Gondwanan distribution on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Gondwana () was a large
Gondwana () was a large
 The continent of Gondwana was named by the Austrian scientist
The continent of Gondwana was named by the Austrian scientist
 The assembly of Gondwana was a protracted process during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic, which remains incompletely understood because of the lack of paleo-magnetic data. Several orogenies, collectively known as the
The assembly of Gondwana was a protracted process during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic, which remains incompletely understood because of the lack of paleo-magnetic data. Several orogenies, collectively known as the 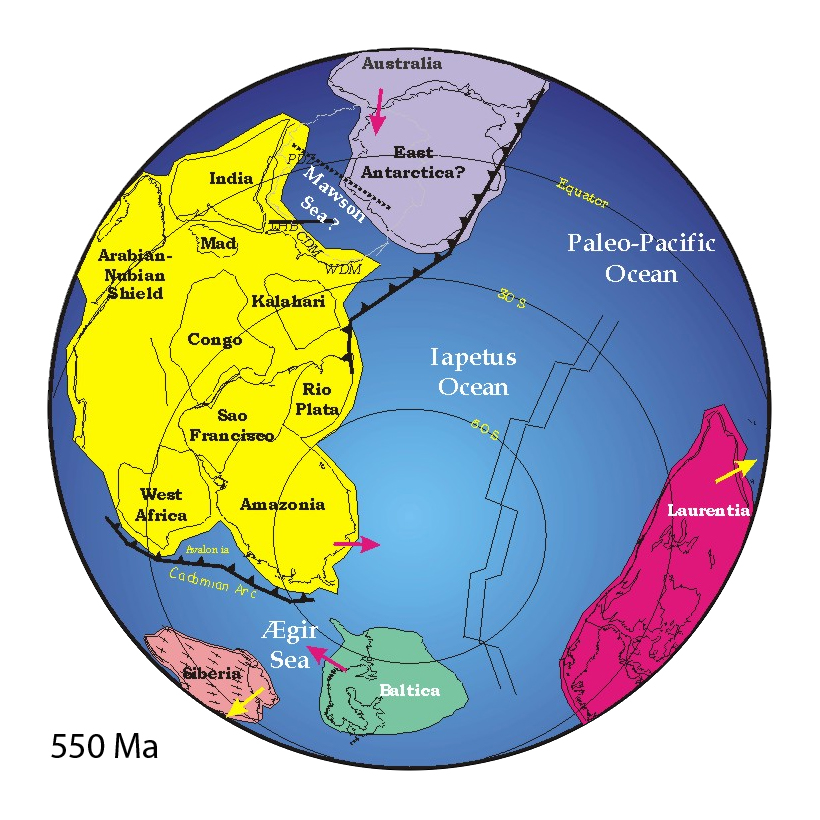 The continent Australia/
The continent Australia/
 Gondwana and
Gondwana and
 The adjective "Gondwanan" is in common use in
The adjective "Gondwanan" is in common use in
 The
The
Graphical subjects dealing with Tectonics and Paleontology
The Gondwana Map Project
* {{Authority control Historical continents Former supercontinents Biogeography Paleozoic paleogeography Mesozoic paleogeography Geology of Africa Geology of Antarctica Geology of Asia Geology of India Geology of Australia Geology of South America Prehistory of Antarctica Paleozoic Africa Paleozoic Antarctica Paleozoic Asia Paleozoic South America Mesozoic Africa Mesozoic Antarctica Mesozoic Asia Mesozoic South America
 Gondwana () was a large
Gondwana () was a large landmass
A landmass, or land mass, is a large region or area of land. The term is often used to refer to lands surrounded by an ocean or sea, such as a continent or a large island. In the field of geology, a landmass is a defined section of continental ...
, often referred to as a supercontinent
In geology, a supercontinent is the assembly of most or all of Earth's continent, continental blocks or cratons to form a single large landmass. However, some geologists use a different definition, "a grouping of formerly dispersed continents", ...
, that formed during the late Neoproterozoic
The Neoproterozoic Era is the unit of geologic time from 1 billion to 538.8 million years ago.
It is the last era of the Precambrian Supereon and the Proterozoic Eon; it is subdivided into the Tonian, Cryogenian, and Ediacaran periods. It is ...
(about 550 million years ago) and began to break up during the Jurassic period
The Jurassic ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of ...
(about 180 million years ago). The final stages of break-up, involving the separation of Antarctica from South America (forming the Drake Passage
The Drake Passage (referred to as Mar de Hoces Hoces Sea"in Spanish-speaking countries) is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atla ...
) and Australia, occurred during the Paleogene
The Paleogene ( ; British English, also spelled Palaeogene or Palæogene; informally Lower Tertiary or Early Tertiary) is a geologic period, geologic period and system that spans 43 million years from the end of the Cretaceous Period million yea ...
. Gondwana was not considered a supercontinent by the earliest definition, since the landmasses of Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, ...
, Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
, and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
were separated from it. To differentiate it from the Indian region of the same name (see ), it is also commonly called Gondwanaland.
Gondwana was formed by the accretion of several craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s. Eventually, Gondwana became the largest piece of continental crust
Continental crust is the layer of igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks that forms the geological continents and the areas of shallow seabed close to their shores, known as continental shelves. This layer is sometimes called ''sial'' be ...
of the Palaeozoic Era, covering an area of about , about one-fifth of the Earth's surface. During the Carboniferous Period
The Carboniferous ( ) is a Period (geology), geologic period and System (stratigraphy), system of the Paleozoic that spans 60 million years from the end of the Devonian Period million years ago (Myr, Mya), to the beginning of the Permian Period, ...
, it merged with Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
to form a larger supercontinent called Pangaea
Pangaea or Pangea () was a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras. It assembled from the earlier continental units of Gondwana, Euramerica and Siberia during the Carboniferous approximately 335 million y ...
. Gondwana (and Pangaea) gradually broke up during the Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretaceo ...
Era. The remnants of Gondwana make up around two-thirds of today's continental area, including South America
South America is a continent entirely in the Western Hemisphere and mostly in the Southern Hemisphere, with a relatively small portion in the Northern Hemisphere at the northern tip of the continent. It can also be described as the southe ...
, Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, Antarctica
Antarctica () is Earth's southernmost and least-populated continent. Situated almost entirely south of the Antarctic Circle and surrounded by the Southern Ocean, it contains the geographic South Pole. Antarctica is the fifth-largest contine ...
, Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
, Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., ...
, Arabia
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, and the Indian Subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
.
The formation of Gondwana began with the East African Orogeny
The East African Orogeny (EAO) is the main stage in the Neoproterozoic assembly of East and West Gondwana (Australia–India–Antarctica and Africa–South America) along the Mozambique Belt.
Gondwana assembly
The notion that Gondwana was asse ...
, the collision of India and Madagascar with East Africa, and was completed with the overlapping Brasiliano and Kuunga orogenies, the collision of South America with Africa, and the addition of Australia and Antarctica, respectively.
Regions that were part of Gondwana shared floral and zoological elements that persist to the present day.
Name
 The continent of Gondwana was named by the Austrian scientist
The continent of Gondwana was named by the Austrian scientist Eduard Suess
Eduard Suess (; 20 August 1831 - 26 April 1914) was an Austrian geologist and an expert on the geography of the Alps. He is responsible for hypothesising two major former geographical features, the supercontinent Gondwana (proposed in 1861) and t ...
, after the region in central India of the same name, which is derived from Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
for "forest of the Gonds
The Gondi (Gōndi) or Gond or Koitur are a Dravidian ethno-linguistic group. They are one of the largest tribal groups in India. They are spread over the states of Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Chhattisgarh, Uttar Pradesh, Telangana, Andhra Prad ...
". The name had been previously used in a geological context, first by H.B. Medlicott in 1872, from which the Gondwana sedimentary sequences (Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleoz ...
-Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest period ...
) are also described.
Some scientists prefer the term "Gondwanaland" to make a clear distinction between the region and the supercontinent.
Formation
 The assembly of Gondwana was a protracted process during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic, which remains incompletely understood because of the lack of paleo-magnetic data. Several orogenies, collectively known as the
The assembly of Gondwana was a protracted process during the Neoproterozoic and Paleozoic, which remains incompletely understood because of the lack of paleo-magnetic data. Several orogenies, collectively known as the Pan-African orogeny
The Pan-African orogeny was a series of major Neoproterozoic orogenic events which related to the formation of the supercontinents Gondwana and Pannotia about 600 million years ago. This orogeny is also known as the Pan-Gondwanan or Saldanian Oro ...
, caused the continental fragments of a much older supercontinent, Rodinia
Rodinia (from the Russian родина, ''rodina'', meaning "motherland, birthplace") was a Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic supercontinent that assembled 1.26–0.90 billion years ago and broke up 750–633 million years ago.
were probably ...
, to amalgamate. One of those orogenic belts, the Mozambique Belt
The Mozambique Belt is a band in the earth's crust that extends from East Antarctica through East Africa up to the Arabian-Nubian Shield. It formed as a suture between plates during the Pan-African orogeny, when Gondwana was formed.
The Mozambiq ...
, formed and was originally interpreted as the suture between East (India, Madagascar, Antarctica, and Australia) and West Gondwana (Africa and South America). Three orogenies were recognised during the 1990s: the East African Orogeny
The East African Orogeny (EAO) is the main stage in the Neoproterozoic assembly of East and West Gondwana (Australia–India–Antarctica and Africa–South America) along the Mozambique Belt.
Gondwana assembly
The notion that Gondwana was asse ...
() and Kuunga orogeny
The Kuunga orogeny (from Swahili, "to unite") was an orogeny that occurred in South-east Africa during the Ediacaran and Cambrian. Composed of three separate orogenic belts (Damara, Zambesi, and Lurio) that are slightly younger than the East Afr ...
(including the Malagasy Orogeny in southern Madagascar) (), the collision between East Gondwana and East Africa in two steps, and the Brasiliano orogeny
Brasiliano orogeny or Brasiliano cycle ( pt, Orogênese Brasiliana and ''Ciclo Brasiliano'') refers to a series of orogenies of Neoproterozoic age exposed chiefly in Brazil but also in other parts of South America. The Brasiliano orogeny is a reg ...
(), the successive collision between South American and African craton
A craton (, , or ; from grc-gre, κράτος "strength") is an old and stable part of the continental lithosphere, which consists of Earth's two topmost layers, the crust and the uppermost mantle. Having often survived cycles of merging and ...
s.
The last stages of Gondwanan assembly overlapped with the opening of the Iapetus Ocean between Laurentia
Laurentia or the North American Craton is a large continental craton that forms the ancient geological core of North America. Many times in its past, Laurentia has been a separate continent, as it is now in the form of North America, althoug ...
and western Gondwana. During this interval, the Cambrian explosion
The Cambrian explosion, Cambrian radiation, Cambrian diversification, or the Biological Big Bang refers to an interval of time approximately in the Cambrian Period when practically all major animal phyla started appearing in the fossil recor ...
occurred. Laurentia was docked against the western shores of a united Gondwana for a brief period near the Precambrian/Cambrian boundary, forming the short-lived and still disputed supercontinent Pannotia
Pannotia (from Greek: '' pan-'', "all", '' -nótos'', "south"; meaning "all southern land"), also known as the Vendian supercontinent, Greater Gondwana, and the Pan-African supercontinent, was a relatively short-lived Neoproterozoic supercontinent ...
.
The Mozambique Ocean
The Mozambique Belt is a band in the earth's crust that extends from East Antarctica through East Africa up to the Arabian-Nubian Shield. It formed as a suture between plates during the Pan-African orogeny, when Gondwana was formed.
The Moz ...
separated the Congo–Tanzania
Tanzania (; ), officially the United Republic of Tanzania ( sw, Jamhuri ya Muungano wa Tanzania), is a country in East Africa within the African Great Lakes region. It borders Uganda to the north; Kenya to the northeast; Comoro Islands and ...
–Bangweulu Block
The Bangweulu Block is a cratonic unit that forms part of the Congo craton of central Africa. The Bangweulu Block however consists of Palaeoproterozoic granitoids and volcanics, and is overlain by a Palaeoproterozoic continental sedimentary succes ...
of central Africa from Neoproterozoic India (India, the Antongil Block in far eastern Madagascar, the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
, and the Napier and Rayner Complexes in East Antarctica
East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying on the Indian Ocean side of the continent, separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It lies almost ...
). The Azania
Azania ( grc, Ἀζανία) is a name that has been applied to various parts of southeastern tropical Africa. In the Roman period and perhaps earlier, the toponym referred to a portion of the Southeast Africa coast extending from northern Keny ...
continent (much of central Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
, the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
and parts of Yemen
Yemen (; ar, ٱلْيَمَن, al-Yaman), officially the Republic of Yemen,, ) is a country in Western Asia. It is situated on the southern end of the Arabian Peninsula, and borders Saudi Arabia to the Saudi Arabia–Yemen border, north and ...
and Arabia) was an island in the Mozambique Ocean.
 The continent Australia/
The continent Australia/Mawson
Sir Douglas Mawson OBE FRS FAA (5 May 1882 – 14 October 1958) was an Australian geologist, Antarctic explorer, and academic. Along with Roald Amundsen, Robert Falcon Scott, and Sir Ernest Shackleton, he was a key expedition leader durin ...
was still separated from India, eastern Africa, and Kalahari by , when most of western Gondwana had already been amalgamated. By 550 Ma, India had reached its Gondwanan position, which initiated the Kuunga orogeny (also known as the Pinjarra orogeny). Meanwhile, on the other side of the newly forming Africa, Kalahari collided with Congo and Rio de la Plata which closed the Adamastor Ocean
The Adamastor Ocean was a "proto-Atlantic" ocean that formed with the break-up of the Rodinia supercontinent 780-750 . It separated the Río de la Plata Craton from the Congo Craton. The inversion of the Adamastor Ocean began about 640 ...
. 540–530 Ma, the closure of the Mozambique Ocean brought India next to Australia–East Antarctica, and both North and South China were in proximity to Australia.
As the rest of Gondwana formed, a complex series of orogenic events assembled the eastern parts of Gondwana (eastern Africa, Arabian-Nubian Shield, Seychelles, Madagascar, India, Sri Lanka, East Antarctica, and Australia) . First the Arabian-Nubian Shield collided with eastern Africa (in the Kenya-Tanzania region) in the East African Orogeny . Then Australia and East Antarctica were merged with the remaining Gondwana in the Kuunga Orogeny.
The later Malagasy orogeny at about 550–515 Mya affected Madagascar, eastern East Africa and southern India. In it, Neoproterozoic India collided with the already combined Azania and Congo–Tanzania–Bangweulu Block, suturing along the Mozambique Belt.
The Terra Australis Orogen developed along Gondwana's western, southern, and eastern margins. Proto-Gondwanan Cambrian arc belts from this margin have been found in eastern Australia, Tasmania, New Zealand, and Antarctica. Though these belts formed a continuous arc chain, the direction of subduction was different between the Australian-Tasmanian and New Zealand-Antarctica arc segments.
Peri-Gondwana development: Paleozoic rifts and accretions
Many terranes were accreted to Eurasia during Gondwana's existence, but the Cambrian or Precambrian origin of many of these terranes remains uncertain. For example, some Palaeozoic terranes and microcontinents that now make up Central Asia, often called the "Kazakh" and "Mongolian terranes", were progressively amalgamated into the continentKazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
in the Late Silurian. Whether these blocks originated on the shores of Gondwana is not known.
In the Early Palaeozoic, the Armorican terrane
The Armorican terrane, Armorican terrane assemblage, or simply Armorica, was a microcontinent or group of continental fragments that rifted away from Gondwana towards the end of the Silurian and collided with Laurussia towards the end of the Car ...
, which today form large parts of France, was part of either Peri-Gondwana or core Gondwana; the Rheic Ocean closed in front of it and the Palaeo-Tethys Ocean opened behind it. Precambrian rocks from the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, defi ...
suggest that it, too, formed part of core Gondwana before its detachment as an orocline
An orocline — from the Greek words for "mountain" and "to bend" — is a bend or curvature of an orogenic (mountain building) belt imposed after it was formed. The term was introduced by S. Warren Carey in 1955 in a paper setting forth how comp ...
in the Variscan orogeny
The Variscan or Hercynian orogeny was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea.
Nomenclature
The name ''Variscan'', comes f ...
close to the Carboniferous–Permian boundary.
South-east Asia was made of Gondwanan and Cathaysia
Cathaysia was a microcontinent or a group of terranes that rifted off Gondwana during the Late Paleozoic. They mostly correspond to modern territory of China, which were split into the North China and South China blocks.
Terminology
The terms " ...
n continental fragments that were assembled during the Mid-Palaeozoic and Cenozoic. This process can be divided into three phases of rifting along Gondwana's northern margin: first, in the Devonian, North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating Direction (geometry), direction or geography.
Etymology
T ...
and South China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
, together with Tarim and Quidam
''Quidam'' ( ) was the ninth stage show produced by Cirque du Soleil. It premiered in April 1996 and has been watched by millions of spectators around the world. ''Quidam'' originated as a big-top show in Montreal and was converted into an arena ...
(north-western China) rifted, opening the Palaeo-Tethys behind them. These terranes accreted to Asia during Late Devonian and Permian. Second, in the Late Carboniferous to Early Permian, Cimmerian terranes opened Meso-Tethys Ocean; Sibumasu and Qiangtang were added to south-east Asia during Late Permian
Late may refer to:
* LATE, an acronym which could stand for:
** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia
** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law
** Local average treatment effect, ...
and Early Jurassic. Third, in the Late Triassic to Late Jurassic, Lhasa
Lhasa (; Lhasa dialect: ; bo, text=ལྷ་ས, translation=Place of Gods) is the urban center of the prefecture-level city, prefecture-level Lhasa (prefecture-level city), Lhasa City and the administrative capital of Tibet Autonomous Regio ...
, West Burma, Woyla terranes opened the Neo-Tethys Ocean; Lhasa collided with Asia during the Early Cretaceous, and West Burma and Woyla during the Late Cretaceous.
Gondwana's long, northern margin remained a mostly passive margin throughout the Palaeozoic. The Early Permian opening of the Neo-Tethys Ocean along this margin produced a long series of terranes, many of which were and still are being deformed in the Himalaya Orogeny. These terranes are, from Turkey to north-eastern India: the Taurides in southern Turkey; the Lesser Caucasus Terrane in Georgia; the Sanand, Alborz, and Lut terranes in Iran; the Mangysglak or Kopetdag Terrane in the Caspian Sea; the Afghan Terrane; the Karakorum Terrane in northern Pakistan; and the Lhasa and Qiangtang terranes in Tibet. The Permian–Triassic widening of the Neo-Tethys pushed all these terranes across the Equator and over to Eurasia.
Southwestern accretions
During the Neoproterozoic to Palaeozoic phase of the Terra Australis Orogen, a series of terranes were rafted from the proto-Andean margin when the Iapteus Ocean opened, to be added back to Gondwana during the closure of that ocean. During the Paleozoic, some blocks which helped to form parts of theSouthern Cone
The Southern Cone ( es, Cono Sur, pt, Cone Sul) is a geographical and cultural subregion composed of the southernmost areas of South America, mostly south of the Tropic of Capricorn. Traditionally, it covers Argentina, Chile, and Uruguay, bou ...
of South America, include a piece transferred from Laurentia when the west edge of Gondwana scraped against southeast Laurentia in the Ordovician
The Ordovician ( ) is a geologic period and System (geology), system, the second of six periods of the Paleozoic Era (geology), Era. The Ordovician spans 41.6 million years from the end of the Cambrian Period million years ago (Mya) to the start ...
. This is the Cuyania
The Precordillera Terrane or Cuyania was an ancient microcontinent or terrane whose history affected many of the older rocks of Cuyo in Argentina. It was separated by oceanic crust from the Chilenia terrane which accreted into it at ~420-390 Ma w ...
or Precordillera terrane
In geology, a terrane (; in full, a tectonostratigraphic terrane) is a crust fragment formed on a tectonic plate (or broken off from it) and accreted or " sutured" to crust lying on another plate. The crustal block or fragment preserves its own ...
of the Famatinian orogeny
The Famatinian orogeny ( es, Orogenia de Famatina) is an orogeny that predates the rise of the Andes and that took place in what is now western South America during the Paleozoic, leading to the formation of the Famatinian orogen also known as ...
in northwest Argentina which may have continued the line of the Appalachians
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
southwards. Chilenia terrane accreted later against Cuyania. The collision of the Patagonian terrane with the southwestern Gondwanan occurred in the late Paleozoic. Subduction-related igneous rocks from beneath the North Patagonian Massif
The North Patagonian Massif or Somún Cura Massif (Spanish language, Spanish: ''Macizo Norpatagónico'', ''Macizo Nordpatagónico'' or ''Macizo de Somún Cura'') is a massif in northern Patagonia located in the Argentine provinces of Río Negro Pro ...
have been dated at 320–330 million years old, indicating that the subduction process initiated in the early Carboniferous. This was relatively short lived (lasting about 20 million years), and initial contact of the two landmasses occurred in the mid-Carboniferous, with broader collision during the early Permian. In the Devonian, an island arc
Island arcs are long chains of active volcanoes with intense seismic activity found along convergent tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the mantle alon ...
named Chaitenia accreted to Patagonia in what is now south-central Chile.
Gondwana as part of Pangaea: Late Paleozoic to Early Mesozoic
Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
formed the Pangaea supercontinent during the Carboniferous. Pangaea began to break up in the Mid-Jurassic when the Central Atlantic opened.
In the western end of Pangaea, the collision between Gondwana and Laurasia closed the Rheic and Palaeo-Tethys oceans. The obliquity of this closure resulted in the docking of some northern terranes in the Marathon
The marathon is a long-distance foot race with a distance of , usually run as a road race, but the distance can be covered on trail routes. The marathon can be completed by running or with a run/walk strategy. There are also wheelchair div ...
, Ouachita, Alleghanian, and Variscan orogenies, respectively. Southern terranes, such as Chortis and Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
, on the other hand, remained largely unaffected by the collision along the southern shores of Laurentia. Some Peri-Gondwanan terranes, such as Yucatán
Yucatán (, also , , ; yua, Yúukatan ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Yucatán,; yua, link=no, Xóot' Noj Lu'umil Yúukatan. is one of the 31 states which comprise the political divisions of Mexico, federal entities of Mexico. I ...
and Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
, were buffered from collisions by major promontories. Other terranes, such as Carolina and Meguma, were directly involved in the collision. The final collision resulted in the Variscan-Appalachian Mountains
The Appalachian Mountains, often called the Appalachians, (french: Appalaches), are a system of mountains in eastern to northeastern North America. The Appalachians first formed roughly 480 million years ago during the Ordovician Period. They ...
, stretching from present-day Mexico to southern Europe. Meanwhile, Baltica
Baltica is a paleocontinent that formed in the Paleoproterozoic and now constitutes northwestern Eurasia, or Europe north of the Trans-European Suture Zone and west of the Ural Mountains.
The thick core of Baltica, the East European Craton, ...
collided with Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
and Kazakhstania
Kazakhstania ( kk, Qazaqstaniya), the Kazakh terranes, or the Kazakhstan Block, is a geological region in Central Asia which consists of the area roughly centered on Lake Balkhash, north and east of the Aral Sea, south of the Siberian craton and ...
which resulted in the Uralian orogeny
The Uralian orogeny refers to the long series of linear deformation and mountain building events that raised the Ural Mountains, starting in the Late Carboniferous and Permian periods of the Palaeozoic Era, 323–299 and 299–251 million years ag ...
and Laurasia
Laurasia () was the more northern of two large landmasses that formed part of the Pangaea supercontinent from around ( Mya), the other being Gondwana. It separated from Gondwana (beginning in the late Triassic period) during the breakup of Pan ...
. Pangaea was finally amalgamated in the Late Carboniferous-Early Permian, but the oblique forces continued until Pangaea began to rift in the Triassic.
In the eastern end, collisions occurred slightly later. The North China
North China, or Huabei () is a List of regions of China, geographical region of China, consisting of the provinces of Beijing, Tianjin, Hebei, Shanxi and Inner Mongolia. Part of the larger region of Northern China (''Beifang''), it lies north ...
, South China
South China () is a geographical and cultural region that covers the southernmost part of China. Its precise meaning varies with context. A notable feature of South China in comparison to the rest of China is that most of its citizens are not n ...
, and Indochina
Mainland Southeast Asia, also known as the Indochinese Peninsula or Indochina, is the continental portion of Southeast Asia. It lies east of the Indian subcontinent and south of Mainland China and is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the west an ...
blocks rifted from Gondwana during the middle Paleozoic and opened the Proto-Tethys Ocean
The Proto-Tethys or Theic Ocean was an ancient ocean that existed from the latest Ediacaran to the Carboniferous (550–330 Ma).
History of concept
The name "Proto-Tethys" has been used inconsistently for several concepts for a supposed predecess ...
. North China docked with Mongolia and Siberia during the Carboniferous–Permian, followed by South China. The Cimmerian
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
blocks then rifted from Gondwana to form the Palaeo-Thethys and Neo-Tethys oceans in the Late Carboniferous, and docked with Asia during the Triassic and Jurassic. Western Pangaea began to rift while the eastern end was still being assembled.
The formation of Pangaea and its mountains had a tremendous impact on global climate and sea levels, which resulted in glaciations and continent-wide sedimentation. In North America, the base of the Absaroka sequence
The Absaroka sequence was a cratonic sequence that extended from the end of the Mississippian through the Permian periods. It is the unconformity between this sequence and the preceding Kaskaskia that divides the Carboniferous into the Mississip ...
coincides with the Alleghanian and Ouachita orogenies and are indicative of a large-scale change in the mode of deposition far away from the Pangaean orogenies. Ultimately, these changes contributed to the Permian–Triassic extinction event
The Permian–Triassic (P–T, P–Tr) extinction event, also known as the Latest Permian extinction event, the End-Permian Extinction and colloquially as the Great Dying, formed the boundary between the Permian and Triassic geologic periods, as ...
and left large deposits of hydrocarbons, coal, evaporite, and metals.
The break-up of Pangaea began with the Central Atlantic magmatic province
The Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the ...
(CAMP) between South America, Africa, North America, and Europe. CAMP covered more than seven million square kilometres over a few million years, reached its peak at , and coincided with the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event, often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, , and is one of the top five major extinction events of the Phanerozoic eon, profoundly affect ...
. The reformed Gondwanan continent was not precisely the same as that which had existed before Pangaea formed; for example, most of Florida
Florida is a state located in the Southeastern region of the United States. Florida is bordered to the west by the Gulf of Mexico, to the northwest by Alabama, to the north by Georgia, to the east by the Bahamas and Atlantic Ocean, and to ...
and southern Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
and Alabama
(We dare defend our rights)
, anthem = "Alabama (state song), Alabama"
, image_map = Alabama in United States.svg
, seat = Montgomery, Alabama, Montgomery
, LargestCity = Huntsville, Alabama, Huntsville
, LargestCounty = Baldwin County, Al ...
is underlain by rocks that were originally part of Gondwana, but this region stayed attached to North America when the Central Atlantic opened.
Break-up
Mesozoic
Antarctica, the centre of the supercontinent, shared boundaries with all other Gondwana continents and the fragmentation of Gondwana propagated clockwise around it. The break-up was the result of the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar igneous province, one of the Earth's most extensivelarge igneous province
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive (sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation ...
s (LIP) , but the oldest magnetic anomalies
In geophysics, a magnetic anomaly is a local variation in the Earth's magnetic field resulting from variations in the chemistry or magnetism of the rocks. Mapping of variation over an area is valuable in detecting structures obscured by overlying ...
between South America, Africa, and Antarctica are found in what is now the southern Weddell Sea
The Weddell Sea is part of the Southern Ocean and contains the Weddell Gyre. Its land boundaries are defined by the bay formed from the coasts of Coats Land and the Antarctic Peninsula. The easternmost point is Cape Norvegia at Princess Martha ...
where initial break-up occurred during the Jurassic .
Opening of western Indian Ocean
Gondwana began to break up in the earlyJurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
following the extensive and fast emplacement of the Karoo-Ferrar
The Karoo and Ferrar Large Igneous Provinces (LIPs) are two large igneous provinces in Southern Africa and Antarctica respectively, collectively known as the Karoo-Ferrar, Gondwana,E.g. or Southeast African LIP, associated with the initial break-u ...
flood basalt
A flood basalt (or plateau basalt) is the result of a giant volcanic eruption or series of eruptions that covers large stretches of land or the ocean floor with basalt lava. Many flood basalts have been attributed to the onset of a hotspot reach ...
s . Before the Karoo plume initiated rifting between Africa and Antarctica, it separated a series of smaller continental blocks from Gondwana's southern, Proto-Pacific margin (along what is now the Transantarctic Mountains
The Transantarctic Mountains (abbreviated TAM) comprise a mountain range of uplifted (primarily sedimentary rock, sedimentary) rock in Antarctica which extend, with some interruptions, across the continent from Cape Adare in northern Victoria La ...
): the Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctic ...
, Marie Byrd Land
Marie Byrd Land (MBL) is an unclaimed region of Antarctica. With an area of , it is the largest unclaimed territory on Earth. It was named after the wife of American naval officer Richard E. Byrd, who explored the region in the early 20th centur ...
, Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., ...
, and Thurston Island
Thurston Island is an ice-covered, glacially dissected island, long, wide and in area, lying a short way off the northwest end of Ellsworth Land, Antarctica. It is the third-largest island of Antarctica, after Alexander Island and Berkner Isl ...
; the Falkland Islands
The Falkland Islands (; es, Islas Malvinas, link=no ) is an archipelago in the South Atlantic Ocean on the Patagonian Shelf. The principal islands are about east of South America's southern Patagonian coast and about from Cape Dubouzet ...
and Ellsworth–Whitmore Mountains The Ellsworth–Whitmore Mountains (EWM) is the innermost of the four or five allochthonous terranes, or tectonic blocks, that form West Antarctica. EWM was located in an embayment off Natal, South Africa, before the break-up of Gondwana during w ...
(in Antarctica) were rotated 90° in opposite directions; and South America south of the Gastre Fault (often referred to as Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and gl ...
) was pushed westward. The history of the Africa-Antarctica break-up can be studied in great detail in the fracture zones and magnetic anomalies flanking the Southwest Indian Ridge
The Southwest Indian Ridge (SWIR) is a mid-ocean ridge located along the floors of the south-west Indian Ocean and south-east Atlantic Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary separating the Somali Plate to the north from the Antarctic Plate t ...
.
The Madagascar block and the Mascarene Plateau
The Mascarene Plateau is a submarine plateau in the Indian Ocean, north and east of Madagascar. The plateau extends approximately , from Seychelles in the north to Réunion in the south. The plateau covers an area of over of shallow water, wi ...
, stretching from the Seychelles
Seychelles (, ; ), officially the Republic of Seychelles (french: link=no, République des Seychelles; Creole: ''La Repiblik Sesel''), is an archipelagic state consisting of 115 islands in the Indian Ocean. Its capital and largest city, V ...
to Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island ...
, were broken off India, causing Madagascar
Madagascar (; mg, Madagasikara, ), officially the Republic of Madagascar ( mg, Repoblikan'i Madagasikara, links=no, ; french: République de Madagascar), is an island country in the Indian Ocean, approximately off the coast of East Africa ...
and Insular India
The term Insular India refers to the isolated landmass which became the Indian subcontinent. Across the latter stages of the Cretaceous and most of the Paleocene, following the breakup of Gondwana, the Indian subcontinent remained an isolated land ...
to be separate landmasses: elements of this break-up nearly coincide with the Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
. The India–Madagascar–Seychelles separations appear to coincide with the eruption of the Deccan basalts, whose eruption site may survive as the Réunion hotspot
The Réunion hotspot is a volcanic hotspot which currently lies under the island of Réunion in the Indian Ocean. The Chagos-Laccadive Ridge and the southern part of the Mascarene Plateau are volcanic traces of the Réunion hotspot.
The hotspo ...
. The Seychelles and the Maldives
Maldives (, ; dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖެ, translit=Dhivehi Raajje, ), officially the Republic of Maldives ( dv, ދިވެހިރާއްޖޭގެ ޖުމްހޫރިއްޔާ, translit=Dhivehi Raajjeyge Jumhooriyyaa, label=none, ), is an archipelag ...
are now separated by the Central Indian Ridge
The Central Indian Ridge (CIR) is a north–south-trending mid-ocean ridge in the western Indian Ocean.
Geological setting
The morphology of the CIR is characteristic of slow to intermediate ridges. The axial valley is 500–1000 m deep; ...
.
During the initial break-up in the Early Jurassic a marine transgression
A marine transgression is a geologic event during which sea level rises relative to the land and the shoreline moves toward higher ground, which results in flooding. Transgressions can be caused by the land sinking or by the ocean basins filling ...
swept over the Horn of Africa
The Horn of Africa (HoA), also known as the Somali Peninsula, is a large peninsula and geopolitical region in East Africa.Robert Stock, ''Africa South of the Sahara, Second Edition: A Geographical Interpretation'', (The Guilford Press; 2004), ...
covering Triassic planation surface
In geology and geomorphology a planation surface is a large-scale surface that is almost flat with the possible exception of some residual hills. The processes that form planation surfaces are labelled collectively planation and are exogenic (chi ...
s with sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicates) ...
, limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
, shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
, marl
Marl is an earthy material rich in carbonate minerals, clays, and silt. When hardened into rock, this becomes marlstone. It is formed in marine or freshwater environments, often through the activities of algae.
Marl makes up the lower part o ...
s and evaporite
An evaporite () is a water-soluble sedimentary mineral deposit that results from concentration and crystallization by evaporation from an aqueous solution. There are two types of evaporite deposits: marine, which can also be described as ocea ...
s.
Opening of eastern Indian Ocean
East Gondwana, comprising Antarctica, Madagascar, India, and Australia, began to separate from Africa. East Gondwana then began to break up when India moved northwest from Australia-Antarctica. TheIndian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began mov ...
and the Australian Plate
The Australian Plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately when India broke ...
are now separated by the Capricorn Plate and its diffuse boundaries. During the opening of the Indian Ocean, the Kerguelen hotspot
The Kerguelen hotspot is a volcanic hotspot at the Kerguelen Plateau in the Southern Indian Ocean. The Kerguelen hotspot has produced basaltic lava for about 130 million years and has also produced the Kerguelen Islands, Naturaliste Plateau, Hear ...
first formed the Kerguelen Plateau
The Kerguelen Plateau (, ), also known as the Kerguelen–Heard Plateau, is an oceanic plateau and a large igneous province (LIP) located on the Antarctic Plate, in the southern Indian Ocean. It is about to the southwest of Australia and is ...
on the Antarctic Plate
The Antarctic Plate is a tectonic plate containing the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau, and some remote islands in the Southern Ocean and other surrounding oceans. After breakup from Gondwana (the southern part of the superconti ...
and then the Ninety East Ridge
The Ninety East Ridge (also rendered as Ninetyeast Ridge, 90E Ridge or 90°E Ridge) is a mid-ocean ridge on the Indian Ocean floor named for its near-parallel strike along the 90th meridian at the center of the Eastern Hemisphere. It is approxima ...
on the Indian Plate
The Indian Plate (or India Plate) is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, the Indian Plate broke away from the other fragments of Gondwana , began mov ...
at . The Kerguelen Plateau and the Broken Ridge
The Broken Ridge or Broken Plateau is an oceanic plateau in the south-eastern Indian Ocean. The Broken Ridge once formed a large igneous province (LIP) together with the Kerguelen Plateau. When Australia and Antarctica started to separate, the ...
, the southern end of the Ninety East Ridge, are now separated by the Southeast Indian Ridge
The Southeast Indian Ridge (SEIR) is a mid-ocean ridge in the southern Indian Ocean. A divergent tectonic plate boundary stretching almost between the Rodrigues Triple Junction () in the Indian Ocean and the Macquarie Triple Junction () in the ...
.
Separation between Australia and East Antarctica
East Antarctica, also called Greater Antarctica, constitutes the majority (two-thirds) of the Antarctic continent, lying on the Indian Ocean side of the continent, separated from West Antarctica by the Transantarctic Mountains. It lies almost ...
began with seafloor spreading occurring . A shallow seaway developed over the South Tasman Rise during the Early Cenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
and as oceanic crust
Oceanic crust is the uppermost layer of the oceanic portion of the tectonic plates. It is composed of the upper oceanic crust, with pillow lavas and a dike complex, and the lower oceanic crust, composed of troctolite, gabbro and ultramafic cumu ...
started to separate the continents during the Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene' ...
global ocean temperature dropped significantly. A dramatic shift from arc- to rift magmatism separated Zealandia
Zealandia (pronounced ), also known as (Māori) or Tasmantis, is an almost entirely submerged mass of continental crust that subsided after breaking away from Gondwanaland 83–79 million years ago.Gurnis, M., Hall, C.E., and Lavier, L.L., ...
, including New Zealand
New Zealand ( mi, Aotearoa ) is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and over 700 smaller islands. It is the sixth-largest island count ...
, the Campbell Plateau
The Campbell Plateau is a large oceanic plateau south of New Zealand and the Chatham Rise. It originated in the Gondwanan breakup and is part of Zealandia, a largely submerged continent. The above sea level parts of the plateau — the Bounty ...
, Chatham Rise
The Chatham Rise is an area of ocean floor to the east of New Zealand, forming part of the Zealandia continent. It stretches for some from near the South Island in the west, to the Chatham Islands in the east. It is New Zealand's most productiv ...
, Lord Howe Rise
The Lord Howe Rise is a deep sea plateau which extends from south west of New Caledonia to the Challenger Plateau, west of New Zealand in the south west of the Pacific Ocean. To its west is the Tasman Basin and to the east is the New Caledonia ...
, Norfolk Ridge
The Norfolk Ridge is a long submarine ridge running between New Caledonia and New Zealand, about 1300 km off the east-coast of Australia.
It is part of a complex region of ridges between the crust of the Pacific Basin and the continental c ...
, and New Caledonia
)
, anthem = ""
, image_map = New Caledonia on the globe (small islands magnified) (Polynesia centered).svg
, map_alt = Location of New Caledonia
, map_caption = Location of New Caledonia
, mapsize = 290px
, subdivision_type = Sovereign st ...
, from West Antarctica
West Antarctica, or Lesser Antarctica, one of the two major regions of Antarctica, is the part of that continent that lies within the Western Hemisphere, and includes the Antarctic Peninsula. It is separated from East Antarctica by the Transant ...
.
Opening of South Atlantic Ocean
The opening of the South Atlantic Ocean divided West Gondwana (South America and Africa), but there is a considerable debate over the exact timing of this break-up. Rifting propagated from south to north along Triassic–Early Jurassic lineaments, but intra-continental rifts also began to develop within both continents in Jurassic–Cretaceous sedimentary basins; subdividing each continent into three sub-plates. Rifting began at Falkland latitudes, forcing Patagonia to move relative to the still static remainder of South America and Africa, and this westward movement lasted until the Early Cretaceous . From there rifting propagated northward during the Late Jurassic or Early Cretaceous most likely forcing dextral movements between sub-plates on either side. South of theWalvis Ridge
The Walvis Ridge (''walvis'' means whale in Dutch and Afrikaans) is an aseismic ocean ridge in the southern Atlantic Ocean. More than in length, it extends from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, near Tristan da Cunha and the Gough Islands, to the African ...
and Rio Grande Rise
The Rio Grande Rise, also called the Rio Grande Elevation or Bromley Plateau, is an aseismic ocean ridge in the southern Atlantic Ocean off the coast of Brazil. Together with the Walvis Ridge off Africa, the Rio Grande Rise forms a V-shaped str ...
the Paraná and Etendeka magmatics resulted in further ocean-floor spreading and the development of rifts systems on both continents, including the Central African Rift System and the Central African Shear Zone
The Central African Shear Zone (CASZ) (or Shear System) is a wrench fault system extending in an ENE direction from the Gulf of Guinea through Cameroon into Sudan.
The structure is not well understood.
, there was still no general agreement about ...
which lasted until . At Brazilian latitudes spreading is more difficult to assess because of the lack of palaeo-magnetic data, but rifting occurred in Nigeria at the Benue Trough
The Benue Trough is a major geological structure underlying a large part of Nigeria and extending about 1,000 km northeast from the Bight of Benin to Lake Chad. It is part of the broader West and Central African Rift System.
Location
The ...
. North of the Equator the rifting began after and continued until .
Early Andean orogeny
The first phases ofAndean orogeny
The Andean orogeny ( es, Orogenia andina) is an ongoing process of orogeny that began in the Early Jurassic and is responsible for the rise of the Andes mountains. The orogeny is driven by a reactivation of a long-lived subduction system along ...
in the Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The J ...
and Early Cretaceous
The Early Cretaceous ( geochronological name) or the Lower Cretaceous (chronostratigraphic name), is the earlier or lower of the two major divisions of the Cretaceous. It is usually considered to stretch from 145 Ma to 100.5 Ma.
Geology
Pro ...
were characterised by extensional tectonics
Extensional tectonics is concerned with the structures formed by, and the tectonic processes associated with, the stretching of a planetary body's crust or lithosphere.
Deformation styles
The types of structure and the geometries formed depend on ...
, rift
In geology, a rift is a linear zone where the lithosphere is being pulled apart and is an example of extensional tectonics.
Typical rift features are a central linear downfaulted depression, called a graben, or more commonly a half-grabe ...
ing, the development of back-arc basin
A back-arc basin is a type of geologic basin, found at some convergent plate boundaries. Presently all back-arc basins are submarine features associated with island arcs and subduction zones, with many found in the western Pacific Ocean. Most of ...
s and the emplacement of large batholith
A batholith () is a large mass of intrusive igneous rock (also called plutonic rock), larger than in area, that forms from cooled magma deep in Earth's crust. Batholiths are almost always made mostly of felsic or intermediate rock types, such ...
s. This development is presumed to have been linked to the subduction of cold oceanic
Oceanic may refer to:
*Of or relating to the ocean
*Of or relating to Oceania
**Oceanic climate
**Oceanic languages
**Oceanic person or people, also called "Pacific Islander(s)"
Places
* Oceanic, British Columbia, a settlement on Smith Island, ...
lithosphere
A lithosphere () is the rigid, outermost rocky shell of a terrestrial planet or natural satellite. On Earth, it is composed of the crust (geology), crust and the portion of the upper mantle (geology), mantle that behaves elastically on time sca ...
. During the mid to Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the ...
(), the Andean orogeny changed significantly in character. Warmer and younger oceanic lithosphere is believed to have started to be subducted beneath South America around this time. Such kind of subduction is held responsible not only for the intense contractional deformation
Deformation can refer to:
* Deformation (engineering), changes in an object's shape or form due to the application of a force or forces.
** Deformation (physics), such changes considered and analyzed as displacements of continuum bodies.
* Defor ...
that different lithologies were subject to, but also the uplift
Uplift may refer to: Science
* Geologic uplift, a geological process
** Tectonic uplift, a geological process
* Stellar uplift, the theoretical prospect of moving a stellar mass
* Uplift mountains
* Llano Uplift
* Nemaha Uplift
Business
* Uplif ...
and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is distin ...
known to have occurred from the Late Cretaceous onward. Plate tectonic
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large te ...
reorganisation since the mid-Cretaceous might also have been linked to the opening
Opening may refer to:
* Al-Fatiha, "The Opening", the first chapter of the Qur'an
* The Opening (album), live album by Mal Waldron
* Backgammon opening
* Chess opening
* A title sequence or opening credits
* , a term from contract bridge
* , ...
of the South Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Africa, Europe and ...
. Another change related to mid-Cretaceous plate tectonic rearrangement was the change of subduction direction of the oceanic lithosphere that went from having south-east motion to having a north-east motion at about 90 million years ago. While subduction direction changed, it remained oblique (and not perpendicular) to the coast of South America, and the direction change affected several subduction zone-parallel faults including Atacama
The Atacama Desert ( es, Desierto de Atacama) is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in the w ...
, Domeyko and Liquiñe-Ofqui.
Cenozoic
Insular India
The term Insular India refers to the isolated landmass which became the Indian subcontinent. Across the latter stages of the Cretaceous and most of the Paleocene, following the breakup of Gondwana, the Indian subcontinent remained an isolated land ...
began to collide with Asia circa , forming the Indian subcontinent
The Indian subcontinent is a list of the physiographic regions of the world, physiographical region in United Nations geoscheme for Asia#Southern Asia, Southern Asia. It is situated on the Indian Plate, projecting southwards into the Indian O ...
, since which more than of crust has been absorbed by the Himalayan-Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa people, ...
an orogen. During the Cenozoic, the orogen resulted in the construction of the Tibetan Plateau
The Tibetan Plateau (, also known as the Qinghai–Tibet Plateau or the Qing–Zang Plateau () or as the Himalayan Plateau in India, is a vast elevated plateau located at the intersection of Central, South and East Asia covering most of the Ti ...
between the Tethyan Himalayas in the south and the Kunlun
The Kunlun Mountains ( zh, s=昆仑山, t=崑崙山, p=Kūnlún Shān, ; ug, كۇئېنلۇن تاغ تىزمىسى / قۇرۇم تاغ تىزمىسى ) constitute one of the longest mountain chains in Asia, extending for more than . In the bro ...
and Qilian mountains in the north.
Later, South America was connected to North America via the Isthmus of Panama
The Isthmus of Panama ( es, Istmo de Panamá), also historically known as the Isthmus of Darien (), is the narrow strip of land that lies between the Caribbean Sea and the Pacific Ocean, linking North and South America. It contains the country ...
, cutting off a circulation of warm water and thereby making the Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
colder, as well as allowing the Great American Interchange
The Great American Biotic Interchange (commonly abbreviated as GABI), also known as the Great American Interchange and the Great American Faunal Interchange, was an important late Cenozoic paleozoogeographic biotic interchange event in which lan ...
.
The break-up of Gondwana can be said to continue in eastern Africa at the Afar Triple Junction
The Afar Triple Junction (also called the Afro-Arabian Rift System) is located along a divergent plate boundary dividing the Nubian, Somali, and Arabian plates. This area is considered a present-day example of continental rifting leading to ...
, which separates the Arabian
The Arabian Peninsula, (; ar, شِبْهُ الْجَزِيرَةِ الْعَرَبِيَّة, , "Arabian Peninsula" or , , "Island of the Arabs") or Arabia, is a peninsula of Western Asia, situated northeast of Africa on the Arabian Plate. ...
, Nubian
Nubian may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Nubia, a region along the Nile river in Southern Egypt and northern Sudan.
*Nubian people
*Nubian languages
*Anglo-Nubian goat, a breed of goat
* Nubian ibex
* , several ships of the Britis ...
, and Somali plates, resulting in rifting in the Red Sea
The Red Sea ( ar, البحر الأحمر - بحر القلزم, translit=Modern: al-Baḥr al-ʾAḥmar, Medieval: Baḥr al-Qulzum; or ; Coptic: ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϩⲁϩ ''Phiom Enhah'' or ⲫⲓⲟⲙ ⲛ̀ϣⲁⲣⲓ ''Phiom ǹšari''; T ...
and East African Rift
The East African Rift (EAR) or East African Rift System (EARS) is an active continental rift zone in East Africa. The EAR began developing around the onset of the Miocene, 22–25 million years ago. In the past it was considered to be part of a ...
.
Australia–Antarctica separation
In the EarlyCenozoic
The Cenozoic ( ; ) is Earth's current geological era, representing the last 66million years of Earth's history. It is characterised by the dominance of mammals, birds and flowering plants, a cooling and drying climate, and the current configura ...
, Australia was still connected to Antarctica 35–40° south of its current location and both continents were largely unglaciated. A rift between the two developed but remained an embayment until the Eocene-Oligocene boundary when the Circumpolar Current developed and the glaciation of Antarctica began.
Australia was warm and wet during the Palaeocene and dominated by rainforest. The opening of the Tasman Gateway at the Eocene-Oligocene boundary () resulted in abrupt cooling but the Oligocene became a period of high rainfall with swamps in southeast Australia. During the Miocene, a warm and humid climate developed with pockets of rainforests in central Australia, but before the end of the period, colder and drier climate severely reduced this rainforest. A brief period of increased rainfall in the Pliocene was followed by drier climate which favoured grassland. Since then, the fluctuation between wet interglacial periods and dry glacial periods has developed into the present arid regime. Australia has thus experienced various climate changes over a 15-million-year period with a gradual decrease in precipitation.
The Tasman Gateway between Australia and Antarctica began to open . Palaeontological evidence indicates the Antarctic Circumpolar Current
The Antarctic Circumpolar Current (ACC) is an ocean current that flows clockwise (as seen from the South Pole) from west to east around Antarctica. An alternative name for the ACC is the West Wind Drift. The ACC is the dominant circulation feat ...
(ACC) was established in the Late Oligocene with the full opening of the Drake Passage
The Drake Passage (referred to as Mar de Hoces Hoces Sea"in Spanish-speaking countries) is the body of water between South America's Cape Horn, Chile and the South Shetland Islands of Antarctica. It connects the southwestern part of the Atla ...
and the deepening of the Tasman Gateway. The oldest oceanic crust in the Drake Passage, however, is -old which indicates that the spreading between the Antarctic and South American plates began near the Eocene/Oligocene boundary. Deep sea environments in Tierra del Fuego
Tierra del Fuego (, ; Spanish for "Land of the Fire", rarely also Fireland in English) is an archipelago off the southernmost tip of the South American mainland, across the Strait of Magellan. The archipelago consists of the main island, Isla G ...
and the North Scotia Ridge
The Scotia Plate () is a tectonic plate on the edge of the South Atlantic and Southern oceans. Thought to have formed during the early Eocene with the opening of the Drake Passage that separates South America from Antarctica, it is a minor pla ...
during the Eocene and Oligocene indicate a "Proto-ACC" opened during this period. Later, , a series of events severally restricted the Proto-ACC: change to shallow marine conditions along the North Scotia Ridge; closure of the Fuegan Seaway, the deep sea that existed in Tierra del Fuego; and uplift of the Patagonian Cordillera. This, together with the reactivated Iceland plume
The Iceland hotspot is a hotspot (geology), hotspot which is partly responsible for the high volcanic activity which has formed the Iceland Plateau and the island of Iceland.
Iceland is one of the most active volcano, volcanic regions in the ...
, contributed to global warming. During the Miocene, the Drake Passage began to widen, and as water flow between South America and the Antarctic Peninsula
The Antarctic Peninsula, known as O'Higgins Land in Chile and Tierra de San Martín in Argentina, and originally as Graham Land in the United Kingdom and the Palmer Peninsula in the United States, is the northernmost part of mainland Antarctic ...
increased, the renewed ACC resulted in cooler global climate.
Since the Eocene, the northward movement of the Australian Plate has resulted in an arc-continent
A continental arc is a type of volcanic arc occurring as an "arc-shape" topographic high region along a continental margin. The continental arc is formed at an active continental margin where two tectonic plates meet, and where one plate has cont ...
collision with the Philippine
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
and Caroline plates and the uplift of the New Guinea Highlands
The New Guinea Highlands, also known as the Central Range or Central Cordillera, is a long chain of mountain ranges on the island of New Guinea, including the island's tallest peak, Puncak Jaya , the highest mountain in Oceania. The range is home ...
. From the Oligocene to the late Miocene, the climate in Australia, dominated by warm and humid rainforests before this collision, began to alternate between open forest and rainforest before the continent became the arid or semiarid landscape it is today.
Biogeography
 The adjective "Gondwanan" is in common use in
The adjective "Gondwanan" is in common use in biogeography
Biogeography is the study of the distribution of species and ecosystems in geographic space and through geological time. Organisms and biological communities often vary in a regular fashion along geographic gradients of latitude, elevation, ...
when referring to patterns of distribution of living organisms, typically when the organisms are restricted to two or more of the now-discontinuous regions that were once part of Gondwana, including the Antarctic flora
Antarctic flora are a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. Presently, species of Antarctica flora reside on several now separated areas of the Southern Hemisphere, includin ...
. For example, the plant family Proteaceae
The Proteaceae form a family of flowering plants predominantly distributed in the Southern Hemisphere. The family comprises 83 genera with about 1,660 known species. Together with the Platanaceae and Nelumbonaceae, they make up the order Pro ...
, known from all continents in the Southern Hemisphere, has a "Gondwanan distribution" and is often described as an archaic, or relict
A relict is a surviving remnant of a natural phenomenon.
Biology
A relict (or relic) is an organism that at an earlier time was abundant in a large area but now occurs at only one or a few small areas.
Geology and geomorphology
In geology, a r ...
, lineage. The distributions in the Proteaceae is, nevertheless, the result of both Gondwanan rafting and later oceanic dispersal.
Post-Cambrian diversification
During theSilurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 24.6 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the shortest period of the Paleozo ...
, Gondwana extended from the Equator (Australia) to the South Pole (North Africa and South America) whilst Laurasia was located on the Equator opposite to Australia. A short-lived Late Ordovician glaciation
The Andean-Saharan glaciation, also known as the Early Palaeozoic Icehouse, the Early Palaeozoic Ice Age, the Late Ordovician glaciation, the end-Ordovician glaciation, or the Hirnantian glaciation, occurred during the Paleozoic from approximatel ...
was followed by a Silurian Hot House period. The End-Ordovician extinction, which resulted in 27% of marine invertebrate families and 57% of genera going extinct, occurred during this shift from Ice House to Hot House.
By the end of the Ordovician, ''Cooksonia
''Cooksonia'' is an extinct group of primitive land plants, treated as a genus, although probably not monophyletic. The earliest ''Cooksonia'' date from the middle of the Silurian (the Wenlock epoch); the group continued to be an important comp ...
'', a slender, ground-covering plant, became the first vascular plant to establish itself on land. This first colonisation occurred exclusively around the Equator on landmasses then limited to Laurasia and, in Gondwana, to Australia. In the Late Silurian, two distinctive lineages, zosterophyll
The zosterophylls are a group of extinct land plants that first appeared in the Silurian period. The taxon was first established by Banks in 1968 as the subdivision Zosterophyllophytina; they have since also been treated as the division Zosteroph ...
s and rhyniophytes, had colonised the tropics. The former evolved into the lycopods
Lycopodiopsida is a class of vascular plants known as lycopods, lycophytes or other terms including the component lyco-. Members of the class are also called clubmosses, firmosses, spikemosses and quillworts. They have dichotomously branching s ...
that were to dominate the Gondwanan vegetation over a long period, whilst the latter evolved into horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a " living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass ...
and gymnosperm
The gymnosperms ( lit. revealed seeds) are a group of seed-producing plants that includes conifers, cycads, ''Ginkgo'', and gnetophytes, forming the clade Gymnospermae. The term ''gymnosperm'' comes from the composite word in el, γυμνό� ...
s. Most of Gondwana was located far from the Equator during this period and remained a lifeless and barren landscape.
West Gondwana drifted north during the Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, whe ...
, bringing Gondwana and Laurasia close together. Global cooling contributed to the Late Devonian extinction
The Late Devonian extinction consisted of several extinction events in the Late Devonian Epoch, which collectively represent one of the five largest mass extinction events in the history of life on Earth. The term primarily refers to a major exti ...
(19% of marine families and 50% of genera went extinct) and glaciation occurred in South America. Before Pangaea had formed, terrestrial plants, such as pteridophyte
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that disperses spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as "cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is hidden. Ferns, ...
s, began to diversify rapidly resulting in the colonisation of Gondwana. The Baragwanathia
''Baragwanathia'' is a genus of extinct lycopsid plants of Late Silurian to Early Devonian age (), fossils of which have been found in Australia, Canada, China and Czechia. The name derives from William Baragwanath who discovered the first spec ...
Flora, found only in the Yea Beds of Victoria, Australia, occurs in two strata separated by or 30 Ma; the upper assemblage is more diverse and includes Baragwanathia, the first primitive herbaceous
Herbaceous plants are vascular plants that have no persistent woody stems above ground. This broad category of plants includes many perennials, and nearly all annuals and biennials.
Definitions of "herb" and "herbaceous"
The fourth edition of t ...
lycopod to evolve from the zosterophylls. During the Devonian, giant club mosses replaced the Baragwanathia Flora, introducing the first trees, and by the Late Devonian this first forest was accompanied by the progymnosperm
The progymnosperms are an extinct group of woody, spore-bearing plants that is presumed to have evolved from the trimerophytes, and eventually gave rise to the seed plants, gymnosperms, ancestral to gymnosperms, acrogymnosperms and angiosperms (f ...
s, including the first large trees ''Archaeopteris
''Archaeopteris'' is an extinct genus of progymnosperm tree with fern-like leaves. A useful index fossil, this tree is found in strata dating from the Upper Devonian to Lower Carboniferous (), the oldest fossils being 385 million years old, ...
''. The Late Devonian extinction probably also resulted in osteolepiform
Osteolepiformes, also known as Osteolepidida, is a group of prehistoric lobe-finned fishes which first appeared during the Devonian period. The order contains the families Canowindridae, Megalichthyidae, Osteolepididae and Tristichopteridae. Th ...
fishes evolving into the amphibian tetrapods, the earliest land vertebrates, in Greenland and Russia. The only traces of this evolution in Gondwana are amphibian footprints and a single jaw from Australia.
The closure of the Rheic Ocean and the formation of Pangaea in the Carboniferous resulted in the rerouting of ocean currents that initiated an Ice House period. As Gondwana began to rotate clockwise, Australia shifted south to more temperate latitudes. An ice cap initially covered most of southern Africa and South America but spread to eventually cover most of the supercontinent, save for northernmost Africa-South America and eastern Australia. Giant lycopod and horsetail forests continued to evolve in tropical Laurasia together with a diversified assemblage of true insects. In Gondwana, in contrast, ice and, in Australia, volcanism decimated the Devonian flora to a low-diversity seed fern flora – the pteridophytes were increasingly replaced by the gymnosperms which were to dominate until the Mid-Cretaceous. Australia, however, was still located near the Equator during the Early Carboniferous, and during this period, temnospondyl
Temnospondyli (from Greek language, Greek τέμνειν, ''temnein'' 'to cut' and σπόνδυλος, ''spondylos'' 'vertebra') is a diverse order (biology), order of small to giant tetrapods—often considered Labyrinthodontia, primitive amphi ...
and lepospondyl
Lepospondyli is a diverse taxon of early tetrapods. With the exception of one late-surviving lepospondyl from the Late Permian of Morocco (''Diplocaulus minumus''), lepospondyls lived from the Early Carboniferous ( Mississippian) to the Early Per ...
amphibians and the first amniote
Amniotes are a clade of tetrapod vertebrates that comprises sauropsids (including all reptiles and birds, and extinct parareptiles and non-avian dinosaurs) and synapsids (including pelycosaurs and therapsids such as mammals). They are disti ...
reptilians evolved, all closely related to the Laurasian fauna, but spreading ice eventually drove these animals away from Gondwana entirely.
The Gondwana ice sheet melted, and sea levels dropped during the Permian and Triassic global warming. During this period, the extinct glossopterids colonised Gondwana and reached peak diversity in the Late Permian when coal-forming forests covered much of Gondwana. The period also saw the evolution of Voltziales
Voltziales is an extinct order of conifers. The group contains the ancestral lineages from which all modern conifer groups emerged. The earliest Voltzialean conifers appear in the Late Carboniferous ( Pennsylvanian). Modern conifer lineages emer ...
, one of the few plant orders to survive the end-Permian extinction (57% of marine families and 83% of genera went extinct) and which came to dominate in the Late Permian and from whom true conifers evolved. Tall lycopods and horsetails
''Equisetum'' (; horsetail, snake grass, puzzlegrass) is the only living genus in Equisetaceae, a family of ferns, which reproduce by spores rather than seeds.
''Equisetum'' is a " living fossil", the only living genus of the entire subclass ...
dominated the wetlands of Gondwana in the Early Permian. Insects co-evolved with glossopterids across Gondwana and diversified with more than 200 species in 21 orders by the Late Permian, many known from South Africa and Australia. Beetles and cockroaches remained minor elements in this fauna. Tetrapod
Tetrapods (; ) are four-limbed vertebrate animals constituting the superclass Tetrapoda (). It includes extant and extinct amphibians, sauropsids ( reptiles, including dinosaurs and therefore birds) and synapsids (pelycosaurs, extinct theraps ...
fossils from the Early Permian have only been found in Laurasia but they became common in Gondwana later during the Permian. The arrival of the therapsid
Therapsida is a major group of eupelycosaurian synapsids that includes mammals, their ancestors and relatives. Many of the traits today seen as unique to mammals had their origin within early therapsids, including limbs that were oriented more ...
s resulted in the first plant-vertebrate-insect ecosystem.
Modern diversification
During the Mid- to Late Triassic, hot-house conditions coincided with a peak in biodiversity — the end-Permian extinction was enormous and so was the radiation that followed. Two families of conifers,Podocarpaceae
Podocarpaceae is a large family of mainly Southern Hemisphere conifers, known in English as podocarps, comprising about 156 species of evergreen trees and shrubs.James E. Eckenwalder. 2009. ''Conifers of the World''. Portland, Oregon: Timber Pre ...
and Araucariaceae
Araucariaceae – also known as araucarians – is an extremely ancient family of coniferous trees. The family achieved its maximum diversity during the Jurassic and Cretaceous periods and the early Cenozoic, when it was distributed almost worldw ...
, dominated Gondwana in the Early Triassic, but ''Dicroidium
''Dicroidium'' is an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns that were widely distributed over Gondwana during the Triassic (). Their fossils are known from South Africa, the Arabian Peninsula, Australia, New Zealand, South America, Madagascar ...
'', an extinct genus of fork-leaved seed ferns, dominated woodlands and forests of Gondwana during most of the Triassic. Conifers evolved and radiated during the period, with six of eight extant families already present before the end of it. Bennettitales
Bennettitales (also known as cycadeoids) is an extinct order of seed plants that first appeared in the Permian period and became extinct in most areas toward the end of the Cretaceous. Bennettitales are among the most common Mesozoic seed plants ...
and Pentoxylales
Pentoxylales is an extinct order of seed plants known from the Jurassic and Early Cretaceous of East Gondwana.
Discovery
The first specimens belonging to Pentoxylales were reported by Birbal Sahni in 1948 from Jurassic-Cretaceous strata of t ...
, two now extinct orders of gymnospermous plants, evolved in the Late Triassic and became important in the Jurassic and Cretaceous. It is possible that gymnosperm biodiversity surpassed later angiosperm biodiversity and that the evolution of angiosperms began during the Triassic but, if so, in Laurasia rather than in Gondwana. Two Gondwanan classes, lycophytes
The lycophytes, when broadly circumscribed, are a vascular plant (tracheophyte) subgroup of the kingdom Plantae. They are sometimes placed in a division Lycopodiophyta or Lycophyta or in a subdivision Lycopodiophytina. They are one of the oldes ...
and sphenophytes, saw a gradual decline during the Triassic while ferns, though never dominant, managed to diversify.
The brief period of icehouse conditions during the Triassic–Jurassic extinction event
The Triassic–Jurassic (Tr-J) extinction event, often called the end-Triassic extinction, marks the boundary between the Triassic and Jurassic periods, , and is one of the top five major extinction events of the Phanerozoic eon, profoundly affect ...
had a dramatic impact on dinosaurs but left plants largely unaffected. The Jurassic was mostly one of hot-house conditions and, while vertebrates managed to diversify in this environment, plants have left little evidence of such development, apart from Cheiroleidiacean conifers and Caytoniales
The Caytoniales (Figs. 1-2) are an extinct order of seed plants known from fossils collected throughout the Mesozoic Era, around . They are regarded as seed ferns because they are seed-bearing plants with fern-like leaves. Although at one time ...
and other groups of seed ferns. In terms of biomass, the Jurassic flora was dominated by conifer families and other gymnosperms that had evolved during the Triassic. The Pteridophyte
A pteridophyte is a vascular plant (with xylem and phloem) that disperses spores. Because pteridophytes produce neither flowers nor seeds, they are sometimes referred to as "cryptogams", meaning that their means of reproduction is hidden. Ferns, ...
s that had dominated during the Palaeozoic were now marginalised, except for ferns. In contrast to Laurentia, very few insect fossils have been found in Gondwana, to a considerable extent because of widespread deserts and volcanism. While plants had a cosmopolitan distribution, dinosaurs evolved and diversified in a pattern that reflects the Jurassic break-up of Pangaea.
The Cretaceous saw the arrival of the angiosperm
Flowering plants are plants that bear flowers and fruits, and form the clade Angiospermae (), commonly called angiosperms. The term "angiosperm" is derived from the Greek words ('container, vessel') and ('seed'), and refers to those plants th ...
s, or flowering plants, a group that probably evolved in western Gondwana (South America-Africa). From there the angiosperms diversified in two stages: the monocots
Monocotyledons (), commonly referred to as monocots, (Lilianae ''sensu'' Chase & Reveal) are grass and grass-like flowering plants (angiosperms), the seeds of which typically contain only one embryonic leaf, or cotyledon. They constitute one of t ...
and magnoliids
Magnoliids (or Magnoliidae or Magnolianae) are a clade of flowering plants. With more than 10,000 species, including magnolias, nutmeg, bay laurel, cinnamon, avocado, black pepper, tulip tree and many others, it is the third-largest group of angio ...
evolved in the Early Cretaceous, followed by the hammamelid dicots. By the Mid-Cretaceous, angiosperms constituted half of the flora in northeastern Australia. There is, however, no obvious connection between this spectacular angiosperm radiation and any known extinction event nor with vertebrate/insect evolution. Insect orders associated with pollination, such as beetle
Beetles are insects that form the order Coleoptera (), in the superorder Endopterygota. Their front pair of wings are hardened into wing-cases, elytra, distinguishing them from most other insects. The Coleoptera, with about 400,000 describ ...
s, flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced ...
, butterflies and moths, and wasps, bees, and ants, radiated continuously from the Permian-Triassic, long before the arrival of the angiosperms. Well-preserved insect fossils have been found in the lake deposits of the Santana Formation
The Santana Group is a geologic group, formerly included as the middle part of the Araripe Group, in the Araripe Basin of northeastern Brazil. The group comprises the Crato, Ipubi and Romualdo Formations and is dated to the Aptian to Albian sta ...
in Brazil, the Koonwarra Lake fauna in Australia, and the Orapa diamond mine
The Orapa diamond mine is the world's largest diamond mine by area. The mine is located in Orapa, a town in the Central District of Botswana about west of the city of Francistown. Orapa ("resting place for lions") is owned by Debswana, a partn ...
in Botswana.
Dinosaurs continued to prosper but, as the angiosperm diversified, conifers, bennettitaleans and pentoxylaleans disappeared from Gondwana 115 Ma together with the specialised herbivorous ornithischia
Ornithischia () is an extinct order of mainly herbivorous dinosaurs characterized by a pelvic structure superficially similar to that of birds. The name ''Ornithischia'', or "bird-hipped", reflects this similarity and is derived from the Greek s ...
ns, whilst generalist browsers, such as several families of sauropodomorph
Sauropodomorpha ( ; from Greek, meaning "lizard-footed forms") is an extinct clade of long-necked, herbivorous, saurischian dinosaurs that includes the sauropods and their ancestral relatives. Sauropods generally grew to very large sizes, had lon ...
Saurischia
Saurischia ( , meaning "reptile-hipped" from the Greek ' () meaning 'lizard' and ' () meaning 'hip joint') is one of the two basic divisions of dinosaurs (the other being Ornithischia), classified by their hip structure. Saurischia and Ornithis ...
, prevailed. The Cretaceous–Paleogene extinction event
The Cretaceous–Paleogene (K–Pg) extinction event (also known as the Cretaceous–Tertiary extinction) was a sudden mass extinction of three-quarters of the plant and animal species on Earth, approximately 66 million years ago. With the ...
killed off all dinosaurs except birds, but plant evolution in Gondwana was hardly affected. Gondwanatheria
Gondwanatheria is an extinct group of mammaliaforms that lived in parts of Gondwana, including Madagascar, India, South America, Africa and Antarctica during the Upper Cretaceous through the Paleogene (and possibly much earlier, if '' Allostaff ...
is an extinct group of non-theria
Theria (; Greek: , wild beast) is a subclass of mammals amongst the Theriiformes. Theria includes the eutherians (including the placental mammals) and the metatherians (including the marsupials) but excludes the egg-laying monotremes.
Ch ...
n mammals with a Gondwanan distribution (South America, Africa, Madagascar, India, Zealandia and Antarctica) during the Late Cretaceous and Palaeogene. Xenarthra
Xenarthra (; from Ancient Greek ξένος, xénos, "foreign, alien" + ἄρθρον, árthron, "joint") is a major clade of placental mammals native to the Americas. There are 31 living species: the anteaters, tree sloths, and armadillos. Ex ...
and Afrotheria
Afrotheria ( from Latin ''Afro-'' "of Africa" + ''theria'' "wild beast") is a clade of mammals, the living members of which belong to groups that are either currently living in Africa or of African origin: golden moles, elephant shrews (also know ...
, two placental clades, are of Gondwanan origin and probably began to evolve separately when Africa and South America separated.
laurel forest
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elo ...
s of Australia, New Caledonia, and New Zealand have a number of species related to those of the laurissilva
Laurel forest, also called laurisilva or laurissilva, is a type of subtropical forest found in areas with high humidity and relatively stable, mild temperatures. The forest is characterized by broadleaf tree species with evergreen, glossy and elo ...
of Valdivia, through the connection of the Antarctic flora
Antarctic flora are a distinct community of vascular plants which evolved millions of years ago on the supercontinent of Gondwana. Presently, species of Antarctica flora reside on several now separated areas of the Southern Hemisphere, includin ...
. These include gymnosperms and the deciduous species of ''Nothofagus'', as well as the New Zealand laurel, ''Corynocarpus laevigatus
Karaka or New Zealand laurel (''Corynocarpus laevigatus'') is an evergreen tree of the family Corynocarpaceae endemic (ecology), endemic to New Zealand. It is common throughout the North Island, North and South Islands to Banks Peninsula (43°45� ...
'', and ''Laurelia novae-zelandiae
''Laurelia novae-zelandiae'', also called pukatea, is a large evergreen tree, endemic to the forests of New Zealand. Pukatea has 'toothed' leaves and produces small flowers. It is a species in the Atherospermataceae (formerly Monimiaceae) family ...
''. New Caledonia and New Zealand became separated from Australia by continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pla ...
85 million years ago. The islands still retain plants that originated in Gondwana and spread to the Southern Hemisphere continents later.
See also
*Continental drift
Continental drift is the hypothesis that the Earth's continents have moved over geologic time relative to each other, thus appearing to have "drifted" across the ocean bed. The idea of continental drift has been subsumed into the science of pla ...
, the movement of the Earth's continents relative to each other
* Australasian realm
The Australasian realm is a biogeographic realm that is coincident with, but not (by some definitions) the same as, the geographical region of Australasia. The realm includes Australia, the island of New Guinea (comprising Papua New Guinea and ...
* Gondwana Rainforests of Australia
The Gondwana Rainforests of Australia, formerly known as the Central Eastern Rainforest Reserves, are the most extensive area of subtropical rainforest in the world. Collectively, the rainforests are a World Heritage Site with fifty separate res ...
* The Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
of Southern Africa
* Plate tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large ...
, a theory which describes the large-scale motions of Earth's lithosphere
* South Polar dinosaurs, which proliferated during the Early Cretaceous (145–100 Mya) while Australia was still linked to Antarctica to form East Gondwana
References
Notes
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* *Graphical subjects dealing with Tectonics and Paleontology
The Gondwana Map Project
* {{Authority control Historical continents Former supercontinents Biogeography Paleozoic paleogeography Mesozoic paleogeography Geology of Africa Geology of Antarctica Geology of Asia Geology of India Geology of Australia Geology of South America Prehistory of Antarctica Paleozoic Africa Paleozoic Antarctica Paleozoic Asia Paleozoic South America Mesozoic Africa Mesozoic Antarctica Mesozoic Asia Mesozoic South America