Growth Imperative on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Growth imperative is a term in economic theory regarding a possible necessity of economic growth. On the micro level, it describes mechanisms that force
Growth imperative is a term in economic theory regarding a possible necessity of economic growth. On the micro level, it describes mechanisms that force
 The first theory of a growth imperative is attributed to
The first theory of a growth imperative is attributed to  On the basis of concepts of
On the basis of concepts of
 An imperative for private households to increase their
An imperative for private households to increase their
 Economic growth has been formulated as an important economic policy goal for decades. Examples include the "growth duty" in British legislation, but also the Canadian Jobs and Growth Act, the African Growth and Opportunity Act or the
Economic growth has been formulated as an important economic policy goal for decades. Examples include the "growth duty" in British legislation, but also the Canadian Jobs and Growth Act, the African Growth and Opportunity Act or the
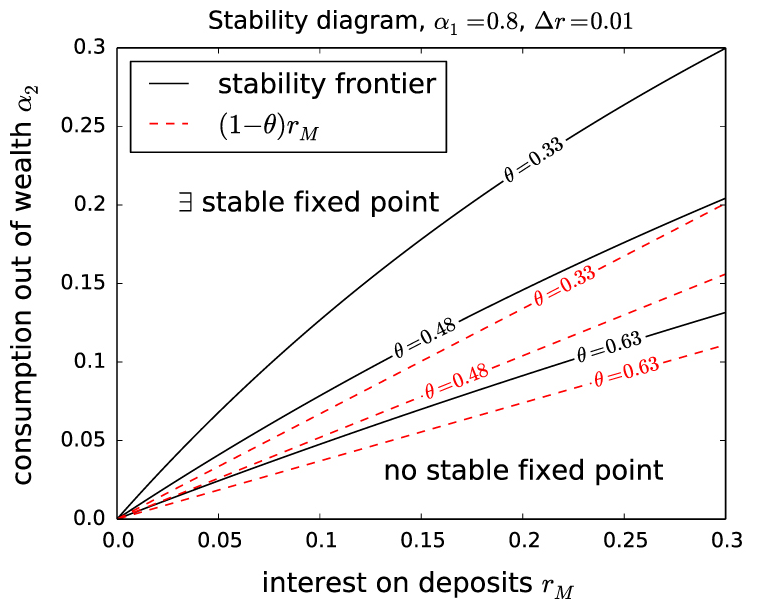 Other authors criticise the results of Beltrani as well as H. C. and M. Binswanger on the basis that they are based on inconsistent economic models and therefore not valid (→ Stock-Flow consistent model).
Those models show how repaid interest is not simply 'removed' from circulation, but flows back into the economy where it can be earned and repeated used to service debts. Models such as those created by Jackson & Victor show that, if no money is accumulated, then all debt can be serviced, and hence that no growth imperative arises from the creation of money as debt, 'per se'. This leads some theorists to conclude that the monetary growth imperative only applies for certain
Other authors criticise the results of Beltrani as well as H. C. and M. Binswanger on the basis that they are based on inconsistent economic models and therefore not valid (→ Stock-Flow consistent model).
Those models show how repaid interest is not simply 'removed' from circulation, but flows back into the economy where it can be earned and repeated used to service debts. Models such as those created by Jackson & Victor show that, if no money is accumulated, then all debt can be serviced, and hence that no growth imperative arises from the creation of money as debt, 'per se'. This leads some theorists to conclude that the monetary growth imperative only applies for certain
attac Germany. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Robert U., last1=Ayres, author-link1=Robert Ayres (scientist), first2=Benjamin, last2=Warr, title=The economic growth engine: how energy and work drive material prosperity, date=2009, publisher=Edward Elgar, isbn=978-1-84844-595-6 {{cite journal, first1=John, last1=Barry, title=A Genealogy of Economic Growth as Ideology and Cold War Core State Imperative, date=2018, journal=New Political Economy, doi=10.1080/13563467.2018.1526268, volume=25, issue=1, pages=18–29, s2cid=159024755, url=https://pure.qub.ac.uk/en/publications/a-genealogy-of-economic-growth-as-ideology-and-cold-war-core-state-imperative(5e92b969-d9d2-4f83-80ca-9279fed59c68).html {{Cite book, first1=Guido, last1=Beltrani, title=Monetäre Aspekte des Wirtschaftswachstums, date=1999, publisher=Universität St. Gallen, oclc=722449216 {{Cite book, first1=Harald, last1=Bender, first2=Norbert, last2=Bernholt, first3=Klaus, last3=Simon, title=Das dienende Geld: die Befreiung der Wirtschaft vom Wachstumszwang, date=2014, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-86581-471-5 {{cite journal, first1=Matthew, last1=Berg, first2=Brian, last2=Hartley, first3=Oliver, last3=Richters, title=A Stock-Flow Consistent Input-Output Model with Applications to Energy Price Shocks, Interest Rates, and Heat Emissions, journal=
Dokumentation: Degrowth 2014
Programme
of the {{ill, International Conference on Degrowth, de, Internationale Degrowth-Konferenz 2014, p. 3. www.degrowth.info. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Richard , last1=Douthwaite, author-link1=Richard Douthwaite, title=The ecology of money, date=2000, publisher=Green Books, isbn=978-1-8700-9881-6 Abschlussbericht der Enquete-Kommission Wachstum, Wohlstand, Lebensqualität
Deutscher
30 March 2017. Federal board of Alliance 90/The Greens
''Neue Zeiten. Neue Antworten.''
April 6, 2018. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Fred, last1=Hirsch, author-link1=Fred Hirsch (professor), title=Social Limits to Growth, date=1976, publisher=Harvard University Press {{Cite book, first1=François, last1=Höpflinger, chapter=Alterssicherungssysteme: Doppelte Herausforderung von demografischer Alterung und Postwachstum, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=53–64, editor-first1=Irmi, editor-last1=Seidl, editor-first2=Angelika, editor-last2=Zahrnt, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft {{Cite journal, first1=Charles , last1=Hulten, title=Growth Accounting, date=2009, doi=10.3386/w15341, journal=NBER Working Paper, issue=w15341, doi-access=free {{Cite journal, first1=Tim, last1=Jackson, author-link1=Tim Jackson (economist), first2=Peter, last2=Victor, title=Does credit create a 'growth imperative'? A quasi-stationary economy with interest-bearing debt, journal= Ecological Economics, date=December 2015, volume=120, pages=32–48, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.09.009 Preprint
PASSAGE Working Paper 15/01
Guildford: University of Surrey. {{Cite journal, first1=Tim, last1=Jackson, author-link1=Tim Jackson (economist), first2=Peter, last2=Victor, title=Productivity and work in the 'green economy' – some theoretical reflections and empirical tests, journal= Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, date=2011, volume=1, pages=101–108, doi=10.1016/j.eist.2011.04.005, issue=1, s2cid=150636345 {{Cite journal, first1=A. Reeves, last1=Johnson, title=Response to "Comment on Johnson's creating dimensional stock-flow inconsistency in Binswanger's model", date=2018, doi=10.1080/01603477.2018.1458631, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, volume=42, issue=2, pages=328–334, s2cid=158990885 {{Cite book, first1=Charles I. , last1=Jones, title=Handbook of Economic Growth, chapter=Growth and Ideas, date=2005, publisher=Elsevier, isbn=978-0-444-52043-2, volume=2, pages=1063–1111, doi=10.1016/S1574-0684(05)01016-6, editor-first1=Philippe, editor-last1=Aghion, editor-first2=Steven N. , editor-last2=Durlauf {{Cite journal, first1=Mathias, last1=Binswanger, title=The growth imperative revisited: a rejoinder to Gilányi and Johnson, date=May 2015, volume=37, pages=648–660, doi=10.1080/01603477.2015.1050333, issue=4, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, s2cid=54606846 {{cite journal, first1=Giorgos , last1=Kallis, author-link1= Giorgos Kallis, title=Socialism without growth, journal= Capitalism Nature Socialism, volume=30 , issue=2, date=2019, pages=189–206, doi=10.1080/10455752.2017.1386695 , s2cid=158796873 {{Cite book, first1=Athanasios , last1=Karathanassis, title=Kapitalistische Naturverhältnisse. Ursachen von Naturzerstörungen – Begründungen einer Postwachstumsökonomie, date=2015, publisher=VSA-Verlag, isbn=978-3-89965-623-7 {{Cite book, first1=Margrit, last1=Kennedy, author-link1=Margrit Kennedy, title=Geld ohne Zinsen und Inflation. Ein Tauschmittel, das jedem dient, year=1991, publisher=Goldmann, isbn=978-3-442-12341-4, pages=26–7 {{Cite journal, first1=Reiner , last1=Kümmel, first2=Dietmar, last2=Lindenberger, title=How energy conversion drives economic growth far from the equilibrium of neoclassical economics, date=December 2014, journal=
basic programme of
''Ausrichtung der Grünen: Die Möchtegern-Liberalen''
'' die tageszeitung'', September 26, 2018. {{Cite book, first1=Joseph, last1=Schumpeter, author-link1=Joseph Schumpeter, title=
ZOE Discussion Paper 3
January 2019, {{Hdl, 10419/201502.
steadystate.org
accessed February 27, 2019. See also Mathias Binswanger, ''Der Wachstumszwang'', 2019, p. 39. {{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=The Growth Spiral: Money, Energy, and Imagination in the Dynamics of the Market Process, date=2013, publisher=Springer, isbn=978-3-642-31881-8, pages=119, doi=10.1007/978-3-642-31881-8 {{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=The Growth Spiral: Money, Energy, and Imagination in the Dynamics of the Market Process, date=2013, publisher=Springer, isbn=978-3-642-31881-8, pages=131, doi=10.1007/978-3-642-31881-8 {{Cite journal, first1=Richard , last1=Smith, url=http://www.paecon.net/PAEReview/issue53/Smith53.pdf, title=Beyond Growth or Beyond Capitalism, volume=53, pages=28–42, journal=
wachstumsimwandel.at, Bundesministerium für Nachhaltigkeit und Tourismus, September 20, 2018. {{Cite book, first1=Ferdinand, last1=Wenzlaff, first2=Christian, last2=Kimmich, first3=Oliver, last3=Richters, hdl=10419/103454, title=Theoretische Zugänge eines Wachstumszwangs in der Geldwirtschaft, date=2014, publisher=Zentrum für Ökonomische und Soziologische Studien, issue=45 Capitalism Sustainability Economic growth
firm
A company, abbreviated as co., is a legal entity representing an association of people, whether natural, legal or a mixture of both, with a specific objective. Company members share a common purpose and unite to achieve specific, declared go ...
s or consumers (households) to increase revenue
In accounting, revenue is the total amount of income generated by the sale of goods and services related to the primary operations of the business.
Commercial revenue may also be referred to as sales or as turnover. Some companies receive reven ...
s or consumption to not endanger their income. On the macro level, a political growth imperative exists if economic growth is necessary to avoid economic and social instability or to retain democratic legitimacy, so that other political goals such as climate change mitigation or a reduction of inequality are subordinated to growth policies.
Current neoclassical, Keynesian
Keynesian economics ( ; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output an ...
and endogenous growth theories do not consider a growth imperative or explicitly deny it, such as Robert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the ...
. In neoclassical economics, adherence to economic growth would be a question of maximizing utility, an intertemporal decision between current and future consumption (see Keynes–Ramsey rule In macroeconomics, the Keynes–Ramsey rule is a necessary condition for the optimality of intertemporal consumption choice. Usually it is express as a differential equation relating the rate of change of consumption with interest rates, time pre ...
). Other sociological and political theories consider several possible causes for pursuing economic growth, for example maximizing profit, social comparison, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these groups ...
( conformity), or political ideologies
An ideology is a set of beliefs or philosophies attributed to a person or group of persons, especially those held for reasons that are not purely epistemic, in which "practical elements are as prominent as theoretical ones." Formerly applied prim ...
, but they do not regard them to be compulsive. Possible growth imperatives are discussed in Marxist theory, Schumpeterian theory of creative destruction
Creative destruction (German: ''schöpferische Zerstörung'') is a concept in economics which since the 1950s is the most readily identified with the Austrian-born economist Joseph Schumpeter who derived it from the work of Karl Marx and pop ...
and ecological economics, as well as in political debates on post-growth
Post-growth is stance on economic growth concerning the limits-to-growth dilemma — recognition that, on a planet of finite material resources, extractive economies and populations cannot grow infinitely. The term "post-growth" acknowledges t ...
and degrowth. It is disputed whether growth imperative is a meaningful concept altogether, who would be affected by it, and which mechanism would be responsible.
Meaning and definitions
At themacroeconomic
Macroeconomics (from the Greek prefix ''makro-'' meaning "large" + ''economics'') is a branch of economics dealing with performance, structure, behavior, and decision-making of an economy as a whole.
For example, using interest rates, taxes, and ...
or political level, the concept of growth imperatives is used by some authors when there seems to be no acceptable political alternative to economic growth, because insufficient growth would lead to economic and social instability up to "severe economic crises". The alternative to growth would not be a stable stationary economy, but uncontrolled shrinkage. The consequences of a renunciation of growth would be inacceptable so that growth appears politically without alternative. While some search for purely "structural theoretical explanations for the commitment to growth", others argue that this macroeconomic phenomenon must be examined at the micro level in line with methodological individualism
In the social sciences, methodological individualism is the principle that subjective individual motivation explains social phenomena, rather than class or group dynamics which are illusory or artificial and therefore cannot truly explain marke ...
to explain how and why individual actors (firms, consumers) act and how this interacts with collective structures, and correspondingly study the growth of enterprises with microeconomics and business administration and the increase of consumption
Consumption may refer to:
*Resource consumption
*Tuberculosis, an infectious disease, historically
* Consumption (ecology), receipt of energy by consuming other organisms
* Consumption (economics), the purchasing of newly produced goods for curren ...
using consumption sociology or consumer choice theory.
The discussion on growth imperatives is part of a standing debate over the primacy of structure or agency in shaping human behavior. In the social sciences the term social coercion is used when situation-related circumstances or strong social pressure determine the behaviour. According to Marxist theory, a coercion for firms to "grow or die" is due to economic competition. According to these Marxists, capitalism "cannot stand still, but must always be either expanding or contracting". Similarly, the environmental economist speaks of a growth imperative for firms only when they are existentially threatened by steadily declining profits and ultimately bankruptcy; in other cases he uses the weaker term growth driver. These definitions can be summarized that a growth imperative exists if exterior conditions make it necessary for agents to increase their economic efforts as to avoid existential consequences.
Microeconomic theories
Firms
 The first theory of a growth imperative is attributed to
The first theory of a growth imperative is attributed to Karl Marx
Karl Heinrich Marx (; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, economist, historian, sociologist, political theorist, journalist, critic of political economy, and socialist revolutionary. His best-known titles are the 1848 ...
. In capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
, zero growth is not possible, because of the mechanisms of competition and accumulation
Accumulation may refer to:
Finance
* Accumulation function, a mathematical function defined in terms of the ratio future value to present value
* Capital accumulation, the gathering of objects of value
Science and engineering
* Accumulate (hi ...
.
Therefore, a company's growth is considered necessary to ensure the survival of the company ("grow or die"): "investment is not an option, or a discretionary decision, it is an imperative that constrains every capitalists' actions and governs the overall economy" Correspondingly, some authors argue that the compulsion to grow can only be defused by overcoming structures of market economies
A market economy is an economic system in which the decisions regarding investment, production and distribution to the consumers are guided by the price signals created by the forces of supply and demand, where all suppliers and consumers are ...
, or by pushing back profit-oriented companies that impropriate the surplus value. Other authors criticize this Marxist perspective: a company could be profitable without growth if a positive accounting profit
Profit, in accounting, is an income distributed to the owner in a profitable market production process (business). Profit is a measure of profitability which is the owner's major interest in the income-formation process of market producti ...
is distributed as dividend
A dividend is a distribution of profits by a corporation to its shareholders. When a corporation earns a profit or surplus, it is able to pay a portion of the profit as a dividend to shareholders. Any amount not distributed is taken to be re-i ...
to the owners. Only if net income had to be retained, companies would be compelled to grow. If a company shows an accounting profit
Profit, in accounting, is an income distributed to the owner in a profitable market production process (business). Profit is a measure of profitability which is the owner's major interest in the income-formation process of market producti ...
, it has not yet achieved an economic profit
In economics, profit is the difference between the revenue that an economic entity has received from its outputs and the total cost of its inputs. It is equal to total revenue minus total cost, including both explicit and implicit costs.
It ...
in the economic sense, because a return on equity and an entrepreneurial salary would have to be paid from it - the profit would not necessarily be available for growth. Therefore, a market economy with profit-oriented companies is compatible with zero growth, as it is in the models of neoclassical theory (→ zero-profit condition).
 On the basis of concepts of
On the basis of concepts of evolutionary economics
Evolutionary economics is part of mainstream economics as well as a heterodox school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Much like mainstream economics, it stresses complex interdependencies, competition, growth, stru ...
, other authors point out that firms can become dependent on growth as a result of certain economic conditions. Joseph Schumpeter
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian-born political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of German-Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at H ...
had described the creative destruction
Creative destruction (German: ''schöpferische Zerstörung'') is a concept in economics which since the 1950s is the most readily identified with the Austrian-born economist Joseph Schumpeter who derived it from the work of Karl Marx and pop ...
in which the existence of firms is endangered if they cannot keep up with the innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entit ...
competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indiv ...
. This is interpreted as a need to invest in new technologies and to expand production - but which investments would be necessary can only be understood in the light of growth theory
Economic growth can be defined as the increase or improvement in the inflation-adjusted market value of the goods and services produced by an economy in a financial year. Statisticians conventionally measure such growth as the percent rate of ...
. Within neoclassical growth accounting Growth accounting is a procedure used in economics to measure the contribution of different factors to economic growth and to indirectly compute the rate of technological progress, measured as a residual, in an economy. Growth accounting decomposes ...
it is largely undisputed that only technological change
Technological change (TC) or technological development is the overall process of invention, innovation and diffusion of technology or processes.From ''The New Palgrave Dictionary otechnical change by S. Metcalfe. •biased and biased techno ...
and new combinations of factors of production
In economics, factors of production, resources, or inputs are what is used in the production process to produce output—that is, goods and services. The utilized amounts of the various inputs determine the quantity of output according to the rel ...
make sustainable growth
Sustainable development is an organizing principle for meeting human development goals while also sustaining the ability of natural systems to provide the natural resources and ecosystem services on which the economy and society depend. The desi ...
of firms and per capita income possible. However, the contribution of single production factors to economic growth has been disputed for decades: While endogenous growth theory concentrates on the role of human capital (ideas, education, innovations), proponents of ecological
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overlaps wi ...
or environmental economics
Environmental economics is a sub-field of economics concerned with environmental issues. It has become a widely studied subject due to growing environmental concerns in the twenty-first century. Environmental economics "undertakes theoretical or ...
emphasize the importance of energy consumption as well as raw materials, which are often non-renewable resource
A non-renewable resource (also called a finite resource) is a natural resource that cannot be readily replaced by natural means at a pace quick enough to keep up with consumption. An example is carbon-based fossil fuels. The original organic mat ...
s (e.g. fossil fuels). While from the human capital perspective no ecologically damaging growth imperative arises, the resource perspective emphasizes that raw material consumption is lucrative for firms because it allows them to substitute expensive labour with cheaper machines. Accordingly, they would constantly invest in new resource-intensive technologies plus the human capital needed for development, which increases resource consumption and compensates advances in energy efficiency
Energy efficiency may refer to:
* Energy efficiency (physics), the ratio between the useful output and input of an energy conversion process
** Electrical efficiency, useful power output per electrical power consumed
** Mechanical efficiency, a ra ...
(rebound effects
The rebound effect, or rebound phenomenon, is the emergence or re-emergence of symptoms that were either absent or controlled while taking a medication, but appear when that same medication is discontinued, or reduced in dosage. In the case of re ...
).
There is also disagreement as to whether these dependencies can be overcome at the company level - provided that this is desired by the owners or the management. Proposals include new management practices, changes in product range, supply chains and distribution channels, as well as the creation of solidarity enterprises, collective enterprises and cooperative
A cooperative (also known as co-operative, co-op, or coop) is "an autonomous association of persons united voluntarily to meet their common economic, social and cultural needs and aspirations through a jointly owned and democratically-contro ...
s. Other authors call for institutional solutions: reforms of corporate law to overcome the legal constraint of public limited companies to maximise profits, reforms of competition law to prevent externalisation at the expense of common goods
Common goods (also called common-pool resources) are defined in economics as goods that are rivalrous and non-excludable. Thus, they constitute one of the four main types based on the criteria:
* whether the consumption of a good by one pers ...
, or an institutional limitation of resource consumption and/or increasing their costs through ecotax
An environmental tax, ecotax (short for ecological taxation), or green tax is a tax levied on activities which are considered to be harmful to the environment and is intended to promote environmentally friendly activities via economic incentives. ...
es or emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission ...
(Cap and Trade
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission t ...
), so that technical innovations would put a stronger focus on resource productivity instead of labour productivity.
Private households
income
Income is the consumption and saving opportunity gained by an entity within a specified timeframe, which is generally expressed in monetary terms. Income is difficult to define conceptually and the definition may be different across fields. Fo ...
and consumption expenditure is rarely discussed. In neoclassical household theory, households try to maximize their utility, whereby, in contrast to the profit maximization of firms, they are not subject to market imperatives. Therefore, a growth imperative is usually not assumed here, but rather a free decision between current and future consumption. This "intertemporal optimization" is represented, for example, by the Keynes-Ramsey rule. In consumption sociology various theories of consumer society
Consumerism is a social and economic order that encourages the acquisition of goods and services in ever-increasing amounts. With the Industrial Revolution, but particularly in the 20th century, mass production led to overproduction—the su ...
examine the influence of social norms on consumption decisions. Examples are conspicuous consumption, which was addressed as early as 1899 by Thorstein Veblen
Thorstein Bunde Veblen (July 30, 1857 – August 3, 1929) was a Norwegian-American economist and sociologist who, during his lifetime, emerged as a well-known critic of capitalism.
In his best-known book, ''The Theory of the Leisure Class'' ...
in his book ''The Theory of the Leisure Class
''The Theory of the Leisure Class: An Economic Study of Institutions'' (1899), by Thorstein Veblen, is a treatise of economics and sociology, and a critique of conspicuous consumption as a function of social class and of consumerism, which are ...
'', or competition with positional good
Positional goods are goods valued only by how they are distributed among the population, not by how many of them there are available in total (as would be the case with other consumer goods). The source of greater worth of positional goods is thei ...
s, which was described by Fred Hirsch in 1976 in the book ''Social Limits to Growth''. Some authors claim that comparison with others and the unfair distribution of income and power would lead to a growth imperative for consumers: Consumers would have to work and consume more and more in order to achieve a minimum level of social participation, because the economically weak are stigmatised. The reasons given for this behaviour are fear and powerlessness, guilt and shame. However, whether these theories can actually justify a compulsion to increase consumption is disputed, as long as it is not a matter of securing one's livelihood (for example because of unemployment).
Another line of argument views certain consumption decisions rather as investments for future growth, but sometimes to increase one's own productivity. Technical products such as vehicles, kitchen appliances or smartphones were used to save time and retain opportunities to earn an income. Over time, these goods would become a necessity, therefore a compulsion to increase one's consumption expenditure could be derived in order to not be left behind technically and economically.
Macroeconomic theories
Political resp. macroeconomic growth imperative
 Economic growth has been formulated as an important economic policy goal for decades. Examples include the "growth duty" in British legislation, but also the Canadian Jobs and Growth Act, the African Growth and Opportunity Act or the
Economic growth has been formulated as an important economic policy goal for decades. Examples include the "growth duty" in British legislation, but also the Canadian Jobs and Growth Act, the African Growth and Opportunity Act or the European
European, or Europeans, or Europeneans, may refer to:
In general
* ''European'', an adjective referring to something of, from, or related to Europe
** Ethnic groups in Europe
** Demographics of Europe
** European cuisine, the cuisines of Europe ...
Stability and Growth Pact
The Stability and Growth Pact (SGP) is an agreement, among all of the 27 member states of the European Union, to facilitate and maintain the stability of the Economic and Monetary Union (EMU). Based primarily on Articles 121 and 126 of the Tre ...
of 1997. This has been criticised as politically adhering to a dogma or ideology by some critics of growth.
The theory of a political growth imperative, on the other hand, argues that economic growth would be necessary to avoid economic or social instability and to retain democratic legitimacy, or to guarantee national security and international competition. Some authors stress that public finances or social insurance
Social insurance is a form of social welfare that provides insurance against economic risks. The insurance may be provided publicly or through the subsidizing of private insurance. In contrast to other forms of social assistance, individuals' ...
systems such as unemployment insurance
Unemployment benefits, also called unemployment insurance, unemployment payment, unemployment compensation, or simply unemployment, are payments made by authorized bodies to unemployed people. In the United States, benefits are funded by a comp ...
or pensions are dependent on growth. Raghuram Rajan
Raghuram Govind Rajan (born 3 February 1963) is an Indian economist and the Katherine Dusak Miller Distinguished Service Professor of Finance at the University of Chicago Booth School of Business. Quote: "I am an Indian citizen. I have always b ...
sees the cause primarily in political promises that are inherent to social systems. Unemployment, which would occur in the event of technical progress and simultaneous lack of economic growth, is identified as a central problem (Okun's law
In economics, Okun's law is an empirically observed relationship between unemployment and losses in a country's production. It is named after Arthur Melvin Okun, who first proposed the relationship in 1962. The "gap version" states that for ever ...
). Thus, growth above the employment threshold is repeatedly called for in political debates, in order to reduce unemployment. Growth enhancing state investment, but also numerous incentives for private investment would not be simply politician's free will but indispensable to prevent social instability through mass unemployment. This situation would be aggravated by international competition
Competition is a rivalry where two or more parties strive for a common goal which cannot be shared: where one's gain is the other's loss (an example of which is a zero-sum game). Competition can arise between entities such as organisms, indiv ...
and free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econ ...
.
As a way out, a redirection of technological development with the help of resource taxes is discussed (ecotax
An environmental tax, ecotax (short for ecological taxation), or green tax is a tax levied on activities which are considered to be harmful to the environment and is intended to promote environmentally friendly activities via economic incentives. ...
, emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission ...
), but also a general reduction of working time
Working(laboring) time is the period of time that a person spends at paid labor. Unpaid labor such as personal housework or caring for children or pets is not considered part of the working week.
Many countries regulate the work week by law, ...
to reduce unemployment. At the same time, a more equal distribution of income is demanded, either by fighting the privatisation of economic rent
In economics, economic rent is any payment (in the context of a market transaction) to the owner of a factor of production in excess of the cost needed to bring that factor into production. In classical economics, economic rent is any payment m ...
s such as land rent
In economics, economic rent is any payment (in the context of a market transaction) to the owner of a factor of production in excess of the cost needed to bring that factor into production. In classical economics, economic rent is any payment m ...
or resource rent In economics, rent is a surplus value after all costs and normal returns have been accounted for, i.e. the difference between the price at which an output from a resource can be sold and its respective extraction and production costs, including nor ...
(→ rentier state
In current political-science and international-relations theory, a rentier state is a state which derives all or a substantial portion of its national revenues from the rent paid by foreign individuals, concerns or governments.Mahdavy 1970, p. ...
), or by calling for an unconditional basic income
Universal basic income (UBI) is a social welfare proposal in which all citizens of a given population regularly receive an unconditional transfer payment, that is, without a means test or need to work. It would be received independently of a ...
.
Monetary system and the role of positive interest rates
For a long time, several authors especially from German-speaking countries have been locating a macroeconomic growth imperative in the monetary system, especially due to the combination ofcredit money
Credit theories of money, also called debt theories of money, are monetary economic theories concerning the relationship between credit and money. Proponents of these theories, such as Alfred Mitchell-Innes, sometimes emphasize that money and cr ...
and compound interest. This is considered to lead inevitably and system-immanently to an exponential growth
Exponential growth is a process that increases quantity over time. It occurs when the instantaneous rate of change (that is, the derivative) of a quantity with respect to time is proportional to the quantity itself. Described as a function, a ...
of debt
Debt is an obligation that requires one party, the debtor, to pay money or other agreed-upon value to another party, the creditor. Debt is a deferred payment, or series of payments, which differentiates it from an immediate purchase. The ...
and interest-bearing deposits. Some proponents of post-growth would derive a general criticism of positive interest rates from that and support ideas such as demurrage
The term "demurrage" from Old French ''demeurage'', from ''demeurer'' – to linger, tarry – originated in vessel chartering and referred to the period when the charterer remained in possession of the vessel after the period normally allowed ...
on currency, a concept from Freiwirtschaft
(German language, German for "free economy") is an economic idea founded by Silvio Gesell in 1916. He called it ' (natural economic order). In 1932, a group of Swiss businessmen used his ideas to found the WIR Bank (WIR).
Structure
Freiwirtschaft ...
, or full-reserve banking
Full-reserve banking (also known as 100% reserve banking, narrow banking, or sovereign money system) is a system of banking where banks do not lend demand deposits and instead, only lend from time deposits. It differs from fractional-reserve bank ...
.
A second line of argument goes back to , his doctoral student Guido Beltrani, and his son . They argue that "a portion of money is constantly removed from circulation" by banks which is mainly responsible for the growth imperative. In his book ''The Growth Spiral'' (2013), Hans Christoph Binswanger estimated a necessary minimum growth rate to be 1.8 %, while Mathias Binswanger (2009) derived a minimum growth rate of 0.45 %, such that enterprises can still generate profits in the aggregate. In his book ''Der Wachstumszwang'' (2019), this minimum rate is lowered to zero as to enable firms to accumulate profits.
 Other authors criticise the results of Beltrani as well as H. C. and M. Binswanger on the basis that they are based on inconsistent economic models and therefore not valid (→ Stock-Flow consistent model).
Those models show how repaid interest is not simply 'removed' from circulation, but flows back into the economy where it can be earned and repeated used to service debts. Models such as those created by Jackson & Victor show that, if no money is accumulated, then all debt can be serviced, and hence that no growth imperative arises from the creation of money as debt, 'per se'. This leads some theorists to conclude that the monetary growth imperative only applies for certain
Other authors criticise the results of Beltrani as well as H. C. and M. Binswanger on the basis that they are based on inconsistent economic models and therefore not valid (→ Stock-Flow consistent model).
Those models show how repaid interest is not simply 'removed' from circulation, but flows back into the economy where it can be earned and repeated used to service debts. Models such as those created by Jackson & Victor show that, if no money is accumulated, then all debt can be serviced, and hence that no growth imperative arises from the creation of money as debt, 'per se'. This leads some theorists to conclude that the monetary growth imperative only applies for certain parameter
A parameter (), generally, is any characteristic that can help in defining or classifying a particular system (meaning an event, project, object, situation, etc.). That is, a parameter is an element of a system that is useful, or critical, when ...
s in the consumption function
In economics, the consumption function describes a relationship between consumption and disposable income. The concept is believed to have been introduced into macroeconomics by John Maynard Keynes in 1936, who used it to develop the notion of a ...
. They argue that ultimately it is not the interest rate but the savings rate that is decisive for the stability of a stationary economy. If any interest income is consumed in full by the lender, i.e., bank or creditor of the bank, it is available again for repayment. Whether a stationary state can be reached, therefore, depends on the saving decisions of those who earn income or own assets. For zero growth it would only be necessary that savings of some are balanced by consumption out of wealth by others (→ life-cycle hypothesis
In economics, the life-cycle hypothesis (LCH) is a model that strives to explain the consumption patterns of individuals.
Background
The hypothesis
Implications
Saving and wealth when income and population are stable
The effect of population ...
). The assumption that banks must retain profits even in a non-growing economy would be unfounded. Accordingly, there would be no grow imperative "inherent" to the monetary system, but zero growth would be impossible as long as actors decide to continuously accumulate financial assets.
In neoclassical theory and all varieties that presuppose the neutrality of money
Neutral or neutrality may refer to:
Mathematics and natural science Biology
* Neutral organisms, in ecology, those that obey the unified neutral theory of biodiversity
Chemistry and physics
* Neutralization (chemistry), a chemical reaction i ...
(classical dichotomy In macroeconomics, the classical dichotomy is the idea, attributed to classical and pre-Keynesian economics, that real and nominal variables can be analyzed separately. To be precise, an economy exhibits the classical dichotomy if real variables su ...
), the money market
The money market is a component of the economy that provides short-term funds. The money market deals in short-term loans, generally for a period of a year or less.
As short-term securities became a commodity, the money market became a compon ...
has no long-term effects on real
Real may refer to:
Currencies
* Brazilian real (R$)
* Central American Republic real
* Mexican real
* Portuguese real
* Spanish real
* Spanish colonial real
Music Albums
* ''Real'' (L'Arc-en-Ciel album) (2000)
* ''Real'' (Bright album) (2010) ...
economic variables such as economic growth. A monetary growth imperative is already excluded here by assumption. However, post-Keynesian
Post-Keynesian economics is a school of economic thought with its origins in '' The General Theory'' of John Maynard Keynes, with subsequent development influenced to a large degree by Michał Kalecki, Joan Robinson, Nicholas Kaldor, Sidney ...
authors who doubt the neutrality of money reject a monetary growth imperative as well.
Political demands to overcome growth imperatives
In September 2018, more than 200scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosoph ...
s asked the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
to turn away from any growth imperative – a similar demand was raised by the participants of the and the post-growth working group of attac Germany. But even within the post-growth
Post-growth is stance on economic growth concerning the limits-to-growth dilemma — recognition that, on a planet of finite material resources, extractive economies and populations cannot grow infinitely. The term "post-growth" acknowledges t ...
or degrowth movement, the existence of growth imperatives is disputed. Among German parties, the demand was included in the political programmes of the Ecological Democratic Party
The Ecological Democratic Party (german: Ökologisch-Demokratische Partei, ÖDP) is a conservative and ecologist minor party in Germany. The ÖDP was founded in 1982.
The strongest level of voting support for the ÖDP is in Bavaria, where in ...
and Alliance 90/The Greens. Green politicians such as Reinhard Loske or Jürgen Trittin
Jürgen Trittin (born 25 July 1954) is a German Green politician. He was Federal Minister for the Environment, Nature Conservation and Nuclear Safety in the government of Chancellor Gerhard Schröder from 1998 to 2005 in Germany.
Early life a ...
call for overcoming growth imperatives. In a dissenting opinion
A dissenting opinion (or dissent) is an opinion in a legal case in certain legal systems written by one or more judges expressing disagreement with the majority opinion of the court which gives rise to its judgment.
Dissenting opinions are norm ...
on the final report of the of the German parliament (Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Common ...
), the experts Michael Müller, , Ulrich Brand, and , as well as the members of the Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Common ...
and the parliamentary group Die Linke, argued that "the question must be answered as to whether progress that is innovative and integrative, socially just and ecologically sustainable is possible without any growth imperative".
Literature
* * * * * Preprint: Oldenburg Discussion Papers in Economics V-414-18, November 2018, . This article was translated from Wachstumszwang in the German Wikipedia which is based on: * .CC-BY-SA
A Creative Commons (CC) license is one of several public copyright licenses that enable the free distribution of an otherwise copyrighted "work".A "work" is any creative material made by a person. A painting, a graphic, a book, a song/lyrics ...
3.0.
References
{{Reflist, refs= {{cite journal, first1=Giorgos , last1= Kallis , author-link1=Giorgos Kallis, first2=Vasilis , last2= Kostakis , first3=Steffen , last3= Lange , first4= Barbara , last4= Muraca , first5= Susan , last5= Paulson , first6= Matthias , last6= Schmelzer , journal=Annual Review of Environment and Resources
The ''Annual Review of Environment and Resources'' is a peer-reviewed scientific journal that publishes review articles about environmental science and environmental engineering. It was first published in 1976 under the name the ''Annual Review of ...
, title=Research On Degrowth, date=2018, volume=43, pages=291–316, doi=10.1146/annurev-environ-102017-025941, issue=1, doi-access=free
{{Cite book, first1=Giacomo, last1=D'Alisa, first2=Federico, last2=Demaria, first3=Giorgios, last3=Kallis, author-link3=Giorgos Kallis, title=Degrowth: A Vocabulary for a New Era, date=2015, publisher=Routledge, isbn=978-1-1380-0077-3
{{Cite journal, first1=Miklós, last1=Antal, journal= Ecological Economics, title=Green goals and full employment: Are they compatible?, date=2014, volume=107, pages=276–286, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2014.08.014
{{Cite journal, first1=Miklós, last1=Antal, first2=Jeroen C.J.M., last2=van den Bergh, journal= Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, title=Macroeconomics, financial crisis and the environment: Strategies for a sustainability transition, date=2013, volume=6, pages=47–66, doi=10.1016/j.eist.2013.01.002, hdl=10419/129023, hdl-access=free
''Jenseits des Wachstumszwangs – Globale Armut und Naturzerstörung solidarisch überwinden''attac Germany. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Robert U., last1=Ayres, author-link1=Robert Ayres (scientist), first2=Benjamin, last2=Warr, title=The economic growth engine: how energy and work drive material prosperity, date=2009, publisher=Edward Elgar, isbn=978-1-84844-595-6 {{cite journal, first1=John, last1=Barry, title=A Genealogy of Economic Growth as Ideology and Cold War Core State Imperative, date=2018, journal=New Political Economy, doi=10.1080/13563467.2018.1526268, volume=25, issue=1, pages=18–29, s2cid=159024755, url=https://pure.qub.ac.uk/en/publications/a-genealogy-of-economic-growth-as-ideology-and-cold-war-core-state-imperative(5e92b969-d9d2-4f83-80ca-9279fed59c68).html {{Cite book, first1=Guido, last1=Beltrani, title=Monetäre Aspekte des Wirtschaftswachstums, date=1999, publisher=Universität St. Gallen, oclc=722449216 {{Cite book, first1=Harald, last1=Bender, first2=Norbert, last2=Bernholt, first3=Klaus, last3=Simon, title=Das dienende Geld: die Befreiung der Wirtschaft vom Wachstumszwang, date=2014, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-86581-471-5 {{cite journal, first1=Matthew, last1=Berg, first2=Brian, last2=Hartley, first3=Oliver, last3=Richters, title=A Stock-Flow Consistent Input-Output Model with Applications to Energy Price Shocks, Interest Rates, and Heat Emissions, journal=
New Journal of Physics
''New Journal of Physics'' is an online-only, open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in all aspects of physics, as well as interdisciplinary topics where physics forms the central theme. The journal was established in 1998 ...
, volume=17, issue=1, date=2015, page=015011, doi=10.1088/1367-2630/17/1/015011, bibcode=2015NJPh...17a5011B , doi-access=free
{{Cite book, chapter=Warum müssen moderne Geldwirtschaften wachsen?, date=2010, editor-first1=Hans Peter, editor-last1=Aubauer, editor-first2=Hermann, editor-last2=Knoflacher, editor-first3=Klaus, editor-last3=Woltron, title=Kapitalismus gezähmt? Sozialer Wohlstand innerhalb der Naturgrenzen, publisher=Peter Lang, isbn=978-3-631-58919-9, pages=203–231, first1=Mathias, last1=Binswanger, first2=Guido , last2=Beltrani, first3=Robert, last3=Kölbl
{{Cite journal, first1=Mathias, last1=Binswanger, title=Is there a growth imperative in capitalist economies? a circular flow perspective, date=2009, volume=31, pages=707–727, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, doi=10.2753/PKE0160-3477310410, issue=4, s2cid=54702411
{{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=Vorwärts zur Mäßigung. Perspektiven einer nachhaltigen Wirtschaft, date=2009, publisher=Murmann, isbn=978-3-86774-072-2
{{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, author-link1=Hans Christoph Binswanger, title=Die Wachstumsspirale: Geld, Energie und Imagination in der Dynamik des Marktprozesses, date=2006, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-554-0
{{Cite book, first1=Mathias , last1=Binswanger , author-link1=Mathias Binswanger, title=Der Wachstumszwang: Warum die Volkswirtschaft immer weiterwachsen muss, selbst wenn wir genug haben, date=2019, publisher=Wiley-CVH, isbn=978-3-527-50975-1
{{Cite book, first1=Mathias, last1=Binswanger, title=Der Wachstumszwang: Warum die Volkswirtschaft immer weiterwachsen muss, selbst wenn wir genug haben, date=2019, publisher=Wiley-CVH, isbn=978-3-527-50975-1, pages=275
{{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, author-link1=Hans Christoph Binswanger, editor-last=Woynowski, editor-first=Boris, hdl=10419/69631, chapter=Wachstumszwang und Wachstumsdrang in der modernen Wirtschaft, title=Wirtschaft ohne Wachstum?! Notwendigkeit und Ansätze einer Wachstumswende, journal=Working Paper, date=2012, pages=46–53, issn=1431-8261, display-editors=etal
{{Cite book, first1=Olivier J., last1=Blanchard, author-link1=Olivier Blanchard, title=Macroeconomics, publisher=Pearson, at=chapter 12
{{Cite book, first1=Olivier J., last1=Blanchard , first2=Stanley , last2=Fischer, title=Lectures on Macroeconomics, date=1989, publisher=MIT Press, isbn=0-262-02283-4, pages=41–43, location=Cambridge
{{Cite journal, first1=Frederik Berend , last1=Blauwhof, title=Overcoming accumulation: Is a capitalist steady-state economy possible?, date=December 2012, pages=254–261, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2012.03.012, issue=84, journal= Ecological Economics, volume=84
{{cite book, first1=Emilio, last1=Carnevali, first2=Matteo, last2= Deleidi, first3=Riccardo, last3=Pariboni, first4=Marco, last4=Veronese Passarella, chapter=Stock-Flow Consistent Dynamic Models: Features, Limitations and Developments, editor-first1=Philip, editor-last1=Arestis, editor-first2=Malcolm, editor-last2=Sawyer, title=Frontiers of Heterodox Macroeconomics, publisher=Palgrave Macmillan, location=Cham, date=2019, pages=223–276, doi=10.1007/978-3-030-23929-9_6, isbn=978-3-030-23928-2, s2cid=202959298 .
{{Cite journal, first1=Oliver, last1=Richters, first2=Andreas, last2=Siemoneit, title=Consistency and Stability Analysis of Models of a Monetary Growth Imperative, journal= Ecological Economics, date=June 2017, volume=136, pages=114–125, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2017.01.017, hdl=10419/144750, hdl-access=free Preprint: VÖÖ Discussion Paper 1, February 2016, {{Hdl, 10419/144750.
{{Cite book, first1=Helmut, last1=Creutz, title=Das Geldsyndrom. Wege zu einer krisenfreien Marktwirtschaft, date=1994, publisher=Ullstein, isbn=978-3-548-35456-9
{{Cite journal , first1 = Christoph, last1=Deutschmann, author-link1=Christoph Deutschmann , title= Moderne Ökonomie ohne Wachstumszwang: ein Wunschtraum? , journal= WSI-Mitteilungen , volume= 67 , pages= 513–521 , date= 2014 , issue=7, doi=10.5771/0342-300X-2014-7-513, s2cid=188792556 , url= http://www.boeckler.de/wsimit_2014_07_deutschmann.pdf
"Konkrete Schritte für eine Gesellschaft und Impulse für eine gemeinsame gesellschaftliche Vision jenseits von Wachstumszwängen standen im Mittelpunkt der Degrowth-Konferenz 2014.Dokumentation: Degrowth 2014
Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung
The Rosa Luxemburg Foundation (german: Rosa-Luxemburg-Stiftung), named in recognition of Rosa Luxemburg, occasionally referred to as ''Rosa-Lux'', is a transnational alternative policy lobby group and educational institution, centered in Germ ...
.
Daniel Constein, Nina Treu: "The focus of this Fourth International Conference on Degrowth for Ecological Sustainability and Social Equity will be on concrete steps towards a society beyond the imperative of growth.Programme
of the {{ill, International Conference on Degrowth, de, Internationale Degrowth-Konferenz 2014, p. 3. www.degrowth.info. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Richard , last1=Douthwaite, author-link1=Richard Douthwaite, title=The ecology of money, date=2000, publisher=Green Books, isbn=978-1-8700-9881-6 Abschlussbericht der Enquete-Kommission Wachstum, Wohlstand, Lebensqualität
Deutscher
Bundestag
The Bundestag (, "Federal Diet") is the German federal parliament. It is the only federal representative body that is directly elected by the German people. It is comparable to the United States House of Representatives or the House of Common ...
, Drucksache 17/13300. p. 749: es müsse "die Frage beantwortet werden, ob ein Fortschritt, der innovativ und integrativ, sozial gerecht und ökologisch verträglich ist, ohne Wachstumszwang möglich ist."
{{Cite journal, first1=Joshua , last1=Farley, first2=Matthew , last2=Burke , first3=Gary, last3=Flomenhoft, first4=Brian, last4=Kelly, first5=D. Forrest, last5=Murray, first6=Stephen, last6=Posner, first7=Matthew, last7=Putnam, first8=Adam, last8=Scanlan, first9=Aaron, last9=Witham, title=Monetary and Fiscal Policies for a Finite Planet, date=June 2013, volume=5, pages=2802–2826, doi=10.3390/su5062802, issue=6, journal= Sustainability, doi-access=free
{{Cite journal, first1=Peter , last1=Ferguson, title=Post-growth policy instruments, volume=7, pages=405–421, doi=10.1504/IJGE.2013.058560, issue=4, journal= International Journal of Green Economics, year=2013
{{Cite book, first1=Peter , last1=Ferguson, title=Post-growth Politics, isbn=978-3-319-78797-8, publisher=Springer, date=2019, doi=10.1007/978-3-319-78799-2, chapter=The Growth Imperative, pages=76, location=Cham
{{Cite book, first1=Peter , last1=Ferguson, title=Post-growth Politics, isbn=978-3-319-78797-8, publisher=Springer, date=2019, doi=10.1007/978-3-319-78799-2, chapter=The Growth Imperative, pages=119, location=Cham
{{Cite book, first1=Peter , last1=Ferguson, title=Post-growth Politics, isbn=978-3-319-78797-8, publisher=Springer, date=2019, doi=10.1007/978-3-319-78799-2, chapter=The Growth Imperative, pages=75–100, location=Cham
{{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, author-link1=Hans Christoph Binswanger, first2=Paschen, last2=von Flotow, title=Geld & Wachstum. Zur Philosophie und Praxis des Geldes, date=1994, publisher=Weitbrecht, isbn=978-3-5227-1670-3, pages=8
{{Cite journal, first1=Giuseppe, last1=Fontana, first2=Malcolm, last2=Sawyer, title=Full Reserve Banking: More 'Cranks' Than 'Brave Heretics', date=September 2016, volume=40, pages=1333–1350, journal= Cambridge Journal of Economics, doi=10.1093/cje/bew016, issue=5, url=http://eprints.whiterose.ac.uk/103348/3/FontanaFull%20Reserve%20Banking.pdf
{{Cite journal, first1=John Bellamy, last1=Foster, author-link1=John Bellamy Foster, first2=Fred, last2=Magdoff, url=https://monthlyreview.org/2010/03/01/what-every-environmentalist-needs-to-know-about-capitalism/, title=What every environmentalist needs to know about capitalism, date=2010, volume=61, pages=1–30, issue=10, journal= Monthly Review
{{Cite book, first1=Jana , last1=Gebauer, first2=Steffen, last2=Lange, first3=Dirk, last3= Posse, chapter= Wirtschaftspolitik für Postwachstum auf Unternehmensebene. Drei Ansätze zur Gestaltung, date=2017, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-86581-823-2, pages=239–253, editor-first1=Frank, editor-last1=Adler, editor-first2=Ulrich , editor-last2 =Schachtschneider , title= Postwachstumspolitiken: Wege zur wachstumsunabhängigen Gesellschaft
{{Cite journal, first1=Zsolt, last1=Gilányi, title=Comment on Johnson's creating dimensional stock-flow inconsistency in Binswanger's model, date=2018, doi=10.1080/01603477.2018.1431791, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, volume=42, issue=2, pages=319–327, s2cid=158184441
{{Cite journal, title=Capitalism's growth imperative, date=2003, volume=27, pages=25–48, doi=10.1093/cje/27.1.25, issue=1, first1=Myron J. , last1=Gordon , author-link1=Myron J. Gordon , first2=Jeffrey S. , last2=Rosenthal, author-link2=Jeff Rosenthal, journal= Cambridge Journal of Economics
{{Cite journal, first1=Jürgen, last1=Grahl, first2=Reiner, last2=Kümmel, url=http://www.fwu.at/assets/userFiles/Wissenschaft_Umwelt/13_2009/2009_13_wachstum_5.pdf, title=Das Loch im Fass – Energiesklaven, Arbeitsplätze und die Milderung des Wachstumszwangs, date=2009, journal=Wissenschaft und Umwelt Interdisziplinär, pages=195–212
''Growth duty: statutory guidance''30 March 2017. Federal board of Alliance 90/The Greens
''Neue Zeiten. Neue Antworten.''
April 6, 2018. Accessed February 6, 2019. {{Cite book, first1=Fred, last1=Hirsch, author-link1=Fred Hirsch (professor), title=Social Limits to Growth, date=1976, publisher=Harvard University Press {{Cite book, first1=François, last1=Höpflinger, chapter=Alterssicherungssysteme: Doppelte Herausforderung von demografischer Alterung und Postwachstum, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=53–64, editor-first1=Irmi, editor-last1=Seidl, editor-first2=Angelika, editor-last2=Zahrnt, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft {{Cite journal, first1=Charles , last1=Hulten, title=Growth Accounting, date=2009, doi=10.3386/w15341, journal=NBER Working Paper, issue=w15341, doi-access=free {{Cite journal, first1=Tim, last1=Jackson, author-link1=Tim Jackson (economist), first2=Peter, last2=Victor, title=Does credit create a 'growth imperative'? A quasi-stationary economy with interest-bearing debt, journal= Ecological Economics, date=December 2015, volume=120, pages=32–48, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.09.009 Preprint
PASSAGE Working Paper 15/01
Guildford: University of Surrey. {{Cite journal, first1=Tim, last1=Jackson, author-link1=Tim Jackson (economist), first2=Peter, last2=Victor, title=Productivity and work in the 'green economy' – some theoretical reflections and empirical tests, journal= Environmental Innovation and Societal Transitions, date=2011, volume=1, pages=101–108, doi=10.1016/j.eist.2011.04.005, issue=1, s2cid=150636345 {{Cite journal, first1=A. Reeves, last1=Johnson, title=Response to "Comment on Johnson's creating dimensional stock-flow inconsistency in Binswanger's model", date=2018, doi=10.1080/01603477.2018.1458631, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, volume=42, issue=2, pages=328–334, s2cid=158990885 {{Cite book, first1=Charles I. , last1=Jones, title=Handbook of Economic Growth, chapter=Growth and Ideas, date=2005, publisher=Elsevier, isbn=978-0-444-52043-2, volume=2, pages=1063–1111, doi=10.1016/S1574-0684(05)01016-6, editor-first1=Philippe, editor-last1=Aghion, editor-first2=Steven N. , editor-last2=Durlauf {{Cite journal, first1=Mathias, last1=Binswanger, title=The growth imperative revisited: a rejoinder to Gilányi and Johnson, date=May 2015, volume=37, pages=648–660, doi=10.1080/01603477.2015.1050333, issue=4, journal= Journal of Post Keynesian Economics, s2cid=54606846 {{cite journal, first1=Giorgos , last1=Kallis, author-link1= Giorgos Kallis, title=Socialism without growth, journal= Capitalism Nature Socialism, volume=30 , issue=2, date=2019, pages=189–206, doi=10.1080/10455752.2017.1386695 , s2cid=158796873 {{Cite book, first1=Athanasios , last1=Karathanassis, title=Kapitalistische Naturverhältnisse. Ursachen von Naturzerstörungen – Begründungen einer Postwachstumsökonomie, date=2015, publisher=VSA-Verlag, isbn=978-3-89965-623-7 {{Cite book, first1=Margrit, last1=Kennedy, author-link1=Margrit Kennedy, title=Geld ohne Zinsen und Inflation. Ein Tauschmittel, das jedem dient, year=1991, publisher=Goldmann, isbn=978-3-442-12341-4, pages=26–7 {{Cite journal, first1=Reiner , last1=Kümmel, first2=Dietmar, last2=Lindenberger, title=How energy conversion drives economic growth far from the equilibrium of neoclassical economics, date=December 2014, journal=
New Journal of Physics
''New Journal of Physics'' is an online-only, open-access, peer-reviewed scientific journal covering research in all aspects of physics, as well as interdisciplinary topics where physics forms the central theme. The journal was established in 1998 ...
, volume=16, doi=10.1088/1367-2630/16/12/125008, issue=12, page=125008, bibcode=2014NJPh...16l5008K , doi-access=free
{{Cite book, first1=Reiner, last1=Kümmel, title=The Second Law of Economics: Energy, Entropy, and the Origins of Wealth, date=2011, publisher=Springer, isbn=978-1-4419-9365-6
{{Cite book, title=The Penguin dictionary of sociology, date=1984, publisher=A. Lane, isbn=978-0-7139-1380-4, pages=45, first1=Nicholas, last1=Abercrombie, first2=Stephen, last2=Hill, first3=Bryan S., last3=Turner, quote=compelled ..by situational circumstances, that is by the structure of society and not by individuals
{{Cite book, first1=Steffen, last1=Lange, title=Macroeconomics Without Growth: Sustainable Economies in Neoclassical, Keynesian and Marxian Theories, date=2018, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-7316-1298-8, pages=109–216
{{Cite journal, first1=Louison, last1=Cahen-Fourot, first2=Marc, last2=Lavoie, author-link2=Marc Lavoie, title=Ecological monetary economics: A post-Keynesian critique, journal= Ecological Economics, date=June 2016, volume=126, pages=163–168, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.03.007
{{cite journal , first1= Philip , last1= Lawn , author-link1=Philip Lawn, title= Is steady-state capitalism viable?: A review of the issues and an answer in the affirmative , journal= Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences
The ''Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences'' is an academic journal published by Wiley-Blackwell on behalf of the New York Academy of Sciences. It is one of the oldest science journals still being published, having been founded in 1823. The ...
, volume= 1219 , issue=1 , date= February 2011 , pages= 1–25 , doi= 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2011.05966.x, pmid= 21332490 , s2cid= 40089385
{{Cite book, first1=Bernard , last1=Lietaer, author-link1=Bernard Lietaer, first2=Christian, last2=Arnsperger, first3=Sally, last3=Goerner, first4=Stefan, last4=Brunnhuber, title=Money and Sustainability: The Missing Link, date=2012, publisher=Triarchy Press, isbn=978-1-908009-75-3
{{Cite book, first1=Reinhard, last1=Loske, title=Abschied vom Wachstumszwang. Konturen einer Politik der Mäßigung, year=2011, publisher=Basilisken Presse, isbn=978-3941365117, edition=2
{{cite book, first1= Karl , last1=Marx, author-link1 =Karl Marx , title= Das Kapital, Band 1 , publisher= Dietz , date= 1965 , pages= 618 , url= http://www.mlwerke.de/me/me23/me23_605.htm#S618
{{Cite book, first1= Karl , last1=Marx, author-link1 =Karl Marx , date=1906 , title= Capital: A Critique of Political Economy , publisher= Modern Library, pages=649
{{cite book, first1=Simon, last1=Mugier, date=2019, title=Wirtschaftswachstum und soziale Frage. Zur soziologischen Bedeutung der ökonomischen Theorie von Hans Christoph Binswanger, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-7316-1383-1
''Wohlstand ohne Wachstumszwang''basic programme of
Ecological Democratic Party
The Ecological Democratic Party (german: Ökologisch-Demokratische Partei, ÖDP) is a conservative and ecologist minor party in Germany. The ÖDP was founded in 1982.
The strongest level of voting support for the ÖDP is in Bavaria, where in ...
Germany 2016. Accessed February 6, 2019.
{{Cite book, first1=Werner, last1=Onken, title=Gerechtes Geld – gerechte Welt: Auswege aus Wachstumszwang und Schuldenkatastrophe: 1891–1991. 100 Jahre Gedanken zu einer natürlichen Wirtschaftsordnung, date=1992, publisher=Verlag für Sozialökonomie, isbn=978-3-87998-433-6
{{Cite journal, first1=Ilhan , last1=Ozturk, title=A literature survey on energy–growth nexus, date=January 2010, volume=38, pages=340–349, doi=10.1016/j.enpol.2009.09.024, issue=1, journal= Energy Policy
{{Cite book, first1=Niko, last1=Paech, author-link1=Niko Paech, title=Befreiung vom Überfluss. Auf dem Weg in die Postwachstumsökonomie, date=2012, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-86581-181-3
{{Cite journal, first1=Niko, last1=Paech, author-link1=Niko Paech, title=Wirtschaften ohne Wachstumszwang, date=2006, pages=30–33, doi=10.14512/oew.v21i3.460, volume=21, issue=3, journal=Ökologisches Wirtschaften
''Ökologisches Wirtschaften'' is an academic journal for socioeconomics and ecological economics.
The journal was introduced in 1986 by (IÖW) and (VÖW). Since 1996 it has been published four times a year with a focus on a specific topic by ...
, doi-access=free
{{Cite book, first1=Cosimo, last1=Perrotta, title=Consumption as an Investment, date=2004, publisher=Routledge, isbn=978-0-4153-0619-5
{{cite journal, first1=Eric, last1=Pineault, title=From Provocation to Challenge: Degrowth, Capitalism and the Prospect of "Socialism without Growth": A Commentary on Giorgios Kallis, journal= Capitalism Nature Socialism, volume=30, issue=2, date=2019, pages=251–266, doi=10.1080/10455752.2018.1457064, s2cid=150255333
{{Cite book, first1=Dirk, last1=Posse, hdl=10419/110257, title=Zukunftsfähige Unternehmen in einer Postwachstumsgesellschaft, date=2015, publisher= Vereinigung für Ökologische Ökonomie, isbn=978-3-9811006-2-4
{{Cite book, first1=Joachim, last1=Radkau, author-link1=Joachim Radkau, chapter=Wachstum oder Niedergang: ein Grundgesetz der Geschichte?, editor-first1=Irmi, editor-last1=Seidl, editor-first2=Angelika, editor-last2=Zahrnt, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=37–52
{{Cite book, first1=Raghuram, last1=Rajan, author-link1=Raghuram Rajan, chapter=Going Bust for Growth, title=Progress and Confusion: The State of Macroeconomic Policy, editor-first1=Olivier, editor-last1=Blanchard, editor-first2=Raghuram, editor-last2=Rajan, editor-first3=Kenneth S., editor-last3=Rogoff, editor-first4=Lawrence, editor-last4=Summers, publisher=MIT Press, pages=267–284
{{Cite journal, first1=André, last1=Reichel, title=Betriebswirtschaftliche Perspektiven. Das Ende des Wirtschaftswachstums, wie wir es kennen, date=2013, pages=15–18, doi=10.14512/oew.v28i1.1262, issue=1, journal=Ökologisches Wirtschaften
''Ökologisches Wirtschaften'' is an academic journal for socioeconomics and ecological economics.
The journal was introduced in 1986 by (IÖW) and (VÖW). Since 1996 it has been published four times a year with a focus on a specific topic by ...
, doi-access=free
{{Cite journal, first1=Oliver , last1=Richters, title=Review of Mathias Binswanger's ''Der Wachstumszwang'', journal=Ökologisches Wirtschaften
''Ökologisches Wirtschaften'' is an academic journal for socioeconomics and ecological economics.
The journal was introduced in 1986 by (IÖW) and (VÖW). Since 1996 it has been published four times a year with a focus on a specific topic by ...
, date=2019, pages=53–55, issue=3
{{cite journal , first1=Oliver , last1= Richters , first2= Andreas , last2= Siemoneit , title= Growth imperatives: Substantiating a contested concept , journal= Structural Change and Economic Dynamics
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such a ...
, volume = 51 , date=2019 , pages=126–137 , doi= 10.1016/j.strueco.2019.07.012, s2cid= 203243535 Preprint: Oldenburg Discussion Papers in Economics V-414-18, November 2018, {{HDL, 10419/184870.
{{cite book , first1= Oliver , last1= Richters , first2= Andreas , last2= Siemoneit , title= Marktwirtschaft reparieren: Entwurf einer freiheitlichen, gerechten und nachhaltigen Utopie , publisher= oekom , location= München , isbn= 978-3-96238-099-1 , date= 2019 , pages= 49–59, hdl=10419/213814
{{Cite book, first1=Oliver, last1=Richters, first2=Andreas, last2=Siemoneit, title=Marktwirtschaft reparieren: Entwurf einer freiheitlichen, gerechten und nachhaltigen Utopie, date=2019, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-96238-099-1, pages=96–116, hdl=10419/213814
{{Cite book, first1=Oliver, last1=Richters, first2=Andreas, last2=Siemoneit, title=Marktwirtschaft reparieren: Entwurf einer freiheitlichen, gerechten und nachhaltigen Utopie, date=2019, publisher=oekom, isbn=978-3-96238-099-1, pages=96–153, hdl=10419/213814
{{cite book , first1= Oliver, last1=Richters, first2= Andreas, last2=Siemoneit , chapter= Wachstumszwänge: Ressourcenverbrauch und Akkumulation als Wettbewerbsverzerrungen , editor-first1=Frank, editor-last1=Adler, editor-first2=Ulrich , editor-last2 =Schachtschneider , title= Postwachstumspolitiken: Wege zur wachstumsunabhängigen Gesellschaft , publisher= oekom, date= 2017 , isbn= 978-3-86581-823-2 , pages= 169–182 , hdl=10419/152267
{{Cite journal, first1=Manuel, last1=Rivera, title=Growth in parliament: Some notes on the persistence of a dogma, date=January 2018, volume=95, pages=1–10, doi=10.1016/j.futures.2017.09.002, journal=Futures, doi-access=free
{{Cite book, first1=Holger, last1=Rogall, title=Ökologische Ökonomie. Eine Einführung, date=2008, publisher=Springer VS, isbn=978-3-5311-6058-0, pages=131, doi=10.1007/978-3-531-91001-7, location=Wiesbaden
{{Cite book, first1=Shervin, last1=Rosen, chapter=Human Capital, title=The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, editor-first1=Matias, editor-last1=Vernengo, editor-first2=Esteban Perez, editor-last2=Caldentey, editor-first3=Barkley J. , editor-last3=Rosser Jr, date=2008, pages=1–15, publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK, isbn=978-1-349-95121-5, doi=10.1057/978-1-349-95121-5_743-2
{{Cite book, first1=Gerhard, last1=Scherhorn, author-link1=Gerhard Scherhorn, chapter=Der innere Zwang zum Wirtschaftswachstum, publisher=Campus, isbn=978-3-593-35461-3, pages=162ff, editor-first1=Bernd, editor-last1=Biervert, editor-first2=Martin, editor-last2=Held, title=Die Dynamik des Geldes: über den Zusammenhang von Geld, Wachstum und Natur, location=Frankfurt/Main, date=1996
{{Cite book, first1=Gerhard, last1=Scherhorn, author-link1=Gerhard Scherhorn, chapter=Unternehmen ohne Wachstumszwang: Zur Ökonomie der Gemeingüter, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=129–144, editor-first1=Irmi, editor-last1=Seidl, editor-first2=Angelika, editor-last2=Zahrnt, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft
{{Cite journal, first1=Matthias, last1=Schmelzer, title=The growth paradigm: History, hegemony, and the contested making of economic growthmanship, date=2015, volume=118, pages=262–271, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2015.07.029, journal= Ecological Economics
{{Cite book, first1=Matthias, last1=Schmelzer, title=The Hegemony of Growth, date=2016, publisher=Cambridge University Press, isbn=978-1-3164-5203-5
Ulrich Schulte''Ausrichtung der Grünen: Die Möchtegern-Liberalen''
'' die tageszeitung'', September 26, 2018. {{Cite book, first1=Joseph, last1=Schumpeter, author-link1=Joseph Schumpeter, title=
Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy
''Capitalism, Socialism, and Democracy'' is a book on economics, sociology, and history by Joseph Schumpeter, arguably his most famous, controversial, and important work. It's also one of the most famous, controversial, and important books on s ...
, date=1942, publisher=Harper & Brothers
{{Cite book, first1=Irmi, last1=Seidl, first2=Angelika, last2=Zahrnt, chapter=Argumente für einen Abschied vom Paradigma des Wirtschaftswachstums, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=24
{{Cite book, first1=Irmi, last1=Seidl, first2=Angelika, last2=Zahrnt, chapter=Staatsfinanzen und Wirtschaftswachstum, title=Postwachstumsgesellschaft: Konzepte für die Zukunft, date=2010, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=978-3-89518-811-4, pages=179–188
{{Cite journal, first1=Andreas, last1=Siemoneit, title=An offer you can't refuse – Enhancing personal productivity through 'efficiency consumption', date=2019, volume=59, doi=10.1016/j.techsoc.2019.101181, journal=Technology in Society, page=101181, hdl=10419/201502, s2cid=202269762 , hdl-access=free PreprintZOE Discussion Paper 3
January 2019, {{Hdl, 10419/201502.
Robert Solow
Robert Merton Solow, GCIH (; born August 23, 1924) is an American economist whose work on the theory of economic growth culminated in the exogenous growth model named after him. He is currently Emeritus Institute Professor of Economics at the ...
said in an interview: "There is nothing intrinsic in the system that says it cannot exist happily in a stationary state". Cited after: Steven Stoll: ''Fear of Fallowing: The specter of a no-growth world''. In: Harper’s Magazine
''Harper's Magazine'' is a monthly magazine of literature, politics, culture, finance, and the arts. Launched in New York City in June 1850, it is the oldest continuously published monthly magazine in the U.S. (''Scientific American'' is older, b ...
, March 2008, pp. 88–94steadystate.org
accessed February 27, 2019. See also Mathias Binswanger, ''Der Wachstumszwang'', 2019, p. 39. {{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=The Growth Spiral: Money, Energy, and Imagination in the Dynamics of the Market Process, date=2013, publisher=Springer, isbn=978-3-642-31881-8, pages=119, doi=10.1007/978-3-642-31881-8 {{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=The Growth Spiral: Money, Energy, and Imagination in the Dynamics of the Market Process, date=2013, publisher=Springer, isbn=978-3-642-31881-8, pages=131, doi=10.1007/978-3-642-31881-8 {{Cite journal, first1=Richard , last1=Smith, url=http://www.paecon.net/PAEReview/issue53/Smith53.pdf, title=Beyond Growth or Beyond Capitalism, volume=53, pages=28–42, journal=
Real-world economics review
''Real-World Economics Review'' is a peer-reviewed open access academic journal of heterodox economics published by the "Post-Autistic Economics Network" since 2000. Since 2011 it is associated with the World Economics Association. It was known fo ...
{{Cite journal, first1=David I. , last1=Stern, title=Energy-GDP Relationship, date=2015, publisher=Palgrave Macmillan UK, isbn=978-1-349-95121-5, journal=The New Palgrave Dictionary of Economics, pages=1–19, doi=10.1057/978-1-349-95121-5_3015-1
{{cite journal, first1=Beth, last1=Stratford, title=The Threat of Rent Extraction in a Resource-constrained Future, journal= Ecological Economics, volume=169, date=March 2020, page=106524, doi=10.1016/j.ecolecon.2019.106524, doi-access=free
{{Cite book, first1=Eckhard, last1=Stratmann-Mertens, author-link1=Eckhard Stratmann-Mertens, first2=Rudolf, last2=Hickel, first3=Jan, last3=Priewe, title=Wachstum: Abschied von einem Dogma: Kontroverse über eine ökologisch-soziale Wirtschaftspolitik, date=1991, publisher=S. Fischer, isbn=978-3-1003-1408-6
{{Cite book, first1=Sebastian, last1= Strunz, first2=Bartosz, last2=Bartkowski, first3=Harry, last3=Schindler, chapter=Is there a monetary growth imperative?, date=2017, publisher=Edward Elgar, isbn=978-1-7834-7356-4, pages=326–355, doi=10.4337/9781783473564.00024, title=Handbook on growth and sustainability, location=Cheltenham, hdl= 10419/108971, url= https://www.econstor.eu/bitstream/10419/108971/1/821132911.pdf, editor-first1=Peter A., editor-last1=Victor, editor-first2=Brett, editor-last2=Dolter Preprint: UFZ Discussion Papers 5/2015, {{Hdl, 10419/108971.
{{Cite journal, first1=Sebastian, last1= Strunz, first2=Bartosz, last2=Bartkowski, first3=Harry, last3=Schindler, title=Mythos monetärer Wachstumszwang. Am Gelde hängt doch alles?, journal=Ökologisches Wirtschaften
''Ökologisches Wirtschaften'' is an academic journal for socioeconomics and ecological economics.
The journal was introduced in 1986 by (IÖW) and (VÖW). Since 1996 it has been published four times a year with a focus on a specific topic by ...
, year= 2017, volume=32, pages=23–25, doi=10.14512/OEW320123, issue=1, doi-access=free
{{Cite journal, first1=Simon, last1=Sturn, first2=Till van, last2=Treeck, url=https://www.spw.de/data/sturn_treeck.pdf, title=Wachstumszwang durch Ungleichheit und Ungleichheit als Wachstumsbremse?, date=2010, volume=177, pages=15–21, journal=SPW – Zeitschrift für sozialistische Politik und Wirtschaft
{{Cite book, first1=Dieter, last1=Suhr, url=http://www.dieter-suhr.info/files/luxe/Downloads/Suhr_Befreiung.pdf, title=Befreiung der Marktwirtschaft vom Kapitalismus. Monetäre Studien zur sozialen, ökonomischen und ökologischen Vernunft, date=1986, publisher=Basis Verlag, isbn=3-88025-415-X, pages=47ff
{{Cite book, editor-first1=Larry E., editor-last1=Sullivan, title=The SAGE glossary of the social and behavioral sciences, date=2009, publisher=SAGE Publications, isbn=978-1-4129-5143-2, pages=81
{{Cite book, first1=Thorstein, last1=Veblen, author-link1=Thorstein Veblen, title=The theory of the leisure class. An economic study in the evolution of institutions, date=1899, publisher=The Macmillan Company
{{Cite journal, first1=Nuno, last1=Videira, first2=François, last2=Schneider, first3=Filka, last3=Sekulova, first4=Giorgos, last4=Kallis, author-link4=Giorgos Kallis, title=Improving understanding on degrowth pathways: an exploratory study using collaborative causal models, journal=Futures, date=2014, volume=55, pages=58–77, doi=10.1016/j.futures.2013.11.001, url=http://polired.upm.es/index.php/territoriosenformacion/article/view/3810
{{Cite book, first1=Hans Christoph, last1=Binswanger, title=Die Wachstumsspirale. Geld, Energie und Imagination in der Dynamik des Marktprozesses, date=2006, publisher=Metropolis, location=Marburg, isbn=3-89518-554-X, pages=331
{{Cite journal, url=https://archiv.wirtschaftsdienst.eu/jahr/2011/8/geldordnung-eine-ordnungspolitische-analyse, first1=Johann, last1=Walter, title=Geldordnung – eine ordnungspolitische Analyse, date=2011, pages=543–549, doi=10.1007/s10273-011-1260-4, issue=8, journal=Wirtschaftsdienst
''Wirtschaftsdienst – Zeitschrift für Wirtschaftspolitik'' ( en, Economics Review – Journal of Economic Policy) is a peer-reviewed academic journal covering economic and social policy issues in Germany or affecting Germany. It also publishes ...
, volume=91, hdl=10419/88820, s2cid=154298933, hdl-access=free
WissenschaftlerInnen fordern Abkehr vom Wachstumszwangwachstumsimwandel.at, Bundesministerium für Nachhaltigkeit und Tourismus, September 20, 2018. {{Cite book, first1=Ferdinand, last1=Wenzlaff, first2=Christian, last2=Kimmich, first3=Oliver, last3=Richters, hdl=10419/103454, title=Theoretische Zugänge eines Wachstumszwangs in der Geldwirtschaft, date=2014, publisher=Zentrum für Ökonomische und Soziologische Studien, issue=45 Capitalism Sustainability Economic growth