of literature
* History of music
* History of nude art
* History of painting
* History of photography
* History of poetry
* History of theatre
* List of art movements
* List of French artistic movements
* List of music styles
* Timeline for invention in the arts
* Timeline of art
* Western art history
* Women artists
Notes
References
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
"Art: The history of ideas in literature and the arts in aesthetic theory and literary criticism"nbsp;– ''The Dictionary of the History of Ideas''
Ars Summum Project
Timelines
''Timeline of Art History''from
Metropolitan Museum of Art
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 100 ...
{{DEFAULTSORT:History Of Art
Art history,
Art historians,
 Th first metal objects produced in China were made almost 4000 years ago, during the
Th first metal objects produced in China were made almost 4000 years ago, during the  The ancient civilizations of Peru and Bolivia nurtured unique artistic traditions, including one of the world's most aesthetically impressive fibre art traditions. Two of the first important cultures from this land are the Chavín culture, Chavín and the Paracas culture.
The Paracas culture of the south coast of Peru is best known for its complex patterned textiles, particularly mantels. The Moche culture, Moche controlled the river valleys of the north coast, while the Nazca culture, Nazca of southern Peru held sway along the coastal deserts and contiguous mountains. The Nazca are best known for the famous Nazca Lines, a group of geoglyphs in a desert in southern Peru. They also produced polychrome ceramics and textiles influenced by the Paracas, and used a palette of at least 10 colours for their pottery. Both cultures flourished around 100–800 AD. Moche pottery is some of the most varied in the world. In the north, the Huari culture, Wari (or Huari) Empire are noted for their stone architecture and sculpture accomplishments.
The Chimú were preceded by a simple ceramic style known as Sican culture#Early Sican, Sicán (700–900 AD). The Chimú produced excellent portrait and decorative works in metal, notably gold but especially silver. Later, the Inca Empire (1100–1533) stretched across the Andes Mountains. They crafted precious metal figurines, and like other civilizations from the same area, complex textiles. Llamas were important animals, because of their wool and for carrying loads.
The ancient civilizations of Peru and Bolivia nurtured unique artistic traditions, including one of the world's most aesthetically impressive fibre art traditions. Two of the first important cultures from this land are the Chavín culture, Chavín and the Paracas culture.
The Paracas culture of the south coast of Peru is best known for its complex patterned textiles, particularly mantels. The Moche culture, Moche controlled the river valleys of the north coast, while the Nazca culture, Nazca of southern Peru held sway along the coastal deserts and contiguous mountains. The Nazca are best known for the famous Nazca Lines, a group of geoglyphs in a desert in southern Peru. They also produced polychrome ceramics and textiles influenced by the Paracas, and used a palette of at least 10 colours for their pottery. Both cultures flourished around 100–800 AD. Moche pottery is some of the most varied in the world. In the north, the Huari culture, Wari (or Huari) Empire are noted for their stone architecture and sculpture accomplishments.
The Chimú were preceded by a simple ceramic style known as Sican culture#Early Sican, Sicán (700–900 AD). The Chimú produced excellent portrait and decorative works in metal, notably gold but especially silver. Later, the Inca Empire (1100–1533) stretched across the Andes Mountains. They crafted precious metal figurines, and like other civilizations from the same area, complex textiles. Llamas were important animals, because of their wool and for carrying loads.
 Originating in 1720 Paris, Rococo is characterized by natural motifs, soft colours, curving lines, asymmetry and themes including love, nature and light-hearted entertainment. Its ideals were delicacy, gaiety, youthfulness and sensuality.
Beginning in France as a reaction against the heavy Baroque grandeur of Louis XIV's court at the Palace of Versailles, the rococo movement became associated particularly with the powerful Madame de Pompadour (1721–1764), the mistress of the new king Louis XV (1710–1774). Because of this, the style was also known as 'Pompadour'. The name of the movement derives from the French 'rocaille', or pebble, and refers to stones and shells that decorate the interiors of caves, as similar shell forms became a common feature in Rococo design. It began as a design and decorative arts style, and was characterized by elegant flowing shapes. Architecture followed and then painting and sculpture. The French painted with whom the term Rococo is most often associated is Jean-Antoine Watteau, whose pastoral scenes, or ''fêtes galantes'', dominate the early part of the 18th century.
Although there are some important Bavarian churches in this style, such as the Pilgrimage Church of Wies, Wieskirche, Rococo is most often associated with secular buildings, principally great palaces and salons where educated elites would meet to discuss literary and philosophical ideas. In Paris, its popularity coincided with the emergence of the salon as a new type of social gathering, the venues for which were often decorated in the Rococo style. Among the most characteristically elegant and refined examples is the Salon Oval de la Princesse of the Hôtel de Soubise, one of the most beautiful 18th century hôtel particulier, mansions in Paris. The Rococo introduced dramatic changes to elite furniture, as it favoured smaller pieces with narrow, sinewy frames and more delicate, often asymmetrical decoration, often including elements of chinoiserie. The taste for Far Eastern objects (mainly Chinese) lead to the use of Chinese painted and lacquered panels for furniture.
The movement spread quickly throughout Europe and as far as Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turkey and China thanks to ornament books featuring cartouche (design), cartouches, arabesques and shell work, as well as designs for wall panels and fireplaces. The most popular were made by Juste-Aurèle Meissonnier (1695–1750), Jacques-François Blondel (1705–1774), Pierre-Edmé Babel (1720–1775) and François de Cuvilliés (1695–1768).
Originating in 1720 Paris, Rococo is characterized by natural motifs, soft colours, curving lines, asymmetry and themes including love, nature and light-hearted entertainment. Its ideals were delicacy, gaiety, youthfulness and sensuality.
Beginning in France as a reaction against the heavy Baroque grandeur of Louis XIV's court at the Palace of Versailles, the rococo movement became associated particularly with the powerful Madame de Pompadour (1721–1764), the mistress of the new king Louis XV (1710–1774). Because of this, the style was also known as 'Pompadour'. The name of the movement derives from the French 'rocaille', or pebble, and refers to stones and shells that decorate the interiors of caves, as similar shell forms became a common feature in Rococo design. It began as a design and decorative arts style, and was characterized by elegant flowing shapes. Architecture followed and then painting and sculpture. The French painted with whom the term Rococo is most often associated is Jean-Antoine Watteau, whose pastoral scenes, or ''fêtes galantes'', dominate the early part of the 18th century.
Although there are some important Bavarian churches in this style, such as the Pilgrimage Church of Wies, Wieskirche, Rococo is most often associated with secular buildings, principally great palaces and salons where educated elites would meet to discuss literary and philosophical ideas. In Paris, its popularity coincided with the emergence of the salon as a new type of social gathering, the venues for which were often decorated in the Rococo style. Among the most characteristically elegant and refined examples is the Salon Oval de la Princesse of the Hôtel de Soubise, one of the most beautiful 18th century hôtel particulier, mansions in Paris. The Rococo introduced dramatic changes to elite furniture, as it favoured smaller pieces with narrow, sinewy frames and more delicate, often asymmetrical decoration, often including elements of chinoiserie. The taste for Far Eastern objects (mainly Chinese) lead to the use of Chinese painted and lacquered panels for furniture.
The movement spread quickly throughout Europe and as far as Ottoman Empire, Ottoman Turkey and China thanks to ornament books featuring cartouche (design), cartouches, arabesques and shell work, as well as designs for wall panels and fireplaces. The most popular were made by Juste-Aurèle Meissonnier (1695–1750), Jacques-François Blondel (1705–1774), Pierre-Edmé Babel (1720–1775) and François de Cuvilliés (1695–1768).
 Inspired by the excavations of the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman cities of Pompeii and
Inspired by the excavations of the Ancient Rome, ancient Roman cities of Pompeii and  Many art historians place the origins of modern art in the late 18th century, others in the mid 19th century. Art historian H. Harvard Arnason stated "a gradual metamorphosis took place in the course of a hundred years." Events such as the age of enlightenment, revolutions and democracies in American Revolution, America and French Revolution, France, and the Industrial Revolution had far reaching affects in western culture. People, commodities, ideas, and information could travel between countries and continents with unprecedented speed and these changes were reflected in the arts. The invention of photography in the 1830s further altered certain aspects of art, particularly painting. By the dawn of the 19th century, a long and gradual paradigm shift was complete, from the Gothic when artists were viewed as craftsmen in the service of the church and monarchies, to the idea of art for art's sake, where the ideas and visions of the individual artist were held in the high regard, with patronage from an increasingly literate, affluent, and urban middle and upper class population that had been emerging for 200 years (particularly in Paris and London). A dichotomy began in the late 18th century between neoclassicism and romanticism that subdivided and continued to run through virtually every new movement in modern art: "Spreading like waves, these "isms" defy national, ethnic, and chronological boundaries; never dominant anywhere for long, they compete or merge with each other in endlessly shifting patterns."
Modern art has consistently moved toward international influences and exchanges, from the exotic curiosity of Orientalism, the deeper influence of Japonisme, to the arts of Oceania, Africa, and the Americas. Conversely modern art has increasingly extended beyond western Europe. In Russia and the USA the arts were developing to a degree that rivaled the leading European countries by the end of the 19th century. Many of the major movements appeared in Latin America, Australia, and Asia too and geography and nationality became increasingly insignificant with each passing decade. By the 20th century important and influential artists were emerging around the world: e.g. Foujita (Japan), Arshile Gorky (Armenia), Diego Rivera and Frida Kahlo (Mexico), Wifredo Lam (Cuba), Edvard Munch (Norwegian), Roberto Matta (Chilean), Mark Rothko (Lithuanian-American), Fernando Botero Angulo (Colombia), Constantin Brâncuși and Victor Brauner (Romania).
Many art historians place the origins of modern art in the late 18th century, others in the mid 19th century. Art historian H. Harvard Arnason stated "a gradual metamorphosis took place in the course of a hundred years." Events such as the age of enlightenment, revolutions and democracies in American Revolution, America and French Revolution, France, and the Industrial Revolution had far reaching affects in western culture. People, commodities, ideas, and information could travel between countries and continents with unprecedented speed and these changes were reflected in the arts. The invention of photography in the 1830s further altered certain aspects of art, particularly painting. By the dawn of the 19th century, a long and gradual paradigm shift was complete, from the Gothic when artists were viewed as craftsmen in the service of the church and monarchies, to the idea of art for art's sake, where the ideas and visions of the individual artist were held in the high regard, with patronage from an increasingly literate, affluent, and urban middle and upper class population that had been emerging for 200 years (particularly in Paris and London). A dichotomy began in the late 18th century between neoclassicism and romanticism that subdivided and continued to run through virtually every new movement in modern art: "Spreading like waves, these "isms" defy national, ethnic, and chronological boundaries; never dominant anywhere for long, they compete or merge with each other in endlessly shifting patterns."
Modern art has consistently moved toward international influences and exchanges, from the exotic curiosity of Orientalism, the deeper influence of Japonisme, to the arts of Oceania, Africa, and the Americas. Conversely modern art has increasingly extended beyond western Europe. In Russia and the USA the arts were developing to a degree that rivaled the leading European countries by the end of the 19th century. Many of the major movements appeared in Latin America, Australia, and Asia too and geography and nationality became increasingly insignificant with each passing decade. By the 20th century important and influential artists were emerging around the world: e.g. Foujita (Japan), Arshile Gorky (Armenia), Diego Rivera and Frida Kahlo (Mexico), Wifredo Lam (Cuba), Edvard Munch (Norwegian), Roberto Matta (Chilean), Mark Rothko (Lithuanian-American), Fernando Botero Angulo (Colombia), Constantin Brâncuși and Victor Brauner (Romania).
 Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century and flourished in the first half of the 19th century with significant and international manifestations in music, literature, and architecture, as well as the visual arts. It grew from a disillusionment with the rationalism of 18th century Enlightenment. Despite being often viewed as the opposite of Neoclassicism, there were some stylistic overlapping with both movements, and many Romantic artists were excited by classicism. The movement focused on intense emotions, imagination, and on the impressive power of nature, a bigger and more powerful force than the one of men, with its potential for disaster. "Neoclassicism is a new revival of classical antiquity... while Romanticism refers not to a specific style but to an attitude of mind that may reveal itself in any number of ways."
One of the earliest expressions of romanticism was in the English landscape garden, carefully designed to appear natural and standing in dramatic contrast to the formal gardens of the time. The concept of the "natural" English garden was adopted throughout Europe and America in the following decades. In architecture, the romantics frequently turned to alternative sources other than the Greek and Roman examples admired by the neo-classicist. Romantic architecture often revived Gothic architecture, Gothic forms and other styles such as exotic eastern models. The Palace of Westminster (Houses of Parliament), London is an example of romantic architecture that is also referred to as Gothic Revival. In painting romanticism is exemplified by the paintings of Francisco Goya in Spain, Eugène Delacroix and Théodore Géricault in France, William Blake, Henry Fuseli, Samuel Palmer, and J. M. W. Turner, William Turner in England, Caspar David Friedrich and Philipp Otto Runge in Germany, Francesco Hayez in Italy, Johan Christian Claussen Dahl in Norway, and Thomas Cole in America. Examples of sculptors of the romantic period include Antoine-Louis Barye, Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux, Auguste Préault, and François Rude. As romanticism ran its course, some aspects of the movement evolved into symbolism.
Romanticism emerged in the late 18th century and flourished in the first half of the 19th century with significant and international manifestations in music, literature, and architecture, as well as the visual arts. It grew from a disillusionment with the rationalism of 18th century Enlightenment. Despite being often viewed as the opposite of Neoclassicism, there were some stylistic overlapping with both movements, and many Romantic artists were excited by classicism. The movement focused on intense emotions, imagination, and on the impressive power of nature, a bigger and more powerful force than the one of men, with its potential for disaster. "Neoclassicism is a new revival of classical antiquity... while Romanticism refers not to a specific style but to an attitude of mind that may reveal itself in any number of ways."
One of the earliest expressions of romanticism was in the English landscape garden, carefully designed to appear natural and standing in dramatic contrast to the formal gardens of the time. The concept of the "natural" English garden was adopted throughout Europe and America in the following decades. In architecture, the romantics frequently turned to alternative sources other than the Greek and Roman examples admired by the neo-classicist. Romantic architecture often revived Gothic architecture, Gothic forms and other styles such as exotic eastern models. The Palace of Westminster (Houses of Parliament), London is an example of romantic architecture that is also referred to as Gothic Revival. In painting romanticism is exemplified by the paintings of Francisco Goya in Spain, Eugène Delacroix and Théodore Géricault in France, William Blake, Henry Fuseli, Samuel Palmer, and J. M. W. Turner, William Turner in England, Caspar David Friedrich and Philipp Otto Runge in Germany, Francesco Hayez in Italy, Johan Christian Claussen Dahl in Norway, and Thomas Cole in America. Examples of sculptors of the romantic period include Antoine-Louis Barye, Jean-Baptiste Carpeaux, Auguste Préault, and François Rude. As romanticism ran its course, some aspects of the movement evolved into symbolism.
 Impressionism emerged in France, under the influences of Realism (art movement), Realism, the Barbizon School, and en plein air painters like Eugène Boudin, Camille Corot, Charles-François Daubigny, Charles- Francois Daubigny, and Johan Barthold Jongkind. Starting in the late 1850s, several of the impressionists had made acquaintances and friendships as students in Paris, notably at the free Académie Suisse and Charles Gleyre's studio. Their progressive work was frequently rejected by the conservative juries of the prestigious Académie des Beaux-Arts, Académie des Beaux Arts salons, a forum where many artist turned to establish their reputations, and many of the young artist were included in a highly publicized, but much ridiculed Salon des Refusés in 1863. In 1874 they formed the Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, Graveurs, independent of the academy, and mounted the first of several impressionist exhibitions in Paris, through to 1886 when their eighth and final exhibition was held. Important figures in the movement included Frédéric Bazille, Gustave Caillebotte, Mary Cassatt, Paul Cézanne, Edgar Degas, Armand Guillaumin, Édouard Manet, Claude Monet, Berthe Morisot, Camille Pissarro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley. Although impressionism was primarily a movement of painters, Degas and Renoir also produced sculptures and others like Auguste Rodin and Medardo Rosso are sometimes linked to impressionism. By 1885 impressionism had achieved some prominence, and yet a younger generation were already pushing the limits beyond impressionism. Artist from Museum of Russian impressionism, Russia, Heidelberg School, Australia, American Impressionism, America and Latin America soon adopted impressionist styles. A few of the original impressionist continued producing significant work into the 1910s and 1920s.
Although not unprecedented, many of the techniques used were in contrast to traditional methods. Paintings were often completed in hours or days with wet paint applied to wet paint (opposed to wet on dry paint, completed in weeks and months). Rather than applying glazes and mixed colors, pure colors were often applied side by side, in thick, opaque, impasto strokes; blending in the eye of the viewer when observed from a distance. Black was used very sparingly, or not at all, and defining lines replaced with nuanced strokes of color forming the subjects, contours, and shapes. Art historian H. W. Janson said "instead of adding to the illusion of real space, it strengthens the unity of the actual painted surface." Impressionist paintings typically depict landscapes, portraits, still lifes, domestic scenes, daily leisure and nightlife, all treated in a realist manner. Compositions were often based on unusual perspectives, appearing spontaneous and candid. The paintings were usually void of didactic, symbolic, or metaphoric meanings, and rarely addressed the biblical, mythological, and historical subjects that were so highly regarded by the academies or the darker and psychological interest explored by the symbolist. The nuances of light, shadow, atmosphere, and reflections of colors from surfaces were examined, sometimes emphasizing changes of these elements in time. The painting itself was the subject of the painting. It was art for art's sake, an idea that had been floating around for a few of decades but it perhaps reached a new high and consistency in impressionism.
Impressionism emerged in France, under the influences of Realism (art movement), Realism, the Barbizon School, and en plein air painters like Eugène Boudin, Camille Corot, Charles-François Daubigny, Charles- Francois Daubigny, and Johan Barthold Jongkind. Starting in the late 1850s, several of the impressionists had made acquaintances and friendships as students in Paris, notably at the free Académie Suisse and Charles Gleyre's studio. Their progressive work was frequently rejected by the conservative juries of the prestigious Académie des Beaux-Arts, Académie des Beaux Arts salons, a forum where many artist turned to establish their reputations, and many of the young artist were included in a highly publicized, but much ridiculed Salon des Refusés in 1863. In 1874 they formed the Société Anonyme Coopérative des Artistes Peintres, Sculpteurs, Graveurs, independent of the academy, and mounted the first of several impressionist exhibitions in Paris, through to 1886 when their eighth and final exhibition was held. Important figures in the movement included Frédéric Bazille, Gustave Caillebotte, Mary Cassatt, Paul Cézanne, Edgar Degas, Armand Guillaumin, Édouard Manet, Claude Monet, Berthe Morisot, Camille Pissarro, Pierre-Auguste Renoir, and Alfred Sisley. Although impressionism was primarily a movement of painters, Degas and Renoir also produced sculptures and others like Auguste Rodin and Medardo Rosso are sometimes linked to impressionism. By 1885 impressionism had achieved some prominence, and yet a younger generation were already pushing the limits beyond impressionism. Artist from Museum of Russian impressionism, Russia, Heidelberg School, Australia, American Impressionism, America and Latin America soon adopted impressionist styles. A few of the original impressionist continued producing significant work into the 1910s and 1920s.
Although not unprecedented, many of the techniques used were in contrast to traditional methods. Paintings were often completed in hours or days with wet paint applied to wet paint (opposed to wet on dry paint, completed in weeks and months). Rather than applying glazes and mixed colors, pure colors were often applied side by side, in thick, opaque, impasto strokes; blending in the eye of the viewer when observed from a distance. Black was used very sparingly, or not at all, and defining lines replaced with nuanced strokes of color forming the subjects, contours, and shapes. Art historian H. W. Janson said "instead of adding to the illusion of real space, it strengthens the unity of the actual painted surface." Impressionist paintings typically depict landscapes, portraits, still lifes, domestic scenes, daily leisure and nightlife, all treated in a realist manner. Compositions were often based on unusual perspectives, appearing spontaneous and candid. The paintings were usually void of didactic, symbolic, or metaphoric meanings, and rarely addressed the biblical, mythological, and historical subjects that were so highly regarded by the academies or the darker and psychological interest explored by the symbolist. The nuances of light, shadow, atmosphere, and reflections of colors from surfaces were examined, sometimes emphasizing changes of these elements in time. The painting itself was the subject of the painting. It was art for art's sake, an idea that had been floating around for a few of decades but it perhaps reached a new high and consistency in impressionism.
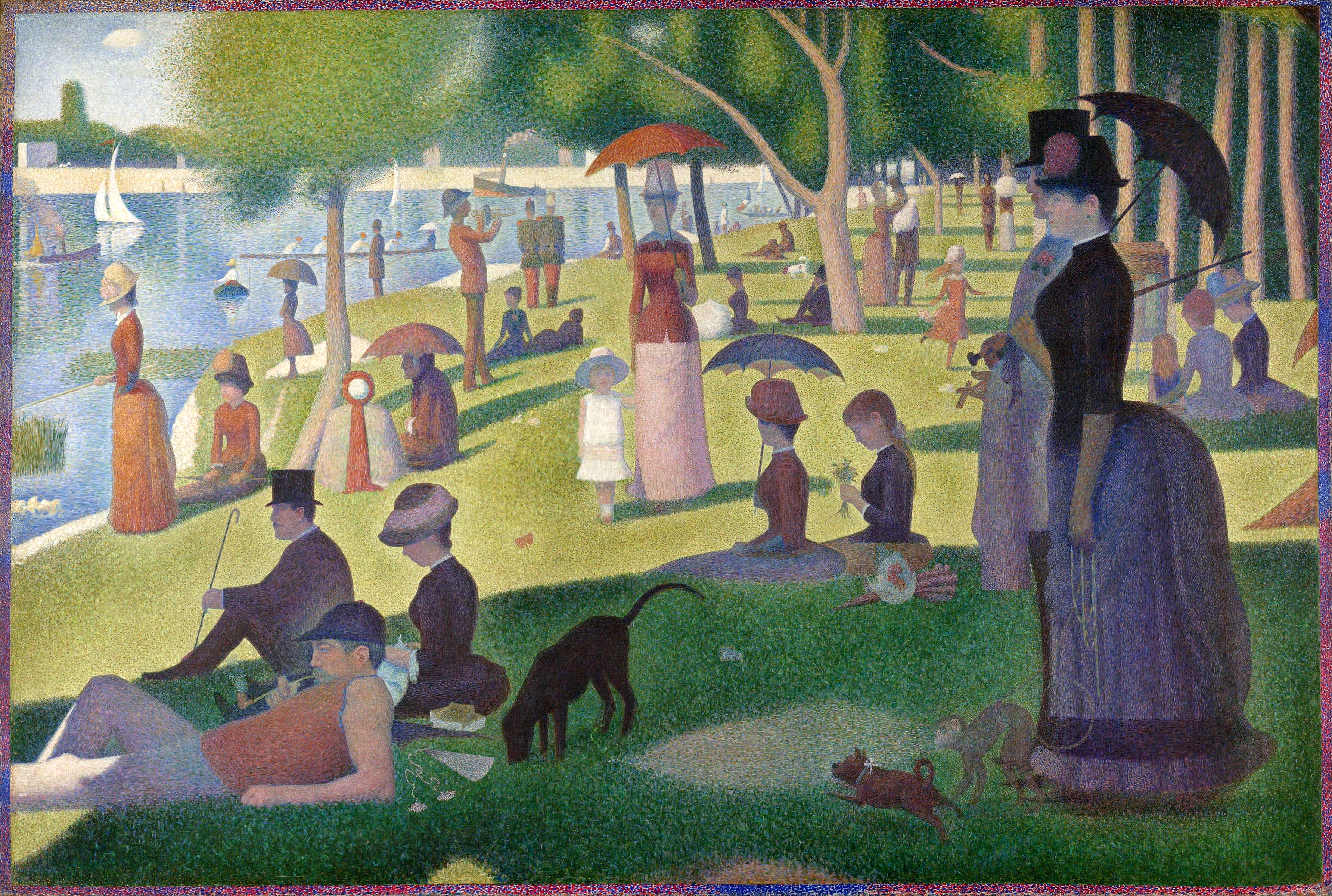 Post-Impressionism is a rather imprecise term applied to a diverse generation of artists. In its strictest sense, it pertains to four highly influential artists: Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat, and Vincent van Gogh. Each passed through an impressionist phase, but ultimately emerged with four very original but different styles. Collectively, their work anticipated, and often directly influenced, much of the avant-garde art that appear before the First World War including fauvism, cubism, expressionism, and early abstraction. Cézanne (particularly influential on cubism) and Van Gogh worked in relative isolation, away from Paris, at critical points in their careers, while Seurat and Gauguin worked in groups, more collaboratively, at key points in their development. Another important artist of the period is Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Toulouse-Lautrec, an influential painter as well as graphic artist. In a broader sense, post-impressionism includes a generation of predominantly French and Belgian artist who worked in a range of styles and groups. Most had come under the sway of impressionism at some point, but pushed their work beyond it into a number of factions as early as the mid-1880s, sometimes as a logical development of impressionism, other times as a reaction against it. Post-Impressionists typically depicted impressionist subjects, but the work, particularly synthetism, often contained symbolism, spiritualism, and moody atmospheres that rarely appeared in impressionism. Unnatural colors, patterns, flat plains, odd perspectives and viewpoints pushed to extremes, all moved the center of modernism a step closer to abstraction with a standard for experimentation.
Neo-Impressionism (Divisionism or Pointillism, c. 1884–1894) explored light and color based on scientific color theories, creating mosaics of brush strokes in pure colors, sometimes laid out in rhythmic patterns with lines influenced by Art Nouveau. The leading artists were Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, others include Henri-Edmond Cross, Maximilien Luce, Albert Dubois-Pillet, and for a period Pissarro and Van Gogh. It was influential on fauvism, and elements of the style appeared in expressionism, cubism, and early abstraction. Synthetism (Cloisonnism c. 1888–1903) Cloisonnism was conceived by Émile Bernard and immediately taken up and developed by Paul Gauguin and others while at an artists' colony in Pont-Aven (Brittany, France). The style resembled cloisonné enamel or stained glass, with flat, bold colors outlined in black or dark colors. Synthetism, exemplified in the work of Gauguin and Paul Sérusier, is slightly a broader term with less emphasis on dark outlines and cloisonné qualities. Other artist include Cuno Amiet, Louis Anquetin, Charles Filiger, Meyer de Haan, Jacob Meyer de Haan, Charles Laval, and Armand Séguin (painter), Armand Seguin. Their work greatly influenced fauvism and expressionism. Les Nabis (c. 1890–1905: Hebrew for prophets or illuminati) was a larger movement in France and Belgium that eclectically drew on progressive elements in synthetism, neo-impressionism, symbolism, and Art Nouveau. Perhaps more influential than the art, were the numerous theories, manifestoes, and infectious enthusiasm for the avant-garde, setting the tone for the proliferation of movements and "isms" in the first quarter of the 20th century. La Revue Blanche often published Les Nabis and symbolist content. The work of Édouard Vuillard, and Pierre Bonnard, ca. 1890–1910 is exemplary of Les Nabis, though both evolved in their styles and produced significant work into the 1940s. Other artist include Maurice Denis, Maxime Dethomas, Meyer de Haan, Henri-Gabriel Ibels, Georges Lacombe (painter), Georges Lacombe, Aristide Maillol, Paul Ranson, Ker-Xavier Roussel, Armand Séguin, Paul Sérusier, Félix Vallotton, Jan Verkade, and others.
Post-Impressionism is a rather imprecise term applied to a diverse generation of artists. In its strictest sense, it pertains to four highly influential artists: Paul Cézanne, Paul Gauguin, Georges Seurat, and Vincent van Gogh. Each passed through an impressionist phase, but ultimately emerged with four very original but different styles. Collectively, their work anticipated, and often directly influenced, much of the avant-garde art that appear before the First World War including fauvism, cubism, expressionism, and early abstraction. Cézanne (particularly influential on cubism) and Van Gogh worked in relative isolation, away from Paris, at critical points in their careers, while Seurat and Gauguin worked in groups, more collaboratively, at key points in their development. Another important artist of the period is Henri de Toulouse-Lautrec, Toulouse-Lautrec, an influential painter as well as graphic artist. In a broader sense, post-impressionism includes a generation of predominantly French and Belgian artist who worked in a range of styles and groups. Most had come under the sway of impressionism at some point, but pushed their work beyond it into a number of factions as early as the mid-1880s, sometimes as a logical development of impressionism, other times as a reaction against it. Post-Impressionists typically depicted impressionist subjects, but the work, particularly synthetism, often contained symbolism, spiritualism, and moody atmospheres that rarely appeared in impressionism. Unnatural colors, patterns, flat plains, odd perspectives and viewpoints pushed to extremes, all moved the center of modernism a step closer to abstraction with a standard for experimentation.
Neo-Impressionism (Divisionism or Pointillism, c. 1884–1894) explored light and color based on scientific color theories, creating mosaics of brush strokes in pure colors, sometimes laid out in rhythmic patterns with lines influenced by Art Nouveau. The leading artists were Georges Seurat and Paul Signac, others include Henri-Edmond Cross, Maximilien Luce, Albert Dubois-Pillet, and for a period Pissarro and Van Gogh. It was influential on fauvism, and elements of the style appeared in expressionism, cubism, and early abstraction. Synthetism (Cloisonnism c. 1888–1903) Cloisonnism was conceived by Émile Bernard and immediately taken up and developed by Paul Gauguin and others while at an artists' colony in Pont-Aven (Brittany, France). The style resembled cloisonné enamel or stained glass, with flat, bold colors outlined in black or dark colors. Synthetism, exemplified in the work of Gauguin and Paul Sérusier, is slightly a broader term with less emphasis on dark outlines and cloisonné qualities. Other artist include Cuno Amiet, Louis Anquetin, Charles Filiger, Meyer de Haan, Jacob Meyer de Haan, Charles Laval, and Armand Séguin (painter), Armand Seguin. Their work greatly influenced fauvism and expressionism. Les Nabis (c. 1890–1905: Hebrew for prophets or illuminati) was a larger movement in France and Belgium that eclectically drew on progressive elements in synthetism, neo-impressionism, symbolism, and Art Nouveau. Perhaps more influential than the art, were the numerous theories, manifestoes, and infectious enthusiasm for the avant-garde, setting the tone for the proliferation of movements and "isms" in the first quarter of the 20th century. La Revue Blanche often published Les Nabis and symbolist content. The work of Édouard Vuillard, and Pierre Bonnard, ca. 1890–1910 is exemplary of Les Nabis, though both evolved in their styles and produced significant work into the 1940s. Other artist include Maurice Denis, Maxime Dethomas, Meyer de Haan, Henri-Gabriel Ibels, Georges Lacombe (painter), Georges Lacombe, Aristide Maillol, Paul Ranson, Ker-Xavier Roussel, Armand Séguin, Paul Sérusier, Félix Vallotton, Jan Verkade, and others.