Hindukush (other) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in
Encyclop├”dia Britannica Towards its southern end, it connects with the White Mountains near the Kabul River.Sp─½n Ghar Range, MOUNTAINS, PAKISTAN-AFGHANISTAN
Encyclop├”dia Britannica It divides the valley of the Amu Darya (the ancient ''Oxus'') to the north from the
Archive
/ref> While the vast majority of the region has been majority-
Hindu Kush
Encyclop├”dia Britannica Some modern scholars remove the space and refer to the mountain range as ''Hindukush''.
Hindu Kush
Encyclop├”dia Iranica Several other theories have been propounded as to the origins of the name. According to Nigel Allan, the term ''Hindu Kush'' has two alternate meanings i.e. 'sparkling snows of India' and 'mountains of India', with ''Kush'' possibly being a soft variant of the Persian ''Kuh'' ('mountain'). Allan states that Hindu Kush was the frontier boundary to Arab geographers. Yet others suggest that the name may be derived from ancient
 The range forms the western section of the ''Hindu Kush Himalayan Region'' (''HKH'') and is the westernmost extension of the
The range forms the western section of the ''Hindu Kush Himalayan Region'' (''HKH'') and is the westernmost extension of the
 Geologically, the range is rooted in the formation of the subcontinent from a region of
Geologically, the range is rooted in the formation of the subcontinent from a region of
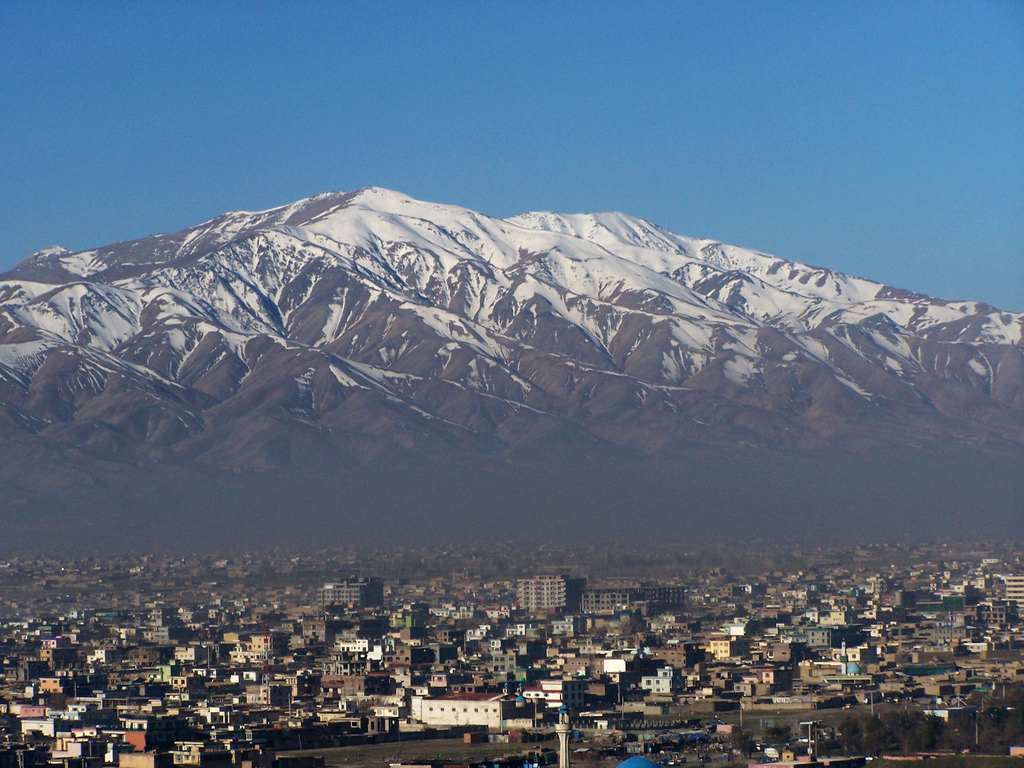
 The high altitudes of the mountains have historical significance in South and Central Asia. The Hindu Kush range was a major center of Buddhism with sites such as the
The high altitudes of the mountains have historical significance in South and Central Asia. The Hindu Kush range was a major center of Buddhism with sites such as the
 The subcontinent and valleys of the Hindu Kush remained unconquered by the Islamic armies until the 9th century, even though they had conquered the southern regions of the Indus River valley such as Sind. Kabul fell to the army of
The subcontinent and valleys of the Hindu Kush remained unconquered by the Islamic armies until the 9th century, even though they had conquered the southern regions of the Indus River valley such as Sind. Kabul fell to the army of
Bobojan Gafurov (June 1974), ''The Courier Journal'', UNESCO, page 13 to the northwest Indian subcontinent under Mahmud's rule. Al Biruni stayed in the region for about fifteen years, learnt Sanskrit, and translated many Indian texts, and wrote about Indian society, culture, sciences, and religion in Persian and Arabic. He stayed for some time in the Hindu Kush region, particularly near Kabul. In 1019, he recorded and described a solar eclipse in what is the modern era Laghman Province of Afghanistan through which Hindu Kush pass. Al Biruni also wrote about early history of the Hindu Kush region and Kabul kings, who ruled the region long before he arrived, but this history is inconsistent with other records available from that era. Al Biruni was supported by Sultan Mahmud. Al Biruni found it difficult to get access to Indian literature locally in the Hindu Kush area, and to explain this he wrote, "Mahmud utterly ruined the prosperity of the country, and performed wonderful exploits by which the Hindus became the atoms scattered in all directions, and like a tale of old in the mouth of the people. (...) This is the reason, too, why Hindu sciences have retired far from those parts of the country conquered by us, and have fled to places which our hand cannot yet reach, to Kashmir, Benares and other places". In the late 12th century, the historically influential Ghurid empire led by Mu'izz al-Din ruled the Hindu Kush region. He was influential in seeding the

 Slavery, as with all major ancient and medieval societies, has been a part of Central Asia and South Asia history. The Hindu Kush mountain passes connected the slave markets of Central Asia with slaves seized in South Asia.Scott C. Levi (2002), ''Hindus beyond the Hindu Kush: Indians in the Central Asian Slave Trade'', Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, Cambridge University Press, Volume 12, Number 3 (Nov. 2002), pages 277ŌĆō288 The seizure and transportation of slaves from the Indian subcontinent became intense in and after the 8th century CE, with evidence suggesting that the slave transport involved "hundreds of thousands" of slaves from India in different periods of Islamic rule era. According to John Coatsworth and others, the slave trading operations during the pre-Akbar Mughal and Delhi Sultanate era "sent thousands of Hindus every year north to Central Asia to pay for horses and other goods". However, the interaction between Central Asia and South Asia through the Hindu Kush was not limited to slavery, it included trading in food, goods, horses and weapons.
The practice of raiding tribes, hunting, and kidnapping people for slave trading continued through the 19th century, at an extensive scale, around the Hindu Kush. According to a British Anti-Slavery Society report of 1874, the governor of Faizabad, Mir Ghulam Bey, kept 8,000 horses and cavalrymen who routinely captured non-Muslims as well as Shia Muslims as slaves. Others alleged to be involved in the slave trade were feudal lords such as Ameer Sheer Ali. The isolated communities in the Hindu Kush were one of the targets of these slave-hunting expeditions.
Slavery, as with all major ancient and medieval societies, has been a part of Central Asia and South Asia history. The Hindu Kush mountain passes connected the slave markets of Central Asia with slaves seized in South Asia.Scott C. Levi (2002), ''Hindus beyond the Hindu Kush: Indians in the Central Asian Slave Trade'', Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, Cambridge University Press, Volume 12, Number 3 (Nov. 2002), pages 277ŌĆō288 The seizure and transportation of slaves from the Indian subcontinent became intense in and after the 8th century CE, with evidence suggesting that the slave transport involved "hundreds of thousands" of slaves from India in different periods of Islamic rule era. According to John Coatsworth and others, the slave trading operations during the pre-Akbar Mughal and Delhi Sultanate era "sent thousands of Hindus every year north to Central Asia to pay for horses and other goods". However, the interaction between Central Asia and South Asia through the Hindu Kush was not limited to slavery, it included trading in food, goods, horses and weapons.
The practice of raiding tribes, hunting, and kidnapping people for slave trading continued through the 19th century, at an extensive scale, around the Hindu Kush. According to a British Anti-Slavery Society report of 1874, the governor of Faizabad, Mir Ghulam Bey, kept 8,000 horses and cavalrymen who routinely captured non-Muslims as well as Shia Muslims as slaves. Others alleged to be involved in the slave trade were feudal lords such as Ameer Sheer Ali. The isolated communities in the Hindu Kush were one of the targets of these slave-hunting expeditions.
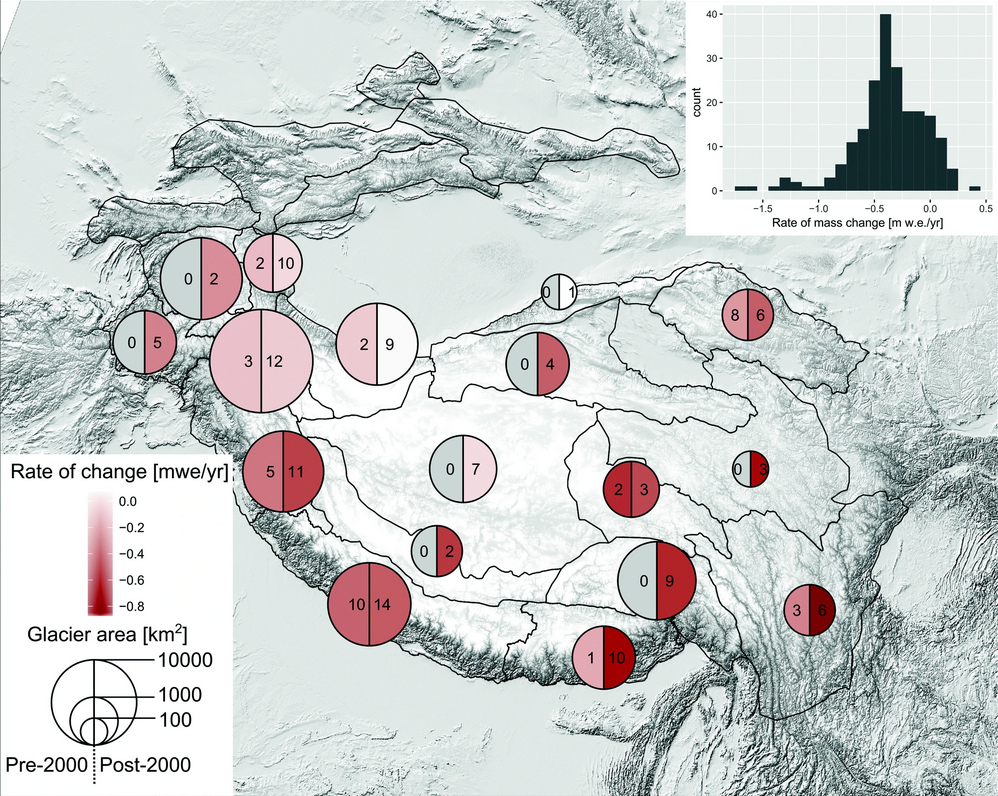 The 2019 Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment concluded that between 1901 to 2014, the Hindu Kush Himalaya (or HKH) region had already experienced warming of 0.1 ┬░C per decade, with the warming rate accelerating to 0.2 ┬░C per decade over the past 50 years.Over the past 50 years, the frequency of warm days and nights had also increased by 1.2 days and 1.7 nights per decade, while the frequency of ''extreme'' warm days and nights had increased by 1.26 days and 2.54 nights per decade. There was also a corresponding decline of 0.5 cold days, 0.85 extreme cold days, 1 cold night, and 2.4 extreme cold nights per decade. The length of the
The 2019 Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment concluded that between 1901 to 2014, the Hindu Kush Himalaya (or HKH) region had already experienced warming of 0.1 ┬░C per decade, with the warming rate accelerating to 0.2 ┬░C per decade over the past 50 years.Over the past 50 years, the frequency of warm days and nights had also increased by 1.2 days and 1.7 nights per decade, while the frequency of ''extreme'' warm days and nights had increased by 1.26 days and 2.54 nights per decade. There was also a corresponding decline of 0.5 cold days, 0.85 extreme cold days, 1 cold night, and 2.4 extreme cold nights per decade. The length of the
''A Country Study: Afghanistan''
Library of Congress * Ervin Gr├Čtzbach, * ''Encyclop├”dia Britannica'', 15th Ed., Vol. 21, pp. 54ŌĆō55, 65, 1987 * ''
Khyber Pass
Geology
{{Authority control Geography of Afghanistan History of Pakistan Iranian Plateau Landforms of Badakhshan Province Landforms of Baghlan Province Landforms of Bamyan Province Landforms of Kabul Province Landforms of Kapisa Province Landforms of Nuristan Province Landforms of Panjshir Province Landforms of Parwan Province Landforms of South Asia Mountain ranges of Afghanistan Mountain ranges of Asia Mountain ranges of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Mountain ranges of Pakistan Mountain ranges of the Himalayas Physiographic provinces Sites along the Silk Road
 The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province of Pakistan". into northwestern Pakistan and far southeastern Tajikistan. The range forms the western section of the ''Hindu Kush Himalayan Region'' (''HKH''); to the north, near its northeastern end, the Hindu Kush buttresses the Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world ...
near the point where the borders of China, Pakistan and Afghanistan meet, after which it runs southwest through Pakistan and into Afghanistan near their border. The eastern end of the Hindu Kush in the north merges with the Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
Range.Karakoram Range: MOUNTAINS, ASIAEncyclop├”dia Britannica Towards its southern end, it connects with the White Mountains near the Kabul River.Sp─½n Ghar Range, MOUNTAINS, PAKISTAN-AFGHANISTAN
Encyclop├”dia Britannica It divides the valley of the Amu Darya (the ancient ''Oxus'') to the north from the
Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
valley to the south. The range has numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir or Terichmir at in the Chitral District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan.
The Hindu Kush range region was a historically significant center of Buddhism, with sites such as the Bamiyan Buddhas
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural c ...
. The range and communities settled in it hosted ancient monasteries, important trade networks and travelers between Central Asia and South Asia.; Columbia UniversitArchive
/ref> While the vast majority of the region has been majority-
Muslim
Muslims ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ģž│┘ä┘ģ┘ł┘å, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
for several centuries now, certain portions of the Hindu Kush only became Islamized relatively recently, such as Kafiristan, which retained ancient polytheistic beliefs until the 19th century when it was converted to Islam by the Durrani Empire
The Durrani Empire ( ps, ž» ž»ž▒ž¦┘å┘Ŗž¦┘å┘ł ┘╝┘ł┘ä┘łž¦┌®┘ģ┘å┘Ŗ; fa, ž¦┘ģ┘Šž▒ž¦ž¬┘łž▒█ī ž»ž▒ž¦┘å█īž¦┘å) or the Afghan Empire ( ps, ž» ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘垦┘å ┘╝┘ł┘ä┘łž¦┌®┘ģ┘å┘Ŗ, label=none; fa, ž¦┘ģ┘Šž▒ž¦ž¬┘łž▒█ī ž¦┘üž║ž¦┘å, label=none), also know ...
and renamed Nuristan ("land of light"). The Hindu Kush range has also been the passageway during the invasions of the Indian subcontinent, and continues to be important to contemporary warfare in Afghanistan.
Name
The earliest known usage of the Persian name ''Hindu Kush'' occurs on a map published about 1000 CE.Fosco Maraini et al.Hindu Kush
Encyclop├”dia Britannica Some modern scholars remove the space and refer to the mountain range as ''Hindukush''.
Etymology
''Hindu Kush'' is generally translated as "Killer of Hindus" or "Hindu-Killer" by most writers. The term was earliest used byIbn Battuta
Abu Abdullah Muhammad ibn Battutah (, ; 24 February 13041368/1369),; fully: ; Arabic: commonly known as Ibn Battuta, was a Berbers, Berber Maghrebi people, Maghrebi scholar and explorer who travelled extensively in the lands of Afro-Eurasia, ...
. According to him ''Hindu Kush'' means Hindu Killer as slaves from the Indian subcontinent died in the harsh climatic conditions of the mountains while being taken from India to Turkestan.Ervin Gr├Čtzbach (2012 Edition, Original: 2003)Hindu Kush
Encyclop├”dia Iranica Several other theories have been propounded as to the origins of the name. According to Nigel Allan, the term ''Hindu Kush'' has two alternate meanings i.e. 'sparkling snows of India' and 'mountains of India', with ''Kush'' possibly being a soft variant of the Persian ''Kuh'' ('mountain'). Allan states that Hindu Kush was the frontier boundary to Arab geographers. Yet others suggest that the name may be derived from ancient
Avestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
, meaning 'water mountain'.
It is also sometimes interpreted as the land of the Hindkowans
Hindkowans (lit. "Indian-speakers"), also known as the Hindki, is a contemporary designation for speakers of Indo-Aryan languages who live among the neighbouring Pashtuns, particularly the speakers of various Hindko dialects of Lahnda. The or ...
( Hindki in Pashto) around the region who speak Hindko
Hindko (, romanized: , ) is a cover term for a diverse group of Lahnda dialects spoken by several million people of various ethnic backgrounds in several areas in northwestern Pakistan, primarily in the provinces of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa and Pun ...
.
According to '' Hobson-Jobson'', a 19th-century British dictionary, ''Hindukush'' might be a corruption of the ancient Latin ''Indicus ( Caucasus);'' the entry mentions the interpretation first given by Ibn Batuta as a popular theory already at that time, despite doubts cast upon it.
Other names
In Vedic Sanskrit, the range was known as ''upari┼øyena'', and inAvestan
Avestan (), or historically Zend, is an umbrella term for two Old Iranian languages: Old Avestan (spoken in the 2nd millennium BCE) and Younger Avestan (spoken in the 1st millennium BCE). They are known only from their conjoined use as the scrip ...
, as ''up─üirisa─ōna'' (from Proto-Iranian
Proto-Iranian or Proto-Iranic is the reconstructed proto-language of the Iranian languages branch of Indo-European language family and thus the ancestor of the Iranian languages such as Pashto, Persian, Sogdian, Zazaki, Ossetian, Mazandarani ...
*''up─ürisaina''- 'covered with juniper'). It can alternatively be interpreted as "beyond the reach of eagles". In the time of Alexander the Great, the mountain range was referred to as the ''Caucasus Indicus'' (as opposed to the Greater Caucasus range between the Caspian Caspian can refer to:
*The Caspian Sea
*The Caspian Depression, surrounding the northern part of the Caspian Sea
*The Caspians, the ancient people living near the Caspian Sea
* Caspian languages, collection of languages and dialects of Caspian p ...
and Black Seas), and as ''Paropamisos'' (see '' Paropamisadae'') by Hellenic Greeks in the late first millennium BCE.
Some 19th-century encyclopedias and gazetteers state that the term ''Hindu Kush'' originally applied only to the peak in the area of the Kushan Pass, which had become a center of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ ╬Ü╬┐ŽāŽā╬▒╬Įß┐Č╬Į; xbc, ╬ÜŽģŽĖ╬▒╬Į╬┐, ; sa, ÓżĢÓźüÓżĘÓżŠÓżŻ ÓżĄÓżéÓżČ; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, ÉŁŖÉŁģÉŁöÉŁŹ ÉŁćÉŁöÉŁĢÉŁō, ; zh, Ķ▓┤ķ££ ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
by the first century.
Geography

Pamir Mountains
The Pamir Mountains are a mountain range between Central Asia and Pakistan. It is located at a junction with other notable mountains, namely the Tian Shan, Karakoram, Kunlun, Hindu Kush and the Himalaya mountain ranges. They are among the world ...
, the Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
and the Himalayas. It divides the valley of the Amu Darya (the ancient ''Oxus'') to the north from the Indus River
The Indus ( ) is a transboundary river of Asia and a trans-Himalayan river of South and Central Asia. The river rises in mountain springs northeast of Mount Kailash in Western Tibet, flows northwest through the disputed region of Kashmir, ...
valley to the south. The range has numerous high snow-capped peaks, with the highest point being Tirich Mir or Terichmir at in the Chitral District of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. To the north, near its northeastern end, the Hindu Kush buttresses the Pamir Mountains near the point where the borders of China, Pakistan and Afghanistan meet, after which it runs southwest through Pakistan and into Afghanistan near their border. The eastern end of the Hindu Kush in the north merges with the Karakoram Range. Towards its southern end, it connects with the Spin Ghar Range near the Kabul River.
Peaks
Many peaks of the range are between , and some are much higher, with an average peak height of . The mountains of the Hindu Kush range diminish in height as they stretch westward. Near Kabul, in the west, they attain heights of ; in the east they extend from .Passes
Numerous high passes ("''kotal''") transect the mountains, forming a strategically important network for the transit of caravans. The most important mountain pass in Afghanistan is the Salang Pass (Kotal-e Salang) () north of Kabul, which links southern Afghanistan to northern Afghanistan. The Salang Tunnel at and the extensive network of galleries on the approach roads was constructed with Soviet financial and technological assistance and involved drilling through the heart of the Hindu Kush; since the start of the wars in Afghanistan it has been an active area of armed conflict with various parties trying to control the strategic tunnel. The range has several other passes in Afghanistan, the lowest of which is the southern Shibar pass () where the Hindu Kush range terminates. Before the Salang Tunnel, another feat of engineering was the road constructed through the Tang-e Gharu gorge near Kabul, replacing the ancient Lataband Pass and greatly reducing travel time towards the Pakistani border at theKhyber Pass
The Khyber Pass (ž«█īž©ž▒ ž»ž▒█ü) is a mountain pass in the Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province of Pakistan, on the border with the Nangarhar Province of Afghanistan. It connects the town of Landi Kotal to the Valley of Peshawar at Jamrud by traversing pa ...
.
Other mountain passes are at altitudes of about or higher, including the Broghil Pass at 12460 feet in Pakistan, and the Dorah Pass between Pakistan and Afghanistan at 14,000 feet. Other high passes in Pakistan include the Lowari Pass at 10,200 feet, the Gomal Pass. The Darmodar Aghost Pass
Darmodar Aghost pass (el. 14,340 ft.) is a high mountain pass in Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and depen ...
is at elevation of .
Watershed
The Hindu Kush form the boundary between the Indus watershed in South Asia, and Amu Darya watershed in Central Asia. Melt water from snow and ice feeds major river systems in Central Asia: the Amu Darya, Helmand River (which is a major source of water for the Sistan Basin in southern Afghanistan and Iran), and the Kabul Riverthe last of which is a major tributary of the Indus River. Smaller rivers with headwaters in the range include the Khash, the Farah and the Arashkan (Harut) rivers. The basins of these rivers serve the ecology and economy of the region, but the water flow in these rivers greatly fluctuates, and reliance on these has been a historical problem with extended droughts being commonplace. The eastern end of the range, with the highest peaks, high snow accumulation allows to long-term water storage.Geology
 Geologically, the range is rooted in the formation of the subcontinent from a region of
Geologically, the range is rooted in the formation of the subcontinent from a region of Gondwana
Gondwana () was a large landmass, often referred to as a supercontinent, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic (about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period (about 180 million years ago). The final stages ...
that drifted away from East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
about 160 million years ago, around the Middle Jurassic
The Middle Jurassic is the second epoch of the Jurassic Period. It lasted from about 174.1 to 163.5 million years ago. Fossils of land-dwelling animals, such as dinosaurs, from the Middle Jurassic are relatively rare, but geological formations co ...
period. The Indian subcontinent, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
and islands of the Indian Ocean rifted further, drifting northeastwards, with the Indian subcontinent colliding with the Eurasian Plate nearly 55 million years ago, towards the end of Palaeocene
The Paleocene, ( ) or Palaeocene, is a geological epoch that lasted from about 66 to 56 million years ago (mya). It is the first epoch of the Paleogene Period in the modern Cenozoic Era. The name is a combination of the Ancient Greek ''palai├ ...
. This collision created the Himalayas, including the Hindu Kush.
The Hindu Kush are a part of the "young Eurasian mountain range consisting of metamorphic rocks such as schist, gneiss and marble, as well as of intrusives such as granite, diorite of different age and size". The northern regions of the Hindu Kush witness Himalayan winter and have glaciers, while its southeastern end witnesses the fringe of Indian subcontinent summer monsoons.
The Hindu Kush range remains geologically active and is still rising; it is prone to earthquakes. The Hindu Kush system stretches about laterally, and its median north-south measurement is about . The mountains are orographically described in several parts. Peaks in the western Hindu Kush rise to over and stretch between Darra-ye Sekari and the Shibar Pass in the west and the Khawak Pass in the east. The central Hindu Kush peaks rise to over , and this section has numerous spurs between the Khawak Pass in the east and the Dur─üh Pass in the west. In 2005 and 2015 there were some major earthquakes.
The eastern Hindu Kush, also known as the "High Hindu Kush", is mostly located in northern Pakistan and the Nuristan and Badakhshan provinces of Afghanistan with peaks over . This section extends from the Dur─üh Pass to the Baroghil Pass at the border between northeastern Afghanistan and north Pakistan. The Chitral District of Pakistan is home to Tirich Mir, Noshaq, and Istoro Nal
Istor-o-Nal is the third highest mountain in the Hindu Kush, in the Chitral District of the North-West Frontier Province of Pakistan. It is the 68th highest independent peak in the world. It crowns a massif with eleven peaks of elevation more tha ...
the highest peaks in the Hindu Kush. The ridges between Khawak Pass and Badakshan is over and are called the Kaja Mohammed range.
Land cover and land use

ICIMOD
The International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development (ICIMOD) is a regional intergovernmental learning and knowledge sharing centre serving the eight regional member countries (RMCs) of thHindu Kush Himalaya(HKH) region - Afghanistan, Ban ...
ŌĆÖs first annual regional 30-meter resolution land cover
Land cover is the physical material at the surface of Earth. Land covers include grass, asphalt, trees, bare ground, water, etc. Earth cover is the expression used by ecologist Frederick Edward Clements that has its closest modern equivalent being ...
database of HKH generated using public domain Landsat images demonstrated that grassland was the most dominant land cover, followed by barren land, which includes areas with bare areas. In 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015, grassland covered 37.2%, 37.6%, 38.7%, and 38.23%, respectively, of the total area of the HKH region. During the same years, the second dominant land cover was barren areas, including bare soil and bare rock. In 2000, 2005, 2010, and 2015, bare soil and bare rock covered 32.1, 31.37, 30.35, and 30.69%. The cropland cover in 2000 was about 5.1% and about 5.41% in 2015. Snow and glacier areas covered about 4% of the high-elevation section in 2018, while waterbodies and riverbeds/channels together accounted for 2%. The weather conditions also have an impact on the land cover patterns across the regions. In the HKH, forest cover is mostly distributed in the south and south-eastern areas, where precipitation is more; the grasslands are mostly distributed in the north and north-western parts, while cropland is mostly found in the southern part of the region.
Flora and fauna
The mountainous areas of Hindu Kush range are mostly barren or at the most sparsely sprinkled with trees and stunted bushes. From about , states Yarshater, " sclerophyllous forests are predominant with Quercus and Olea (wild olive); above that, up to a height of about one finds coniferous forests with Cedrus,Picea
A spruce is a tree of the genus ''Picea'' (), a genus of about 35 species of coniferous evergreen trees in the family Pinaceae, found in the northern temperate and boreal (taiga) regions of the Earth. ''Picea'' is the sole genus in the subfami ...
, Abies, Pinus, and juniper
Junipers are coniferous trees and shrubs in the genus ''Juniperus'' () of the cypress family Cupressaceae. Depending on the taxonomy, between 50 and 67 species of junipers are widely distributed throughout the Northern Hemisphere, from the Arcti ...
s". The inner valleys of the Hindu Kush see little rain and have desert vegetation. On the other hand, Eastern Himalaya is home to multiple biodiversity hotspots, and 353 new species (242 plants, 16 amphibian
Amphibians are tetrapod, four-limbed and ectothermic vertebrates of the Class (biology), class Amphibia. All living amphibians belong to the group Lissamphibia. They inhabit a wide variety of habitats, with most species living within terres ...
s, 16 reptile
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians ( ...
s, 14 fish, two birds, two mammal
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a neocortex (a region of the brain), fur or ...
s and 61+ invertebrates) have been discovered there in between 1998 and 2008, with an average of 35 new species finds every year. With Eastern Himalaya included, the entire Hindu Kush Himalaya region is home to an estimated 35,000+ŌĆēspecies of plants and 200+ŌĆēspecies of animals.
History
 The high altitudes of the mountains have historical significance in South and Central Asia. The Hindu Kush range was a major center of Buddhism with sites such as the
The high altitudes of the mountains have historical significance in South and Central Asia. The Hindu Kush range was a major center of Buddhism with sites such as the Bamiyan Buddhas
The Buddhas of Bamiyan (or Bamyan) were two 6th-century monumental statues carved into the side of a cliff in the Bamyan valley of Hazarajat region in central Afghanistan, northwest of Kabul at an elevation of . Carbon dating of the structural c ...
. It has also been the passageway during the invasions of the Indian subcontinent, a region where the Taliban and al-Qaeda
Al-Qaeda (; , ) is an Islamic extremism, Islamic extremist organization composed of Salafist jihadists. Its members are mostly composed of Arab, Arabs, but also include other peoples. Al-Qaeda has mounted attacks on civilian and military ta ...
grew, and a scene of modern era warfare in Afghanistan. Ancient mines producing lapis lazuli
Lapis lazuli (; ), or lapis for short, is a deep-blue metamorphic rock used as a semi-precious stone that has been prized since antiquity for its intense color.
As early as the 7th millennium BC, lapis lazuli was mined in the Sar-i Sang mines, ...
are found in Kowkcheh Valley, while gem-grade emerald
Emerald is a gemstone and a variety of the mineral beryl (Be3Al2(SiO3)6) colored green by trace amounts of chromium or sometimes vanadium.Hurlbut, Cornelius S. Jr. and Kammerling, Robert C. (1991) ''Gemology'', John Wiley & Sons, New York, p ...
s are found north of Kabul in the valley of the Panjsher River and some of its tributaries. According to Walter Schumann, the West Hindu Kush mountains have been the source of the finest Lapis lazuli for thousands of years.
Buddhism was widespread in the ancient Hindu Kush region. The ancient artwork of Buddhism includes the giant rock-carved statues called the Bamiyan Buddhas, in the southern and western end of the Hindu Kush.Deborah Klimburg-Salter (1989), The Kingdom of Bamiyan: Buddhist art and culture of the Hindu Kush, Naples ŌĆō Rome: Istituto Universitario Orientale & Istituto Italiano per il Medio ed Estremo Oriente, (Reprinted by Shambala) These statues were destroyed by Taliban Islamists in 2001. The southeastern valleys of Hindu Kush connecting towards the Indus Valley region were a major center that hosted monasteries, religious scholars from distant lands, trade networks and merchants of the ancient Indian subcontinent.
One of the early Buddhist schools, the Mah─üs─üß╣āghika- Lokottarav─üda, was prominent in the area of Bamiyan. The Chinese Buddhist monk Xuanzang visited a Lokottarav─üda monastery in the 7th century CE, at Bamiyan, Afghanistan. Birchbark and palm leaf manuscripts of texts in this monastery's collection, including Mah─üy─üna s┼½tras
The Mahāyāna sūtras are a broad genre of Buddhist scriptures (''sūtra'') that are accepted as canonical and as ''buddhavacana'' ("Buddha word") in Mahāyāna Buddhism. They are largely preserved in the Chinese Buddhist canon, the Tibetan B ...
, have been discovered in the caves of Hindu Kush, and these are now a part of the Sch├Ėyen Collection. Some manuscripts are in the G─ündh─ür─½ language and Kharoß╣Żß╣Łh─½ script, while others are in Sanskrit and written in forms of the Gupta script
The Gupta script (sometimes referred to as Gupta Brahmi script or Late Brahmi script)Sharma, Ram. '' 'Brahmi Script' ''. Delhi: BR Publishing Corp, 2002 was used for writing Sanskrit and is associated with the Gupta Empire of the Indian subcon ...
.
According to Alfred Foucher, the Hindu Kush and nearby regions gradually converted to Buddhism by the 1st century CE, and this region was the base from where Buddhism crossed the Hindu Kush expanding into the Oxus valley region of Central Asia. Buddhism later disappeared and locals were forced to convert to Islam. Richard Bulliet also proposes that the area north of Hindu Kush was center of a new sect that had spread as far as Kurdistan, remaining in existence until the Abbasid times. The area eventually came under the control of the Hindu Shahi dynasty of Kabul.The History and Culture of the Indian People: The struggle for empire.-2d ed, Page 3 The Islamic conquest of the area happened under Sabuktigin who conquered Jayapala's dominion west of Peshawar in the 10th century.
Ancient
The significance of the Hindu Kush mountain ranges has been recorded since the time ofDarius I
Darius I ( peo, ÉÄŁÉÄĀÉÄ╝ÉÄ╣ÉÄ║ÉÄóÉÅü ; grc-gre, ╬ö╬▒Žü╬Ąß┐¢╬┐Žé ; ŌĆō 486 BCE), commonly known as Darius the Great, was a Persian ruler who served as the third King of Kings of the Achaemenid Empire, reigning from 522 BCE until his ...
of the Achaemenid Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, ÉĦÉÅüÉÅé, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest em ...
. Alexander entered the Indian subcontinent through the Hindu Kush as his army moved past the Afghan Valleys in the spring of 329 BCE. He moved towards the Indus Valley river region in the Indian subcontinent in 327 BCE, his armies building several towns in this region over the intervening two years.
After Alexander died in 323 BCE, the region became part of the Seleucid Empire
The Seleucid Empire (; grc, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ Žäß┐Č╬Į ╬Ż╬Ą╬╗╬ĄŽģ╬║╬╣╬┤ß┐Č╬Į, ''Basile├Ła t┼Źn Seleukid┼Źn'') was a Greek state in West Asia that existed during the Hellenistic period from 312 BC to 63 BC. The Seleucid Empire was founded by the ...
, according to the ancient history of Strabo
Strabo''Strabo'' (meaning "squinty", as in strabismus) was a term employed by the Romans for anyone whose eyes were distorted or deformed. The father of Pompey was called "Pompeius Strabo". A native of Sicily so clear-sighted that he could see ...
written in the 1st century BCE, before it became a part of the Indian Maurya Empire
The Maurya Empire, or the Mauryan Empire, was a geographically extensive Iron Age historical power in the Indian subcontinent based in Magadha, having been founded by Chandragupta Maurya in 322 BCE, and existing in loose-knit fashion until 1 ...
around 305 BCE. The region became a part of the Kushan Empire
The Kushan Empire ( grc, ╬Æ╬▒Žā╬╣╬╗╬Ą╬»╬▒ ╬Ü╬┐ŽāŽā╬▒╬Įß┐Č╬Į; xbc, ╬ÜŽģŽĖ╬▒╬Į╬┐, ; sa, ÓżĢÓźüÓżĘÓżŠÓżŻ ÓżĄÓżéÓżČ; Brahmi: , '; BHS: ; xpr, ÉŁŖÉŁģÉŁöÉŁŹ ÉŁćÉŁöÉŁĢÉŁō, ; zh, Ķ▓┤ķ££ ) was a syncretic empire, formed by the Yuezhi, i ...
around the start of the common era.
Medieval era
The lands north of the Hindu Kush, in theHephthalite
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ╬Ę╬▓╬┐╬┤╬▒╬╗╬┐, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
dominion, Buddhism was the predominant religion by mid 1st millennium CE. These Buddhists were religiously tolerant and they co-existed with followers of Zoroastrianism, Manichaeism, and Nestorian Christianity. This Central Asia region along the Hindu Kush was taken over by Western Turks and Arabs by the eighth century, facing wars with mostly Iranians. One major exception was the period in the mid to late seventh century when the Tang dynasty from China destroyed the Northern Turks and extended its rule all the way to the Oxus River valley and regions of Central Asia bordering all along the Hindu Kush.
 The subcontinent and valleys of the Hindu Kush remained unconquered by the Islamic armies until the 9th century, even though they had conquered the southern regions of the Indus River valley such as Sind. Kabul fell to the army of
The subcontinent and valleys of the Hindu Kush remained unconquered by the Islamic armies until the 9th century, even though they had conquered the southern regions of the Indus River valley such as Sind. Kabul fell to the army of Al-Ma'mun
Abu al-Abbas Abdallah ibn Harun al-Rashid ( ar, žŻž©┘ł ž¦┘äž╣ž©ž¦ž│ ž╣ž©ž» ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć ž©┘å ┘枦ž▒┘ł┘å ž¦┘äž▒ž┤┘Ŗž», Ab┼½ al-╩┐Abb─üs ╩┐Abd All─üh ibn H─ür┼½n ar-Rash─½d; 14 September 786 ŌĆō 9 August 833), better known by his regnal name Al-Ma'mu ...
, the seventh Abbasid caliph, in 808 and the local king agreed to accept Islam and pay annual tributes to the caliph. However, states Andr├® Wink, inscriptional evidence suggests that the Kabul area near Hindu Kush had an early presence of Islam. When the extraction of silver from the mines in the Hindu Kush was at its greatest (c.850), the value of silver in relation to gold dropped, and the content of silver in the Carolingian ''denarius'' was increased so that it should maintain its intrinsic value.
The range came under the control of the Hindu Shahi dynasty of Kabul but was conquered by Sabuktigin who took all of Jayapala's dominion west of Peshawar.
Mahmud of Ghazni
Yam─½n-ud-Dawla Abul-Q─üß╣Żim MaßĖźm┼½d ibn Seb├╝kteg─½n ( fa, ; 2 November 971 ŌĆō 30 April 1030), usually known as Mahmud of Ghazni or Mahmud Ghaznavi ( fa, ), was the founder of the Turkic Ghaznavid dynasty, ruling from 998 to 1030. At th ...
came to power in 998 CE, in Ghazna, Afghanistan, south of Kabul and the Hindu Kush range. He began a military campaign that rapidly brought both sides of the Hindu Kush range under his rule. From his mountainous Afghani base, he systematically raided and plundered kingdoms in north India from east of the Indus river to west of Yamuna river seventeen times between 997 and 1030. Mahmud of Ghazni raided the treasuries of kingdoms, sacked cities, and destroyed Hindu temples, with each campaign starting every spring, but he and his army returned to Ghazni and the Hindu Kush base before monsoons arrived in the northwestern part of the subcontinent. He retracted each time, only extending Islamic rule into western Punjab.
In 1017, the Iranian Islamic historian Al-Biruni was deported after a war that Mahmud of Ghazni won,Al-BiruniBobojan Gafurov (June 1974), ''The Courier Journal'', UNESCO, page 13 to the northwest Indian subcontinent under Mahmud's rule. Al Biruni stayed in the region for about fifteen years, learnt Sanskrit, and translated many Indian texts, and wrote about Indian society, culture, sciences, and religion in Persian and Arabic. He stayed for some time in the Hindu Kush region, particularly near Kabul. In 1019, he recorded and described a solar eclipse in what is the modern era Laghman Province of Afghanistan through which Hindu Kush pass. Al Biruni also wrote about early history of the Hindu Kush region and Kabul kings, who ruled the region long before he arrived, but this history is inconsistent with other records available from that era. Al Biruni was supported by Sultan Mahmud. Al Biruni found it difficult to get access to Indian literature locally in the Hindu Kush area, and to explain this he wrote, "Mahmud utterly ruined the prosperity of the country, and performed wonderful exploits by which the Hindus became the atoms scattered in all directions, and like a tale of old in the mouth of the people. (...) This is the reason, too, why Hindu sciences have retired far from those parts of the country conquered by us, and have fled to places which our hand cannot yet reach, to Kashmir, Benares and other places". In the late 12th century, the historically influential Ghurid empire led by Mu'izz al-Din ruled the Hindu Kush region. He was influential in seeding the
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206ŌĆō1526).
, shifting the base of his Sultanate from south of the Hindu Kush range and Ghazni towards the Yamuna River and Delhi. He thus helped bring Islamic rule to the northern plains of the Indian subcontinent.
The Moroccan traveler Ibn Battuta arrived in the Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate was an Islamic empire based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for 320 years (1206ŌĆō1526).
by passing through the Hindu Kush. The mountain passes of the Hindu Kush range were used by Timur and his army and they crossed to launch the 1398 invasion of the northern Indian subcontinent. Timur, also known as Temur or Tamerlane in Western scholarly literature, marched with his army to Delhi, plundering and killing all the way. He arrived in the capital Delhi where his army looted and killed its residents. Then he carried the wealth and the captured slaves, returning to his capital through the Hindu Kush.
Babur
Babur ( fa, , lit= tiger, translit= B─übur; ; 14 February 148326 December 1530), born M─½rz─ü Zah─½r ud-D─½n Muhammad, was the founder of the Mughal Empire in the Indian subcontinent. He was a descendant of Timur and Genghis Khan through his ...
, the founder of the Mughal Empire, was a patrilineal descendant of Timur with roots in Central Asia. He first established himself and his army in Kabul and the Hindu Kush region. In 1526, he made his move into north India, and won the Battle of Panipat, ending the last Delhi Sultanate dynasty, and starting the era of the Mughals.
Slavery

 Slavery, as with all major ancient and medieval societies, has been a part of Central Asia and South Asia history. The Hindu Kush mountain passes connected the slave markets of Central Asia with slaves seized in South Asia.Scott C. Levi (2002), ''Hindus beyond the Hindu Kush: Indians in the Central Asian Slave Trade'', Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, Cambridge University Press, Volume 12, Number 3 (Nov. 2002), pages 277ŌĆō288 The seizure and transportation of slaves from the Indian subcontinent became intense in and after the 8th century CE, with evidence suggesting that the slave transport involved "hundreds of thousands" of slaves from India in different periods of Islamic rule era. According to John Coatsworth and others, the slave trading operations during the pre-Akbar Mughal and Delhi Sultanate era "sent thousands of Hindus every year north to Central Asia to pay for horses and other goods". However, the interaction between Central Asia and South Asia through the Hindu Kush was not limited to slavery, it included trading in food, goods, horses and weapons.
The practice of raiding tribes, hunting, and kidnapping people for slave trading continued through the 19th century, at an extensive scale, around the Hindu Kush. According to a British Anti-Slavery Society report of 1874, the governor of Faizabad, Mir Ghulam Bey, kept 8,000 horses and cavalrymen who routinely captured non-Muslims as well as Shia Muslims as slaves. Others alleged to be involved in the slave trade were feudal lords such as Ameer Sheer Ali. The isolated communities in the Hindu Kush were one of the targets of these slave-hunting expeditions.
Slavery, as with all major ancient and medieval societies, has been a part of Central Asia and South Asia history. The Hindu Kush mountain passes connected the slave markets of Central Asia with slaves seized in South Asia.Scott C. Levi (2002), ''Hindus beyond the Hindu Kush: Indians in the Central Asian Slave Trade'', Journal of the Royal Asiatic Society, Cambridge University Press, Volume 12, Number 3 (Nov. 2002), pages 277ŌĆō288 The seizure and transportation of slaves from the Indian subcontinent became intense in and after the 8th century CE, with evidence suggesting that the slave transport involved "hundreds of thousands" of slaves from India in different periods of Islamic rule era. According to John Coatsworth and others, the slave trading operations during the pre-Akbar Mughal and Delhi Sultanate era "sent thousands of Hindus every year north to Central Asia to pay for horses and other goods". However, the interaction between Central Asia and South Asia through the Hindu Kush was not limited to slavery, it included trading in food, goods, horses and weapons.
The practice of raiding tribes, hunting, and kidnapping people for slave trading continued through the 19th century, at an extensive scale, around the Hindu Kush. According to a British Anti-Slavery Society report of 1874, the governor of Faizabad, Mir Ghulam Bey, kept 8,000 horses and cavalrymen who routinely captured non-Muslims as well as Shia Muslims as slaves. Others alleged to be involved in the slave trade were feudal lords such as Ameer Sheer Ali. The isolated communities in the Hindu Kush were one of the targets of these slave-hunting expeditions.
Modern era
In the early 19th century, the Sikh Empire expanded underRanjit Singh
Ranjit Singh (13 November 1780 ŌĆō 27 June 1839), popularly known as Sher-e-Punjab or "Lion of Punjab", was the first Maharaja of the Sikh Empire, which ruled the northwest Indian subcontinent in the early half of the 19th century. He s ...
in the northwest as far as the Hindu Kush range. However, the people of so-called Kafiristan practiced had ancient polytheistic traditions until the 1896 invasion and conversion to Islam at the hands of Afghans under Amir Abdur Rahman Khan.
The Hindu Kush served as a geographical barrier to the British Empire, leading to a paucity of information and scarce direct interaction between the British colonial officials and Central Asian peoples. The British had to rely on tribal chiefs, Sadozai and Barakzai noblemen for information, and they generally downplayed the reports of slavery and other violence for geo-political strategic considerations.
In the colonial era, the Hindu Kush was considered, informally, the dividing line between Russian and British areas of influence in Afghanistan. During the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because the ...
the Hindu Kush range became a strategic theatre, especially during the 1980s when Soviet forces and their Afghan allies fought the Afghan mujahideen channelled through Pakistan. After the Soviet withdrawal and the end of the Cold War, many mujahideen morphed into Taliban and al-Qaeda forces imposing a strict interpretation of Islamic law (Sharia
Sharia (; ar, ž┤ž▒┘Ŗž╣ž®, shar─½╩┐a ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the H ...
), with Kabul, these mountains, and other parts of Afghanistan as their base. Other Mujahideen joined the Northern Alliance to oppose the Taliban rule.
After the 11 September 2001 terror attacks in New York City and Washington D.C., the American and ISAF campaign against Al Qaeda and their Taliban allies made the Hindu Kush once again a militarised conflict zone.
Climate change
 The 2019 Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment concluded that between 1901 to 2014, the Hindu Kush Himalaya (or HKH) region had already experienced warming of 0.1 ┬░C per decade, with the warming rate accelerating to 0.2 ┬░C per decade over the past 50 years.Over the past 50 years, the frequency of warm days and nights had also increased by 1.2 days and 1.7 nights per decade, while the frequency of ''extreme'' warm days and nights had increased by 1.26 days and 2.54 nights per decade. There was also a corresponding decline of 0.5 cold days, 0.85 extreme cold days, 1 cold night, and 2.4 extreme cold nights per decade. The length of the
The 2019 Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment concluded that between 1901 to 2014, the Hindu Kush Himalaya (or HKH) region had already experienced warming of 0.1 ┬░C per decade, with the warming rate accelerating to 0.2 ┬░C per decade over the past 50 years.Over the past 50 years, the frequency of warm days and nights had also increased by 1.2 days and 1.7 nights per decade, while the frequency of ''extreme'' warm days and nights had increased by 1.26 days and 2.54 nights per decade. There was also a corresponding decline of 0.5 cold days, 0.85 extreme cold days, 1 cold night, and 2.4 extreme cold nights per decade. The length of the growing season
A season is a division of the year marked by changes in weather, ecology, and the amount of daylight. The growing season is that portion of the year in which local conditions (i.e. rainfall, temperature, daylight) permit normal plant growth. Whil ...
has increased by 4.25 days per decade. There is less conclusive evidence of light precipitation becoming less frequent while heavy precipitation became both more frequent and more intense. Finally, since 1970s glaciers have retreated everywhere in the region beside Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
, eastern Pamir, and western Kunlun, where there has been an unexpected increase in snowfall. Glacier retreat had been followed by an increase in the number of glacial lake
A glacial lake is a body of water with origins from glacier activity. They are formed when a glacier erodes the land and then melts, filling the depression created by the glacier.
Formation
Near the end of the last glacial period, roughly 10,0 ...
s, some of which may be prone to dangerous floods.
In the future, if the Paris Agreement
The Paris Agreement (french: Accord de Paris), often referred to as the Paris Accords or the Paris Climate Accords, is an international treaty on climate change. Adopted in 2015, the agreement covers climate change mitigation, Climate change a ...
goal of 1.5 ┬░C of global warming is not exceeded, warming in the HKH will be at least 0.3 ┬░C higher, and at least 0.7 ┬░C higher in the hotspots of northwest Himalaya and Karakoram. If the Paris Agreement goals are broken, then the region is expected to warm by 1.7ŌĆō2.4 ┬░C in the near future (2036ŌĆō2065) and by 2.2ŌĆō3.3 ┬░C (2066ŌĆō2095) near the end of the century under the "intermediate" Representative Concentration Pathway 4.5 (RCP4.5). Under the high-warming RCP8.5 scenario where the annual emissions continue to increase for the rest of the century, the expected regional warming is 2.3ŌĆō3.2 ┬░C and 4.2ŌĆō6.5 ┬░C, respectively. Under all scenarios, winters will warm more than the summers, and the Tibetan Plateau, the central Himalayan Range, and the Karakoram will continue to warm more than the rest of the region. Climate change will also lead to the degradation of up to 81% of the region's permafrost
Permafrost is ground that continuously remains below 0 ┬░C (32 ┬░F) for two or more years, located on land or under the ocean. Most common in the Northern Hemisphere, around 15% of the Northern Hemisphere or 11% of the global surface ...
by the end of the century.
Future precipitation is projected to increase as well, but CMIP5 models struggle to make specific projections due to the region's topography: the most certain finding is that the monsoon precipitation in the region will increase by 4ŌĆō12% in the near future and by 4ŌĆō25% in the long term. There has also been modelling of the changes in snow cover, but it is limited to the end of century under the RCP 8.5 scenario: it projects declines of 30ŌĆō50% in the Indus Basin, 50ŌĆō60% in the Ganges basin, and 50ŌĆō70% in the Brahmaputra Basin, as the snowline elevation in these regions will rise by between 4.4 and 10.0 m/yr. There has been more extensive modelling of glacier trends: it is projected that one third of all glaciers in the extended HKH region will be lost by 2100 even if the warming is limited to 1.5 ┬░C (with over half of that loss in the Eastern Himalaya region), while RCP 4.5 and RCP 8.5 are likely to lead to the losses of 50% and >67% of the region's glaciers over the same timeframe. Glacier melt is projected to accelerate regional river flows until the amount of meltwater peaks around 2060, going into an irreversible decline afterwards. Since precipitation will continue to increase even as the glacier meltwater contribution declines, annual river flows are only expected to diminish in the western basins where contribution from the monsoon is low: however, irrigation and hydropower generation would still have to adjust to greater interannual variability and lower pre-monsoon flows in all of the region's rivers.
Future development and adaptation
A range of adaptation efforts are already undertaken across the HKH region: however, they suffer from underinvestment and insufficient coordination between the various state, institutional and other non-state efforts, and need to be "urgently" strengthened in order to be commensurate with the challenges ahead. The 2019 Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment outlined three main "storylines" for the region between now and 2080: "business-as-usual" (or "muddling through"), with no significant change from the current trends and development/adaptation initiatives proceeding as they do now; "downhill", where the intensity of global climate change is high, local initiatives fail and regional cooperation breaks down; and "prosperous", where extensive cooperation allows region's communities to weather "moderate" climate change and increase their living standards while also preserving the region's biodiversity. In addition, it described two alternate pathways through which the "prosperous" future can be achieved: the first focuses on top-down, large-scale development and the latter describes a bottom-up, decentralized alternative.Ethnography
Pre-Islamic populations of the Hindu Kush included Shins, Yeshkuns,Biddulph, p.12 Chiliss, Neemchas Koli,Biddulph, p.9 Palus, Gaware,Biddulph, p.11 and Krammins.See also
*Mount Imeon
Mount Imeon () is an ancient name for the Central Asian complex of mountain ranges comprising the present Hindu Kush, Pamir and Tian Shan, extending from the Zagros Mountains in the southwest to the Altay Mountains in the northeast, and linked to ...
* Paropamisus Mountains
* ''A Short Walk in the Hindu Kush
''A Short Walk in the Hindu Kush'' is a 1958 book by the English travel writer Eric Newby. It is an autobiographical account of his adventures in the Hindu Kush, around the Nuristan mountains of Afghanistan, ostensibly to make the first mounta ...
''
* Geography of Afghanistan
* Geography of Pakistan
*Karakoram
The Karakoram is a mountain range in Kashmir region spanning the borders of Pakistan, China, and India, with the northwest extremity of the range extending to Afghanistan and Tajikistan. Most of the Karakoram mountain range falls under the ...
* Hindustan
*List of highest mountains
Currently, There are at least 108 mountains on Earth with elevations of or greater above sea level. The vast majority of these mountains are located on the edge of the Indian plate, Indian and Eurasian plate, Eurasian plates in China, India, ...
(a list of mountains above 7,200m)
* List of mountain ranges
* 2002 Hindu Kush earthquakes
*2005 Hindu Kush earthquake
The 2005 Hindu Kush earthquake hit northeastern Afghanistan with a magnitude of 6.5 on December 12 at 21:47 (UTC). According to the United States Geological Survey's ShakeMap and Did You Feel It? products, the maximum Mercalli intensity was V ('' ...
Notes
References
Citations
Sources
; Works cited * (facsimile of the original edition).Further reading
* Drew, Frederic (1877). ''The Northern Barrier of India: A Popular Account of the Jammoo and Kashmir Territories with Illustrations''. Frederic Drew. 1st edition: Edward Stanford, London. Reprint: Light & Life Publishers, Jammu, 1971 * Gibb, H. A. R. (1929). ''Ibn Batt┼½ta: Travels in Asia and Africa, 1325ŌĆō1354''. Translated and selected by H. A. R. Gibb. Reprint: Asian Educational Services, New Delhi and Madras, 1992 * Gordon, T. E. (1876). ''The Roof of the World: Being the Narrative of a Journey over the High Plateau of Tibet to the Russian Frontier and the Oxus Sources on Pamir.'' Edinburgh. Edmonston and Douglas. Reprint: ChŌĆÖeng Wen Publishing Company. Tapei, 1971 * Leitner, Gottlieb Wilhelm (1890). ''Dardistan in 1866, 1886 and 1893: Being An Account of the History, Religions, Customs, Legends, Fables and Songs of Gilgit, Chilas, Kandia (Gabrial) Yasin, Chitral, Hunza, Nagyr and other parts of the Hindukush, as also a supplement to the second edition of The Hunza and Nagyr Handbook. And An Epitome of Part III of the author's 'The Languages and Races of Dardistan. Reprint, 1978. Manjusri Publishing House, New Delhi. * Newby, Eric. (1958). ''A Short Walk in the Hindu Kush
''A Short Walk in the Hindu Kush'' is a 1958 book by the English travel writer Eric Newby. It is an autobiographical account of his adventures in the Hindu Kush, around the Nuristan mountains of Afghanistan, ostensibly to make the first mounta ...
''. Secker, London. Reprint: Lonely Planet.
* Yule, Henry and Burnell, A. C. (1886). ''Hobson-Jobson: The Anglo-Indian Dictionary''. 1996 reprint by Wordsworth Editions Ltd.
''A Country Study: Afghanistan''
Library of Congress * Ervin Gr├Čtzbach, * ''Encyclop├”dia Britannica'', 15th Ed., Vol. 21, pp. 54ŌĆō55, 65, 1987 * ''
An Advanced History of India
''An Advanced History of India'' is a book on Indian history written by R.C. Majumdar, Hem Chandra Raychaudhuri, H.C. Raychaudhuri and Kalikinkar Datta, first published in 1946.
This renowned book consists of two parts. And similarly, according ...
'', by R. C. Majumdar
Ramesh Chandra Majumdar (known as R. C. Majumdar; 4 December 1888 ŌĆō 11 February 1980) was a historian and professor of Indian history. Majumdar is a noted historian of modern India. He was a former Sheriff of Kolkata.
Early life and educatio ...
, H. C. Raychaudhuri, K.Datta, 2nd Ed., MacMillan and Co., London, pp. 336ŌĆō37, 1965
* ''The Cambridge History of India, Vol. IV: The Mughul Period'', by W. Haig & R. Burn, S. Chand & Co., New Delhi, pp. 98ŌĆō99, 1963
External links
Khyber Pass
Geology
{{Authority control Geography of Afghanistan History of Pakistan Iranian Plateau Landforms of Badakhshan Province Landforms of Baghlan Province Landforms of Bamyan Province Landforms of Kabul Province Landforms of Kapisa Province Landforms of Nuristan Province Landforms of Panjshir Province Landforms of Parwan Province Landforms of South Asia Mountain ranges of Afghanistan Mountain ranges of Asia Mountain ranges of Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Mountain ranges of Pakistan Mountain ranges of the Himalayas Physiographic provinces Sites along the Silk Road