Heathrow T5 Station AB on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major
 Heathrow is west of central
Heathrow is west of central

 Heathrow Airport began in 1929 as a small airfield (
Heathrow Airport began in 1929 as a small airfield (
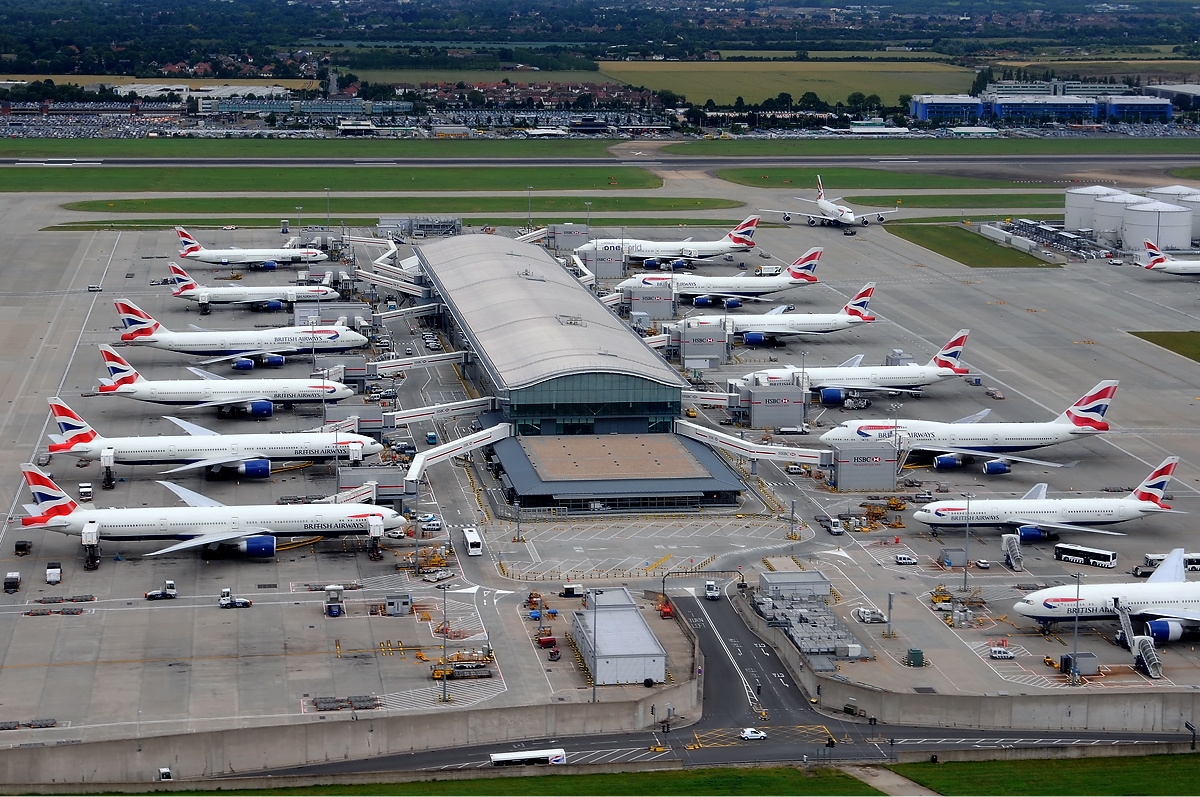


 Heathrow Airport is used by over 80 airlines flying to 185 destinations in 84 countries. The airport is the primary hub of British Airways and is a base for
Heathrow Airport is used by over 80 airlines flying to 185 destinations in 84 countries. The airport is the primary hub of British Airways and is a base for
retrieved 20 January 2021
 The airport's newest terminal, officially known as the Queen's Terminal, was opened on 4 June 2014 and has 24 gates. Designed by Spanish architect
The airport's newest terminal, officially known as the Queen's Terminal, was opened on 4 June 2014 and has 24 gates. Designed by Spanish architect
 Terminal 3 opened as the Oceanic Terminal on 13 November 1961 to handle flight departures for long-haul routes for foreign carriers to the United States, Asia and other Far Eastern destinations. At this time the airport had a direct helicopter service to Central London from the gardens on the roof of the terminal building. Renamed Terminal 3 in 1968, it was expanded in 1970 with the addition of an arrivals building. Other facilities added included the UK's first
Terminal 3 opened as the Oceanic Terminal on 13 November 1961 to handle flight departures for long-haul routes for foreign carriers to the United States, Asia and other Far Eastern destinations. At this time the airport had a direct helicopter service to Central London from the gardens on the roof of the terminal building. Renamed Terminal 3 in 1968, it was expanded in 1970 with the addition of an arrivals building. Other facilities added included the UK's first
 Opened in 1986, Terminal 4 has 22 gates and is situated to the south of the southern runway next to the cargo terminal and is connected to Terminals 2 and 3 by the
Opened in 1986, Terminal 4 has 22 gates and is situated to the south of the southern runway next to the cargo terminal and is connected to Terminals 2 and 3 by the
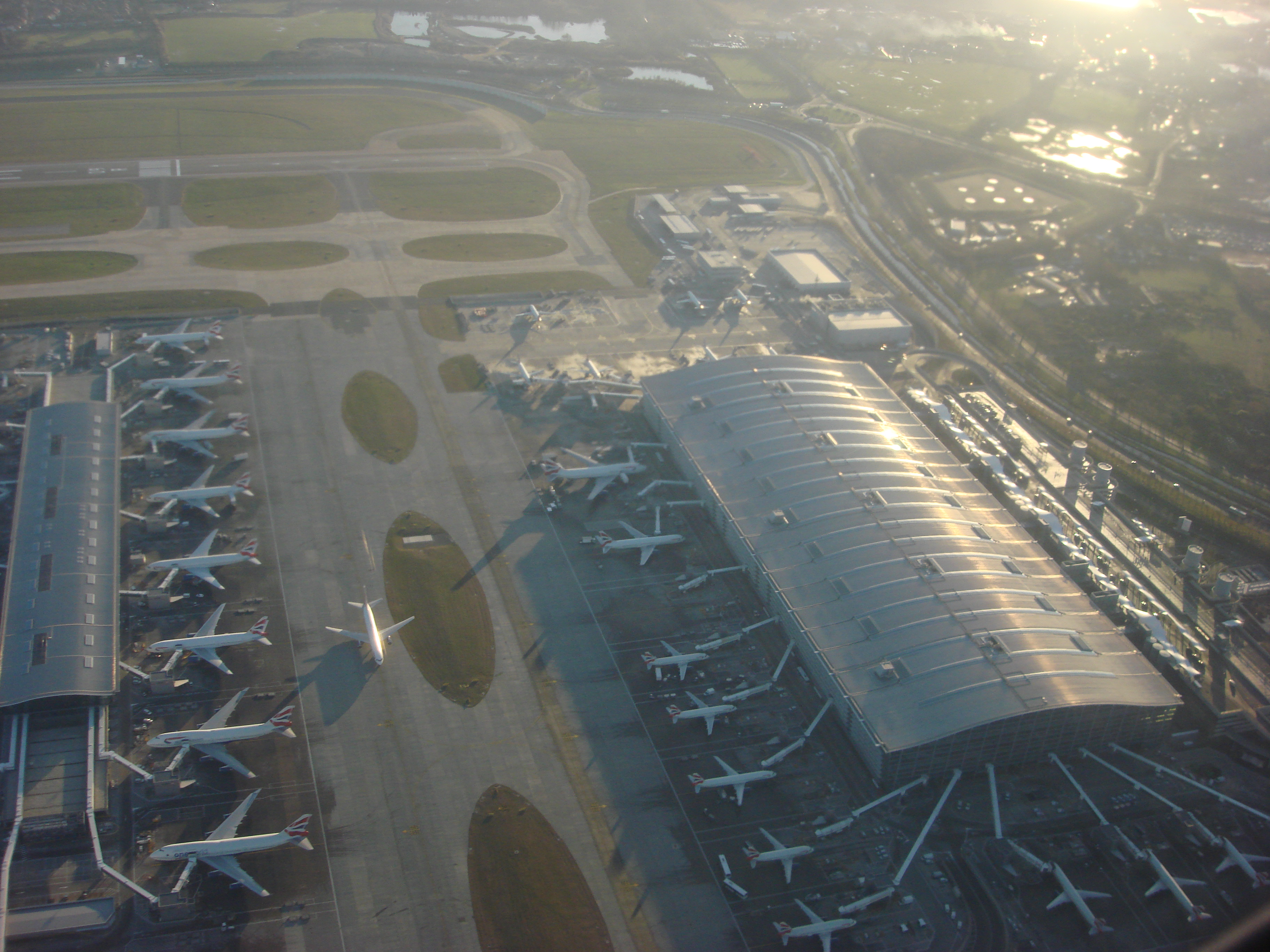 Terminal 5 lies between the northern and southern runways at the western end of the Heathrow site and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 14 March 2008, some 19 years after its inception. It opened to the public on 27 March 2008, and British Airways and its partner company Iberia have exclusive use of this terminal, which has 50 gates, including 3 hardstands. The first passenger to enter Terminal 5 was a UK expatriate, ex-pat from Kenya who passed through security at 04:30 on the day. He was presented with a boarding pass by British Airways CEO Willie Walsh for the first departing flight, BA302 to Paris. During the two weeks after its opening, operations were disrupted by problems with the terminal's IT systems, coupled with insufficient testing and staff training, which caused over 500 flights to be cancelled. Until March 2012, Terminal 5 was exclusively used by British Airways as its global hub; however, because of the merger, on 25 March Iberia (airline), Iberia's operations at Heathrow were moved to the terminal, making it the home of International Airlines Group. On 7 July 2020, American Airlines, American moved to terminal 5, to allow for easier connections from American's transatlantic flights to British Airways flights during the pandemic. However, all the American flights, except JFK, have returned to Terminal 3. However, Iberia moved its flights to Terminal 3 before the reopening due to the pandemic. China Southern Airlines used Terminal 5 due to the pandemic until it was relocated to Terminal 4 in November 2022.
Built at £4.3 billion, the terminal consists of a four-story main terminal building (Concourse A) and two satellite buildings linked to the main terminal by an underground people mover transit system. Concourse A has dedicated British Airways's narrowbody fleet for flights around the UK and the rest of Europe, the first satellite (Concourse B) includes dedicated stands for BA and Iberia's widebody fleet except for the Airbus A380, and the second satellite (Concourse C), includes 7 dedicated aircraft stands for the A380. It became fully operational on 1 June 2011. Terminal 5 was voted Skytrax World's Best Airport Terminal 2014 in the Annual World Airport Awards.
The main terminal building (Concourse A) has an area of while Concourse B covers . It has 60 aircraft stands and capacity for 30 a million passengers annually as well as more than 100 shops and restaurants. It is also home to British Airways' Flagship lounge, the Concorde Room, alongside four further British Airways branded lounges. One of those lounges is the British Airways Arrivals Lounge which is located land-side.
A further building, designated Concourse D and of similar size to Concourse C, may yet be built to the east of the existing site, providing up to another 16 stands. Following British Airways' merger with Iberia (airline), Iberia, this may become a priority since the combined business will require accommodation at Heathrow under one roof to maximise the cost savings envisaged under the deal. A proposal for Concourse D was featured in Heathrow's most recent capital investment plan.
The transport network around the airport has been extended to cope with the increase in passenger numbers. New branches of both the Heathrow Express and the Underground's Piccadilly line serve a new shared Heathrow Terminal 5 station. A dedicated spur route, motorway spur links the terminal to the M25 (between junctions 14 and 15). The terminal has 3,800 spaces multi-storey car park. A more distant long-stay car park for business passengers is connected to the terminal by a personal rapid transit system, the London Heathrow Terminal 5 PRT, Heathrow Pod, which became operational in the spring of 2011. Within the terminal complex, an automated people mover (APM) system, known as the Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit, is used to transport passengers between the satellite buildings.
Terminal 5 lies between the northern and southern runways at the western end of the Heathrow site and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 14 March 2008, some 19 years after its inception. It opened to the public on 27 March 2008, and British Airways and its partner company Iberia have exclusive use of this terminal, which has 50 gates, including 3 hardstands. The first passenger to enter Terminal 5 was a UK expatriate, ex-pat from Kenya who passed through security at 04:30 on the day. He was presented with a boarding pass by British Airways CEO Willie Walsh for the first departing flight, BA302 to Paris. During the two weeks after its opening, operations were disrupted by problems with the terminal's IT systems, coupled with insufficient testing and staff training, which caused over 500 flights to be cancelled. Until March 2012, Terminal 5 was exclusively used by British Airways as its global hub; however, because of the merger, on 25 March Iberia (airline), Iberia's operations at Heathrow were moved to the terminal, making it the home of International Airlines Group. On 7 July 2020, American Airlines, American moved to terminal 5, to allow for easier connections from American's transatlantic flights to British Airways flights during the pandemic. However, all the American flights, except JFK, have returned to Terminal 3. However, Iberia moved its flights to Terminal 3 before the reopening due to the pandemic. China Southern Airlines used Terminal 5 due to the pandemic until it was relocated to Terminal 4 in November 2022.
Built at £4.3 billion, the terminal consists of a four-story main terminal building (Concourse A) and two satellite buildings linked to the main terminal by an underground people mover transit system. Concourse A has dedicated British Airways's narrowbody fleet for flights around the UK and the rest of Europe, the first satellite (Concourse B) includes dedicated stands for BA and Iberia's widebody fleet except for the Airbus A380, and the second satellite (Concourse C), includes 7 dedicated aircraft stands for the A380. It became fully operational on 1 June 2011. Terminal 5 was voted Skytrax World's Best Airport Terminal 2014 in the Annual World Airport Awards.
The main terminal building (Concourse A) has an area of while Concourse B covers . It has 60 aircraft stands and capacity for 30 a million passengers annually as well as more than 100 shops and restaurants. It is also home to British Airways' Flagship lounge, the Concorde Room, alongside four further British Airways branded lounges. One of those lounges is the British Airways Arrivals Lounge which is located land-side.
A further building, designated Concourse D and of similar size to Concourse C, may yet be built to the east of the existing site, providing up to another 16 stands. Following British Airways' merger with Iberia (airline), Iberia, this may become a priority since the combined business will require accommodation at Heathrow under one roof to maximise the cost savings envisaged under the deal. A proposal for Concourse D was featured in Heathrow's most recent capital investment plan.
The transport network around the airport has been extended to cope with the increase in passenger numbers. New branches of both the Heathrow Express and the Underground's Piccadilly line serve a new shared Heathrow Terminal 5 station. A dedicated spur route, motorway spur links the terminal to the M25 (between junctions 14 and 15). The terminal has 3,800 spaces multi-storey car park. A more distant long-stay car park for business passengers is connected to the terminal by a personal rapid transit system, the London Heathrow Terminal 5 PRT, Heathrow Pod, which became operational in the spring of 2011. Within the terminal complex, an automated people mover (APM) system, known as the Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit, is used to transport passengers between the satellite buildings.
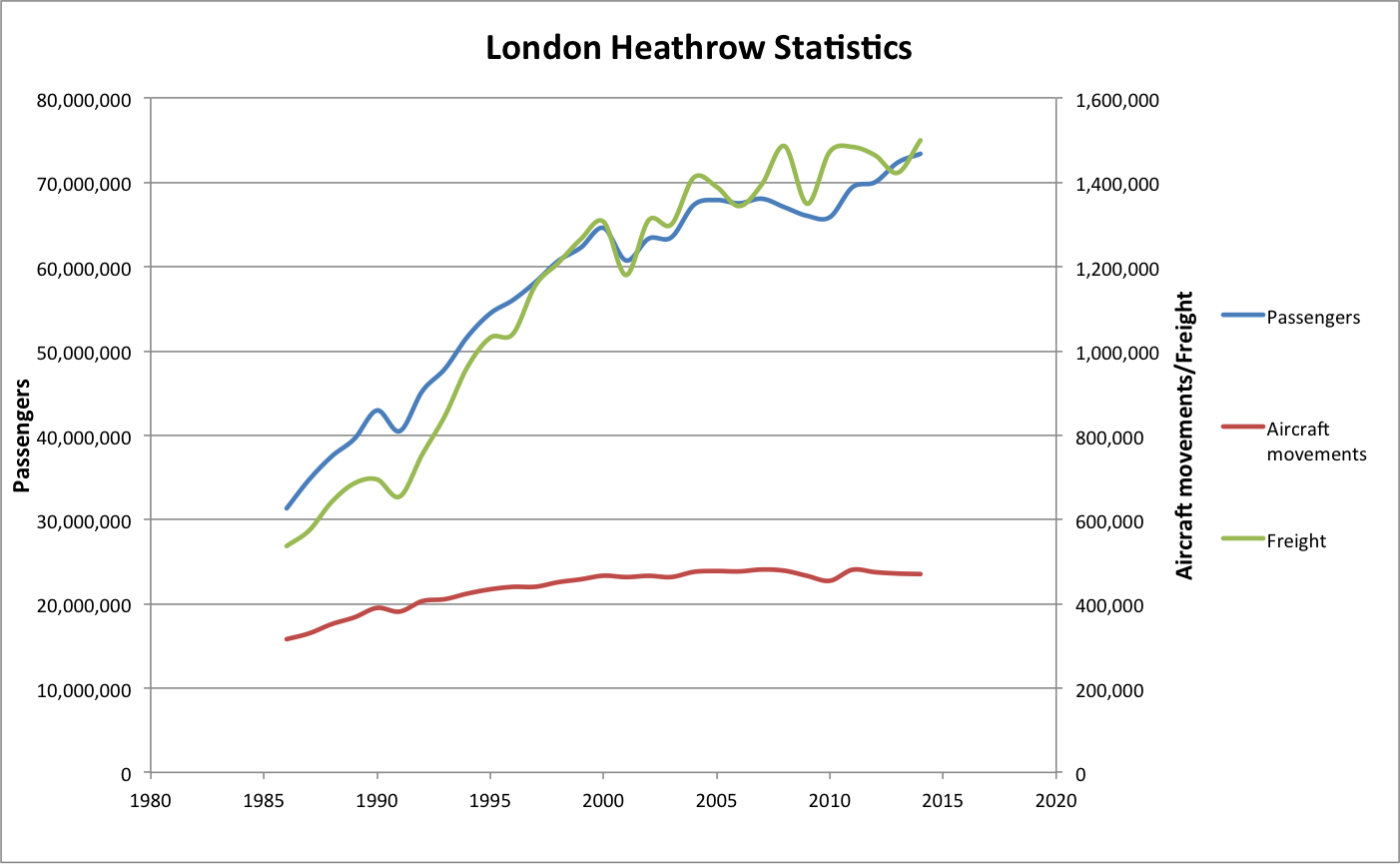 When ranked by World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, passenger traffic, Heathrow is the sixth busiest internationally, behind Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Beijing Capital International Airport, Dubai International Airport, Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, and Haneda Airport, Tokyo Haneda Airport, for the 12 months ending December 2015. London Heathrow Airport was noted as the best-connected airport globally in 2019 according to the OAG (company), OAG's Megahubs Index with a connectivity score of 317. Dominant carrier British Airways was recorded as holding a 51% share of flights at the hub.
In 2015, Heathrow was List of the busiest airports in Europe, the busiest airport in Europe in total passenger traffic, with 14% more passengers than Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport and 22% more than Istanbul Atatürk Airport. Heathrow was the fourth busiest European airport by cargo traffic in 2013, after Frankfurt Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.
In 2020, Heathrow's passenger numbers dropped sharply by over 72%, (a decrease of 58 million travellers compared to 2019), due to the impact caused by restrictions and/or bans on travel caused by the global
When ranked by World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, passenger traffic, Heathrow is the sixth busiest internationally, behind Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Beijing Capital International Airport, Dubai International Airport, Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, and Haneda Airport, Tokyo Haneda Airport, for the 12 months ending December 2015. London Heathrow Airport was noted as the best-connected airport globally in 2019 according to the OAG (company), OAG's Megahubs Index with a connectivity score of 317. Dominant carrier British Airways was recorded as holding a 51% share of flights at the hub.
In 2015, Heathrow was List of the busiest airports in Europe, the busiest airport in Europe in total passenger traffic, with 14% more passengers than Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport and 22% more than Istanbul Atatürk Airport. Heathrow was the fourth busiest European airport by cargo traffic in 2013, after Frankfurt Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.
In 2020, Heathrow's passenger numbers dropped sharply by over 72%, (a decrease of 58 million travellers compared to 2019), due to the impact caused by restrictions and/or bans on travel caused by the global
 The head office of
The head office of
58
. "Speedbird House, PO Box 10, London Heathrow Airport, Hounslow, Middlesex, TW6 2JA, UK." before the completion of Waterside (building), Waterside, the current BA head office in
200
. Retrieved from Google Books on 12 February 2010. , . To the north of the airfield lies the Northern Perimeter Road, along which most of Heathrow's car rental agencies are based, and Bath Road, which runs parallel to it, but outside the airport campus. This is nicknamed "The Strip" by locals, because of its continuous line of airport hotels.

 * Heathrow Express: a non-stop service direct to Paddington railway station, London Paddington; trains leave every 15 minutes for the 15-minute journey (21 minutes to and from Terminal 5). Trains depart from Heathrow Terminal 5 station or Heathrow Central railway station, Heathrow Central station (Terminals 2 & 3). Free transfer service operates between Terminal 4 and Heathrow Central to connect with services from London and Terminal 5.
* Elizabeth Line: a stopping service to Abbey Wood railway station, Abbey Wood via London Paddington station, Paddington and central London – trains leave every 30 minutes. Calls at Hayes & Harlington railway station, Hayes & Harlington for connecting trains to Reading railway station, Reading. It will also serve the line to Shenfield railway station, Shenfield from 2023.
* London Underground (Piccadilly line): four stations serve the airport: Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 tube station, Terminal 2 & 3, Heathrow Terminal 4 tube station, Terminal 4 and Heathrow Terminal 5 station, Terminal 5 serve the passenger terminals; Hatton Cross tube station, Hatton Cross serves the maintenance areas. The usual journey time from Heathrow Central to Central London is around 40–50 minutes.
* Heathrow Express: a non-stop service direct to Paddington railway station, London Paddington; trains leave every 15 minutes for the 15-minute journey (21 minutes to and from Terminal 5). Trains depart from Heathrow Terminal 5 station or Heathrow Central railway station, Heathrow Central station (Terminals 2 & 3). Free transfer service operates between Terminal 4 and Heathrow Central to connect with services from London and Terminal 5.
* Elizabeth Line: a stopping service to Abbey Wood railway station, Abbey Wood via London Paddington station, Paddington and central London – trains leave every 30 minutes. Calls at Hayes & Harlington railway station, Hayes & Harlington for connecting trains to Reading railway station, Reading. It will also serve the line to Shenfield railway station, Shenfield from 2023.
* London Underground (Piccadilly line): four stations serve the airport: Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 tube station, Terminal 2 & 3, Heathrow Terminal 4 tube station, Terminal 4 and Heathrow Terminal 5 station, Terminal 5 serve the passenger terminals; Hatton Cross tube station, Hatton Cross serves the maintenance areas. The usual journey time from Heathrow Central to Central London is around 40–50 minutes.
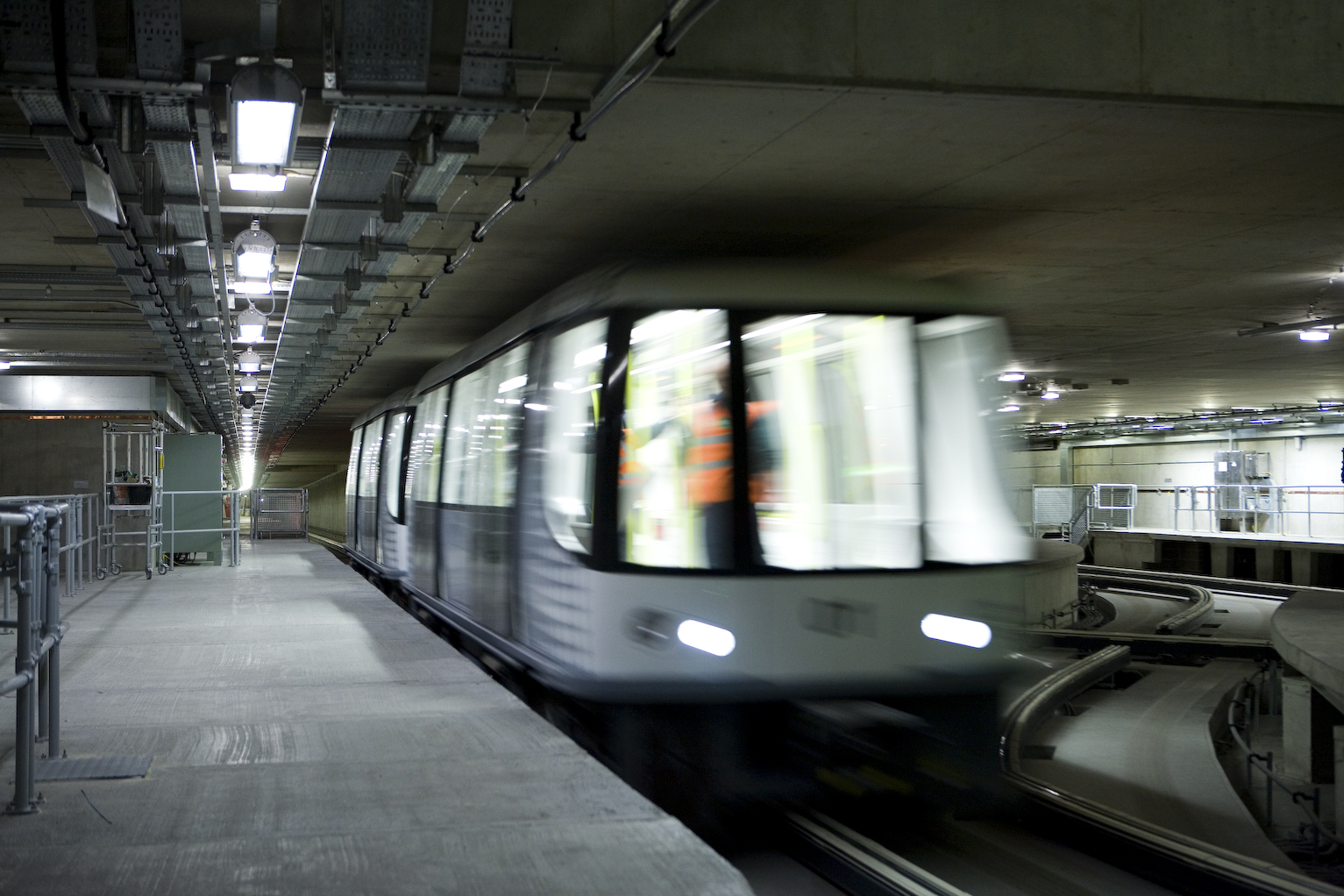 An underground automated people mover system known as the ''Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit'' operates within Terminal 5, linking the main terminal with the satellite Terminals 5B and 5C. The Transit operates entirely airside (airport), airside using Bombardier Innovia APM 200 people mover vehicles.
An underground automated people mover system known as the ''Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit'' operates within Terminal 5, linking the main terminal with the satellite Terminals 5B and 5C. The Transit operates entirely airside (airport), airside using Bombardier Innovia APM 200 people mover vehicles.
 Heathrow is accessible via the nearby M4 motorway or A4 road (Great Britain), A4 road (Terminals 2–3), the
Heathrow is accessible via the nearby M4 motorway or A4 road (Great Britain), A4 road (Terminals 2–3), the
 * On 17 January 2008, a British Airways Boeing 777, Boeing 777-236ER, G-YMMM, operating British Airways Flight 38, flight BA038 from Beijing, crash-landed at Heathrow. The aircraft landed on grass short of the south runway, then slid to the edge of the runway and stopped on the threshold, leading to 18 minor injuries. The aircraft was later found to have suffered a loss of thrust caused by fuel icing.
* On 28 September 2022, there was a ground collision involving a Korean Air Boeing 777 that was about to take off to Seoul, and an Icelandair Boeing 757 which had landed from Reykjavik. The 777 aborted its takeoff and no injuries were reported, but the aircraft suffered minor damage.
* On 17 January 2008, a British Airways Boeing 777, Boeing 777-236ER, G-YMMM, operating British Airways Flight 38, flight BA038 from Beijing, crash-landed at Heathrow. The aircraft landed on grass short of the south runway, then slid to the edge of the runway and stopped on the threshold, leading to 18 minor injuries. The aircraft was later found to have suffered a loss of thrust caused by fuel icing.
* On 28 September 2022, there was a ground collision involving a Korean Air Boeing 777 that was about to take off to Seoul, and an Icelandair Boeing 757 which had landed from Reykjavik. The 777 aborted its takeoff and no injuries were reported, but the aircraft suffered minor damage.
 There is a long history of expansion proposals for Heathrow since it was first designated as a civil airport. Following the cancellation of the Maplin project in 1974, a fourth terminal was proposed but expansion beyond this was ruled out. However, the Airports Inquiries of 1981–83 and the 1985 Airports Policy White Paper considered further expansion and, following a four-year-long public inquiry in 1995–99, Terminal 5 was approved. In 2003, after many studies and consultations, the Future of Air Transport White Paper was published which proposed a third runway at Heathrow, as well as a second runway at Stansted Airport. In January 2009, the Transport Secretary at the time, Geoff Hoon announced that the Brown ministry, British government supported the expansion of Heathrow by building a third runway and a sixth terminal building. This decision followed the 2003 white paper on the Air transport and the environment (United Kingdom)#Airport development strategy, future of air transport in the UK, and a public consultation in November 2007. This was a controversial decision which met with widespread opposition because of the expected greenhouse gas emissions, impact on local communities, as well as noise and air pollution concerns.
Before the 2010 United Kingdom general election, 2010 general election, the Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties announced that they would prevent the construction of any third runway or further material expansion of the airport's operating capacity. The Mayor of London, then Boris Johnson, took the position that London needs more airport capacity, favouring the construction of an entirely Thames Estuary Airport, new airport in the Thames Estuary rather than expanding Heathrow. After the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition took power, it was announced that the third runway expansion was cancelled. Two years later, leading Conservatives were reported to have changed their minds on the subject.
Another proposal for expanding Heathrow's capacity was the Heathrow Hub, which aims to extend both runways to a total length of about 7,000 metres and divide them into four so that they each provide two, full-length runways, allowing simultaneous take-offs and landings while decreasing noise levels.
In July 2013, the airport submitted three new proposals for expansion to the Airports Commission, which was established to review airport capacity in the southeast of England. The Airports Commission was chaired by Sir Howard Davies. He, at the time of his appointment, was in the employ of GIC Private Limited (formerly known as Government Investment Corporation of Singapore) and a member of its International Advisory Board. GIC Private Limited was then (2012), as it remains today, one of Heathrow's principal owners. Sir Howard Davies resigned from these positions upon confirmation of his appointment to lead the Airports Commission, although it has been observed that he failed to identify these interests when invited to complete the Airports Commission's register of interests. Each of the three proposals that were to be considered by Sir Howard Davies's commission involved the construction of a third runway, either to the north, northwest or southwest of the airport.
The commission released its interim report in December 2013, shortlisting three options: the north-west third runway option at Heathrow, extending an existing runway at Heathrow, and a second runway at Gatwick Airport. After this report was published, the government confirmed that no options had been ruled out for airport expansion in the South-east and that a new runway would not be built at Heathrow before 2015. The full report was published on 1 July 2015, and backed a third, north-west, runway at Heathrow. Reaction to the report was generally adverse, particularly from London Mayor Boris Johnson. One senior Conservative told Channel 4: "Howard Davies has dumped an utter steaming pile of poo on the Prime Minister's desk." On 25 October 2016, the government confirmed that Heathrow would be allowed to build a third runway; however, a final decision would not be taken until winter of 2017/18, after consultations and government votes. The earliest opening year would be 2025.
On 5 June 2018, the UK Cabinet approved the third runway, with a full vote planned for Parliament. On 25 June 2018, the House of Commons voted, 415–119, in favour of the third runway. The bill received support from most MPs in the Conservative and Labour parties. A judicial review against the decision was launched by four London local authorities affected by the expansion—Wandsworth, Richmond, Hillingdon and Hammersmith and Fulham—in partnership with Greenpeace and London mayor Sadiq Khan. Khan previously stated he would take legal action if it were passed by Parliament.
In February 2020, the Court of Appeal ruled that the plans for a third runway were illegal since they did not adequately take into account the government's commitments to the Paris climate agreement. However, this ruling was later overturned by the Supreme Court in December 2020.
There is a long history of expansion proposals for Heathrow since it was first designated as a civil airport. Following the cancellation of the Maplin project in 1974, a fourth terminal was proposed but expansion beyond this was ruled out. However, the Airports Inquiries of 1981–83 and the 1985 Airports Policy White Paper considered further expansion and, following a four-year-long public inquiry in 1995–99, Terminal 5 was approved. In 2003, after many studies and consultations, the Future of Air Transport White Paper was published which proposed a third runway at Heathrow, as well as a second runway at Stansted Airport. In January 2009, the Transport Secretary at the time, Geoff Hoon announced that the Brown ministry, British government supported the expansion of Heathrow by building a third runway and a sixth terminal building. This decision followed the 2003 white paper on the Air transport and the environment (United Kingdom)#Airport development strategy, future of air transport in the UK, and a public consultation in November 2007. This was a controversial decision which met with widespread opposition because of the expected greenhouse gas emissions, impact on local communities, as well as noise and air pollution concerns.
Before the 2010 United Kingdom general election, 2010 general election, the Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties announced that they would prevent the construction of any third runway or further material expansion of the airport's operating capacity. The Mayor of London, then Boris Johnson, took the position that London needs more airport capacity, favouring the construction of an entirely Thames Estuary Airport, new airport in the Thames Estuary rather than expanding Heathrow. After the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition took power, it was announced that the third runway expansion was cancelled. Two years later, leading Conservatives were reported to have changed their minds on the subject.
Another proposal for expanding Heathrow's capacity was the Heathrow Hub, which aims to extend both runways to a total length of about 7,000 metres and divide them into four so that they each provide two, full-length runways, allowing simultaneous take-offs and landings while decreasing noise levels.
In July 2013, the airport submitted three new proposals for expansion to the Airports Commission, which was established to review airport capacity in the southeast of England. The Airports Commission was chaired by Sir Howard Davies. He, at the time of his appointment, was in the employ of GIC Private Limited (formerly known as Government Investment Corporation of Singapore) and a member of its International Advisory Board. GIC Private Limited was then (2012), as it remains today, one of Heathrow's principal owners. Sir Howard Davies resigned from these positions upon confirmation of his appointment to lead the Airports Commission, although it has been observed that he failed to identify these interests when invited to complete the Airports Commission's register of interests. Each of the three proposals that were to be considered by Sir Howard Davies's commission involved the construction of a third runway, either to the north, northwest or southwest of the airport.
The commission released its interim report in December 2013, shortlisting three options: the north-west third runway option at Heathrow, extending an existing runway at Heathrow, and a second runway at Gatwick Airport. After this report was published, the government confirmed that no options had been ruled out for airport expansion in the South-east and that a new runway would not be built at Heathrow before 2015. The full report was published on 1 July 2015, and backed a third, north-west, runway at Heathrow. Reaction to the report was generally adverse, particularly from London Mayor Boris Johnson. One senior Conservative told Channel 4: "Howard Davies has dumped an utter steaming pile of poo on the Prime Minister's desk." On 25 October 2016, the government confirmed that Heathrow would be allowed to build a third runway; however, a final decision would not be taken until winter of 2017/18, after consultations and government votes. The earliest opening year would be 2025.
On 5 June 2018, the UK Cabinet approved the third runway, with a full vote planned for Parliament. On 25 June 2018, the House of Commons voted, 415–119, in favour of the third runway. The bill received support from most MPs in the Conservative and Labour parties. A judicial review against the decision was launched by four London local authorities affected by the expansion—Wandsworth, Richmond, Hillingdon and Hammersmith and Fulham—in partnership with Greenpeace and London mayor Sadiq Khan. Khan previously stated he would take legal action if it were passed by Parliament.
In February 2020, the Court of Appeal ruled that the plans for a third runway were illegal since they did not adequately take into account the government's commitments to the Paris climate agreement. However, this ruling was later overturned by the Supreme Court in December 2020.
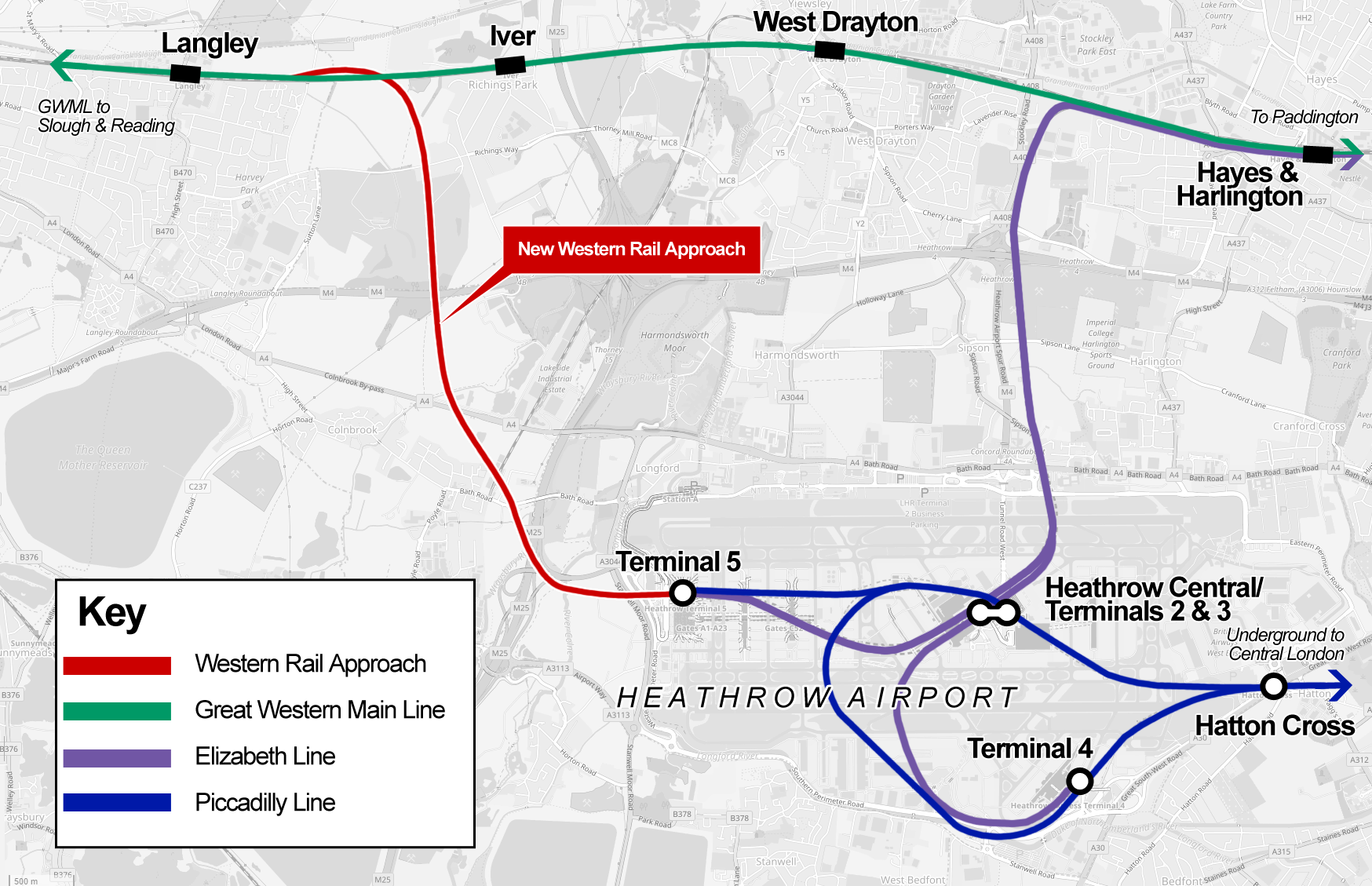 Currently, all rail connections with Heathrow airport run along an east-west alignment to and from central London, and a number of schemes have been proposed over the years to develop new rail transport links with other parts of London and with stations outside the city. This mainline rail service is due to be extended to central London and Essex when the Elizabeth line, currently under construction, opens.
A 2009 proposal to create a southern link with via the Waterloo–Reading line was abandoned in 2011 due to lack of funding and difficulties with a high number of Level crossings in the United Kingdom, level crossings on the route into London, and a plan to link Heathrow to the planned High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line (with a new station, ) was also dropped from the HS2 plans in March 2015.
Among other schemes that have been considered is a rapid transport link between Heathrow and Gatwick Airports, known as ''Heathwick'', which would allow the airports to operate jointly as an airline hub; In 2018, the Department for Transport began to invite proposals for privately funded rail links to Heathrow Airport. Projects being considered under this initiative include:
* the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a proposal for a spur from the Great Western Main Line to link Heathrow to , , the South West England, South West, South Wales and the West Midlands (region), West Midlands;
* Heathrow Southern Railway, a similar scheme to the abandoned Airtrack proposal, which would connect Terminal 5 station with or , , , Guildford railway station (Surrey), Guildford and ;
* HS4Air, a proposal for a new high-speed railway line which would link HS2 to the High Speed 1 line and the Channel Tunnel via a southern route, with stations at Heathrow and Gatwick Airports.
Currently, all rail connections with Heathrow airport run along an east-west alignment to and from central London, and a number of schemes have been proposed over the years to develop new rail transport links with other parts of London and with stations outside the city. This mainline rail service is due to be extended to central London and Essex when the Elizabeth line, currently under construction, opens.
A 2009 proposal to create a southern link with via the Waterloo–Reading line was abandoned in 2011 due to lack of funding and difficulties with a high number of Level crossings in the United Kingdom, level crossings on the route into London, and a plan to link Heathrow to the planned High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line (with a new station, ) was also dropped from the HS2 plans in March 2015.
Among other schemes that have been considered is a rapid transport link between Heathrow and Gatwick Airports, known as ''Heathwick'', which would allow the airports to operate jointly as an airline hub; In 2018, the Department for Transport began to invite proposals for privately funded rail links to Heathrow Airport. Projects being considered under this initiative include:
* the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a proposal for a spur from the Great Western Main Line to link Heathrow to , , the South West England, South West, South Wales and the West Midlands (region), West Midlands;
* Heathrow Southern Railway, a similar scheme to the abandoned Airtrack proposal, which would connect Terminal 5 station with or , , , Guildford railway station (Surrey), Guildford and ;
* HS4Air, a proposal for a new high-speed railway line which would link HS2 to the High Speed 1 line and the Channel Tunnel via a southern route, with stations at Heathrow and Gatwick Airports.
Heritage Publications (Hounslow Library)
* Smith, Graham. (2003) ''Taking to the Skies: the Story of British Aviation 1903–1939''. Countryside * Smith, Ron. (2002) ''British Built Aircraft Vol.1''. Greater London: Tempus * Sturtivant, Ray. (1995) ''Fairey Aircraft: in Old Photographs''. Alan Sutton * Taylor, H.A. (1974) ''Fairey Aircraft since 1915''. Putnam . * Taylor, John WR. (1997) ''Fairey Aviation: Archive Photographs''. Chalford
Heathrow Community Engagement Board website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Heathrow Heathrow Airport, Airports in the London region Airports established in 1946 Heathrow Airport Holdings Buildings and structures in the London Borough of Hillingdon Public inquiries in the United Kingdom Transport in the London Borough of Hillingdon Proposed transport infrastructure in London Tourist attractions in the London Borough of Hillingdon 1946 establishments in England Airports in England
international airport
An international airport is an airport with customs and border control facilities enabling passengers to travel between countries around the world. International airports are usually larger than domestic airports and they must feature longer ...
in London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others being Gatwick
Gatwick Airport (), also known as London Gatwick , is a major international airport near Crawley, West Sussex, England, south of Central London. In 2021, Gatwick was the third-busiest airport by total passenger traffic in the UK, after Hea ...
, City
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
, Luton
Luton () is a town and unitary authority with borough status, in Bedfordshire, England. At the 2011 census, the Luton built-up area subdivision had a population of 211,228 and its built-up area, including the adjacent towns of Dunstable an ...
, Stansted
London Stansted Airport is a tertiary international airport serving London, England, United Kingdom. It is located near Stansted Mountfitchet, Essex, England, northeast of Central London.
London Stansted serves over 160 destinations acro ...
and Southend
Southend-on-Sea (), commonly referred to as Southend (), is a coastal city and unitary authority area with borough status in southeastern Essex, England. It lies on the north side of the Thames Estuary, east of central London. It is bordered ...
). The airport facility is owned and operated by Heathrow Airport Holdings
Heathrow Airport Holdings is the United Kingdom-based operator of Heathrow Airport. The company also operated Gatwick Airport, Stansted Airport, Edinburgh Airport and several other UK airports, but was forced by the Competition Commission to se ...
. In 2021, it was the seventh-busiest airport in the world by international passenger traffic and eighth-busiest in Europe by total passenger traffic.
Heathrow was founded as a small airfield in 1929 but was developed into a much larger airport after World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. The airport lies west of Central London
Central London is the innermost part of London, in England, spanning several boroughs. Over time, a number of definitions have been used to define the scope of Central London for statistics, urban planning and local government. Its characteris ...
on a site that covers . It was gradually expanded over seventy-five years and now has two parallel east-west runway
According to the International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO), a runway is a "defined rectangular area on a land aerodrome prepared for the landing and takeoff of aircraft". Runways may be a man-made surface (often asphalt concrete, as ...
s, four operational passengers terminals and one cargo terminal. The airport is the primary hub for both British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a populati ...
and Virgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic, a trading name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited and Virgin Atlantic International Limited, is a British airline with its head office in Crawley, England. The airline was established in 1984 as British Atlantic Airways, and w ...
.
Location
 Heathrow is west of central
Heathrow is west of central London
London is the capital and largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary down to the North Sea, and has been a majo ...
. It is located west of Hounslow
Hounslow () is a large suburban district of West London, west-southwest of Charing Cross. It is the administrative centre of the London Borough of Hounslow, and is identified in the London Plan as one of the 12 metropolitan centres in Gr ...
, 3 miles south of Hayes, and 3 miles north-east of Staines-upon-Thames
Staines-upon-Thames is a market town in northwest Surrey, England, around west of central London. It is in the Borough of Spelthorne, at the confluence of the River Thames and Colne. Historically part of Middlesex, the town was transferred to ...
.
Heathrow falls entirely within the boundaries of the London Borough of Hillingdon
The London Borough of Hillingdon () is the largest and westernmost borough in West London, England. It was formed from the districts of Hayes and Harlington, Ruislip-Northwood, Uxbridge, and Yiewsley and West Drayton in the ceremonial county ...
, and under the Twickenham postcode area
The TW postcode area, also known as the Twickenham postcode area,Royal Mail, ''Address Management Guide'', (2004) is a group of twenty postcode districts in south-east England, within thirteen post towns. These cover parts of south-west London a ...
, with the postcode TW6. It is surrounded by the villages of Sipson
Sipson is a village in the London Borough of Hillingdon, the westernmost borough of Greater London, England. It is west of Charing Cross and near the north perimeter of London Heathrow Airport.
History
Toponymy
The village's name was recorded ...
, Harlington, Harmondsworth
Harmondsworth is a village in the London Borough of Hillingdon in the county of Greater London with a short border to the south onto Heathrow Airport, London Heathrow Airport. The village has no railway stations, but adjoins the M4 motorway and t ...
, and Longford
Longford () is the county town of County Longford in Ireland. It has a population of 10,008 according to the 2016 census. It is the biggest town in the county and about one third of the county's population lives there. Longford lies at the meet ...
to the north and the neighbourhoods of Cranford and Hatton
Hatton may refer to:
Places Canada
* Hatton, Saskatchewan
England
* Hatton, Cheshire West and Chester, a former civil parish
* Hatton, Derbyshire
* Hatton, Lincolnshire
* Hatton, London, in the London Borough of Hounslow
* Hatton, Shropshire, a ...
to the east. To the south lie Feltham
Feltham () is a town in West London, England, from Charing Cross. Historically part of Middlesex, it became part of the London Borough of Hounslow in 1965. The parliamentary constituency of Feltham and Heston has been held by Labour Party MPs ...
, Bedfont
Bedfont is a suburb in the London Borough of Hounslow, approximately west of Centre of London, Charing Cross. Originally a distinct village, Bedfont has a large central conservation area around Bedfont Green. The majority of the housing was bui ...
and Stanwell
Stanwell is a village close to two of the three main towns in the Borough of Spelthorne, Surrey, about west of central London. A small corner of its land is vital industrial land serving Heathrow Airport – most of the rest is residential ...
while to the west Heathrow is separated from Slough
Slough () is a town and unparished area in the unitary authority of the same name in Berkshire, England, bordering west London. It lies in the Thames Valley, west of central London and north-east of Reading, at the intersection of the M4 ...
, Horton Horton may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Horton Glacier, Adelaide Island, Antarctica
* Horton Ledge, Queen Elizabeth Land, Antarctica
Australia
* Horton, Queensland, a town and locality in the Bundaberg Region
* Horton River (Australia), ...
and Windsor
Windsor may refer to:
Places Australia
* Windsor, New South Wales
** Municipality of Windsor, a former local government area
* Windsor, Queensland, a suburb of Brisbane, Queensland
**Shire of Windsor, a former local government authority around Wi ...
in Berkshire by the M25 motorway
The M25 or London Orbital Motorway is a major road encircling most of Greater London. The motorway is one of the most important roads in the UK and one of the busiest. Margaret Thatcher opened the final section in 1986, making the M25 the lon ...
. The airport is located within the Hayes and Harlington parliamentary constituency.
As the airport is located west of London and as its runways run east-west, an airliner's landing approach is usually directly over the conurbation
A conurbation is a region comprising a number of metropolises, cities, large towns, and other urban areas which through population growth and physical expansion, have merged to form one continuous urban or industrially developed area. In most ca ...
of London when the wind is from the west, as it is most of the time.
The airport forms part of a travel to work area
A travel to work area or TTWA is a statistical tool used by UK Government agencies and local authorities, especially by the Department for Work and Pensions and Jobcentres, to indicate an area where the population would generally commute to a ...
with Slough
Slough () is a town and unparished area in the unitary authority of the same name in Berkshire, England, bordering west London. It lies in the Thames Valley, west of central London and north-east of Reading, at the intersection of the M4 ...
, the west part of Greater London, and the north part of Surrey.
History

 Heathrow Airport began in 1929 as a small airfield (
Heathrow Airport began in 1929 as a small airfield (Great West Aerodrome
The Great West Aerodrome, also known as Harmondsworth Aerodrome or Heathrow Aerodrome, was a grass airfield, operational between 1930 and 1944. It was on the southeast edge of the hamlet of Heathrow, in the parish of Harmondsworth. The Fairey Av ...
) on land southeast of the hamlet of Heathrow
Heathrow Airport (), called ''London Airport'' until 1966 and now known as London Heathrow , is a major international airport in London, England. It is the largest of the six international airports in the London airport system (the others bei ...
from which the airport takes its name. At that time the land consisted of farms, market garden
A market garden is the relatively small-scale production of fruits, vegetables and flowers as cash crops, frequently sold directly to consumer
A consumer is a person or a group who intends to order, or uses purchased goods, products, or s ...
s and orchard
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of larg ...
s; there was a "Heathrow Farm" approximately where the modern Terminal 2 is situated, a "Heathrow Hall" and a "Heathrow House." This hamlet was largely along a country lane (Heathrow Road), which ran roughly along the east and south edges of the present central terminals area.
Development of the whole Heathrow area as a much larger airport began in 1944 during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
. It was stated to be for long-distance military aircraft bound for the Far East; by the time the airfield was nearing completion, World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposin ...
had ended, and the UK Government continued to develop the airport as a civil airport. The airport was opened on 25 March 1946 as London Airport and was renamed Heathrow Airport in 1966. The layout for the airport was designed by Sir Frederick Gibberd
Sir Frederick Ernest Gibberd (7 January 1908 – 9 January 1984) was an English architect, town planner and landscape designer. He is particularly known for his work in Harlow, Essex, and for the BISF house, a design for a prefabricated counc ...
, who designed the original terminals and central area buildings, including the original control tower and the multi-faith Chapel of St George's.
Operations
Facilities


 Heathrow Airport is used by over 80 airlines flying to 185 destinations in 84 countries. The airport is the primary hub of British Airways and is a base for
Heathrow Airport is used by over 80 airlines flying to 185 destinations in 84 countries. The airport is the primary hub of British Airways and is a base for Virgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic, a trading name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited and Virgin Atlantic International Limited, is a British airline with its head office in Crawley, England. The airline was established in 1984 as British Atlantic Airways, and w ...
. It has four passenger terminals (numbered 2 to 5) and a cargo terminal. Of Heathrow's 78 million passengers in 2017, 94% were international travellers; the remaining 6% were bound for (or arriving from) places in the UK. The busiest single destination in passenger numbers is New York, with over 3 million passengers flying between Heathrow and JFK Airport in 2013.
In the 1950s, Heathrow had six runways, arranged in three pairs at different angles in the shape of a hexagram
, can be seen as a compound composed of an upwards (blue here) and downwards (pink) facing equilateral triangle, with their intersection as a regular hexagon (in green).
A hexagram ( Greek language, Greek) or sexagram (Latin) is a six-pointed ...
with the permanent passenger terminal in the middle and the older terminal along the north edge of the field; two of its runways would always be within 30° of the wind direction. As the required length for runways has grown, Heathrow now has only two parallel runways running east-west. These are extended versions of the two east-west runways from the original hexagram. From the air, almost all of the original runways can still be seen, incorporated into the present system of taxiways. North of the northern runway and the former taxiway and aprons, now the site of extensive car parks, is the entrance to the access tunnel and the site of Heathrow's unofficial "gate guardian
A gate guardian or gate guard is a withdrawn piece of equipment, often an aircraft, armoured vehicle, artillery piece, or locomotive, mounted on a plinth and used as a static display near to and forming a symbolic display of "guarding" the main ...
". For many years the home of a 40% scale model of a British Airways Concorde
The Aérospatiale/BAC Concorde () is a retired Franco-British supersonic airliner jointly developed and manufactured by Sud Aviation (later Aérospatiale) and the British Aircraft Corporation (BAC).
Studies started in 1954, and France an ...
, G-CONC, the site has been occupied by a model of an Emirates Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was annou ...
since 2008.
Heathrow Airport has Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of th ...
, Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, Free Church
A free church is a Christian denomination that is intrinsically separate from government (as opposed to a state church). A free church does not define government policy, and a free church does not accept church theology or policy definitions from ...
, Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism.Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
, Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
and Sikh
Sikhs ( or ; pa, ਸਿੱਖ, ' ) are people who adhere to Sikhism, Sikhism (Sikhi), a Monotheism, monotheistic religion that originated in the late 15th century in the Punjab region of the Indian subcontinent, based on the revelation of Gu ...
chaplains. There is a multi-faith prayer room and counselling room in each terminal, in addition to St. George's Interdenominational Chapel in an underground vault adjacent to the old control tower, where Christian services take place. The chaplains organise and lead prayers at certain times in the prayer room.
The airport has its resident press corps, consisting of six photographers and one TV crew, serving all the major newspapers and television stations around the world.
Most of Heathrow's internal roads are initial letter coded by area: N in the north (e.g. Newall Road), E in the east (e.g. Elmdon Road), S in the south (e.g. Stratford Road), W in the west (e.g. Walrus Road), C in the centre (e.g. Camborne Road).
Flight movements
Aircraft destined for Heathrow are usually routed to one of four holding points.Air traffic controller
Air traffic control specialists, abbreviated ATCS, are personnel responsible for the safe, orderly, and expeditious flow of air traffic in the global air traffic control system. Usually stationed in air traffic control centers and control ...
s at Heathrow Approach Control (based in Swanwick, Hampshire
Swanwick () is a village in Hampshire, England, east of the River Hamble and north of the M27 motorway.
The village is located within the borough of Fareham and is the site of the London Area Control Centre (LACC) and the London Terminal Contro ...
) then guide the aircraft to their final approach, merging aircraft from the four holds into a single stream of traffic, sometimes as close as apart. Considerable use is made of continuous descent approach
Continuous descent approach (CDA), also known as optimized profile descent (OPD), is a method by which aircraft approach airports prior to landing. It is designed to reduce fuel consumption and noise compared to other conventional descents. Inst ...
techniques to minimise the environmental effects of incoming aircraft, particularly at night. Once an aircraft is established on its final approach, control is handed over to Heathrow Tower.
When runway alternation was introduced, aircraft generated significantly more noise on departure than when landing, so a preference for westerly operations during daylight was introduced, which continues to this day.During periods of westerly operation, aircraft continue to fly in a westerly direction with an easterly tailwind component of up to , if the runway is dry and there is no significant crosswind. In this mode, aircraft take off towards the west and land from the east over London, thereby minimising the impact of noise on the most densely populated areas. Heathrow's two runways generally operate in segregated mode, whereby landings are allocated to one runway and takeoffs to the other. To further reduce noise nuisance to people beneath the approach and departure routes, the use of runways 27R and 27L is swapped at 15:00 each day if the wind is from the west. When landings are easterly there is no alternation; 09L remains the landing runway and 09R the takeoff runway due to the legacy of the now rescinded Cranford Agreement
The Cranford Protocol or Cranford Agreement was an oral undertaking given in 1952 by the British Government to the residents of Cranford in London regarding the usage of the runways at London Heathrow Airport to reduce the impact of aircraft no ...
, pending taxiway works to allow the roles to be reversed. Occasionally, landings are allowed on the nominated departure runway, to help reduce airborne delays and to position landing aircraft closer to their terminal, reducing taxi times.
Night-time flights at Heathrow are subject to restrictions. Between 23:00 and 04:00, the noisiest aircraft (rated QC/8 and QC/16) cannot be scheduled for operation. Also, during the night quota period (23:30–06:00) there are four limits:
* A limit on the number of flights allowed;
* A Quota Count system which limits the total amount of noise permitted, but allows operators to choose to operate fewer noisy aircraft or a greater number of quieter planes;
* QC/4 aircraft cannot be scheduled for operation.
* A voluntary agreement with the airlines that no early morning arrivals will be scheduled to land before 04:30.
A trial of "noise relief zones" ran from December 2012 to March 2013, which concentrated approach flight paths into defined areas compared with the existing paths which were spread out. The zones used alternated weekly, meaning residents in the "no-fly" areas received respite from aircraft noise for set periods. However, it was concluded that some residents in other areas experienced a significant disbenefit as a result of the trial and that it should therefore not be taken forward in its current form. Heathrow received more than 25,000 noise complaints in just three months over the summer of 2016, but around half were made by the same ten people.
In 2017, Heathrow introduced "Fly Quiet & Green", a quarterly published league table (currently suspended due to the Covid pandemic) that awards points to the 50 busiest airlines at the airport, ostensibly based on their performance relative to each other across a range of 7 environmental benchmarks, such as emissions. Heathrow has acknowledged, but not attempted to refute, ongoing criticism over discrepancies and a lack of transparency around the way in which the figures are manipulated. The airport has always refused to publish a breakdown showing how many "Fly Quiet points" each performance benchmark has contributed towards the total score it awards to an airline, thereby putting obstacles in the way of any independent auditing of the published results. Among other criticisms of the league table are the unexplained omission of some of the poorer performers among the 50 busiest airlines and the emphasis on relative rather than absolute performance, so an airline could well improve its "Fly Quiet" score quarter-on-quarter even if its environmental performance had in fact worsened over the period.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
Heathrow has seen a large increase in cargo-only flights, not only by already established carriers at the airport operating cargo-only flights using passenger aircraft, but also several cargo-only airlines.- Heathrow Newsretrieved 20 January 2021
Arrival stacks
Inbound aircraft to London Heathrow Airport typically follow one of several Standard Arrival Routes (STARs). The STARs each terminate at one of four differentRNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
waypoints, and these also define four "stacks" where aircraft can be held
Held may refer to:
Places
* Held Glacier
People Arts and media
* Adolph Held (1885–1969), U.S. newspaper editor, banker, labor activist
*Al Held (1928–2005), U.S. abstract expressionist painter.
*Alexander Held (born 1958), German television ...
, if necessary until they are cleared to begin their approach to land. Stacks are sections of airspace
Airspace is the portion of the atmosphere controlled by a country above its territory, including its territorial waters or, more generally, any specific three-dimensional portion of the atmosphere. It is not the same as aerospace, which is the ...
where inbound aircraft will normally use the pattern closest to their arrival route. They can be visualised as invisible helter skelters in the sky. Each stack descends in 1000 ft (300 m) intervals from 16,000 ft (4,000m) down to 8000 ft (2,100m). Aircraft hold between 7,000 feet and 15,000 feet at 1,000-foot intervals. If these holds become full, aircraft are held at more distant points before being cleared onward to one of the four main holds.
The following four stacks are currently in place:
* The Bovingdon stack (BNN) is for arrivals from the northwest. It extends above the village of Bovingdon
Bovingdon is a village in Hertfordshire, England, southwest of Hemel Hempstead, and it is a civil parish within the local authority area of Dacorum. It forms the largest part of the ward of Bovingdon, Flaunden and Chipperfield, which had a po ...
and the town of Chesham
Chesham (, , or ) is a market town and civil parish in Buckinghamshire, England, south-east of the county town of Aylesbury, north-west of central London, and part of the London commuter belt. It is in the Chess Valley, surrounded by farmla ...
, and uses the RNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
waypoint BNN, which is situated on the former RAF Bovingdon
Royal Air Force Bovingdon or more simply RAF Bovingdon is a former Royal Air Force station located near the village of Bovingdon, Hertfordshire, England, about south-west of Hemel Hempstead and south-east of Berkhamsted.
During the Second W ...
airfield.
* The Biggin Hill
Biggin Hill is a settlement on the south-eastern outskirts of Greater London, England, within the London Borough of Bromley. Within the boundaries of the historic county of Kent, prior to 1965 it was also in the administrative county of Kent. I ...
stack (BIG) on the southeast edge of Greater London is for arrivals from the southeast. It uses the RNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
waypoint BIG, which is situated on London Biggin Hill Airport
London Biggin Hill Airport is an operational general aviation airport at Biggin Hill in the London Borough of Bromley, located south-southeast of Central London. The airport was formerly a Royal Air Force station RAF Biggin Hill, and a sma ...
.
* The Lambourne
Lambourne is a civil parish in the Epping Forest district of Essex, England. It is located approximately 4.5 miles (7 km) South of Epping and 5 miles (8 km) northwest of Romford. It covers an area of , and in 2001 its population was 1,8 ...
stack (LAM) in Essex is for arrivals from the northeast. It uses the RNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
waypoint LAM, which is situated adjacent to Stapleford Aerodrome
Stapleford Aerodrome is an operational general aviation aerodrome in the Epping Forest (district), Epping Forest district of Essex, England, near the village of Abridge. It is about south of North Weald Airfield and north of Romford. The airf ...
.
* The Ockham stack (OCK) in Surrey is for arrivals from the southwest. It uses the RNAV
Area navigation (RNAV, usually pronounced as "''ar-nav"'') is a method of instrument flight rules (IFR) navigation that allows an aircraft to choose any course within a network of navigation beacons, rather than navigate directly to and from t ...
waypoint OCK, which is situated on the former Wisley Airfield
Wisley Airfield is a former wartime airfield located in the Parish of Ockham near Wisley in Surrey, England. Originally a grass airstrip, the runway was converted to tarmac in 1952 and used to test aircraft built at Weybridge by Vickers. Flying ...
.
Third runway
In September 2012, theGovernment of the United Kingdom
ga, Rialtas a Shoilse gd, Riaghaltas a Mhòrachd
, image = HM Government logo.svg
, image_size = 220px
, image2 = Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom (HM Government).svg
, image_size2 = 180px
, caption = Royal coat of arms of t ...
established the Airports Commission
The Airports Commission was an independent commission established in September 2012 by the Government of the United Kingdom to consider how the UK can "maintain its status as an international hub for aviation and immediate actions to improve th ...
, an independent commission chaired by Sir Howard Davies
Sir Howard John Davies (born 12 February 1951) is a British economist and author, who is the chairman of NatWest Group and the former director of the London School of Economics.
He was the first chairman of the Financial Services Authority. Da ...
to examine various options for increasing capacity at UK airports. In July 2015, the commission backed a third runway
The expansion of Heathrow Airport is a series of proposals to add to the runways at Heathrow Airport, London's busiest airport beyond its two long runways which are intensively used to serve four terminals and a large cargo operation. The plans ...
at Heathrow, which the government approved in October 2016. However, the England and Wales Court of Appeal
The Court of Appeal (formally "His Majesty's Court of Appeal in England", commonly cited as "CA", "EWCA" or "CoA") is the highest court within the Senior Courts of England and Wales, and second in the legal system of England and Wales only to ...
rejected this plan for a third runway at Heathrow, on the basis that the government failed to consider climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to E ...
and the environmental impact of aviation
Like other emissions resulting from fossil fuel combustion, aircraft engines produce gases, noise, and particulates, raising environmental concerns over their global effects and their effects on local air quality.
Jet airliners contribute to ...
. On 16 December 2020, the UK Supreme Court
The Supreme Court of the United Kingdom (initialism: UKSC or the acronym: SCOTUK) is the final court of appeal in the United Kingdom for all civil cases, and for criminal cases originating in England, Wales and Northern Ireland. As the Unite ...
lifted the ban on the third runway expansion, allowing the construction plan to go ahead.
Regulation
Until it was required to sell Gatwick and Stansted Airports, Heathrow Airport Holdings held a dominant position in the London aviation market and has been heavily regulated by the Civil Aviation Authority (CAA) as to how much it can charge airlines to land. The annual increase in landing charge per passenger was capped at inflation minus 3% until 1 April 2003. From 2003 to 2007 charges increased by inflation plus 6.5% per year, taking the fee to £9.28 per passenger in 2007. In March 2008, the CAA announced that the charge would be allowed to increase by 23.5% to £12.80 from 1 April 2008 and by inflation plus 7.5% for each of the following four years. In April 2013, the CAA announced a proposal for Heathrow to charge fees calculated by inflation minus 1.3%, continuing until 2019. Whilst the cost of landing at Heathrow is determined by the CAA and Heathrow Airport Holdings, the allocation oflanding slot __NOTOC__
A landing slot, takeoff slot, or airport slot is a permission granted by the owner of an airport designated as Level 3 (Coordinated Airport), which allows the grantee to schedule a landing or departure at that airport during a specific t ...
s to airlines is carried out by Airport Co-ordination Limited (ACL).
Until 2008, air traffic between Heathrow and the United States was strictly governed by the countries' bilateral Bermuda II
Bermuda II was a bilateral air transport agreement between the governments of the United Kingdom and the United States signed on 23 July 1977 as a renegotiation of the original 1946 Bermuda air services agreement. A new open skies agreement was ...
treaty. The treaty originally allowed only British Airways, Pan Am
Pan American World Airways, originally founded as Pan American Airways and commonly known as Pan Am, was an American airline that was the principal and largest international air carrier and unofficial overseas flag carrier of the United States ...
and TWA
Trans World Airlines (TWA) was a major American airline which operated from 1930 until 2001. It was formed as Transcontinental & Western Air to operate a route from New York City to Los Angeles via St. Louis, Kansas City, and other stops, with ...
to fly from Heathrow to the US. In 1991, Pan Am and TWA sold their rights to United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
and American Airlines
American Airlines is a major airlines of the United States, major US-based airline headquartered in Fort Worth, Texas, within the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex. It is the Largest airlines in the world, largest airline in the world when measured ...
respectively, while Virgin Atlantic was added to the list of airlines allowed to operate on these routes. The Bermuda bilateral agreement conflicted with the Right of the Establishment of the United Kingdom concerning its EU membership, and as a consequence, the UK was ordered to drop the agreement in 2004. A new "open skies
The freedoms of the air are a set of commercial aviation rights granting a country's airlines the privilege to enter and land in another country's airspace. They were formulated as a result of disagreements over the extent of aviation liberalis ...
" agreement was signed by the United States and the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been des ...
on 30 April 2007 and came into effect on 30 March 2008. Shortly afterwards, additional US airlines, including Northwest Airlines
Northwest Airlines Corp. (NWA) was a major American airline founded in 1926 and absorbed into Delta Air Lines, Inc. by a merger. The merger, approved on October 29, 2008, made Delta the largest airline in the world until the American Airlines ...
, Continental Airlines
Continental Airlines, simply known as Continental, was a major United States airline founded in 1934 and eventually headquartered in Houston, Texas. It had ownership interests and brand partnerships with several carriers.
Continental started o ...
, US Airways
US Airways (formerly USAir) was a major United States airline that operated from 1937 until its merger with American Airlines in 2015. It was originally founded in History of aviation in Pittsburgh, Pittsburgh as a mail delivery airline called ...
and Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the List of airlines by foundation date, world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atla ...
started services to Heathrow.
The airport was criticised in 2007 for overcrowding and delays; according to Heathrow Airport Holdings, Heathrow's facilities were originally designed to accommodate 55 a million passengers annually. The number of passengers using the airport reached a record 70 million in 2012. In 2007 the airport was voted the world's least favourite, alongside Chicago O'Hare
Chicago O'Hare International Airport , sometimes referred to as, Chicago O'Hare, or simply O'Hare, is the main international airport serving Chicago, Illinois, located on the city's Northwest Side, approximately northwest of the Loop busine ...
, in a TripAdvisor survey. However, the opening of Terminal 5 in 2008 has relieved some pressure on terminal facilities, increasing the airport's terminal capacity to 90 million passengers per year. A tie-up is also in place with McLaren Applied Technologies to optimise the general procedure, reducing delays and pollution.
With only two runways, operating at over 98% of their capacity, Heathrow has little room for more flights, although the increasing use of larger aircraft such as the Airbus A380 will allow some increase in passenger numbers. It is difficult for existing airlines to obtain landing slots to enable them to increase their services from the airport, or for new airlines to start operations. To increase the number of flights, Heathrow Airport Holdings has proposed using the existing two runways in 'mixed mode' whereby aircraft would be allowed to take off and land on the same runway. This would increase the airport's capacity from its current 480,000 movements per year to as many as 550,000 according to British Airways CEO Willie Walsh. Heathrow Airport Holdings has also proposed building a third runway to the north of the airport, which would significantly increase traffic capacity.
Security
Policing of the airport is the responsibility of theaviation security
Airport security includes the techniques and methods used in an attempt to protect passengers, staff, aircraft, and airport property from malicious harm, crime, terrorism, and other threats.
Aviation security is a combination of measures and hum ...
, a unit of the Metropolitan Police
The Metropolitan Police Service (MPS), formerly and still commonly known as the Metropolitan Police (and informally as the Met Police, the Met, Scotland Yard, or the Yard), is the territorial police force responsible for law enforcement and ...
, although the British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurkhas ...
, including armoured vehicles of the Household Cavalry
The Household Cavalry (HCav) is made up of the two most senior regiments of the British Army, the Life Guards and the Blues and Royals (Royal Horse Guards and 1st Dragoons). These regiments are divided between the Household Cavalry Regiment st ...
, has occasionally been deployed at the airport during periods of heightened security. Full body scanner
A full-body scanner is a device that detects objects on or inside a person's body for security screening purposes, without physically removing clothes or making physical contact. Unlike metal detectors, full-body scanners can detect non-metal o ...
s are now used at the airport, and passengers who object to their use after being selected are required to submit to a hand search in a private room. The scanners display passengers' bodies as cartoon figures, with indicators showing where concealed items may be.
For many decades Heathrow had a reputation for theft from baggage by baggage handlers. This led to the airport being nicknamed "Thiefrow", with periodic arrests of baggage handlers. Following the widespread disruption caused by reports of drone sightings at Gatwick Airport, and a subsequent incident at Heathrow, a drone detection system was installed airport-wide to attempt to combat possible future disruption caused by the illegal use of drones.
Terminals
Terminal 2
 The airport's newest terminal, officially known as the Queen's Terminal, was opened on 4 June 2014 and has 24 gates. Designed by Spanish architect
The airport's newest terminal, officially known as the Queen's Terminal, was opened on 4 June 2014 and has 24 gates. Designed by Spanish architect Luis Vidal Luis Vidal may refer to:
* Luis Vidal (footballer, born 1916) (1916-1999), Chilean football defender and manager
* Luis Vidal (footballer, born 1952) (born 1952), Chilean football defender
* Luis Vidal (architect) (born 1969), Spanish archit ...
, it was built on the site that had been occupied by the original Terminal 2 and the Queens Building. The main complex was completed in November 2013 and underwent six months of testing before opening to passengers. It includes a satellite pier (T2B), a 1,340-space car park, and a cooling station to generate chilled water. There are 52 shops and 17 bars and restaurants.
Most flights from Terminal 2 are coming from northern Europe or west Europe. It is used by all Star Alliance
Star Alliance is the world's largest global airline alliance. Founded on 14 May 1997, its CEO is Jeffrey Goh and its headquarters is located in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. , Star Alliance is the largest of the three global alliances by passenger ...
members who fly from Heathrow (consolidating the airlines under Star Alliance's co-location policy "Move Under One Roof"), SkyTeam
SkyTeam is one of the world's three major airline alliances. Founded in June 2000, SkyTeam was the last of the three alliances to be formed, the first two being Star Alliance and Oneworld, respectively. Its annual passenger count is 630 million ...
new member China Airlines
China Airlines (CAL; ) is the state-owned flag carrier of the Republic of China (Taiwan), and one of its two major airlines along with EVA Air. It is headquartered in Taoyuan International Airport and operates over 1,400 flights weekly (inclu ...
and several short haul unaffiliated carriers. Terminal 2 is also the only terminal at Heathrow to accommodate small aircraft. JetBlue
JetBlue Airways Corporation (stylized as jetBlue) is a major American low cost airline, and the seventh largest airline in North America by passengers carried. The airline is headquartered in the Long Island City neighborhood of the New York C ...
is the only non-aligned long haul flight operating from this terminal. Terminal 2 is one of the two terminals that operate UK and Irish domestic flights. The airlines moved from their original locations over six months, with only 10% of flights operating from there in the first six weeks (United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
' transatlantic flights) to avoid the opening problems seen at Terminal 5. On 4 June 2014, United Airlines
United Airlines, Inc. (commonly referred to as United), is a major American airline headquartered at the Willis Tower in Chicago, Illinois.
became the first airline to move into Terminal 2 from Terminals 1 and 4 followed by All Nippon Airways
, also known as ANA (''Ē-enu-ē'') or is an airline in Japan. Its headquarters are located in Shiodome City Center in the Shiodome area of Minato ward of Tokyo. It operates services to both domestic and international destinations and had mo ...
, Air Canada
Air Canada is the flag carrier and the largest airline of Canada by the size and passengers carried. Air Canada maintains its headquarters in the borough of Saint-Laurent, Montreal, Quebec. The airline, founded in 1937, provides scheduled and ...
and Air China
Air China Limited () is the flag carrier of the People's Republic of China and one of the "Big Three" mainland Chinese airlines (alongside China Southern Airlines and China Eastern Airlines). Air China's headquarters are in Shunyi District, ...
from Terminal 3. Air New Zealand
Air New Zealand Limited () is the flag carrier airline of New Zealand. Based in Auckland, the airline operates scheduled passenger flights to 20 domestic and 30 international destinations in 18 countries, primarily around and within the Pacific ...
, Asiana Airlines
Asiana Airlines Inc. ( ) is a South Korean airline headquartered in Seoul.Home
." Asiana Airlines. Retrieved 13 September 2 ...
, ." Asiana Airlines. Retrieved 13 September 2 ...
Croatia Airlines
Croatia Airlines Ltd. is the state-owned flag carrier airline of Croatia. Its headquarters are in Buzin near Zagreb and operates domestic and international services mainly to European destinations. Its main hub is Zagreb International Airport wi ...
, LOT Polish Airlines
LOT Polish Airlines, legally incorporated as Polskie Linie Lotnicze LOT S.A. (, ''flight''), is the flag carrier of Poland. Established in 1928, LOT was a founding member of IATA and remains one of the world's oldest airlines in operation. Wit ...
, South African Airways
South African Airways (SAA) is the flag carrier airline of South Africa. Founded in 1934, the airline is headquartered in Airways Park at O. R. Tambo International Airport in Johannesburg and operated a hub-and-spoke network, serving ten destin ...
, and TAP Air Portugal
TAP Air Portugal is the currently state-owned flag carrier airline of Portugal, headquartered at Lisbon Airport which also serves as its hub. TAP – Transportes Aéreos Portugueses – has been a member of the Star Alliance since 2005 and oper ...
moved in on 22 October 2014.
The original Terminal 2 opened as the Europa Building in 1955 and was the airport's oldest terminal. It had an area of and was designed to handle around 1.2 million passengers annually. In its final years, it accommodated up to 8 million. A total of 316 million passengers passed through the terminal in its lifetime. The building was demolished in 2010, along with the Queens Building which had housed airline company offices.
Terminal 3
 Terminal 3 opened as the Oceanic Terminal on 13 November 1961 to handle flight departures for long-haul routes for foreign carriers to the United States, Asia and other Far Eastern destinations. At this time the airport had a direct helicopter service to Central London from the gardens on the roof of the terminal building. Renamed Terminal 3 in 1968, it was expanded in 1970 with the addition of an arrivals building. Other facilities added included the UK's first
Terminal 3 opened as the Oceanic Terminal on 13 November 1961 to handle flight departures for long-haul routes for foreign carriers to the United States, Asia and other Far Eastern destinations. At this time the airport had a direct helicopter service to Central London from the gardens on the roof of the terminal building. Renamed Terminal 3 in 1968, it was expanded in 1970 with the addition of an arrivals building. Other facilities added included the UK's first moving walkway
A moving walkway, also known as an autowalk, moving pavement, moving sidewalk, people-mover, travolator, or travelator, is a slow-moving conveyor mechanism that transports people across a horizontal or inclined plane over a short to medium distan ...
s. In 2006, the new £105 million Pier 6 was completed to accommodate the Airbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was annou ...
superjumbo; Emirates
Emirates may refer to:
* United Arab Emirates, a Middle Eastern country
* Emirate, any territory ruled by an emir
** Gulf emirates, emirates located on the Persian Gulf
** Emirates of the United Arab Emirates, the individual emirates
* The Emirat ...
and Qantas
Qantas Airways Limited ( ) is the flag carrier of Australia and the country's largest airline by fleet size, international flights, and international destinations. It is the world's third-oldest airline still in operation, having been founded ...
operate regular flights from Terminal 3 using the Airbus A380.
Redevelopment of Terminal 3's forecourt by the addition of a new four-lane drop-off area and a large pedestrianised plaza, complete with a canopy to the front of the terminal building, was completed in 2007. These improvements were intended to improve passengers' experience, reduce traffic congestion and improve security. As part of this project, Virgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic, a trading name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited and Virgin Atlantic International Limited, is a British airline with its head office in Crawley, England. The airline was established in 1984 as British Atlantic Airways, and w ...
was assigned its dedicated check-in area, known as 'Zone A', which features a large sculpture and atrium.
, Terminal 3 has an area of with 28 gates, and in 2011 it handled 19.8 million passengers on 104,100 flights. Most flights from Terminal 3 are long haul flights from North America, Asia and other foreign countries other than Europe. Terminal 3 is home to Oneworld
Oneworld (stylised as oneworld; Computer reservations system, CRS: *O) is an airline alliance founded on 1 February 1999. The alliance's stated objective is to be the first choice airline alliance for the world's frequent international traveller ...
members (with the exception of Malaysia Airlines
Malaysia Airlines Berhad (MAB; ms, Penerbangan Malaysia Berhad), formerly known as Malaysian Airline System (MAS; ), and branded as Malaysia Airlines, is the flag carrier airline of Malaysia and a member of the Oneworld airline alliance. (The ...
, Qatar Airways
Qatar Airways Company Q.C.S.C. ( ar, القطرية, ''al-Qaṭariya''), operating as Qatar Airways, is the state-owned flag carrier airline of Qatar. Headquartered in the Qatar Airways Tower in Doha, the airline operates a hub-and-spoke netw ...
and Royal Air Maroc
Royal Air Maroc (; ar, الخطوط الملكية المغربية, , literally ''Royal Moroccan Lines'' or ''Royal Moroccan Airlines''; ber, ⴰⵎⵓⵏⵉ ⴰⵢⵍⴰⵍ ⴰⴳⵍⴷⴰⵏ ⵏ ⴰⵎⵓⵔⴰⴽⵓⵛ, ''Amuni Aylal Age ...
, all of which use Terminal 4), SkyTeam
SkyTeam is one of the world's three major airline alliances. Founded in June 2000, SkyTeam was the last of the three alliances to be formed, the first two being Star Alliance and Oneworld, respectively. Its annual passenger count is 630 million ...
members Aeroméxico
Aerovías de México, S.A. de C.V. () operating as Aeroméxico (; stylized as AM), is the flag carrier airline of Mexico, based in Mexico City. It operates scheduled services to more than 90 destinations in Mexico; North, South and Central Ameri ...
, Air France
Air France (; formally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. It is a subsidiary of the Air France–KLM Group and a founding member of the SkyTeam global air ...
, Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the List of airlines by foundation date, world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atla ...
, KLM
KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, legally ''Koninklijke Luchtvaart Maatschappij N.V.'' (literal translation: Royal Aviation Company Plc.), is the flag carrier airline of the Netherlands. KLM is headquartered in Amstelveen, with its hub at nearby Amste ...
and Middle East Airlines
Middle East Airlines – Air Liban S.A.L. ( ar, طيران الشرق الأوسط ـ الخطوط الجوية اللبنانية ''Ṭayyarān al-Sharq al-Awsaṭ – al-Khuṭūṭ al-jawiyyah al-lubnāniyyah''), more commonly known as Middle ...
, and several long haul unaffiliated carriers.
Terminal 4
Heathrow Cargo Tunnel
The Heathrow Cargo Tunnel is a road tunnel in the London Borough of Hillingdon, London, UK that serves London Heathrow Airport.
History
In December 1968, the tunnel first opened, to connect Terminals 1, 2 and 3 to the newly opened cargo ter ...
. The terminal has an area of and is now home to the SkyTeam
SkyTeam is one of the world's three major airline alliances. Founded in June 2000, SkyTeam was the last of the three alliances to be formed, the first two being Star Alliance and Oneworld, respectively. Its annual passenger count is 630 million ...
alliance, except new member China Airlines
China Airlines (CAL; ) is the state-owned flag carrier of the Republic of China (Taiwan), and one of its two major airlines along with EVA Air. It is headquartered in Taoyuan International Airport and operates over 1,400 flights weekly (inclu ...
which remained at Terminal 2, and Aeroméxico
Aerovías de México, S.A. de C.V. () operating as Aeroméxico (; stylized as AM), is the flag carrier airline of Mexico, based in Mexico City. It operates scheduled services to more than 90 destinations in Mexico; North, South and Central Ameri ...
, Air France
Air France (; formally ''Société Air France, S.A.''), stylised as AIRFRANCE, is the flag carrier of France headquartered in Tremblay-en-France. It is a subsidiary of the Air France–KLM Group and a founding member of the SkyTeam global air ...
, Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the List of airlines by foundation date, world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atla ...
, KLM
KLM Royal Dutch Airlines, legally ''Koninklijke Luchtvaart Maatschappij N.V.'' (literal translation: Royal Aviation Company Plc.), is the flag carrier airline of the Netherlands. KLM is headquartered in Amstelveen, with its hub at nearby Amste ...
and Middle East Airlines
Middle East Airlines – Air Liban S.A.L. ( ar, طيران الشرق الأوسط ـ الخطوط الجوية اللبنانية ''Ṭayyarān al-Sharq al-Awsaṭ – al-Khuṭūṭ al-jawiyyah al-lubnāniyyah''), more commonly known as Middle ...
, which use Terminal 3, Oneworld carriers Malaysia Airlines
Malaysia Airlines Berhad (MAB; ms, Penerbangan Malaysia Berhad), formerly known as Malaysian Airline System (MAS; ), and branded as Malaysia Airlines, is the flag carrier airline of Malaysia and a member of the Oneworld airline alliance. (The ...
, Qatar Airways
Qatar Airways Company Q.C.S.C. ( ar, القطرية, ''al-Qaṭariya''), operating as Qatar Airways, is the state-owned flag carrier airline of Qatar. Headquartered in the Qatar Airways Tower in Doha, the airline operates a hub-and-spoke netw ...
, Royal Air Maroc
Royal Air Maroc (; ar, الخطوط الملكية المغربية, , literally ''Royal Moroccan Lines'' or ''Royal Moroccan Airlines''; ber, ⴰⵎⵓⵏⵉ ⴰⵢⵍⴰⵍ ⴰⴳⵍⴷⴰⵏ ⵏ ⴰⵎⵓⵔⴰⴽⵓⵛ, ''Amuni Aylal Age ...
, and Gulf Air
Gulf Air ( ar, طيران الخليج ''Ṭayarān al-Khalīj'') is the state-owned airline and the flag carrier of Bahrain, which was founded in 1950 by British Pilot Freddie Bosworth as Gulf Aviation. Headquartered in Muharraq, the airline ...
and to most unaffiliated carriers. It has undergone a £200m upgrade to enable it to accommodate 45 airlines with an upgraded forecourt to reduce traffic congestion and improve security. Most flights that go to Terminal 4 are flights coming from East Europe, Central Asia, North Africa and the Middle East as well as a few flights to Europe. An extended check-in area with renovated piers and departure lounges and a new baggage system were installed, and four new stands were built to accommodate the Airbus A380; Etihad Airways
Etihad Airways ( ar, شَرِكَة ٱلْاِتِّحَاد لِلطَّيْرَان, sharikat al-ittiḥād li-ṭ-ṭayarān) is one of two flag carriers of the United Arab Emirates (the other being Emirates). Its head office is in Khalifa ...
, Korean Air, Malaysia Airlines
Malaysia Airlines Berhad (MAB; ms, Penerbangan Malaysia Berhad), formerly known as Malaysian Airline System (MAS; ), and branded as Malaysia Airlines, is the flag carrier airline of Malaysia and a member of the Oneworld airline alliance. (The ...
and Qatar Airways
Qatar Airways Company Q.C.S.C. ( ar, القطرية, ''al-Qaṭariya''), operating as Qatar Airways, is the state-owned flag carrier airline of Qatar. Headquartered in the Qatar Airways Tower in Doha, the airline operates a hub-and-spoke netw ...
operate regular A380 flights. Gulf Air
Gulf Air ( ar, طيران الخليج ''Ṭayarān al-Khalīj'') is the state-owned airline and the flag carrier of Bahrain, which was founded in 1950 by British Pilot Freddie Bosworth as Gulf Aviation. Headquartered in Muharraq, the airline ...
and El Al operate regular Boeing 787 flights.
Terminal 5
 Terminal 5 lies between the northern and southern runways at the western end of the Heathrow site and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 14 March 2008, some 19 years after its inception. It opened to the public on 27 March 2008, and British Airways and its partner company Iberia have exclusive use of this terminal, which has 50 gates, including 3 hardstands. The first passenger to enter Terminal 5 was a UK expatriate, ex-pat from Kenya who passed through security at 04:30 on the day. He was presented with a boarding pass by British Airways CEO Willie Walsh for the first departing flight, BA302 to Paris. During the two weeks after its opening, operations were disrupted by problems with the terminal's IT systems, coupled with insufficient testing and staff training, which caused over 500 flights to be cancelled. Until March 2012, Terminal 5 was exclusively used by British Airways as its global hub; however, because of the merger, on 25 March Iberia (airline), Iberia's operations at Heathrow were moved to the terminal, making it the home of International Airlines Group. On 7 July 2020, American Airlines, American moved to terminal 5, to allow for easier connections from American's transatlantic flights to British Airways flights during the pandemic. However, all the American flights, except JFK, have returned to Terminal 3. However, Iberia moved its flights to Terminal 3 before the reopening due to the pandemic. China Southern Airlines used Terminal 5 due to the pandemic until it was relocated to Terminal 4 in November 2022.
Built at £4.3 billion, the terminal consists of a four-story main terminal building (Concourse A) and two satellite buildings linked to the main terminal by an underground people mover transit system. Concourse A has dedicated British Airways's narrowbody fleet for flights around the UK and the rest of Europe, the first satellite (Concourse B) includes dedicated stands for BA and Iberia's widebody fleet except for the Airbus A380, and the second satellite (Concourse C), includes 7 dedicated aircraft stands for the A380. It became fully operational on 1 June 2011. Terminal 5 was voted Skytrax World's Best Airport Terminal 2014 in the Annual World Airport Awards.
The main terminal building (Concourse A) has an area of while Concourse B covers . It has 60 aircraft stands and capacity for 30 a million passengers annually as well as more than 100 shops and restaurants. It is also home to British Airways' Flagship lounge, the Concorde Room, alongside four further British Airways branded lounges. One of those lounges is the British Airways Arrivals Lounge which is located land-side.
A further building, designated Concourse D and of similar size to Concourse C, may yet be built to the east of the existing site, providing up to another 16 stands. Following British Airways' merger with Iberia (airline), Iberia, this may become a priority since the combined business will require accommodation at Heathrow under one roof to maximise the cost savings envisaged under the deal. A proposal for Concourse D was featured in Heathrow's most recent capital investment plan.
The transport network around the airport has been extended to cope with the increase in passenger numbers. New branches of both the Heathrow Express and the Underground's Piccadilly line serve a new shared Heathrow Terminal 5 station. A dedicated spur route, motorway spur links the terminal to the M25 (between junctions 14 and 15). The terminal has 3,800 spaces multi-storey car park. A more distant long-stay car park for business passengers is connected to the terminal by a personal rapid transit system, the London Heathrow Terminal 5 PRT, Heathrow Pod, which became operational in the spring of 2011. Within the terminal complex, an automated people mover (APM) system, known as the Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit, is used to transport passengers between the satellite buildings.
Terminal 5 lies between the northern and southern runways at the western end of the Heathrow site and was opened by Queen Elizabeth II on 14 March 2008, some 19 years after its inception. It opened to the public on 27 March 2008, and British Airways and its partner company Iberia have exclusive use of this terminal, which has 50 gates, including 3 hardstands. The first passenger to enter Terminal 5 was a UK expatriate, ex-pat from Kenya who passed through security at 04:30 on the day. He was presented with a boarding pass by British Airways CEO Willie Walsh for the first departing flight, BA302 to Paris. During the two weeks after its opening, operations were disrupted by problems with the terminal's IT systems, coupled with insufficient testing and staff training, which caused over 500 flights to be cancelled. Until March 2012, Terminal 5 was exclusively used by British Airways as its global hub; however, because of the merger, on 25 March Iberia (airline), Iberia's operations at Heathrow were moved to the terminal, making it the home of International Airlines Group. On 7 July 2020, American Airlines, American moved to terminal 5, to allow for easier connections from American's transatlantic flights to British Airways flights during the pandemic. However, all the American flights, except JFK, have returned to Terminal 3. However, Iberia moved its flights to Terminal 3 before the reopening due to the pandemic. China Southern Airlines used Terminal 5 due to the pandemic until it was relocated to Terminal 4 in November 2022.
Built at £4.3 billion, the terminal consists of a four-story main terminal building (Concourse A) and two satellite buildings linked to the main terminal by an underground people mover transit system. Concourse A has dedicated British Airways's narrowbody fleet for flights around the UK and the rest of Europe, the first satellite (Concourse B) includes dedicated stands for BA and Iberia's widebody fleet except for the Airbus A380, and the second satellite (Concourse C), includes 7 dedicated aircraft stands for the A380. It became fully operational on 1 June 2011. Terminal 5 was voted Skytrax World's Best Airport Terminal 2014 in the Annual World Airport Awards.
The main terminal building (Concourse A) has an area of while Concourse B covers . It has 60 aircraft stands and capacity for 30 a million passengers annually as well as more than 100 shops and restaurants. It is also home to British Airways' Flagship lounge, the Concorde Room, alongside four further British Airways branded lounges. One of those lounges is the British Airways Arrivals Lounge which is located land-side.
A further building, designated Concourse D and of similar size to Concourse C, may yet be built to the east of the existing site, providing up to another 16 stands. Following British Airways' merger with Iberia (airline), Iberia, this may become a priority since the combined business will require accommodation at Heathrow under one roof to maximise the cost savings envisaged under the deal. A proposal for Concourse D was featured in Heathrow's most recent capital investment plan.
The transport network around the airport has been extended to cope with the increase in passenger numbers. New branches of both the Heathrow Express and the Underground's Piccadilly line serve a new shared Heathrow Terminal 5 station. A dedicated spur route, motorway spur links the terminal to the M25 (between junctions 14 and 15). The terminal has 3,800 spaces multi-storey car park. A more distant long-stay car park for business passengers is connected to the terminal by a personal rapid transit system, the London Heathrow Terminal 5 PRT, Heathrow Pod, which became operational in the spring of 2011. Within the terminal complex, an automated people mover (APM) system, known as the Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit, is used to transport passengers between the satellite buildings.
Terminal assignments
As of July 2022, Heathrow's four passenger terminals are assigned as follows: Following the opening of Terminal 5 in March 2008, a complex programme of terminal moves was implemented. This saw many airlines move to be grouped in terminals by airline alliance as far as possible."Heathrow looks ahead", Airports (Key Publishing), September/October 2007, p. 30. Following the opening of Phase 1 of the new Terminal 2 in June 2014, all Star Alliance member airlines (with the exception of new member Air India which moved in early 2017) along with Aer Lingus and Germanwings relocated to Terminal 2 in a phased process completed on 22 October 2014. Additionally, by 30 June 2015 all airlines left Terminal 1 in preparation for its demolition to make room for the construction of Phase 2 of Terminal 2. Some other airlines made further minor moves at a later point, e.g.Delta Air Lines
Delta Air Lines, Inc., typically referred to as Delta, is one of the major airlines of the United States and a legacy carrier. One of the List of airlines by foundation date, world's oldest airlines in operation, Delta is headquartered in Atla ...
merging all departures in Terminal 3 instead of a split between Terminals 3 and 4.
Terminal usage during COVID-19 pandemic
Heathrow Airport has four terminals with a total of 115 gates, 66 of which can support wide-body aircraft and 24 gates that can support anAirbus A380
The Airbus A380 is a large wide-body airliner that was developed and produced by Airbus. It is the world's largest passenger airliner and only full-length double-deck jet airliner.
Airbus studies started in 1988, and the project was annou ...
. Due to the COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
, Heathrow's services were sharply reduced. It announced that as of 6 April 2020, the airport would be transitioning to single-runway operations and that it would be temporarily closing Terminals 3 and 4, moving all remaining flights into Terminals 2 or 5. Dual runway operations were restored in August 2020. Heathrow returned to single-runway operations on 9 November 2020. On 11 December 2020, Heathrow announced Terminal 4 would be shut until the end of 2021. Terminal 3 was reopened for use by Virgin Atlantic and Delta on 15 July 2021, and Terminal 4 was reopened on 14 June 2022.
Former Terminal 1
Terminal 1 opened in 1968 and was inaugurated by Elizabeth II, Queen Elizabeth II in April 1969.''Above Us The Skies: The Story of BAA'' – 1991 (Michael Donne – BAA plc), p. 40 Terminal 1 was the Heathrow base for British Airways' (BA) domestic and European network and a few of its long haul routes before Terminal 5 opened. The acquisition of British Midland International (BMI) in 2012 by BA's owner International Airlines Group meant British Airways took over BMI's short-haul and medium-haul destinations from the terminal. Terminal 1 was also the main base for mostStar Alliance
Star Alliance is the world's largest global airline alliance. Founded on 14 May 1997, its CEO is Jeffrey Goh and its headquarters is located in Frankfurt am Main, Germany. , Star Alliance is the largest of the three global alliances by passenger ...
members though some were also based at Terminal 3.
Terminal 1 closed at the end of June 2015, the site is now being used to extend Terminal 2 which opened in June 2014. A number of the newer gates used by Terminal 1 were built as part of the Terminal 2 development and are being retained. The last tenants along with British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a populati ...
were El Al, Icelandair (moved to Terminal 2 25 March 2015) and LATAM Brasil (the third to move in to Terminal 3 on 27 May 2015). British Airways was the last operator in Terminal 1. Two flights of this carrier, one departing to Hanover and one arriving from Baku, marked the terminal closure on 29 June 2015. British Airways operations have been relocated to Terminals 3 and 5.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
The following airlines operate regularly scheduled passenger flights at London Heathrow Airport:Cargo
Traffic and statistics
Overview
 When ranked by World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, passenger traffic, Heathrow is the sixth busiest internationally, behind Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Beijing Capital International Airport, Dubai International Airport, Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, and Haneda Airport, Tokyo Haneda Airport, for the 12 months ending December 2015. London Heathrow Airport was noted as the best-connected airport globally in 2019 according to the OAG (company), OAG's Megahubs Index with a connectivity score of 317. Dominant carrier British Airways was recorded as holding a 51% share of flights at the hub.
In 2015, Heathrow was List of the busiest airports in Europe, the busiest airport in Europe in total passenger traffic, with 14% more passengers than Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport and 22% more than Istanbul Atatürk Airport. Heathrow was the fourth busiest European airport by cargo traffic in 2013, after Frankfurt Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.
In 2020, Heathrow's passenger numbers dropped sharply by over 72%, (a decrease of 58 million travellers compared to 2019), due to the impact caused by restrictions and/or bans on travel caused by the global
When ranked by World's busiest airports by passenger traffic, passenger traffic, Heathrow is the sixth busiest internationally, behind Hartsfield–Jackson Atlanta International Airport, Beijing Capital International Airport, Dubai International Airport, Chicago's O'Hare International Airport, and Haneda Airport, Tokyo Haneda Airport, for the 12 months ending December 2015. London Heathrow Airport was noted as the best-connected airport globally in 2019 according to the OAG (company), OAG's Megahubs Index with a connectivity score of 317. Dominant carrier British Airways was recorded as holding a 51% share of flights at the hub.
In 2015, Heathrow was List of the busiest airports in Europe, the busiest airport in Europe in total passenger traffic, with 14% more passengers than Paris–Charles de Gaulle Airport and 22% more than Istanbul Atatürk Airport. Heathrow was the fourth busiest European airport by cargo traffic in 2013, after Frankfurt Airport, Paris Charles de Gaulle and Amsterdam Airport Schiphol.
In 2020, Heathrow's passenger numbers dropped sharply by over 72%, (a decrease of 58 million travellers compared to 2019), due to the impact caused by restrictions and/or bans on travel caused by the global COVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
.
Annual traffic statistics
Overview
In table
Busiest routes
Heathrow Airport processed 80,884,310 passengers in 2019, but only 22,109,723 in 2020 and 19,393,145 in 2021, due to theCOVID-19 pandemic
The COVID-19 pandemic, also known as the coronavirus pandemic, is an ongoing global pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The novel virus was first identif ...
. In 2021, Dubai International Airport was the most popular route with 808,620 passengers. The table below shows the 10 busiest international routes at the airport in 2021.
Other facilities
 The head office of
The head office of Heathrow Airport Holdings
Heathrow Airport Holdings is the United Kingdom-based operator of Heathrow Airport. The company also operated Gatwick Airport, Stansted Airport, Edinburgh Airport and several other UK airports, but was forced by the Competition Commission to se ...
(formerly BAA Limited) is located in the Compass Centre by Heathrow's northern runway, a building that previously served as a British Airways flight crew centre. The World Business Centre Heathrow consists of three buildings. 1 World Business Centre houses offices of Heathrow Airport Holdings, Heathrow Airport itself, and Scandinavian Airlines. Previously International Airlines Group had its head office in 2 World Business Centre.
At one time the British Airways head office was located within Heathrow Airport at Speedbird House"World Airline Directory." ''Flight International''. 26 March – 1 April 199758
. "Speedbird House, PO Box 10, London Heathrow Airport, Hounslow, Middlesex, TW6 2JA, UK." before the completion of Waterside (building), Waterside, the current BA head office in
Harmondsworth
Harmondsworth is a village in the London Borough of Hillingdon in the county of Greater London with a short border to the south onto Heathrow Airport, London Heathrow Airport. The village has no railway stations, but adjoins the M4 motorway and t ...
, in June 1998.McKellar, Susie and Penny Sparke. "The Contemporary Office." ''Interior Design and Identity''. Manchester University Press, 2004200
. Retrieved from Google Books on 12 February 2010. , . To the north of the airfield lies the Northern Perimeter Road, along which most of Heathrow's car rental agencies are based, and Bath Road, which runs parallel to it, but outside the airport campus. This is nicknamed "The Strip" by locals, because of its continuous line of airport hotels.
Transport
Public transport

Train
 * Heathrow Express: a non-stop service direct to Paddington railway station, London Paddington; trains leave every 15 minutes for the 15-minute journey (21 minutes to and from Terminal 5). Trains depart from Heathrow Terminal 5 station or Heathrow Central railway station, Heathrow Central station (Terminals 2 & 3). Free transfer service operates between Terminal 4 and Heathrow Central to connect with services from London and Terminal 5.
* Elizabeth Line: a stopping service to Abbey Wood railway station, Abbey Wood via London Paddington station, Paddington and central London – trains leave every 30 minutes. Calls at Hayes & Harlington railway station, Hayes & Harlington for connecting trains to Reading railway station, Reading. It will also serve the line to Shenfield railway station, Shenfield from 2023.
* London Underground (Piccadilly line): four stations serve the airport: Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 tube station, Terminal 2 & 3, Heathrow Terminal 4 tube station, Terminal 4 and Heathrow Terminal 5 station, Terminal 5 serve the passenger terminals; Hatton Cross tube station, Hatton Cross serves the maintenance areas. The usual journey time from Heathrow Central to Central London is around 40–50 minutes.
* Heathrow Express: a non-stop service direct to Paddington railway station, London Paddington; trains leave every 15 minutes for the 15-minute journey (21 minutes to and from Terminal 5). Trains depart from Heathrow Terminal 5 station or Heathrow Central railway station, Heathrow Central station (Terminals 2 & 3). Free transfer service operates between Terminal 4 and Heathrow Central to connect with services from London and Terminal 5.
* Elizabeth Line: a stopping service to Abbey Wood railway station, Abbey Wood via London Paddington station, Paddington and central London – trains leave every 30 minutes. Calls at Hayes & Harlington railway station, Hayes & Harlington for connecting trains to Reading railway station, Reading. It will also serve the line to Shenfield railway station, Shenfield from 2023.
* London Underground (Piccadilly line): four stations serve the airport: Heathrow Terminals 2 & 3 tube station, Terminal 2 & 3, Heathrow Terminal 4 tube station, Terminal 4 and Heathrow Terminal 5 station, Terminal 5 serve the passenger terminals; Hatton Cross tube station, Hatton Cross serves the maintenance areas. The usual journey time from Heathrow Central to Central London is around 40–50 minutes.
Bus and coach
Many bus and coach services operate from the large Heathrow Central bus station, which serves Terminal 2 and Terminal 3. Services also operate from the bus stations located at Terminal 4 and Terminal 5.Inter-terminal transport
Terminals 2 and 3 are within walking distance of each other. Transfers from Terminals 2 and 3 to Terminal 4 and 5 are provided by Elizabeth line and Heathrow Express trains and the London Underground Piccadilly line. Direct transfer between Terminals 4 and 5 is provided by London Buses routes London Buses route 482, 482 and London Buses route 490, 490. Transit passengers remaining Airside (airport), airside are provided with free dedicated transfer buses between terminals. The ULTra (rapid transit), Heathrow Pod personal rapid transit system shuttles passengers between Terminal 5 and the business car park using 21 small, driverless transportation pods. The pods are battery-powered and run on-demand on a four-kilometre track, each able to carry up to four adults, two children, and their luggage. Plans exist to extend the Pod system to connect Terminals 2 and 3 to remote car parks. An underground automated people mover system known as the ''Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit'' operates within Terminal 5, linking the main terminal with the satellite Terminals 5B and 5C. The Transit operates entirely airside (airport), airside using Bombardier Innovia APM 200 people mover vehicles.
An underground automated people mover system known as the ''Heathrow Terminal 5 Transit, Transit'' operates within Terminal 5, linking the main terminal with the satellite Terminals 5B and 5C. The Transit operates entirely airside (airport), airside using Bombardier Innovia APM 200 people mover vehicles.
Hotel access
The Hotel Hoppa bus network connects all terminals to major hotels in the area.Taxi
Taxis are available at all terminals.Car
 Heathrow is accessible via the nearby M4 motorway or A4 road (Great Britain), A4 road (Terminals 2–3), the
Heathrow is accessible via the nearby M4 motorway or A4 road (Great Britain), A4 road (Terminals 2–3), the M25 motorway
The M25 or London Orbital Motorway is a major road encircling most of Greater London. The motorway is one of the most important roads in the UK and one of the busiest. Margaret Thatcher opened the final section in 1986, making the M25 the lon ...
(Terminals 4 and 5) and the A30 road (Terminal 4). There are drop-off and pick-up areas at all terminals and short- and long-stay multi-storey car parks. All the Heathrow forecourts are drop-off only. There are further car parks, not run by Heathrow Airport Holdings, just outside the airport: the most recognisable is the National Car Parks facility, although there are many other options; these car parks are connected to the terminals by shuttle buses.
Four parallel tunnels under the northern runway connect the M4 Heathrow spur and the A4 road to Terminals 2–3. The two larger tunnels are each two lanes wide and are used for motorised traffic. The two smaller tunnels were originally reserved for pedestrians and bicycles; to increase traffic capacity the cycle lanes have been modified to each take a single lane of cars, although bicycles still have priority over cars. Pedestrian access to the smaller tunnels has been discontinued, with the free bus services being used instead.
Bicycle
There are (mainly off-road) bicycle routes to some of the terminals.Transport for London free maps 'London Cycling Guide 6' covers Terminals 1, 2 & 3 while 'London Cycling Guide 9' covers Terminal 4 (as of the June 2007 revision). Free bicycle parking places are available in car parks 1 and 1A, at Terminal 4, and to the North and South of Terminal 5's Interchange Plaza. Cycling is not currently allowed through the main tunnel to access Terminals 2 and 3 (Terminal 1 closed in 2015).Cycling and Motorcycling mapIncidents and accidents
* On 3 March 1948, Sabena Douglas DC-3 OO-AWH crashed in fog. Three crew and 19 of the 22 passengers on board died. * On 31 October 1950, British European Airways, BEA Vickers VC.1 Viking, Vickers Viking G-AHPN crashed at Heathrow after hitting the runway during a go-around. Three crew and 25 passengers died. * On 16 January 1955, a British European Airways, BEA Vickers Viscount (registered as G-AMOK) crashed into barriers whilst taking off in the fog from a disused runway strip parallel to the desired runway. There were two injuries. * On 22 June 1955, a British Overseas Airways Corporation, BOAC de Havilland Dove (registration: G-ALTM) crashed just short of the runway during a filming flight when the pilot shut down the incorrect engine. There were no casualties. * On 1 October 1956, XA897, an Avro Vulcan strategic bomber of the Royal Air Force, 1956 London Heathrow Avro Vulcan crash, crashed at Heathrow after an approach in bad weather. The Vulcan was the first to be delivered to the RAF and was returning from a demonstration flight to Australia and New Zealand. The pilot and co-pilot ejected and survived, but the four other occupants were killed.Blackman, Tony (2007). ''Vulcan Test Pilot: My Experiences in the Cockpit of a Cold War Icon.'' London: Grub Street. . p. 142. * On 7 January 1960, Vickers Viscount G-AOHU of BEA was damaged beyond economic repair when the nose wheel collapsed on landing. A fire then developed and burnt out the fuselage. There were no casualties among the 59 people on board. * On 27 October 1965, BEA Vickers Vanguard G-APEE, flying from Edinburgh, crashed on Runway 28R while attempting to land in poor visibility. All 30 passengers and six crew on board died. * On 8 April 1968, BOAC Flight 712 Boeing 707 G-ARWE, departing for Australia via Singapore, suffered an engine fire just after take-off. The engine fell from the wing into a nearby gravel pit in Staines-upon-Thames, Staines, before the plane managed to perform an emergency landing with the wing on fire. However, the plane was consumed by fire once on the ground. Five people – four passengers and a flight attendant – died, while 122 survived. The flight attendant, Barbara Jane Harrison, Barbara Harrison, who helped with the evacuation, was posthumously awarded the George Cross. * On 3 July 1968, the port flap operating rod of 1968 Heathrow BKS Air Transport Airspeed Ambassador crash, G-AMAD, an Airspeed Ambassador operated by BKS Air Transport failed due to fatigue, thereby allowing the port flaps to retract. This resulted in a rolling movement to the port which could not be controlled during the approach, causing the aircraft to contact the grass and swerve towards the terminal building. It hit two parked British European Airways Hawker Siddeley Trident aircraft, burst into flames and came to rest against the ground floor of the terminal building. Six of the eight crew died, as did eight horses on board. Trident G-ARPT was written off, and Trident G-ARPI was badly damaged, but subsequently repaired, only to be lost in the Staines crash in 1972. * On 18 June 1972, Trident G-ARPI, operating as British European Airways Flight 548, BEA548, crashed in a field close to the Crooked Billet Public House, Staines, two minutes after taking off. All 118 passengers and crew on board died. * On 5 November 1997, an Airbus 340-300 (G-VSKY) operated byVirgin Atlantic
Virgin Atlantic, a trading name of Virgin Atlantic Airways Limited and Virgin Atlantic International Limited, is a British airline with its head office in Crawley, England. The airline was established in 1984 as British Atlantic Airways, and w ...
made an emergency landing from Los Angeles after trying to shake free the main landing gear. It failed to do so. The plane landed but the undersides of engines 1, 2, and 4 were damaged. The plane broke runway lights as well as causing damage to the runway and the right landing gear was torn off the plane. Seven people sustained minor injuries in the evacuation but no more injuries were reported. * On 17 January 2008, a British Airways Boeing 777, Boeing 777-236ER, G-YMMM, operating British Airways Flight 38, flight BA038 from Beijing, crash-landed at Heathrow. The aircraft landed on grass short of the south runway, then slid to the edge of the runway and stopped on the threshold, leading to 18 minor injuries. The aircraft was later found to have suffered a loss of thrust caused by fuel icing.
* On 28 September 2022, there was a ground collision involving a Korean Air Boeing 777 that was about to take off to Seoul, and an Icelandair Boeing 757 which had landed from Reykjavik. The 777 aborted its takeoff and no injuries were reported, but the aircraft suffered minor damage.
* On 17 January 2008, a British Airways Boeing 777, Boeing 777-236ER, G-YMMM, operating British Airways Flight 38, flight BA038 from Beijing, crash-landed at Heathrow. The aircraft landed on grass short of the south runway, then slid to the edge of the runway and stopped on the threshold, leading to 18 minor injuries. The aircraft was later found to have suffered a loss of thrust caused by fuel icing.
* On 28 September 2022, there was a ground collision involving a Korean Air Boeing 777 that was about to take off to Seoul, and an Icelandair Boeing 757 which had landed from Reykjavik. The 777 aborted its takeoff and no injuries were reported, but the aircraft suffered minor damage.
Terrorism and security incidents
* On 8 June 1968, James Earl Ray, the man convicted of the 4 April 1968 assassination of Martin Luther King Jr., was captured and arrested at Heathrow Airport while attempting to leave the United Kingdom for Rhodesia (now Zimbabwe) on a false Canadian passport. * On 6 September 1970, El Al Flight 219 experienced an attempted hijack by two Popular Front for the Liberation of Palestine, PFLP members. One hijacker was killed and the other was subdued as the plane made an emergency landing at Heathrow Airport. * On 19 May 1974, the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA planted a series of bombs in the Terminal 1 car park. Two people were injured by the explosions. * On 26 November 1983, the Brink's-Mat robbery occurred, in which 6,800 gold bars worth nearly £26,000,000 were taken from a vault near Heathrow. Only a small amount of the gold was recovered and only two men were convicted of the crime. * On 17 April 1986, semtex explosives were found in the bag of a pregnant Irishwoman attempting to board an El Al flight. The explosives had been given to her by her Jordanian boyfriend and the father of her unborn child Nizar Hindawi. The incident became known as the Hindawi Affair. *On 21 December 1988, Pan Am Flight 103 exploded mid-air over the town of Lockerbie, killing all 259 onboard and eleven people on the ground. The flight originated from Frankfurt as a feeder flight with a change of aircraft at Heathrow and was on its transatlantic leg to New York's JFK airport at the time of the incident. An unaccompanied suitcase containing a boombox radio/cassette player which housed the explosive was checked in at Malta and forwarded as interline baggage for this flight at Frankfurt, wherein it made its way to the transatlantic leg. * In 1994, over six days, Heathrow was targeted three times (8, 10, and 13 March) by the Provisional Irish Republican Army, IRA, which fired 12 mortars. Heathrow was a symbolic target due to its importance to the UK economy, and much disruption was caused when areas of the airport were closed over the period. The gravity of the incident was heightened because Elizabeth II, the Queen was being flown back to Heathrow by the RAF on 10 March. * In March 2002, thieves stole US$3,000,000 that had arrived on aSouth African Airways
South African Airways (SAA) is the flag carrier airline of South Africa. Founded in 1934, the airline is headquartered in Airways Park at O. R. Tambo International Airport in Johannesburg and operated a hub-and-spoke network, serving ten destin ...
flight. Just a few weeks earlier, a similar amount of money was stolen from a British Airways
British Airways (BA) is the flag carrier airline of the United Kingdom. It is headquartered in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a populati ...
flight that arrived from Bahrain.
* In February 2003, the British Army was deployed to Heathrow along with 1,000 police officers in response to intelligence reports suggesting that al-Qaeda terrorists might launch surface-to-air missile attacks at British or American airliners.
* On 17 May 2004, Scotland Yard's Flying Squad foiled an attempt by seven men to steal £40,000,000 in gold bullion and a similar quantity of cash from the Swissport warehouse at Heathrow.
* On 25 February 2008, Greenpeace activists protesting against the planned construction of a third runway managed to cross the ramp and climb atop a British Airways Airbus A320 family, Airbus A320, which had just arrived from Manchester Airport. At about 09:45 GMT the protesters unveiled a "Climate Emergency – No Third Runway" banner over the aircraft's Vertical stabiliser, tailfin. By 11:00 GMT four arrests had been made.
* In October 2010, an Angolan national was being deported on a British Airways plane. Security guards were heavy-handed with him and they put him in a dangerous position, leading to asphyxia. He did not survive.
* On 13 July 2015, thirteen activists belonging to the climate change protest group Plane Stupid managed to break through the perimeter fence and get onto the northern runway. They chained themselves together in protest, disrupting hundreds of flights. All were eventually arrested.
*In June 2022, there was a lot of chaos as many flights were cancelled.
*In June 2022, many protesters gathered at Heathrow and Gatwick airports to protest the Rwanda asylum plan, UK-Rwanda deal. A flight which was supposed to carry asylum seekers from the UK to Rwanda was cancelled.
Other incidents
* On 18 December 2010, 'heavy' (9 cm, according to the Heathrow Winter Resilience Enquiry) snowfall caused the closure of the entire airport, causing one of the largest incidents at Heathrow of all time. Some 4,000 flights were cancelled over five days and 9,500 passengers spent the night at Heathrow on 18 December following the initial snowfall. The problems were caused not only by snow on the runways but also by snow and ice on the 198 parking stands which were all occupied by aircraft. * On 12 July 2013, the Emergency locator transmitter, ELT on an Ethiopian Airlines Boeing 787 Dreamliner parked at Heathrow airport caught fire due to a short circuit. There were no passengers aboard and no injuries. * From 12 September 2019, the climate change campaign group, Heathrow Pause attempted to disrupt flights into and out of Heathrow Airport in London by flying Miniature UAV, drones in the airport's exclusion zone. The action was unsuccessful in disrupting flights and nineteen people were arrested.Future expansion and plans
Runway and terminal expansion
 There is a long history of expansion proposals for Heathrow since it was first designated as a civil airport. Following the cancellation of the Maplin project in 1974, a fourth terminal was proposed but expansion beyond this was ruled out. However, the Airports Inquiries of 1981–83 and the 1985 Airports Policy White Paper considered further expansion and, following a four-year-long public inquiry in 1995–99, Terminal 5 was approved. In 2003, after many studies and consultations, the Future of Air Transport White Paper was published which proposed a third runway at Heathrow, as well as a second runway at Stansted Airport. In January 2009, the Transport Secretary at the time, Geoff Hoon announced that the Brown ministry, British government supported the expansion of Heathrow by building a third runway and a sixth terminal building. This decision followed the 2003 white paper on the Air transport and the environment (United Kingdom)#Airport development strategy, future of air transport in the UK, and a public consultation in November 2007. This was a controversial decision which met with widespread opposition because of the expected greenhouse gas emissions, impact on local communities, as well as noise and air pollution concerns.
Before the 2010 United Kingdom general election, 2010 general election, the Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties announced that they would prevent the construction of any third runway or further material expansion of the airport's operating capacity. The Mayor of London, then Boris Johnson, took the position that London needs more airport capacity, favouring the construction of an entirely Thames Estuary Airport, new airport in the Thames Estuary rather than expanding Heathrow. After the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition took power, it was announced that the third runway expansion was cancelled. Two years later, leading Conservatives were reported to have changed their minds on the subject.
Another proposal for expanding Heathrow's capacity was the Heathrow Hub, which aims to extend both runways to a total length of about 7,000 metres and divide them into four so that they each provide two, full-length runways, allowing simultaneous take-offs and landings while decreasing noise levels.
In July 2013, the airport submitted three new proposals for expansion to the Airports Commission, which was established to review airport capacity in the southeast of England. The Airports Commission was chaired by Sir Howard Davies. He, at the time of his appointment, was in the employ of GIC Private Limited (formerly known as Government Investment Corporation of Singapore) and a member of its International Advisory Board. GIC Private Limited was then (2012), as it remains today, one of Heathrow's principal owners. Sir Howard Davies resigned from these positions upon confirmation of his appointment to lead the Airports Commission, although it has been observed that he failed to identify these interests when invited to complete the Airports Commission's register of interests. Each of the three proposals that were to be considered by Sir Howard Davies's commission involved the construction of a third runway, either to the north, northwest or southwest of the airport.
The commission released its interim report in December 2013, shortlisting three options: the north-west third runway option at Heathrow, extending an existing runway at Heathrow, and a second runway at Gatwick Airport. After this report was published, the government confirmed that no options had been ruled out for airport expansion in the South-east and that a new runway would not be built at Heathrow before 2015. The full report was published on 1 July 2015, and backed a third, north-west, runway at Heathrow. Reaction to the report was generally adverse, particularly from London Mayor Boris Johnson. One senior Conservative told Channel 4: "Howard Davies has dumped an utter steaming pile of poo on the Prime Minister's desk." On 25 October 2016, the government confirmed that Heathrow would be allowed to build a third runway; however, a final decision would not be taken until winter of 2017/18, after consultations and government votes. The earliest opening year would be 2025.
On 5 June 2018, the UK Cabinet approved the third runway, with a full vote planned for Parliament. On 25 June 2018, the House of Commons voted, 415–119, in favour of the third runway. The bill received support from most MPs in the Conservative and Labour parties. A judicial review against the decision was launched by four London local authorities affected by the expansion—Wandsworth, Richmond, Hillingdon and Hammersmith and Fulham—in partnership with Greenpeace and London mayor Sadiq Khan. Khan previously stated he would take legal action if it were passed by Parliament.
In February 2020, the Court of Appeal ruled that the plans for a third runway were illegal since they did not adequately take into account the government's commitments to the Paris climate agreement. However, this ruling was later overturned by the Supreme Court in December 2020.
There is a long history of expansion proposals for Heathrow since it was first designated as a civil airport. Following the cancellation of the Maplin project in 1974, a fourth terminal was proposed but expansion beyond this was ruled out. However, the Airports Inquiries of 1981–83 and the 1985 Airports Policy White Paper considered further expansion and, following a four-year-long public inquiry in 1995–99, Terminal 5 was approved. In 2003, after many studies and consultations, the Future of Air Transport White Paper was published which proposed a third runway at Heathrow, as well as a second runway at Stansted Airport. In January 2009, the Transport Secretary at the time, Geoff Hoon announced that the Brown ministry, British government supported the expansion of Heathrow by building a third runway and a sixth terminal building. This decision followed the 2003 white paper on the Air transport and the environment (United Kingdom)#Airport development strategy, future of air transport in the UK, and a public consultation in November 2007. This was a controversial decision which met with widespread opposition because of the expected greenhouse gas emissions, impact on local communities, as well as noise and air pollution concerns.
Before the 2010 United Kingdom general election, 2010 general election, the Conservative and Liberal Democrat parties announced that they would prevent the construction of any third runway or further material expansion of the airport's operating capacity. The Mayor of London, then Boris Johnson, took the position that London needs more airport capacity, favouring the construction of an entirely Thames Estuary Airport, new airport in the Thames Estuary rather than expanding Heathrow. After the Conservative-Liberal Democrat coalition took power, it was announced that the third runway expansion was cancelled. Two years later, leading Conservatives were reported to have changed their minds on the subject.
Another proposal for expanding Heathrow's capacity was the Heathrow Hub, which aims to extend both runways to a total length of about 7,000 metres and divide them into four so that they each provide two, full-length runways, allowing simultaneous take-offs and landings while decreasing noise levels.
In July 2013, the airport submitted three new proposals for expansion to the Airports Commission, which was established to review airport capacity in the southeast of England. The Airports Commission was chaired by Sir Howard Davies. He, at the time of his appointment, was in the employ of GIC Private Limited (formerly known as Government Investment Corporation of Singapore) and a member of its International Advisory Board. GIC Private Limited was then (2012), as it remains today, one of Heathrow's principal owners. Sir Howard Davies resigned from these positions upon confirmation of his appointment to lead the Airports Commission, although it has been observed that he failed to identify these interests when invited to complete the Airports Commission's register of interests. Each of the three proposals that were to be considered by Sir Howard Davies's commission involved the construction of a third runway, either to the north, northwest or southwest of the airport.
The commission released its interim report in December 2013, shortlisting three options: the north-west third runway option at Heathrow, extending an existing runway at Heathrow, and a second runway at Gatwick Airport. After this report was published, the government confirmed that no options had been ruled out for airport expansion in the South-east and that a new runway would not be built at Heathrow before 2015. The full report was published on 1 July 2015, and backed a third, north-west, runway at Heathrow. Reaction to the report was generally adverse, particularly from London Mayor Boris Johnson. One senior Conservative told Channel 4: "Howard Davies has dumped an utter steaming pile of poo on the Prime Minister's desk." On 25 October 2016, the government confirmed that Heathrow would be allowed to build a third runway; however, a final decision would not be taken until winter of 2017/18, after consultations and government votes. The earliest opening year would be 2025.
On 5 June 2018, the UK Cabinet approved the third runway, with a full vote planned for Parliament. On 25 June 2018, the House of Commons voted, 415–119, in favour of the third runway. The bill received support from most MPs in the Conservative and Labour parties. A judicial review against the decision was launched by four London local authorities affected by the expansion—Wandsworth, Richmond, Hillingdon and Hammersmith and Fulham—in partnership with Greenpeace and London mayor Sadiq Khan. Khan previously stated he would take legal action if it were passed by Parliament.
In February 2020, the Court of Appeal ruled that the plans for a third runway were illegal since they did not adequately take into account the government's commitments to the Paris climate agreement. However, this ruling was later overturned by the Supreme Court in December 2020.
New transport proposals
 Currently, all rail connections with Heathrow airport run along an east-west alignment to and from central London, and a number of schemes have been proposed over the years to develop new rail transport links with other parts of London and with stations outside the city. This mainline rail service is due to be extended to central London and Essex when the Elizabeth line, currently under construction, opens.
A 2009 proposal to create a southern link with via the Waterloo–Reading line was abandoned in 2011 due to lack of funding and difficulties with a high number of Level crossings in the United Kingdom, level crossings on the route into London, and a plan to link Heathrow to the planned High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line (with a new station, ) was also dropped from the HS2 plans in March 2015.
Among other schemes that have been considered is a rapid transport link between Heathrow and Gatwick Airports, known as ''Heathwick'', which would allow the airports to operate jointly as an airline hub; In 2018, the Department for Transport began to invite proposals for privately funded rail links to Heathrow Airport. Projects being considered under this initiative include:
* the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a proposal for a spur from the Great Western Main Line to link Heathrow to , , the South West England, South West, South Wales and the West Midlands (region), West Midlands;
* Heathrow Southern Railway, a similar scheme to the abandoned Airtrack proposal, which would connect Terminal 5 station with or , , , Guildford railway station (Surrey), Guildford and ;
* HS4Air, a proposal for a new high-speed railway line which would link HS2 to the High Speed 1 line and the Channel Tunnel via a southern route, with stations at Heathrow and Gatwick Airports.
Currently, all rail connections with Heathrow airport run along an east-west alignment to and from central London, and a number of schemes have been proposed over the years to develop new rail transport links with other parts of London and with stations outside the city. This mainline rail service is due to be extended to central London and Essex when the Elizabeth line, currently under construction, opens.
A 2009 proposal to create a southern link with via the Waterloo–Reading line was abandoned in 2011 due to lack of funding and difficulties with a high number of Level crossings in the United Kingdom, level crossings on the route into London, and a plan to link Heathrow to the planned High Speed 2 (HS2) railway line (with a new station, ) was also dropped from the HS2 plans in March 2015.
Among other schemes that have been considered is a rapid transport link between Heathrow and Gatwick Airports, known as ''Heathwick'', which would allow the airports to operate jointly as an airline hub; In 2018, the Department for Transport began to invite proposals for privately funded rail links to Heathrow Airport. Projects being considered under this initiative include:
* the Western Rail Approach to Heathrow, a proposal for a spur from the Great Western Main Line to link Heathrow to , , the South West England, South West, South Wales and the West Midlands (region), West Midlands;
* Heathrow Southern Railway, a similar scheme to the abandoned Airtrack proposal, which would connect Terminal 5 station with or , , , Guildford railway station (Surrey), Guildford and ;
* HS4Air, a proposal for a new high-speed railway line which would link HS2 to the High Speed 1 line and the Channel Tunnel via a southern route, with stations at Heathrow and Gatwick Airports.
See also
*Airports of London *Heathrow Worldwide Distribution Centre *List of airports in the United Kingdom and the British Crown DependenciesNotes
References
Citations
Bibliography
* Cotton, Jonathan; Mills, John & Clegg, Gillian. (1986) ''Archaeology in West Middlesex''. Uxbridge: London Borough of Hillingdon * Gallop, Alan. (2005) ''Time Flies: Heathrow at 60''. Stroud: Sutton Publishing * Helpenny, Bruce B. (1992) ''Action Stations Vol.8: Military Airfields of Greater London''. * Le Blond, Paul. (2018) ''Inside London's Airports Policy: Indecision, decision and counter-decision,'' ICE Publishing, * Sherwood, Philip. (1990) ''The History of Heathrow''. Uxbridge: London Borough of Hillingdon * Sherwood, Philip (editor). (1993) ''The Villages of Harmondsworth''. West Middlesex Family History Society, * Sherwood, Philip. (1999) ''Heathrow: 2000 Years of History''. Stroud: Sutton Publishing * Sherwood, Philip. (2006) ''Around Heathrow Past & Present''. Sutton Publishing ** (Contains many pairs of photographs, old (or in one case a painting), and new, each pair made from the same viewpoint.) * Sherwood, Philip. (2009) ''Heathrow: 2000 Years of History''. Stroud: The History Press * Sherwood, Philip. (2012) ''Around Heathrow Through Time''. Amberley Publishing, * Sherwood, Tim. (1999) ''Coming in to Land: A Short History of Hounslow, Hanworth and Heston Aerodromes'' 1911–1946Heritage Publications (Hounslow Library)
* Smith, Graham. (2003) ''Taking to the Skies: the Story of British Aviation 1903–1939''. Countryside * Smith, Ron. (2002) ''British Built Aircraft Vol.1''. Greater London: Tempus * Sturtivant, Ray. (1995) ''Fairey Aircraft: in Old Photographs''. Alan Sutton * Taylor, H.A. (1974) ''Fairey Aircraft since 1915''. Putnam . * Taylor, John WR. (1997) ''Fairey Aviation: Archive Photographs''. Chalford
External links
*Heathrow Community Engagement Board website
{{DEFAULTSORT:Heathrow Heathrow Airport, Airports in the London region Airports established in 1946 Heathrow Airport Holdings Buildings and structures in the London Borough of Hillingdon Public inquiries in the United Kingdom Transport in the London Borough of Hillingdon Proposed transport infrastructure in London Tourist attractions in the London Borough of Hillingdon 1946 establishments in England Airports in England