 |
HMS Good Hope (1901)
HMS ''Good Hope'' was one of four ''Drake''-class armoured cruisers built for the Royal Navy around 1900; she was originally named ''Africa'', but was renamed before she was launched. She became flagship of the 1st Cruiser Squadron of the Atlantic Fleet in 1906, and was the flagship of the 2nd Cruiser Squadron in 1908. She was reduced to reserve in 1913, but was recommissioned in mid-1914. When war was declared in August 1914, ''Good Hope'' was ordered to reinforce the 4th Cruiser Squadron and became the flagship of Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock. Cradock moved the available ships of his squadron later that month to the coast of South America to search for German commerce raiders. He was then ordered further south to the Strait of Magellan to block any attempt of the German East Asia Squadron to penetrate into the South Atlantic. He found the German squadron on 1 November off the coast of Chile. The German squadron outnumbered Cradock's force and were individually more po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Cape Colony
The Cape Colony ( nl, Kaapkolonie), also known as the Cape of Good Hope, was a British colony in present-day South Africa named after the Cape of Good Hope, which existed from 1795 to 1802, and again from 1806 to 1910, when it united with three other colonies to form the Union of South Africa. The British colony was preceded by an earlier corporate colony that became an original Dutch colony of the same name, which was established in 1652 by the Dutch East India Company (VOC). The Cape was under VOC rule from 1652 to 1795 and under rule of the Napoleonic Batavia Republic from 1803 to 1806. The VOC lost the colony to Great Britain following the 1795 Battle of Muizenberg, but it was acceded to the Batavia Republic following the 1802 Treaty of Amiens. It was re-occupied by the British following the Battle of Blaauwberg in 1806, and British possession affirmed with the Anglo-Dutch Treaty of 1814. The Cape of Good Hope then remained in the British Empire, becoming self- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Barbette
Barbettes are several types of gun emplacement in terrestrial fortifications or on naval ships. In recent naval usage, a barbette is a protective circular armour support for a heavy gun turret. This evolved from earlier forms of gun protection that eventually led to the pre-dreadnought. The name ''barbette'' ultimately comes from fortification - it originally meant a raised platform or mound, as in the French phrase ''en barbette'', which refers to the practice of firing a cannon over a parapet rather than through an embrasure in a fortification's casemate. The former gives better angles of fire but less protection than the latter. The disappearing gun was a variation on the barbette gun; it consisted of a heavy gun on a carriage that would retract behind a parapet or into a gunpit for reloading. Barbettes were primarily used in coastal defences, but saw some use in a handful of warships, and some inland fortifications. The term is also used for certain aircraft gun mounts. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Rear Admiral
Rear admiral is a senior naval flag officer rank, equivalent to a major general and air vice marshal and above that of a commodore and captain, but below that of a vice admiral. It is regarded as a two star " admiral" rank. It is often regarded as a two-star rank with a NATO code of OF-7. The term originated in the days of naval sailing squadrons and can trace its origins to the Royal Navy. Each naval squadron was assigned an admiral as its head, who commanded from the centre vessel and directed the squadron's activities. The admiral would in turn be assisted by a vice admiral, who commanded the lead ships that bore the brunt of a battle. In the rear of the squadron, a third admiral commanded the remaining ships and, as this section was considered to be in the least danger, the admiral in command of it was typically the most junior. This has continued into the modern age, with rear admiral the most junior admiralty of many navies. In most European navies, the equivalent ran ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
4th Cruiser Squadron (United Kingdom)
The 4th Cruiser Squadron and (also known as Cruiser Force H) was a formation of cruisers of the British Royal Navy from 1907 to 1914 and then again from 1919 to 1946. The squadron was first established in 1907, replacing the North America and West Indies Station. It became a training squadron based in Home waters but which was to make three cruises annually, including to the West Indies. In April 1907 it comprised , , and . On 1 May 1912, the Fourth Cruiser Squadron was renamed the Training Squadron. With the appointment in 1913 of Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock the squadron ceased to be a training squadron and became part of the First Fleet. During World War I, the 4th Cruiser Squadron was commanded by Rear Admiral Christopher Cradock; the squadron was effectively annihilated at the Battle of Coronel 1 November 1914. From April 1919 to 1939, it was in the East Indies The East Indies (or simply the Indies), is a term used in historical narratives of the Age of Di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
_underway_c1947.jpg) |
Reserve Fleet
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; an equivalent expression in unofficial modern US naval usage is "ghost fleet". In earlier times, especially in British usage, the ships were said to be "laid up in ordinary". Overview Such ships are held in reserve against a time when it may be necessary to call them back into service. They are usually tied up in backwater areas near naval bases or shipyards in order to speed the reactivation process. They may be modified for storage during such a period, for instance by having rust-prone areas sealed off or wrapped in plastic or, in the case of sailing warships, the masts removed. While being held in the reserve fleet, ships typically have a minimal crew (known informally as a skeleton crew) to ensure that they stay in somewhat usable ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
2nd Cruiser Squadron (United Kingdom)
The 2nd Cruiser Squadron was a formation of cruisers of the British Royal Navy from 1904 to 1919 and from 1921 to 1941 and again from 1946 to 1952. History First formation The 2nd Cruiser Squadron was first formed in December, 1904 then placed under the command of Prince Louis of Battenberg in February 1905. He was then succeeded by Rear-Admiral Charles Adair on 23 February, 1907. The squadron was first assigned to the Atlantic Fleet until February 1909. In March 1909 it was transferred to the 2nd Division of the Home Fleet till April 1912. From May 1912 until July 1914 it was in the First Fleet. Between August 1914 and November 1918 it was part of the Grand Fleet. The squadron was commanded by twelve Admirals before it was disbanded on 1 February 1919. Second formation The 2nd Cruiser squadron was reformed on 14 May 1921 and was allocated to the Atlantic Fleet until 1932 when that fleet was re-designated Home Fleet. The Squadron was disbanded in 1941. Third Formation In O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
Atlantic Fleet (United Kingdom)
The Atlantic Fleet was a naval fleet of the Royal Navy. It existed for two separate periods; 1909 until 1914, and then 1919 until 1932. History On 14 December 1904 the Channel Fleet was re-styled the 'Atlantic Fleet'.National Archives records The Atlantic Fleet lasted until 1912 when rising tensions with Germany forced the Royal Navy to relook at fleet formations and the Atlantic Fleet became the 3rd Battle Squadron. The Atlantic Fleet was based at Gibraltar to reinforce either the Channel Fleet or the Mediterranean Fleet, from January 1905 to February 1907. It remained at Gibraltar until April 1912. The Atlantic Fleet was again formed after the end of World War I, when British naval forces were reorganised to reflect the changed economic and political situation in Europe. The fleet was created upon the disbandment of the Grand Fleet in April 1919, absorbing many, but not all of its elements. It was placed under a Commander-in-Chief, who for part of that year held the title of C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
|
1st Cruiser Squadron
The First Cruiser Squadron was a Royal Navy squadron of cruisers that saw service as part of the Grand Fleet during the World War I then later as part of the Mediterranean during the Interwar period and World War II it first established in 1904 and existed until 1952. History First formation The squadron was formed in December 1904 when Cruiser Squadron was re-designated the 1st Cruiser Squadron. In March 1909, then consisting of battlecruisers, it was assigned to the 1st Division of the Home Fleet until April 1912. When the First World War began, the squadron was assigned to the Mediterranean Fleet where it participated in the pursuit of the German battlecruiser and the light cruiser . It joined then Grand Fleet in January 1915 where it participated in the battles of Dogger Bank and the Battle of Jutland. It was disbanded after the battle as three of its four ships had been sunk in June 1916. In July 1917 H.M. Ships , and were detached from the 3rd Light Cruiser Squa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the first, largest, fastest, most heavily armed, or best known. Over the years, the term "flagship" has become a metaphor used in industries such as broadcasting, automobiles, education, technology, airlines, and retail to refer to their highest profile or most expensive products and locations. Naval use In common naval use, the term ''flagship'' is fundamentally a temporary designation; the flagship is wherever the admiral's flag is being flown. However, admirals have always needed additional facilities, including a meeting room large enough to hold all the captains of the fleet and a place for the admiral's staff to make plans and draw up orders. Historically, only larger ships could accommodate such requirements. The term was also used b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Ship Naming And Launching
Ceremonial ship launching involves the performance of ceremonies associated with the process of transferring a vessel to the water. It is a nautical tradition in many cultures, dating back thousands of years, to accompany the physical process with ceremonies which have been observed as public celebration and a solemn blessing, usually but not always, in association with the launch itself. Ship launching imposes stresses on the ship not met during normal operation and, in addition to the size and weight of the vessel, represents a considerable engineering challenge as well as a public spectacle. The process also involves many traditions intended to invite good luck, such as christening by breaking a sacrificial bottle of champagne over the bow as the ship is named aloud and launched. Methods There are three principal methods of conveying a new ship from building site to water, only two of which are called "launching". The oldest, most familiar, and most widely used is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by Kingdom of England, English and Kingdom of Scotland, Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Kingdom of France, France. The modern Royal Navy traces its origins to the early 16th century; the oldest of the British Armed Forces, UK's armed services, it is consequently known as the Senior Service. From the middle decades of the 17th century, and through the 18th century, the Royal Navy vied with the Dutch Navy and later with the French Navy for maritime supremacy. From the mid 18th century, it was the world's most powerful navy until the World War II, Second World War. The Royal Navy played a key part in establishing and defending the British Empire, and four Imperial fortress colonies and a string of imperial bases and coaling stations secured the Royal Navy's ability to assert naval superiority ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
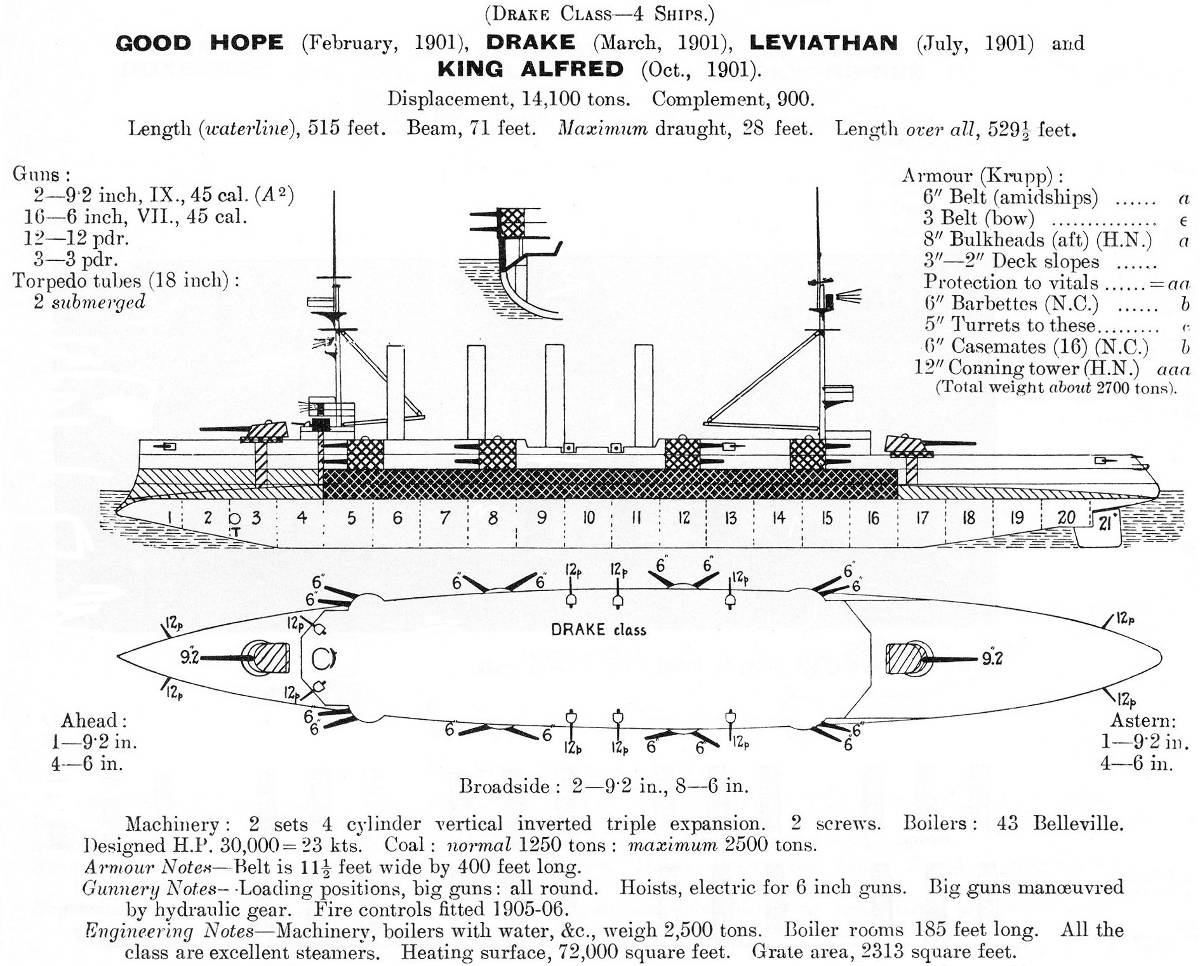 |
Drake Class Cruiser
The ''Drake'' class was a four-ship class of armoured cruisers built around 1900 for the Royal Navy. Design and description The ''Drake'' class were enlarged and improved versions of the designed by Sir William White, Chief Constructor of the Royal Navy, to counter the new French armoured cruiser . The ships had an overall length of , a beam of and a deep draught of . They displaced and proved to be good seaboats in service. Their crew consisted of 900 officers and other ranks. The ships were powered by two 4-cylinder triple-expansion steam engines, each driving one shaft, using steam provided by 43 Belleville boilers. The engines produced a total of and the ''Drake''s easily reached their designed speed of .Chesneau & Kolesnik, p. 69 They carried a maximum of of coal.Friedman 2012, p. 336 The main armament of the ''Drake''-class ships consisted of two breech-loading (BL) Mk X guns in single gun turrets, one each fore and aft of the superstructure. They fired shell ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |