Gauḍa (city) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Gauḍa (also known as Gaur, Gour, Lakhnauti, and Jannatabad) is a historic city of
 The
The
 Gauda was widely known as Gaur during the Bengal Sultanate. The founder of the sultanate, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, was Delhi's governor in
Gauda was widely known as Gaur during the Bengal Sultanate. The founder of the sultanate, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, was Delhi's governor in
Oriental Scenery Fig 4.jpg, Ruins at the ancient city of Gour, 1795
Darashbari Mosque PRG 8155.jpg, Darasbari Mosque
Chika alias Chamkan Mosque at Gaur in Malda District 12.jpg, Chamkan Mosque
Chapai KhaniaDighiMosque 03Jun16 MG 4940.jpg, Khania Dighi Mosque
Chapai DhaniChakMosque 03Jun16 MG 4958.jpg, Dhani Chowk Mosque
Tanti Para Mosque at Gaur in Malda District 09.jpg, Tantipara Mosque
Chapai KhaniaDighiMosque 03Jun16 MG 4937.jpg,
Lucochuri Darwaja.JPG, Hide and Seek Doorway
Rohanpur Octagonal Tomb 04.jpg, Rohanpur Octagonal Tomb
DG 85 - 09 SAINT SHEKH NIAMOT ULLAH MOSQUE 15 CENTURY CHANPAI NAWAB GONJ IMG 3196.jpg, Mughal viceregal lodge
DG 87 - 09 MAJAR OF SAINT SHAH NIAMOT ULLAH 1664 CHANPAI NAWAB GONJ IMG 2595.jpg, Mughal Sufi shrine

 The city in its prime measured . from north to south, with a breadth of . With suburbs it covered an area of , and in the 16th century the Portuguese historian Faria y Sousa described it as containing 1,200,000 inhabitants. The ramparts of this walled city (which was surrounded by extensive suburbs) still exist; they were works of vast labour, and were on the average about high, and 180 to thick at the base. The facing of masonry and the buildings with which they were covered have now disappeared, and the embankments themselves are overgrown with dense jungle. The western side of the city was washed by the Ganges, and within the space enclosed by these embankments and the river stood the city of Gauḍa proper, with the fort containing the palace in its south-west corner. Radiating north, south and east from the city, other embankments are to be traced running through the suburbs and extending in certain directions for 30 or 40 m. Surrounding the palace is an inner embankment of similar construction to that which surrounds the city, and even more overgrown with jungle. A deep
The city in its prime measured . from north to south, with a breadth of . With suburbs it covered an area of , and in the 16th century the Portuguese historian Faria y Sousa described it as containing 1,200,000 inhabitants. The ramparts of this walled city (which was surrounded by extensive suburbs) still exist; they were works of vast labour, and were on the average about high, and 180 to thick at the base. The facing of masonry and the buildings with which they were covered have now disappeared, and the embankments themselves are overgrown with dense jungle. The western side of the city was washed by the Ganges, and within the space enclosed by these embankments and the river stood the city of Gauḍa proper, with the fort containing the palace in its south-west corner. Radiating north, south and east from the city, other embankments are to be traced running through the suburbs and extending in certain directions for 30 or 40 m. Surrounding the palace is an inner embankment of similar construction to that which surrounds the city, and even more overgrown with jungle. A deep
 According to ''
According to ''
 The
The
Gaur
at
Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, and one of the most prominent capitals of classical and medieval India
Medieval India refers to a long period of Post-classical history of the Indian subcontinent between the "ancient period" and "modern period". It is usually regarded as running approximately from the breakup of the Gupta Empire in the 6th cen ...
, being the capital city
A capital city or capital is the municipality holding primary status in a country, state, province, Department (country subdivision), department, or other subnational entity, usually as its seat of the government. A capital is typically a city ...
of Bengal
Bengal ( ; bn, বাংলা/বঙ্গ, translit=Bānglā/Bôngô, ) is a geopolitical, cultural and historical region in South Asia, specifically in the eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal, predom ...
under several kingdoms. The Gauḍa region Gauda may refer to:
* Gauda, a caste of Odisha
* Gauḍa (city), Bengal
* Gauḍa (region), Bengal
* Gauda Kingdom, a kingdom during the 5th to 7th century in Bengal (present-day Gauda city)
* Gauda (king), ruler of Numidia during 1st century BC
* ...
was also a province of several pan-Indian empires. During the seventh century, the Gauda Kingdom
The Gauḍa Kingdom (Gāuṛ Rājya) or Shashankas, was a classic kingdom during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal (modern-day West Bengal and Bangladesh) in 4th century CE or possibly ea ...
was founded by King Shashanka
Shashanka (IAST: Śaśāṃka) was the first independent king of a unified polity in the Bengal region, called the Gauda Kingdom and is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in the 7th century, some historians place his rule between circ ...
, whose reign corresponds with the beginning of the Bengali calendar
The Bengali Calendar or Bangla Calendar ( bn, বঙ্গাব্দ , , Baṅgābda), colloquially ( bn, বাংলা সন, Baṅgla Śon), is a solar calendar used in the Bengal region of the Indian subcontinent. A revised version of th ...
. Gauda gradually became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis. It was conquered by Bakhtiyar Khalji
Ikhtiyār al-Dīn Muḥammad Bakhtiyār Khaljī, (Pashto :اختيار الدين محمد بختيار غلزۍ, fa, اختیارالدین محمد بختیار خلجی, bn, ইখতিয়ারউদ্দীন মুহম্মদ � ...
, a lieutenant of the Ghurid
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from th ...
ruler Muhammad of Ghor
Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad ibn Sam ( fa, معز الدین محمد بن سام), also Mu'izz ad-Din Muhammad Ghori, also Ghūri ( fa, معز الدین محمد غوری) (1144 – March 15, 1206), commonly known as Muhammad of Ghor, also Gh ...
in 1203.
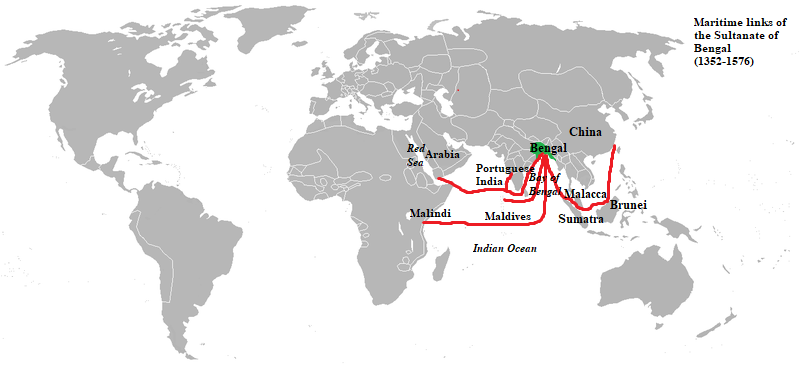
For a period of 112 years, between 1453 and 1565, Gauda was the capital of the Bengal Sultanate. In 1500, Gauda was the fifth-most populous city in the world, with a population of 200,000, as well as one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent. The Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
left detailed accounts of the city. The Sultans built a citadel, many mosques, a royal palace, canals and bridges. Buildings featured glazed tiles.
The city thrived until the collapse of the Bengal Sultanate in the 16th century, when the Mughal Empire
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
took control of the region. When the Mughal Emperor Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northern ...
invaded the region, he renamed the city Jannatabad ("heavenly city"). Most of the surviving structures in Gauda are from the period of the Bengal Sultanate. The city was sacked by Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
. An outbreak of the plague contributed to the city's downfall. The course of the Ganges
The Ganges ( ) (in India: Ganga ( ); in Bangladesh: Padma ( )). "The Ganges Basin, known in India as the Ganga and in Bangladesh as the Padma, is an international river to which India, Bangladesh, Nepal and China are the riparian states." is ...
was once located near the city, but a change in the river's course caused Gauda to lose its strategic importance. A new Mughal capital developed later in Dhaka
Dhaka ( or ; bn, ঢাকা, Ḍhākā, ), formerly known as Dacca, is the capital and largest city of Bangladesh, as well as the world's largest Bengali-speaking city. It is the eighth largest and sixth most densely populated city ...
.
Gauda was one of the most prominent capitals in the history of Bengal
The history of Bengal is intertwined with the history of the broader Indian subcontinent and the surrounding regions of South Asia and Southeast Asia. It includes modern-day Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal and Assam's Karimga ...
and the history of the Indian subcontinent
According to consensus in modern genetics, anatomically modern humans first arrived on the Indian subcontinent from Africa between 73,000 and 55,000 years ago. Quote: "Y-Chromosome and Mt-DNA data support the colonization of South Asia by m ...
, and a centre of stately medieval architecture. Gauda's ruins were depicted in the artwork of European painters during the 18th and 19th centuries. Colonial officials, such as Francis Buchanan-Hamilton
Francis Buchanan (15 February 1762 – 15 June 1829), later known as Francis Hamilton but often referred to as Francis Buchanan-Hamilton, was a Scottish physician who made significant contributions as a geographer, zoologist, and botanist whil ...
and William Francklin
William Francklin (1763–1839) was an English orientalist and army officer.
Education and military career
Francklin was the eldest son of Thomas Francklin, by his wife Miss Venables. He was admitted on the foundation at Westminster in 1777, whe ...
, left detailed surveys of the former Bengali capital.
Geography
Location
Gauḍa is located at . It straddles the Bangladesh-India border, with most of its ruins on the Indian side and a few structures on the Bangladeshi side, it was once one of the most populous cities in the world. The ruins of this former city now straddle theinternational border
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
and are divided between the Malda district
Malda district, also spelt Maldah or Maldaha (, , often ), is a district in West Bengal, India. It lies 347 km (215 miles) north of Kolkata, the capital of West Bengal. Mango, jute and silk are the most notable products of this district. T ...
of West Bengal
West Bengal (, Bengali: ''Poshchim Bongo'', , abbr. WB) is a state in the eastern portion of India. It is situated along the Bay of Bengal, along with a population of over 91 million inhabitants within an area of . West Bengal is the fourt ...
and Chapai Nawabganj District
Chapainawabganj (Bengali: চাঁপাইনবাবগঞ্জ) is located in the north-western part of Bangladesh. It is a part of the Rajshahi Division, and was formerly a sub-division of Malda district. The north and west part of Chap ...
of Rajshahi Division
Rajshahi Division ( bn, রাজশাহী বিভাগ) is one of the eight first-level administrative divisions of Bangladesh. It has an area of and a population at the 2011 Census of 18,484,858. Rajshahi Division consists of 8 district ...
. The Kotwali Gate, formerly part of the citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
In ...
, now marks the border checkpoint
A border checkpoint is a location on an international border where travelers or goods are inspected and allowed (or denied) passage through. Authorization often is required to enter a country through its borders. Access-controlled borders ofte ...
between the two countries.
History
Kingdom of Gauda
After the fall of theGupta Empire
The Gupta Empire was an ancient Indian empire which existed from the early 4th century CE to late 6th century CE. At its zenith, from approximately 319 to 467 CE, it covered much of the Indian subcontinent. This period is considered as the Gol ...
, western Bengal was ruled by the Gauda Kingdom
The Gauḍa Kingdom (Gāuṛ Rājya) or Shashankas, was a classic kingdom during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal (modern-day West Bengal and Bangladesh) in 4th century CE or possibly ea ...
and eastern Bengal by the Samatata
Samataṭa (Brahmi script: ''sa-ma-ta-ṭa'') was an ancient geopolitical division of Bengal in the eastern Indian subcontinent. The Greco-Roman account of ''Sounagoura'' is linked to the kingdom of Samatata. Its territory corresponded to much ...
Kingdom. Gauda was founded by Shashanka
Shashanka (IAST: Śaśāṃka) was the first independent king of a unified polity in the Bengal region, called the Gauda Kingdom and is a major figure in Bengali history. He reigned in the 7th century, some historians place his rule between circ ...
, one of the pioneering Bengali kings in history. Shashanka's reign falls approximately between 590 and 625. The origin of the Bengali calendar falls within the reign of Shashanka.
Pala Empire
 The
The Pala Empire
The Pāla Empire (r. 750-1161 CE) was an imperial power during the post-classical period in the Indian subcontinent, which originated in the region of Bengal. It is named after its ruling dynasty, whose rulers bore names ending with the suffi ...
was founded in the Gauda region during the rise of Gopala
Gopala (Bangla: গোপাল) (ruled c. 750s–770s CE) was the founder of the Pala dynasty of Bihar and Bengal regions of the Indian Subcontinent. The last morpheme of his name ''Pala'' means "protector" and was used as an ending for the name ...
as king with the approval of an assembly of chieftains. The Pala Emperors carried the title ''Lord of Gauda''. The empire ruled for four centuries and its territory included large parts of northern India. According to historian D. C. Sicar, the term ''Gauda'' is an appropriate name for the Pala Empire itself. The Pala period saw the development of the Bengali language
Bengali ( ), generally known by its endonym Bangla (, ), is an Indo-Aryan languages, Indo-Aryan language native to the Bengal region of South Asia. It is the official, national, and most widely spoken language of Bangladesh and the second m ...
, script
Script may refer to:
Writing systems
* Script, a distinctive writing system, based on a repertoire of specific elements or symbols, or that repertoire
* Script (styles of handwriting)
** Script typeface, a typeface with characteristics of handw ...
and other aspects of Bengali culture. Indeed, the term ''Gaudiya'' (of Gauda) became synonymous with Bengal and Bengalis
Bengalis (singular Bengali bn, বাঙ্গালী/বাঙালি ), also rendered as Bangalee or the Bengali people, are an Indo-Aryan peoples, Indo-Aryan ethnolinguistic group originating from and culturally affiliated with the ...
.
Sena kingdom
Gauda became known as Lakhnauti during theSena dynasty
The Sena dynasty was a Hindu dynasty during the early medieval period on the Indian subcontinent, that ruled from Bengal through the 11th and 12th centuries. The empire at its peak covered much of the north-eastern region of the Indian subcont ...
. The name was in honour of the Sena ruler Lakhsman Sena.
Sultanate period
Delhi Sultanate
On a campaign towards Tibet in 1206, Bakhtiyar left Shiran Khalji to govern Bengal as a substitute. Bakhtiyar would die after the failure of this expedition, officially leaving Shiran as the next governor of Lakhnauti who would shortly be succeeded byAli Mardan Khalji
Rukn ad-Dīn ʿAlī Mardān Khaljī ( bn, রোকনউদ্দীন আলী মর্দান খলজী, fa, ركن الدین علی مردان خلجی) was a 13th-century governor of Bengal, a member of the Khalji dynasty of Bengal ...
and Iwaz Khalji
Ḥusām ad-Dīn ʿIwaz bin Ḥusayn Khaljī ( bn, হুসামউদ্দীন ইওজ বিন হোসেন খলজী, fa, حسام الدین عوض بن حسین خلجی), later known by his regnal title as Ghiyāth ad-Dīn � ...
. The latter would declare independence from Delhi which would also lead to his death.
Independent Lakhnauti
In 1281,Nasiruddin Bughra Khan
Nasiruddin Bughra Khan ( bn, নাসিরউদ্দিন বুগরা খান, fa, ناصر الدین بغرا خان) was the Governor (1281–1287) and later an independent Sultan (1287–1291) of Bengal. He was the son of ...
, the Governor of Lakhnauti, declared independence from the Delhi Sultanate. He would be succeeded by his son, Rukunuddin Kaikaus who expanded the kingdom. During his rule, the Lakhnauti-based kingdom expanded into Satgaon
Saptagram ( Bengali: সপ্তগ্রাম; colloquially called ''Satgaon'') was a major port, the chief city and sometimes capital of southern Bengal, in ancient and medieval times, the location presently being in the Hooghly district in ...
in the south, Bihar
Bihar (; ) is a state in eastern India. It is the 2nd largest state by population in 2019, 12th largest by area of , and 14th largest by GDP in 2021. Bihar borders Uttar Pradesh to its west, Nepal to the north, the northern part of West Be ...
in the west, Devkot
Bangarh is an ancient city situated in Gangarampur, West Bengal, India. Bangarh was the ancient city which was the administrative centre of Kotivarsha Vishaya (territorial division), itself part of the wider administrative unit of Pundravardha ...
in the north. His successor was Shamsuddin Firuz Shah, who played pivotal roles in completing Kaikaus' work in Satgaon before proceeding to take over Mymensingh
Mymensingh ( bn, ময়মনসিংহ) is the capital of Mymensingh Division, Bangladesh. Located on the bank of Brahmaputra River, about north of the national capital Dhaka, it is a major financial center and educational hub of north ...
and Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
. In 1303, Firuz's nephew Sikandar Khan Ghazi
Sikandar Khān Ghāzī ( fa, , bn, সিকান্দার খান গাজী) was the first wazir of Srihat under the Lakhnauti Kingdom ruled by Shamsuddin Firuz Shah. Prior to this, Khan was one of the commanders of the Battles of ...
and commander-in-chief Syed Nasiruddin
Syed Shah Nasiruddin ( bn, শাহ সৈয়দ নাসিরুদ্দীন, ar, شاه سيد ناصر الدين) was a Sufi saint and military leader associated with the spread of Islam in Bengal in the 14th century. As the commande ...
teamed up with Shah Jalal
Jalāl Mujarrad Kunyāʾī (), popularly known as Shah Jalal, was a celebrated Sufi figure of Bengal. His name is often associated with the Conquest of Sylhet and the spread of Islam into the region, part of a long history of interactions betw ...
and his forces in the Conquest of Sylhet
The Conquest of Sylhet ( bn, শ্রীহট্টের বিজয়, Srīhôtter Bijôy, Conquest of Srihatta) predominantly refers to an Islamic conquest of Srihatta (present-day Sylhet, Bangladesh) led by Sikandar Khan Ghazi, the mili ...
against the Gour Kingdom
The Kingdom of Gour was one of the greater of the many petty kingdoms of the medieval Sylhet region. According to legend, it was founded by Gurak, off-shooting from Kamarupa's Jaintia Kingdom in 630. Much of its early history is considered leg ...
. Sylhet was successfully incorporated into Firuz's Lakhnauti kingdom. His successor, Ghiyasuddin Bahadur Shah would lose independence to the Delhi Sultanate once again.
Bengal Sultanate

 Gauda was widely known as Gaur during the Bengal Sultanate. The founder of the sultanate, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, was Delhi's governor in
Gauda was widely known as Gaur during the Bengal Sultanate. The founder of the sultanate, Shamsuddin Ilyas Shah, was Delhi's governor in Satgaon
Saptagram ( Bengali: সপ্তগ্রাম; colloquially called ''Satgaon'') was a major port, the chief city and sometimes capital of southern Bengal, in ancient and medieval times, the location presently being in the Hooghly district in ...
. Ilyas Shah rebelled and overthrew Gaur's governor Alauddin Ali Shah
Alī Mubārak ( fa, علی مبارک), better known by his regnal title `Alā ad-Dīn `Alī Shāh ( bn, আলাউদ্দীন আলী শাহ, fa, علاء الدین علی شاه; r. 1338–1342) was an independent Sultan of Lak ...
in 1342. Ilyas Shah united the Bengal region into a separate independent state from Delhi in 1352. Pandua became the first capital of the sultanate. In 1450, Sultan Mahmud Shah of Bengal
Nāṣiruddīn Maḥmūd Shāh ( bn, নাসিরউদ্দীন মাহমুদ শাহ, fa, ; ) was the first Sultan of Bengal belonging to the restored Ilyas Shahi dynasty. Formerly a farmer, he was selected as the next ruler of ...
announced the transfer of Bengal's capital from Pandua to Gaur. The transfer was completed by 1453. Gaur served as the Bengali sultanate's capital for over one hundred years until 1565.
Gaur was one of the most densely populated cities in the Indian subcontinent, with a population rivalling that of Fatehpur Sikri
Fatehpur Sikri () is a town in the Agra District of Uttar Pradesh, India. Situated 35.7 kilometres from the district headquarters of Agra, Fatehpur Sikri itself was founded as the capital of Mughal Empire in 1571 by Emperor Akbar, serving this ...
. The city had a citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
In ...
, a royal palace and durbar
Durbar can refer to:
* Conference of Rulers, a council of Malay monarchs
* Durbar festival, a yearly festival in several towns of Nigeria
* Durbar floor plate, a hot-rolled structural steel that has been designed to give excellent slip resistance ...
, many mosques, residences for aristocrats and merchants, and bazaars. Portuguese
Portuguese may refer to:
* anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Portugal
** Portuguese cuisine, traditional foods
** Portuguese language, a Romance language
*** Portuguese dialects, variants of the Portuguese language
** Portu ...
travellers left detailed and extensive accounts of Gaur. The Portuguese compared the affluence of the city with Lisbon. The royal palace was divided into three compartments. A high wall enclosed the palace. A moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
surrounded the palace on three sides and was connected to the Ganges, which guarded the western side of the citadel. According to a contemporary Vaishnava poet, Sultan Alauddin Hussain Shah
Ala-ud-din Husain Shah ( bn, আলাউদ্দিন হোসেন শাহ (1494–1519)Majumdar, R.C. (ed.) (2006). ''The Delhi Sultanate'', Mumbai: Bharatiya Vidya Bhavan, pp.215-20 was an independent late medieval Sultan of Bengal, who ...
once saw a procession led by Sri Chaitanya on the opposite bank of the river. The first compartment in the north included the durbar. An inscription of Sultan Rukunuddin Barbak Shah
Ruknuddīn Bārbak Shāh ( bn, রোকনউদ্দীন বারবক শাহ, fa, ; r. 1459–1474) was the son and successor of Sultan Nasiruddin Mahmud Shah. Initially appointed as the governor of Satgaon during the reign of his fa ...
mentions a fountain
A fountain, from the Latin "fons" (genitive "fontis"), meaning source or spring, is a decorative reservoir used for discharging water. It is also a structure that jets water into the air for a decorative or dramatic effect.
Fountains were ori ...
and water channel located halfway from the Dakhil Darwaza gate. The gate still stands today. According to the Portuguese and medieval Bengali poet Krittibas Ojha
Mahakavi Krittibas Ojha (; 1381–1461) was a medieval Bengali poet. His major contribution to Bengali literature and culture was Indian epic '' Rāmāyaṇa'' in Bengali. His work, the ''Śrīrām Pā̃cālī'', is popularly known as the ''Krit ...
, the road from the Dakhil Darwaza to the durbar had nine well-guarded gates, of which two can still be identified today. The second compartment was the living quarter of the Sultan which was adorned with glazed tiles of various colours. The third compartment was the harem
Harem (Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A hare ...
. Many artefacts have been recovered from the palace grounds, including enamelled bricks and Chinese porcelain
Chinese ceramics show a continuous development since pre-dynastic times and are one of the most significant forms of Chinese art and ceramics globally. The first pottery was made during the Palaeolithic era. Chinese ceramics range from constru ...
. In 1521, a Portuguese visitor saw Sultan Nusrat Shah
Nāsir ad-Dīn Naṣrat Shāh ( bn, নাসিরউদ্দীন নুসরত শাহ, fa, ناصر الدین نصرت شاه; r. 1519–1533), also known as Nusrat Shah, was the second Sultan of Bengal belonging to the Hussain Shahi ...
enjoying polo being played on the plains below the citadel. Gaur was the center of regional politics. The deposed Arakanese king Min Saw Mon
Narameikhla Min Saw Mon ( Arakanese:နရမိတ်လှ မင်းစောမွန်; , Arakanese transliteration: Meng Sao Mwan, Arakanese pronunciation: ; also known as Suleiman Shah; 1380–1433) was the last king of Launggyet Dynas ...
was granted asylum in Gaur. The Sultan of Bengal dispatched a military expedition from Gaur to achieve the Reconquest of Arakan
The restoration of Min Saw Mon was a military campaign led by the Bengal Sultanate to help Min Saw Mon regain control of his Launggyet Dynasty. The campaign was successful. Min Saw Mon was restored to the Launggyet throne, and northern Arakan becam ...
.
The Portuguese historian Castenhada de Lopez described the houses of Gaur. Most buildings were one-storeyed with ornamental floor tiles, courtyard
A courtyard or court is a circumscribed area, often surrounded by a building or complex, that is open to the sky.
Courtyards are common elements in both Western and Eastern building patterns and have been used by both ancient and contemporary ...
s and gardens. There were canals and bridges. Bengal attracted many Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
n merchants during the Sultanate period and Gaur was a centre of the trade like other erstwhile Bengali cities, including Pandua, Chittagong
Chittagong ( /ˈtʃɪt əˌɡɒŋ/ ''chit-uh-gong''; ctg, চিটাং; bn, চিটাগং), officially Chattogram ( bn, চট্টগ্রাম), is the second-largest city in Bangladesh after Dhaka and third largest city in B ...
, Sonargaon
Sonargaon ( bn, সোনারগাঁও; pronounced as ''Show-naar-gaa''; lit. ''Golden Hamlet'') is a historic city in central Bangladesh. It corresponds to the Sonargaon Upazila of Narayanganj District in Dhaka Division.
Sonargaon is on ...
and Satgaon
Saptagram ( Bengali: সপ্তগ্রাম; colloquially called ''Satgaon'') was a major port, the chief city and sometimes capital of southern Bengal, in ancient and medieval times, the location presently being in the Hooghly district in ...
. Bengal also attracted immigrants from North India, the Middle East, and Central Asia.
In the 16th-century, Gaur was occupied by the Mughal emperor Humayun
Nasir-ud-Din Muhammad ( fa, ) (; 6 March 1508 – 27 January 1556), better known by his regnal name, Humāyūn; (), was the second emperor of the Mughal Empire, who ruled over territory in what is now Eastern Afghanistan, Pakistan, Northern ...
who sought to name it as Jannatabad (heavenly city). The city was looted and plundered during Sher Shah Suri
Sher Shah Suri ( ps, شیرشاه سوری)
(1472, or 1486 – 22 May 1545), born Farīd Khān ( ps, فرید خان)
, was the founder of the Sur Empire in India, with its capital in Sasaram in modern-day Bihar. He standardized the silver coin ...
's invasion. After 1565, Sultan Sulaiman Khan Karrani shifted the capital to Tandah. In 1575, Gaur was conquered by a Mughal contingent led by Munim Khan
Munʿim Khān ( fa, ) was a Mughal general under both emperors Humayun and Akbar. He was titled ''Khān-i-Khānān'' ('Khan of Khans') when Emperor Akbar appointed him as Prime Minister of the Mughal Empire in 1560. In 1564, he became the Su ...
. The Bengal Sultanate ended during the Battle of Rajmahal
The Battle of Rajmahal ( bn, রাজমহলের জঙ্গ) was a battle that took place between the Mughal Empire and the Karrani Dynasty that ruled the Sultanate of Bengal in the 16th century. The battle resulted in a decisive victory f ...
in 1576.
Arabesque
The arabesque is a form of artistic decoration consisting of "surface decorations based on rhythmic linear patterns of scrolling and interlacing foliage, tendrils" or plain lines, often combined with other elements. Another definition is "Foli ...
and terracotta
Terracotta, terra cotta, or terra-cotta (; ; ), in its material sense as an earthenware substrate, is a clay-based ceramic glaze, unglazed or glazed ceramic where the pottery firing, fired body is porous.
In applied art, craft, construction, a ...
Beautiful view of Gunmant Mosque.jpg, Gunmant Mosque
Chamkati Masjid 05.jpg, Chamkati Mosque
Tomb of Fateh Khan.JPG, ''Do-chala
The architecture of Bengal, which comprises the modern country of Bangladesh and the Indian states of West Bengal, Tripura and Assam's Barak Valley, has a long and rich history, blending indigenous elements from the Indian subcontinent, with influ ...
'' tomb
Gumti Gate at Gaur in Malda District 03.jpg, Fading enamelled bricks on Gumti Gate
Chapai ChotoSonaMashjidShomadhi MG 5051.jpg, Gravestones resembling the Tomb of Cyrus
The Tomb of Cyrus ( – ''Ârâmgâh ye Kuroš Bozorg'') is the final resting place of Cyrus the Great, the founder of the ancient Achaemenid Empire. The mausoleum is located in Pasargadae, an archaeological site in the Fars Province of Iran.
...
Baisgazi Wall 03.jpg, Baisgazi Wall (city wall)
Mughal period
The Mughals built several structures in Gaur. The two-storeyed Mughal Tahakhana complex was a resting place for viceroys. The ''tahkhana'' in Persian means a building with a cool environment. The name indicates that the complex had an indoor ventilation system to moderate humid temperatures. The complex was also used as a Sufikhanqah
A khanqah ( fa, خانقاه) or khangah ( fa, خانگاه; also transliterated as ''khankah'', ''khaneqa'', ''khanegah'' or ''khaneqah''; also Arabized ''hanegah'', ''hanikah'', ''hanekah'', ''khankan''), also known as a ribat (), is a buildin ...
. The Lukochori Darwaza (hide and seek gate) was erected on the road that led to the complex. The construction of these structures can be traced to the reign of viceroy Shah Shuja. An outbreak of the plague and a change in the course of the Ganges caused the city to be abandoned. Since then the area has been a heap of ruins in the wilderness
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
and almost overgrown with jungle.
Historical measurements and statistics
moat
A moat is a deep, broad ditch, either dry or filled with water, that is dug and surrounds a castle, fortification, building or town, historically to provide it with a preliminary line of defence. In some places moats evolved into more extensive ...
protects it on the outside. To the north of the outer embankment lies the Sagar Dighi, a great reservoir, 1600 yd. by 800 yd., dating from 1126.
Fergusson in his ''History of Eastern Architecture'' thus describes the general architectural style of Gauḍa:
Notable structures
 According to ''
According to ''Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition
The ''Encyclopædia Britannica'' Eleventh Edition (1910–1911) is a 29-volume reference work, an edition of the ''Encyclopædia Britannica''. It was developed during the encyclopaedia's transition from a British to an American publication. So ...
'', "The Tantipar mosque (1475–1480) has beautiful moulding in brick, and the Lotan mosque of the same period is unique in retaining its glazed tiles. The citadel
A citadel is the core fortified area of a town or city. It may be a castle, fortress, or fortified center. The term is a diminutive of "city", meaning "little city", because it is a smaller part of the city of which it is the defensive core.
In ...
, of the Muslim period, was strongly fortified with a rampart and entered through a magnificent gateway called the Dakhil Darwaza (1459–1474). At the south-east corner was a palace, surrounded by a wall of brick high, of which a part is standing. Nearby were the royal tombs. Within the citadel is the Kadam Rasul mosque (1530), which is still used, and close outside is a tall tower called the Firoz Minar
Firoz Minar (also known as Firuz Minar) (''English'': Tower of Firoz/Firuz) is a five-storeyed tower situated at Gaur, West Bengal, India. It was built by Sultan Saifuddin Firuz Shah of the Habshi dynasty between 1485 and 1489. It was built in th ...
(perhaps signifying tower of victory). There are a number of Muslim buildings on the banks of the Sagar Dighi, including, notably, the tomb of the saint Makhdum Shaikh Akhi Siraj (died 1357), and in the neighbourhood is a burning ghat
Ghat, a term used in the Indian subcontinent, depending on the context could refer either to a range of stepped hills with valleys (ghati in Hindi), such as the Eastern Ghats and Western Ghats; or the series of steps leading down to a body of ...
, traditionally the only one allowed to the use of the Hindus by their Muslim conquerors, and still greatly venerated and frequented by them. Many inscriptions of historical importance have been found in the ruins.."
Preservation
 The
The Archaeological Survey of India
The Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) is an Indian government agency that is responsible for archaeological research and the conservation and preservation of cultural historical monuments in the country. It was founded in 1861 by Alexande ...
and the Department of Archaeology in Bangladesh are responsible for preserving heritage structures in the area. The Bangladeshi Archaeology Department has carried out several projects in both the Bangladeshi and Indian sides of Gauda.
The Indian archaeological survey is also carrying out excavations of a mound about a kilometre from the Chikha building within the Baisgaji Wall where remains of a palace are turning up. A permanent artefact and photographic exhibition highlighting the major monuments of Gour and the restoration work is undertaken by the ASI is being held at the Metcalfe Hall
Metcalfe Hall is a heritage building situated in Kolkata, India, at the junction of Strand Road and Hare Street in the heart of the city's business district. The architecture is reflective of the British imperial architecture at the middle of ...
, Kolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
. Among the exhibits are also some fine specimens of brick moulding and glazed tiles from Gour.
Transport
Bus and rail transport are available fromKolkata
Kolkata (, or , ; also known as Calcutta , the official name until 2001) is the capital of the Indian state of West Bengal, on the eastern bank of the Hooghly River west of the border with Bangladesh. It is the primary business, comme ...
to Malda town. The nearest railway station is Gour Malda. Although, it is desirable to visit Gauda via Malda Town
Malda or English Bazar is a city in the Indian state of West Bengal. It is the sixth largest city (urban agglomeration) in West Bengal. It is the headquarters of the Malda district as well as of the Malda division of West Bengal. It consists o ...
railway station. Gauda can be accessed through the Sonamosjid checkpoint on the Bangladesh-India border. The checkpoint is located near the Choto Sona Mosque in Chapai Nawabganj district, Bangladesh.
Notes
References
* endnotes: ** M. Martin (Buchanan Hamilton), ''Eastern India'', vol. iii. (1831); ** G. H. Ravenshaw, ''Gaur'' (1878); ** James Fergusson, ''History of Indian and Eastern Architecture'' (1876); ** ''Reports of the Archaeological Surveyor'', Bengal Circle (1900–1904).External links
Gaur
at
Banglapedia
''Banglapedia:'' ''the'' ''National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh'' is the first Bangladeshi encyclopedia. It is available in print, CD-ROM format and online, in both Bengali and English. The print version comprises fourteen 500-page volumes. The f ...
*
*
{{DEFAULTSORT:Gauda (city)
Bengal Sultanate
Archaeological sites in Bangladesh
Chapai Nawabganj District
Former populated places in Bangladesh
Buildings and structures in West Bengal
Cities and towns in Malda district
Former populated places in India
Archaeological sites in West Bengal
Former capital cities in India
Ruins in India
Maldah
Capitals of Bengal
Ruins in Bangladesh
Tourist attractions in Malda district