Govan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Govan ( ;
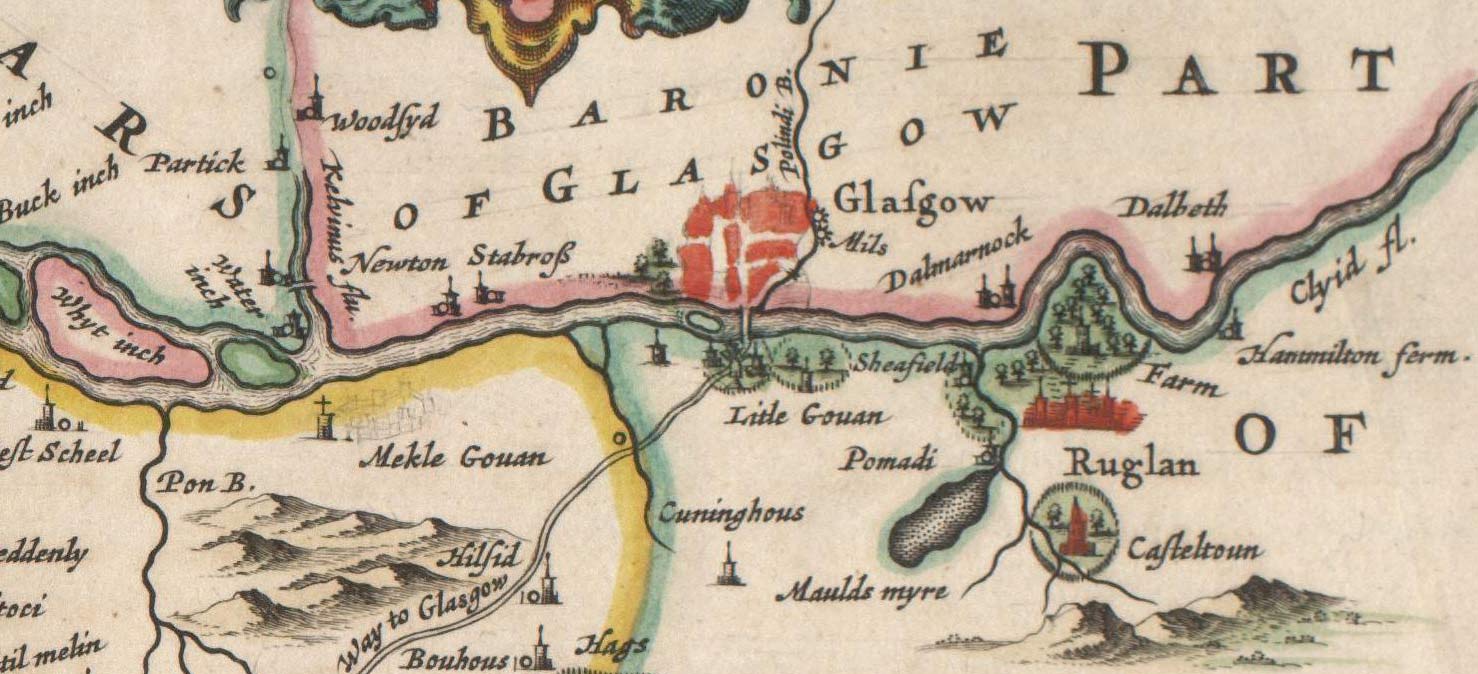 There is an oddity whereby part of eighteenth-century parish of Govan (which was in
There is an oddity whereby part of eighteenth-century parish of Govan (which was in  By the early part of the 19th century, Govan was rapidly losing its rural appearance and assuming the character of a town with the development of new industries and factories, including Reid's Dye Works and Pollok's Silk Mill. Town officials arranged for the deepening of the Clyde in 1759, the reclamation of the channels between the islands (The Whyte Inch, The Black Inch, and The King's Inch), and the construction of quays and docks. This facilitated the development of shipbuilding as a major industry. By the 1860s, the village needed a higher order of administration and it was made a
By the early part of the 19th century, Govan was rapidly losing its rural appearance and assuming the character of a town with the development of new industries and factories, including Reid's Dye Works and Pollok's Silk Mill. Town officials arranged for the deepening of the Clyde in 1759, the reclamation of the channels between the islands (The Whyte Inch, The Black Inch, and The King's Inch), and the construction of quays and docks. This facilitated the development of shipbuilding as a major industry. By the 1860s, the village needed a higher order of administration and it was made a
 Traditionally viewed as a lower working-class area, Govan has typically supported the Labour Party, but the Scottish National Party (SNP) has also been strong there. In 1973 SNP won a by-election with Margo MacDonald as their candidate. The SNP won another by-election victory in 1988, this time with Jim Sillars as candidate. The latest victory for the SNP was in the 2007 Scottish parliamentary elections, when Nicola Sturgeon became the MSP for the constituency.
The area has had a reputation for deprivation and poverty, partly due to the construction of housing estates in the 1930s to relieve the overcrowded slum district of The Gorbals, Glasgow. The most famous of these housing estates is Moorepark, sometimes referred to jocularly as "The Wine Alley" - this area was named by ''
Traditionally viewed as a lower working-class area, Govan has typically supported the Labour Party, but the Scottish National Party (SNP) has also been strong there. In 1973 SNP won a by-election with Margo MacDonald as their candidate. The SNP won another by-election victory in 1988, this time with Jim Sillars as candidate. The latest victory for the SNP was in the 2007 Scottish parliamentary elections, when Nicola Sturgeon became the MSP for the constituency.
The area has had a reputation for deprivation and poverty, partly due to the construction of housing estates in the 1930s to relieve the overcrowded slum district of The Gorbals, Glasgow. The most famous of these housing estates is Moorepark, sometimes referred to jocularly as "The Wine Alley" - this area was named by ''
 Govan was at one point the centre of the world-renowned Clydeside shipbuilding industry. In 1841, Robert Napier began iron shipbuilding in Govan, and in 1843 produced its first ship, the ''Vanguard''. He also procured a contract with the
Govan was at one point the centre of the world-renowned Clydeside shipbuilding industry. In 1841, Robert Napier began iron shipbuilding in Govan, and in 1843 produced its first ship, the ''Vanguard''. He also procured a contract with the
p. 14.
/ref> In 1999,
''Ships Monthly.''
June 1985. * ''Ibis'' (1886)Clydebuilt Database - Shipping Times, Stuart Cameron * ''Akasha'' (1886) * ''Livadia'' (1880) *''Victoria'' (1886) * RMS ''Campania'' (1891) * RMS ''Lucania'' (1893) * HMS ''Venus'' (1895) * HMS ''Diana'' (1895) * HMS ''Highflyer'' (1898) * HMS ''Hermes'' (1898) * HMS ''Cressy'' (1899) * HMS ''Aboukir'' (1900) * HMS ''Good Hope'' (1901) * HMS ''Bedford'' (1901) * SS ''Armadale Castle'' (1903) *RMS ''Port Kingston'' (1904) renamed RMS ''Tahiti'' * HMS ''Cochrane'' (1905) * HMS ''Commonwealth'' (1905) * RMS ''Empress of Britain'' (1906) * RMS ''Empress of Ireland'' (1906) * * HMS ''Indomitable'' (1907) * SS ''Balmoral Castle'' (1910) * HMS ''New Zealand'' (1911) * HMAS ''Sydney'' (1912) * RMS ''Empress of Russia'' (1913) * RMS ''Empress of Asia'' (1913) * SS ''Calgarian'' (1913) * HMS ''Valiant'' (1914) * HMS ''Renown'' (1916) * RMS ''Empress of Canada'' (1922) * SS ''Athenia'' (1922) * ''Aorangi'' (1922) * TSS ''Tuscania'' (1923) * SS ''Letitia'' (1924) * MV ''Speybank'' (1926) * HMS ''Berwick'' (1926) * HMS ''Norfolk'' (1928) * RMS ''Empress of Japan'' (1930) * HMS ''Delight'' (1932) * HMS ''Woolwich'' (1934) * HMS ''Liverpool'' (1937) * HMS ''Phoebe'' (1937) * HMS ''Howe'' (1940) * HMS ''Bellona'' (1942) * HMS ''Implacable'' (1942) * HMS ''Theseus'' (1944) * HMS ''Chichester'' * HMS ''Blake'' (1945) * SS ''Karanja'' (1948) * TS ''Oxfordshire'' (1955) * TS/SS ''Empress of Britain'' (1956) * TS ''Leecliffe Hall'' (1961) * HMS ''Fife'' (1964) * HMS ''Antrim'' (1967) * USNS ''Harkness'' (1968) * ''Jervis Bay'' (1969) *''Pacifique'' (1969) * USNS ''Chauvenet'' (1970) * ''Pacific Peace'' (1981) * MV ''Selkirk Settler'' (1983) * MV ''Saskatchewan Pioneer'' (1983) * ''St. Lawrence Seaway'' (1983) * ''Sir Charles Parsons'' (1985) * MV ''Norsea'' (1986) * MV ''Havis'' (1992) * ''Sea Launch Commander'' (1996) * RFA ''Wave Ruler'' (2003) * RFA ''Mounts Bay'' (2004) * HMS ''Daring'' (2006) * HMS ''Dauntless'' (2007) * HMS ''Diamond'' (2007) * HMS ''Dragon'' (2008) * HMS ''Defender'' (2009). * HMS ''Duncan'' (2010) A list of almost 3000 ships built at Govan has been collected in the "Clydebuilt Database". The ships were built by the following companies: Robert Napier & Company, Randolph Elder & Company, Dobbie Hedderwick & Co., Dobie & Company, Mackie & Thomson, Smith & Rodgers, London & Glasgow Engineering and Iron Shipbuilding Co. Ltd., William Beardmore & Company, John Elder & Company, Fairfield Shipbuilding & Eng. Co. Ltd., Alexander Stephens & Sons, J & G Thomson, Harland & Wolff and more.
"Iain Robertson"
, Sunny Govan
* Chick Young, football pundit
* Johnny Beattie, actor and stand-up comedian
* Bill Martin, songwriter, music publisher and impresario
* Dame Elish Angiolini, Lord Advocate of Scotland and former Solicitor General for Scotland, brought up in Govan
* Peter Barr, nurseryman and merchant better known as "The Daffodil King"
* Jim Craig, Celtic player and Lisbon Lion
*
Govan Community Council
Get into GovanGovan, the Place and the People
Fairfield Heritage
Govan Maps 1857-1934, National Library of Scotland
{{authority control Areas of Glasgow Ports and harbours of Scotland Civil parishes of Scotland Burghs
Cumbric
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the '' Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the sout ...
?: ''Gwovan'?''; Scots
Scots usually refers to something of, from, or related to Scotland, including:
* Scots language, a language of the West Germanic language family native to Scotland
* Scots people, a nation and ethnic group native to Scotland
* Scoti, a Latin na ...
: ''Gouan''; Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well a ...
: ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'') is a district, parish, and former burgh
A burgh is an autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland and Northern England, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. ...
now part of south-west City of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated west of Glasgow city centre, on the south bank of the River Clyde, opposite the mouth of the River Kelvin and the district of Partick. Historically it was part of the County of Lanark.
In the early medieval period, the site of the present Govan Old churchyard was established as a Christian centre for the Brittonic Kingdom of Alt Clut (Dumbarton Rock) and its successor realm, the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to a ...
. This latter kingdom, established in the aftermath of the Viking siege and capture of Alt Clut by Vikings from Dublin in AD 870, created the sandstone sculptures known today as the Govan Stones.
Govan was the site of a ford and later a ferry which linked the area with Partick for seasonal cattle drovers. In the eighteenth and nineteenth centuries, textile
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not t ...
mills and coal mining
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron from ...
were important; in the early-nineteenth century, shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other Watercraft, floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roo ...
emerged as Govan's principal industry. In 1864, Govan gained burgh status, and was the fifth-largest burgh in Scotland. It was incorporated into the City of Glasgow in 1912.
History
Early history
Recent studies of thearchaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, architecture, biofact (archaeology), biofacts ...
of Govan Old have revealed the presence of an ancient Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
church. Two associated Christian burials are radiocarbon dated to the 5th or 6th centuries, making Govan the earliest known Christian site in the region. Govan is believed to have then been part of a kingdom ruled from Dumbarton Rock, known as ''Alt Clut'', the rock on the Clyde. During the Viking Age
The Viking Age () was the period during the Middle Ages when Norsemen known as Vikings undertook large-scale raiding, colonizing, conquest, and trading throughout Europe and reached North America. It followed the Migration Period
The ...
, following the sack of Dumbarton Rock in 870, Govan is believed to have been one of the major centres of the Kingdom of Strathclyde
Strathclyde (lit. " Strath of the River Clyde", and Strað-Clota in Old English), was a Brittonic successor state of the Roman Empire and one of the early medieval kingdoms of the Britons, located in the region the Welsh tribes referred to a ...
. In 1855, an elaborately carved sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates ...
sarcophagus was found during digging in the churchyard. It is now kept inside the church, as part of the Govan Stones museum collection. It may have been used to contain the body or relics of St. Constantine, a Pictish king killed seemingly killed by Vikings in 876/7 - the style of carving indicates an origin in the late 9th or early 10th century.
Govan's earliest recorded name may be found in the '' Historia regum Anglorum'' attributed to Symeon of Durham. This is a 12th-century Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power ...
source, but one believed to be based on much earlier materials; it records a place near Dumbarton Rock named ''Ouania''. Based on this, Govan's Cumbric language
Cumbric was a variety of the Common Brittonic language spoken during the Early Middle Ages in the ''Hen Ogledd'' or "Old North" in what is now the counties of Westmorland, Cumberland and northern Lancashire in Northern England and the southe ...
name has been reconstructed as *''(G)uovan''. Govan is ''Baile a' Ghobhainn'' (the smith's town) in Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well a ...
. Bishop Leslie in his ''Scotia Descriptio'' of 1578 says it got its name from the excellence of its ale ''(God-win)'', whereas Chalmers in his ''Caledonia'' says it is derived from Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well a ...
, ''Gamhan'' (a ditch)."A History Of Glasgow & Govan (1883)", ''Ordnance Gazetteer Of Scotland''
The earliest references to Govan are found in connection with the Christian church. In 1136, when Glasgow Cathedral was formally consecrated, King David I (1124–53) gave to the See the lands of Partick and also of the church at Govan (on opposite sides of the River Clyde), which became a prebend of Glasgow. Govan Old Parish Church
Govan Old Parish Church is the name of the original parish church serving Govan in Glasgow from the 5th or 6th century AD until 2007. In that year, the Church of Scotland united the two Govan congregations with Linthouse and established the pari ...
was rebuilt in 1762, 1826, and again 1884-1888. Within it and its roughly circular churchyard is one of the finest collections of Early Christian stones in the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, known as the Govan Stones, dating from the c.9th to 11th centuries.
Not much is known about any medieval village that may have surrounded the church until 1454 when it is recorded that whole houses, barns and mills in the village were brought down by a great flood.
By the 16th century, extensive coal mine workings had been developed around Craigton and Drumoyne.
 There is an oddity whereby part of eighteenth-century parish of Govan (which was in
There is an oddity whereby part of eighteenth-century parish of Govan (which was in Lanarkshire
Lanarkshire, also called the County of Lanark ( gd, Siorrachd Lannraig; sco, Lanrikshire), is a historic county, lieutenancy area and registration county in the central Lowlands of Scotland.
Lanarkshire is the most populous county in Scot ...
) is counted as being within Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
. There existed a hospital in the area, and as quasi-religious foundations were not taxed, it had never been assigned to a sheriffdom. Thus, when Renfrewshire was created out of a sheriffdom of Lanarkshire in the early fifteenth century, the lands associated with the hospital ( Polmadie) were not technically in the newly created shire, as they were not part of the sheriffdom. They were, however, very much a part of the physical landscape that became Renfrewshire. A similar uncertainty existed regarding the nearby lands of Pollokshields and Westends. People lived with the inconsistency in the records. When the railway was to be built in the late nineteenth century, however, the confusion over proper descriptions in the land titles made necessary legal transactions difficult and had to be reconciled. The county added to the description of these lands, the phrase: "but now by annexation in the County of Renfrew."
 By the early part of the 19th century, Govan was rapidly losing its rural appearance and assuming the character of a town with the development of new industries and factories, including Reid's Dye Works and Pollok's Silk Mill. Town officials arranged for the deepening of the Clyde in 1759, the reclamation of the channels between the islands (The Whyte Inch, The Black Inch, and The King's Inch), and the construction of quays and docks. This facilitated the development of shipbuilding as a major industry. By the 1860s, the village needed a higher order of administration and it was made a
By the early part of the 19th century, Govan was rapidly losing its rural appearance and assuming the character of a town with the development of new industries and factories, including Reid's Dye Works and Pollok's Silk Mill. Town officials arranged for the deepening of the Clyde in 1759, the reclamation of the channels between the islands (The Whyte Inch, The Black Inch, and The King's Inch), and the construction of quays and docks. This facilitated the development of shipbuilding as a major industry. By the 1860s, the village needed a higher order of administration and it was made a burgh
A burgh is an autonomous municipal corporation in Scotland and Northern England, usually a city, town, or toun in Scots. This type of administrative division existed from the 12th century, when King David I created the first royal burghs. ...
in 1864, under the General Police (Scotland) Act 1862
A general officer is an officer of high rank in the armies, and in some nations' air forces, space forces, and marines or naval infantry.
In some usages the term "general officer" refers to a rank above colonel."general, adj. and n.". OED ...
. At the time, it was the fifth largest burgh in Scotland and contained within its boundaries, the areas of Plantation, Cessnock, Ibrox, Craigton and Drumoyne. in 1901 the Burgh boundaries increased further west to include Linthouse
Linthouse is a neighbourhood in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated directly south of the River Clyde and lies immediately west of Govan, with other adjacent areas including Shieldhall and the Southern General Hospital to the west, ...
and West Drumoyne.
With Morris Pollok
Morris may refer to:
Places
Australia
*St Morris, South Australia, place in South Australia
Canada
* Morris Township, Ontario, now part of the municipality of Morris-Turnberry
* Rural Municipality of Morris, Manitoba
** Morris, Manitob ...
as its first Provost, the Burgh and its Commissioners ensured that during the next 48 years Govan became a well-equipped, modern town. During the late 19th century, the population of Govan increased more than tenfold: from 9,000 in 1864 to 95,000 by 1907. In 1901 Govan was the 7th largest town in Scotland. In 1912, Glasgow annexed Govan after a series of annexation battles.
A prominent feature of the Govan landscape was the Doomster or Moot Hill, which stood near the river, north of the present Govan Cross. It was removed in the early 19th century and Reid's Dyeworks was erected on the site. The origins of the Doomster Hill are a mystery. One hypothesis is that it was a prehistoric burial mound
Burial, also known as interment or inhumation, is a method of final disposition whereby a dead body is placed into the ground, sometimes with objects. This is usually accomplished by excavating a pit or trench, placing the deceased and objec ...
. In 1996, a team from Channel 4
Channel 4 is a British free-to-air public broadcast television network operated by the state-owned enterprise, state-owned Channel Four Television Corporation. It began its transmission on 2 November 1982 and was established to provide a four ...
's '' Time Team'' programme carried out an archeological excavation at the site. They suggested that the hill may have been a 12th-century Norman motte
A motte-and-bailey castle is a European fortification with a wooden or stone keep situated on a raised area of ground called a motte, accompanied by a walled courtyard, or bailey, surrounded by a protective ditch and palisade. Relatively eas ...
.
20th century to the present
 Traditionally viewed as a lower working-class area, Govan has typically supported the Labour Party, but the Scottish National Party (SNP) has also been strong there. In 1973 SNP won a by-election with Margo MacDonald as their candidate. The SNP won another by-election victory in 1988, this time with Jim Sillars as candidate. The latest victory for the SNP was in the 2007 Scottish parliamentary elections, when Nicola Sturgeon became the MSP for the constituency.
The area has had a reputation for deprivation and poverty, partly due to the construction of housing estates in the 1930s to relieve the overcrowded slum district of The Gorbals, Glasgow. The most famous of these housing estates is Moorepark, sometimes referred to jocularly as "The Wine Alley" - this area was named by ''
Traditionally viewed as a lower working-class area, Govan has typically supported the Labour Party, but the Scottish National Party (SNP) has also been strong there. In 1973 SNP won a by-election with Margo MacDonald as their candidate. The SNP won another by-election victory in 1988, this time with Jim Sillars as candidate. The latest victory for the SNP was in the 2007 Scottish parliamentary elections, when Nicola Sturgeon became the MSP for the constituency.
The area has had a reputation for deprivation and poverty, partly due to the construction of housing estates in the 1930s to relieve the overcrowded slum district of The Gorbals, Glasgow. The most famous of these housing estates is Moorepark, sometimes referred to jocularly as "The Wine Alley" - this area was named by ''The Independent
''The Independent'' is a British online newspaper. It was established in 1986 as a national morning printed paper. Nicknamed the ''Indy'', it began as a broadsheet and changed to tabloid format in 2003. The last printed edition was publishe ...
'' newspaper in April 1994 as one of the worst areas in Britain, with drug abuse being a widespread problem and unemployment standing at nearly 30% (up to three times the national average at the time).
It was parodied by the BBC sitcom '' Rab C. Nesbitt''. Although Govan was the stated setting for the show, episodes were seldom filmed there.
Despite these developments, there were numerous older buildings around Govan until quite recently, most notably the terraces and tenements situated around Govan Road. These were not cleared until well into the 1970s. However, there is the potential for tourism development, for example, the planned development of the Govan Old site, which hosts the historically significant stone carvings, has led to the development of the surrounding townscape and new infrastructure. Such developments benefit the aesthetic and connective appeal of the Govan area for future visitors.
Economy
 Govan was at one point the centre of the world-renowned Clydeside shipbuilding industry. In 1841, Robert Napier began iron shipbuilding in Govan, and in 1843 produced its first ship, the ''Vanguard''. He also procured a contract with the
Govan was at one point the centre of the world-renowned Clydeside shipbuilding industry. In 1841, Robert Napier began iron shipbuilding in Govan, and in 1843 produced its first ship, the ''Vanguard''. He also procured a contract with the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were foug ...
to produce vessels, notably the ''Jackal
Jackals are medium-sized canids native to Africa and Eurasia. While the word "jackal" has historically been used for many canines of the subtribe canina, in modern use it most commonly refers to three species: the closely related black-backe ...
'', the ''Lizard
Lizards are a widespread group of squamate reptiles, with over 7,000 species, ranging across all continents except Antarctica, as well as most oceanic island chains. The group is paraphyletic since it excludes the snakes and Amphisbaenia al ...
'', and the ''Bloodhound
The bloodhound is a large scent hound, originally bred for hunting deer, wild boar and, since the Middle Ages, for tracking people. Believed to be descended from hounds once kept at the Abbey of Saint-Hubert, Belgium, in French it is called ...
''. He also allowed naval officers in training to visit the shipyard to familiarise themselves with the new vessels. Napier's Shipyard in Govan was later acquired by William Beardmore and Company in 1876 and incorporated into William Beardmore and Company in around 1900.
Govan's other major shipbuilding firm was founded in the 1860s as: Randolph, Elder and Company, later becoming John Elder and Company. In 1885, the yard moved further west to its present site and was reorganised as the Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company Ltd. This company continued until 1965, when it filed for bankruptcy. The following year in 1966, the yard was again reorganised as Fairfields and guaranteed by the government in response. The following year, Fairfields and the other major Clydeside yards (Stephens, Connels, Yarrows and John Browns) were merged to form Upper Clyde Shipbuilders (UCS).
In 1971, Upper Clyde Shipbuilders went into receivership and the Conservative government led by Edward Heath
Sir Edward Richard George Heath (9 July 191617 July 2005), often known as Ted Heath, was a British politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1970 to 1974 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 1965 to 1975. Heath a ...
refused to give them a £6,000,000 loan. Rather than go on strike, which was the traditional form of industrial action, the union leadership of the yards decided to have a work-in and complete the orders that the shipyards had in place. In this way they dispelled the idea of the workers being "work-shy" and also wanted to illustrate the long-term viability of the yards. Fairfield Shipbuilding and Engineering Company was renamed Govan Shipbuilders in 1973.
In 1977, the Labour government of James Callaghan passed the Aircraft and Shipbuilding Industries Act which nationalised Govan and grouped it with other major British shipyards as British Shipbuilders. In May 1979, Margaret Thatcher was elected Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
and her ministry soon began its privatisation programme. British Aerospace, established by the same act, was privatised in 1981. British Shipbuilders road to privatisation was not as swift, and the group was sold piece by piece throughout the course of the 1980s.
Kværner of Norway, as part of a planned development of a large international shipbuilding group, took over Govan. British Shipbuilders' sale of Govan to the Norwegian firm was completed in 1988, and the yard was renamed Kvaerner Govan.Birklerp. 14.
/ref> In 1999,
GEC
GEC or Gec may refer to:
Education
* Gedo Education Committee, in Somalia
* Glen Eira College, in Caulfield East, Victoria, Australia
* Goa Engineering College, India
* Government Engineering College (disambiguation)
* Guild for Exceptional ...
's Marconi Marine division purchased the yard when Kværner announced its departure from the shipbuilding industry. GEC's Marconi Marine division already owned YSL (purchased in 1985) and VSEL (purchased in 1995). Marconi Electronic Systems and its Marconi Marine unit were sold to British Aerospace in 1999 to form BAE Systems. The shipbuilding operations became BAE Systems Marine, which subsequently became part of BVT Surface Fleet BVT may refer to:
* The Bobby Van Trust, a group of charities that improve home security in the UK
* BVT Surface Fleet, former name of BAE Systems Maritime – Naval Ships, British naval shipbuilding company
* Bandwidth-variable transponder, a type ...
, a naval shipbuilding joint venture between BAE Systems and VT Group, which became BAE Systems Surface Ships in 2009.
Alexander Stephen and Sons also established a shipyard in nearby Linthouse
Linthouse is a neighbourhood in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated directly south of the River Clyde and lies immediately west of Govan, with other adjacent areas including Shieldhall and the Southern General Hospital to the west, ...
in 1870. The yard eventually closed in the wake of the collapse of the Upper Clyde Shipbuilders consortium in 1971.
Ships built at Govan
* PS Vanguard (1843) *PS Scotia (1861)
PS ''Scotia'' was a steam paddle passenger vessel that ran between England and Ireland from 1847 to 1861, and then became an American Civil War blockade runner.
History
She was built by Money Wigram & Sons at Blackwall Yard, London in 1847 for ...
* HMS ''Northampton'' (1876)
* HMS ''Nelson'' (1876)
* HMS ''Curacoa'' (1878)
* SS ''Arizona'' (1879)Johnston, Ian. "Govan Shipyard" i''Ships Monthly.''
June 1985. * ''Ibis'' (1886)Clydebuilt Database - Shipping Times, Stuart Cameron * ''Akasha'' (1886) * ''Livadia'' (1880) *''Victoria'' (1886) * RMS ''Campania'' (1891) * RMS ''Lucania'' (1893) * HMS ''Venus'' (1895) * HMS ''Diana'' (1895) * HMS ''Highflyer'' (1898) * HMS ''Hermes'' (1898) * HMS ''Cressy'' (1899) * HMS ''Aboukir'' (1900) * HMS ''Good Hope'' (1901) * HMS ''Bedford'' (1901) * SS ''Armadale Castle'' (1903) *RMS ''Port Kingston'' (1904) renamed RMS ''Tahiti'' * HMS ''Cochrane'' (1905) * HMS ''Commonwealth'' (1905) * RMS ''Empress of Britain'' (1906) * RMS ''Empress of Ireland'' (1906) * * HMS ''Indomitable'' (1907) * SS ''Balmoral Castle'' (1910) * HMS ''New Zealand'' (1911) * HMAS ''Sydney'' (1912) * RMS ''Empress of Russia'' (1913) * RMS ''Empress of Asia'' (1913) * SS ''Calgarian'' (1913) * HMS ''Valiant'' (1914) * HMS ''Renown'' (1916) * RMS ''Empress of Canada'' (1922) * SS ''Athenia'' (1922) * ''Aorangi'' (1922) * TSS ''Tuscania'' (1923) * SS ''Letitia'' (1924) * MV ''Speybank'' (1926) * HMS ''Berwick'' (1926) * HMS ''Norfolk'' (1928) * RMS ''Empress of Japan'' (1930) * HMS ''Delight'' (1932) * HMS ''Woolwich'' (1934) * HMS ''Liverpool'' (1937) * HMS ''Phoebe'' (1937) * HMS ''Howe'' (1940) * HMS ''Bellona'' (1942) * HMS ''Implacable'' (1942) * HMS ''Theseus'' (1944) * HMS ''Chichester'' * HMS ''Blake'' (1945) * SS ''Karanja'' (1948) * TS ''Oxfordshire'' (1955) * TS/SS ''Empress of Britain'' (1956) * TS ''Leecliffe Hall'' (1961) * HMS ''Fife'' (1964) * HMS ''Antrim'' (1967) * USNS ''Harkness'' (1968) * ''Jervis Bay'' (1969) *''Pacifique'' (1969) * USNS ''Chauvenet'' (1970) * ''Pacific Peace'' (1981) * MV ''Selkirk Settler'' (1983) * MV ''Saskatchewan Pioneer'' (1983) * ''St. Lawrence Seaway'' (1983) * ''Sir Charles Parsons'' (1985) * MV ''Norsea'' (1986) * MV ''Havis'' (1992) * ''Sea Launch Commander'' (1996) * RFA ''Wave Ruler'' (2003) * RFA ''Mounts Bay'' (2004) * HMS ''Daring'' (2006) * HMS ''Dauntless'' (2007) * HMS ''Diamond'' (2007) * HMS ''Dragon'' (2008) * HMS ''Defender'' (2009). * HMS ''Duncan'' (2010) A list of almost 3000 ships built at Govan has been collected in the "Clydebuilt Database". The ships were built by the following companies: Robert Napier & Company, Randolph Elder & Company, Dobbie Hedderwick & Co., Dobie & Company, Mackie & Thomson, Smith & Rodgers, London & Glasgow Engineering and Iron Shipbuilding Co. Ltd., William Beardmore & Company, John Elder & Company, Fairfield Shipbuilding & Eng. Co. Ltd., Alexander Stephens & Sons, J & G Thomson, Harland & Wolff and more.
Transport
Govan is served by Govan Subway Station, Ibrox Subway Station and Cessnock Subway Station on the Glasgow subway system.Govan railway station
Govan railway station was a railway station in Govan, a district of Glasgow, Scotland. The station was originally part of an extension to the Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway
The Glasgow and Paisley Joint Railway was the section of railwa ...
opened on 2 December 1868. It closed permanently to regular passenger services on 9 May 1921.
Regular bus services, mainly operated by McGill's Bus Services and First Glasgow, offer frequent routes to Glasgow City Centre, as well as to numerous locations in Renfrewshire
Renfrewshire () ( sco, Renfrewshire; gd, Siorrachd Rinn Friù) is one of the 32 council areas of Scotland.
Located in the west central Lowlands, it is one of three council areas contained within the boundaries of the historic county of Re ...
.
Sports
Govan borders the district of Ibrox, home to the Scottish football club Rangers F.C. who traditionally incorporate the red and black civic colours in the socks of their kit; their Ibrox Stadium has a stand named for Govan (the closest to the heart of the burgh), although officially this was re-named after their former player Sandy Jardine in 2014. Govan is home to the Scottish Junior football team Benburb F.C. who until March 2014 played at Tinto Park ( Drumoyne) then moved to the adjacent New Tinto Park. They share a rivalry withSt Anthony's F.C.
St Anthony's Football Club is a Scottish non-league football club based in Glasgow. Nicknamed ''the Ants'', they play in green-and-white hooped kits and currently operate in the .
History
Founded in 1902, they were members of the Scottish Jun ...
who originated from the Helen Street area of Govan, but are now based further west at Shieldhall. Linthouse
Linthouse is a neighbourhood in the city of Glasgow, Scotland. It is situated directly south of the River Clyde and lies immediately west of Govan, with other adjacent areas including Shieldhall and the Southern General Hospital to the west, ...
and Parkgrove were 19th century senior sides, who fell into decline and are now defunct.
There were two other sporting venues for local residents and workers located in the south of Govan (with no space available in the industrial northern area at the Clyde): White City Stadium and Albion Greyhound Stadium
The Albion Greyhound Stadium was a greyhound racing stadium in Glasgow.
Origins
Albion in Glasgow opened on 21 April 1928 on the Broomloan Road and was described as good size track with a circumference of 457 yards. The first hare installed w ...
, both now entirely demolished.
Media
Govan is served by community radio station Sunny Govan, broadcasting on 103.5FM to the city of Glasgow and surrounding districts, discussing local issues and providing advice, and with diverse musical output covering soul, hip-hop and reggae. Govan has had several local newspapers over the years such as the Govan Chronicle and ''Govan Press'' published by the Cossar Family (1851-1983) and by John Maclean (2006–2014) which also served the communities of Kinning Park, Cardonald, Penilee and Hillington, and the ''Govan Post'' (1983–1988) published by Cook, Paton & Co. of Paisley, now part of Dunfermline Press.Religion
Church of Scotland
The church of Govan was a prebend of Glasgow. It was dedicated to St Constantine, who had been buried at Govan. On 13 July 1577, the teinds of Govan were granted to the University of Glasgow, and the Principal of the University ex officio was appointed minister of the parish. This settlement was set aside on 20 December 1621, and only the patronage of Govan was left to the University. There was a chapel in the parish at Partick. Govan Church was rebuilt in 1762, and again in 1826. A later rebuilding was begun in 1884 and was opened 19 May 1888.List of Provosts of Govan
*1864-1867 Morris Pollok *1867-1869 William Cruickshank *1869-1872 Thomas Reid *1872-1880 James Wilson *1880-1883 John Thompson *1883-1886 Alexander Campbell *1886-1889 George Ferguson *1889-1892 Neil McLean *1892-1901 James Kirkwood *1901-1904 John Marr *1904-1908 Sir John Anthony *1908-1912 David McKechniePopular culture
* Scottish TV sitcom '' Rab C Nesbitt'' is set in Govan; although the series is mostly filmed elsewhere. * Channel 4's Time Team filmed a Series 4 episode in Govan, where they excavated the Churchyard at Govan Old, home of the Govan Stones, and a local carpark to the immediate east of Water Row.Notable people
* Mary Barbour, resident in Govan while helping to organise the Glasgow Rent Strikes *Isabella Elder
Isabella Ure Elder
(15 March 1828 – 18 November 1905) was a Scottish philanthropist who took a particular interest in education, especially of women, and in the welfare of the people of Govan in Glasgow. In Govan alone, Elder was responsi ...
, philanthropist who gifted Elder Park
Elder Park is a public open space in the city of Adelaide, South Australia on the southern bank of the River Torrens and that is bordered by the Adelaide Festival Centre and North Terrace.
The park is named after the Elder family who w ...
and to the people of Govan, as well as many other projects.
* Hugh Binning child genius, professor of philosophy and minister of Govan
* Leo Blair (senior)
Leo Charles Lynton Blair (born Charles Leonard Augustus Parsons; 4 August 192316 November 2012) was a British barrister and law lecturer at Durham University. He was the author of the book ''The Commonwealth Public Service''. He was the fathe ...
, father of former Prime Minister Tony Blair
Sir Anthony Charles Lynton Blair (born 6 May 1953) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007 and Leader of the Labour Party from 1994 to 2007. He previously served as Leader of the ...
and high court judge Sir William Blair, raised on Golspie Street
* Ivor Cutler avant garde performer
* Sir Alex Ferguson, football manager and player widely known for managing Manchester United from 1986 to 2013 (won more trophies than any other manager, considered one of the greatest of all time)
* James Hedderwick, poet and newspaper proprietor, born and raised in Govan.
* Jimmy Speirs, footballer (scored the winning goal in the 1911 FA Cup Final, received the Military Medal during the First World War)
* James Kelman, writer
* George MacLeod
George Fielden MacLeod, Baron MacLeod of Fuinary, (17 June 1895 – 27 June 1991) was a Scottish soldier and clergyman; he was one of the best known, most influential and unconventional Church of Scotland ministers of the 20th century. He ...
, minister of the Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Scottish Reformation, Reformation of 1560, when it split from t ...
's Govan Old Parish Church
Govan Old Parish Church is the name of the original parish church serving Govan in Glasgow from the 5th or 6th century AD until 2007. In that year, the Church of Scotland united the two Govan congregations with Linthouse and established the pari ...
(founded the Iona Community
The Iona Community, founded in 1938 by George MacLeod, is an ecumenical Christian community of men and women from different walks of life and different traditions within Christianity.
It and its publishing house, Wild Goose Publications, are hea ...
, whose offices are still based in Govan)
* David Meiklejohn, Rangers and Scotland footballer
* Andrew Melville minister of Govan, reformer and scholar at Glasgow and St Andrews (exiled)
* Belle Moore, Olympic Gold Medalist
* Thomas Ashburton Picken
Thomas Ashburton Picken (c. 1818 – 23 January 1891), known professionally as T. Picken, was a Scottish-born watercolourist, engraver and lithographer working in England between around 1834 and 1875. He worked for the printing firm Day and ...
, lithographer
* Johnny Quigley, footballer
* Jimmy Reid, trade unionist
* Iain Robertson
Iain Robertson (born 27 May 1981) is a BAFTA award winning Scottish actor. He portrayed Lex in cult Glasgow gang film, '' Small Faces'', though Robertson is also known for his work in the long-running children's drama, '' Grange Hill'' and '' ...
, actor, Sunny Govan
George Rossi
George Rossi (28 September 1961 – 5 January 2022) was a Scottish actor, best known for playing Duncan Lennox in '' The Bill'' from 1998 to 2003.
Early life and education
Rossi was born in Govan, Glasgow, on 28 September 1961. He was of I ...
, Scottish actor
See also
* Glasgow Govan (UK Parliament constituency)Notes
References
*External links
Govan Community Council
Get into Govan
Fairfield Heritage
Govan Maps 1857-1934, National Library of Scotland
{{authority control Areas of Glasgow Ports and harbours of Scotland Civil parishes of Scotland Burghs