|
Freiwirtschaft
(German for "free economy") is an economic idea founded by Silvio Gesell in 1916. He called it ' (natural economic order). In 1932, a group of Swiss businessmen used his ideas to found the WIR Bank (WIR). Structure Freiwirtschaft consists of three central aspects, usually summed up as the Three Fs: * ' (free money) ** All money is issued for a ''limited'' period by ''constant'' value (neither inflation, nor deflation). ** Long-term saving requires investment in bonds or stocks. * ' (free land) ** All land is commonly owned or else the property of public institutions and can only be rented from the community or from government, respectively, not purchased (''see also Georgism''). * ' (free trade) History The basic economic ideas of Freiwirtschaft were published in 1890 by the Hungarian-Austrian economist Theodor Hertzka in his novel ''Freiland - ein soziales Zukunftsbild'' (''Freeland - A Social Anticipation''). Flaws of the monetary system Freiwirtschaft claims that curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freiwirtschaft
(German for "free economy") is an economic idea founded by Silvio Gesell in 1916. He called it ' (natural economic order). In 1932, a group of Swiss businessmen used his ideas to found the WIR Bank (WIR). Structure Freiwirtschaft consists of three central aspects, usually summed up as the Three Fs: * ' (free money) ** All money is issued for a ''limited'' period by ''constant'' value (neither inflation, nor deflation). ** Long-term saving requires investment in bonds or stocks. * ' (free land) ** All land is commonly owned or else the property of public institutions and can only be rented from the community or from government, respectively, not purchased (''see also Georgism''). * ' (free trade) History The basic economic ideas of Freiwirtschaft were published in 1890 by the Hungarian-Austrian economist Theodor Hertzka in his novel ''Freiland - ein soziales Zukunftsbild'' (''Freeland - A Social Anticipation''). Flaws of the monetary system Freiwirtschaft claims that curre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silvio Gesell
Johann Silvio Gesell (; 17 March 1862 – 11 March 1930) was a German-Argentine economist, merchant, and the founder of Freiwirtschaft, an economic model for market socialism. In 1900 he founded the magazine ''Geld-und Bodenreform'' (''Monetary and Land Reform''), but it soon closed for financial reasons. During one of his stays in Argentina, where he lived in a vegetarian commune, Gesell started the magazine ''Der Physiokrat'' together with Georg Blumenthal. In 1914, it closed due to censorship. The Bavarian Soviet Republic, in which he participated, had a violent end and Gesell was detained for several months on a charge of treason, but was acquitted by a Munich court after a speech he gave in his own defense. Life Silvio Gesell's mother was Walloon and his father was German, originally from Aachen, who worked as a clerk in the then-Prussian district of Malmedy, now part of Belgium. Silvio was the seventh of nine children. After visiting the public Bürgerschule in Sankt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Freigeld
As part of the theory of Freiwirtschaft, Freigeld ('free money', ) is a monetary (or exchange) unit proposed by Silvio Gesell. Properties Freigeld has several special properties: * It is maintained by a monetary authority to be ''spending-power stable'' (no inflation or deflation) by means of printing more money or withdrawing money from circulation. * It is ''cash flow safe'' (a scheme is put in place to ensure that the money is returned into the cash flow – for example, by demurrage – requiring stamps to be purchased and periodically attached to the money to keep it valid). * It is convertible into other currencies. * It is localized to a certain area (it is a local currency). The name results from the idea that there is no incentive to store or hoard Freigeld as it will automatically lose its value after some time. It is claimed that as a result, interest rates could decrease to zero. Theory According to Gesell, all human-produced goods are subject to expensive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Theodor Hertzka
Theodor Hertzka, or Hertzka Tivadar (July 13, 1845, Budapest – October 22, 1924, Wiesbaden) was a Jewish-Hungarian people, Hungarian-Austrians, Austrian economist and journalist. Life He studied at the universities of Vienna and Budapest, and in 1872 became a member of the editorial staff of the ''Neue Freie Presse'' of Vienna. In 1879 he founded the newspaper ''Wiener Allgemeine Zeitung'', which he edited until 1886. He was a friend of Johannes Brahms. Hertzka has been called the "Austrian Edward Bellamy, Bellamy", because his novel ''Freiland, ein soziales Zukunftsbild'' London: Chatto & Windus, 1891. had a similar theme to that of Edward Bellamy's novel ''Looking Backward''. Though Hertzka was not a Zionist and his utopian vision was directed at human beings in genera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Georgism
Georgism, also called in modern times Geoism, and known historically as the single tax movement, is an economic ideology holding that, although people should own the value they produce themselves, the economic rent derived from land—including from all natural resources, the commons, and urban locations—should belong equally to all members of society. Developed from the writings of American economist and social reformer Henry George, the Georgist paradigm seeks solutions to social and ecological problems, based on principles of land rights and public finance which attempt to integrate economic efficiency with social justice. Georgism is concerned with the distribution of economic rent caused by land ownership, natural monopolies, pollution rights, and control of the commons, including title of ownership for natural resources and other contrived privileges (e.g. intellectual property). Any natural resource which is inherently limited in supply can generate economic rent, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WIR Bank
The WIR Bank, formerly the Swiss Economic Circle (German: ''Wirtschaftsring-Genossenschaft''), or WIR, is an independent complementary currency system in Switzerland that serves businesses in hospitality, construction, manufacturing, retail and professional services. WIR issues and manages a private currency, called the WIR franc, which is used in combination with the Swiss franc to generate dual-currency transactions. System The WIR franc is an electronic currency reflected in clients' trade accounts and so there is no paper money. The intentions of starting were in increased sales, cash flow and profits for a qualified participant. WIR created a credit system which issues credit, in WIR francs, to its members. The credit lines are secured by members pledging assets which ensures that the currency is asset-backed. When two members enter into a transaction with both Swiss francs and WIR francs it reduces the amount of cash needed by the buyer; the seller does not discount it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Schools Of Economic Thought
In the history of economic thought, a school of economic thought is a group of economics, economic thinkers who share or shared a common perspective on the way economy, economies work. While economists do not always fit into particular schools, particularly in modern times, classifying economists into schools of thought is common. Economic thought may be roughly divided into three phases: premodern (Greco-Roman, History of India, Indian, Persian Empire, Persian, Caliphate, Islamic, and Imperial era of Chinese history, Imperial Chinese), early modern (mercantilist, physiocrats) and modern (beginning with Adam Smith and classical economics in the late 18th century, and Karl Marx and Friedrich Engels, Friedrich Engels' Marxian economics in the mid 19th century). Systematic economic theory has been developed mainly since the beginning of what is termed the modern era. Currently, the great majority of economists follow an approach referred to as mainstream economics (sometimes called 'o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Local Currencies
In economics, a local currency is a currency that can be spent in a particular geographical locality at participating organisations. A regional currency is a form of local currency encompassing a larger geographical area, while a community currency might be local or be used for exchange within an online community. A local currency acts as a complementary currency to a national currency, rather than replacing it, and aims to encourage spending within a local community, especially with locally owned businesses. Such currencies may not be backed by a national government nor be legal tender. About 300 complementary currencies, including local currencies, are listed in the Complementary Currency Resource Center worldwide database. Terminology Some definitions: * Complementary currency - is used as a complement to a national currency, as a medium of exchange, which is usually not legal tender. * Community currency - a complementary currency used by a group with a common bond, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Ideologies
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the production, use, and management of scarce resources'. A given economy is a set of processes that involves its culture, values, education, technological evolution, history, social organization, political structure, legal systems, and natural resources as main factors. These factors give context, content, and set the conditions and parameters in which an economy functions. In other words, the economic domain is a social domain of interrelated human practices and transactions that does not stand alone. Economic agents can be individuals, businesses, organizations, or governments. Economic transactions occur when two groups or parties agree to the value or price of the transacted good or service, commonly expressed in a certain currency. Howev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
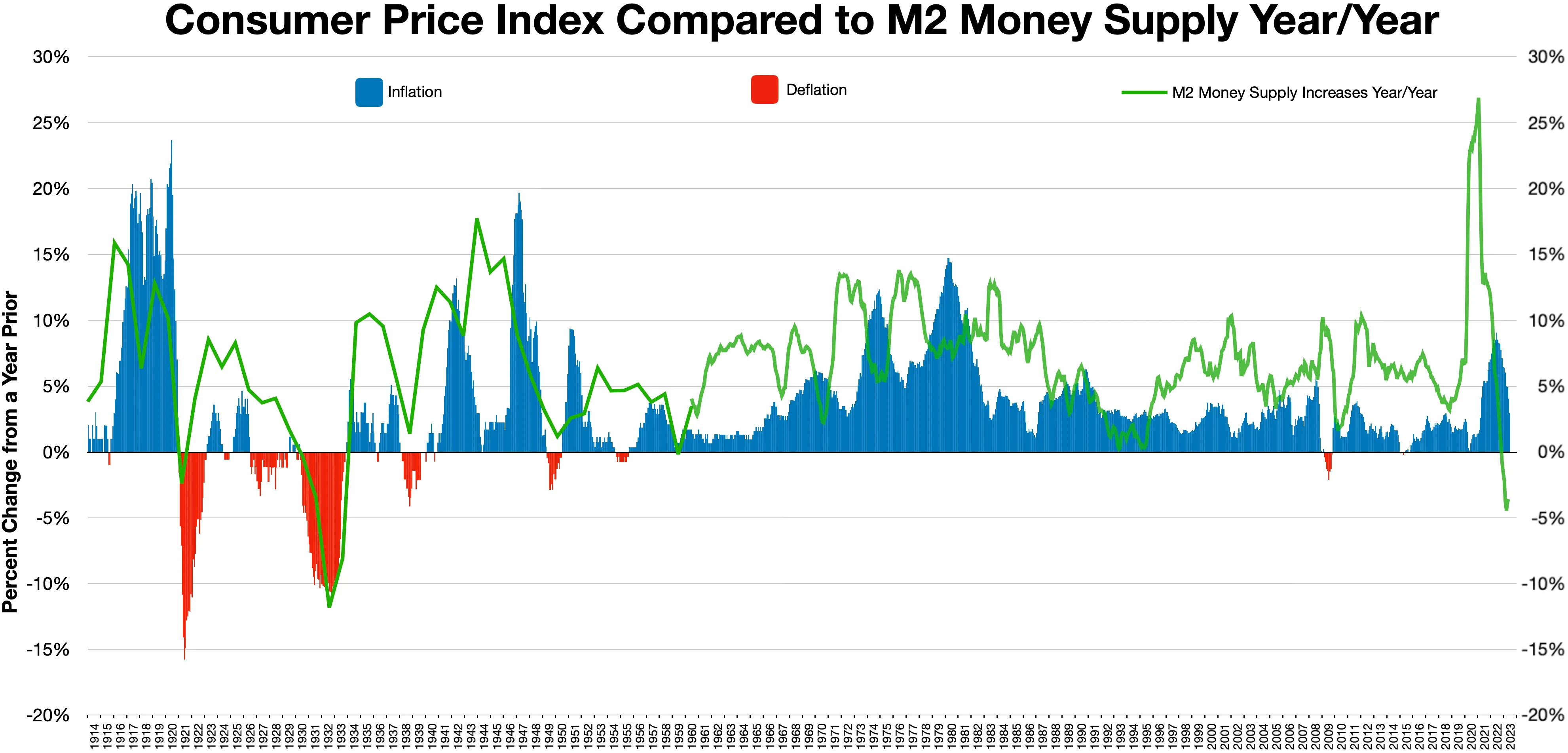
Deflation (economics)
In economics, deflation is a decrease in the general price level of goods and services. Deflation occurs when the inflation rate falls below 0% (a negative inflation rate). Inflation reduces the value of currency over time, but sudden deflation increases it. This allows more goods and services to be bought than before with the same amount of currency. Deflation is distinct from disinflation, a slow-down in the inflation rate, i.e. when inflation declines to a lower rate but is still positive. Economists generally believe that a sudden deflationary shock is a problem in a modern economy because it increases the real value of debt, especially if the deflation is unexpected. Deflation may also aggravate recessions and lead to a deflationary spiral. Some economists argue that prolonged deflationary periods are related to the underlying of technological progress in an economy, because as productivity increases ( TFP), the cost of goods decreases. Deflation usually happens when supp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflation (economics)
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduction in the purchasing power of money. The opposite of inflation is deflation, a sustained decrease in the general price level of goods and services. The common measure of inflation is the inflation rate, the annualized percentage change in a general price index. As prices do not all increase at the same rate, the consumer price index (CPI) is often used for this purpose. The employment cost index is also used for wages in the United States. Most economists agree that high levels of inflation as well as hyperinflation—which have severely disruptive effects on the real economy—are caused by persistent excessive growth in the money supply. Views on low to moderate rates of inflation are more varied. Low or moderate inflation may be attri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Feedback
Feedback occurs when outputs of a system are routed back as inputs as part of a chain of cause-and-effect that forms a circuit or loop. The system can then be said to ''feed back'' into itself. The notion of cause-and-effect has to be handled carefully when applied to feedback systems: History Self-regulating mechanisms have existed since antiquity, and the idea of feedback had started to enter economic theory in Britain by the 18th century, but it was not at that time recognized as a universal abstraction and so did not have a name. The first ever known artificial feedback device was a float valve, for maintaining water at a constant level, invented in 270 BC in Alexandria, Egypt. This device illustrated the principle of feedback: a low water level opens the valve, the rising water then provides feedback into the system, closing the valve when the required level is reached. This then reoccurs in a circular fashion as the water level fluctuates. Centrifugal governors were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
_per_capita_in_2020.png)